Design of Synaptic Driving Circuit for TFT eFlash-Based Processing-In-Memory Hardware Using Hybrid Bonding
Abstract
:1. Introduction
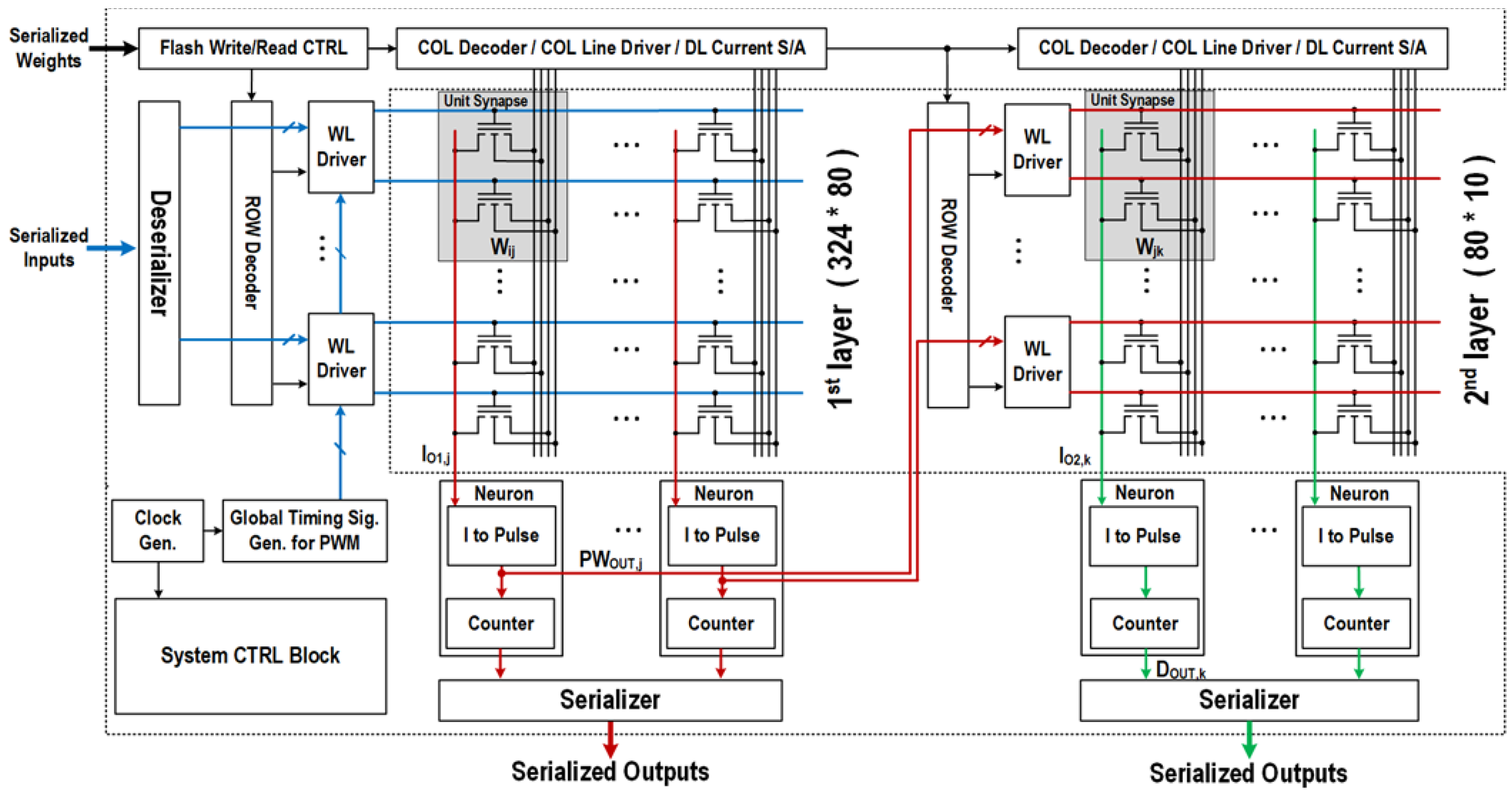
2. System Architecture
3. Circuit Description
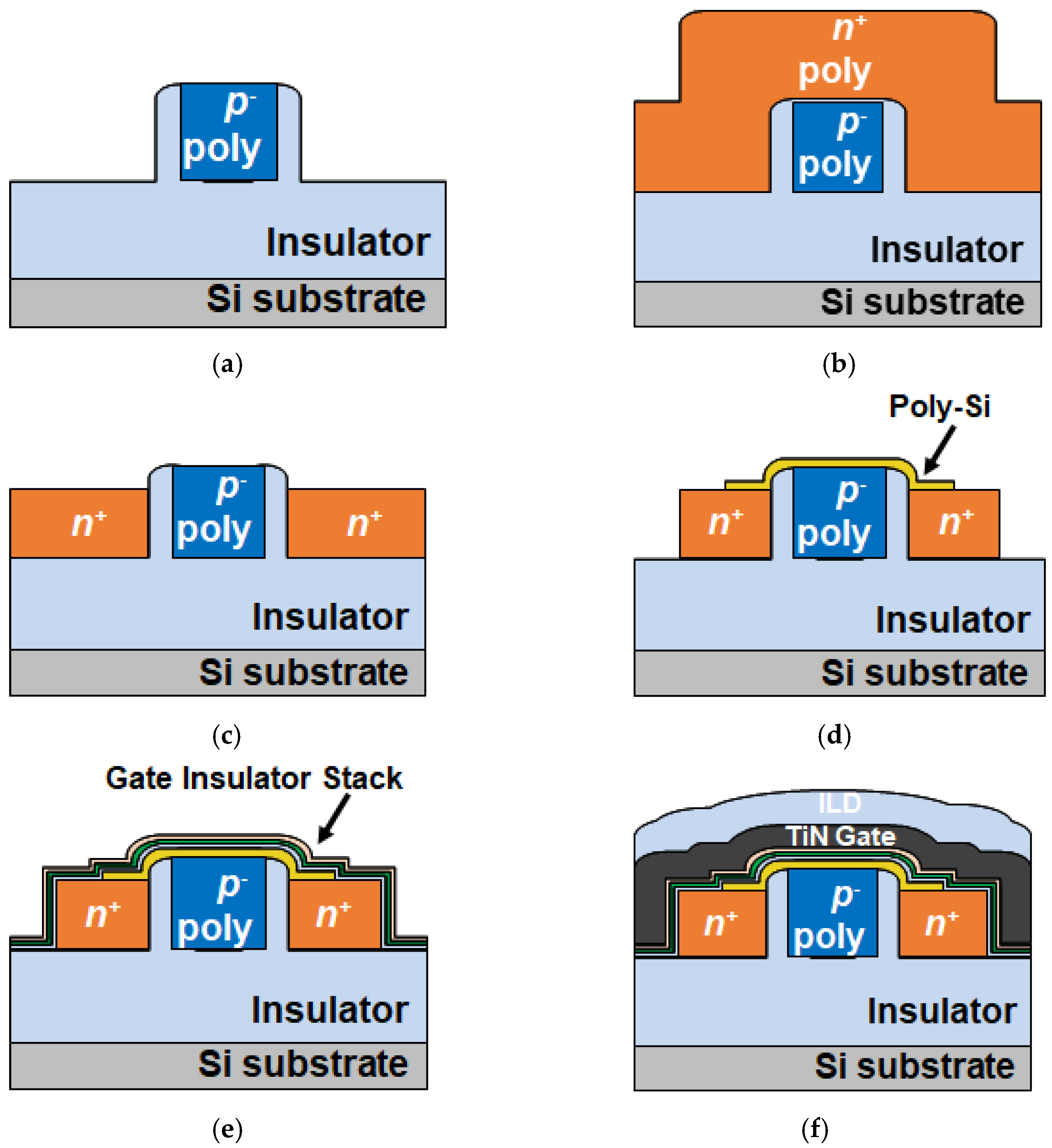
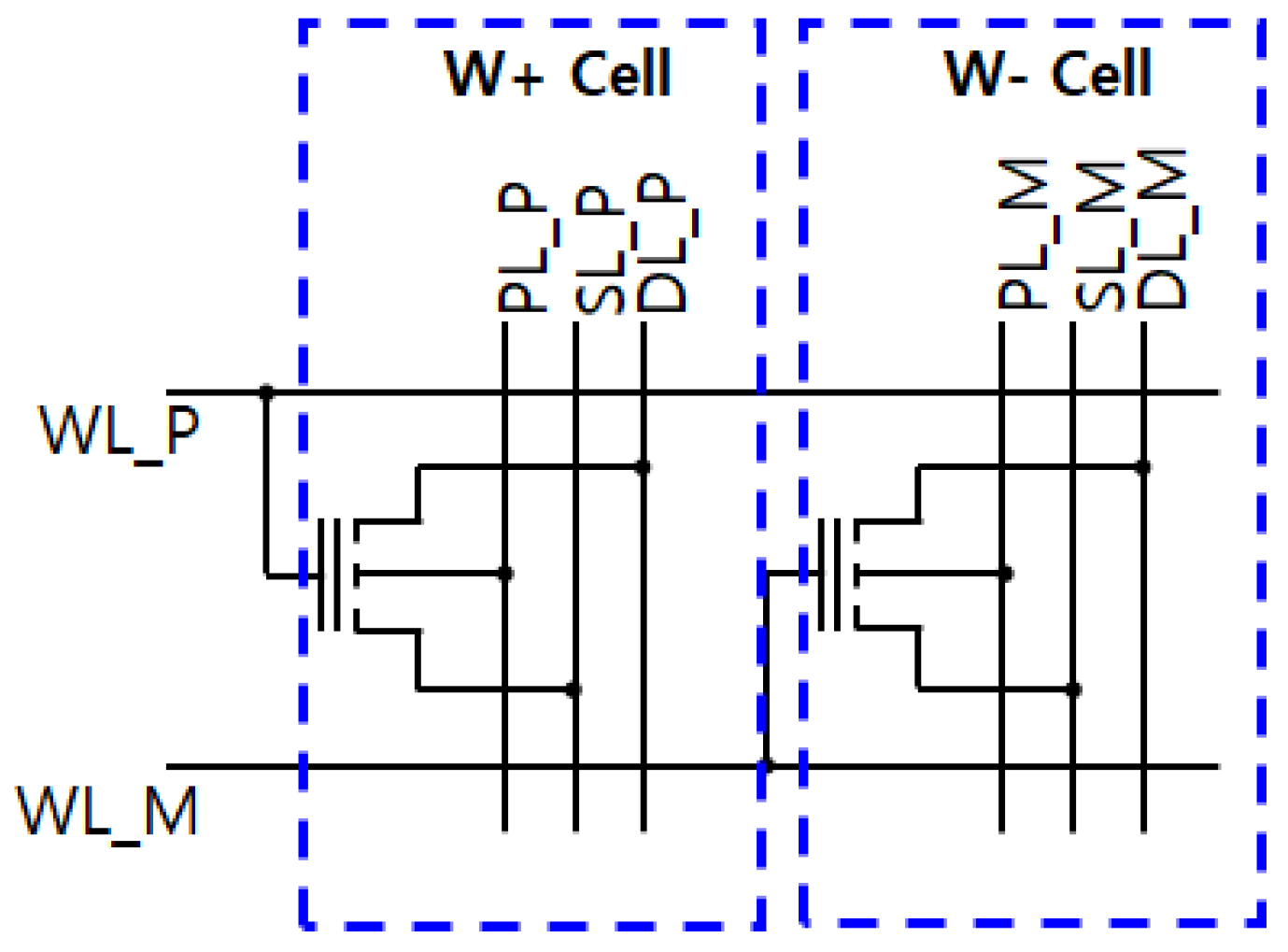
3.1. TFT eFlash-Based Synapse Cell
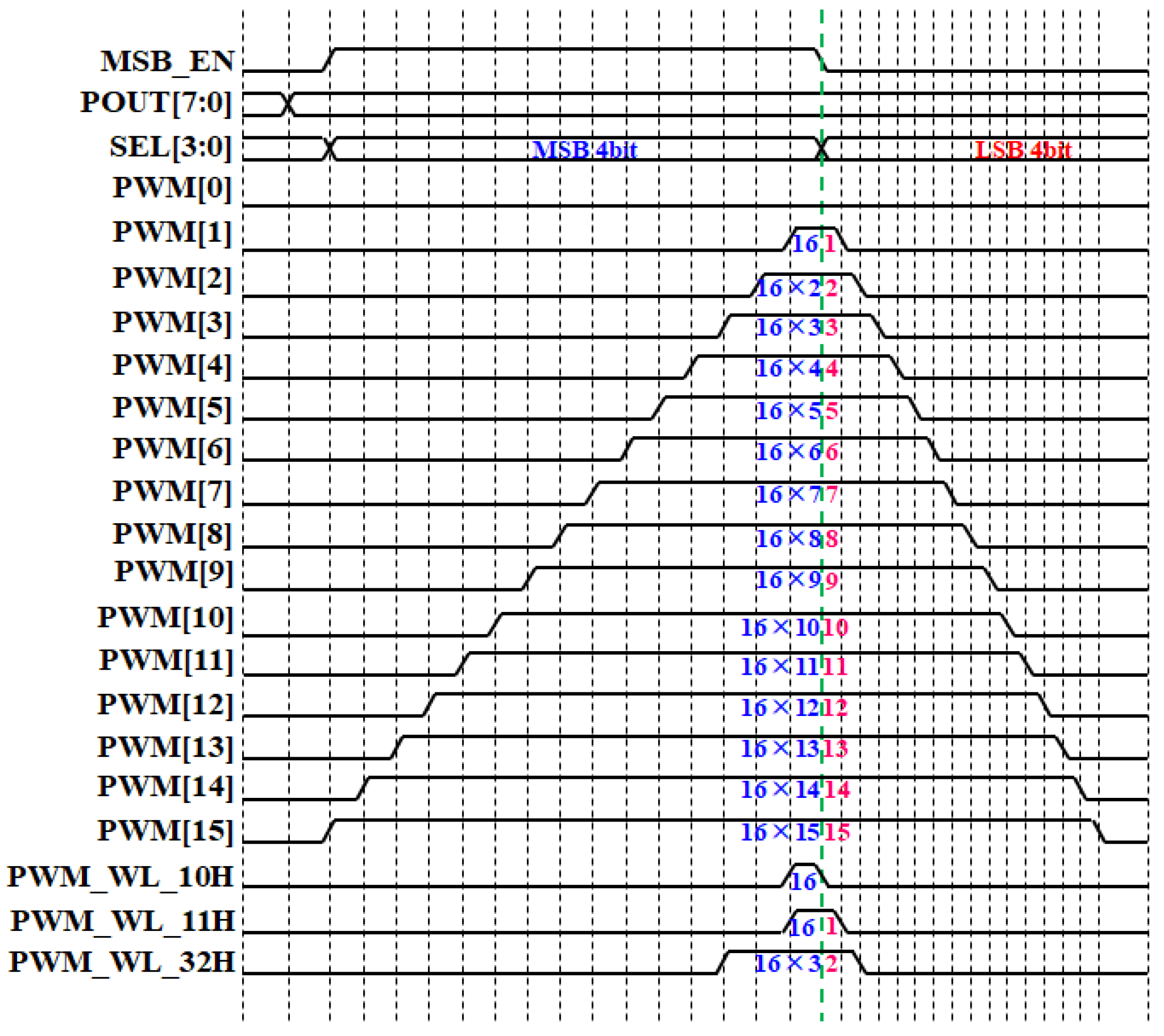
3.2. Pulse Width Modulation Circuit Using Deserializer and Global Signals
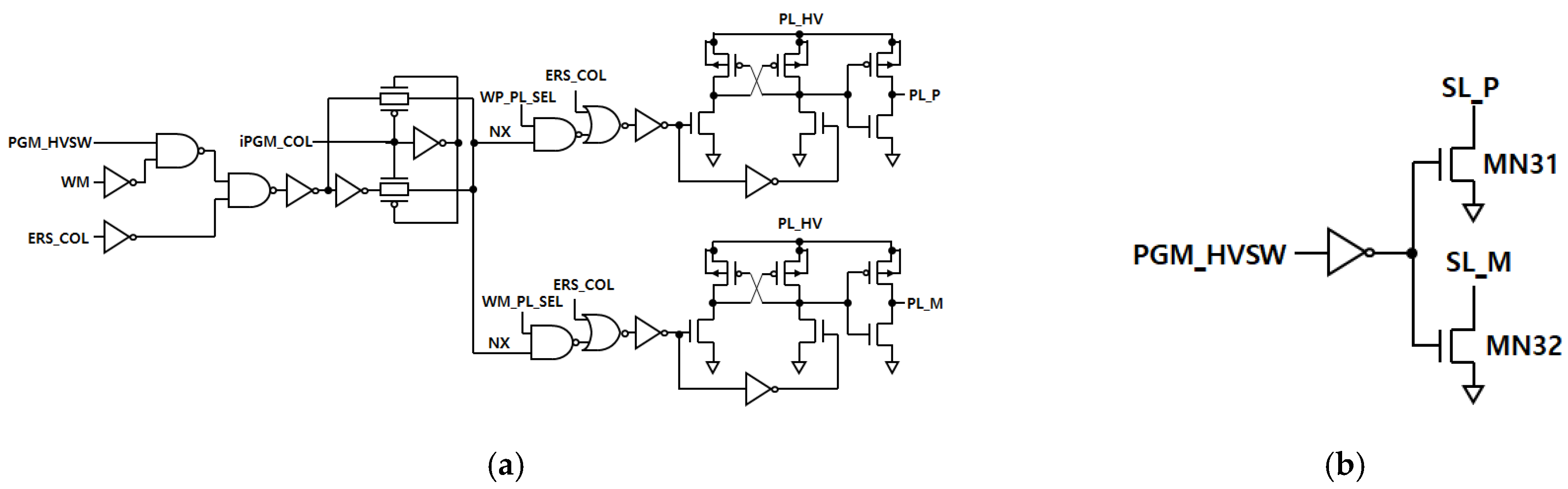
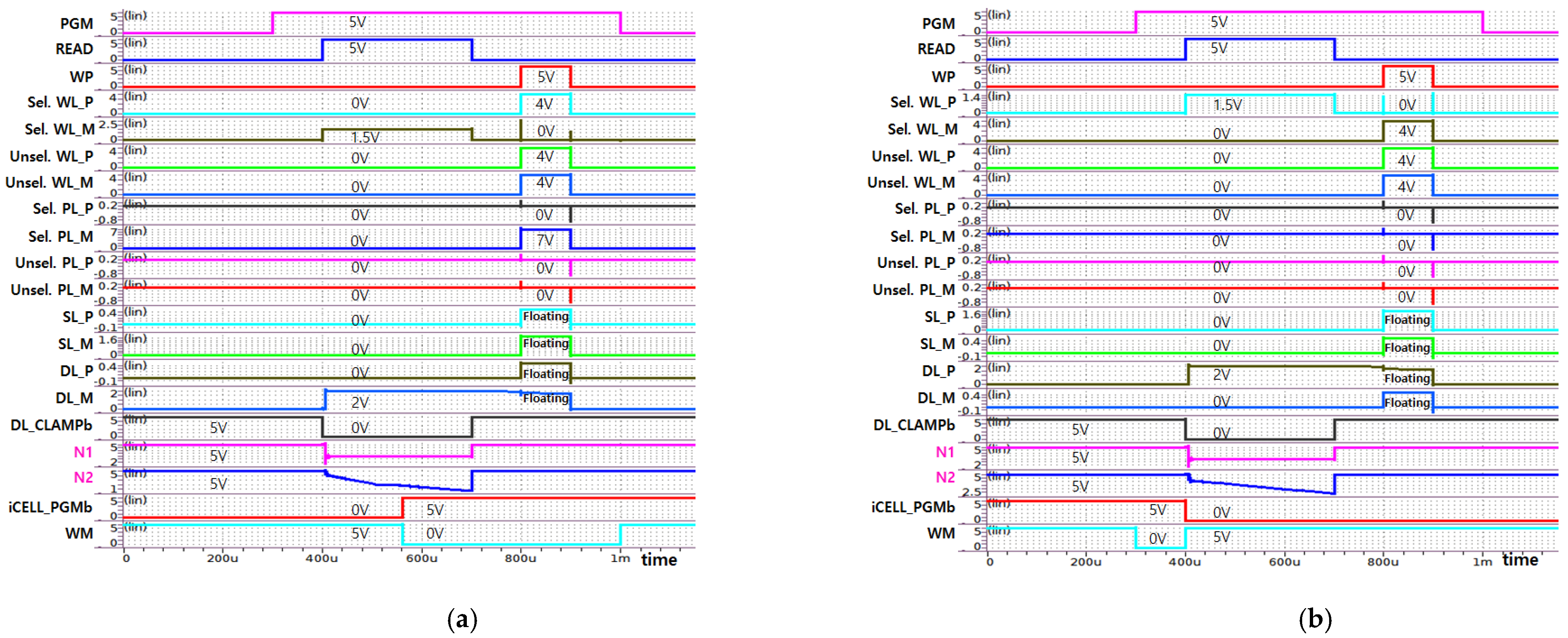
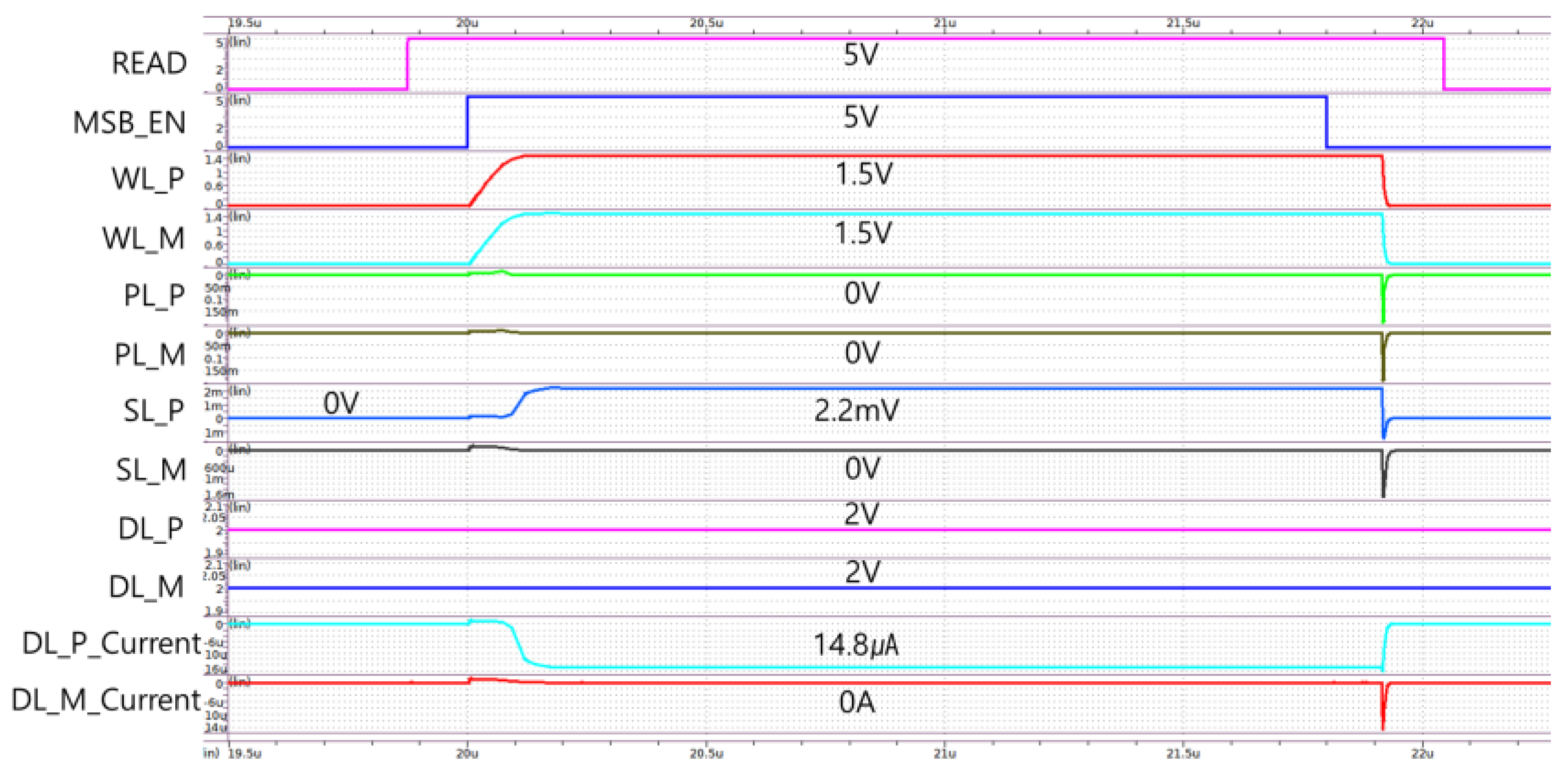
3.3. Synaptic Driving Circuit
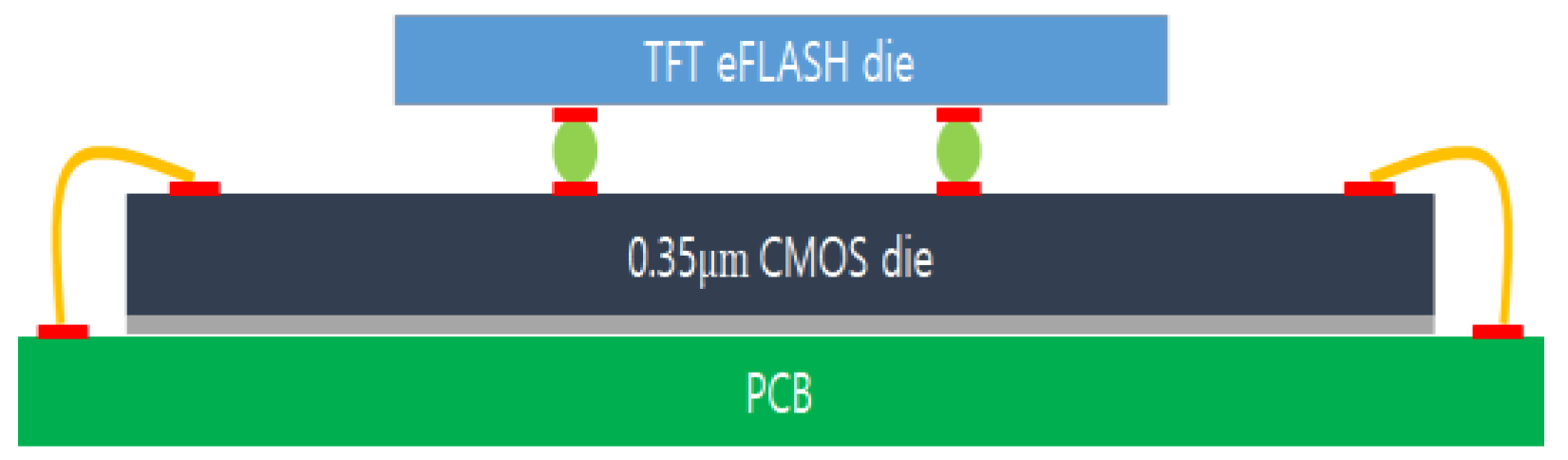
4. Chip Packing Using Hybrid Bonding Technology
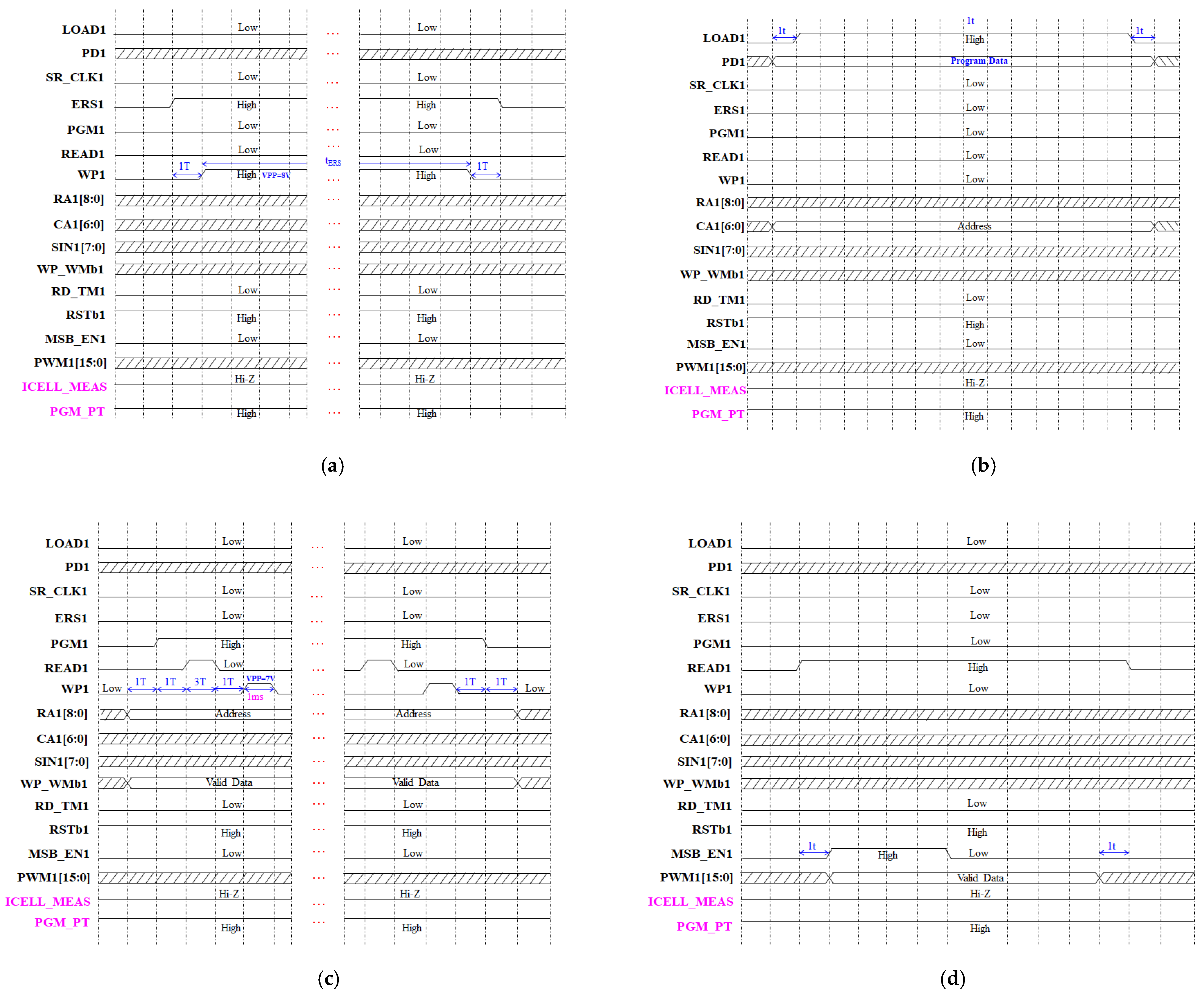
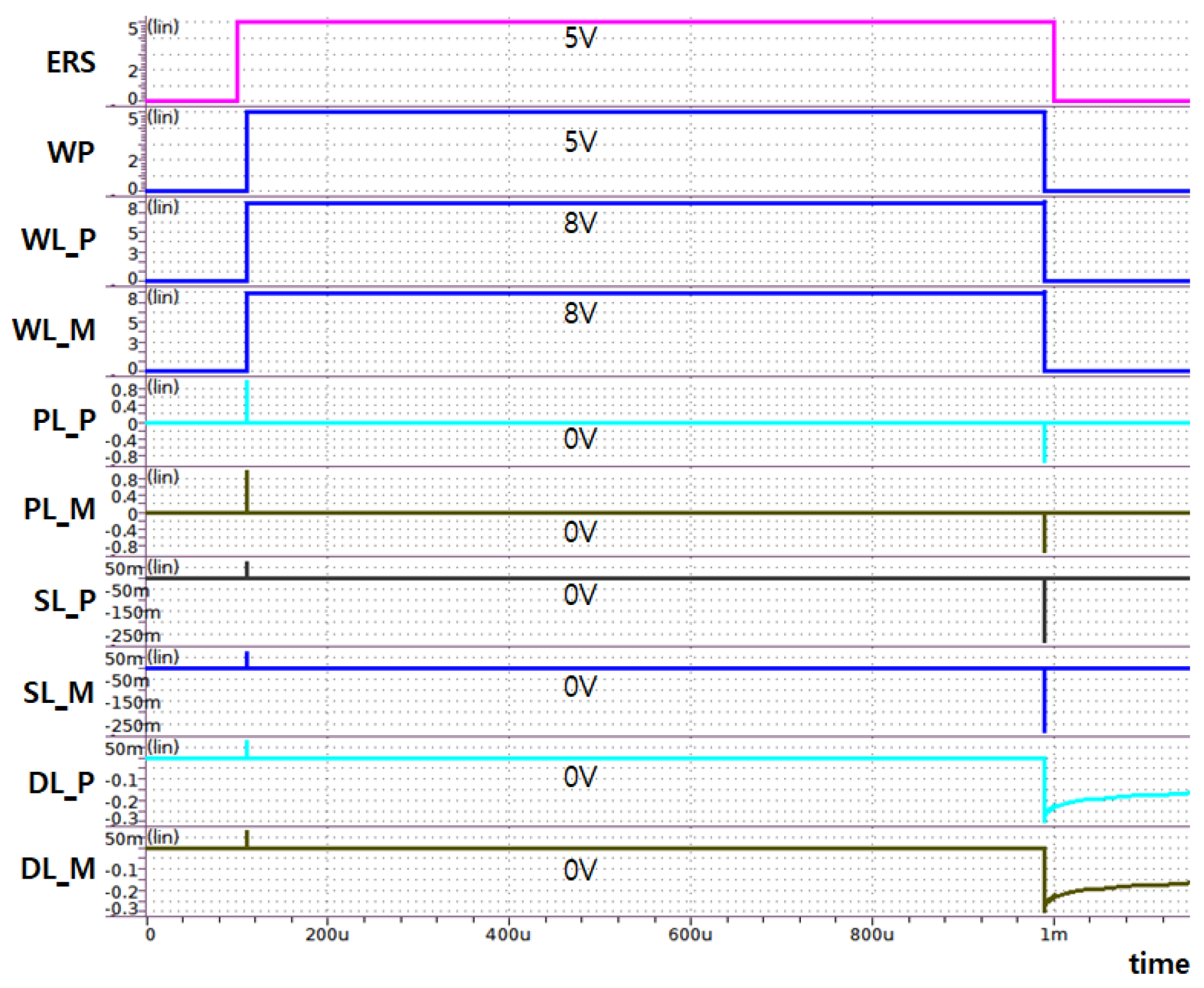
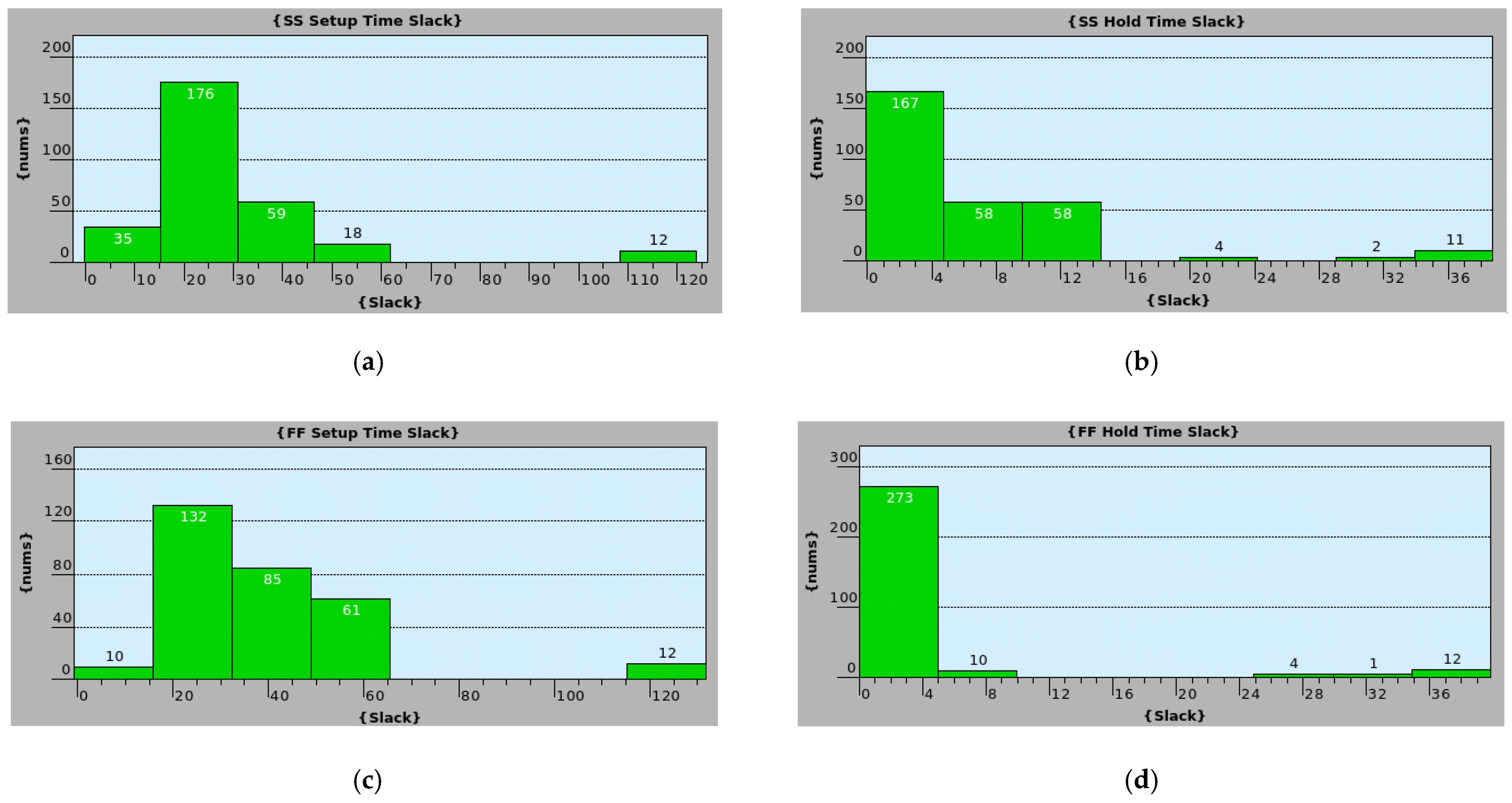
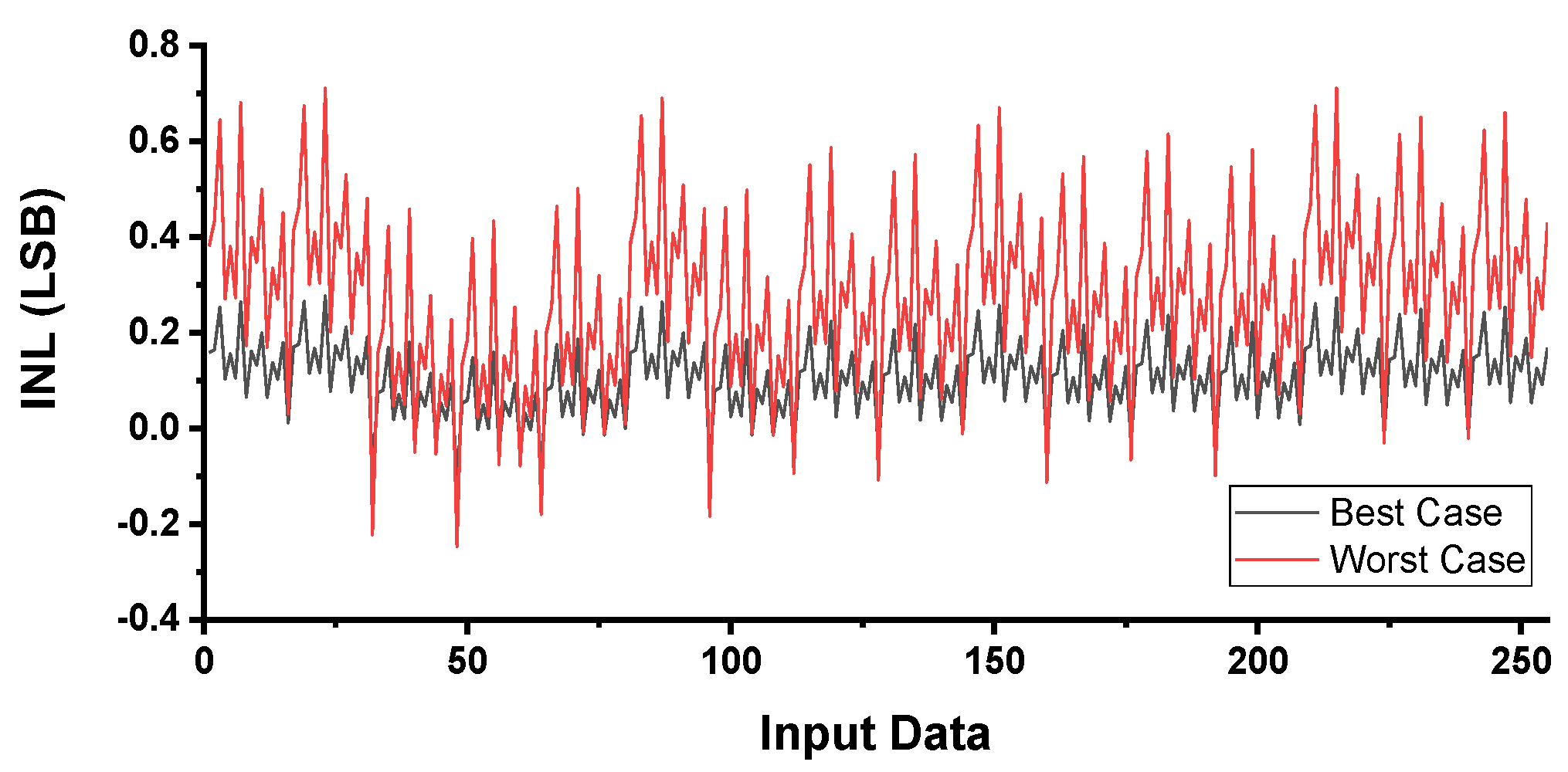
5. Simulation Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 3–8 December 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), Ottawa, ON, Canada, 10–13 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Conference (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Ioffe, S.; Vanhoucke, V.; Alemi, A. Inception-v4, Inception-ResNet and the Impact of Residual Connections on Learning. In Proceedings of the Thirty-First AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, San Francisco, CA, USA, 4–9 February 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, M.; Le, Q.V. EfficientNet: Rethinking Model Scaling for Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the Machine Learning Research, Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–15 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hubara, I.; Courbariaux, M.; Soudry, D.; El-Yaniv, R.; Bengio, Y. Binarized Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), Barcelona, Spain, 5–10 December 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Rastegari, M.; Ordonez, V.; Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. XNOR-Net: ImageNet Classification Using Binary Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 8–16 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.; Smaragdis, P. Bitwise Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), San Diego, CA, USA, 7–9 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Iandola, F.N.; Han, S.; Moskewicz, M.W.; Ashraf, K.; Dally, W.J.; Keutzer, K. SqueezeNet: AlexNet-level accuracy with 50× fewer parameters and <0.5 MB model size. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1602.07360. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; van der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely Connected Convolutional Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Conference (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 22–25 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.G.; Zhu, M.; Chen, B.; Kalenichenko, D.; Wang, W.; Weyand, T.; Andreetto, M.; Adam, H. MobileNets: Efficient Convolutional Neural Networks for Mobile Vision Applications. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.04861. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, X.; Lin, M.; Sun, J. Shufflenet: An extremely efficient convolutional neural network for mobile devices. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 19–21 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz, M. 1.1 Computing’s Energy Problem (and what we can do about it). In Proceedings of the IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 9–13 February 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.-H.H.; Krishna, T.; Emer, J.S.; Sze, V. Eyeriss: An Energy-Efficient Reconfigurable Accelerator for Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2017, 52, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moons, B.; Verhelst, M. An Energy-Efficient Precision-Scalable ConvNet Processor in 40-Nm CMOS. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2017, 52, 903–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whatmough, P.N.; Lee, S.K.; Lee, H.; Rama, S.; Brooks, D.; Wei, G. 14.3 A 28nm SoC with a 1.2GHz 568nJ/Prediction Sparse Deep-Neural-Network Engine with >0.1 Timing Error Rate Tolerance for IoT Applications. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 5–9 February 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sze, V.; Chen, Y.-H.; Yang, T.-J.; Emer, J.S. Efficient Processing of Deep Neural Networks: A Tutorial and Survey. Proc. IEEE 2017, 105, 2295–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, M.; Gonugondla, S.K.; Patil, A.; Shanbhag, N.R. A Multi-Functional In-Memory Inference Processor Using a Standard 6T SRAM Array. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2018, 53, 642–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, A.; Chandrakasan, A.P. CONV-SRAM: An Energy-Efficient SRAM With In-Memory Dot-Product Computation Neural Networks. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2019, 54, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Son, H.; Cho, H.; Lee, J.; Bae, S.; Kim, B.; Park, H.-J.; Sim, J.-Y. A Multilayer-Learning Current-Mode Neuromorphic System with Analog-Error Compensation. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2019, 13, 986–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bankman, D.; Yang, L.; Moons, B.; Verhelst, M.; Murmann, B. An Always-On 3.8 ΜJ/86% CIFAR-10 Mixed-Signal Binary CNN Processor With All Memory on Chip in 28-Nm CMOS. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2019, 54, 158–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.; Sinangil, M.E.; Erbagci, B.; Sun, D.; Khwa, W.; Liao, H.; Wang, Y.; Chang, J. A 351TOPS/W and 372.4GOPS Compute-in-Memory SRAM Macro in 7 nm FinFET CMOS for Machine-Learning Applications. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 16–20 February 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Ye, W.; Dou, C.; Si, X.; Xu, X.; Liu, J.; Shang, D.; Gao, J.; Zhang, F.; Liu, Y.; et al. Efficient and Robust Nonvolatile Computing-In-Memory Based on Voltage Division in 2T2R RRAM With Input-Dependent Sensing Control. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II 2021, 68, 1640–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.-H.; Chang, M.; Khwa, W.-S.; Chih, Y.-D.; Chang, M.-F.; Raychowdhury, A. A 40-Nm 118.44-TOPS/W Voltage-Sensing Compute-in-Memory RRAM Macro With Write Verification and Multi-Bit Encoding. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2022, 57, 845–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murali, G.; Sun, X.; Yu, S.; Lim, S.K. Heterogeneous mixed-signal monolithic 3-D in-memory computing using resistive RAM. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. VLSI Syst. 2020, 29, 386–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, W.-M.; Kwon, D.; Woo, S.Y.; Lee, S.; Yoo, H.; Kim, J.; Park, B.-G.; Lee, J.-H. Hardware-Based Spiking Neural Network Using a TFT-Type AND Flash Memory Array Architecture Based on Direct Feedback Alignment. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 73121–73132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPartland, R.J.; Singh, R. 1.25 volt, low cost, embedded flash memory for low density applications. In Proceedings of the Symposium on VLSI Circuits, Honolulu, HI, USA, 15–17 June 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Song, S.H.; Chun, K.C.; Kim, C.H. A logic-compatible embedded flash memory for zero-standby power system-on-chips featuring a multi-story high voltage switch and a selective refresh scheme. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2013, 48, 1302–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Operation | Node | WL | DL | SL | PL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ERS | Chip Erase | VERS | 0 V | 0 V | 0 V |
| PGM | Sel. WL & Sel. DL/SL | 0 V | Floating | Floating | VPGM |
| Sel. WL & Unsel. DL/SL | 0 V | Floating | Floating | 0 V | |
| Unsel. WL & Sel. DL/SL | VINHP | Floating | Floating | VPGM | |
| Unsel. WL & Unsel. DL/SL | VINHP | Floating | Floating | 0 V | |
| Read | Sel. WL & Sel. DL/SL | VRD | VDL | 0 V | 0 V |
| Unsel. WL & Sel. DL/SL | 0 V | VDL | 0 V | 0 V |
| Input | Synaptic Weight | Icell |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | +1 | IW+ |
| 1 | −1 | −IW− |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | +1 | 0 |
| 0 | −1 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Function | WP_WMb | Synapse Cell | WL_P | SL_P | PL_P | DL_P | WL_M | SL_M | PL_M | DL_M |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Program Mode | 1 | Sel. Row & Sel. Col | 0 V | Floating | VPGM | Floating | VINHP | Floating | 0 V | Floating |
| Sel. Row & Unsel. Col | 0 V | |||||||||
| Unsel. Row & Sel. Col | VINHP | VPGM | ||||||||
| Unsel. Row & Unsel. Col | 0 V | |||||||||
| 0 | Sel. Row & Sel. Col | VINHP | Floating | 0 V | Floating | 0 V | Floating | VPGM | Floating | |
| Sel. Row & Unsel. Col | 0 V | |||||||||
| Unsel. Row & Sel. Col | VINHP | VPGM | ||||||||
| Unsel. Row & Unsel. Col | 0 V | |||||||||
| Erase Mode | X | Chip Erase | VERS | 0 V | 0 V | Floating | VERS | 0 V | 0 V | Floating |
| Operating Mode | WL_HV | PL_HV | WRTb_PG | WRT_NG | WRTb_NG |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chip Erase | VERS | VDD | 0 V | WL_HV | 0 V |
| Page Buffer Load | VINH | VDD | WL_HV | 0 V | VDD |
| Program | VINH | VPGM | 0 V | WL_HV | 0 V |
| Shift Register Load | VINH | VDD | WL_HV | 0 V | VDD |
| Read | VINH | VDD | WL_HV | 0 V | VDD |
| Test Read | VINH | VDD | WL_HV | 0 V | VDD |
| Function | WP_WMb | Synapse Cell | WL_P | SL_P | PL_P | DL_P | WL_M | SL_M | PL_M | DL_M |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TEST Read Mode | 1 | Sel. Row & Sel. Col | VREAD | 0 V | 0 V | VDD | 0 V | 0 V | 0 V | VDD |
| Sel. Row & Unsel. Col | Floating | Floating | ||||||||
| Unsel. Row & Sel. Col | 0 V | VDD | VDD | |||||||
| Unsel. Row & Unsel. Col | Floating | Floating | ||||||||
| 0 | Sel. Row & Sel. Col | 0 V | 0 V | 0 V | VDD | VREAD | 0 V | 0 V | VDD | |
| Sel. Row & Unsel. Col | Floating | Floating | ||||||||
| Unsel. Row & Sel. Col | VDD | 0 V | VDD | |||||||
| Unsel. Row & Unsel. Col | Floating | Floating | ||||||||
| Read Mode | X | Sel. Row & Sel. Col | PWM | 0 V | 0 V | VDL | PWM | 0 V | 0 V | VDL |
| Metric | TVLSI’21 [25] | VLSI’00 [27] | JSSC’13 [28] | This Work |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Process | 40 nm RRAM | 0.25 μm Logic | 65 nm Logic | 0.35 μm Logic |
| Cell Type | RRAM | FG eFlash | FG eFlash | TFT eFlash |
| Erase Method | Filament | FN tunneling | FN Tunneling | Electron injection |
| Program Method | Filament | CHE Injection | FN Tunneling | Hole Injection |
| Cell Current(ON state) | 100 μA | >10 μA | 2.19 μA | 50 nA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, Y.; Jin, H.; Kim, D.; Ha, P.; Park, M.-K.; Hwang, J.; Lee, J.; Woo, J.-M.; Choi, J.; Lee, C.; et al. Design of Synaptic Driving Circuit for TFT eFlash-Based Processing-In-Memory Hardware Using Hybrid Bonding. Electronics 2023, 12, 678. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12030678
Kim Y, Jin H, Kim D, Ha P, Park M-K, Hwang J, Lee J, Woo J-M, Choi J, Lee C, et al. Design of Synaptic Driving Circuit for TFT eFlash-Based Processing-In-Memory Hardware Using Hybrid Bonding. Electronics. 2023; 12(3):678. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12030678
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Younghee, Hongzhou Jin, Dohoon Kim, Panbong Ha, Min-Kyu Park, Joon Hwang, Jongho Lee, Jeong-Min Woo, Jiyeon Choi, Changhyuk Lee, and et al. 2023. "Design of Synaptic Driving Circuit for TFT eFlash-Based Processing-In-Memory Hardware Using Hybrid Bonding" Electronics 12, no. 3: 678. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12030678
APA StyleKim, Y., Jin, H., Kim, D., Ha, P., Park, M.-K., Hwang, J., Lee, J., Woo, J.-M., Choi, J., Lee, C., Kwak, J. Y., & Son, H. (2023). Design of Synaptic Driving Circuit for TFT eFlash-Based Processing-In-Memory Hardware Using Hybrid Bonding. Electronics, 12(3), 678. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12030678








