The Influence of Conformity and Global Learning on Social Systems of Cooperation: Agent-Based Models of the Spatial Prisoner’s Dilemma Game
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Model
2.1. A Prisoner’s Dilemma Game on a Lattice
2.2. Strategy Updating of Agents
2.2.1. Neighborhood Model (NHD)
2.2.2. Random Sampling Model (RSP)
2.2.3. Reference Neighborhood Model (RND)
2.3. Simulation Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
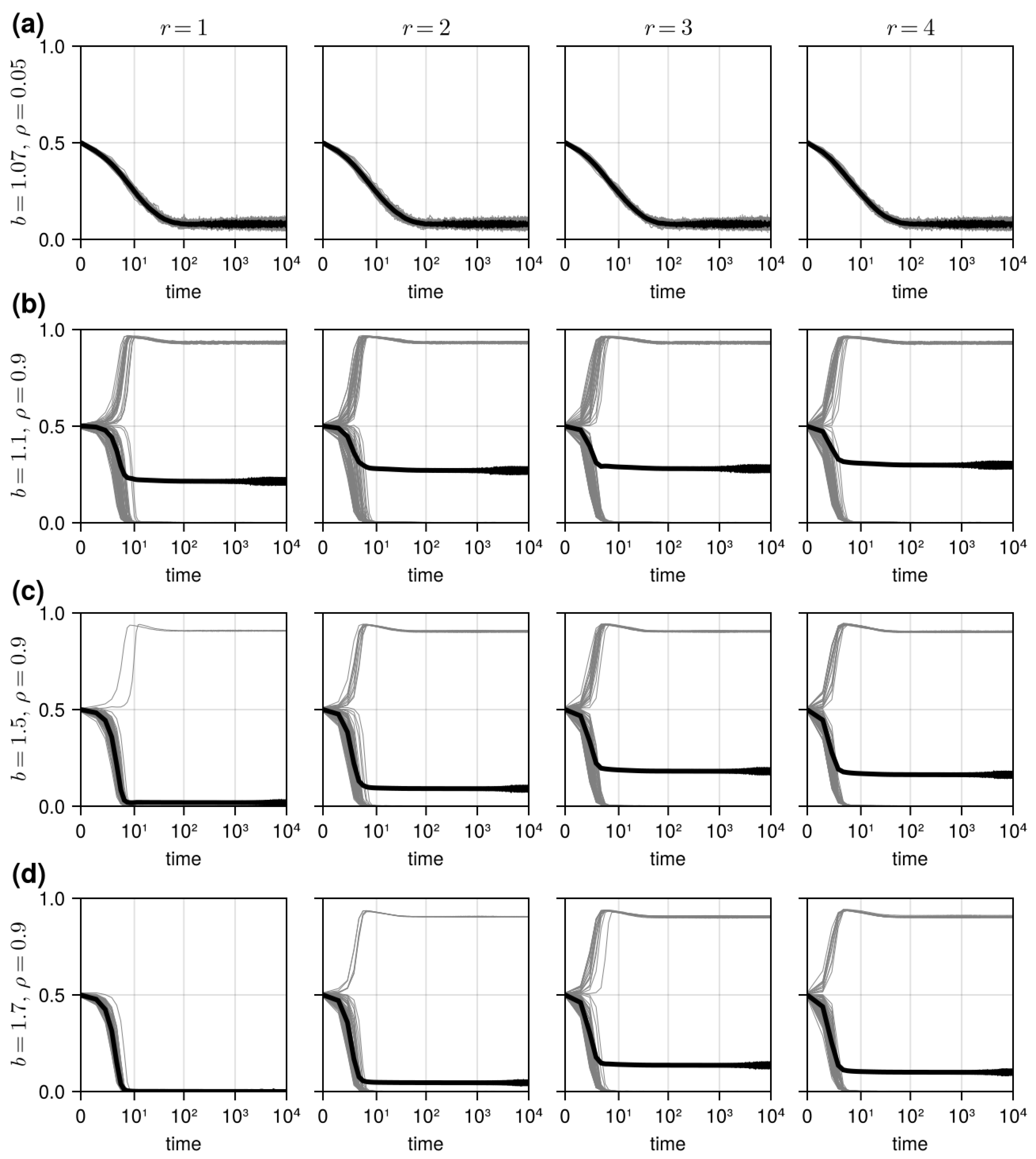
3.1. Results in Neighborhood Model
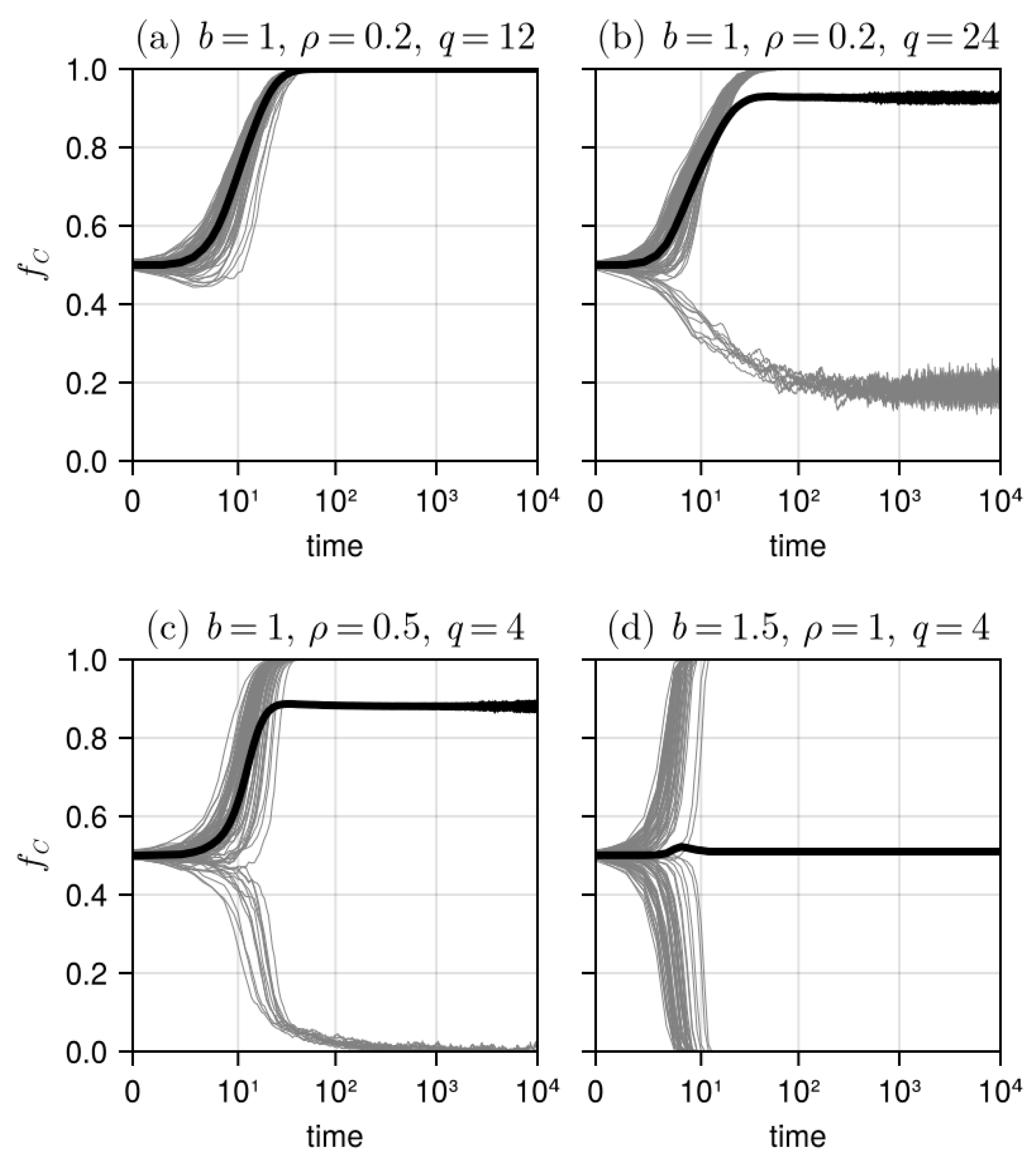
3.2. Results in Random Sampling Model
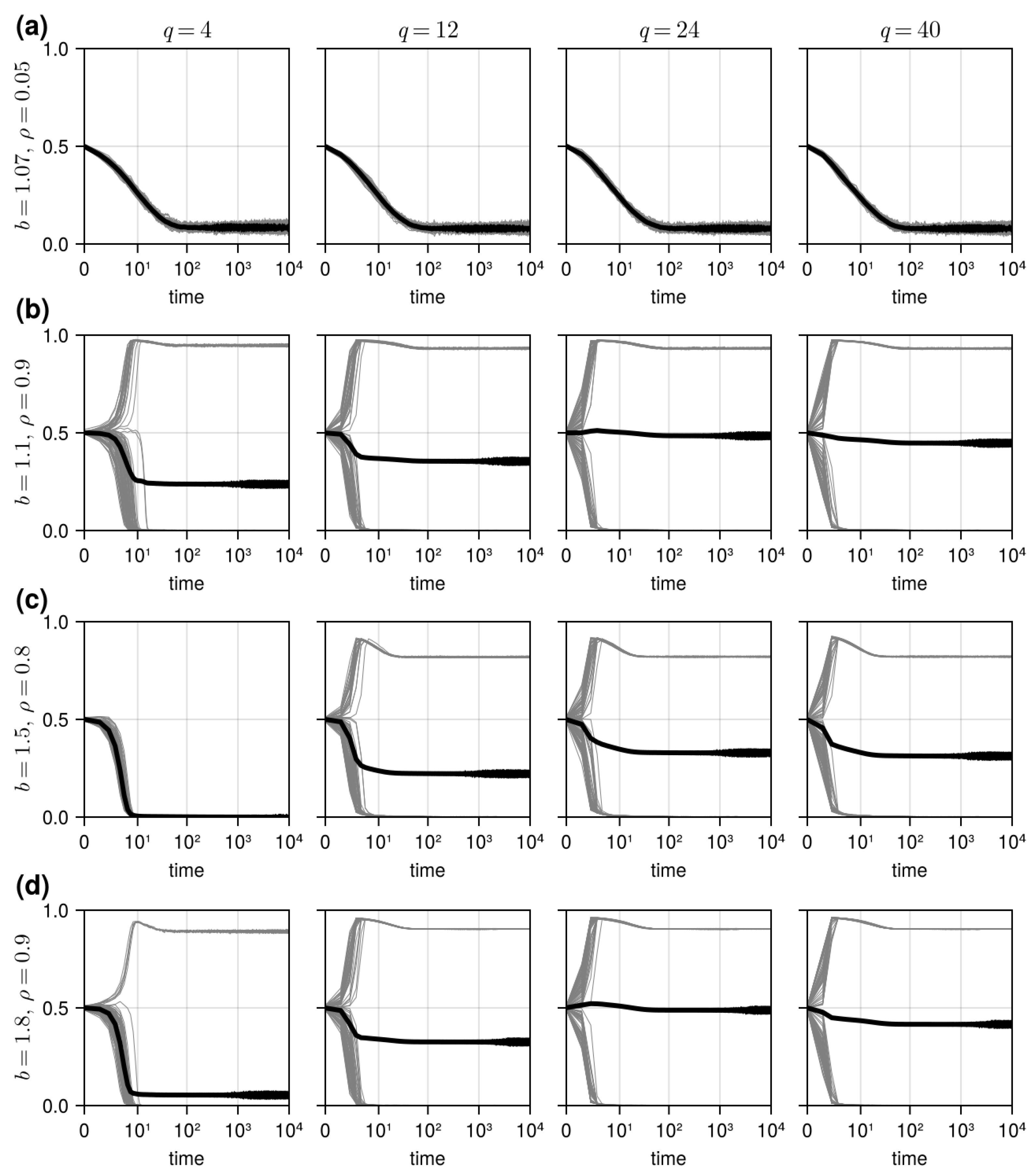
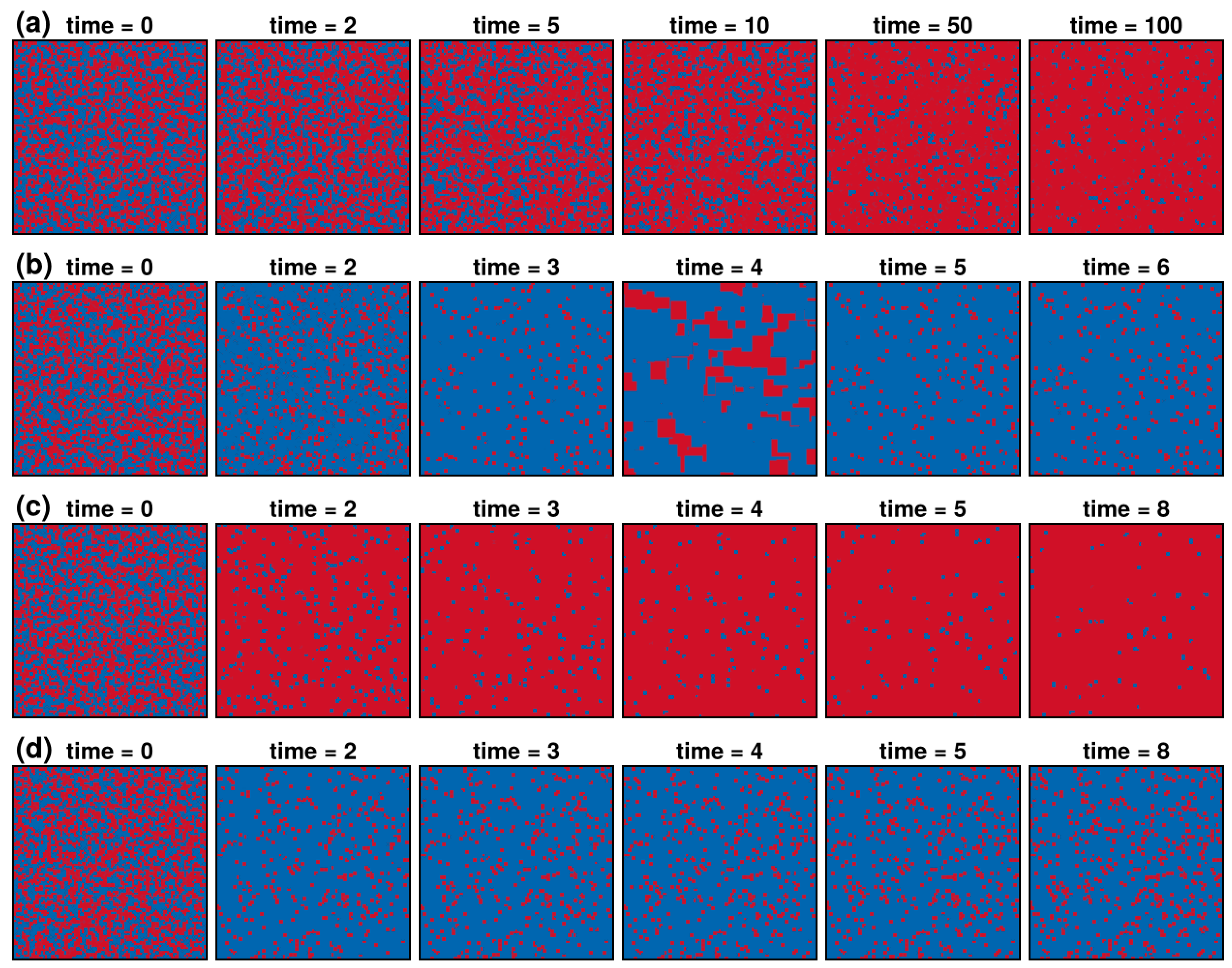
3.3. Results in Reference Neighborhood Model
3.4. Statistical Analysis of Simulation Results
3.5. Comparing Model Results Under Equal Parameter Conditions
4. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IG | Interaction Group |
| LG | Learning Group |
| PD | Prisoner’s Dilemma |
| PO | Payoff-Biased |
| CF | Conformity-Biased |
| NHD | Neighborhood Model |
| RSP | Random Sampling Model |
| RND | Random Neighborhood Model |
References
- Ye, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, Y.; Du, W.; Chen, T. A novel public opinion polarization model based on BA network. Systems 2022, 10, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, J.; Rauhut, H.; Schweitzer, F.; Helbing, D. How social influence can undermine the wisdom of crowd effect. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 103, 9020–9025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, W.D. The evolution of altruistic behavior. Am. Nat. 1963, 97, 354–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, M.A. Five rules for the evolution of cooperation. Science 2006, 314, 1560–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiske, S.T. Social Beings: Core Motives in Social Psychology, 3rd ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Efferson, C.; Lalive, R.; Richerson, P.J.; Mcelreath, R.; Lubell, M. Conformists and mavericks: The empirics of frequency-dependent cultural transmission. Evol. Hum. Behav. 2008, 29, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traulsen, A.; Semmann, D.; Sommerfeld, R.D.; Krambeck, H.J.; Milinski, M. Human strategy updating in evolutionary games. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 2962–2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, R.; Richerson, P.J. Culture and the Evolutionary Process; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Bernheim, B.D. A theory of conformity. J. Political Econ. 1994, 102, 841–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, P.-B.; Wu, Z.-X. Impact of conformity on the evolution of cooperation in the prisoner’s dilemma game. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2013, 392, 1500–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, A.; Tanaka, M.; Tanimoto, J. How does conformity promote the enhancement of cooperation in the network reciprocity in spatial prisoner’s dilemma games? Chaos Solitons Fractals 2020, 138, 109997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Guo, H.; Geng, Y.; Shi, L. The effect of conformity on the evolution of cooperation in multigame. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2019, 516, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szolnoki, A.; Perc, M. Conformity enhances network reciprocity in evolutionary social dilemmas. J. R. Soc. Interface 2015, 12, 20141299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.-X.; Tian, L. Enhancement of cooperation through conformity-driven reproductive ability. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2017, 103, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szolnoki, A.; Wang, Z.; Perc, M. Wisdom of groups promotes cooperation in evolutionary social dilemmas. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maynard Smith, J. Evolution and the Theory of Games; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Weibull, J.W. Evolutionary Game Theory; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, B.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X. Conformity-based cooperation in online social networks: The effect of heterogeneous social influence. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2015, 81, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Huang, C.; Dai, Q.; Yang, J. Evolutionary game dynamics of combining the payoff-driven and conformity-driven update rules. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2020, 140, 110146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Li, Y.; Jiang, L. Dual effects of conformity on the evolution of cooperation in social dilemmas. Phys. Rev. E 2023, 108, 024123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szolnoki, A.; Perc, M. Leaders should not be conformists in evolutionary social dilemmas. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Z.; Xu, J.; Dai, D.; Liang, T.; Mao, D.; Zhao, D. Rational conformity behavior can promote cooperation in the prisoner’s dilemma game. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2018, 112, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Huang, C.; Dai, Q.; Yang, J. The effects of the conformity threshold on cooperation in spatial prisoner’s dilemma games. EPL 2019, 128, 18001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, C.; Chu, T.; Weissing, F.J. Cooperation in networks where the learning environment differs from the interaction environment. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shigaki, K.; Tanimoto, J.; Wang, Z.; Kokubo, S.; Hagishima, A.; Ikegaya, N. Referring to the social performance promotes cooperation in spatial prisoner’s dilemma games. Phys. Rev. E 2012, 86, 031141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.-K. Play locally, learn globally: Group selection and structural basis of cooperation. J. Bioecon. 2008, 10, 239–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtsuki, H.; Nowak, M.A.; Pacheco, J.M. Breaking the symmetry between interaction and replacement in evolutionary dynamics on graphs. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 98, 108106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deutsch, M.; Gerard, H.B. A study of normative and informational social influences upon individual judgment. J. Abnorm. Soc. Psychol. 1955, 51, 629–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claidière, N.; Whiten, A. Integrating the study of conformity and culture in humans and nonhuman animals. Psychol. Bull. 2012, 138, 126–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.-X.; Wang, Y.-H. Cooperation enhanced by the difference between interaction and learning neighborhoods for evolutionary spatial prisoner’s dilemma games. Phys. Rev. E 2007, 75, 041114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, R.; Arita, T. Evolution of cooperation on different combinations of interaction and replacement networks with various intensity of selection. Int. J. Bio-Inspired Comput. 2011, 3, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengel, F. Conformism and cooperation in a local interaction model. J. Evol. Econ. 2009, 19, 397–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, L.; Perc, M. Degree mixing in multilayer networks impedes the evolution of cooperation. Phys. Rev. E 2014, 89, 052813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtsuki, H.; Pacheco, J.M.; Nowak, M.A. Evolutionary graph theory: Breaking the symmetry between interaction and replacement. J. Theor. Biol. 2007, 246, 681–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabó, G.; Tőke, C. Evolutionary prisoner’s dilemma game on a square lattice. Phys. Rev. E 1998, 58, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perc, M.; Szolnoki, A. Coevolutionary games—A mini review. Biosystems 2010, 99, 109–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szabó, G.; Fáth, G. Evolutionary games on graphs. Phys. Rep. 2007, 446, 97–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, M.A.; May, R.M. Evolutionary games and spatial chaos. Nature 1992, 359, 826–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Miao, Q.; Zhang, J. Impact of neighborhood separation on the spatial reciprocity in the prisoner’s dilemma game. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2013, 51, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datseris, G.; Vahdati, A.R.; DuBois, T.C. Agents.jl: A performant and feature-full agent-based modeling software of minimal code complexity. Simulation 2024, 100, 1019–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Han, W.; Li, H.; Cheng, H.; Dai, Q.; Yang, J. Public cooperation in two-layer networks with asymmetric interaction and learning environments. Appl. Math. Comput. 2019, 340, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Kokubo, S.; Tanimoto, J.; Fukuda, E.; Shigaki, K. Insight into the so-called spatial reciprocity. Phys. Rev. E 2013, 88, 315–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendell, L.; Fogarty, L.; Laland, K.N. Rogers’ paradox recast and resolved: Population structure and the evolution of social learning strategies. Evolution 2010, 64, 534–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, F.C.; Pinheiro, F.L.; Lenaerts, T.; Pacheco, J.M. The role of diversity in the evolution of cooperation. J. Theor. Biol. 2012, 299, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Qu, S.; Kong, L. The impact of cooperation network evolution on communication technology innovation: A network interaction perspective. Systems 2025, 13, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veile, J.W.; Schmidt, M.-C.; Voigt, K.-I. Toward a new era of cooperation: How industrial digital platforms transform business models in Industry 4.0. J. Bus. Res. 2022, 143, 387–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weder, F.; Yarnold, J.; Mertl, S.; Hübner, R.; Elmenreich, W.; Sposato, R. Social learning of sustainability in a pandemic—Changes to sustainability understandings, attitudes, and behaviors during the global pandemic in a higher education setting. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molleman, L.; van den Berg, P.; Weissing, F.J. Consistent individual differences in human social learning strategies. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Lange, P.A.M.; Joireman, J.; Parks, C.D.; van Dijk, E. The psychology of social dilemmas: A review. Organ. Behav. Hum. Decis. Process. 2013, 120, 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smaldino, P.E. Social identity and cooperation in cultural evolution. Behav. Process. 2019, 161, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szolnoki, A.; Perc, M. Conditional strategies and the evolution of cooperation in spatial public goods games. Phys. Rev. E 2012, 85, 026104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Han, W.; Yang, W.; Wang, J.; Xia, C.; Li, H.-j.; Shi, Y. Impact of resource-based conditional interaction on cooperation in spatial social dilemmas. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2022, 594, 127055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barabási, A.-L.; Bonabeau, E. Scale-free networks. Sci. Am. 2003, 288, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, F.C.; Pacheco, J.M. Scale-free networks provide a unifying framework for the emergence of cooperation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 95, 098104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña, J.; Volken, H.; Pestelacci, E.; Tomassini, M. Conformity hinders the evolution of cooperation on scale-free networks. Phys. Rev. E 2009, 80, 016110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watts, D.J.; Strogatz, S.H. Collective dynamics of ‘small-world’ networks. Nature 1998, 393, 440–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Lv, W.; Cheng, X.; Wen, Y.; Yang, X. Evolution of strategies in evolution games on small-world networks and applications. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2024, 189, 115676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inaba, M.; Akiyama, E. Evolution of cooperation in multiplex networks through asymmetry between interaction and replacement. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 9814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grujić, J.; Lenaerts, T. Do people imitate when making decisions? Evidence from a spatial Prisoner’s Dilemma experiment. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2020, 7, 200618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badea, C.; Binning, K.R.; Sherman, D.K.; Boza, M.; Kende, A. Conformity to group norms: How group-affirmation shapes collective action. J. Exp. Soc. Psychol. 2021, 95, 104153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Huang, C.; Dai, Q.; Yang, J. The effects of attribute persistence on cooperation in evolutionary games. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2018, 115, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

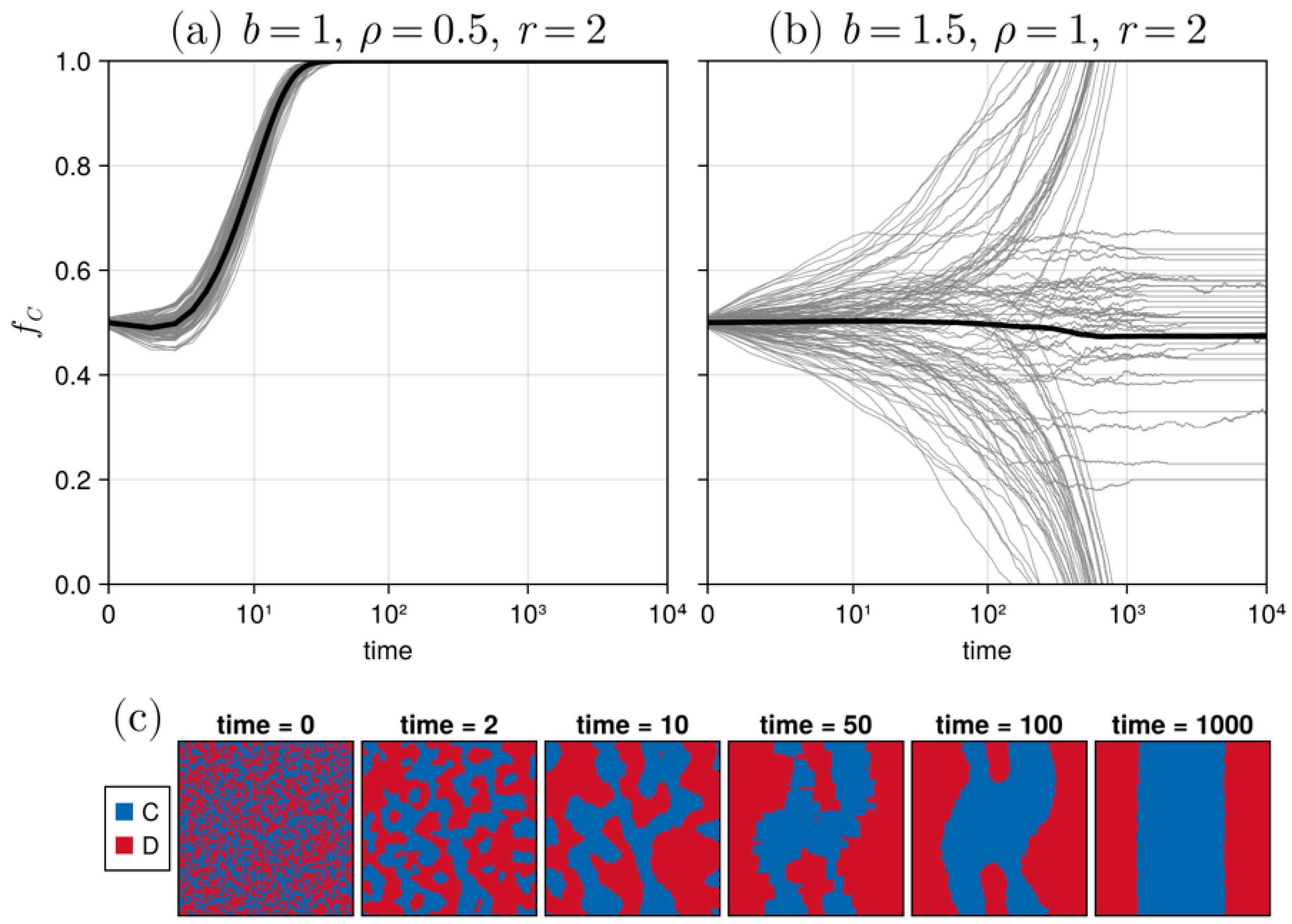
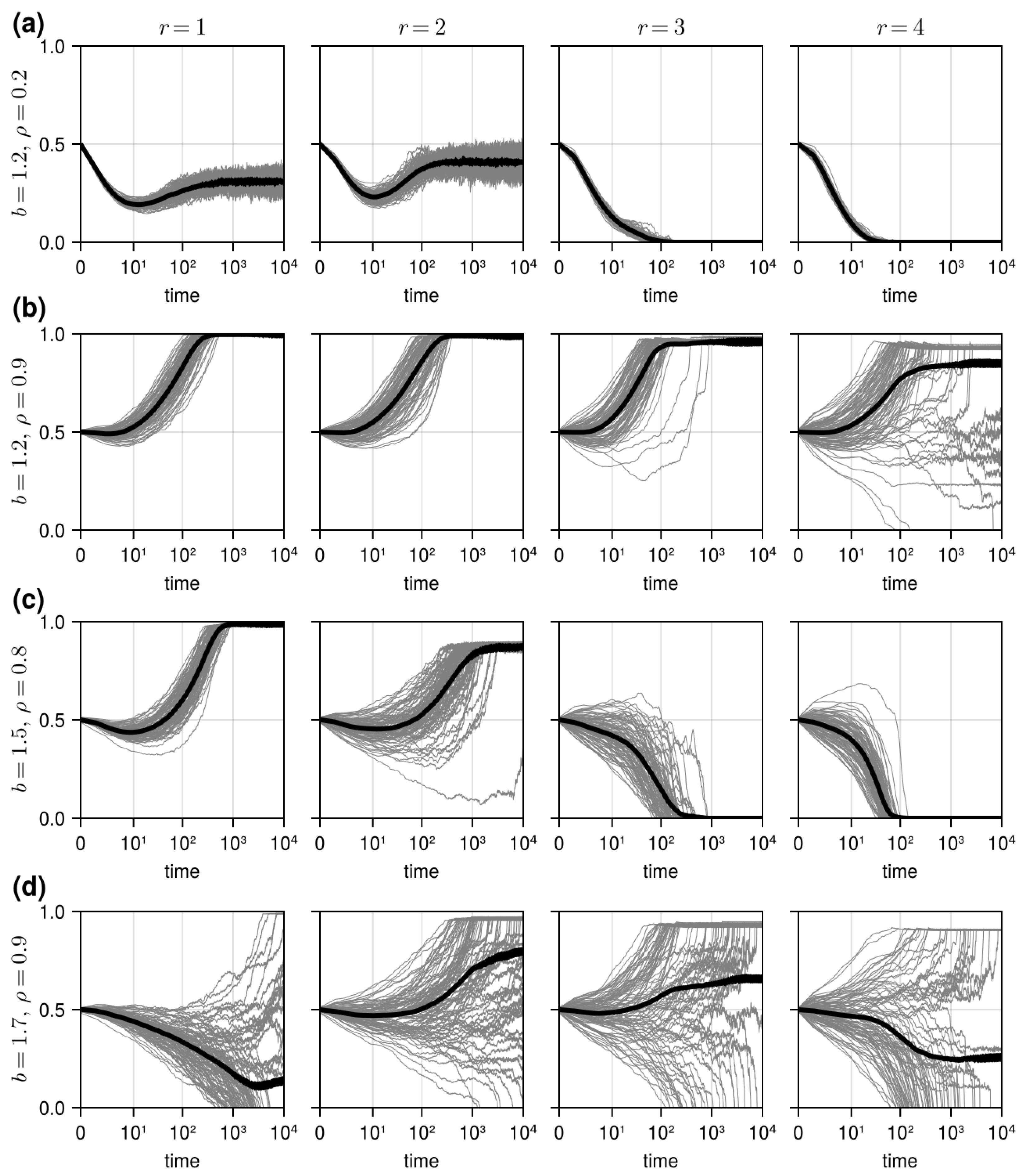
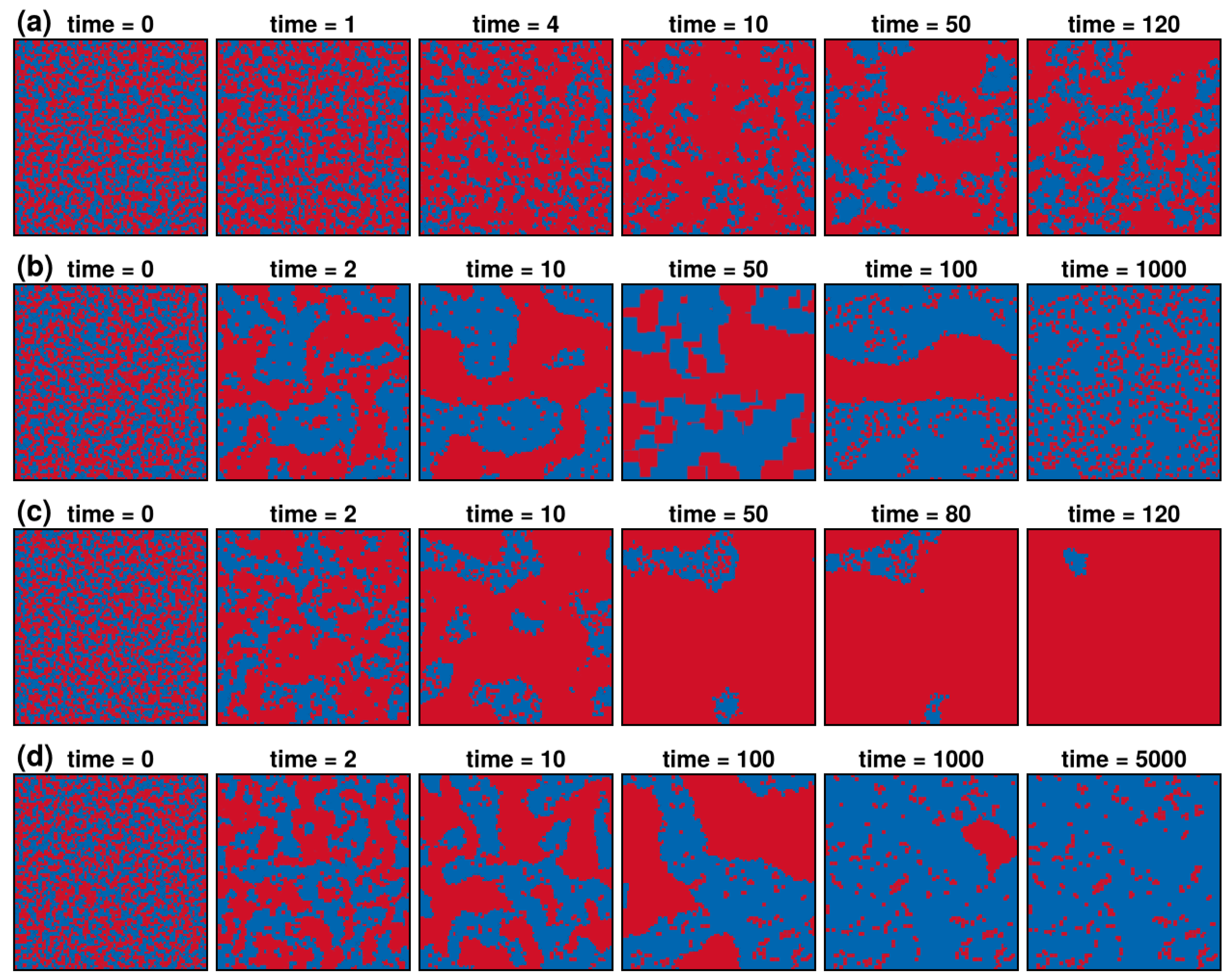
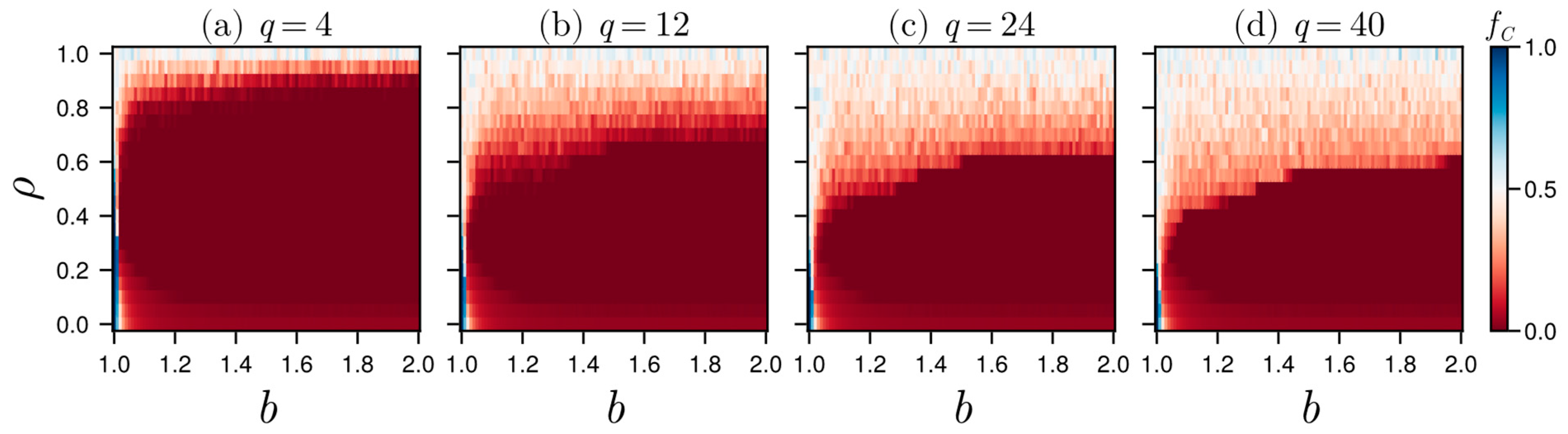



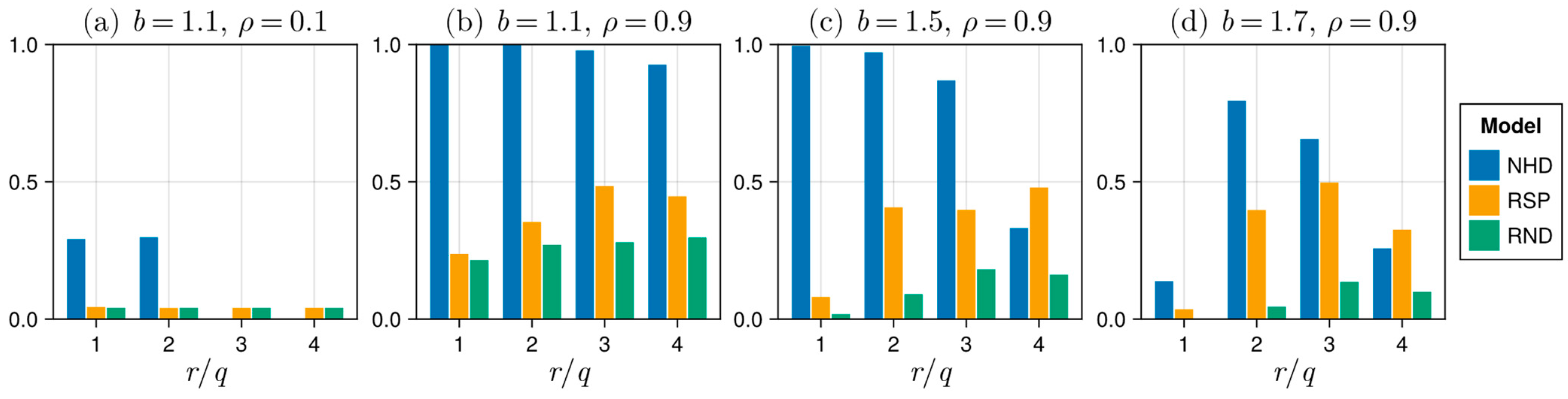
| Studies on Conformity | Studies on Differing IGs and LGs | This Study |
|---|---|---|
| effect of global conformity on cooperation in differing IGs and LGs | ||
| Gap: global conformity was not covered | Gap: only payoff-biased learning was employed |
| Parameter | Meaning | Value | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| b | Temptation to defect payoff | 1, 1.01, …, 2 | [13,38] |
| Proportion of conformist | 0, 0.05, …, 1 | [13,18] | |
| r | Radius of neighbors (in NHD and RND) | 1, 2, 3, 4 | [25,39] |
| q | Number of samples (in RSP) | 4, 12, 24, 40 | [25] |
| Variable | Coefficient | Std. Error | t | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Intercept) | 0.5814 | 0.0079 | 73.35 | <2 × 10−16 |
| model RND | −0.2065 | 0.0032 | −64.87 | <2 × 10−16 |
| model RSP | −0.1347 | 0.0032 | −42.3 | <2 × 10−16 |
| r/q | −0.0073 | 0.0012 | −6.33 | 2.49 × 10−10 |
| b | −0.3331 | 0.0045 | −74.74 | <2 × 10−16 |
| 0.4211 | 0.0043 | 98.09 | <2 × 10−16 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, Y. The Influence of Conformity and Global Learning on Social Systems of Cooperation: Agent-Based Models of the Spatial Prisoner’s Dilemma Game. Systems 2025, 13, 288. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13040288
Kim Y. The Influence of Conformity and Global Learning on Social Systems of Cooperation: Agent-Based Models of the Spatial Prisoner’s Dilemma Game. Systems. 2025; 13(4):288. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13040288
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Yunhwan. 2025. "The Influence of Conformity and Global Learning on Social Systems of Cooperation: Agent-Based Models of the Spatial Prisoner’s Dilemma Game" Systems 13, no. 4: 288. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13040288
APA StyleKim, Y. (2025). The Influence of Conformity and Global Learning on Social Systems of Cooperation: Agent-Based Models of the Spatial Prisoner’s Dilemma Game. Systems, 13(4), 288. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13040288





