RCA-GAN: An Improved Image Denoising Algorithm Based on Generative Adversarial Networks
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- We proposed the RCA-GAN image denoising algorithm which enhances crucial features by incorporating residual learning into the generator’s backbone network, thus improving the model’s capability to recover image details and edge information.
- We devised a cooperative attention mechanism that proves highly effective in dealing with complex noise distributions. It can model and address intricate noise distributions within images, thereby enhancing the accurate restoration of the original image information.
- We constructed a Multimodal Loss Function that guides network parameter optimization by weighting and summing perceptual feature loss, pixel space content loss, texture loss, and adversarial loss, thereby enhancing the model’s reconstruction performance for image texture details.
2. Background Techniques
2.1. Generative Adversarial Network
2.2. Residual Learning
3. Design of Network Architecture and Denoising Model
3.1. RCA-GAN Network Architecture
3.1.1. Generator Network Architecture
3.1.2. Discriminator Network Architecture
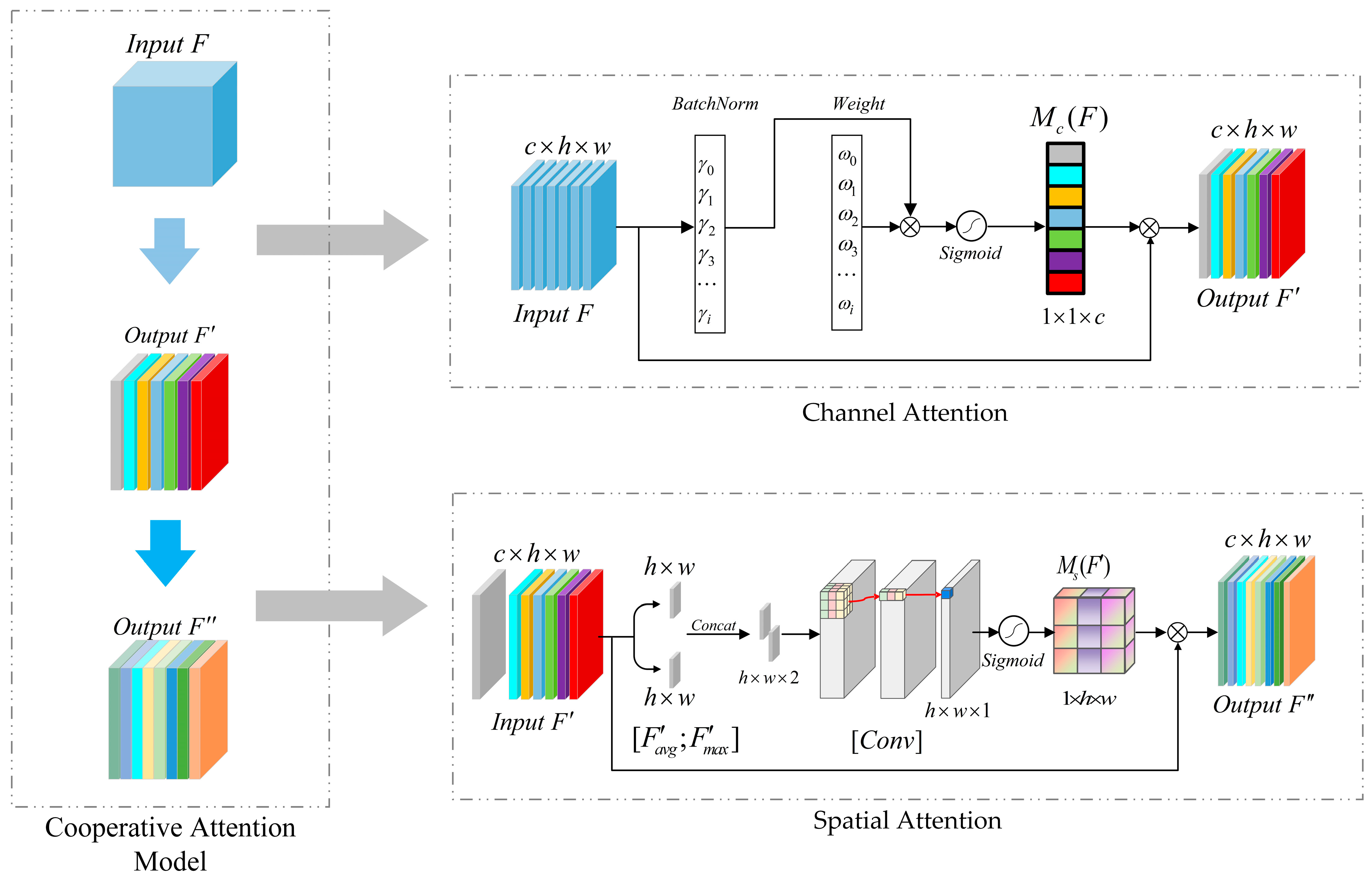
3.2. Cooperative Attention Mechanism
3.3. Multimodal Loss Function
4. Experimental Comparisons and Analysis
4.1. Data Set
4.2. Experimental Environment
4.3. Evaluation Metrics
4.3.1. PSNR
4.3.2. SSIM
4.4. Experimental Results
4.4.1. Quantitative Analysis
4.4.2. Qualitative Analysis
4.4.3. Loss Function Ablation Experiments
4.4.4. Analysis of Different Weight Coefficients in the Loss Function
4.4.5. Analysis of Visual Tasks and Applications
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ihara, S.; Saito, H.; Yoshinaga, M.; Avala, L.; Murayama, M. Deep learning-based noise filtering toward millisecond order imaging by using scanning transmission electron microscopy. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 13462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Zhou, F. Self-Supervised Image Denoising for Real-World Images with Context-Aware Transformer. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 14340–14349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, W.; Siddiqi, M.H.; Almadhor, A. Adaptively Directed Image Restoration Using Resilient Backpropagation Neural Network. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Syst. 2023, 16, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vimala, B.B.; Srinivasan, S.; Mathivanan, S.K.; Muthukumaran, V.; Babu, J.C.; Herencsar, N.; Vilcekova, L. Image Noise Removal in Ultrasound Breast Images Based on Hybrid Deep Learning Technique. Sensors 2023, 23, 1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Zhou, D.; Yang, H.; Yang, S. Two-subnet network for real-world image denoising. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, R.; Li, C.; Chen, H.; Li, S.; Gu, J.; Loy, C.C. Generating Aligned Pseudo-Supervision from Non-Aligned Data for Image Restoration in Under-Display Camera. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 5013–5022. [Google Scholar]
- Han, L.; Zhao, Y.; Lv, H.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Bi, G. Remote Sensing Image Denoising Based on Deep and Shallow Feature Fusion and Attention Mechanism. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ng, M.K.; Zhuang, L.; Gao, L.; Zhang, B. Nonlocal Self-Similarity-Based Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Image Denoising with 3-D Convolutional Neural Network. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X. Research progress of deep learning in low-dose CT image denoising. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2023, 199, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Zhang, F.; Fan, H.; Zhang, C. Brief review of image denoising techniques. Vis. Comput. Ind. Biomed. Art 2019, 2, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismael, A.A.; Baykara, M. Digital Image Denoising Techniques Based on Multi-Resolution Wavelet Domain with Spatial Filters: A Review. Trait. Signal 2021, 38, 639–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostadin, D.; Alessandro, F.; Vladimir, K.; Karen, E. Image restoration by sparse 3D transform-domain collaborative filtering. Proc. SPIE 2008, 6812, 681207. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, T.; Lv, X. An overview of digital image analog noise removal based on traditional filtering. Proc. SPIE 2023, 12707, 665–672. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Sodhi, S.S. Comparative Analysis of Gaussian Filter, Median Filter and Denoise Autoenocoder. In Proceedings of the 2020 7th International Conference on Computing for Sustainable Global Development (INDIACom), New Delhi, India, 12–14 March 2020; pp. 45–51. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J. Wavelet domain denoising method based on multistage median filtering. J. China Univ. Posts Telecommun. 2013, 20, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.-T.; Chen, M.-Y.; Shen, J.-H.; Wang, L.-L.; Yen, N.Y.; Liu, C.-H. X-ray bio-image denoising using directional-weighted-mean filtering and block matching approach. J. Ambient Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2018, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erkan, U.; Thanh, D.N.H.; Hieu, L.M.; Enginoglu, S. An Iterative Mean Filter for Image Denoising. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 167847–167859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Zhang, W.; Su, X.; Xu, Z. Optical Remote Sensing Image Denoising and Super-Resolution Reconstructing Using Optimized Generative Network in Wavelet Transform Domain. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X. A denoising approach via wavelet domain diffusion and image domain diffusion. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2017, 76, 13545–13561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, P.; Tavakoli, A. A new algorithm for image inpainting in Fourier transform domain. Comput. Appl. Math. 2019, 38, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Sun, J. BM3D-Net: A Convolutional Neural Network for Transform-Domain Collaborative Filtering. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2018, 25, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, H.C.; Schuler, C.J.; Harmeling, S. Image denoising: Can plain neural networks compete with BM3D? In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, RI, USA, 16–21 June 2012; pp. 2392–2399. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Zuo, W.; Chen, Y.; Meng, D.; Zhang, L. Beyond a Gaussian Denoiser: Residual Learning of Deep CNN for Image Denoising. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2017, 26, 3142–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Mittal, A.; Aggarwal, N. ResDNN: Deep residual learning for natural image denoising. IET Image Process. 2020, 14, 2425–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Xie, H.; Xue, N.; Zhang, A. Research on underwater image denoising based on dual-channels residual network. Comput. Eng. 2023, 49, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, R.; Zou, H.; Pang, C.; Zhong, Y.; Liu, Z.; Luo, X. Image denoising via deep residual convolutional neural networks. Signal Image Video Process. 2021, 15, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, J.; Chao, H.; Yang, M. Image Blind Denoising with Generative Adversarial Network Based Noise Modeling. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 3155–3164. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.; Yan, P.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, H.; Shi, Y.; Mou, X.; Kalra, M.K.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, L.; Wang, G. Low-Dose CT Image Denoising Using a Generative Adversarial Network With Wasserstein Distance and Perceptual Loss. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2018, 37, 1348–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.-L.; Zhao, L.-L.; Xiao, L. Image Denoising Based on GAN with Optimization Algorithm. Electronics 2022, 11, 2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative Adversarial Nets. In Proceedings of the Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, QC, Canada, 8–13 December 2014. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albawi, S.; Mohammed, T.A.; Al-Zawi, S. Understanding of a convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Engineering and Technology (ICET), Antalya, Turkey, 21–23 August 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ketkar, N.; Moolayil, J. Convolutional Neural Networks. In Deep Learning with Python: Learn Best Practices of Deep Learning Models with PyTorch; Ketkar, N., Moolayil, J., Eds.; Apress: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2021; pp. 197–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Sohail, A.; Zahoora, U.; Qureshi, A.S. A survey of the recent architectures of deep convolutional neural networks. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2020, 53, 5455–5516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, F.; Yang, W.; Peng, S.; Zhou, J. A Survey of Convolutional Neural Networks: Analysis, Applications, and Prospects. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2022, 33, 6999–7019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Z.; Zhong, G.; Yu, H. A review on the attention mechanism of deep learning. Neurocomputing 2021, 452, 48–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zeng, Q.; Zhou, T.; Wu, H. Image super-resolution reconstruction based on attention mechanism and feature fusion. Comput. Eng. 2021, 47, 269–275+283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Yu, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Wang, X. Image super-resolution reconstruction based on depth residual adaptive attention network. Comput. Eng. 2023, 49, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, F.; Dan, J. CBAM-GAN: Generative Adversarial Networks Based on Convolutional Block Attention Module. In Artificial Intelligence and Security; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 227–236. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, D.; Fowlkes, C.; Tal, D.; Malik, J. A database of human segmented natural images and its application to evaluating segmentation algorithms and measuring ecological statistics. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 7–14 July 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Roth, S.; Black, M.J. Fields of Experts: A Framework for Learning Image Priors. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition, San Diego, CA, USA, 20–25 June 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, C.; Tu, D.; Liu, J. Re-GAN: Residual generative adversaria network algorithm. J. Image Graph. 2021, 26, 594–604. [Google Scholar]














| Hardware Configuration Items | Hardware Configuration |
|---|---|
| CPU | Intel(R) Core(TM) i9-10900X CPU @ 3.70 GHz |
| GPU | NVIDIA GeForce GTX 3080 |
| Memory | 64.0 GB |
| Hard disk capacity | 4 TB |
| Hardware configuration items | Hardware configuration |
| Software Configuration Items | Software Configuration |
|---|---|
| Operating system | Windows 10 64-bit |
| Python | 3.7 |
| PyTorch | 1.8 |
| Cuda | 11.2 |
| Development tools | PyCharm 2020.2.1 |
| Metrics | PSNR(dB) | SSIM | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Noisy () | 15 | 25 | 50 | 15 | 25 | 50 |
| Initial value | 24.71 | 20.69 | 15.07 | 0.8451 | 0.7075 | 0.4610 |
| BM3D | 32.57 | 28.91 | 26.75 | 0.9293 | 0.8506 | 0.6889 |
| DnCNN | 33.01 | 30.75 | 27.33 | 0.9407 | 0.8692 | 0.7529 |
| WGAN-VGG | 33.27 | 31.46 | 28.21 | 0.9432 | 0.8719 | 0.7806 |
| Re-GAN | 33.54 | 31.99 | 28.25 | 0.9489 | 0.8729 | 0.7875 |
| RCA-GAN | 33.76 | 31.98 | 28.94 | 0.9503 | 0.8764 | 0.8005 |
| Denoising Algorithm | Running Time/s | |
|---|---|---|
| CPU | GPU | |
| BM3D | 13.55 | - |
| DnCNN | 7.51 | 0.17 |
| WGAN-VGG | 6.64 | 0.15 |
| Re-GAN | 6.07 | 0.14 |
| RCA-GAN | 5.49 | 0.11 |
| Loss Function | PSNR/dB | SSIM |
|---|---|---|
| MSE | 31.59 | 0.9262 |
| LWGAN-GP | 32.10 | 0.9389 |
| Lpercep + LWGAN-GP | 32.38 | 0.9472 |
| Lpercep + Lcon + LWGAN-GP | 33.81 | 0.9489 |
| Lpercep + Lcon + Ltex + LWGAN-GP | 33.80 | 0.9503 |
| Loss Weight | PSNR/dB | SSIM | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.8 | 0.01 | 0.001 | 1.0 | 33.57 | 0.9371 |
| 1.2 | 0.01 | 0.001 | 1.0 | 32.65 | 0.9435 |
| 1.0 | 0.03 | 0.001 | 1.0 | 33.13 | 0.9319 |
| 1.0 | 0.05 | 0.001 | 1.0 | 33.69 | 0.9156 |
| 1.0 | 0.01 | 0.003 | 1.0 | 32.81 | 0.9389 |
| 1.0 | 0.01 | 0.005 | 1.0 | 31.76 | 0.9415 |
| 1.0 | 0.01 | 0.001 | 0.8 | 33.64 | 0.9352 |
| 1.0 | 0.01 | 0.001 | 1.2 | 33.52 | 0.9387 |
| 1.0 | 0.01 | 0.001 | 1.0 | 33.80 | 0.9503 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Luo, S.; Ma, L.; Huang, M. RCA-GAN: An Improved Image Denoising Algorithm Based on Generative Adversarial Networks. Electronics 2023, 12, 4595. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12224595
Wang Y, Luo S, Ma L, Huang M. RCA-GAN: An Improved Image Denoising Algorithm Based on Generative Adversarial Networks. Electronics. 2023; 12(22):4595. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12224595
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yuming, Shuaili Luo, Liyun Ma, and Min Huang. 2023. "RCA-GAN: An Improved Image Denoising Algorithm Based on Generative Adversarial Networks" Electronics 12, no. 22: 4595. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12224595
APA StyleWang, Y., Luo, S., Ma, L., & Huang, M. (2023). RCA-GAN: An Improved Image Denoising Algorithm Based on Generative Adversarial Networks. Electronics, 12(22), 4595. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12224595






