Attenuation Characterization of Terahertz Waves in Foggy and Rainy Conditions at 0.1–1 THz Frequencies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- In terms of fog attenuation, based on Rayleigh approximation theory and Mie theory, we investigated the influence of advection fog and radiation fog on terahertz waves and determined the attenuation in fog at diverse temperatures and visibility at 0.1–1 THz. In addition, we used a more accurate Rayleigh approximation theory and compared it with the results obtained with a reference [18].
- In terms of rain attenuation, the rain was divided into four types: drizzle, moderate rain, downpour, and rainstorm, based on the rainfall rate, and we comprehensively compared and analyzed the rain attenuation of terahertz waves under Joss, M-P, and Weibull distributions.
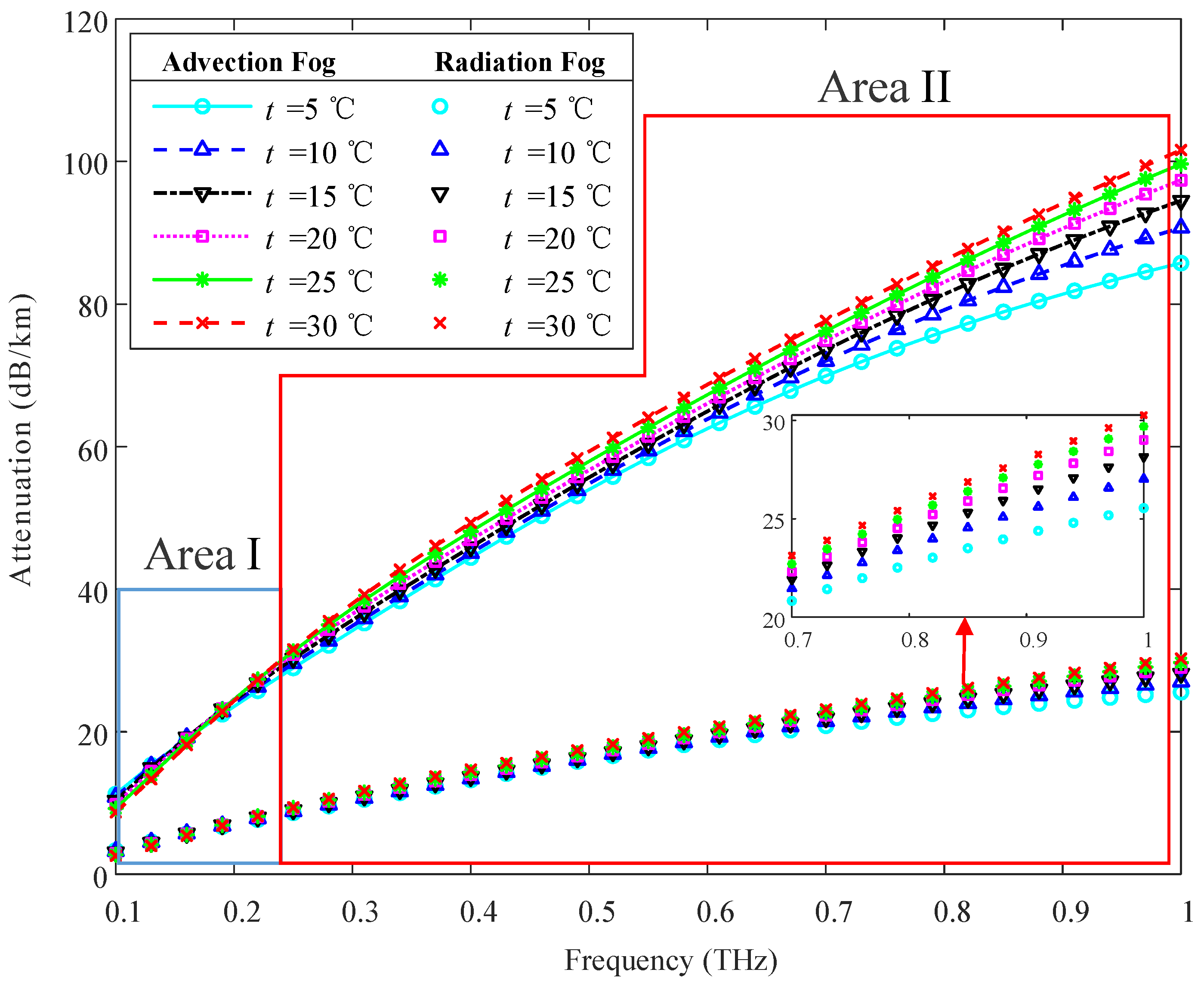
- The results indicate that visibility and frequency have a more significant effect than temperature on fog attenuation. The differences at 1 THz between the attenuation caused by advection fog and radiation fog are 8461.31 dB, 1986.81 dB, 250.82 dB, and 24.98 dB, corresponding to visibility of 30 m, 50 m, 100 m, and 200 m, respectively. Additionally, rainfall rate and frequency have a greater impact than raindrop distribution on rain attenuation. The rainfall attenuation significantly varies under different distributions, with the maximum difference being 3256.35 dB and the minimum difference being 0.34 dB at 1 THz.
2. Propagation Mechanism and Particle Distribution
2.1. Propagation Mechanism
2.2. Fog Droplet Distribution
2.3. Raindrop Distribution
3. Theoretical Model
3.1. Rayleigh Approximation Theory
3.2. Mie Theory
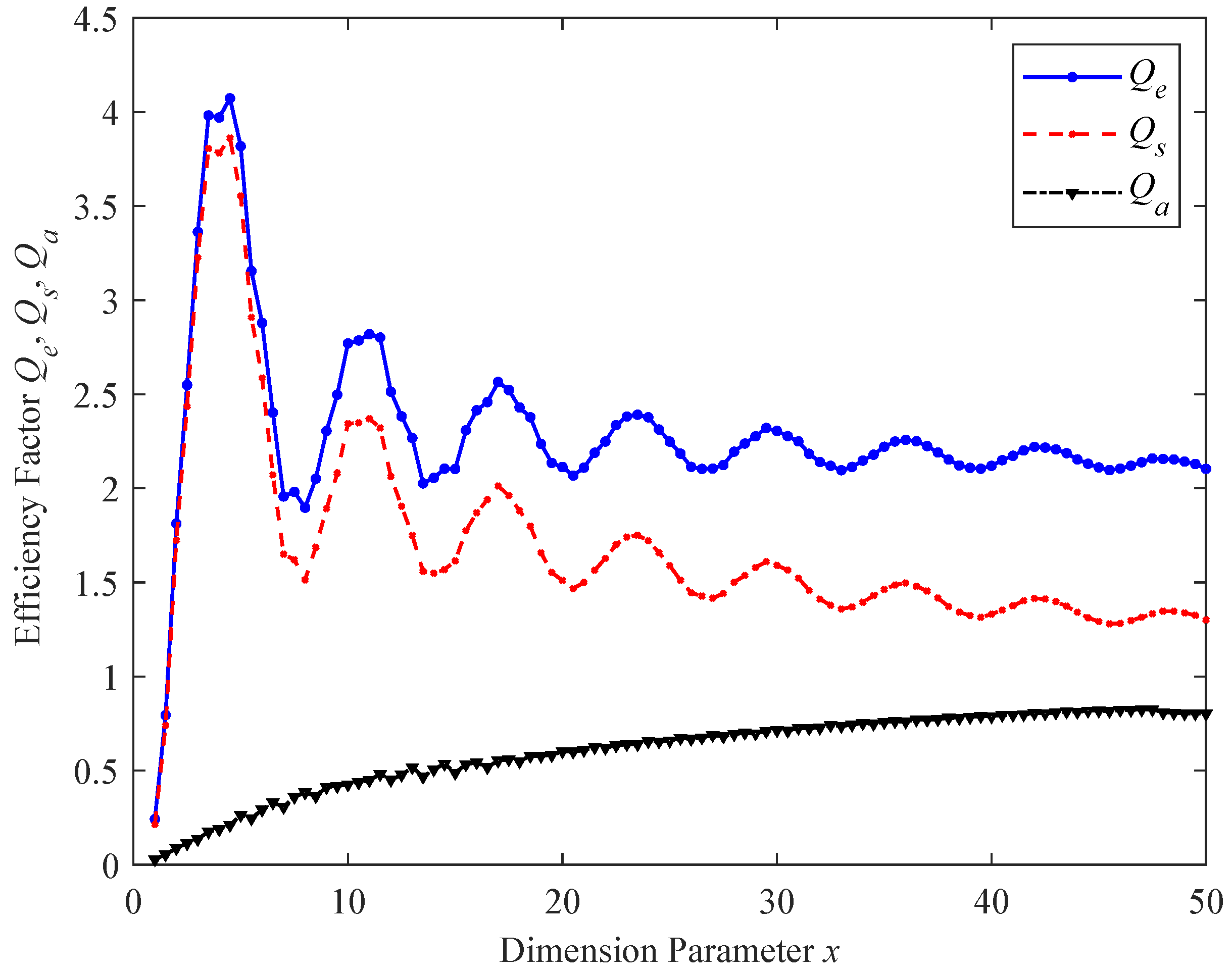
4. Results and Analysis
4.1. Fog Attenuation Based on the Rayleigh Approximation
4.2. Fog Attenuation Based on Mie Theory
4.3. Rain Attenuation Based on Mie Theory
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rikkinen, K.; Kyosti, P.; Leinonen, M.E.; Berg, M.; Parssinen, A. THz Radio Communication: Link Budget Analysis toward 6G. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2020, 58, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, S.; Amin, O.; Shihada, B.; Alouini, M.S. What should 6G be? Nat. Electron. 2020, 3, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Abbasi, N.A.; Kürner, T.; Molisch, A.F. Terahertz Wireless Channels: A Holistic Survey on Measurement, Modeling, and Analysis. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2022, 24, 1670–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Ma, X.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Niu, Z.; Kuang, N.; Chen, W.; Li, L.; Li, S. A Survey on Terahertz Communications. China Commun. 2019, 16, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, K.; Yi, H.; He, D.; Ai, B.; Zhong, Z. Towards 6G: Paradigm of Realistic Terahertz Channel Modeling. China Commun. 2021, 18, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittleman, D.M. Twenty Years of Terahertz Imaging. Opt. Express. 2018, 26, 9417–9431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sengupta, K.; Nagatsuma, T.; Mittleman, D.M. Terahertz Integrated Electronic and Hybrid Electronic-Photonic Systems. Nat. Electron. 2018, 1, 622–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarieddeen, H.; Alouini, M.S.; Al-Naffouri, T.Y. An Overview of Signal Processing Techniques for Terahertz Communications. Proc. IEEE. 2021, 109, 1628–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Headland, D.; Monnai, Y.; Abbott, D.; Fumeaux, C.; Withayachumnankul, W. Tutorial: Terahertz Beamforming, from Concepts to Realizations. APL Phontonics 2018, 3, 051101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.; Sarieddeen, H.; Ballal, T.; Wymeersch, H.; Alouini, M.S.; Al-Naffouri, T.Y. A Tutorial on Terahertz-Band Localization for 6G Communication Systems. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2022, 4, 1780–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemic, F.; Abadal, S.; Tavernier, W.; Stroobant, P.; Colle, D.; Alarcón, E.; Marquez-Barja, J.; Famaey, J. Survey on Terahertz Nanocommunication and Networking: A Top-Down Perspective. IEEE J. Sel. 2021, 39, 1506–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, S.; Kinugawa, M.; Wakiyama, S.; Sayama, S.; Kamei, T. Rain Attenuation in the Microwave-to-Terahertz Waveband. Wireless Eng. Technol. 2016, 7, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su, K.; Moeller, L.; Barat, R.B.; Federici, J.F. Experimental Comparison of Performance Degradation from Terahertz and Infrared Wireless Links in Fog. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A-Opt. Image Sci. Vis. 2012, 29, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Siles, G.A.; Riera, J.M.; Garcia-del-Pino, P. Atmospheric Attenuation in Wireless Communication Systems at Millimeter and THz Frequencies. IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag. 2015, 57, 48–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, E.B.; Jeon, T.I.; Grischkowsky, D.R. Long-Path THz-TDS Atmospheric Measurements Between Buildings. IEEE Trans. Terahertz Sci. Technol. 2015, 5, 742–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, T.; Wiatrek, A.; Preußler, S.; Grigat, M.; Braun, R.P. Link Budget Analysis for Terahertz Fixed Wireless Links. IEEE Trans. Terahertz Sci. Technol. 2012, 2, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Q.; Liu, D.; Tong, J. Study on the Scattering Effect of Terahertz Waves in Near-Surface Atmosphere. IEEE Access. 2018, 6, 49007–49018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haiying, L.; Zhensen, W.; Leke, L.; Zhenwei, Z.; Changsheng, L.; Xin, Z. The Analysis of Advection Fog Attenuation Algorithms in Terahertz Wave Band. In Proceedings of the 2014 XXXIth URSI General Assembly and Scientific Symposium (URSI GASS), Beijing, China, 16–23 August 2014; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Mandehgar, M.; Grischkowsky, D.R. Broadband THz Signals Propagate Through Dense Fog. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2015, 27, 383–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golovachev, Y.; Etinger, A.; Pinhasi, G.A.; Pinhasi, Y. Propagation Properties of Sub-Millimeter Waves in Foggy Conditions. J. Appl. Phys. 2019, 125, 151612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Baidhani, A.; Fan, H.H. Learning for detection: A deep learning wireless communication receiver over Rayleigh fading channels. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computing, Networking and Communications (ICNC), Honolulu, HI, USA, 18–21 February 2019; pp. 6–10. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Déniz, E.; Gómez, L.; Gómez, H.W. The slashed-Rayleigh fading channel distribution. Math. Probl. Eng. 2019, 2019, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, J.; Vorrius, F.; Lamb, L.; Moeller, L.; Federici, J.F. Experimental Comparison of Terahertz and Infrared Signaling in Laboratory-Controlled Rain. J. Infrared Millim. Terahertz Waves. 2015, 36, 856–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Vorrius, F.; Lamb, L.; Moeller, L.; Federici, J.F. Comparison of Experimental and Theoretical Determined Terahertz Attenuation in Controlled Rain. J. Infrared Millim. Terahertz Waves 2015, 36, 1195–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, L.; Menezes, L.; Moraes, P. Rain Attenuation at THz Frequencies from Historical Data Collected in Brasilia, Brazil. In Proceedings of the 2021 USNC-URSI Radio Science Meeting (USCN-URSI RSM), Honolulu, HI, USA, 9–13 August 2021; pp. 45–50. [Google Scholar]
- Yoseva, M.; Hashiguchi, H.; Vonnisa, M.; Luini, L.; Nugroho, S.; Shafii, M.A. Characteristics of Rain Attenuation for Microwave-to-terahertz Waveband from Raindrop Size Distribution Observation in Indonesia. In Proceedings of the 2019 PhotonIcs and Electromagnetics Research Symposium—Spring (PIERS-Spring), Rome, Italy, 17–20 June 2019; pp. 362–367. [Google Scholar]
- Norouzian, F.; Marchetti, E.; Gashinova, M.; Hoare, E.; Constantinou, C.; Gardner, P.; Cherniakov, M. Rain Attenuation at Millimeter Wave and Low-THz Frequencies. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2020, 68, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohren, C.F.; Huffman, D.R. Absorption and Scattering of Light by Small Particles; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2008; Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/200455938_Absorption_and_scattering_of_light_by_small_particles (accessed on 10 February 2022).
- Xizheng, K.; Dongdong, M.; Jiani, L. Study Attenuation of Laser Transmission in Fog. J. Light Scat. 2009, 21, 104–109. [Google Scholar]
- Joss, J. The Variation of Raindrop Size Distributions at Locarno. Proc. Int. Conf. Cloud Phys. 1968, 1968, 369–373. Available online: https://cir.nii.ac.jp/crid/1570291226437816064 (accessed on 15 May 2022).
- Marshall, J.S.; Palmer, W. The Distribution of Raindrops with Size. J. Meteorol. 1948, 5, 165–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Sano, M.; Sekine, M. Weibull Raindrop-Size Distribution and Its Application to Rain Attenuation. IEE Proc. Microwaves Antennas. Propag. 1997, 144, 197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attenuation Due to Clouds and Fog. Document Rec. ITU-R P. 840-8, 2019, International Telecommunication Union. Available online: https://www.itu.int/rec/R-REC-P.840/en (accessed on 12 November 2021).
- Mätzler, C. MATLAB Functions for Mie Scattering and Absorption, 2nd ed.; Institute of Applied Physics, University of Bern: Bern, Switzerland, 2002. [Google Scholar]




| Fog Level | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Horizontal Visibility (km) | >10 | 1–10 | 0.5–1 | 0.2–0.5 | 0.05–0.2 | <0.05 |
| Designation | Clear day | Mist | Fog | Heavy fog | Dense fog | Strong fog |
| Parameter | Parameter Values in Fog | Parameter Values in Rain |
|---|---|---|
| Particle Radius | 1∼60 m | 0.01∼40 mm |
| Frequency Band | 0.1∼1 THz | 0.1∼1 THz |
| Refractive Index | 1.5 + 0.01 i | 1.5 + 0.01 i |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liao, X.; Fan, L.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Z.; Wang, G.; Li, X.; Zhang, J. Attenuation Characterization of Terahertz Waves in Foggy and Rainy Conditions at 0.1–1 THz Frequencies. Electronics 2023, 12, 1684. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12071684
Liao X, Fan L, Wang Y, Yu Z, Wang G, Li X, Zhang J. Attenuation Characterization of Terahertz Waves in Foggy and Rainy Conditions at 0.1–1 THz Frequencies. Electronics. 2023; 12(7):1684. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12071684
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiao, Xi, Linjie Fan, Yang Wang, Ziming Yu, Guangjian Wang, Xianjin Li, and Jie Zhang. 2023. "Attenuation Characterization of Terahertz Waves in Foggy and Rainy Conditions at 0.1–1 THz Frequencies" Electronics 12, no. 7: 1684. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12071684
APA StyleLiao, X., Fan, L., Wang, Y., Yu, Z., Wang, G., Li, X., & Zhang, J. (2023). Attenuation Characterization of Terahertz Waves in Foggy and Rainy Conditions at 0.1–1 THz Frequencies. Electronics, 12(7), 1684. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12071684







