An Objective Effect Evaluation Framework for Vectorization Models on Patent Semantic Similarity Measurement
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Works
2.1. Vectorization Approaches of Patent Text
2.2. Approaches to Comparative Evaluation of Patent Semantic Similarity
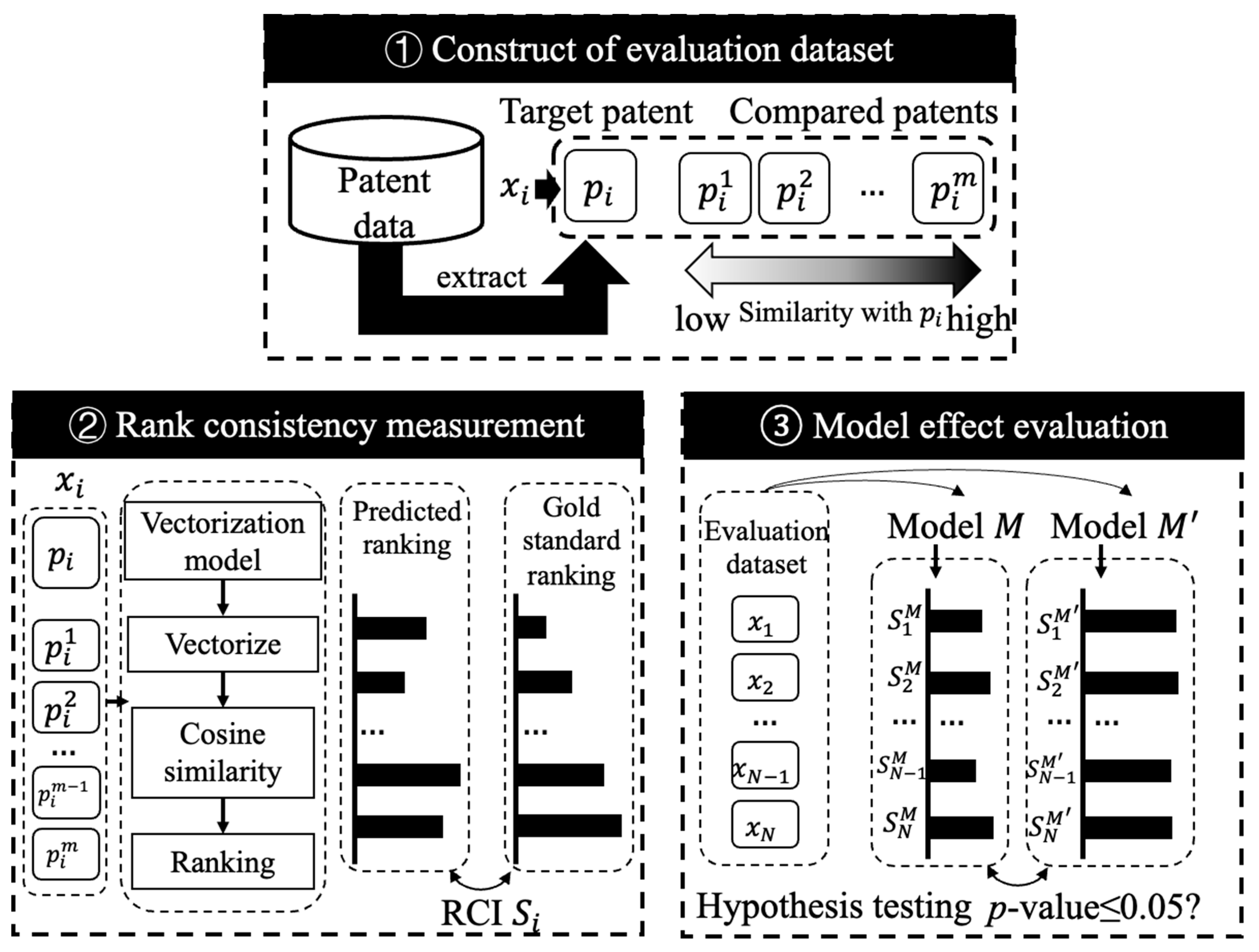
3. Framework
4. Empirical Study
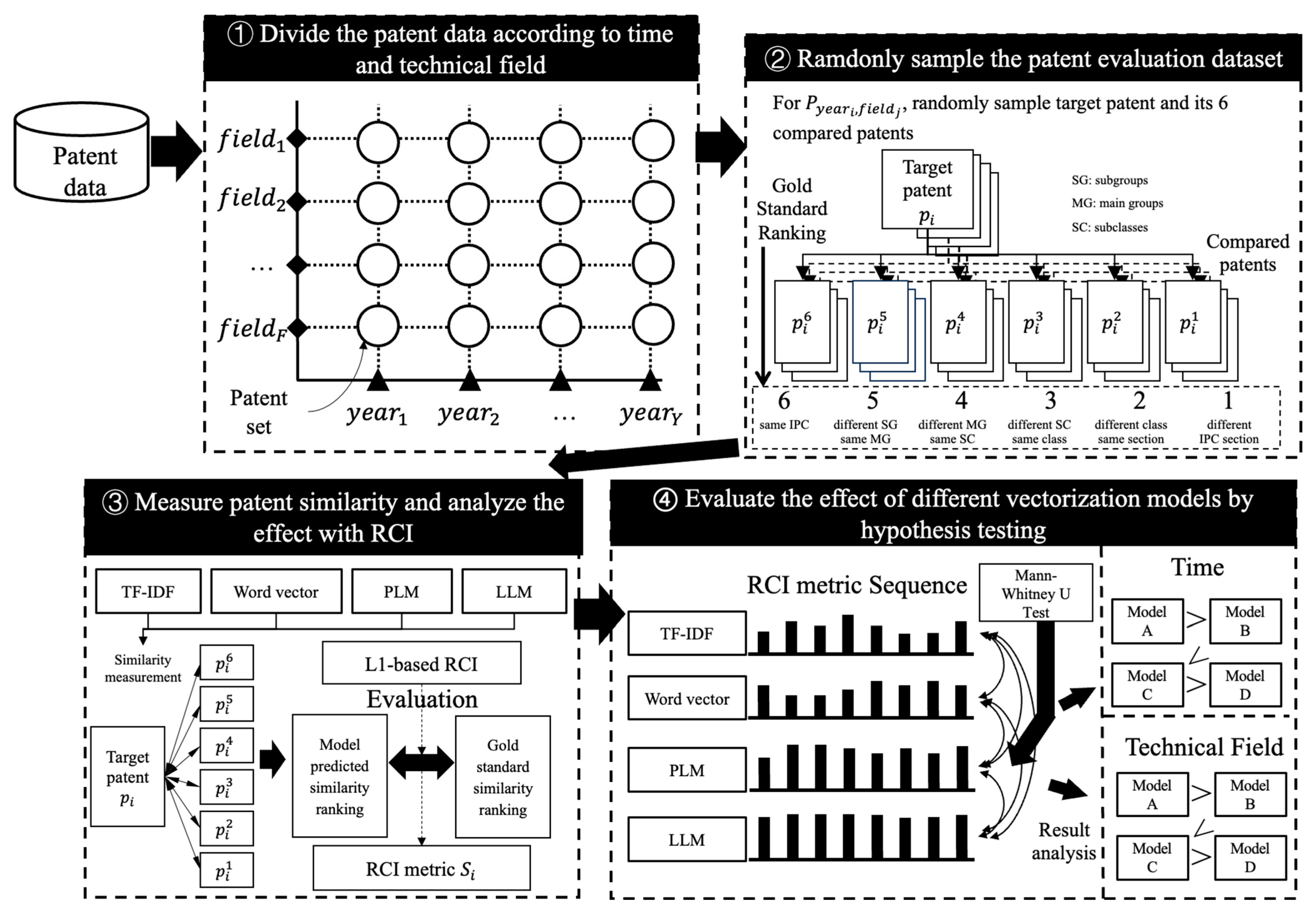
4.1. Automatic Construction of Evaluation Dataset
4.2. Settings of Empirical Study
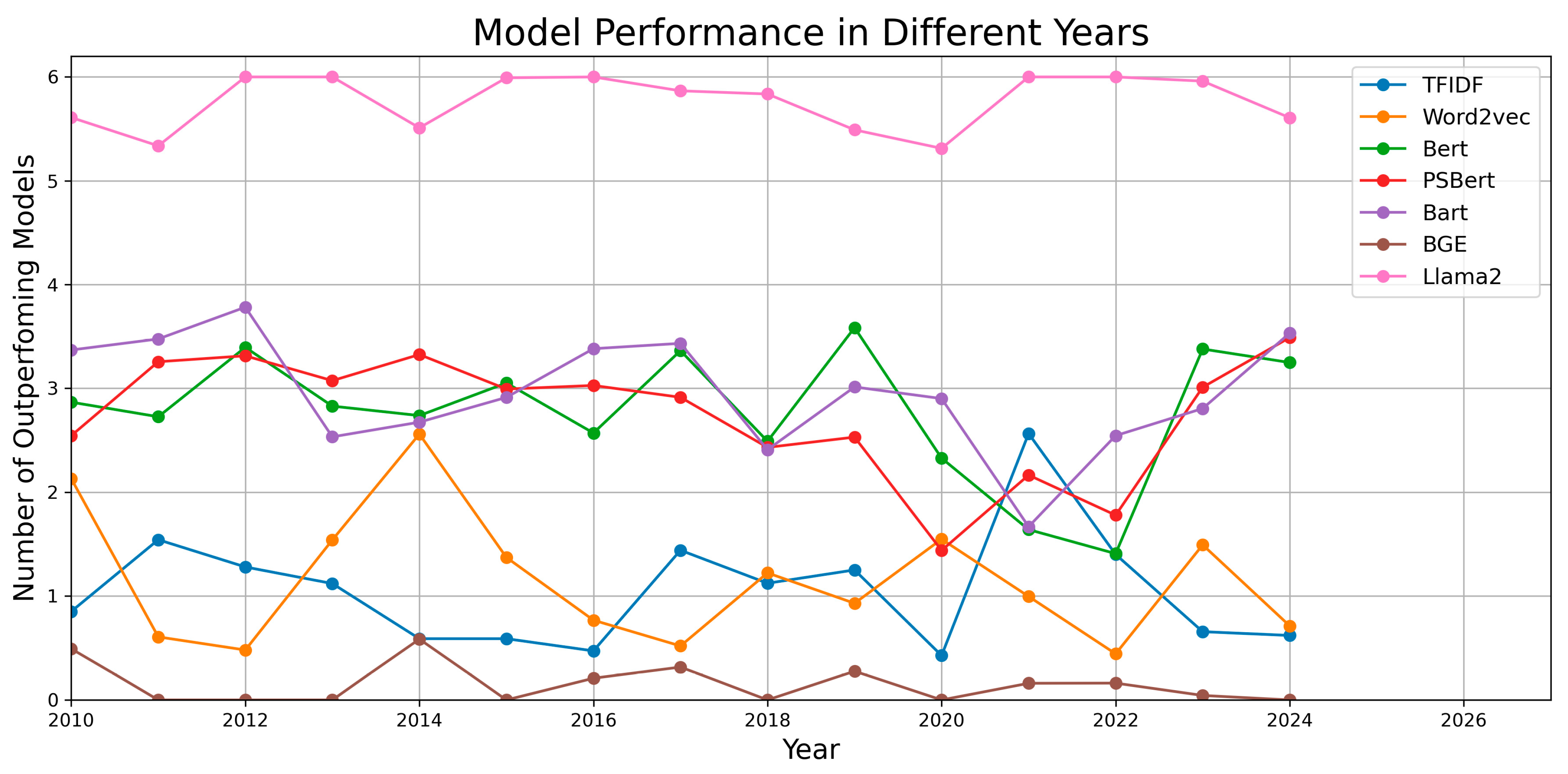
4.3. Results in Different Years
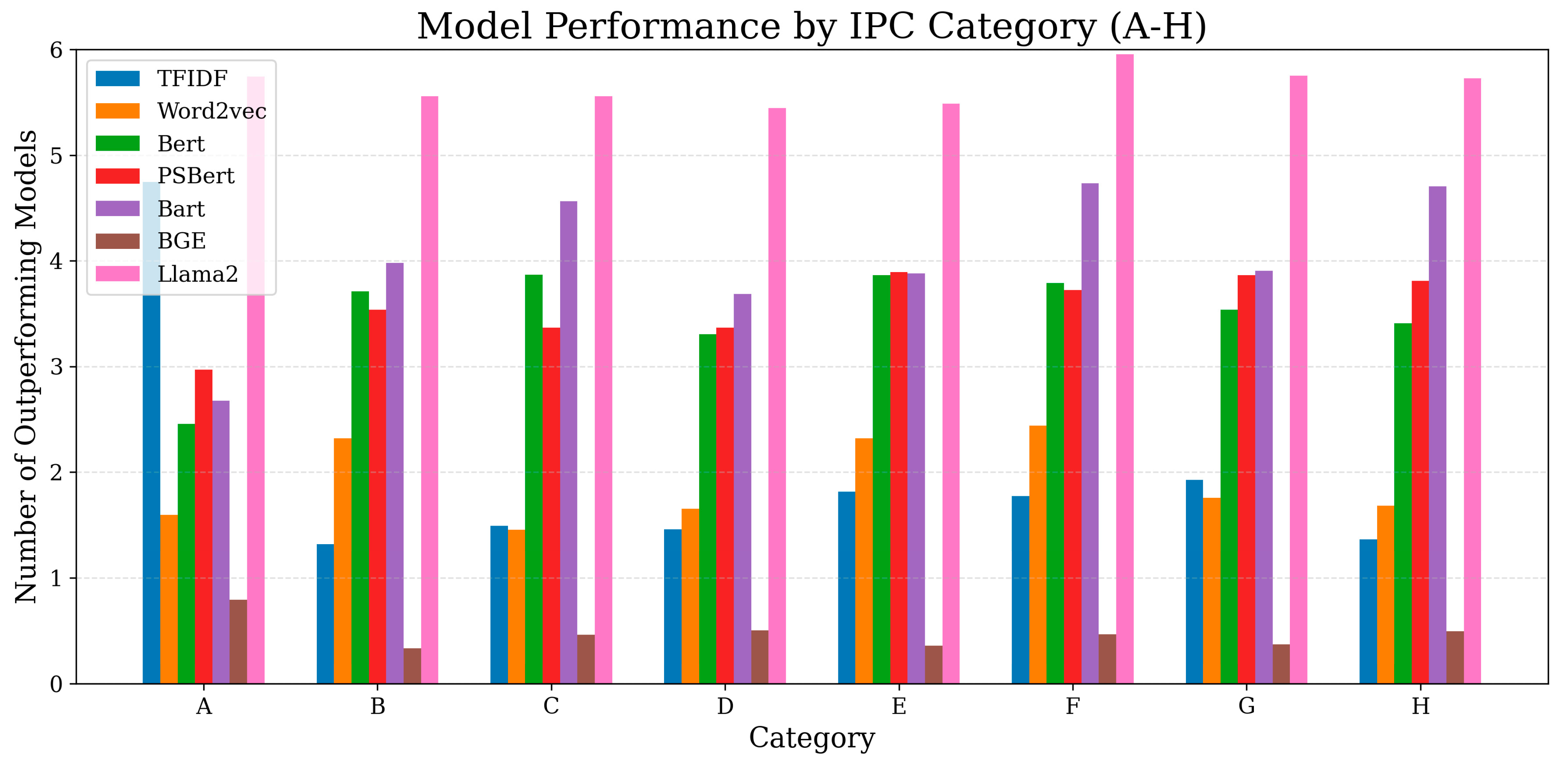
4.4. Results in Different Technical Fields
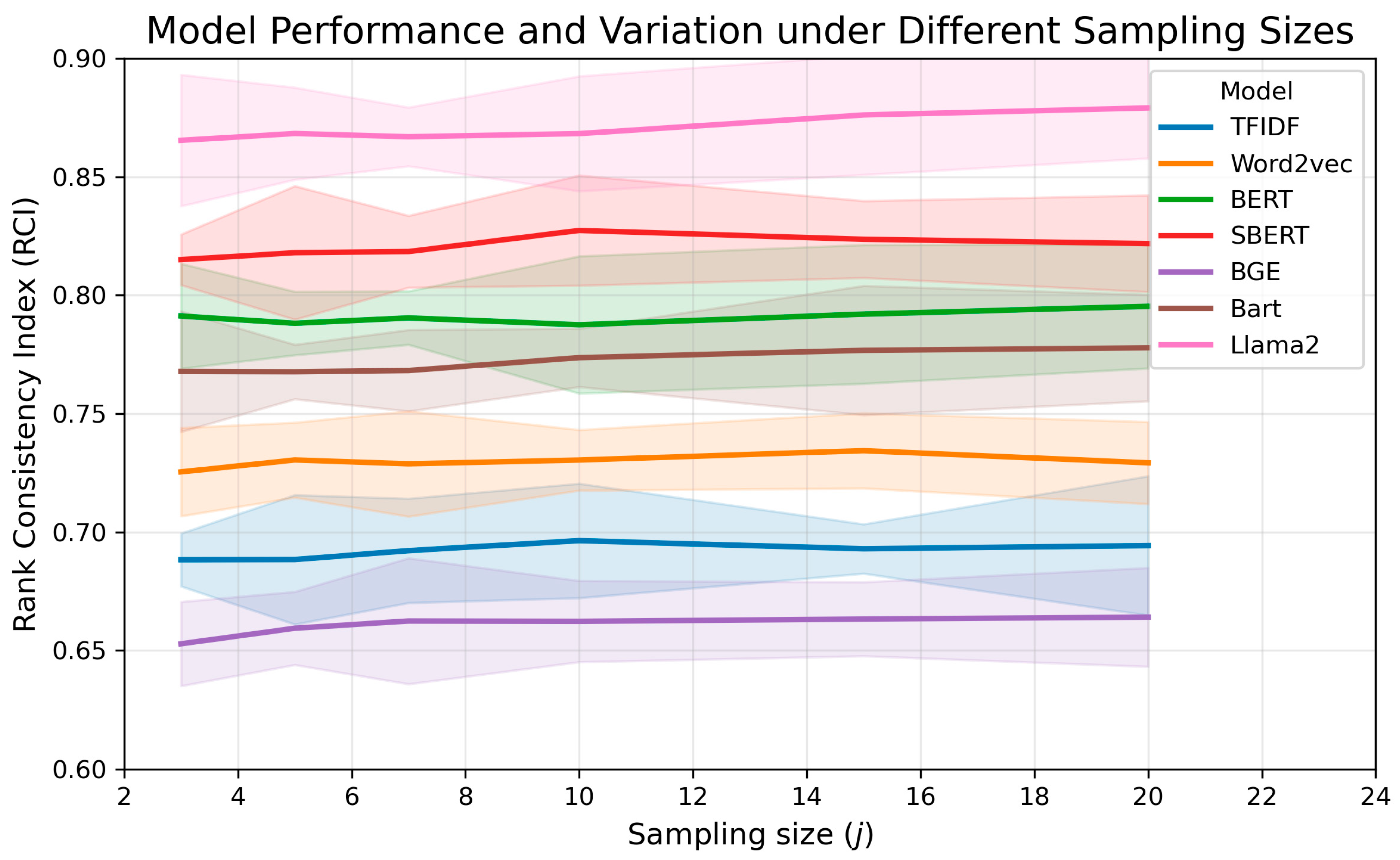
4.5. Robustness Analysis
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LLM | Large Language Model |
| RCI | Rank Consistency Index |
| TFIDF | Term Frequency Inverse Document Frequency |
| PLM | Pre-Trained Language Model |
| VSM | Vector Space Model |
| IPC | International Patent Classification |
References
- Arts, S.; Cassiman, B.; Gomez, J.C. Text matching to measure patent similarity. Strateg. Manag. J. 2018, 39, 62–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Zhuge, H. Automatic construction of classification dimensions by clustering texts based on common words. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 238, 122292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Block, C.; Wustmans, M.; Laibach, N.; Bröring, S. Semantic bridging of patents and scientific publications–The case of an emerging sustainability-oriented technology. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2021, 167, 120689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trappey, A.; Trappey, C.V.; Hsieh, A. An intelligent patent recommender adopting machine learning approach for natural language processing: A case study for smart machinery technology mining. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2021, 164, 120511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Li, S.; Cao, Y.; Wang, Y. Multi-task learning based high-value patent and standard-essential patent identification model. Inf. Process. Manag. 2023, 60, 103327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Meng, X.; Wu, Y.; Chan, C.S.; Pang, T. Semantic matching efficiency of supply and demand texts on online technology trading platforms: Taking the electronic information of three platforms as an example. Inf. Process. Manag. 2020, 57, 102258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahmirzadi, O.; Lugowski, A.; Younge, K. Text similarity in vector space models: A comparative study. In Proceedings of the 2019 18th IEEE International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications (ICMLA), Boca Raton, FL, USA, 16–19 December 2019; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 659–666. [Google Scholar]
- Petukhova, A.; Matos-Carvalho, J.P.; Fachada, N. Text clustering with LLM embeddings. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.15112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Y.; He, G.; Jiang, J.; Jiang, J.; Zhao, W.X.; Wen, J.-R. Complex knowledge base question answering: A survey. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2022, 35, 11196–11215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Mudhiganti, S.K.R.; Sharma, M. Patentformer: A novel method to automate the generation of patent applications. In Proceedings of the 2024 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing: Industry Track, Miami, FL, USA, 12–16 November 2024; pp. 1361–1380. [Google Scholar]
- Mikolov, T.; Sutskever, I.; Chen, K.; Corrado, G.; Dean, J. Distributed representations of words and phrases and their compositionality. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1310.4546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Lei, C.; Jinde, J.; Naixuan, Z. Measuring Patent Similarity with Word Embedding and Statistical Features. Data Anal. Knowl. Discov. 2019, 3, 53–59. [Google Scholar]
- Jeon, D.; Ahn, J.M.; Kim, J.; Lee, C. A doc2vec and local outlier factor approach to measuring the novelty of patents. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2022, 174, 121294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.-W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 3–5 June 2019; Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2019; pp. 4171–4186. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Ji, N.; Ding, Q.; Zhang, F.; Long, Y.; Ye, X.; Chen, Y. Enhancing patent text classification with Bi-LSTM technique and alpine skiing optimization for improved diagnostic accuracy. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2025, 84, 9257–9286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghighian Roudsari, A.; Afshar, J.; Lee, W.; Lee, S. PatentNet: Multi-label classification of patent documents using deep learning based language understanding. Scientometrics 2022, 127, 207–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekamiri, H.; Hain, D.S.; Jurowetzki, R. Patentsberta: A deep nlp based hybrid model for patent distance and classification using augmented sbert. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2024, 206, 123536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosonocky, C.W.; Wilke, C.O.; Marcotte, E.M.; Ellington, A.D. Mining patents with large language models elucidates the chemical function landscape. Digit. Discov. 2024, 3, 1150–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeom, J.; Lee, H.; Byun, H.; Kim, Y.; Byun, J.; Choi, Y.; Kim, S.; Song, K. Tc-llama 2: Fine-tuning LLM for technology and commercialization applications. J. Big Data 2024, 11, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keraghel, I.; Morbieu, S.; Nadif, M. Beyond words: A comparative analysis of LLM embeddings for effective clustering. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Intelligent Data Analysis, Stockholm, Sweden, 24–26 April 2024; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 205–216. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L.; Scherz, P.A.; Goetz, S. Towards Better Evaluation for Generated Patent Claims. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2505.11095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Q.; Xu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Wang, M.; Chen, Z.; Sun, Y.; Gu, Y.; Li, X.; Yu, G. Enhancing the Patent Matching Capability of Large Language Models via the Memory Graph. In Proceedings of the 48th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, Padua, Italy, 13–18 July 2025; pp. 337–347. [Google Scholar]
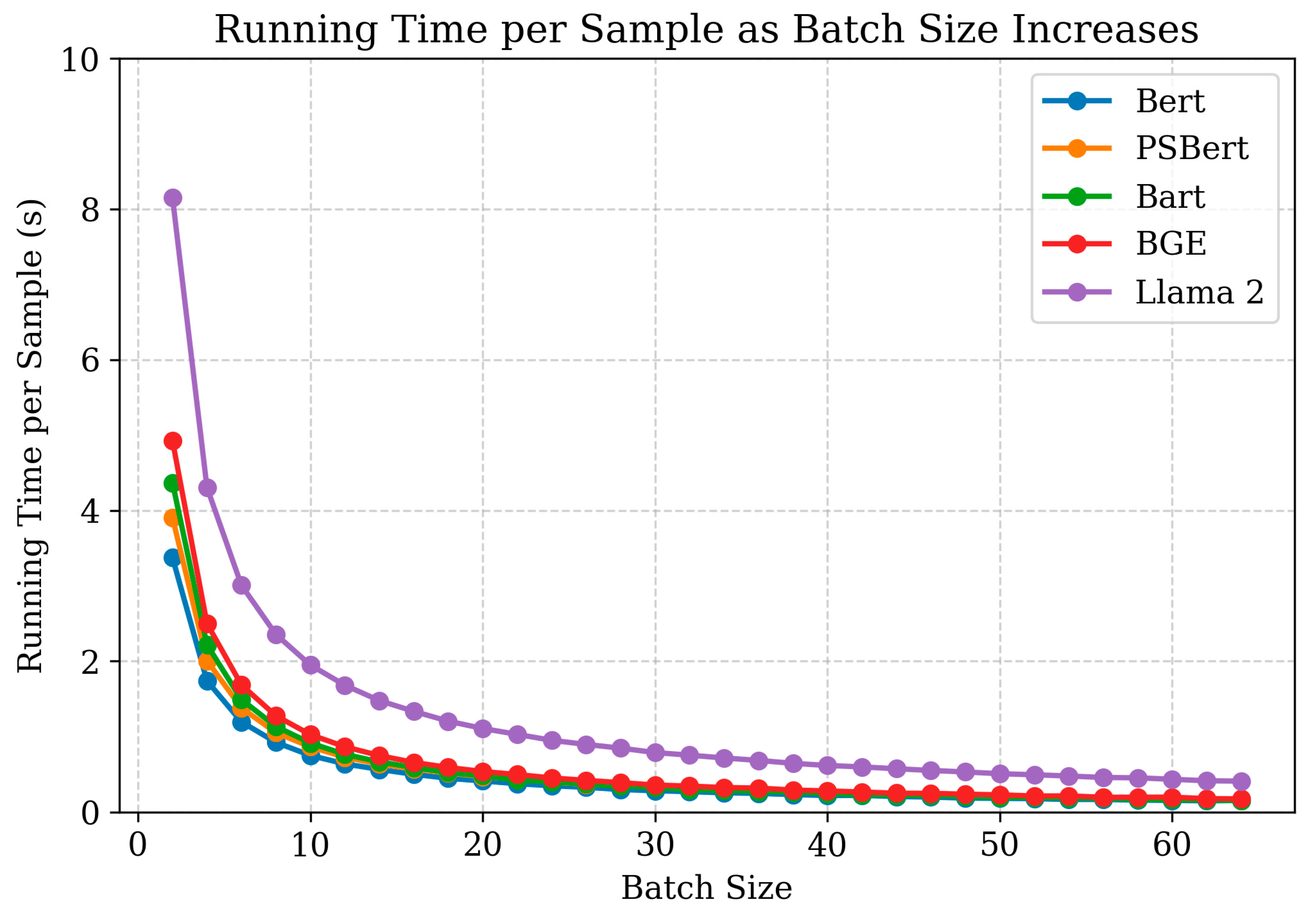
| Model | Dimension | Hardware | Batch Size | Running Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TFIDF | 20,000 | CPU | 1 | 0.14 s |
| Word2vec | 300 | CPU | 1 | 1.36 s |
| Bert | 768 | CPU | 1 | 32.5 s |
| PSBert | 768 | CPU | 1 | 29.3 s |
| BGE | 768 | CPU | 1 | 34.2 s |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Zhou, J.; Cao, M. An Objective Effect Evaluation Framework for Vectorization Models on Patent Semantic Similarity Measurement. Electronics 2025, 14, 4056. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14204056
Li J, Zhou J, Cao M. An Objective Effect Evaluation Framework for Vectorization Models on Patent Semantic Similarity Measurement. Electronics. 2025; 14(20):4056. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14204056
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jiazheng, Jian Zhou, and Mengyun Cao. 2025. "An Objective Effect Evaluation Framework for Vectorization Models on Patent Semantic Similarity Measurement" Electronics 14, no. 20: 4056. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14204056
APA StyleLi, J., Zhou, J., & Cao, M. (2025). An Objective Effect Evaluation Framework for Vectorization Models on Patent Semantic Similarity Measurement. Electronics, 14(20), 4056. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14204056





