Digital Oasis: How Green Infrastructure Is Reshaping China’s Energy Resilience Landscape
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review and Hypothesis Development
2.1. Policy Background
2.2. Literature Review
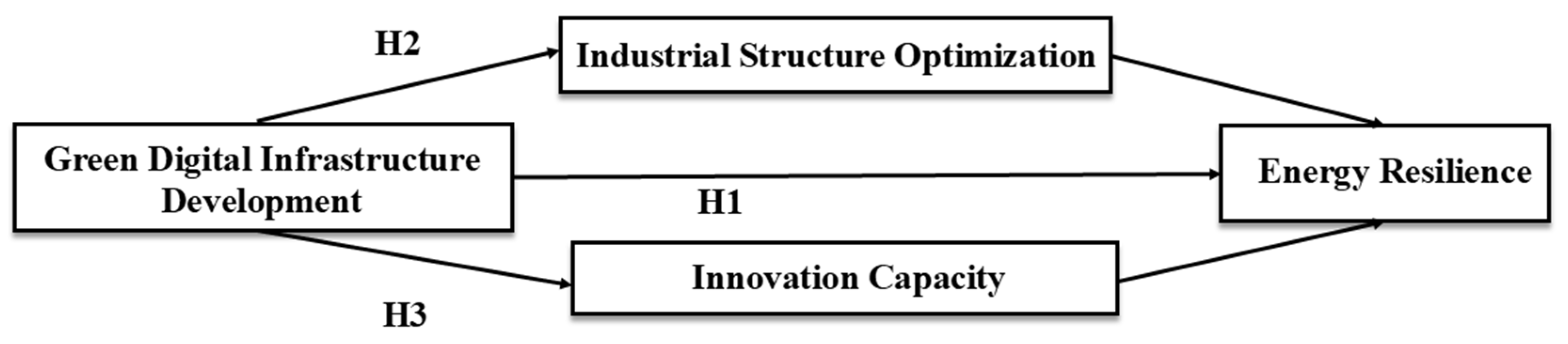
2.3. Research Hypotheses
3. Research Design
3.1. Data Sources
3.2. Variable Definitions
3.3. Model Specification
4. Empirical Analysis
4.1. Descriptive Analysis
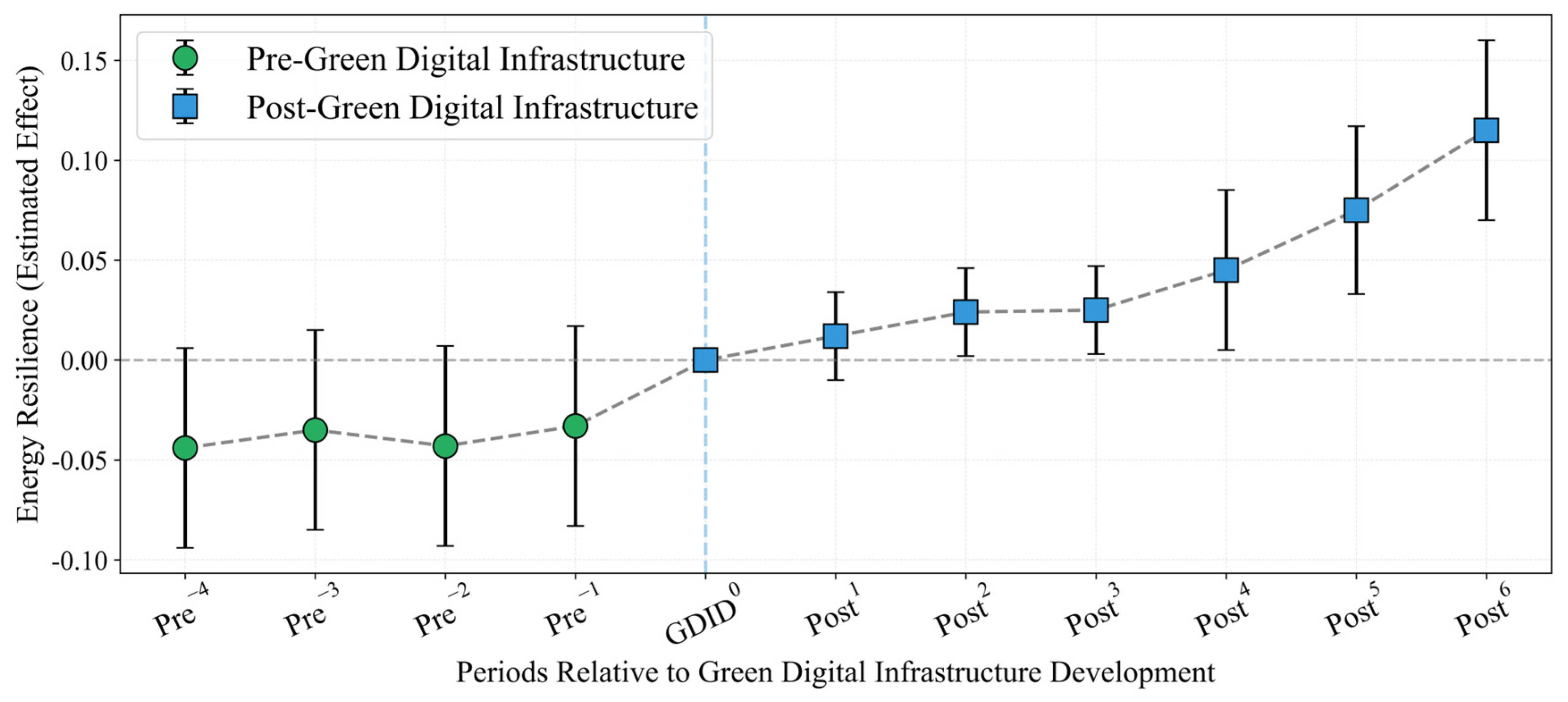
4.2. Impact of Green Digital Infrastructure on Energy Resilience
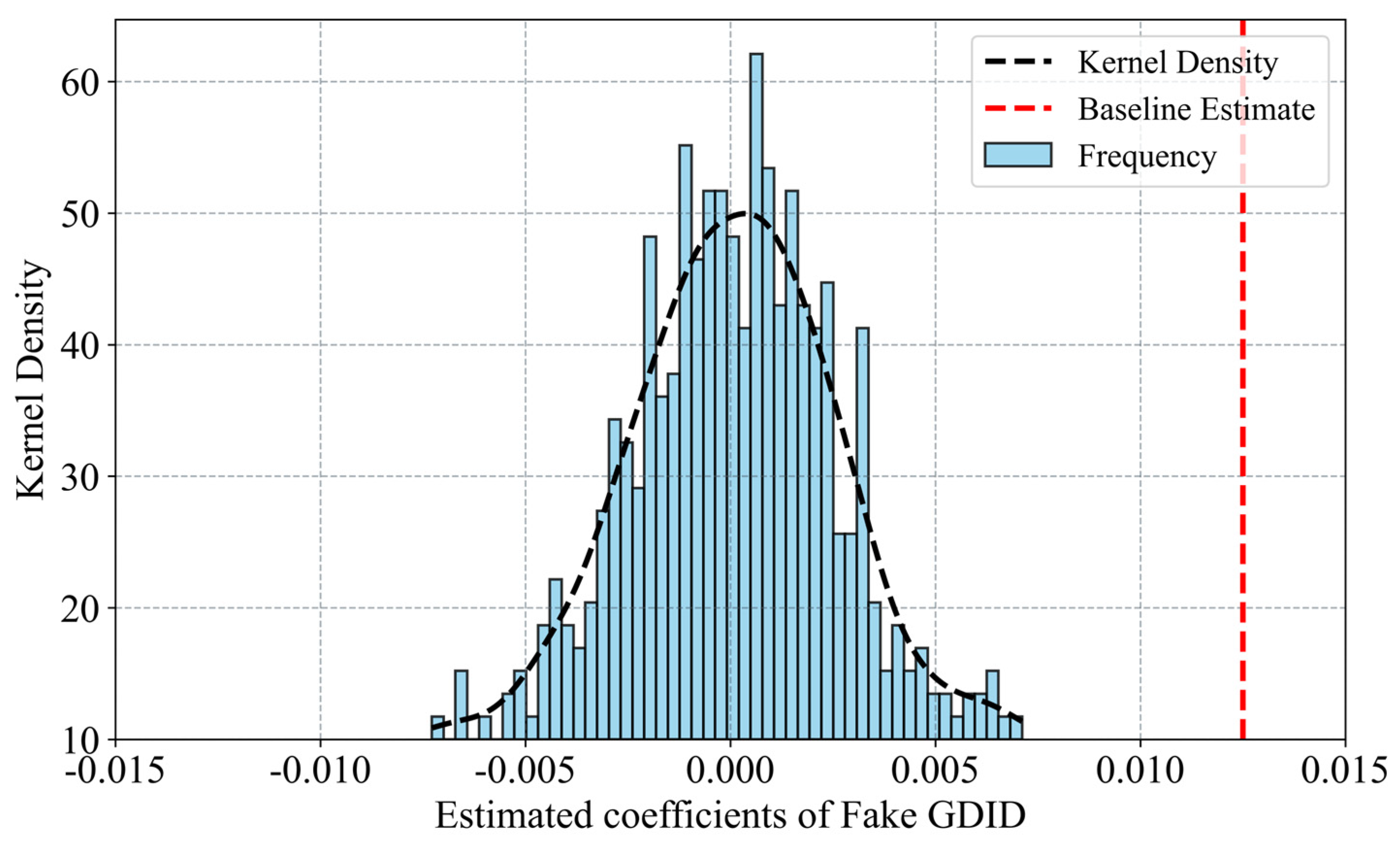
4.3. Robustness Tests
4.4. Heterogeneity Analysis
4.5. Mechanism Exploration
4.5.1. Industrial Structure Optimization Mechanism
4.5.2. Innovation Capacity Enhancement Mechanism
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions and Implications
6.1. Summary of Key Findings
6.2. Theoretical Implications
6.3. Practical Implications
6.4. Limitations and Future Research Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lei, X.; Xu, X. Storm clouds over innovation: Typhoon shocks and corporate R&D activities. Econ. Lett. 2024, 244, 112014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Xu, X. Climate crisis on energy bills: Who bears the greater burden of extreme weather events? Econ. Lett. 2025, 247, 112103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Fu, Y. Interconnectedness among supply chain disruptions, energy crisis, and oil market volatility on economic resilience. Energy Econ. 2025, 108290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balayev, R.; Rzayeva, U.; Ahmadzadeh, E.; Mirzammadova, K. Enhancing sustainable urban areas through digital green infrastructure: Achieving tangible outcomes. East.-Eur. J. Enterp. Technol. 2024, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, R.; Pauleit, S. From multifunctionality to multiple ecosystem services? A conceptual framework for multifunctionality in green infrastructure planning for urban areas. Ambio 2014, 43, 516–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauleit, S.; Vasquéz, A.; Maruthaveeran, S.; Liu, L.; Cilliers, S.S. Urban green infrastructure in the Global South. Urban Ecol. Glob. South 2021, 107–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkou, M.; Tarigan, A.K.; Hanslin, H.M. The multifunctionality concept in urban green infrastructure planning: A systematic literature review. Urban For. Urban Green. 2023, 85, 127975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolgui, A.; Ivanov, D. 5G in digital supply chain and operations management: Fostering flexibility, end-to-end connectivity and real-time visibility through internet-of-everything. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2022, 60, 442–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lin, H. How to leverage flexibility-oriented HRM systems to build organizational resilience in the digital era: The mediating role of intellectual capital. J. Intellect. Cap. 2024, 25, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesse, B.-J.; Heinrichs, H.U.; Kuckshinrichs, W. Adapting the theory of resilience to energy systems: A review and outlook. Energy Sustain. Soc. 2019, 9, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasser, P.; Lustenberger, P.; Cinelli, M.; Kim, W.; Spada, M.; Burgherr, P.; Hirschberg, S.; Stojadinovic, B.; Sun, T.Y. A review on resilience assessment of energy systems. Sustain. Resilient Infrastruct. 2021, 6, 273–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatto, A.; Drago, C. A taxonomy of energy resilience. Energy Policy 2020, 136, 111007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berjawi, A.; Walker, S.; Patsios, C.; Hosseini, S. An evaluation framework for future integrated energy systems: A whole energy systems approach. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 145, 111163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Bilan, S. Green infrastructure: Systematic literature review. Econ. Res. -Ekon. Istraživanja 2022, 35, 343–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaręba, A. Multifunctional and multiscale aspects of green infrastructure in contemporary research. Probl. Ekorozwoju 2014, 9, 149–156. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.W.; Tran, T. An evaluation of local comprehensive plans toward sustainable green infrastructure in US. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerome, G.; Sinnett, D.; Burgess, S.; Calvert, T.; Mortlock, R. A framework for assessing the quality of green infrastructure in the built environment in the UK. Urban For. Urban Green. 2019, 40, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, X.; Deng, X. Building green infrastructure for mitigating urban flood risk in Beijing, China. Urban For. Urban Green. 2024, 93, 128218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xu, L.; Zhu, R.; Ma, Q.; Shi, Y.; Lu, Z. Changes and characteristics of green infrastructure network based on spatio-temporal priority. Land 2022, 11, 901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, J.C.; Monteiro, R.; Silva, V.R. Planning a green infrastructure network from theory to practice: The case study of Setúbal, Portugal. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, K.; Dong, X.; Jiang, Q.; Zhao, J. Assessing energy resilience and its greenhouse effect: A global perspective. Energy Econ. 2021, 104, 105659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y. Climate change adaptation with energy resilience in energy districts—A state-of-the-art review. Energy Build. 2023, 279, 112649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Ng, T.S.; Su, B. Energy-economic resilience with multi-region input–output linear programming models. Energy Econ. 2019, 84, 104569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhang, J. China’s inter-provincial energy security resilience assessment over space and time: An improved gray relational projection model. Energies 2023, 16, 3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharmin, F.; Dhakal, S. A composite energy resilience performance indicator for Bangladesh. Energy Sources Part B Econ. Plan. Policy 2022, 17, 2149901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdurasulovich, K.K.; Khodjabaevna, K.R.; Gulshat, K. Green Data Centers and Renewable Energy Sources. In Digital Sustainability; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2025; pp. 152–174. [Google Scholar]
- Kröger, W. Achieving resilience of large-scale engineered infrastructure systems. Resilient Struct. Infrastruct. 2019, 289–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, J.; Ahmad, M.W.; Rezgui, Y.; Hippolyte, J.-L. Operational supply and demand optimisation of a multi-vector district energy system using artificial neural networks and a genetic algorithm. Appl. Energy 2019, 235, 699–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, A. Resilience of urban social-ecological-technological systems (SETS): A review. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 99, 104910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, X.; Ding, H.; Zhang, N.; Song, M. Revitalizing industrial structure: Unleashing the potential of energy technology innovation. J. Evol. Econ. 2025, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, K.; Huang, H.; Bilal, M.; Xu, X. Distributed incentives for intelligent offloading and resource allocation in digital twin driven smart industry. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2022, 19, 3133–3143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yang, Z.; Jin, C.; Wang, J. How an industrial internet platform empowers the digital transformation of SMEs: Theoretical mechanism and business model. J. Knowl. Manag. 2023, 27, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cui, L.; Wu, L.; Lowry, P.B.; Kumar, A.; Tan, K.H. Digitalization and network capability as enablers of business model innovation and sustainability performance: The moderating effect of environmental dynamism. J. Inf. Technol. 2024, 39, 687–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strazzullo, S.; Cricelli, L.; Grimaldi, M.; Ferruzzi, G. Connecting the path between open innovation and industry 4.0: A review of the literature. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, M.; Khan, N.; Omri, A. Environmental policy stringency, ICT, and technological innovation for achieving sustainable development: Assessing the importance of governance and infrastructure. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 365, 121581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaidan, E.; Ghofrani, A.; Abulibdeh, A.; Jafari, M. Accelerating the change to smart societies-a strategic knowledge-based framework for smart energy transition of urban communities. Front. Energy Res. 2022, 10, 852092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoppelletto, A.; Orlandi, L.B. Cultural and digital collaboration infrastructures as sustainability enhancing factors: A configurational approach. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2022, 179, 121645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbanyele, W.; Huang, H.; Muchenje, L.T.; Zhao, J. How does climate regulatory risk influence labor employment decisions? Evidence from a quasi-natural experiment. China Econ. Rev. 2024, 87, 102236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Mbanyele, W.; Zhang, L.; Chen, X.-L.; Song, M. Nonnegligible transition risks towards net-zero economy: Lessons from green finance initiatives in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 375, 124132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, H.; Mbanyele, W.; Wei, Z.; Li, X. How does green industrial policy affect corporate green innovation? Evidence from the green factory identification in China. Energy Econ. 2025, 141, 108047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, H.; Mbanyele, W.; Wang, F.; Liu, H. Does the issuance of green bonds nudge environmental responsibility engagements? Evidence from the Chinese green bond market. Financ. Innov. 2024, 10, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
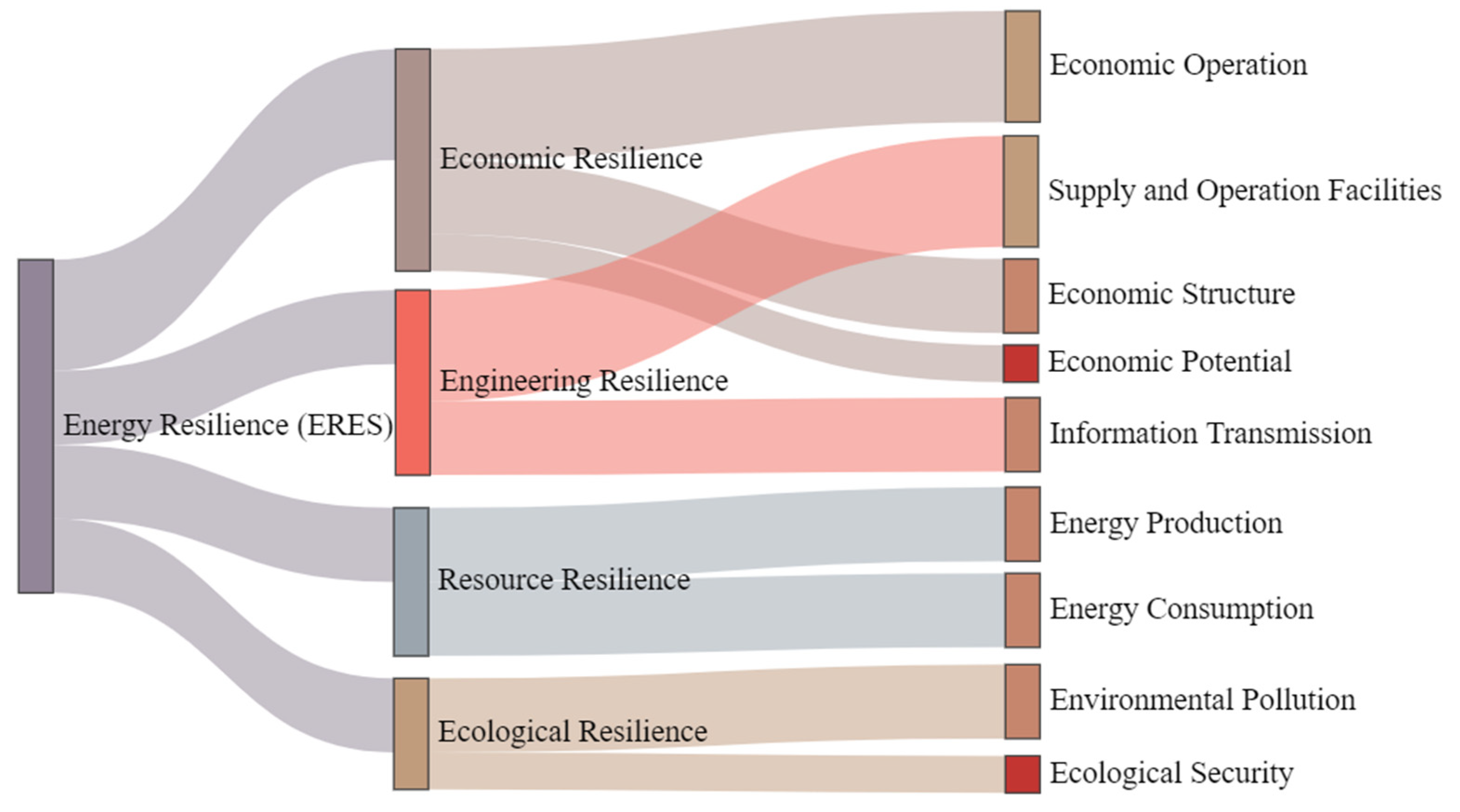


| Primary Indicators | Secondary Indicators | Tertiary Indicators | Attribute |
|---|---|---|---|
| Economic Resilience | Economic Operation | Energy Industry Investment (CNY 100 million) | + |
| Industrial Producer Price Index | + | ||
| Total Energy Consumption/GDP (10,000 tons of standard coal/CNY 100 million) | − | ||
| Economic Structure | Industrial Added Value/GDP (%) | + | |
| Total Import and Export/GDP (%) | + | ||
| Economic Potential | Number of Patent Applications | + | |
| Engineering Resilience | Supply and Operation Facilities | Power Generation Capacity (10,000 kW) | + |
| Transmission Line Circuit Length (km) | + | ||
| Total Gas Pipeline Length (km) | + | ||
| Information Transmission | Internet Penetration Rate (%) | + | |
| Mobile Phone Penetration Rate (units/100 people) | + | ||
| Resource Resilience | Energy Production | Energy Production/Year-end Total Population (10,000 tons of standard coal/10,000 people) | + |
| Energy Production Diversification Index | + | ||
| Energy Consumption | Energy Production/Total Energy Consumption (%) | + | |
| Energy Consumption/Year-end Total Population (10,000 tons of standard coal/10,000 people) | − | ||
| Ecological Resilience | Ecological Security | Forest Coverage Rate (%) | + |
| Environmental Pollution | Per Capita Carbon Emissions (10,000 tons/10,000 people) | − | |
| Incidents of Sudden Environmental Events (times) | − |
| Variable | N | Mean | S.D. | Min | Median | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ERES | 330 | 0.4419 | 0.0604 | 0.2844 | 0.4407 | 0.6466 |
| PGDP | 330 | 10.7430 | 0.5960 | 9.4210 | 10.7130 | 12.1510 |
| UR | 330 | 0.5620 | 0.1230 | 0.3120 | 0.5500 | 0.8960 |
| IS | 330 | 0.4530 | 0.0770 | 0.1920 | 0.4470 | 0.5930 |
| OPEN | 330 | 0.3360 | 0.4030 | 0.0350 | 0.1960 | 1.8370 |
| ISO | 330 | 0.4380 | 0.0840 | 0.2870 | 0.4260 | 0.8290 |
| IC | 330 | 10.4950 | 1.3890 | 7.1670 | 10.5380 | 13.7440 |
| Variable | (1) | (2) |
|---|---|---|
| ERES | ERES | |
| GDID | 0.0137 ** | 0.0125 ** |
| (2.39) | (2.18) | |
| PGDP | 0.0246 *** | |
| (3.42) | ||
| UR | 0.0835 ** | |
| (2.16) | ||
| IS | −0.0318 * | |
| (−1.75) | ||
| OPEN | 0.0097 | |
| (1.42) | ||
| City | Yes | Yes |
| Year | Yes | Yes |
| N | 330 | 330 |
| R2 | 0.642 | 0.683 |
| Variable | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ERES | ERES | ERES | ERES | |
| GDID | 0.0121 ** | 0.0118 ** | 0.0116 ** | 0.0129 ** |
| (2.11) | (2.06) | (2.07) | (2.25) | |
| SCITY | 0.0082 * | |||
| (1.78) | ||||
| LCITY | 0.0096 * | |||
| (1.85) | ||||
| Controls | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| City | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Year | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| N | 330 | 330 | 330 | 330 |
| R2 | 0.692 | 0.694 | 0.675 | 0.688 |
| Variable | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| High Economic Development | Low Economic Development | High Digital Foundation | Low Digital Foundation | |
| ERES | ERES | ERES | ERES | |
| GDID | 0.0183 *** | 0.0092 * | 0.0164 ** | 0.0085 |
| (2.72) | (1.68) | (2.35) | (1.44) | |
| Controls | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| City | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Year | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| R2 | 0.709 | 0.652 | 0.712 | 0.645 |
| Inter-group Difference | 0.0091 ** | 0.0079 * | ||
| Variable | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ISO | ERES | IC | ERES | |
| GDID | 0.0193 ** | 0.0112 * | 0.0980 *** | 0.0110 * |
| (2.22) | (1.95) | (2.76) | (1.92) | |
| ISO | 0.0675 *** | |||
| (2.82) | ||||
| IC | 0.0153 ** | |||
| (2.15) | ||||
| Controls | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| City | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Year | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| N | 330 | 330 | 330 | 330 |
| R2 | 0.658 | 0.697 | 0.675 | 0.692 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lei, X.; Xu, J.; Chen, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhao, K. Digital Oasis: How Green Infrastructure Is Reshaping China’s Energy Resilience Landscape. Systems 2025, 13, 306. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13050306
Lei X, Xu J, Chen Y, Liu C, Zhao K. Digital Oasis: How Green Infrastructure Is Reshaping China’s Energy Resilience Landscape. Systems. 2025; 13(5):306. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13050306
Chicago/Turabian StyleLei, Xue, Jian Xu, You Chen, Chang Liu, and Kunjian Zhao. 2025. "Digital Oasis: How Green Infrastructure Is Reshaping China’s Energy Resilience Landscape" Systems 13, no. 5: 306. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13050306
APA StyleLei, X., Xu, J., Chen, Y., Liu, C., & Zhao, K. (2025). Digital Oasis: How Green Infrastructure Is Reshaping China’s Energy Resilience Landscape. Systems, 13(5), 306. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13050306









