Abstract
The COVID-19 pandemic has necessitated profound changes in the business and technology landscapes, compelling organizations to reassess their Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems. Traditional ERP systems have demonstrated significant limitations in agility, scalability, and resilience, prompting a strategic shift towards cloud-based ERP solutions. This systematic literature review (SLR) aims to critically evaluate the transformation of ERP systems through the adoption of Microservice Architecture (MSA) and the integration of Managed Service Providers (MSPs), highlighting their role in enhancing system flexibility and operational continuity in a post-pandemic world. We conducted a systematic analysis of 124 scholarly articles published since 2010 to compare traditional ERP systems with MSA-based Cloud ERP solutions. Key insights reveal that MSA significantly improves system modularity and adaptability, addressing the shortcomings of monolithic architectures. Additionally, MSPs offer crucial support in managing the complexities of cloud transitions, ensuring security and efficiency. Our findings underscore the importance of a holistic approach to ERP modernization, integrating technological advancements with strategic business objectives. This study not only fills a critical gap in the literature but also provides actionable recommendations for practitioners and policymakers aiming to enhance ERP systems’ resilience and agility. Future research directions are proposed to further explore the synergistic potential of cloud ERP, MSA, and MSPs in fostering innovative and sustainable business practices.
1. Introduction
1.1. Motivation and Background
The COVID-19 pandemic, which began in early 2020, has significantly transformed the corporate world, pushing businesses into a “new normal” characterized by increased uncertainty. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems have become crucial in this context, with IT capabilities playing a pivotal role in maintaining competitive advantages. The evolution towards Microservice Architecture-based Cloud ERP, supported by Managed Service Providers (MSPs), represents a significant shift from traditional Monolithic Architecture, offering a more adaptable and business-focused framework. This paper proposes a new model for leveraging Microservice Architecture-based Cloud ERP through MSPs, highlighting its importance for the post-pandemic business landscape.
ERP systems revolutionize how enterprises manage resources by offering an integrated and comprehensive approach. Evolving from earlier methodologies like Material Requirements Planning (MRP), Production Resource Planning (MRP II), and Management Information Systems (MIS), ERP systems automate key functions including treasury, accounting, purchasing, production, and sales. Initially adopted by major corporations in Europe, the United States, and Japan during the 1990s, ERP systems unify various operational processes and facilitate the seamless flow of resources and information across departments, enhancing data consolidation and operational efficiency.
Traditionally, ERP systems have been deployed on premises, requiring substantial investment in hardware and software. This approach often leads to significant challenges in managing the total cost of ownership (TCO), including ongoing expenses for updates and maintenance. In contrast, cloud-based ERP solutions, utilizing Software as a Service (SaaS), offer scalability, flexibility, and reduced initial costs. Despite these advantages, the adoption of Cloud ERP has been slower than expected, primarily due to concerns over data security, system customization difficulties, and the inertia of transitioning from established on-premise systems.
The onset of the COVID-19 pandemic marked a watershed moment, sharply defining pre- and post-pandemic corporate eras. The widespread shift to remote work emphasized the importance of robust operations, leading to a trend toward adopting Microservice-based Cloud ERP systems. These systems offer greater resilience compared to traditional Monolithic Architecture ERPs, which are more prone to disruptions. This paper proposes a new theoretical model for resilient and sustainable ERP solutions, validated with practical evidence, emphasizing the strategic imperative for businesses to adopt flexible, durable technological frameworks to navigate global challenges effectively.
1.2. Theoretical Background
1.2.1. Cloud ERP Concept, Type, and Managed Service Providers (MSPs)
Cloud ERP, as defined by Salim, Sedera et al. (2015) [1], is a paradigm enabling access to IT resources—including servers, storage, and software—via the Internet. This model eliminates reliance on local hardware, allowing access from any location using IT devices. Unlike traditional IT asset purchases, Cloud ERP adopts a “lease in possession” approach, where users pay for usage while the service provider manages maintenance and operations.
Cloud services are broadly categorized into Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS), each offering different levels of control and flexibility. This segmentation helps organizations choose the most suitable model based on cost, scalability, and control needs.
Peng and Gala (2014) [2] and Seethamraju (2015) [3] discuss the economic and technical benefits of adopting cloud-based ERP systems, highlighting their capacity to meet modern business demands and align with strategic objectives. Transitioning to the cloud, however, requires a fundamental redesign of ERP systems.
With the growth of the cloud computing market, Managed Service Providers (MSPs) have emerged as key players, offering a broad spectrum of services, from consultancy and system architecture design to implementation and maintenance. MSPs, evolving from traditional IT roles such as consulting firms and system integrators, play a crucial role in facilitating the transition to modern ERP systems by providing the necessary expertise and resources. Sunshine (2021) [4] discusses the cybersecurity risks associated with MSPs and Cloud Service Providers (CSPs), emphasizing their importance in safeguarding customer data. Venkatesh and Singhal (2017) [5] refine the definition of managed services and underscore the need for MSPs to innovate and remain competitive in the rapidly changing IT landscape.
1.2.2. Concept of MSA and Comparison with Monolithic Architecture
Microservice Architecture (MSA) offers a forward-thinking approach to software development, addressing the constraints of traditional Monolithic Architecture. In a Monolithic setup, an application’s components are closely interlinked and deployed as a single unit, making updates, scalability, and maintenance complex.
In contrast, MSA breaks down a large application into smaller, independently deployable services, each focused on a specific business function. This allows for independent development, deployment, and scaling, providing agility and flexibility. Additionally, failures in a single service can be isolated, preventing broader system impacts.
Hazrati et al. (2017) [6] observed that MSA significantly boosts business process efficiency and decision-making capabilities. Klock et al. (2017) [7] demonstrated its flexibility in managing variable workloads with the MicroADO tool, optimizing ERP systems. Studies by Baškarada et al. (2018) [8], Götz et al. (2018) [9], and De Alwis et al. (2018) [10] support the transition to microservices to address the shortcomings of monolithic systems, enhancing modularity, easing maintenance, and increasing adaptability.
1.3. Objective and Structure of the Study
This study conducts a systematic literature review (SLR) to analyze the impact of Microservice Architectures (MSAs) and Managed Service Providers (MSPs) on cloud ERP solutions in the post-pandemic era. It aims to identify emerging trends, challenges, and opportunities, providing insights critical for theorists and practitioners involved in the design, implementation, and management of advanced ERP systems. This research is vital for evolving ERP systems that meet the dynamic needs of organizations, ensuring resilience, continuity, and competitive advantages.
The paper is organized as follows: Section 2 introduces the research context. Section 3 outlines the SLR methodology and presents results from the descriptive analysis. Section 4 discusses the comparative analysis results, organizing factors into 12 criteria based on the literature. Section 5 suggests future research directions and concludes the discussion.
2. Research Context
2.1. Research Objectives
The integration of Microservice Architectures (MSA) into Cloud ERP systems across various industries prompts an investigation into associated risks, including policy, economic, process, organizational, and technical factors. This study aims to identify threats to the security, stability, and reliability of MSA-based Cloud ERP systems and to compile and categorize these threats into a structured ontology. This approach will (1) provide researchers and practitioners with a comprehensive overview of potential risks to their current or future systems and (2) facilitate the sharing of strategies for mitigating and preventing recognized security threats.
The objectives of this research are outlined as follows:
O1: Evaluate shifts in ERP system requirements driven by the pandemic, with a focus on increased agility, scalability, and resilience.
O2: Analyze the transition from traditional ERP systems to cloud-based solutions, assessing how well cloud ERP benefits align with strategic business objectives.
O3: Investigate the adoption of Microservices Architecture in ERP systems, emphasizing its contribution to system adaptability and ease of maintenance.
O4: Assess the role of Managed Service Providers in supporting cloud ERP implementations and managing the complexities of the transition.
O5: Synthesize existing research on cloud ERP, MSA, and MSPs to identify emerging trends, challenges, and strategic directions for future enterprise system innovations.
2.2. Research Questions
To comprehensively understand the evolution, current state, and future prospects of microservices architecture-based Cloud ERP systems managed by service providers, this study employs a systematic literature review (SLR). Table 1 outlines the key research questions addressed in this review.

Table 1.
Research questions with their motivations and relevant objectives.
3. Research Methodology
3.1. Paper Selection Procedure
This subsection describes the methodology employed to select papers for our systematic literature review. The process included choosing databases, defining keywords and search strings, and outlining paper-filtering steps. Initially, one author screened the papers, which were then independently verified by two other authors. This multi-step approach guaranteed a rigorous and unbiased selection, ensuring the inclusion of a wide array of relevant literature.
3.1.1. Database Selection
The search strategy for this study was both general and targeted, developed using the population and intervention framework suggested by Pettigrew and Roberts [11]. “Population” pertains to the application domains of cloud ERP and microservices architecture, while “intervention” includes aspects like security, affordability, and conformance. We refined our initial search string (S1) to a more comprehensive version (S2) by incorporating these areas along with twelve additional keywords, enhancing the precision and scope of our database search. This methodology ensured the retrieval of studies highly relevant to our research objectives.
Initial and Refined Search Strings:
- S1: {Cloud ERP}
- S2: {Cloud ERP}, {Cloud Computing}, {Software as a Service}, {SaaS}, {Microservice}, {Micro-service}, {Micro Service}, {Architecture}, {design}, {system}, {structure}, {Managed Service Provider}, {Cloud Service Provider}
To ensure the retrieval of relevant studies, we adhered to the guidelines outlined by Kuhrmann et al. [12]. Accordingly, we utilized the following online academic libraries for our research:
- IEEE Xplorer “https://ieeexplore.ieee.org (6 June 2024)”.
- ACM Digital Library “https://dl.acm.org (6 June 2024)”.
- SpringerLink “https://link.springer.com (6 June 2024)”.
- ScienceDirect “https://www.sciencedirect.com (6 June 2024)”.
- Wiley Online Library “https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com (6 June 2024)”.
- Scopus “www.scopus.com (6 June 2024)”.
- Web of Science “www.webofscience.com (6 June 2024)”.
To ensure comprehensive coverage, our search included both automated methods and recursive snowballing techniques, as recommended by Wohlin [13,14]. In backward snowballing, we evaluated the references of selected papers, while forward snowballing involved assessing papers that cited our initially approved studies. We applied this process recursively to each newly approved paper using Google Scholar for forward tracing. This dual approach significantly increased the thoroughness of our literature review.
3.1.2. Paper Selection
Papers retrieved through the automatic search underwent a two-stage screening process. In the first stage, we assessed the relevance of each paper by reviewing its title and abstract. In the second stage, we evaluated the full texts to determine if they met our inclusion criteria. All papers were screened independently by two authors; discrepancies were resolved through discussion. Papers identified through the snowballing process underwent a similar independent review by the two authors before a decision was made on their inclusion or exclusion. This rigorous screening approach ensured that only the most relevant and high-quality papers were selected for our review.
3.1.3. Paper Filtering
To optimize the retrieval process, our study applied stringent inclusion and exclusion criteria. We restricted our selection to peer-reviewed articles from journals and conferences. The automated search was designed to capture papers published from 2010 to 2023, including early publications. Moreover, we limited our focus to papers written in English that specifically address Cloud ERP systems or microservices architecture. Detailed descriptions of these criteria are presented in Table 2 (Inclusion Criteria) and Table 3 (Exclusion Criteria). These parameters ensured that our review concentrated on the most relevant and authoritative sources.

Table 2.
Inclusion criteria.

Table 3.
Exclusion criteria.
3.1.4. Quality Assessment
As advised by Peterson et al. [15], the quality assessment of identified papers is crucial for mapping studies to ensure sufficient information is available for data extraction. Therefore, we conducted a quality assessment process to evaluate the overall strength and details of selected papers. A questionnaire consisting of four items was developed, inspired by [16,17] and adapted to our research topic. The assessment criteria and associated scores are summarized in Table 4. In this study, a score of 1 is awarded when an item can be answered with “Yes”, and a score of 0 is awarded when the answer is “No” (QA1). For QA2, a score of 1 is given to studies presenting a detailed and validated solution regarding how to adopt Cloud ERP or MSA. In the case of MSP, a score of 0.5 is given to studies that provide only an overview, whereas a score of 0 is assigned to those lacking a clear solution. For QA3, a score of 1 is attributed to studies with three or more citations, and a score of 0 is awarded for studies with fewer than three citations, as determined by Google Scholar, to avoid penalizing early publications. For QA4, paper sources are ranked following the CORE conference ranking (A or B (+1), C (+0.5), and not ranked (0)) and the Journal Citation Reports (JCR) (Q1-2 (+1), Q3-4 (+0.5), and not ranked (0)). Each criterion is treated equally, and the total score for each study is calculated by summing the four values. Only studies with a quality score of 2 or higher are included in this study.

Table 4.
Quality assessment criteria.
3.1.5. Descriptive Analysis of Papers
Our paper selection process was methodically conducted to ensure the inclusion of high-quality and relevant literature. Initially, our search across various digital libraries yielded 2571 references, as detailed in Table 5 and Appendix A. To streamline the selection process, we excluded duplicate papers based on the following principles: (1) If a paper was indexed in Scopus or WoS but also in other journals, we excluded it from Scopus and WoS. (2) If a paper was indexed in both Scopus and WoS, we excluded it from Scopus. As a result, 73 papers were excluded, refining the selection to 2498 unique papers.

Table 5.
Number of studies returned by each repository.
Next, we applied the inclusion and exclusion criteria outlined in Table 2 and Table 3. This process excluded 1519 papers, leaving 979 for further consideration. These criteria ensured that only papers directly relevant to our research objectives were retained.
The remaining 979 papers underwent a thorough review of titles, abstracts, and keywords, leading to the exclusion of 882 papers. This narrowed the selection to 97 papers with strong potential for inclusion.
To ensure a comprehensive literature review, we employed snowball sampling techniques, reviewing the references of selected papers and identifying additional relevant studies. This approach added 27 papers to our pool.
Finally, Table 6 shows that the selected papers underwent a rigorous full-text review based on predefined criteria, resulting in a final selection of 124 papers for inclusion. These papers were meticulously categorized by publication type (journal articles or conference presentations), publication year, and source country, providing a systematic overview of the research landscape and ensuring diverse perspectives and insights.

Table 6.
The details of the paper selection process.
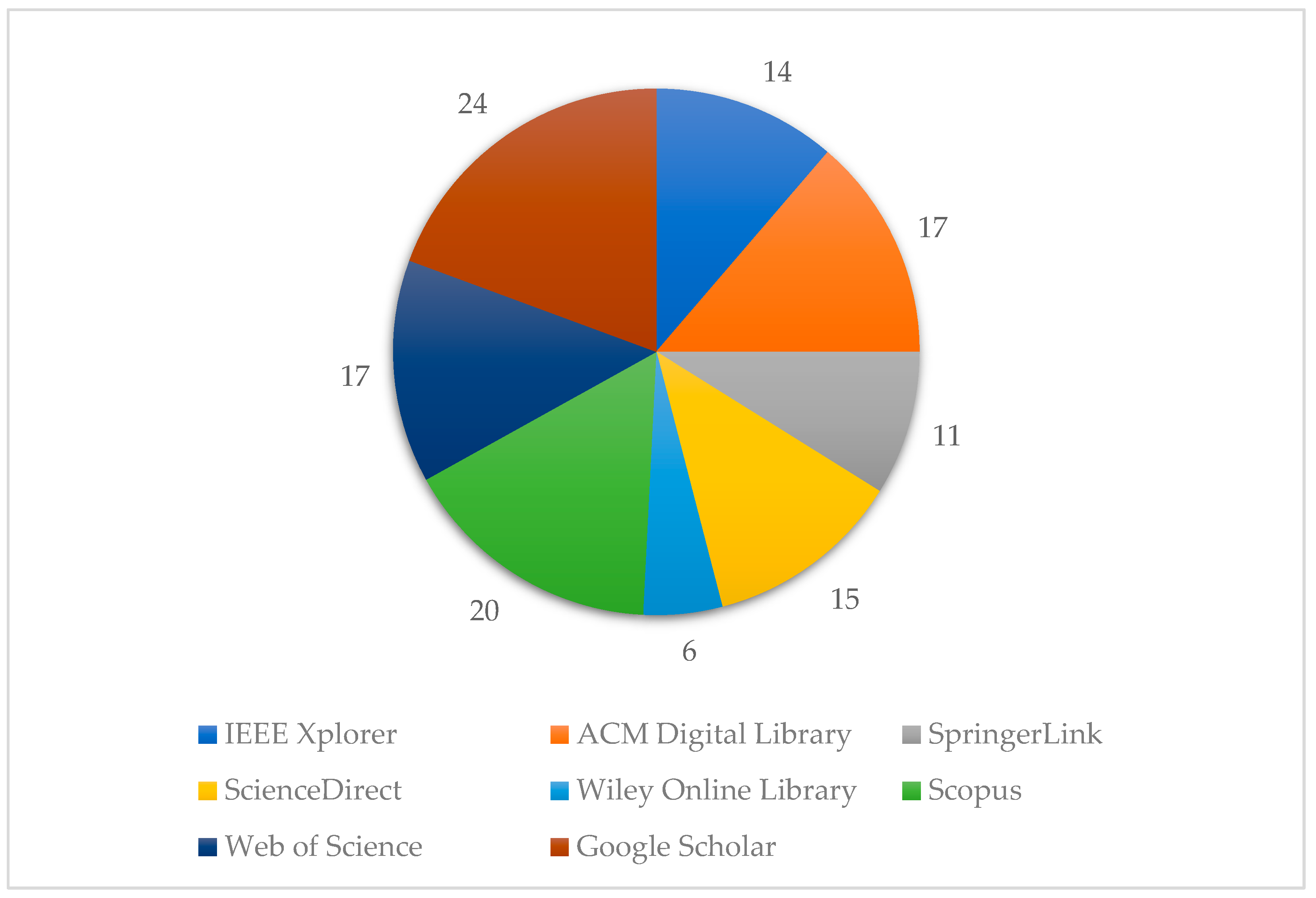
The 124 selected publications across various online academic libraries as follows; 24 papers from Google Scholar identified through snowballing, 20 from Scopus, 17 (plus 2 from snowballing) from ACM Digital Library, 17 from Web of Science, 14 from IEEE Xplorer, 15 (plus 1 from snowballing) from ScienceDirect, 11 from SpringerLink, and 6 from Wiley Online Library. This distribution is visually summarized in Figure 1, highlighting the diverse academic libraries that contributed to the research published between 2010 and 2023.
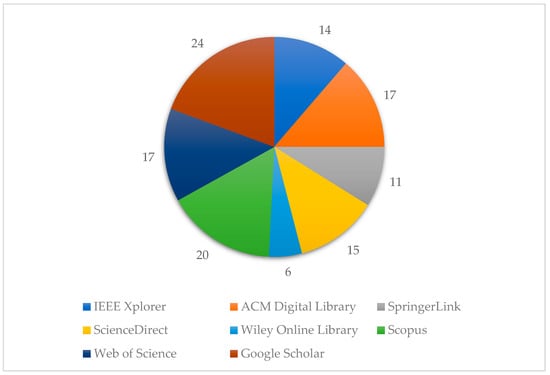
Figure 1.
The type of repository selected in this study.
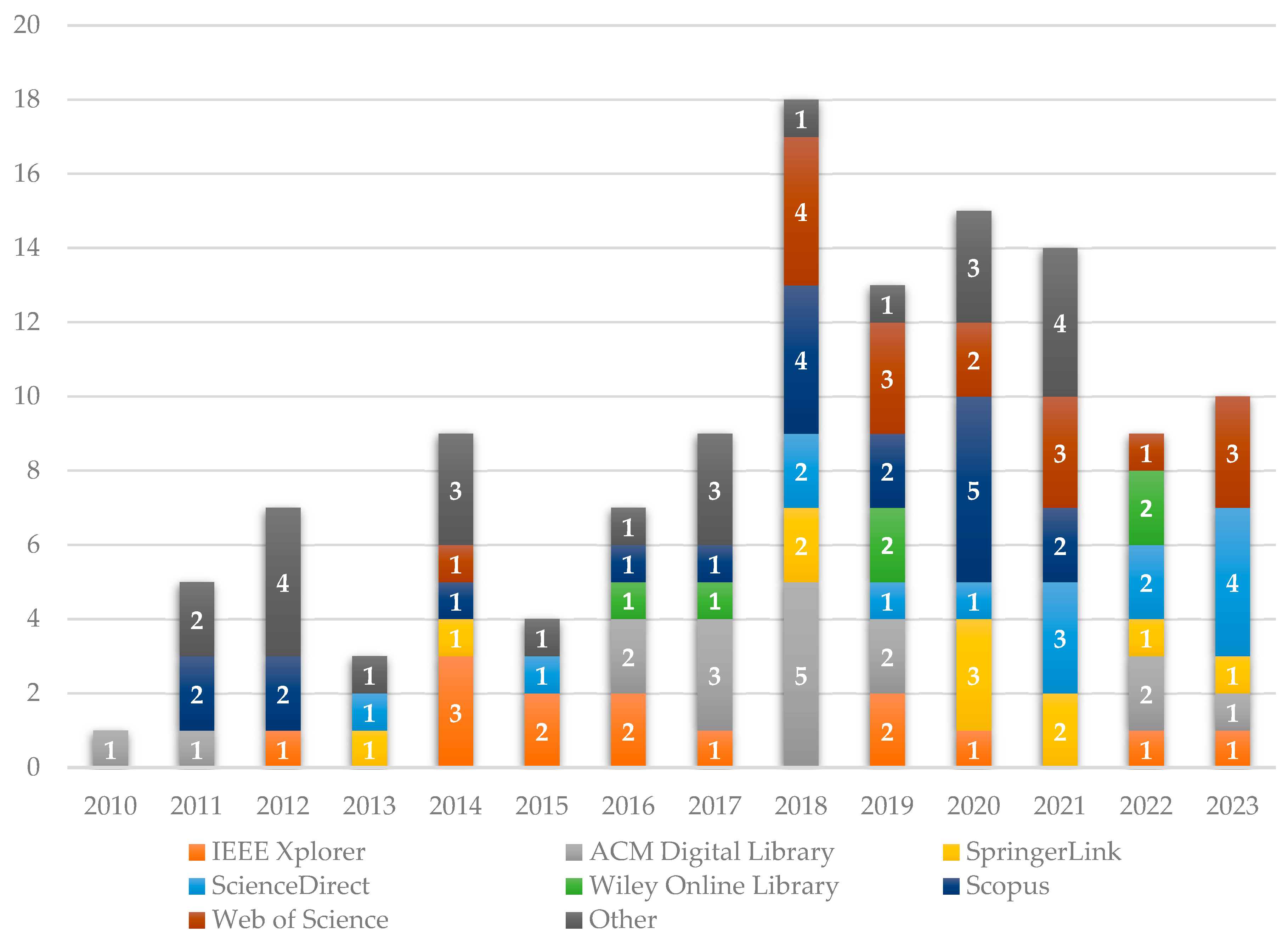
The temporal distribution of the publications, presented in Figure 2, shows a modest number of papers from 2010 to 2013. A noticeable increase in publications began in 2014, with a significant rise from 2018 onwards. This trend underscores the escalating academic and industrial interest in Cloud ERP and microservices architecture over the past decade.
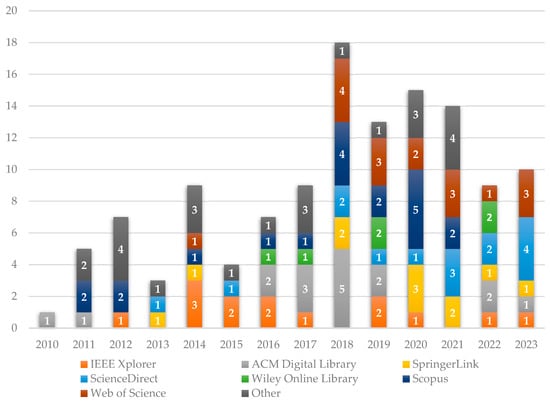
Figure 2.
Number of papers published per year.
4. Comparative Strategy and Discussion about the Results of the Analysis
4.1. Comparative Strategy
This study modifies the “Suitability Assessment Guideline for Adopting Cloud Computing in The Public Sector” developed by the Korea Information and Communication Technology Association [18] to suit the private sector. In the private sector, setting common adoption criteria is challenging due to industry-specific characteristics and individual business situations. Therefore, based on criteria calculated by public evaluation organizations, we aimed to use objective criteria that include economically significant factors for companies. This means that our study not only applies public sector guidelines but also expands economic factors to be fully utilized in the private sector. Additionally, we decided to apply a broader concept, as cloud ERP is part of SaaS, which is a subset of cloud computing. This approach enables comparative analysis based on common criteria. These factors have been organized into four main categories to enhance their relevance in the decision-making process for companies considering cloud ERP adoption.
The updated guidelines systematically address the financial implications and challenges of migrating to cloud ERP. By incorporating economic considerations, they provide a framework for evaluating the viability and strategic benefits of cloud ERP, ensuring that the transition meets technical, security, and financial efficiency standards. Focusing on economic aspects, the guidelines equip decision-makers with a powerful tool for evaluating cloud ERP adoption (Table 7). This structured approach helps in understanding potential cost savings, scalability, and operational efficiencies, along with the necessary technology infrastructure investments. It also aids stakeholders in navigating the complexities of cloud transitions, providing strategic and financial insights for informed decision-making.

Table 7.
Considerations for the adoption of the cloud—Major Category.
By comprehensively addressing these categories, organizations can make well-informed decisions about cloud adoption, ensuring that their strategies are aligned with their strategic goals, economically viable, organizationally feasible, and technically sound. This structured evaluation not only helps mitigate risks associated with cloud adoption but also maximizes the benefits derived from cloud computing technologies.
4.2. Comparative Methodology
The comparative methodology in this study involved categorizing the 124 papers obtained from the systematic literature review into three intermediate classifications, each aligned with the four main categories of cloud adoption: policy, economics, pro-cess and organization, and technology (Table 8). These classifications were predefined to address distinct aspects of cloud adoption, facilitating a detailed comparative anal-ysis within each category.

Table 8.
Considerations for the adoption of the cloud—Minor Category.
This study employs a rigorous analytical framework by categorizing 124 papers from a systematic literature review into 12 subcategories, following the taxonomy outlined in Section 4.2. The literature is divided into four broad classifications, policy, economics, process and organization, and technology, each further segmented into three subcategories focused on Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), Microservices Architecture (MSA), and Managed Service Providers (MSP). This structured approach facilitates a detailed exploration of the complex landscape of cloud adoption. The benefits of this methodology are outlined as follows:
- Understanding Nuances: Segmenting the literature into subcategories allows for a nuanced examination of specific aspects within each major category. This granular approach highlights the unique challenges and advantages of cloud adoption across different technical and organizational contexts.
- Comparative Analysis: Organizing the papers into well-defined categories sets the foundation for a systematic comparative analysis. This method emphasizes the differences and similarities among topics, trends, and findings, providing a comprehensive framework for side-by-side evaluations.
- Comprehensive Exploration: The categorization ensures a thorough examination of all facets of cloud adoption. It covers a wide array of topics within each subcategory, offering a complete view of the research landscape and pinpointing key themes and emerging trends.
- Generating Insights: This structured comparative approach is crucial for producing significant insights into cloud adoption considerations. It aids stakeholders in understanding how to effectively navigate the complexities of cloud computing in areas like ERP, MSA, and MSP, providing valuable perspectives for informed decision-making.
This comprehensive and comparative strategy enhances both academic and practical discourse on cloud adoption, equipping stakeholders with a profound understanding of cloud computing’s impact. The approach not only deepens the analysis but also enriches the broader knowledge base. This prepares the ground for future research and the development of practical strategies in cloud computing.
4.3. Discussion about the Results of Mapping by Category
4.3.1. Policy Factors Impact (RQ2, RQ3)
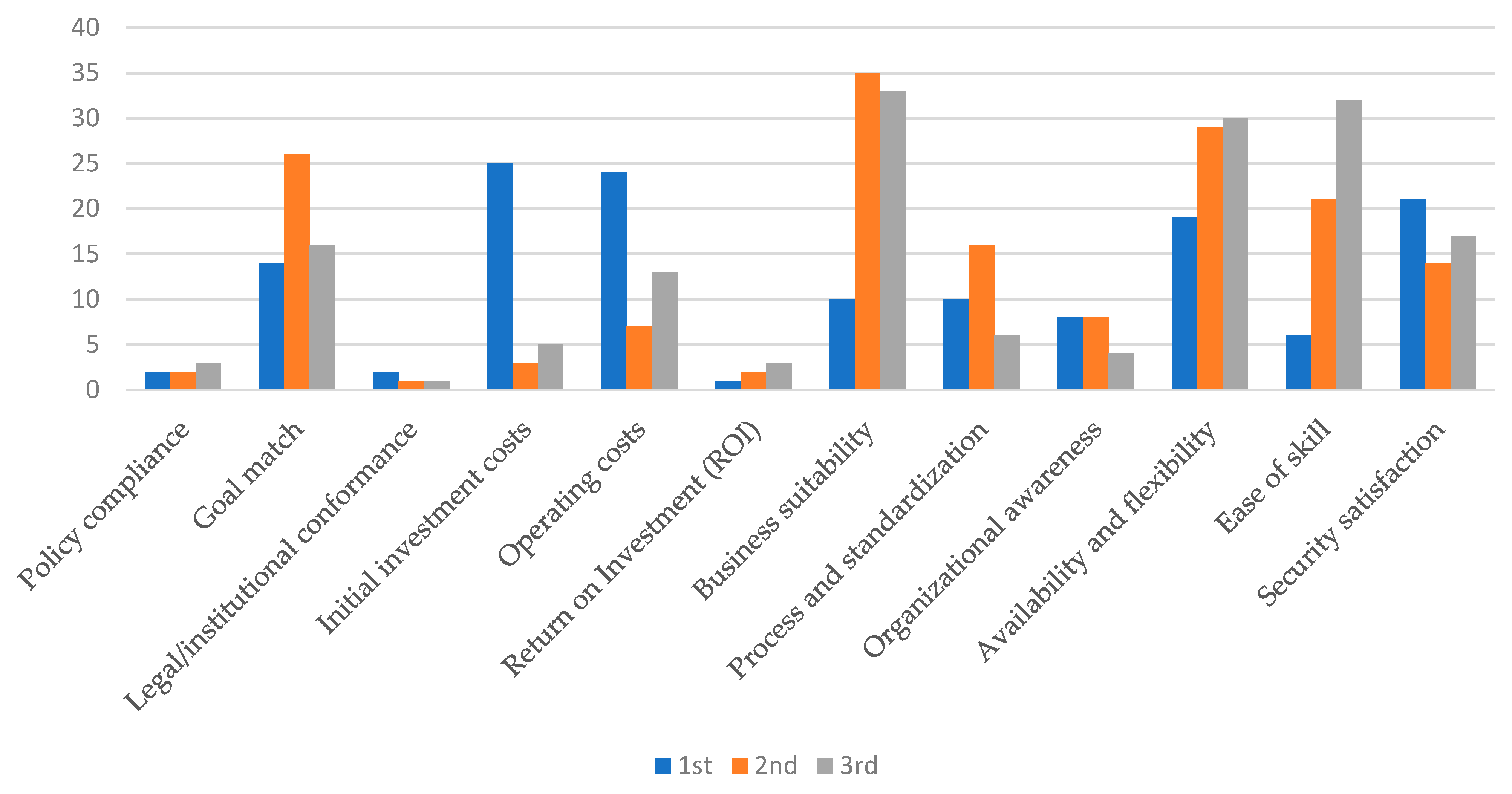
The analysis underscores goal match as the predominant factor in the adoption of cloud ERP and MSA technologies, emphasizing the importance of aligning these technologies with organizational objectives. Interestingly, policy compliance and adherence to legal frameworks have not surfaced as significant considerations. This finding suggests that the existing policies and legal regimes are currently adequate in supporting the integration of these technologies. Strategic alignment remains paramount; however, the existing policy landscape seems to adequately encompass the requisite provisions for technology adoption.
4.3.2. Economic Factors Impact (RQ2)
The study identifies initial investment and operating costs as the primary economic determinants for adopting cloud ERP and MSA technologies. The importance of these costs, however, shifts over time; while they are critical at the initial period, their significance decreases in later periods. This suggests that as organizations stabilize their use of these technologies, the focus on economic factors may shift toward other key considerations.
4.3.3. Process and Organizational Factors Impact (RQ1, RQ2, RQ3, RQ5)
Business suitability has been identified as the most critical factor influencing the adoption of cloud ERP and MSA, increasingly gaining prominence over other considerations. This trend underscores growing strategic diligence as organizations aim to ensure that technological solutions are in harmony with broader business objectives. Particularly in contexts of heightened uncertainty, the alignment of technology with business needs becomes increasingly scrutinized, highlighting a shift towards strategic coherence in technology adoption.
4.3.4. Technical Factors Impact (RQ4, RQ5)
The findings reveal that all three subcategories within the technical factors—usability, scalability, and integration capabilities—are consistently regarded as crucial throughout the adoption process of cloud ERP and MSA. This uniform emphasis across different time frames indicates that these technologies are not yet fully mature and are still in the adoption phase. The persistent focus on technical factors suggests a need for ongoing evaluation and adaptation as these technologies continue to evolve and as new challenges and capabilities emerge.
Table 9 presents a comprehensive breakdown of findings categorized by major and minor factors influencing the adoption of cloud ERP and MSA technologies. The table details the frequency and ratio of each factor, revealing significant insights derived from the study's analysis.

Table 9.
Results of mapping by category.
4.4. Discussion about Comparative Analysis by Period
4.4.1. Analysis of First Period (2010–2015)
During the initial period from 2010 to 2015, 29 relevant research papers were identified, predominantly focusing on Cloud ERP. This era marked the rise of Big Data, prompting many global companies to transition towards Global ERP systems. The heightened interest in Cloud ERP during this time reflects the growing awareness of its potential benefits. In contrast, research on Microservices Architecture (MSA) and Managed Service Providers (MSP) was limited, as these concepts were still in their nascent stages.
The analysis indicates that economic factors, especially cost reduction, were critical during this period. Security and availability also emerged as significant concerns. Although Cloud ERP was promising in aligning with business goals and operations, it faced challenges in policy compliance and legal/institutional conformity. These discrepancies played a pivotal role in the adoption of new technologies, underscoring the need to address legal and administrative challenges when implementing Cloud ERP systems.
4.4.2. Analysis of the Second Period (2016~2019)
During this period, 47 relevant research papers were identified, showing a more balanced distribution across Cloud ERP, Microservices Architecture (MSA), and Managed Service Providers (MSP). This time was marked by active discussions on artificial intelligence, with notable integrations such as AlphaGo and Watson into corporate strategies. Concurrently, discussions about MSA gained significant momentum.
In terms of Cloud ERP, there was a distinct shift from the earlier economic focus to prioritizing goal conformity and work suitability. This transition reflected growing skepticism about the effectiveness of Monolithic Architecture as business operations became more diverse and segmented.
Security and availability continued to be significant concerns, with an increased emphasis on the technical ease of adoption provided by Microservices Architecture. This shift facilitated discussions on the scalability and agility of Cloud ERP systems, underlining their potential to meet evolving business demands.
4.4.3. Analysis of the Third Period (2020~2023)
In this period, beginning in 2020, the study identified 29 relevant research papers, with a balanced focus on Cloud ERP and Microservices Architecture (MSA), and fewer on Managed Service Providers (MSP). This phase was distinctly marked by the global impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, which accelerated the adoption of remote work practices and intensified the need for business continuity.
During these disruptions, the rationale for adopting Cloud ERP shifted significantly compared to that during the first period (2010–2015). While the earlier emphasis was on economic feasibility, the focus subsequently pivoted to the suitability of Cloud ERP solutions for achieving business goals and ensuring continuity. This change underscores the growing recognition of the need for flexible and resilient IT infrastructures to handle unpredictable challenges.
Security and availability have been consistent areas of concern throughout all periods, but these issues became even more critical during this third period due to the challenges posed by remote work and the necessity of securing distributed IT environments effectively.
Overall, the analysis of this period illustrates how priorities and considerations for adopting Cloud ERP and related technologies have evolved, shaped by contemporary challenges such as the COVID-19 pandemic.
4.4.4. Conclusion of Comparison by Period
The comparative analysis conducted across three distinct periods from 2010 to 2021 has illuminated the evolving priorities and considerations surrounding Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), Microservices Architecture (MSA), and Managed Service Providers (MSP) in the context of cloud technology. In total, 124 research papers were analyzed, with the following distribution: 63 papers focused on ERP, 36 on MSA, and 6 on MSP.
Figure 3 summarizes the comparative analysis of priorities and considerations across three periods (2010–2021) for Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), Microservices Architecture (MSA), and Managed Service Providers (MSP) within cloud technology adoption.
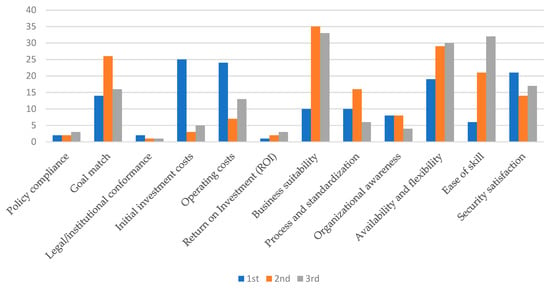
Figure 3.
Clustering the selected studies regarding Cloud ERP, MSA, and MSP.
Table 10 presents a compilation of studies selected based on keywords associated with Cloud ERP, Microservices Architecture (MSA), and Managed Service Providers (MSP). These studies offer a comprehensive view of the shifts in focus and methodology observed over the last decade.

Table 10.
Comparison of each period.
During the first period (2010–2015), the emphasis was primarily on the initial investment cost and operating cost associated with ERP implementations. This focus suggests that enterprises were primarily concerned with the comparative and security aspects of IT investments and operating costs. Additionally, the period witnessed a significant interest in Cloud ERP, driven by emerging technologies and the potential for cost reduction.
In the second period (2016–2019), there was a notable shift towards emphasizing target conformity and work suitability following the implementation of ERP systems. This shift reflects a growing recognition of the importance of aligning ERP systems with organizational goals and improving work processes. Moreover, discussions around MSA began to gain traction during this period, coinciding with the increasing diversification of corporate activities and the rise of artificial intelligence technologies.
The third period (2020~2023) was profoundly influenced by the COVID-19 pandemic, leading to a renewed emphasis on work suitability and resilience in the face of unprecedented challenges. As remote work became the norm, the importance of business continuity and the suitability of Cloud ERP solutions for maintaining operations gained prominence. Additionally, security and availability remained critical considerations throughout all periods, with heightened importance attributed to these aspects amidst the growing adoption of remote work and distributed IT environments.
Overall, the analysis underscores the dynamic nature of enterprise IT landscapes and the evolving priorities driving the adoption of ERP, MSA, MSP, and Cloud Technology. From an initial focus on cost reduction to a heightened emphasis on goal alignment, work suitability, and resilience in the face of external disruptions, the study highlights the shifting paradigms shaping the adoption and utilization of these technologies over time.
5. Conclusions
The comprehensive analysis of 124 research papers spanning from 2010 to 2023 has provided invaluable insights into the transformative journey of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems, Microservices Architecture (MSA), Managed Service Providers (MSP), and Cloud Technology. Through distinct phases delineated by shifting priorities and challenges, the study illuminates the evolution of organizational technology strategies, culminating in the recognition of MSA-based Cloud ERP as a potent solution, particularly in response to the exigencies of the COVID-19 crisis.
During the first period (2010–2015), the burgeoning potential of Cloud ERP systems was a focal point, propelled by the constraints imposed by traditional on-premise IT infrastructure. Enterprises, grappling with the limitations of legacy systems, embarked on a paradigm shift towards cloud-based solutions, driven by the promise of enhanced scalability, cost-efficiency, and security. Notably, the discourse of this era was steeped in economic considerations, with emphasis placed on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) analyses, which underscored the substantial benefits of cloud adoption in optimizing system configuration, operational efficiency, and robust security frameworks. As the technological landscape continued to evolve during the second period (2016–2019), the spotlight shifted towards nuanced discussions on business suitability and adaptability in the face of dynamic market dynamics. While interest in Cloud ERP waned slightly, the emergence of Microservices Architecture (MSA) heralded a new era of modular, agile system design. MSA, with its emphasis on granular service components and decentralized architecture, addressed the burgeoning complexities of modern business environments, emphasizing the importance of goal alignment, operational flexibility, and responsiveness to evolving market demands. This period witnessed a paradigmatic shift in the discourse surrounding ERP systems, with increasing recognition of the imperative to transcend traditional monolithic architectures in favor of more agile, adaptable frameworks. The onset of the COVID-19 pandemic in the third period (2020–2023) precipitated unprecedented disruptions across global industries, underscoring the imperative for organizational resilience and adaptability. In this tumultuous landscape, Cloud ERP, MSA, and MSP emerged as indispensable tools for navigating the complexities of remote work, supply chain disruptions, and fluctuating market demands. The discourse of this period underscores the renewed emphasis on business continuity, goal suitability, and operational resilience in the face of pervasive uncertainty.
5.1. Implications of the Study and Practice
The findings of this study provide a strong foundation for future research in the fields of Cloud ERP systems, Microservice Architecture (MSA), and Managed Service Providers (MSPs). Here are several key research implications:
- Exploring Hybrid Models: Future research should investigate the hybrid integration of on-premise and cloud-based ERP systems. This hybrid approach could offer insights into balancing legacy systems’ stability with the flexibility of cloud solutions, particularly in industries with high compliance requirements.
- Longitudinal Studies on Adoption and Impact: Conducting longitudinal studies would provide a deeper understanding of the long-term impacts of transitioning to Cloud ERP and MSA. These studies could explore how organizational performance, agility, and resilience evolve over extended periods.
- Impact of Emerging Technologies: With the rapid advancement of technologies such as AI, IoT, and blockchain, future research should investigate their integration with Cloud ERP and MSA. These technologies could provide significant enhancements in automation, data analytics, and supply chain transparency.
- Organizational Change Management: The transition to cloud-based solutions involves significant changes in organizational processes and culture. Research should explore the best practices for managing these changes, including training, stakeholder engagement, and the development of new skill sets within the workforce.
- Role of MSPs in Different Contexts: Investigate the role of MSPs in various organizational contexts, including small- and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) versus large corporations. Understanding how MSPs can best support different types of organizations could enhance the effectiveness of cloud ERP implementations.
By addressing these areas, future research can contribute significantly to the development of more robust, secure, and effective cloud ERP solutions, ultimately enhancing organizational performance and resilience in an increasingly complex and uncertain business environment.
This research addresses the critical gap in the literature concerning the transition to Cloud ERP systems based on Microservice Architecture, recognizing their potential as sustainable solutions in an era marked by increasing uncertainty. The findings of this study suggest several important implications for practice:
- Guidance for Technology Adoption: The study provides deep insights into the factors driving cloud ERP adoption, such as economic efficiencies, technological advancements, and organizational readiness. These insights can guide decision-makers in evaluating the feasibility and advantages of adopting cloud-based ERP solutions, ensuring that technology choices align with broader business strategies.
- Risk Mitigation Strategies: By identifying and thoroughly analyzing potential risks associated with cloud ERP systems, including security vulnerabilities and possible operational disruptions, the research offers actionable strategies for risk mitigation. Organizations can utilize these strategies to develop comprehensive risk management frameworks that enhance system security and stability.
- Strategic Alignment: Emphasizing the importance of aligning cloud ERP solutions with organizational objectives and business processes, the study provides practical recommendations for integrating ERP systems in a manner that supports strategic business goals. This alignment is crucial for maximizing the returns on ERP investments and for achieving long-term business success.
- Resilience and Business Continuity: The COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the necessity for resilient and continuous business operations. The study demonstrates how cloud ERP systems can significantly bolster an organization’s resilience and continuity planning. Practical insights derived from this research can help organizations enhance their ability to operate effectively amidst ongoing disruptions and uncertainties.
- Future-Proofing Strategies: Discussing emerging trends and potential future directions, the study serves as a resource for organizations aiming to future-proof their ERP systems. Insights into new technologies, evolving industry practices, and potential strategic shifts are crucial for planning and adapting to future business landscapes. These insights can inform strategic decisions and help in navigating long-term changes effectively.
These implications collectively offer a roadmap for organizations to navigate the complexities of adopting and integrating cloud ERP systems in a manner that is both strategic and sustainable. As businesses continue to face a rapidly changing global environment, leveraging these insights will be critical in maintaining competitive advantages and operational excellence.
5.2. Limitations of the Study
Despite the comprehensive nature of this systematic literature review, several limitations must be acknowledged, which may influence the validity of the study and its findings. The study primarily focuses on literature from 2010 to 2023, potentially excluding relevant earlier works that could provide additional insights. Additionally, the selection process, while rigorous, might have introduced bias by prioritizing certain types of publications or specific academic databases. The review includes only papers published in English, potentially overlooking valuable research published in other languages, which could limit the comprehensiveness of the findings. Although a wide range of databases were searched, it is possible that some relevant studies were not included due to the limitations of database indexing and search algorithms, resulting in an incomplete representation of the existing body of knowledge. The quality assessment process, while structured, relies on specific criteria that may not capture all aspects of a study’s quality, and the subjective nature of some criteria, such as the perceived relevance and depth of analysis, could affect the consistency of the assessment. The fields of Cloud ERP, MSA, and MSPs are rapidly evolving, so the findings of this review may quickly become outdated as new technologies and practices emerge, highlighting the need for continual updates to the literature review. The limitations identified in this study open several avenues for future research, which can build on the current findings and address the gaps identified.
5.3. Future Research Directions
The transformative upheavals precipitated by the COVID-19 crisis underscore the pressing need for further research to elucidate the evolving contours of Management Information Systems (MIS) and organizational technology strategies. As enterprises grapple with the imperatives of remote work, supply chain disruptions, and evolving market dynamics, several avenues for future research emerge:
- The Contact-less World and MIS Evolution: Exploring the ramifications of the contact-less paradigm for MIS architectures, functionalities, and organizational workflows. Investigating how organizations can leverage emerging technologies to facilitate seamless collaboration, communication, and operational efficiency in a distributed work environment.
- Future Trends in MIS: Anticipating the trajectory of MIS evolution in the post-pandemic era, with an emphasis on emerging trends such as AI-driven analytics, blockchain integration, and IoT-enabled business processes. Examining how these technologies can be harnessed to enhance decision-making, streamline operations, and drive innovation across diverse industry verticals.
- Transformations in the Nature of Work: Investigating the profound shifts in work dynamics precipitated by technological advancements and societal changes. Analyzing the implications of remote work, gig economy platforms, and hybrid work models on organizational structures, employee productivity, and workforce management practices.
- MIS and Risk Mitigation: Exploring strategies for minimizing risks and enhancing resilience in the face of uncertainty through robust MIS frameworks. Investigating how organizations can leverage Big Data analytics, AI-driven insights, and real-time monitoring to mitigate operational risks, anticipate market trends, and adapt to changing business landscapes.
- Integration of External Data Sources: Examining the challenges and opportunities associated with integrating external data sources into enterprise MIS systems. Investigating strategies for aggregating, analyzing, and leveraging diverse datasets to enhance organizational decision-making, customer insights, and competitive advantages.
- The Role of Emerging Technologies in MIS: Analyzing the impact of emerging technologies such as quantum computing, edge computing, and 5G networks on MIS functionalities and applications. Exploring how these technologies can revolutionize data processing, enhance system performance, and enable new forms of digital interaction and collaboration.
In conclusion, the dynamic interplay between technological innovation, organizational strategies, and external exigencies underscores the imperative for ongoing research to elucidate the evolving contours of Management Information Systems. By embracing interdisciplinary approaches and leveraging emerging technologies, researchers can contribute to the development of robust, agile MIS frameworks that empower organizations to thrive in an era of perpetual change and uncertainty.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.L.; methodology, C.L. and H.F.K.; validation, C.L. formal analysis, C.L.; investigation, C.L.; resources, C.L.; writing—original draft preparation, C.L.; writing—review and editing, C.L. and H.F.K.; visualization, C.L.; supervision, B.G.L.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Appendix A

Table A1.
Papers included in the literature review.
Table A1.
Papers included in the literature review.
| SEQ | Category | Title Digital Library | Digital Library | Year | Policy Compliance | Goal Match | Legal/Institutional Conformance | Initial Investment Costs | Operating Costs | Return on Investment (ROI) | Business Suitability | Process and Standardization | Organizational Awareness | Availability and Flexibility | Ease of Skill | Security Satisfaction |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ERP | Competitive advantages of the ERP: new perspectives [19] | ACM | 2010 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||||
| 2 | ERP | The impact of cloud computing on ERP implementations in higher education [20] | GS | 2011 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||||
| 3 | ERP | ERP in the Cloud–Benefits and Challenges [21] | Scopus | 2011 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||||
| 4 | ERP | Cloud Computing and Enterprise Resource Planning Systems [22] | Scopus | 2011 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||||||
| 5 | ERP | Cloud Computing for Standard ERP systems: Reference Framework and Research Agenda [23] | GS | 2011 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||||||
| 6 | ERP | ERP on cloud: Implementation strategies and challenges [24] | IEEE | 2012 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||||
| 7 | ERP | Benefits and drawbacks of cloud-based versus traditional ERP systems [25] | GS | 2012 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||
| 8 | ERP | In-house versus in-cloud ERP systems, a comparative study [26] | Scopus | 2012 | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||
| 9 | ERP | Advantages and disadvantages of adopting ERP systems serving as SaaS from the perspective of SaaS Users [27] | GS | 2012 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||||
| 10 | ERP | Cloud ERP: Implementation of enterprise resource planning using cloud computing technology [28] | GS | 2012 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||||||
| 11 | ERP | Challenges involved in the implementation of ERP on demand solution: cloud computing [29] | GS | 2012 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||||
| 12 | ERP | Cloud enterprise systems: a review of the literature and its adoption [30] | Scopus | 2012 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||||
| 13 | ERP | Exploring factors for adopting ERP as SaaS [31] | SD | 2013 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||||||
| 14 | ERP | A comparative study of cloud-based ERP systems with traditional ERP and analysis of cloud ERP implementation [32] | GS | 2013 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||
| 15 | ERP | Potential concerns and common benefits of cloud-based Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) [33] | Springer | 2013 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||||
| 16 | ERP | Cloud ERP: a new dilemma for modern organizations? [1] | WoS | 2014 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||||
| 17 | ERP | Cloud computing as an operational model for ERP services: definitions and challenges [34] | GS | 2014 | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||
| 18 | ERP | A framework for evaluating cloud Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems [35] | Springer | 2014 | ● | ● | ||||||||||
| 19 | ERP | Cloud ERP adoption opportunities and concerns: a comparison of SMEs and large companies [36] | GS | 2014 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||
| 20 | ERP | Cloud and traditional ERP systems in small and medium enterprises [37] | IEEE | 2014 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||||
| 21 | ERP | Competition and challenges in adopting cloud ERP [38] | GS | 2014 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||
| 22 | ERP | Cloud computing and ERP: a framework of promises and challenges [39] | Scopus | 2014 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||||
| 23 | ERP | Secured Document Management through a Third Party Auditor Scheme in Cloud Computing [40] | IEEE | 2014 | ● | ● | ||||||||||
| 24 | ERP | A Comprehensive study on Cloud computing [41] | IEEE | 2014 | ● | ● | ||||||||||
| 25 | ERP | A Cloud computing platform for ERP application [42] | SD | 2015 | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||
| 26 | ERP | Determinants of cloud ERP adoption in Saudi Arabia: an empirical study [43] | IEEE | 2015 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||||
| 27 | ERP | Cloud ERP adoption opportunities and concerns: the role of organizational size [44] | IEEE | 2015 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||||
| 28 | ERP | Cloud ERP Systems: Anatomy of Adoption Factors & Attitudes [45] | GS | 2015 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||
| 29 | ERP | An analysis of the perceived benefits and drawbacks of cloud ERP systems: a South African study [46] | Scopus | 2016 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||||
| 30 | ERP | Implementation of IDEA, BATS, ARIMA and the Queuing model for task scheduling in cloud computing [47] | IEEE | 2016 | ● | |||||||||||
| 31 | ERP | Compliance, network, security and the human factors in cloud ERP implementation [48] | Wiley | 2016 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||||||
| 32 | ERP | Cloud ERP Implementation [49] | GS | 2016 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||||
| 33 | ERP | Identification of challenges and their ranking in the implementation of cloud ERP [50] | Scopus | 2017 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||
| 34 | ERP | A Requirements Elicitation Tool for Cloud-Based ERP Software Product Line [51] | ACM | 2017 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||||
| 35 | ERP | Research on Knowledge Transfer about the Whole Process of ERP Implementation Based on Cloud Computing [52] | ACM | 2017 | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||
| 36 | ERP | Optimized Multi-Objective Resource Assignment and Server Consolidation in the Cloud Environment (OMORASCCE) [53] | GS | 2018 | ● | |||||||||||
| 37 | ERP | Role of cloud ERP on performance from an organization contingent resource-based view perspective [54] | WoS | 2018 | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||
| 38 | ERP | A Hybrid model for exploring the antecedents of cloud ERP continuance [55] | Scopus | 2018 | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||
| 39 | ERP | Prioritizing the factors affecting cloud ERP adoption—an analytic hierarchy process approach [56] | WoS | 2018 | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||
| 40 | ERP | Understanding the landscape of research in Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems adoption [57] | ACM | 2018 | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||
| 41 | ERP | Reducing integration complexity of cloud-based ERP systems [58] | ACM | 2018 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||||
| 42 | ERP | Cloud ERP Systems for Small-and-Medium Enterprises: A Case Study in the Food Industry [59] | Scopus | 2018 | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||
| 43 | ERP | Do Cloud ERP Systems Retire? An ERP Lifecycle Perspective [60] | SD | 2018 | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||
| 44 | ERP | What drives cloud ERP continuance? An integrated view [61] | WoS | 2018 | ● | ● | ||||||||||
| 45 | ERP | IT leadership and ERP: a challenging day for a new leader [62] | Springer | 2018 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||||
| 46 | ERP | Cloud-Based Intelligent System for Supply Chain Management: A Future Roadmap for SCM Technologies [63] | Springer | 2018 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||||
| 47 | ERP | Service Oriented Machine-learning Application for Reconfigurable Predictive Maintenance System [64] | Scopus | 2019 | ● | |||||||||||
| 48 | ERP | Towards a better understanding of determinant logistical factors in SMEs for cloud ERP adoption in developing economies [65] | WoS | 2019 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||||
| 49 | ERP | ERP: An elastic resource provisioning approach for cloud applications [66] | WoS | 2019 | ● | |||||||||||
| 50 | ERP | An empirical investigation of organizations’ switching intention to cloud enterprise resource planning: a cost-benefit perspective [67] | WoS | 2019 | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||
| 51 | ERP | Examining the impact of Cloud ERP on sustainable performance: A dynamic capability view [68] | WoS | 2020 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||||||
| 52 | ERP | What drives organizations to switch to cloud ERP systems? The impacts of enablers and inhibitors [69] | WoS | 2020 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||
| 53 | ERP | Understanding cloud ERP continuance intention and individual performance: a TTF-driven perspective [70] | Scopus | 2020 | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||
| 54 | ERP | Hybrid IT and Multi Cloud an Emerging Trend and Improved Performance in Cloud Computing [71] | Springer | 2020 | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||
| 55 | ERP | Moving enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems to the cloud: the challenge of infrastructural embeddedness [72] | Scopus | 2020 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||||
| 56 | ERP | A Cloud-Based Data Collaborative Approach to Combatting the COVID-19 Pandemic and Solving Major Technology Challenges [73] | GS | 2021 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||||||
| 57 | ERP | Business Process Re-engineering to Support the Sustainability of the Sales Commodities in Large Transactions with the Quotation System [74] | GS | 2021 | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||
| 58 | ERP | The effect of ERP on firm performance through information quality and supply chain integration in the COVID-19 era [75] | Scopus | 2021 | ● | ● | ||||||||||
| 59 | ERP | Effective Cloud Resource Utilization in the Cloud ERP Decision-Making Process for Industry 4.0 in the United States [76] | WoS | 2021 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||||||
| 60 | ERP | Re-examination and expansion of the EUCS Model on Cloud-based ERP systems [77] | Scopus | 2021 | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||
| 61 | ERP | Critical Implementation Factors for Cloud-Based Enterprise Resources Planning in the Nigerian Maritime Transport and Supply Chain [78] | GS | 2021 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||
| 62 | ERP | Framework and deployment of a cloud-based advanced planning and scheduling system [79] | SD | 2021 | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||
| 63 | ERP | A Study of Factors Influencing the Adoption of Cloud-Based ERP System: The Perspective of Transaction Cost Economics [80] | Springer | 2021 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||||||
| 64 | ERP | Challenges of Cloud-ERP Adoptions in SMEs [81] | SD | 2022 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||||
| 65 | ERP | Factors Affecting Cloud ERP Adoption Decisions in Organizations [82] | SD | 2022 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||
| 66 | ERP | Comparison of SaaS and IaaS in cloud ERP implementation: the lessons from the practitioners [83] | WoS | 2022 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||||
| 67 | ERP | Digital Business Transformation: Exploration of the Use of Erp Based Private Cloud to Improve Managing System in the Company (Case Study on One of Public Company in Indonesia) [84] | ACM | 2022 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||||||
| 68 | ERP | Hybrid Clouds Arising from Software as a Service Adoption: Challenges, Solutions, and Future Research Directions [85] | ACM | 2023 | ● | ● | ||||||||||
| 69 | ERP | Influential Characteristics and Benefits of Cloud ERP Adoption in New Zealand SMEs: A Vendors’ Perspective [86] | IEEE | 2023 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||||||
| 70 | ERP | Cloud ERP systems architectural challenges on cloud adoption in large international organizations: A sociomaterial perspective [87] | SD | 2023 | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||
| 71 | ERP | Investigating ERP System Customization: A Focus on Cloud-ERP [88] | SD | 2023 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||||
| 72 | ERP | Cloud-Based ERP Construction Process Framework in the Customer’s Perspective [89] | WoS | 2023 | ● | ● | ||||||||||
| 73 | ERP | Digital Transformation and Real Options: Evaluating the Investment in Cloud ERP [90] | WoS | 2023 | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||
| 74 | MSA | Microservices Architecture Enables DevOps: Migration to a Cloud-Native Architecture [91] | IEEE | 2016 | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||
| 75 | MSA | Modelling and managing deployment costs of microservice-based cloud applications [92] | ACM | 2016 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||||||
| 76 | MSA | Evaluation of conceptual and software model in implementing Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) with procedural approach of bpmn2 and micro service architecture [3] | GS | 2017 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||||||
| 77 | MSA | Workload-based clustering of coherent feature sets in microservice architectures [4] | IEEE | 2017 | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||
| 78 | MSA | Continuous software engineering—A microservice architecture perspective [93] | Wiley | 2017 | ● | ● | ||||||||||
| 79 | MSA | Application of mobile agent technology to microservice architecture [94] | ACM | 2017 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||||
| 80 | MSA | Architecting Microservices: Practical Opportunities and Challenges [5] | WoS | 2018 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||||
| 81 | MSA | Challenges of production microservices [6] | SD | 2018 | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||
| 82 | MSA | Function-Splitting Heuristics for THE Discovery of Microservices in Enterprise Systems [7] | Scopus | 2018 | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||
| 83 | MSA | From Monolith to Microservices: A Classification of Refactoring Approaches [95] | Scopus | 2018 | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||
| 84 | MSA | Contextual Understanding of Microservice Architecture: Current and Future Directions [96] | ACM | 2018 | ● | |||||||||||
| 85 | MSA | An extensible fault tolerance testing framework for microservice-based cloud applications [97] | ACM | 2018 | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||
| 86 | MSA | Microservice architecture in industrial software delivery on edge devices [98] | ACM | 2018 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||||
| 87 | MSA | Challenges in Documenting Microservice-Based IT Landscape: A Survey from an Enterprise Architecture Management Perspective [99] | IEEE | 2019 | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||
| 88 | MSA | Integrating an Association Rule Mining Agent in an ERP System: A Proposal and a Computational Scalability Analysis [100] | Scopus | 2019 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||||||
| 89 | MSA | Research on the Application of the SME Manufacturing Cloud Platform Based on a Micro Service Architecture [8] | SD | 2019 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||||
| 90 | MSA | Light and Shadow of the Microservice Architecture [101] | GS | 2019 | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||
| 91 | MSA | Framework for Interaction between Databases and Microservice Architectures [102] | IEEE | 2019 | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||
| 92 | MSA | Performance Modeling for Cloud Microservice Applications [103] | ACM | 2019 | ● | |||||||||||
| 93 | MSA | Toward a knowledge model focusing on microservices and cloud computing [104] | Wiley | 2019 | ● | ● | ||||||||||
| 94 | MSA | Testing microservice architectures for operational reliability [105] | Wiley | 2019 | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||
| 95 | MSA | The applicability of palladio for assessing the quality of cloud-based microservice architectures [106] | ACM | 2019 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||||||
| 96 | MSA | Architecture for a Microservice-based System, A Report [107] | GS | 2020 | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||
| 97 | MSA | Event-based Customization of Multi-tenant SaaS Using Microservices [108] | Scopus | 2020 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||||||
| 98 | MSA | Using microservices to customize multi-tenant software-as-a-service [109] | Springer | 2020 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||||||
| 99 | MSA | Analysis of Kubernetes for the Development of a Distributed Healthcare System Using the COVID-19 Healthcare App [110] | Scopus | 2020 | ● | |||||||||||
| 100 | MSA | Phenoflow: A Microservice Architecture for Portable Workflow-based Phenotype Definitions [111] | Scopus | 2020 | ● | ● | ||||||||||
| 101 | MSA | Research on a new and integrated medical and health clouding system based on a configurable microservice architecture [112] | IEEE | 2020 | ● | ● | ||||||||||
| 102 | MSA | Tracing the Effects of COVID-19 Over Small and Medium Enterprises [113] | GS | 2020 | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||
| 103 | MSA | Security in Microservices Architectures [114] | SD | 2020 | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||
| 104 | MSA | Remodularization Analysis for Microservice Discovery Using Syntactic and Semantic Clustering [115] | Springer | 2020 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||||||
| 105 | MSA | Microservice Remodularisation of Monolithic Enterprise Systems for Embedding in Industrial IoT Networks [116] | Springer | 2021 | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||
| 106 | MSA | Evaluating Service-Oriented and Microservice Architecture Patterns to Deploy eHealth Applications in the Cloud Computing Environment [117] | WoS | 2021 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||||||
| 107 | MSA | Securing microservices and microservice architectures: A systematic mapping study [118] | SD | 2021 | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||
| 108 | MSA | Research on load balancing technology for microservice architectures [119] | GS | 2021 | ● | ● | ||||||||||
| 109 | MSA | Using a Microservice Architecture as a Load Prediction Strategy for the Management System of University Public Services [120] | WoS | 2021 | ● | ● | ||||||||||
| 110 | MSP | SLA-Based Resource Allocation for Software as a Service Provider (SaaS) in Cloud Computing Environments [121] | ACM | 2011 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||||||
| 111 | MSA | A systematic mapping study: The new age of software architecture from monolithic to microservice architecture—awareness and challenges [122] | Wiley | 2022 | ● | ● | ||||||||||
| 112 | MSA | The operation and maintenance governance of microservices architecture systems: A systematic literature review [123] | Wiley | 2022 | ● | ● | ||||||||||
| 113 | MSA | Introducing Cloud-Assisted Micro-Service-Based Software Development Framework for Healthcare Systems [124] | IEEE | 2022 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||||||
| 114 | MSA | Analysis of Microservice Evolution using Cohesion Metrics [125] | ACM | 2022 | ● | ● | ||||||||||
| 115 | MSA | Boosting the visibility of services in microservice architecture [126] | Springer | 2023 | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||
| 116 | MSA | Microservice architecture recovery based on intra-service and inter-service features [127] | SD | 2023 | ● | ● | ||||||||||
| 117 | MSA | Cloud–edge microservices architecture and service orchestration: An integral solution for a real-world deployment experience [128] | SD | 2023 | ● | ● | ||||||||||
| 118 | MSA | From Monolith to Microservice: Measuring Architecture Maintainability [129] | WoS | 2023 | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||
| 119 | MSP | On the Viability of a Cloud Virtual Service Provider [130] | ACM | 2016 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |||||
| 120 | MSP | Managed Service Providers: Not Just Another TLA (Three-Letter Acronym) [131] | GS | 2017 | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||
| 121 | MSP | Innovating Managed Service Business Models [10] | GS | 2017 | ● | ● | ● | |||||||||
| 122 | MSP | Impact of Cloud-based Infrastructure on Telecom Managed Service Models [132] | GS | 2020 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||||||
| 123 | MSP | The rise of MSP & CSP vulnerabilities: storehouses for secure data [9] | SD | 2021 | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||||||||
| 124 | MSP | Cloud-CoCoSo: Cloud Model-Based Combined Compromised Solution Model for Trusted Cloud Service Provider Selection [133] | Springer | 2022 | ● | ● | ● |
References
- Salim, S.A.; Sedera, D.; Sawang, S.; Alarifi, A.H.E.; Atapattu, M. Moving from Evaluation to Trial: How do SMEs Start Adopting Cloud ERP? Australas. J. Inf. Syst. 2015, 19, S219–S254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, G.C.A.; Gala, C. Cloud ERP: A new dilemma to modern organisations? J. Comput. Inf. Syst. 2014, 54, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seethamraju, R. Adoption of software as a service (SaaS) enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems in small and medium sized enterprises (SMEs). Inf. Syst. Front. 2014, 17, 475–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunshine, Y. The rise of MSP & CSP vulnerabilities: Storehouses for secure data. Comput. Fraud Secur. 2021, 2021, 15–19. [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesh, R.; Singhal, T.K. Innovating Managed Services Business Models. Indian J. Sci. Technol. 2017, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazrati, V.; Maeen, M.; Assareh, R. Evaluation of conceptual and software model in implementing enterprise resource planning (erp) with procedural approach of bpmn2 and micro service architecture. QUID Investig. Cienc. Y Tecnol. 2017, 1, 2046–2053. [Google Scholar]
- Klock, S.; Van Der Werf JM, E.; Guelen, J.P.; Jansen, S. Workload-based clustering of coherent feature sets in microservice architectures. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Software Architecture (ICSA), Gothenburg, Sweden, 3–7 April 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Baškarada, S.; Nguyen, V.; Koronios, A. Architecting microservices: Practical opportunities and challenges. J. Comput. Inf. Syst. 2018, 60, 428–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Götz, B.; Schel, D.; Bauer, D.; Henkel, C.; Einberger, P.; Bauernhansl, T. Challenges of production microservices. Procedia CIRP 2018, 67, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Alwis, A.A.C.; Barros, A.; Polyvyanyy, A.; Fidge, C. Function-splitting heuristics for discovery of microservices in enterprise systems. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Service-Oriented Computing, Hangzhou, China, 12–15 November 2018; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Petticrew, M.; Roberts, H. Systematic Reviews in the Social Sciences: A Practical Guide; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Kuhrmann, M.; Fernández, D.M.; Daneva, M. On the pragmatic design of literature studies in software engineering: An experience-based guideline. Empir. Softw. Eng. 2017, 22, 2852–2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohlin, C. Guidelines for snowballing in systematic literature studies and a replication in software engineering. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Evaluation and Assessment in Software Engineering, London, UK, 13–14 May 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wohlin, C. Second-generation systematic literature studies using snowballing. In Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Evaluation and Assessment in Software Engineering, Limerick, Ireland, 1–3 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Petersen, K.; Vakkalanka, S.; Kuzniarz, L. Guidelines for conducting systematic mapping studies in software engineering: An update. Inf. Softw. Technol. 2015, 64, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M.S.; Riaz, S.; Abid, A.; Umer, T.; Zikria, Y.B. Role of iot technology in agriculture: A systematic literature review. Electronics 2020, 9, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, A.; Insfran, E.; Abrahão, S. Usability evaluation methods for the web: A systematic mapping study. Inf. Softw. Technol. 2011, 53, 789–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CCForum Chaiman. Suitability Assessment Guideline for Adopting Cloud Computing in The Public Sector. Cloud Computing Standard Forum. October 2013. Available online: http://www.ccsf.or.kr/template07/file/board/Default/14660430790.pdf (accessed on 4 June 2024).
- Sánchez, J.L.; Yagüe, A. Competitive advantages of the ERP: New perspectives. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Product Focused Software, Limerick, Ireland, 21–23 June 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Goel, S.; Kiran, R.; Garg, D. Impact of cloud computing on ERP implementations in higher education. Institutions 2011, 5, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenart, A. ERP in the Cloud–Benefits and Challenges. In Proceedings of the EuroSymposium on Systems Analysis and Design, Gdansk, Poland, 29 September 2011; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Saini, S.L.; Saini, D.K.; Yousif, J.H.; Khandage, S.V. Cloud computing and enterprise resource planning systems. In Proceedings of the world Congress on Engineering, London, UK, 6–8 July 2011; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Schubert, P.; Adisa, F. loud Computing for Standard Erp Systems: Reference Framework and Research Agenda; Universität Koblenz-Landau, Campus Koblenz: Universitätsbibliothek, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Appandairajan, P.; Zafar Ali Khan, N.; Madiajagan, M. ERP on Cloud: Implementation strategies and challenges. In Proceedings of the 2012 International Conference on Cloud Computing Technologies, Applications and Management (ICCCTAM), Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 8–10 December 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, J.; Faker, P.; Fesak, A.; Stuart, T. Benefits and drawbacks of cloud-based versus traditional ERP systems. Proceedings of the 2012–13 Course on Advanced Resource Planning, The Netherlands, December 2012. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/235759024_Benefits_and_Drawbacks_of_Cloud-Based_versus_Traditional_ERP_Systems (accessed on 9 July 2024).
- Elragal, A.; El Kommos, M. In-house versus in-cloud ERP systems: A comparative study. J. Enterp. Resour. Plan. Stud. 2012, 2012, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoseini, L. Advantages and Disadvantages of Adopting ERP Systems Served as SaaS from the Perspective of SaaS Users. Master’s Thesis, School of Information and Communication Technology, KTH, Stockholm, Sweden, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kiadehi, E.F.; Mohammadi, S. Cloud ERP: Implementation of enterprise resource planning using cloud computing technology. J. Basic Appl. Sci. Res. 2012, 2, 11422–11427. [Google Scholar]
- Purohit, G.N.; Jaiswal, M.P.; Pandey, S. Challenges involved in implementation of ERP on demand solution: Cloud computing. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Issues 2012, 9, 481. [Google Scholar]
- Salleh, S.M.; Teoh, S.Y.; Chan, C. Cloud Enterprise Systems: A Review of Literature and Its Adoption. In Proceedings of the Pacific Asia Conference on Information Systems, PACIS 2012, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, 11–15 July 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Johansson, B.; Ruivo, P. Exploring factors for adopting ERP as SaaS. Procedia Technol. 2013, 9, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navaneethakrishnan, C. A comparative study of cloud based ERP systems with traditional ERP and analysis of cloud ERP implementation. Int. J. Eng. Comput. Sci. 2013, 2, 2866–2869. [Google Scholar]
- Parthasarathy, S. Potential concerns and common benefits of cloud-based enterprise resource planning (ERP). In Cloud Computing; Springer: London, UK, 2013; pp. 177–195. [Google Scholar]
- Awad, H.A.H. Cloud computing as an operational model for ERP services: Definitions and challenges. Int. J. Innov. Appl. Stud. 2014, 8, 499. [Google Scholar]
- Chandrakumar, T.; Parthasarathy, S. A framework for evaluating cloud enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems. In Continued Rise of the Cloud; Springer: London, UK, 2014; pp. 161–175. [Google Scholar]
- Johansson, B.; Alajbegovic, A.; Alexopoulos, V.; Desalermos, A. Cloud ERP adoption opportunities and concerns: A comparison between SMES and large companies. In Proceedings of the Pre-ECIS 2014 Workshop “IT Operations Management” (ITOM2014), Tel Aviv, Israel, 8 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Saini, I.; Khanna, A.; Peddoju, S.K. Cloud and traditional ERP systems in small and medium enterprises. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Information Systems and Computer Networks (ISCON), Mathura, India, 1–2 March 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Weng, F.; Hung, M.-C. Competition and challenge on adopting cloud ERP. Int. J. Innov. Manag. Technol. 2014, 5, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, F.; Rohde, M.E. Cloud computing and ERP: A framework of promises and challenges. In Proceedings of the 25th Australasian Conference on Information Systems, Auckland, New Zealand, 8–10 December 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Parasuraman, K.; Srinivasababu, P.; Angelin, S.R.; Devi, T.A.M. Secured document management through a third party auditor scheme in cloud computing. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Electronics, Communication and Computational Engineering (ICECCE), Hosur, India, 17–18 November 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Nandgaonkar, S.V.; Raut, A.B. A comprehensive study on cloud computing. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Mob. Comput. 2014, 3, 733–738. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.-S.; Liang, W.-Y.; Hsu, H.-Y. A cloud computing platform for ERP applications. Appl. Soft Comput. 2015, 27, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlBar, A.M.; Hoque, M.R. Determinants of cloud ERP adoption in Saudi Arabia: An empirical study. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Cloud Computing (ICCC), Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, 26–29 April 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Johansson, B.; Alajbegovic, A.; Alexopoulo, V.; Desalermos, A. Cloud ERP adoption opportunities and concerns: The role of organizational size. In Proceedings of the 2015 48th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Kauai, HI, USA, 5–8 January 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Haddara, M.; Fagerstrøm, A.; Mæland, B. Cloud ERP Systems: Anatomy of Adoption Factors & Attitudes. J. Enterp. Resour. Plan. Stud. (JERPS) 2015, 22, 521212. [Google Scholar]
- Scholtz, B.; Atukwase, D. An analysis of the perceived benefits and drawbacks of cloud ERP systems: A South African study. In Information Technology in Environmental Engineering; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 75–87. [Google Scholar]
- Gawali, M.B.; Shinde, S.K. Implementation of IDEA, BATS, ARIMA and queuing model for task scheduling in cloud computing. In Proceedings of the 2016 Fifth International Conference on Eco-Friendly Computing and Communication Systems (ICECCS), Bhopal, India, 8–9 December 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, S.; Misra, S.C. Compliance, network, security and the people related factors in cloud ERP implementation. Int. J. Commun. Syst. 2016, 29, 1395–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carutasu, N.; Carutasu, G. Cloud ERP implementation. FAIMA Bus. Manag. J. 2016, 4, 31. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, S.; Misra, S.C.; Singh, A.; Kumar, V.; Kumar, U. Identification of challenges and their ranking in the implementation of cloud ERP: A comparative study for SMEs and large organizations. Int. J. Qual. Reliab. Manag. 2017, 34, 1056–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmoniem, M.A.A.; Nasr, E.S.; Gheith, M.H. A Requirements Elicitation Tool for Cloud-Based ERP Software Product Line. In Proceedings of the 3rd Africa and Middle East Conference on Software Engineering, Cairo, Egypt, 12–13 December 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Z. Research on Knowledge Transfer about the Whole Process of ERP Implementation Based on Cloud Computing. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Information Technology, Singapore, 27–29 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Priyanka, C.P.; Subbiah, S. Optimized Multi Objective Resource Assignment and Server Consolidation in Cloud Environment (OMORASCCE). Int. J. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2018, 7, 91–103. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, S.; Kumar, S.; Singh, S.K.; Foropon, C.; Chandra, C. Role of cloud ERP on the performance of an organization: Contingent resource-based view perspective. Int. J. Logist. Manag. 2018, 29, 659–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.-M. A hybrid model for exploring the antecedents of cloud ERP continuance: Roles of quality determinants and task-technology fit. Int. J. Web Inf. Syst. 2019, 15, 215–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meghana, H.L.; Mathew, A.O.; Rodrigues, L.L.R. Prioritizing the factors affecting cloud ERP adoption—An analytic hierarchy process approach. Int. J. Emerg. Mark. 2018, 13, 1559–1577. [Google Scholar]
- Valdebenito, J.; Quelopana, A. Understanding the landscape of research in Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems adoption. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Computers in Management and Business, Oxford, UK, 25–27 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Muslmani, B.K.; Kazakzeh, S.; Ayoubi, E.; Aljawarneh, S. Reducing integration complexity of cloud-based ERP systems. In Proceedings of the First International Conference on Data Science, E-learning and Information Systems, Madrid, Spain, 1–2 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zadeh, A.H.; Akinyemi, B.A.; Jeyaraj, A.; Zolbanin, H.M. Cloud ERP systems for small-and-medium enterprises: A case study in the food industry. J. Cases Inf. Technol. (JCIT) 2018, 20, 53–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demi, S.; Haddara, M. Do cloud ERP systems retire? An ERP lifecycle perspective. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2018, 138, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.-M. What drives cloud ERP continuance? An integrated view. J. Enterp. Inf. Manag. 2018, 31, 724–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carton, R.; Richmond, W. IT leadership and ERP: A challenging day for a new leader. J. Inf. Technol. Teach. Cases 2018, 8, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baral, M.M.; Verma, A. Cloud-based intelligent system for supply chain management: A future roadmap for SCM technologies. In Nanoelectronics, Circuits and Communication Systems: Proceeding of NCCS 2017; Springer: Singapore, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.M.; Chakravorti, N.; Weinert, N.; Munnoch, R.; Jadhav, S. Service Oriented Machine-learning Application for Reconfigurable Predictive Maintenance System. In Proceedings of the Lecture Notes in Engineering and Computer Science: Proceedings of the World Congress on Engineering, London, UK, 3–5 July 2019. [Google Scholar]
- AL-Shboul, M.A. Towards better understanding of determinants logistical factors in SMEs for cloud ERP adoption in developing economies. Bus. Process Manag. J. 2019, 25, 887–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Wu, Z.; Zuo, D.; Zhang, Z. ERP: An elastic resource provisioning approach for cloud applications. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.-W.; Hsu, P.-Y. An empirical investigation of organizations’ switching intention to cloud enterprise resource planning: A cost-benefit perspective. Inf. Dev. 2019, 35, 290–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Meissonier, R.; Drave, V.A.; Roubaud, D. Examining the impact of Cloud ERP on sustainable performance: A dynamic capability view. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2020, 51, 102028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.-W. What drives organizations to switch to cloud ERP systems? The impacts of enablers and inhibitors. J. Enterp. Inf. Manag. 2020, 33, 600–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.-M. Understanding cloud ERP continuance intention and individual performance: A TTF-driven perspective. Benchmarking: Int. J. 2020, 27, 1591–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gundu, S.R.; Panem, C.A.; Thimmapuram, A. Hybrid IT and multi cloud an emerging trend and improved performance in cloud computing. SN Comput. Sci. 2020, 1, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hustad, E.; Sørheller, V.U.; Jørgensen, E.H.; Vassilakopoulou, P. Moving enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems to the cloud: The challenge of infrastructural embeddedness. Int. J. Inf. Syst. Proj. Manag. 2020, 8, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappellari, M.; Belstner, J.; Rodriguez, B.; Sedayao, J. A Cloud-Based Data Collaborative to Combat the COVID-19 Pandemic and to Solve Major Technology Challenges. Future Internet 2021, 13, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budiman, K.; Subhan, S.; Efrilianda, D.A. Business Process re-engineering to support the sustainability of the construction industry and sales commodities in large scale transaction during Covid 19 with integrating ERP and Quotation System. Sci. J. Inform. 2021, 8, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirmanta, P.; Tarigan, Z.; Basana, S. The effect of ERP on firm performance through information quality and supply chain integration in Covid-19 era. Uncertain Supply Chain. Manag. 2021, 9, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinho, M.; Prakash, V.; Garg, L.; Savaglio, C.; Bawa, S. Effective Cloud Resource Utilisation in Cloud ERP Decision-Making Process for Industry 4.0 in the United States. Electronics 2021, 10, 959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weli, W. Re-examination and expanding the EUCS Model on Cloud-based ERP system. J. Inf. Organ. Sci. 2021, 45, 115–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuranga, A.; Maslin, M.; Maarop, N. Critical Implementation Factors for Cloud-Based Enterprise Resources planning in the Nigerian Maritime Transport and Supply Chain. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 1051, 012022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.C.; Chen, C.C.; Liu, J.L.; Chu, P.C. Framework and deployment of a cloud-based advanced planning and scheduling system. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2021, 70, 102088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.C.; Chen, C.-D. A Study of Factors Influencing the Adoption of Cloud-Based ERP System: The Perspective of Transaction Cost Economics. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Human-Computer Interaction, Washington, DC, USA, 24–29 July 2021; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Gøthesen, S.; Langseth, M.; Haddara, M. Challenges of Cloud-ERP Adoptions in SME. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2022, 196, 973–981. [Google Scholar]
- Christiansen, V.; Haddara, M.; Langseth, M. Factors affecting cloud ERP adoption decisions in organizations. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2022, 196, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.H.W.; Yu, W.; Wang, C. Comparison of SaaS and IaaS in cloud ERP implementation: The lessons from the practitioners. VINE J. Inf. Knowl. Manag. Syst. 2024, 54, 683–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deniswara, K.; Prabowo, H.; Mulyawan, A.N. Digital Business Transformation: Exploration of the Use of Erp Based Private Cloud to Improve Managing System in the Company (Case Study on One of Public Company in Indonesia). In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Industrial and Business Engineering, Macau, China, 27–29 September 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Seifert, M.; Kuehnel, S.; Sackmann, S. Hybrid clouds arising from software as a service adoption: Challenges, solutions, and future research directions. ACM Comput. Surv. 2023, 55, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tongsuksai, S.; Mathrani, S.; Weerasinghe, K. Influential characteristics and benefits of cloud ERP adoption in New Zealand SMEs: A vendors’ perspective. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 23956–23979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulsson, V.; Johansson, B. Cloud ERP systems architectural challenges on cloud adoption in large international organizations: A sociomaterial perspective. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2023, 219, 797–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, H.F.; Haddara, M.; Langseth, M. Investigating ERP system customization: A focus on cloud-ERP. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2023, 219, 915–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-S.; Oh, D.-S.; Kim, S.-H. Cloud-based ERP construction process framework in the customer’s perspective. Comput. Sci. Inf. Syst. 2023, 20, 25–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano Almansa, J.M.; Tarifa Fernández, J.; Sánchez Pérez, A.M. Digital Transformation and Real Options: Evaluating the Investment in Cloud ERP. Inz. Ekon. -Eng. Econ. 2023, 34, 397–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balalaie, A.; Heydarnoori, A.; Jamshidi, P. Microservices architecture enables devops: Migration to a cloud-native architecture. IEEE Softw. 2016, 33, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitner, P.; Cito, J.; Stöckli, E. Modelling and managing deployment costs of microservice-based cloud applications. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Utility and Cloud Computing, Shanghai, China, 6–9 December 2016. [Google Scholar]
- O’Connor, R.V.; Elger, P.; Clarke, P.M. Continuous software engineering—A microservices architecture perspective. J. Softw. Evol. Process 2017, 29, e1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higashino, M. Application of mobile agent technology to microservice architecture. In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Information Integration and Web-Based Applications & Services, Salzburg, Austria, 4–6 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Fritzsch, J.; Bogner, J.; Zimmermann, A.; Wagner, S. From monolith to microservices: A classification of refactoring approaches. In Software Engineering Aspects of Continuous Development and New Paradigms of Software Production and Deployment, Proceedings of the DEVOPS 2018, Chateau de Villebrumier, France, 5–6 March 2018; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 5–6 March 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Cerny, T.; Donahoo, M.J.; Trnka, M. Contextual understanding of microservice architecture: Current and future directions. ACM SIGAPP Appl. Comput. Rev. 2018, 17, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Zuo, D.; Zhang, Z. An extensible fault tolerance testing framework for microservice-based cloud applications. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Communication and Information Processing, Qingdao, China, 2–4 November 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Gelbke, L. Microservice architecture in industrial software delivery on edge devices. In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Agile Software Development: Companion, Porto, Portugal, 21–25 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kleehaus, M.; Matthes, F. Challenges in Documenting Microservice-Based IT Landscape: A Survey from an Enterprise Architecture Management Perspective. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 23rd International Enterprise Distributed Object Computing Conference (EDOC), Paris, France, 28–31 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- De Souza, R.M.M.; Vilasbôas, F.G.; Notargiacomo, P.; de Castro, L.N. Integrating an Association Rule Mining Agent in an ERP System: A Proposal and a Computational Scalability Analysis. ICAART 2019, 2, 778–786. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, I. Light and Shadow of Microservice Architecture. Korean J. Arch. Stud. 2019, 60, 283–315. [Google Scholar]
- El Kholy, M.; El Fatatry, A. Framework for interaction between databases and microservice architecture. IT Prof. 2019, 21, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jindal, A.; Podolskiy, V.; Gerndt, M. Performance modeling for cloud microservice applications. In Proceedings of the 2019 ACM/SPEC International Conference on Performance Engineering, Mumbai, India, 7–11 April 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Apel, S.; Hertrampf, F.; Späthe, S. Toward a knowledge model focusing on microservices and cloud computing. Concurr. Comput. Pract. Exp. 2020, 32, e5414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrantuono, R.; Russo, S.; Guerriero, A. Testing microservice architectures for operational reliability. Softw. Test. Verif. Reliab. 2020, 30, e1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinaku, F.; Bilgery, D.; Becker, S. The applicability of palladio for assessing the quality of cloud-based microservice architectures. In Proceedings of the 13th European Conference on Software Architecture, Paris, France, 9–13 September 2019; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, M.; Ali, S.; Jilani, A. Architecture for Microservice Based System. A Report. 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Nordli, E.T.; Nguyen, P.H.; Chauvel, F.; Song, H. Event-Based Customization of Multi-tenant SaaS Using Microservices. In Coordination Models and Languages: Proceedings of the COORDINATION 2020, Valletta, Malta, 15–19 June 2020; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Song, H.; Chauvel, F.; Nguyen, P.H. Using microservices to customize multi-tenant software-as-a-service. In Microservices; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 299–331. [Google Scholar]
- Prassanna, J.; Mohanty, S.; Jinturkar, P.S.; Pandey, P. Analysis of Kubernetes for Distributed Healthcare System Development using COVID-19 Healthcare App. Int. J. Cur. Res. Rev. 2021, 13, 96. [Google Scholar]
- Chapman, M.; Rasmussen, L.V.; Pacheco, J.A.; Curcin, V. Phenoflow: A microservice architecture for portable workflow-based phenotype definitions. AMIA Annu. Symp. Proc. 2021, 2021, 142–151. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, D.; Zhang, X.; Chen, L. Research of new integrated medical and health clouding system based on configurable microservice architecture. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 23rd International Conference on Computational Science and Engineering (CSE), Guangzhou, China, 29 December–1 January 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Bonazzi, R.; Cimmino, F.M.; Beuchat, J.-L.; Vérolet, F. Tracing effects of COVID-19 over small and medium enterprises. In Proceedings of the ENTRENOVA—ENTerprise REsearch InNOVAtion Conference, Virtual, 10–12 September 2020; Volume 6, pp. 309–321. [Google Scholar]
- Mateus-Coelho, N.; Cruz-Cunha, M.; Ferreira, L.G. Security in Microservices Architectures. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2021, 181, 1225–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Alwis AA, C.; Barros, A.; Fidge, C.; Polyvyanyy, A. Remodularization analysis for microservice discovery using syntactic and semantic clustering. In Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Advanced Information Systems Engineering, Grenoble, France, 8–12 June 2020; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- De Alwis AA, C.; Barros, A.; Fidge, C.; Polyvyanyy, A. Microservice remodularisation of monolithic enterprise systems for embedding in industrial IoT networks. In Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Advanced Information Systems Engineering, Melbourne, Australia, 28 June–2 July 2021; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Calderón-Gómez, H.; Mendoza-Pittí, L.; Vargas-Lombardo, M.; Gómez-Pulido, J.M.; Rodríguez-Puyol, D.; Sención, G.; Polo-Luque, M.L. Evaluating Service-Oriented and Microservice Architecture Patterns to Deploy eHealth Applications in Cloud Computing Environment. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannousse, A.; Yahiouche, S. Securing microservices and microservice architectures: A systematic mapping study. Comput. Sci. Rev. 2021, 41, 100415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Liang, G.; Gao, Y.; Gao, W.; Zhang, W. Research on load balancing technology for microservice architecture. MATEC Web Conf. 2021, 336, 08002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Lee, M.Y.; Chen, X.; Tseng, H.W.; Yang, C.F.; Lee, S.F. Using Microservice Architecture as a Load Prediction Strategy for Management System of University Public Service. Sens. Mater. 2021, 33, 805–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Garg, S.K.; Buyya, R. SLA-based resource allocation for software as a service provider (SaaS) in cloud computing environments. In Proceedings of the 2011 11th IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Cluster, Cloud and Grid Computing, Newport Beach, CA, USA, 23–26 May 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Razzaq, A.; Ghayyur, S.A.K. A systematic mapping study: The new age of software architecture from monolithic to microservice architecture—Awareness and challenges. Comput. Appl. Eng. Educ. 2023, 31, 421–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Jiang, Y.X.; Wang, Z.; Huo, Q.E.; Dai, J.; Xie, S.L.; Li, R.; Feng, M.T.; Xu, Y.S.; Jiang, Z.P. The operation and maintenance governance of microservices architecture systems: A systematic literature review. J. Softw. Evol. Process 2023, 35, e2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaki, J.; Islam, S.R.; Alghamdi, N.S.; Abdullah-Al-Wadud, M.; Kwak, K.S. Introducing cloud-assisted micro-service-based software development framework for healthcare systems. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 33332–33348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, M.G.; De França, B.B.N. Analysis of Microservice Evolution using Cohesion Metrics. In Proceedings of the 16th Brazilian Symposium on Software Components, Architectures, and Reuse, Uberlandia, Brazil, 3–4 October 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Tokmak, A.V.; Akbulut, A.; Catal, C. Boosting the visibility of services in microservice architecture. Clust. Comput. 2023, 27, 3099–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Hu, P.; Kong, X.; Ouyang, W.; Li, B.; Xu, H.; Shao, T. Microservice architecture recovery based on intra-service and inter-service features. J. Syst. Softw. 2023, 204, 111754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roda-Sanchez, L.; Garrido-Hidalgo, C.; Royo, F.; Maté-Gómez, J.L.; Olivares, T.; Fernández-Caballero, A. Cloud–edge microservices architecture and service orchestration: An integral solution for a real-world deployment experience. Internet Things 2023, 22, 100777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.H.; Osman, M.H.; Novia, I.A.; Muhammad, M.S. From Monolith to Microservice: Measuring Architecture Maintainability. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2023, 14, 857–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Joe-Wong, C.; Brinton, C.G.; Tan, C.W.; Ha, S.; Chiang, M. On the viability of a cloud virtual service provider. ACM Sigmetrics Perform. Eval. Rev. 2016, 44, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louissaint, S. Managed Service Providers: Not Just Another TLA (Three-Letter Acronym). GPSolo 2017, 34, 36. [Google Scholar]
- Anicho, O.; Abdullah, T. Impact of Cloud-based Infrastructure on Telecom Managed Services Models. Data Sci. J. Comput. Appl. Inform. 2020, 4, 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.; Khan, D.A. Cloud-CoCoSo: Cloud model-based combined compromised solution model for trusted cloud service provider selection. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2022, 47, 10307–10332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).