Solid Lipid Nanoparticles for Skin Delivery of Trans-Resveratrol: Impact of Preparation Methods on Formulation Stability
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Development of SLNs
2.2. Time Stability Testing of Formulations
2.3. Hydrodynamic Diameter Polydispersity Index and Zeta Potential Analysis
2.4. Encapsulation Efficiency
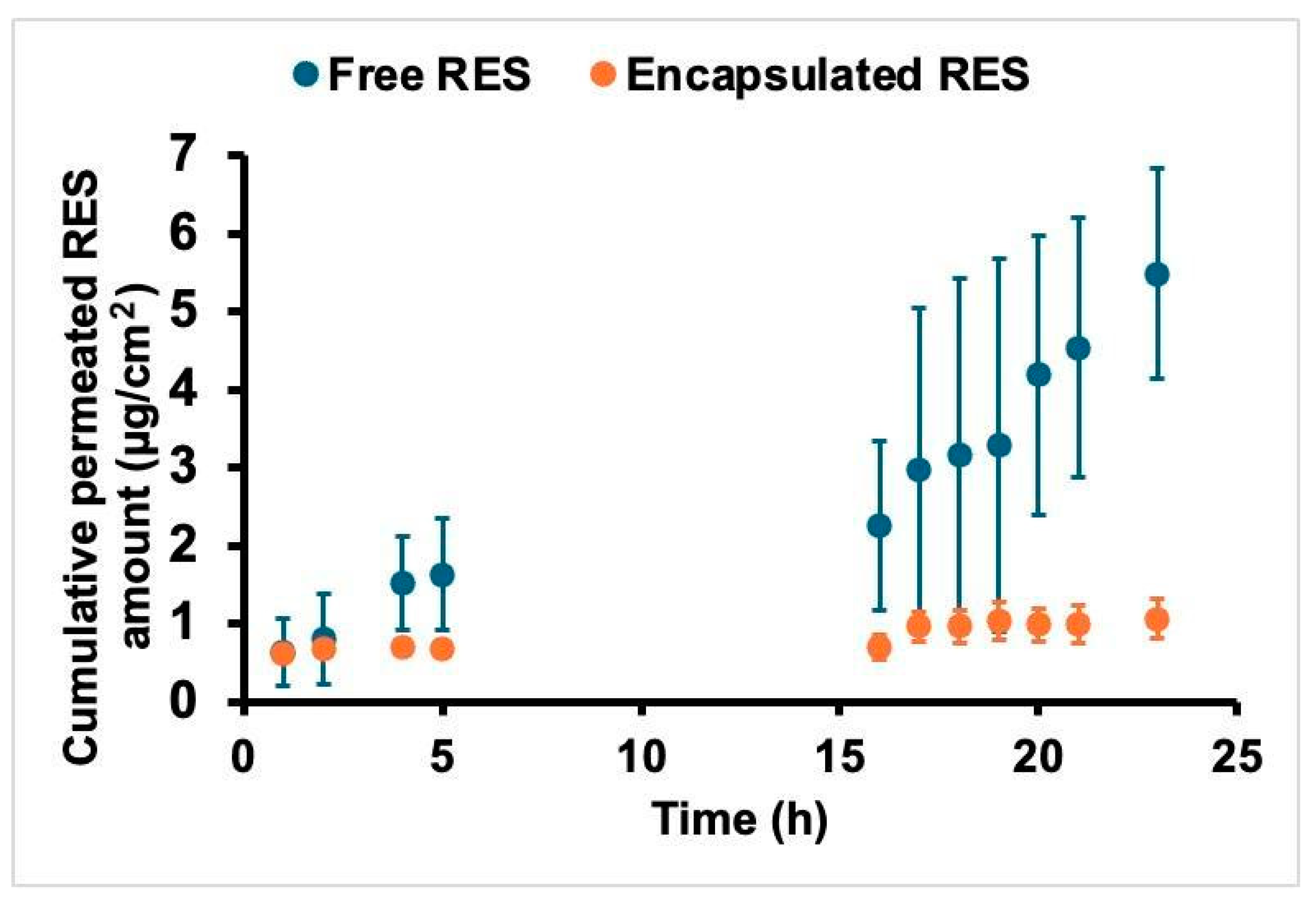
2.5. Skin Permeation
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Diaz-Gerevini, G.T.; Repossi, G.; Dain, A.; Tarres, M.C.; Das, U.N.; Eynard, A.R. Beneficial Action of Resveratrol: How and Why? Nutrition 2016, 32, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frémont, L. Biological Effects of Resveratrol. Life Sci. 2000, 66, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baur, J.A.; Sinclair, D.A. Therapeutic Potential of Resveratrol: The in vivo Evidence. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 493–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehnert, W.; Mäder, K. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles: Production, Characterization and Applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 83–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, R.H.; Mäder, K.; Gohla, S. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLN) for Controlled Drug Delivery—A Review of the State of the Art. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2000, 50, 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, L.; Daozhou, L.; Ying, C.; Qibing, M.; Siyuan, Z. A Resveratrol-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carrier Hydrogel to Enhance the Anti-UV Irradiation and Anti-Oxidant Efficacy. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 204, 111786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldati, P.P.; Polonini, H.C.; Paes, C.Q.; Restrepob, J.A.S.; Creczynksi-Pasa, T.B.; Chaves, M.G.A.M.; Brandão, M.A.F.; Pittella, F.; Raposo, N.R.B. Controlled Release of Resveratrol from Lipid Nanoparticles Improves Antioxidant Effect. In Proceedings of the IFAC-PapersOnLine; Elsevier B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; Volume 51, pp. 16–21. [Google Scholar]
- Gokce, E.H.; Korkmaz, E.; Dellera, E.; Sandri, G.; Cristina Bonferoni, M.; Ozer, O. Resveratrol-Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles versus Nanostructured Lipid Carriers: Evaluation of Antioxidant Potential for Dermal Applications. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samprasit, W.; Suriyaamporn, P.; Sriamornsak, P.; Opanasopit, P.; Chamsai, B. Resveratrol-Loaded Lipid-Based Nanocarriers for Topical Delivery: Comparative Physical Properties and Antioxidant Activity. OpenNano 2024, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardeike, J.; Hommoss, A.; Müller, R.H. Lipid Nanoparticles (SLN, NLC) in Cosmetic and Pharmaceutical Dermal Products. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 366, 170–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.J.; Lee, M.K.; Kim, C.K. Altered Chemical and Biological Activities of All-Trans Retinoic Acid Incorporated in Solid Lipid Nanoparticle Powders. J. Control Release 2004, 100, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agayan, R.R.; Horvath, T.; McNaughton, B.H.; Anker, J.N.; Kopelman, R. Optical Manipulation of Metal-Silica Hybrid Nanoparticles. Opt. Trapp. Opt. Micromanipulation 2004, 5514, 502–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detoni, C.B.; Souto, G.D.; da Silva, A.L.M.; Pohlmann, A.R.; Guterres, S.S. Photostability and Skin Penetration of Different E -Resveratrol-Loaded Supramolecular Structures. Photochem. Photobiol. 2012, 88, 913–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souto, E.B.; Fangueiro, J.F.; Fernandes, A.R.; Cano, A.; Sanchez-Lopez, E.; Garcia, M.L.; Severino, P.; Paganelli, M.O.; Chaud, M.V.; Silva, A.M. Physicochemical and Biopharmaceutical Aspects Influencing Skin Permeation and Role of SLN and NLC for Skin Drug Delivery. Heliyon 2022, 8, e08938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labouta, H.I.; El-Khordagui, L.K.; Kraus, T.; Schneider, M. Mechanism and Determinants of Nanoparticle Penetration through Human Skin. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 4989–4999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, D.; Xie, C.; Huang, K.; Zhu, C. The Production and Characteristics of Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLNs). Biomaterials 2003, 24, 1781–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jores, K.; Mehnert, W.; Drechsler, M.; Bunjes, H.; Johann, C.; Mäder, K. Investigations on the Structure of Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLN) and Oil-Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles by Photon Correlation Spectroscopy, Field-Flow Fractionation and Transmission Electron Microscopy. J. Control Release 2004, 95, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honary, S.; Zahir, F. Effect of Zeta Potential on the Properties of Nano-Drug Delivery Systems—A Review (Part 1). Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2013, 12, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, R.H.; Radtke, M.; Wissing, S.A. Nanostructured Lipid Matrices for Improved Microencapsulation of Drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 242, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, M.; Jain, A.; Mishra, A.; Muthu, M.; Singh, S. Development of Repaglinide Loaded Solid Lipid Nanocarrier: Selection of Fabrication Method. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2010, 7, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danaei, M.; Dehghankhold, M.; Ataei, S.; Hasanzadeh Davarani, F.; Javanmard, R.; Dokhani, A.; Khorasani, S.; Mozafari, M.R. Impact of Particle Size and Polydispersity Index on the Clinical Applications of Lipidic Nanocarrier Systems. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-K.; Howard, M.D.; Dziubla, T.D.; Rinehart, J.J.; Jay, M.; Lu, X. Uniformity of Drug Payload and Its Effect on Stability of Solid Lipid Nanoparticles Containing an Ester Prodrug. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souto, E.B.; Müller, R.H. Lipid Nanoparticles: Effect on Bioavailability and Pharmacokinetic Changes. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2010, 197, 115–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ourique, A.F.; Melero, A.; de Bona da Silva, C.; Schaefer, U.F.; Pohlmann, A.R.; Guterres, S.S.; Lehr, C.-M.; Kostka, K.-H.; Beck, R.C.R. Improved Photostability and Reduced Skin Permeation of Tretinoin: Development of a Semisolid Nanomedicine. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2011, 79, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melero, A.; Ferreira Ourique, A.; Stanisçuaski Guterres, S.; Raffin Pohlmann, A.; Lehr, C.-M.; Ruver Beck, R.C.; Schaefer, U. Nanoencapsulation in Lipid-Core Nanocapsules Controls Mometasone Furoate Skin Permeability Rate and Its Penetration to the Deeper Skin Layers. Ski. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2014, 27, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wissing, S. Cosmetic Applications for Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLN). Int. J. Pharm. 2003, 254, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.-Y.; Fang, C.-L.; Liu, C.-H.; Su, Y.-H. Lipid Nanoparticles as Vehicles for Topical Psoralen Delivery: Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLN) versus Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (NLC). Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2008, 70, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcês, A.; Amaral, M.H.; Sousa Lobo, J.M.; Silva, A.C. Formulations Based on Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLN) and Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (NLC) for Cutaneous Use: A Review. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 112, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Components (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | F1-RES | F2 | F2-RES | |
| Stearic acid (SA) | 5.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 |
| Soy phosphatidylcholine (SPC) | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 |
| Polysorbate 80 (T80) | 3.5 | 3.5 | 3.5 | 3.5 |
| Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) | - | - | 0.45 | 0.45 |
| Poloxamer 407 ® (P407) | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| Glycerin (GLI) | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.15 |
| Trans-resveratrol (RES) | - | 0.25 | - | 0.25 |
| Phenonip ® | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.75 |
| Ethanol P.A. | 1.25 | 1.25 | 1.25 | 1.25 |
| Ultra-pure water | q.s.p. | q.s.p. | q.s.p. | q.s.p. |
| Magnetic Stirrer | |||||||||
| Days | Size (nm) | PdI | ZP (mV) | ||||||
| 70 °C | 75 °C | 80 °C | 70 °C | 75 °C | 80 °C | 70 °C | 75 °C | 80 °C | |
| 1 | 295.4 | 1068.1 | 316.7 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.2 | −28.3 | −16.7 | −18.3 |
| 7 | 287.4 | 412.5 | 319.2 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.3 | −23.8 | −18.2 | −22.0 |
| 15 | 312.1 | 846.2 | 341.9 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.3 | −19.5 | −19.0 | −21.2 |
| 30 | 317.0 | 1167.6 | 329.0 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.3 | −18.9 | −16.7 | −20.0 |
| 50 | 311.4 | 1197.7 | 366.1 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.3 | −19.9 | −22.1 | −20.8 |
| 90 | 358.5 | 1262.0 | 378.6 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | −20.7 | −22.6 | −22.2 |
| Turrax 11,000 rpm | |||||||||
| Days | Size (nm) | PdI | ZP (mV) | ||||||
| 70 °C | 75 °C | 80 °C | 70 °C | 75 °C | 80 °C | 70 °C | 75 °C | 80 °C | |
| 1 | 313.1 | 313.6 | 284.6 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.2 | −20.4 | −19.1 | −18.9 |
| 7 | 317.6 | 323.3 | 266.8 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.2 | −18.6 | −15.9 | −19.3 |
| 15 | 318.9 | 323.3 | 285.8 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.3 | −19.8 | −15.9 | −19.5 |
| 30 | 319.6 | 330.3 | 313.6 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.3 | −21.2 | −17.6 | −19.7 |
| 50 | 769.9 | 336.8 | 745.3 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.3 | −19.7 | −20.9 | −24.2 |
| 90 | 788.4 | 347.0 | 1100.8 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.3 | −20.9 | −20.8 | −20.3 |
| Turrax 24,000 rpm | |||||||||
| Days | Size (nm) | PdI | ZP (mV) | ||||||
| 70 °C | 75 °C | 80 °C | 70 °C | 75 °C | 80 °C | 70 °C | 75 °C | 80 °C | |
| 1 | 248.5 | 367.6 | 272.4 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.2 | −22.2 | −21.3 | −22.5 |
| 7 | 228.6 | 381.0 | 285.8 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.2 | −19.8 | −20.0 | −20.9 |
| 15 | 365.7 | 384.5 | 298.5 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.2 | −21.2 | −20.7 | −21.2 |
| 30 | 246.9 | 387.8 | 314.4 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | −19.4 | −20.3 | −18.6 |
| 50 | 291.1 | 388.5 | 317.9 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.2 | −20.1 | −20.3 | −25.1 |
| 90 | 316.6 | 393.1 | 330.9 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.2 | −16.3 | −20.6 | −22.9 |
| Magnetic Stirrer | |||||||||
| Days | Size (nm) | PdI | ZP (mV) | ||||||
| 70 °C | 75 °C | 80 °C | 70 °C | 75 °C | 80 °C | 70 °C | 75 °C | 80 °C | |
| 1 | 905.0 | 273.9 | 442.0 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 27.6 | 26.3 | 25.2 |
| 7 | 835.4 | 346.8 | 610.0 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 26.5 | 27.9 | 24.5 |
| 15 | 928.8 | 401.9 | 665.0 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 25.3 | 29.2 | 27.4 |
| 30 | 1171.5 | 455.3 | 694.6 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 21.7 | 30.7 | 28.7 |
| 50 | 1225.0 | 518.0 | 712.1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 32.7 | 28.9 | 28.7 |
| 90 | 1307.4 | 535.5 | 782.7 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 27.2 | 28.2 | 28.3 |
| Turrax 11,000 rpm | |||||||||
| Days | Size (nm) | PdI | ZP (mV) | ||||||
| 70 °C | 75 °C | 80 °C | 70 °C | 75 °C | 80 °C | 70 °C | 75 °C | 80 °C | |
| 1 | 242.5 | 219.4 | 298.7 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 22.5 | 26.5 | 27.9 |
| 7 | 302.6 | 501.5 | 358.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 14.7 | 29.5 | 32.6 |
| 15 | 332.1 | 584.2 | 420.5 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 18.7 | 28.3 | 23.6 |
| 30 | 459.4 | 662.7 | 455.2 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 24.8 | 28.7 | 29.5 |
| 50 | 504.5 | 683.1 | 452.7 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 23.2 | 31.5 | 31.9 |
| 90 | 556.1 | 765.6 | 611.9 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 24.2 | 30.9 | 23.1 |
| Turrax 24,000 rpm | |||||||||
| Days | Size (nm) | PdI | ZP (mV) | ||||||
| 70 °C | 75 °C | 80 °C | 70 °C | 75 °C | 80 °C | 70 °C | 75 °C | 80 °C | |
| 1 | 169.3 | 183.0 | 251.7 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 26.1 | 25.1 | 28.4 |
| 7 | 198.2 | 311.7 | 273.8 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 32.4 | 28.8 | 30.5 |
| 15 | 219.5 | 335.0 | 318.5 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 22.0 | 25.3 | 26.7 |
| 30 | 257.3 | 392.1 | 354.2 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 31.7 | 24.7 | 32.7 |
| 50 | 274.1 | 396.8 | 430.5 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 26.1 | 27.9 | 30.8 |
| 90 | 301.7 | 402.3 | 478.8 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 27.3 | 29.3 | 31.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cruz, A.T.; Di Filippo, L.D.; Duarte, J.L.; Guillot, A.J.; Pérez-García, A.; Melero, A.; Chorilli, M. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles for Skin Delivery of Trans-Resveratrol: Impact of Preparation Methods on Formulation Stability. Cosmetics 2025, 12, 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics12010007
Cruz AT, Di Filippo LD, Duarte JL, Guillot AJ, Pérez-García A, Melero A, Chorilli M. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles for Skin Delivery of Trans-Resveratrol: Impact of Preparation Methods on Formulation Stability. Cosmetics. 2025; 12(1):7. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics12010007
Chicago/Turabian StyleCruz, Andressa Tardim, Leonardo Delello Di Filippo, Jonatas Lobato Duarte, Antonio José Guillot, Alberto Pérez-García, Ana Melero, and Marlus Chorilli. 2025. "Solid Lipid Nanoparticles for Skin Delivery of Trans-Resveratrol: Impact of Preparation Methods on Formulation Stability" Cosmetics 12, no. 1: 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics12010007
APA StyleCruz, A. T., Di Filippo, L. D., Duarte, J. L., Guillot, A. J., Pérez-García, A., Melero, A., & Chorilli, M. (2025). Solid Lipid Nanoparticles for Skin Delivery of Trans-Resveratrol: Impact of Preparation Methods on Formulation Stability. Cosmetics, 12(1), 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics12010007









