Design of Composite Disturbance Observer and Continuous Terminal Sliding Mode Control for Piezoelectric Nanopositioning Stage
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Modeling and Conventional Control Design
2.1. Modeling of the Piezoelectric Nanopositioning Stage
2.2. Analysis of Disturbances in the Piezoelectric Nanopositioning Stage
2.3. Design of Conventional Composite Control Strategy
3. Design of New Control Strategy
3.1. Composite Disturbance Observer Design
3.2. Continuous Terminal Sliding Mode Control Design
3.3. Composite Control Structure
4. Simulation Results and Experimental Tests
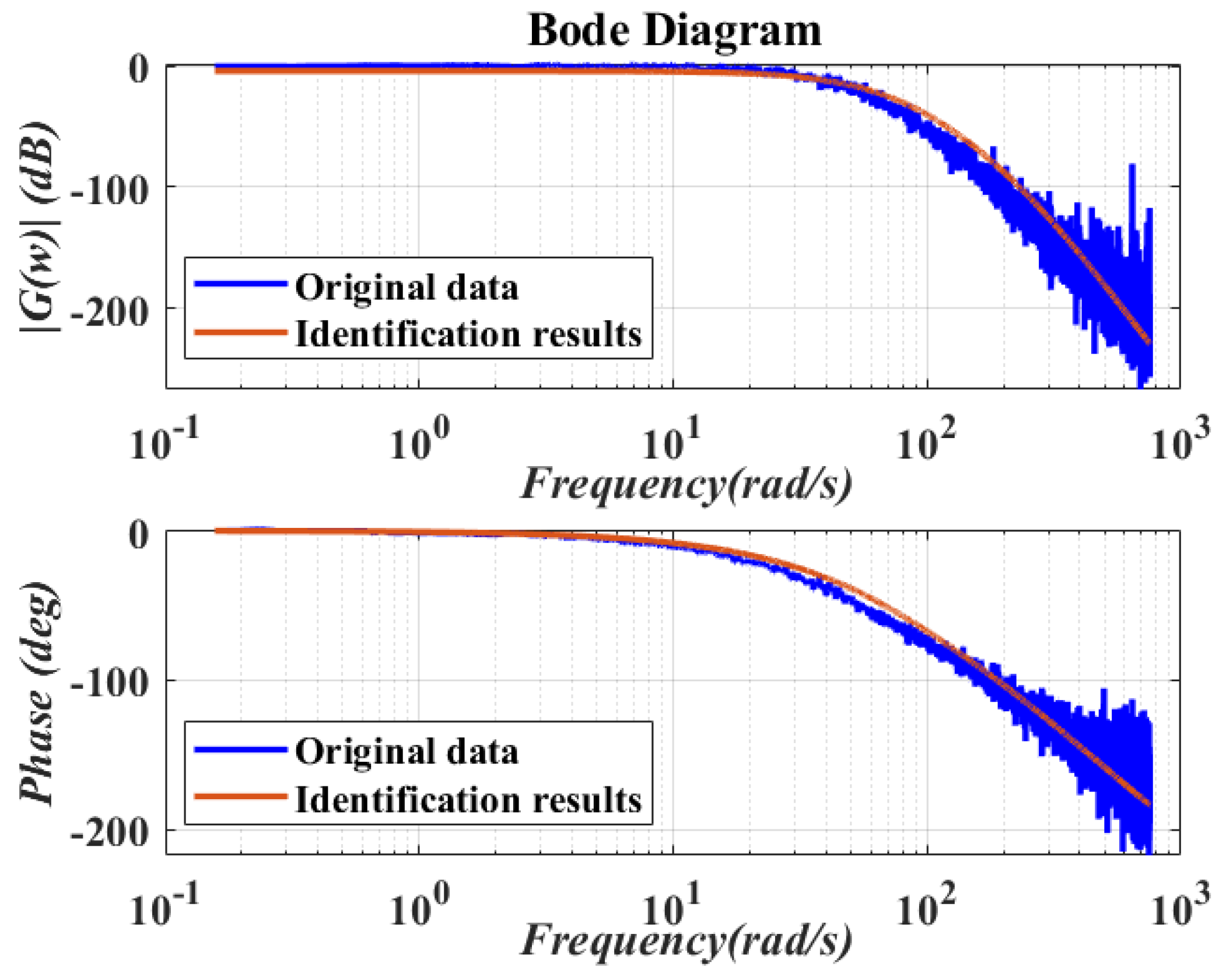
4.1. Experimental Setup and Model Identification
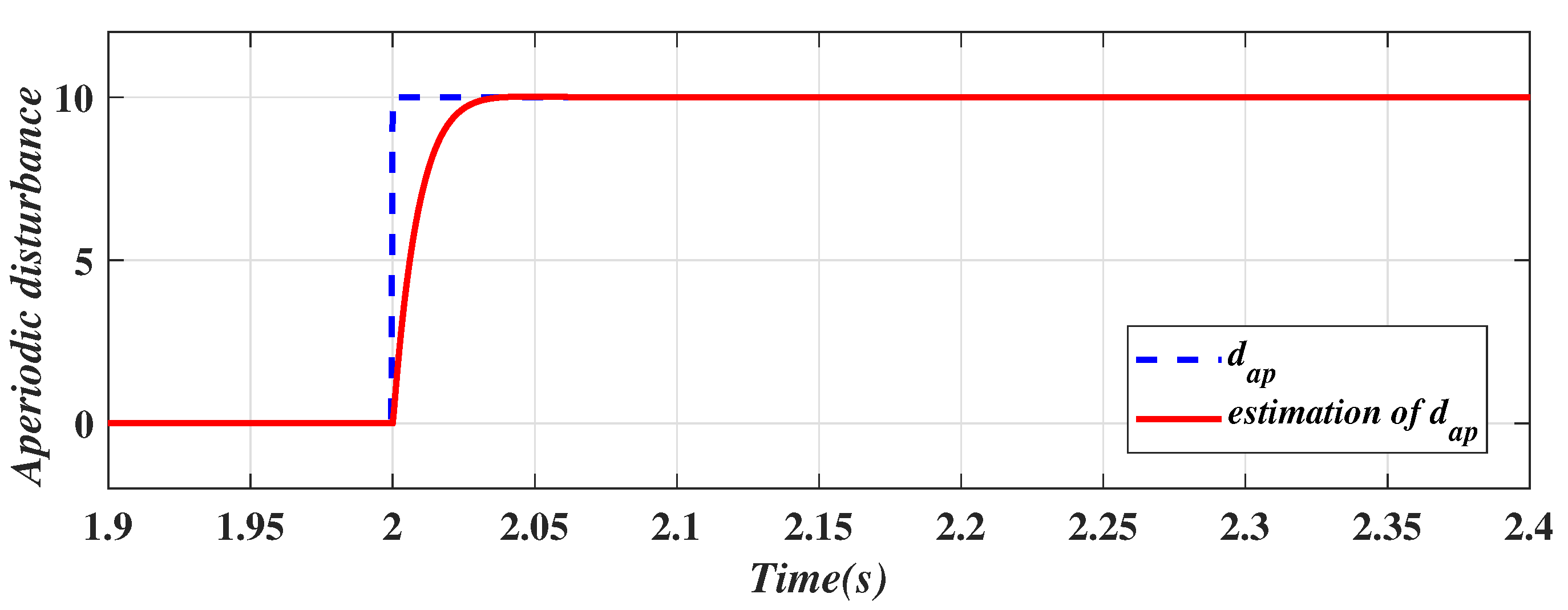
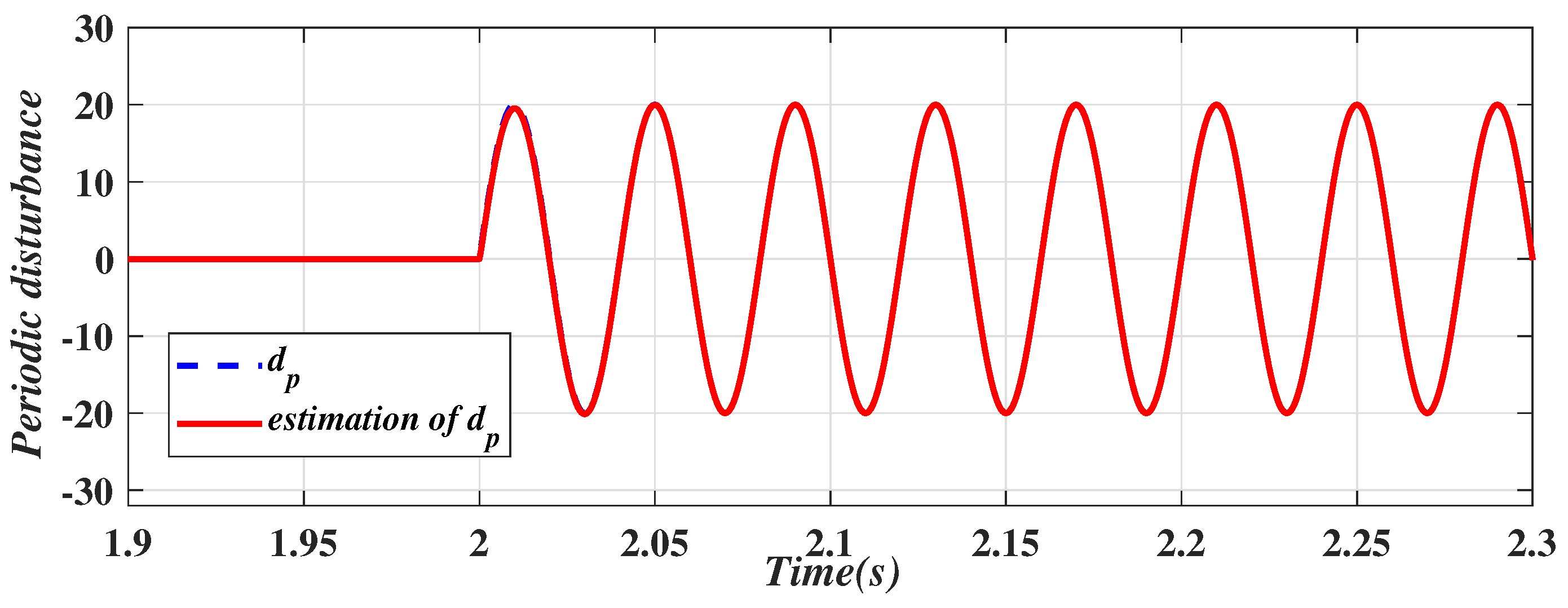
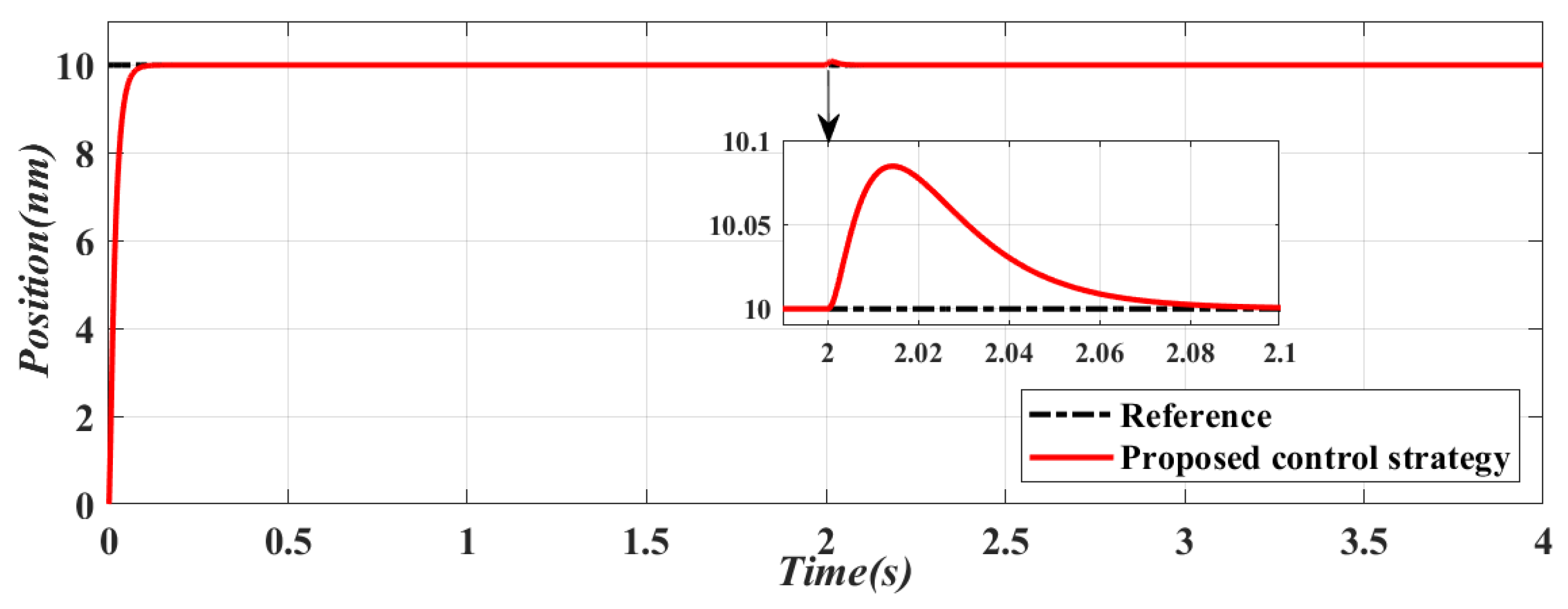
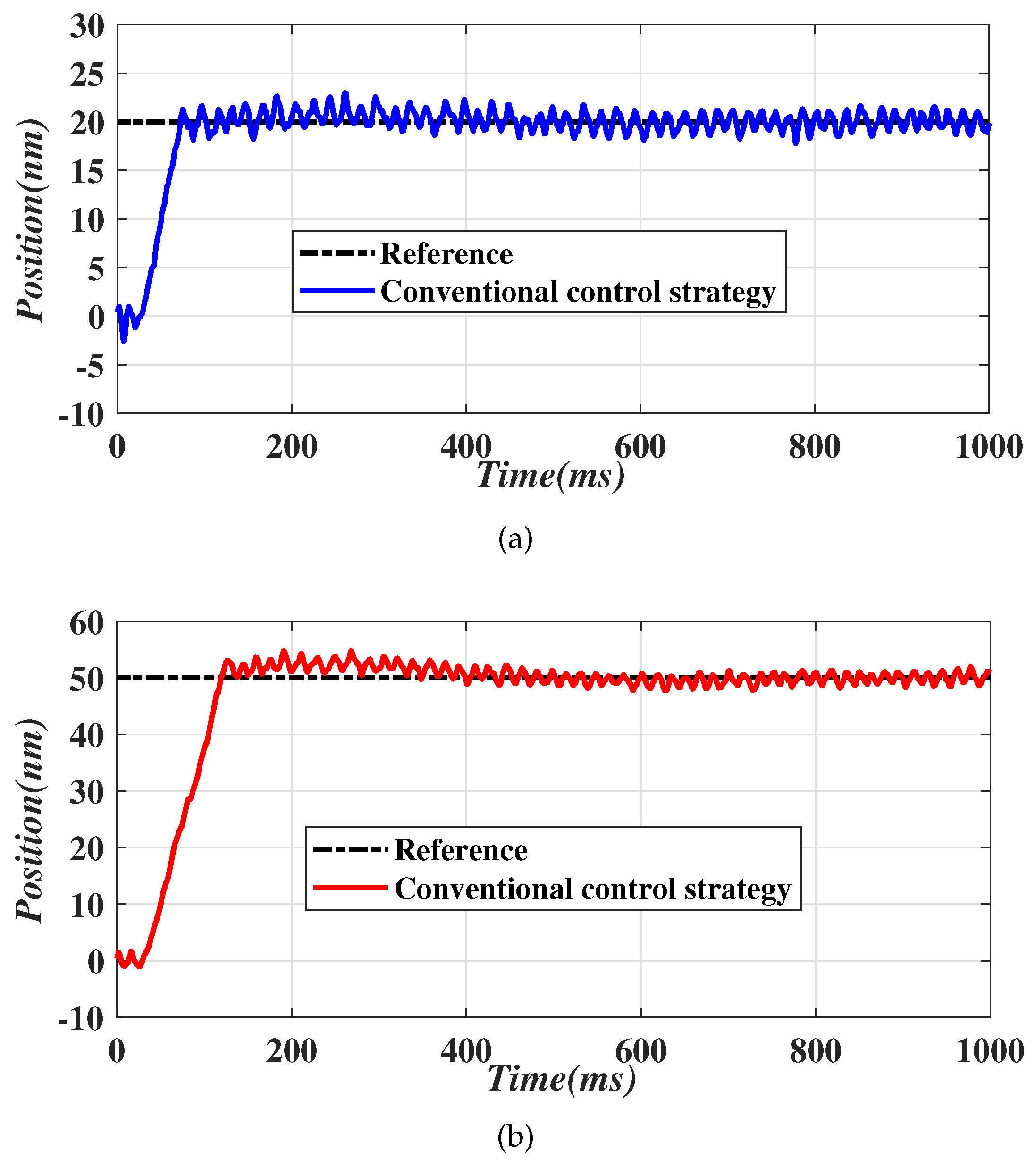
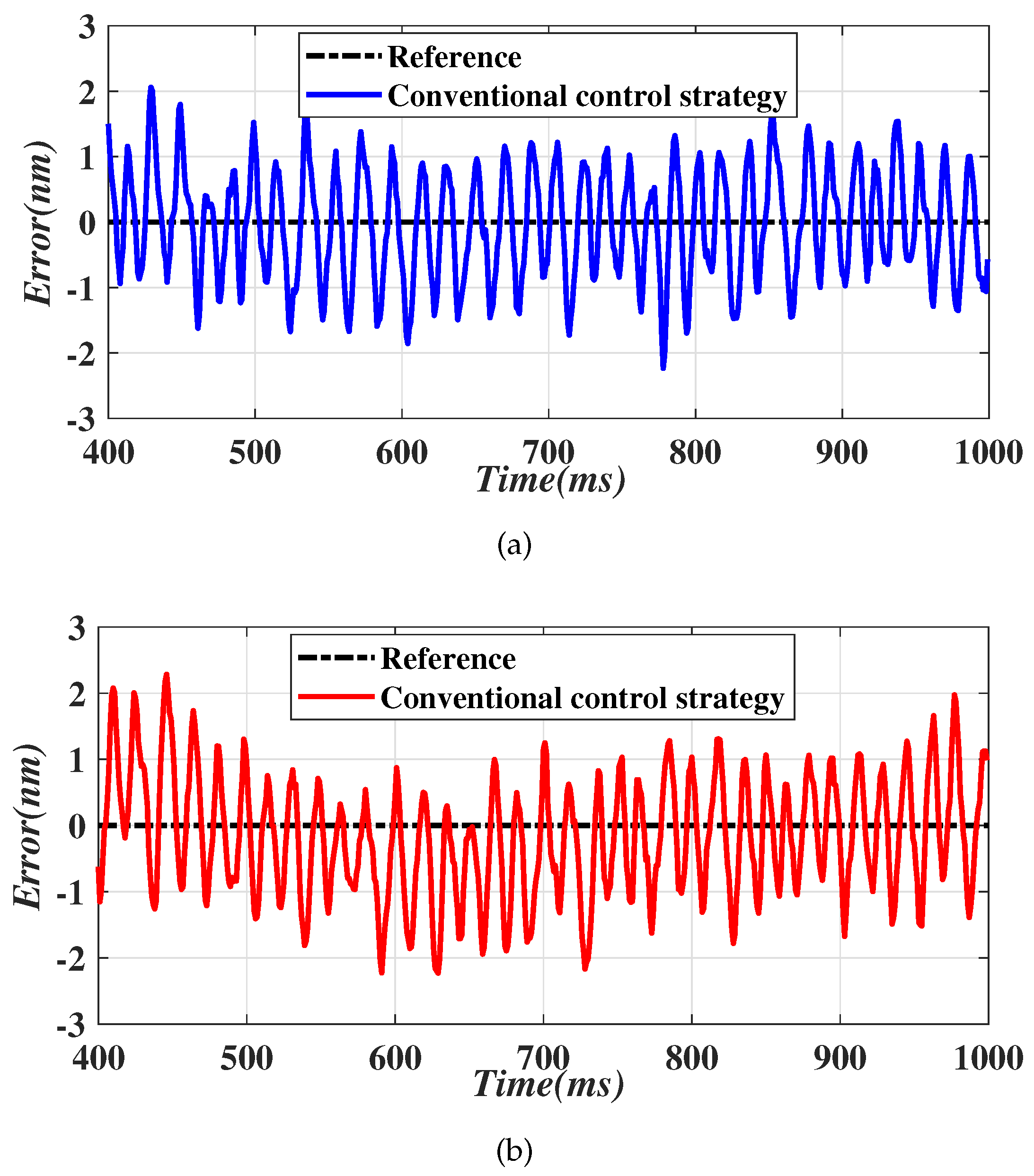
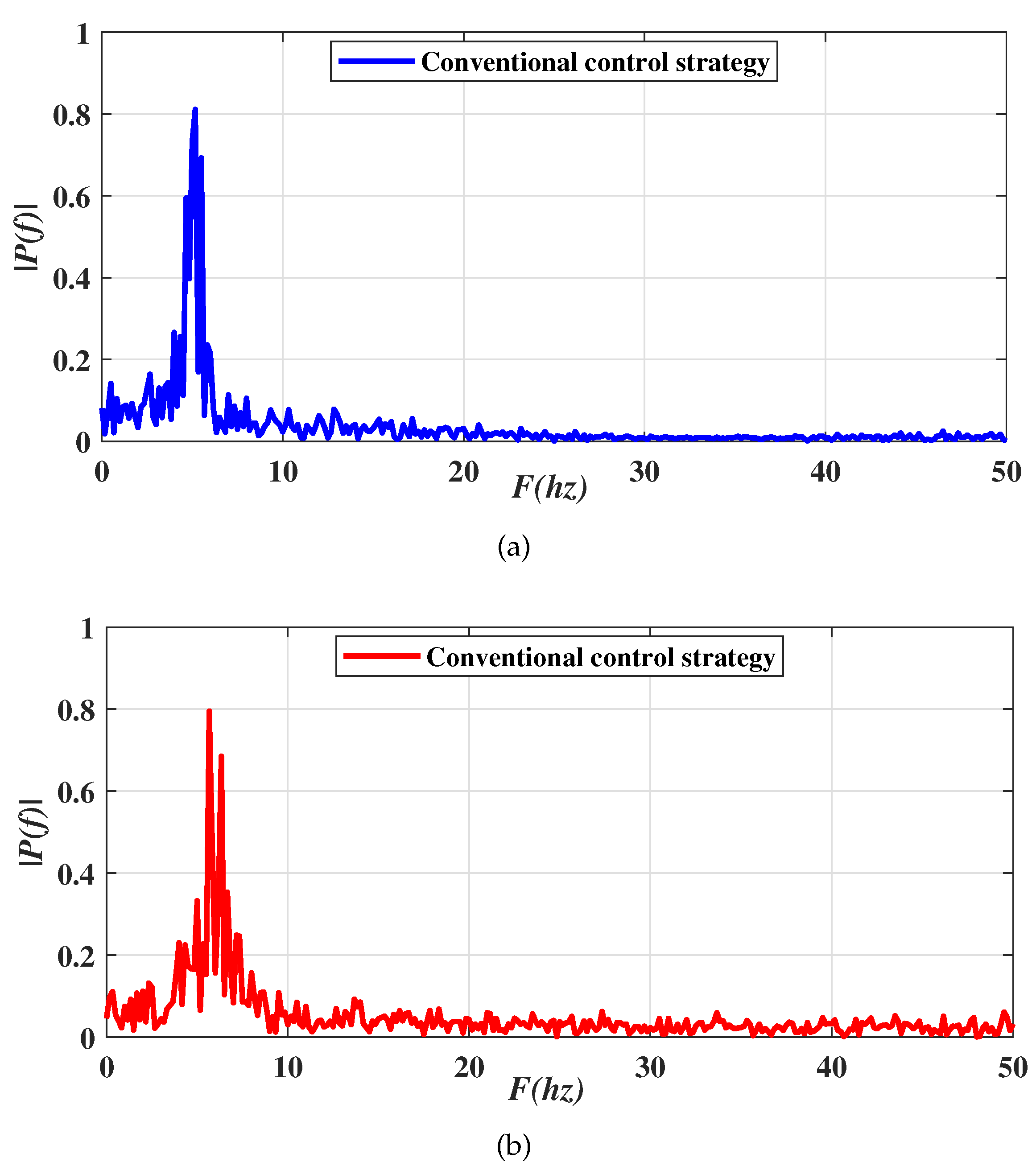
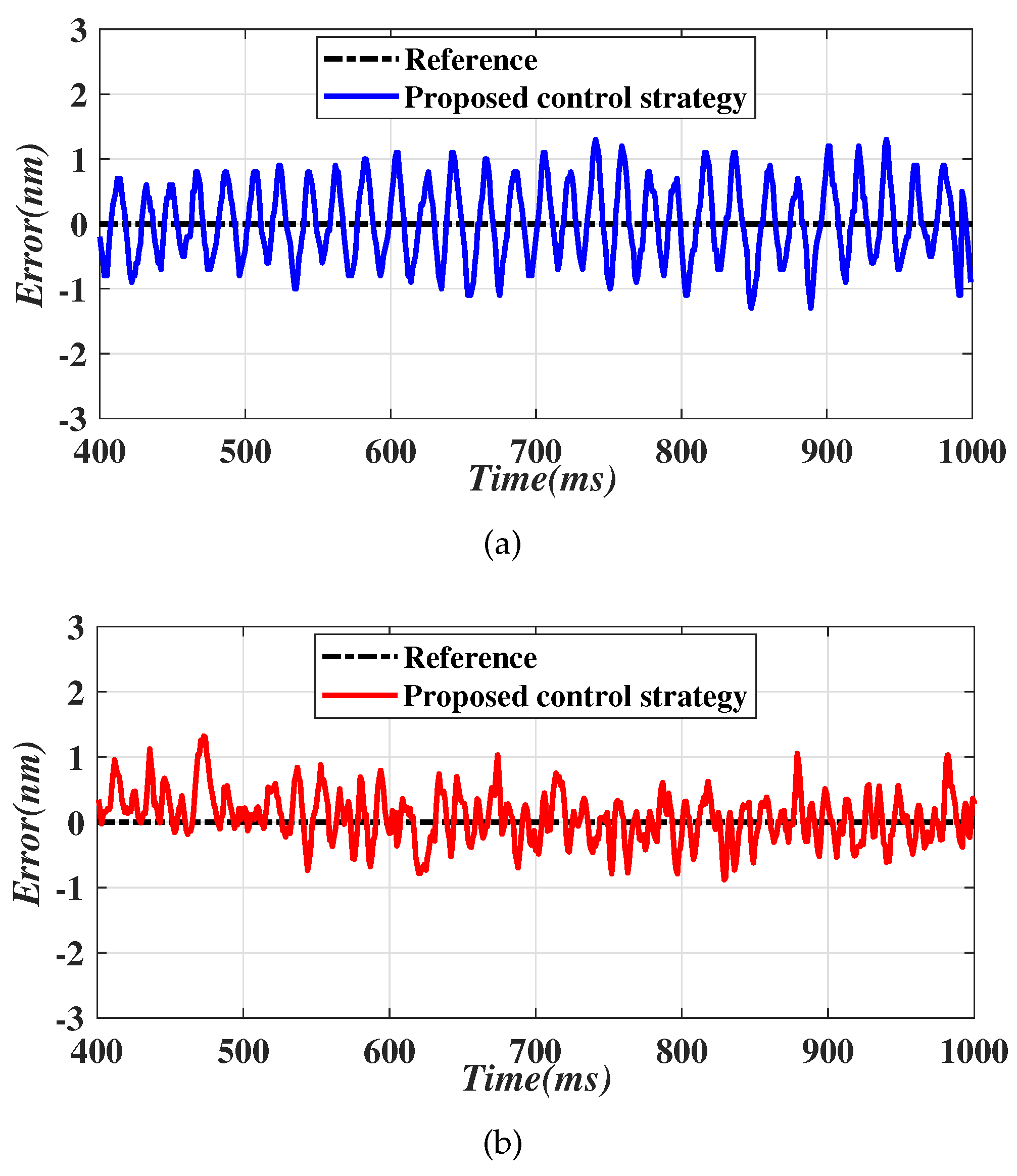
4.2. Simulation Results
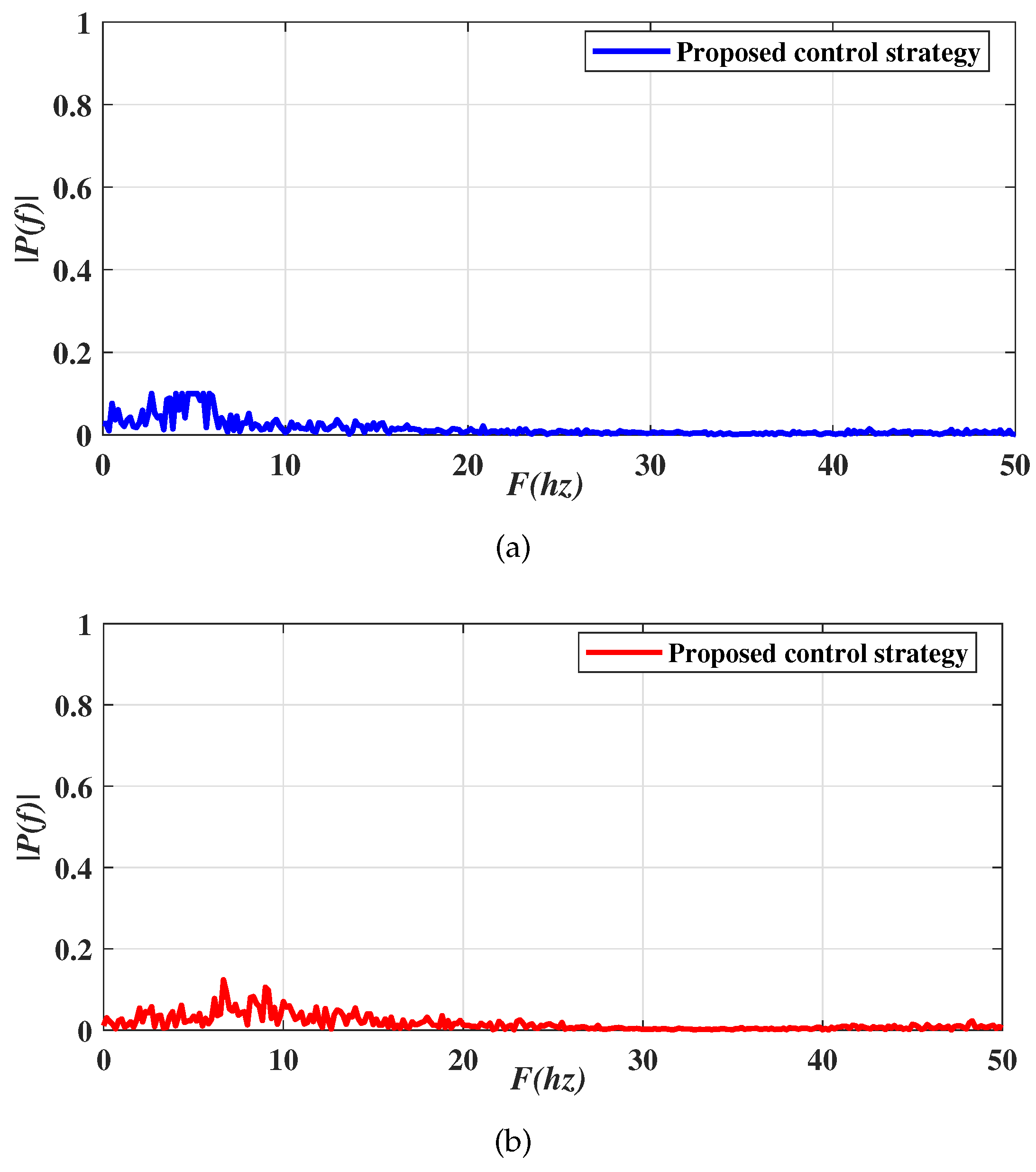
4.3. Experiment Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vorbringer-Dorozhovets, N.; Hausotte, T.; Manske, E.; Shen, J.; Jaeger, G. Novel control scheme for a high-speed metrological scanning probe microscope. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2011, 22, 094012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Xie, M.; Manske, E.; Wu, H.; Ma, J.; Wang, R.; Kang, S. Design and control of a piezoactuated microfeed mechanism for cell injection. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 105, 4941–4952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, G.; Zhu, L. An experimental comparison of proportional-integral, sliding mode, and robust adaptive control for piezo-actuated nanopositioning stages. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2014, 85, 055112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, C.; Ding, Y.; Gu, G.; Zhu, L. Damping control of piezo-actuated nanopositioning stages with recursive delayed position feedback. IEEE-ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2017, 22, 855–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habineza, D.; Zouari, M.; Le, G.Y.; Rakotondrabe, M. Multivariable compensation of hysteresis, creep, badly damped vibration, and cross couplings in multiaxes piezoelectric actuators. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2018, 15, 1639–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gu, G.; Zhu, L.; Su, C.; Ding, H. Motion control of piezoelectric positioning stages: Modeling, controller design, and experimental evaluation. IEEE-ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2013, 18, 1459–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xu, Q. Design and robust repetitive control of a new parallel-kinematic XY piezostage for micro/nanomanipulation. IEEE-ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2012, 17, 1120–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q. Piezoelectric nanopositioning control using second-order discrete-time terminal sliding-mode strategy. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 12, 7738–7748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q. Digital sliding mode prediction control of piezoelectric micro/nanopositioning system. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2015, 23, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Yao, B. Adaptive robust precision motion control of a piezoelectric positioning stage. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2008, 16, 1039–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, S.; Wu, C.; Sun, Z. Design and implementation of clutch control for automotive transmissions using terminal-sliding-mode control and uncertainty observer. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2016, 65, 1890–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhou, M.; Yu, X. Design and implementation of terminal sliding mode control method for PMSM speed regulation system. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2016, 9, 1879–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, S.; Lan, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Zhou, X. Continuous terminal sliding modecontrol with extended state observer for PMSM speed regulation system. Trans. Inst. Meas. Control 2017, 39, 1195–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q. Precision motion control of piezoelectric nanopositioning stage with chattering-free adaptive sliding mode control. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2016, 25, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.; Li, F.; Yang, C. An improved homogeneous polynomial approach for adaptive sliding-mode control of markov jump systems with actuator faults. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2020, 65, 955–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lin, H. Backstepping fuzzy sliding mode control for the antiskid braking system of unmanned aerial vehicles. Electronics 2020, 9, 1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoszewicz, A.; Adamiak, K. Discrete-time sliding-mode control with a desired switching variable generator. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2020, 65, 1807–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamiz, A.; Tirandaz, H.; Barambones, O. Neural dynamic sliding mode control of nonlinear systems with both matched and mismatched uncertainties. J. Frankl. Inst.-Eng. Appl. Math. 2019, 356, 4577–4600. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, C.; Wang, X.; Li, S.; Chen, X. Improved integral sliding mode control methods for speed control of PMSM system. J. Int. J. Innov. Comput. Inf. Control 2011, 7, 1971–1982. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.; Han, F.; Yu, X. Chattering free full-order sliding mode control. Automatica 2014, 50, 1310–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, H.; Yu, X.; Xu, L.; Rsetam, K.; Cao, Z. Chattering free full-order sliding mode control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 5647–5656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S. Design of unknown input observer for nonlinear systems with time-varying delays. Intl. J. Dyn. Control 2015, 3, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zheng, W.; Li, S.; Wu, B.; Cheng, M. Design of a prediction-accuracy-enhanced continuous-time MPC for sisturbed systems via a disturbance observer. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 5807–5816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, J.; Yang, J.; Li, S. A disturbance observer enhanced composite cascade control with experimental studies. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2013, 11, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liu, Z. Adaptive speed control for permanent-magnet synchronous motor system with variations of load inertia. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2009, 56, 5807–5816. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J. From PID to active disturbance rejection control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2009, 56, 900–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Li, S.; Yu, X. Sliding-mode control for systems with mismatched uncertainties via a disturbance observer. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Yang, J.; Guo, L.; Li, S. Disturbance-observer-based control and related methods-an overview. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 1083–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, Y.; Yang, J.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, C.; Li, S.; Yu, H. Robust speed regulation for PMSM servo system with multiple sources of disturbances via an augmented disturbance observer. IEEE-ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2018, 23, 769–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yan, Y.; Yang, J.; Li, S.; Li, Q. Robust voltage regulation of a DC-AC inverter with load variations via a HDOBC approach. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II 2019, 66, 1172–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayem, A.; Cao, Z.; Man, Z. Model free ESO-based repetitive control for rejecting periodic and aperiodic disturbances. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 3433–3441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, H. Nonlinear Systems, 3rd ed.; Prentice Hall: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002; pp. 110–125. [Google Scholar]
- Sami, I.; Ullah, S.; Ullah, N.; Ro, J.-S. Sensorless fractional order composite sliding mode control design for wind generation system. ISA Trans. 2021, 111, 275–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sami, I.; Ullah, S.; Ali, Z.; Ullah, N.; Ro, J.-S. A super twisting fractional order terminal sliding mode control for DFIG-based wind energy conversion system. Energies 2020, 13, 2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qiao, P.; Yang, J.; Dai, C.; Xiao, X. Design of Composite Disturbance Observer and Continuous Terminal Sliding Mode Control for Piezoelectric Nanopositioning Stage. Electronics 2021, 10, 2242. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10182242
Qiao P, Yang J, Dai C, Xiao X. Design of Composite Disturbance Observer and Continuous Terminal Sliding Mode Control for Piezoelectric Nanopositioning Stage. Electronics. 2021; 10(18):2242. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10182242
Chicago/Turabian StyleQiao, Pengyu, Jun Yang, Chen Dai, and Xi Xiao. 2021. "Design of Composite Disturbance Observer and Continuous Terminal Sliding Mode Control for Piezoelectric Nanopositioning Stage" Electronics 10, no. 18: 2242. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10182242
APA StyleQiao, P., Yang, J., Dai, C., & Xiao, X. (2021). Design of Composite Disturbance Observer and Continuous Terminal Sliding Mode Control for Piezoelectric Nanopositioning Stage. Electronics, 10(18), 2242. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10182242






