Iterative Maximum Ratio Combining Detector for Satellite Multiple-Input Multiple-Output/Orthogonal Time–Frequency Space Systems Based on Soft-Symbol Interference Cancelation
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A satellite–terrestrial downlink MIMO-OTFS system is constructed for NTN-TDL-A, NTN-TDL-B, NTN-TDL-C, NTN-TDL-D channel models under the 3GPP TR 38.811 standard, antenna arrays of different sizes, and different modulation orders.
- An iterative maximum ratio combining detection algorithm based on hard-decision interference cancelation (ICH-IMRC) is proposed, which performs signal detection in the delay–Doppler (DD) domain. In each iteration, interference cancelation is performed on the symbols followed by MRC detection, and the estimated signal is output by the hard judgment. Relaxation parameters are introduced for the hard judgment of the symbols to improve the convergence speed.
- An iterative maximum ratio combining detection algorithm based on soft-symbol interference cancelation (S-IMRC) is proposed. The detection symbols are updated by performing IMRC detection on received symbols that are already interference-canceled, where interference cancelation is performed using the expectations of the other symbols. Next, the estimated signal is soft-judged based on maximum-likelihood estimation. Due to the influence of the relaxation parameters on the BER of the system, the optimal relaxation parameters are obtained with the Sparrow Search Algorithm (SSA) to further improve system reliability.
2. MIMO-OTFS System Model and Transmit–Receive Structure
2.1. MIMO-OTFS System Model
2.2. MIMO-OTFS Transmitter
2.3. MIMO-OTFS Receiver
3. Iterative Maximum Ratio Merger Detection Based on Symbol Interference Cancelation
3.1. IMRC Detector Based on Hard-Decision Interference Cancelation
3.2. IMRC Detector Based on Soft-Symbol Interference Cancelation
| Algorithm 1 S-IMRC detector |
|
3.3. SSA-Based Optimal Relaxation Parameters
4. Results and Performance Analyses
4.1. Simulation Parameters
4.2. Complexity Analysis
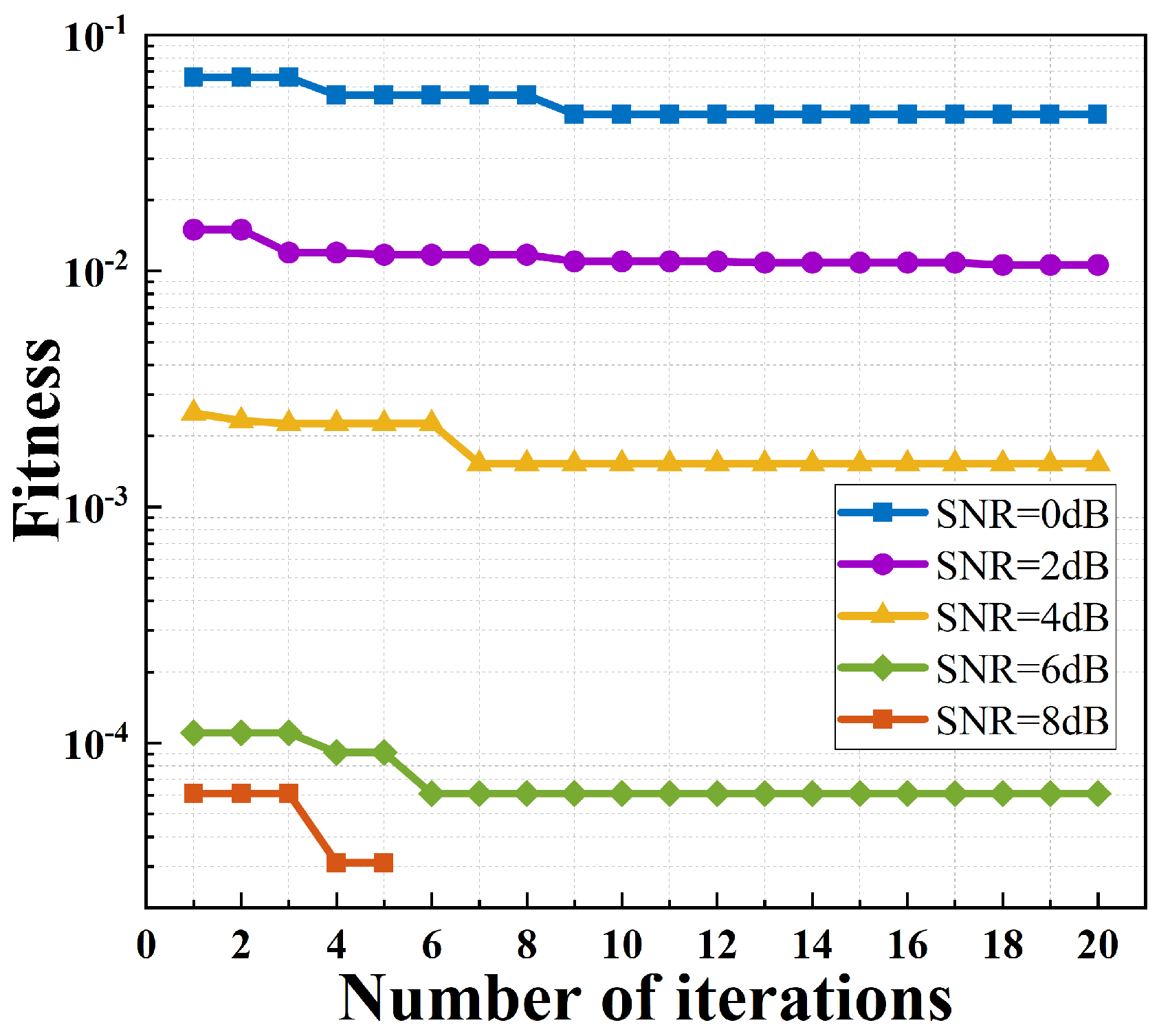
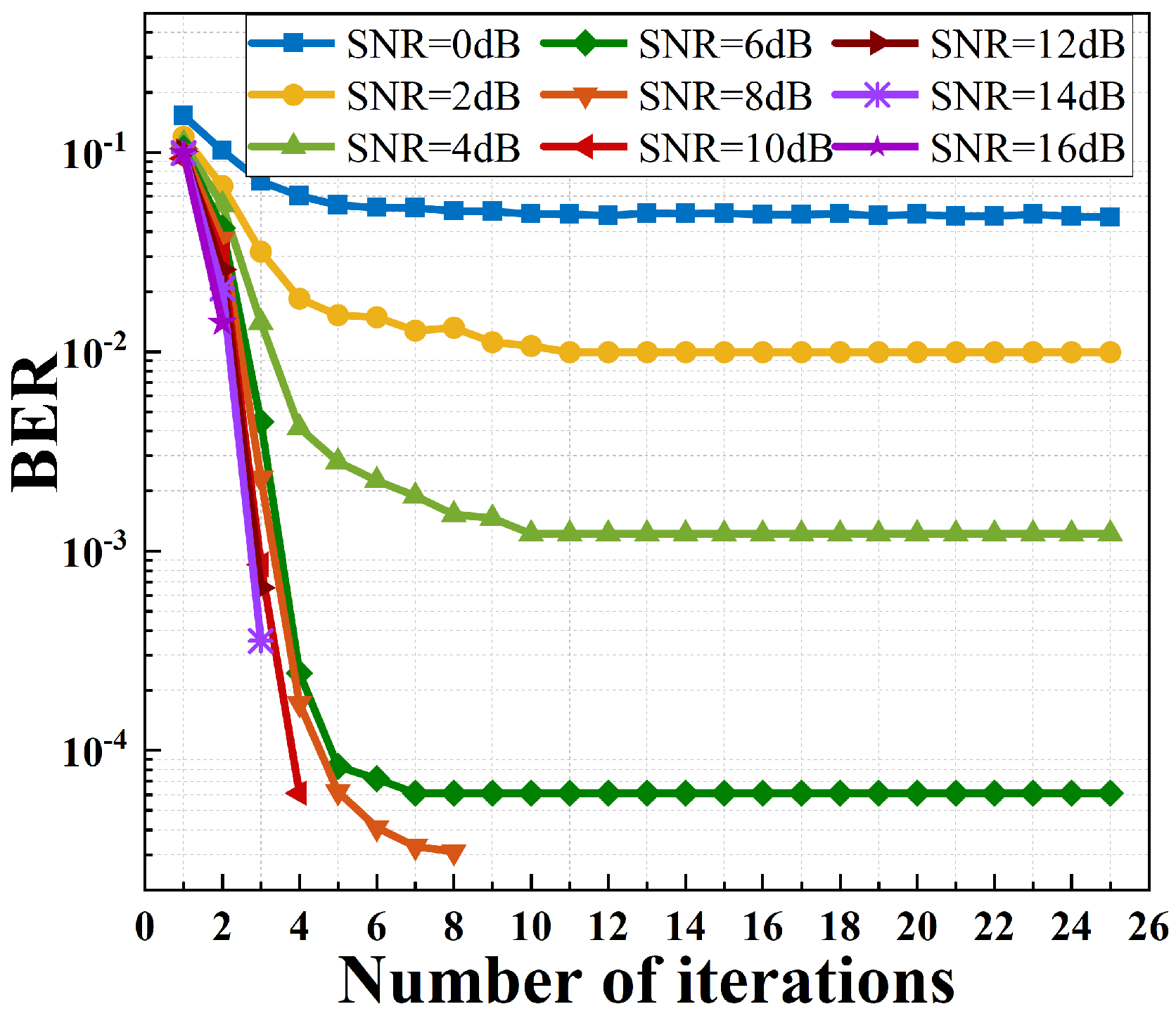
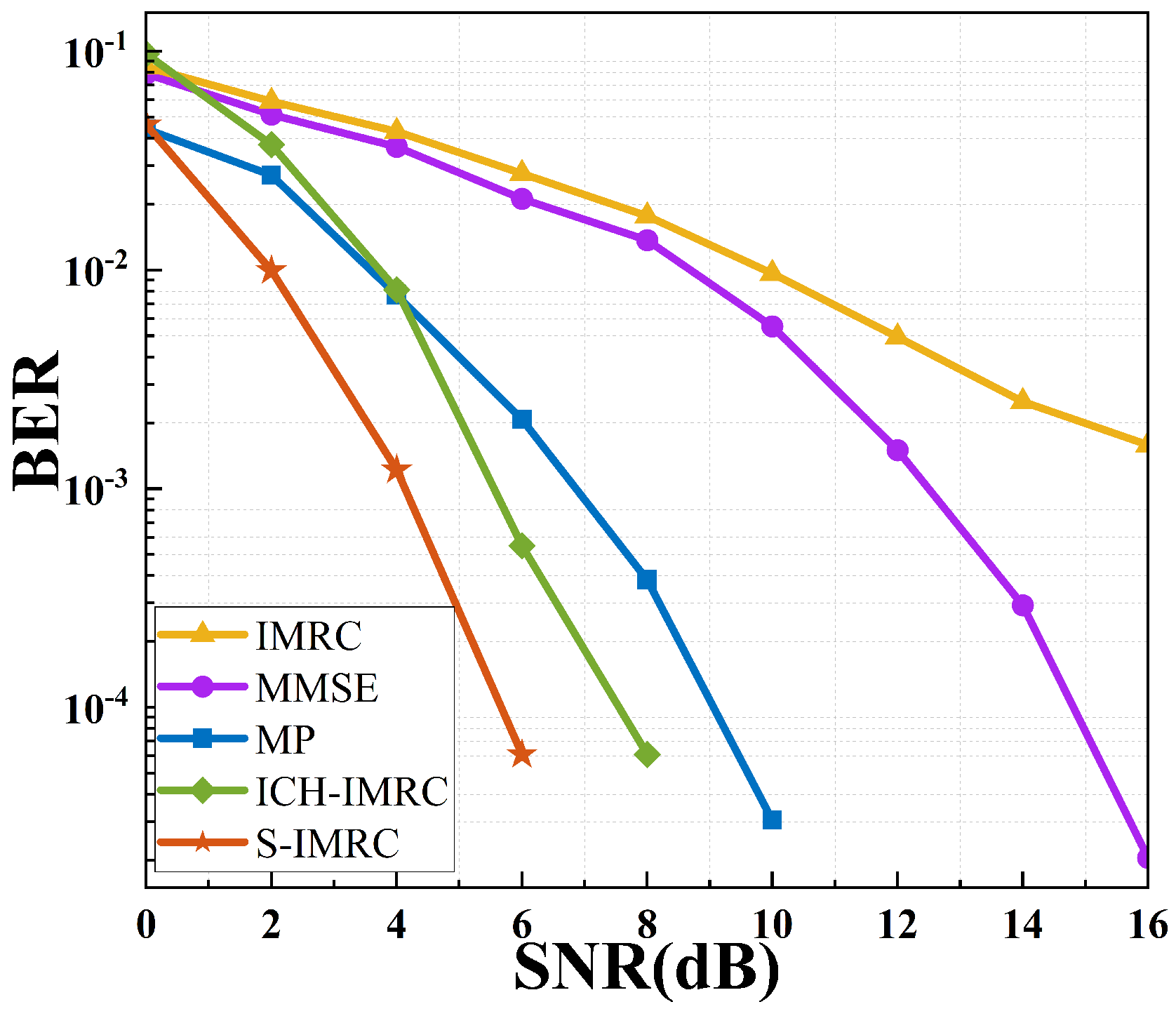
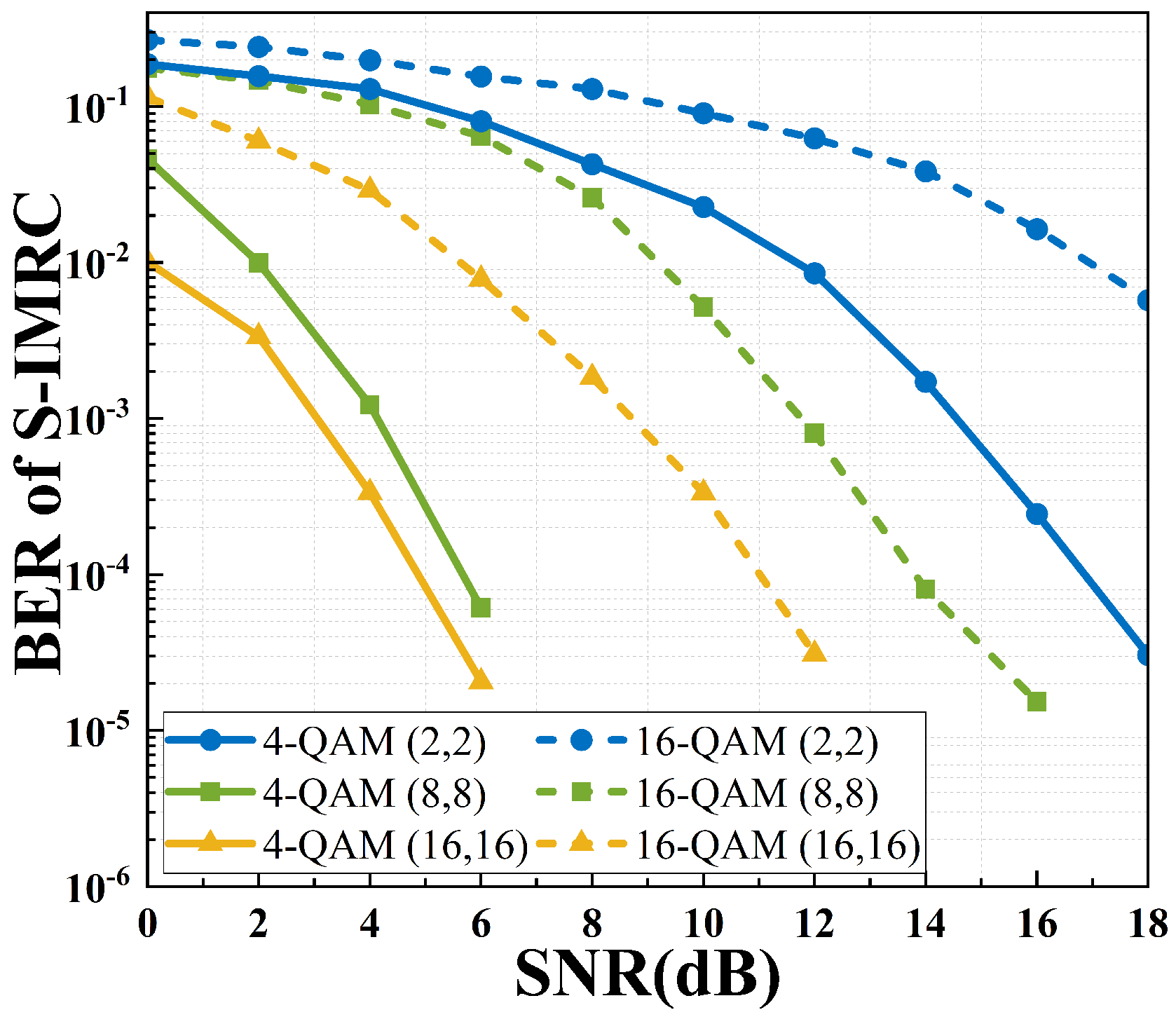
4.3. Simulation Results and Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, M.; Zhang, Q.; Yao, H.; Gao, R.; Zhao, Y.; Guizani, M. Resource Allocation and Deep Learning-Based Joint Detection Scheme in Satellite NOMA Systems. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2024, 24, 526–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-X.; Huang, J.; Wang, H.; Gao, X.; You, X.; Hao, Y. 6G Wireless Channel Measurements and Models: Trends and Challenges. IEEE Veh. Technol. Mag. 2020, 15, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yao, H.; Gao, R.; Xin, X.; Feng, T.; Tian, Q.; Feng, W.; Chen, D. Swarm-Intelligence-Based Routing and Wavelength Assignment in Optical Satellite Networks. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2024, 11, 1303–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, F.; Zhang, Q.; Yao, H.; Xin, X.; Gao, R.; Guizani, M. Joint Multi-Task Offloading and Resource Allocation for Mobile Edge Computing Systems in Satellite IoT. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2023, 72, 7783–7795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Mukherjee, M.; Zhou, J.; Lloret, J. Channel Modeling and Characteristics for 6G Wireless Communications. IEEE Netw. 2021, 35, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, S.; Qi, Z.; Haipeng, Y.; Ran, G.; Xiangjun, X.; Feng, T.; Weiying, F.; Dong, C. Iterative signal detection based soft interference cancelation for satellite–terrestrial downlink NOMA systems. China Commun. 2024, 21, 249–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, F.; Zhang, Q.; Yao, H.; Xin, X.; Wang, F.; Xu, M.; Xiong, Z.; Niyato, D. Multi-Agent DDPG Based Resource Allocation in NOMA-Enabled Satellite IoT. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2024, 72, 6287–6300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadani, R.; Rakib, S.; Tsatsanis, M.; Monk, A.; Goldsmith, A.J.; Molisch, A.F.; Calderbank, R. Orthogonal Time Frequency Space Modulation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 19–22 March 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Hu, J.; Yue, Y.; Xue, X.; Liang, W.; Li, Z. Outage Probability for OTFS Based Downlink LEO Satellite Communication. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2022, 71, 3355–3360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzzi, S.; Caire, G.; Colavolpe, G.; D’Andrea, C.; Foggi, T.; Piemontese, A.; Ugolini, A. LEO Satellite Diversity in 6G Non-Terrestrial Networks: OFDM vs. OTFS. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2023, 27, 3013–3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Shen, W.; Xing, C.; An, J.; Hanzo, L. Joint Bayesian Channel Estimation and Data Detection for OTFS Systems in LEO Satellite Communications. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2022, 70, 4386–4399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Li, Z.; Hu, J.; Tie, Z.; Li, S.; Liang, W.; Ding, Z. OTFS Enabled LEO Satellite Communications: A Promising Solution to Severe Doppler Effects. IEEE Netw. 2024, 38, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaj, T.; Viterbo, E. Low Complexity Iterative Rake Detector for Orthogonal Time Frequency Space Modulation. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 25–28 May 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, G.; Yu, J.; Li, G.; Li, Y. OTFS-Based Communication and Navigation Integrated Signal Transmission for LEO Satellites. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 22nd International Conference on Communication Technology (ICCT), Nanjing, China, 11–14 November 2022; pp. 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; He, R.; Ai, B.; Yang, M.; Zhong, Z.; Zhang, H. OTFS modulation performance in a satellite-to-ground channel at sub-6-GHz and millimeter-wave bands with high mobility. Front. Inf. Technol. Electron. Eng. 2021, 22, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busari, S.A.; Huq, M.S.K.; Mumtaz, S.; Dai, L.; Rodriguez, J. Millimeter-Wave Massive MIMO Communication for Future Wireless Systems: A Survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2018, 20, 836–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younas, T.; Li, J.; Arshad, J. On Bandwidth Efficiency Analysis for LS-MIMO with Hardware Impairments. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 5994–6001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, H.; Liu, G.; Imran, M.A.; Wen, S.; Zhang, L. Efficient Channel Equalization and Symbol Detection for MIMO OTFS Systems. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2022, 21, 6672–6686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Dai, L.; An, J.; Fan, P.; Heath, R.W. Channel Estimation for Orthogonal Time Frequency Space (OTFS) Massive MIMO. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2019, 67, 4204–4217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.; Wu, Y.; An, J.; Xing, C.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, W. Random Access with Massive MIMO-OTFS in LEO Satellite Communications. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2022, 40, 2865–2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bora, A.S.; Phan, K.T.; Hong, Y. Spatially Correlated MIMO-OTFS for LEO Satellite Communication Systems. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops (ICC Workshops), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 16–20 May 2022; pp. 723–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yao, H.; Xin, X.; Zhao, Y.; Gao, R. Optimizing Cost-Efficient SFC Routing in NTNs: A Novel Transformer-Ant Colony Optimization Framework. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Xin, X.; Zhang, Q.; Yao, H.; Gao, R.; Li, Z.; Wang, F. Advanced decision scheme to mitigate phase impairments in coherent optical transmission systems. Opt. Express 2024, 32, 44854–44871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Ma, S.; Yang, X. Tensor-based low-complexity channel estimation for mmWave massive MIMO-OTFS systems. J. Commun. Inf. Netw. 2020, 5, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Zheng, J.; Bai, B.; Jiang, J.; Chu, H. Generalized Index Modulation for MIMO-OTFS Transmission. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2023, 12, 907–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaj, T.; Viterbo, E. Low-Complexity Linear Diversity-Combining Detector for MIMO-OTFS. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2022, 11, 288–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Wang, W.; You, L.; Song, X.; Hong, Y.; Gao, X.; Fettweis, G. Deterministic Pilot Design and Channel Estimation for Downlink Massive MIMO-OTFS Systems in Presence of the Fractional Doppler. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2021, 20, 7151–7165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Shan, C.; Zhao, H.; Yuan, W.; Zhang, R. A Modified Structured SAMP Channel Estimation Method for FDD MIMO-OTFS Systems. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2024, 13, 3005–3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raviteja, P.; Hong, Y.; Viterbo, E.; Biglieri, E. Practical Pulse-Shaping Waveforms for Reduced-Cyclic-Prefix OTFS. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 68, 957–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Study on New Radio (NR) to Support Non-Terrestrial Networks (Release 15); 3GPP Rep. TR 38.811 V15.2.0; 3GPP: Sophia Antipolis, France, 2020.
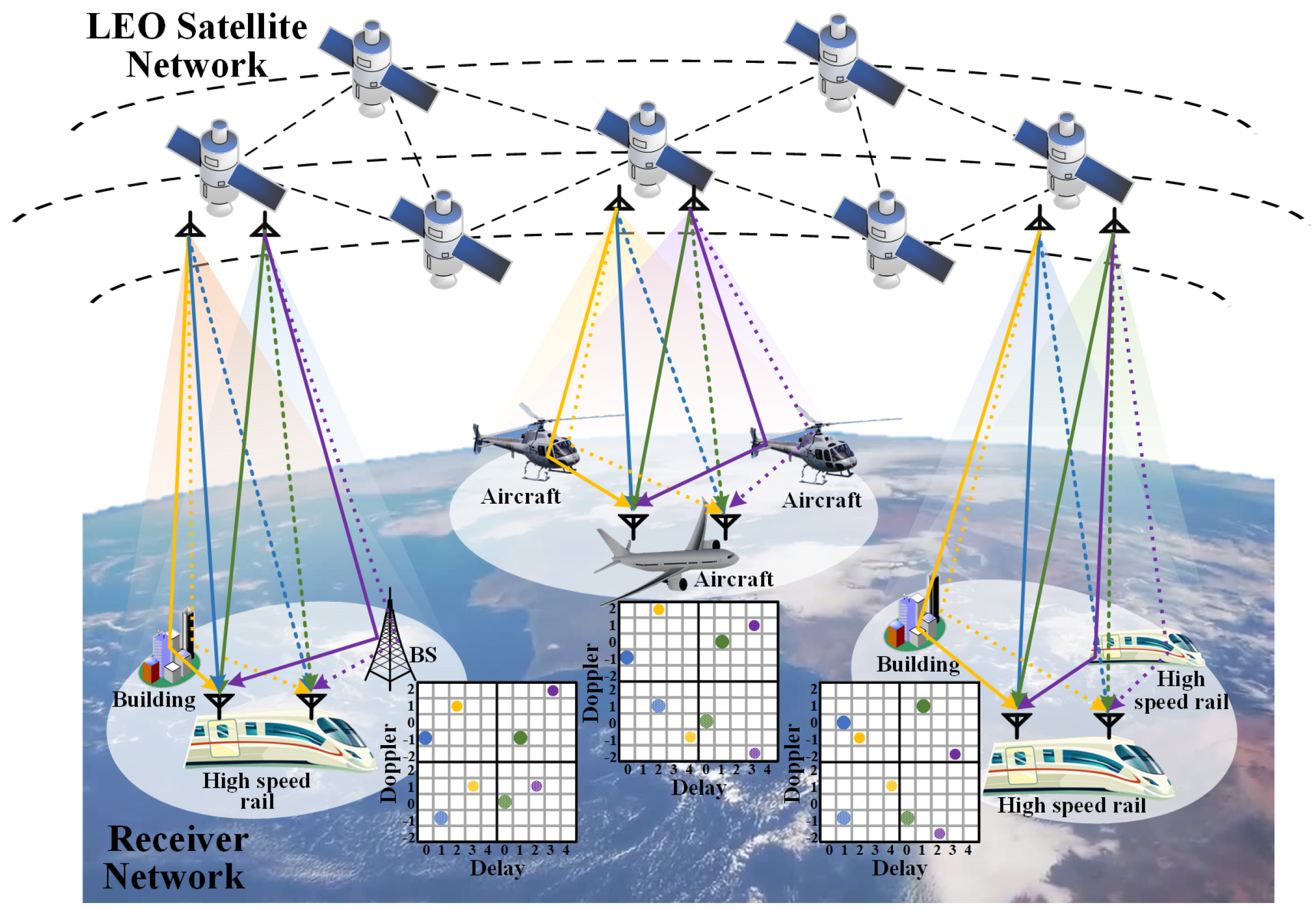

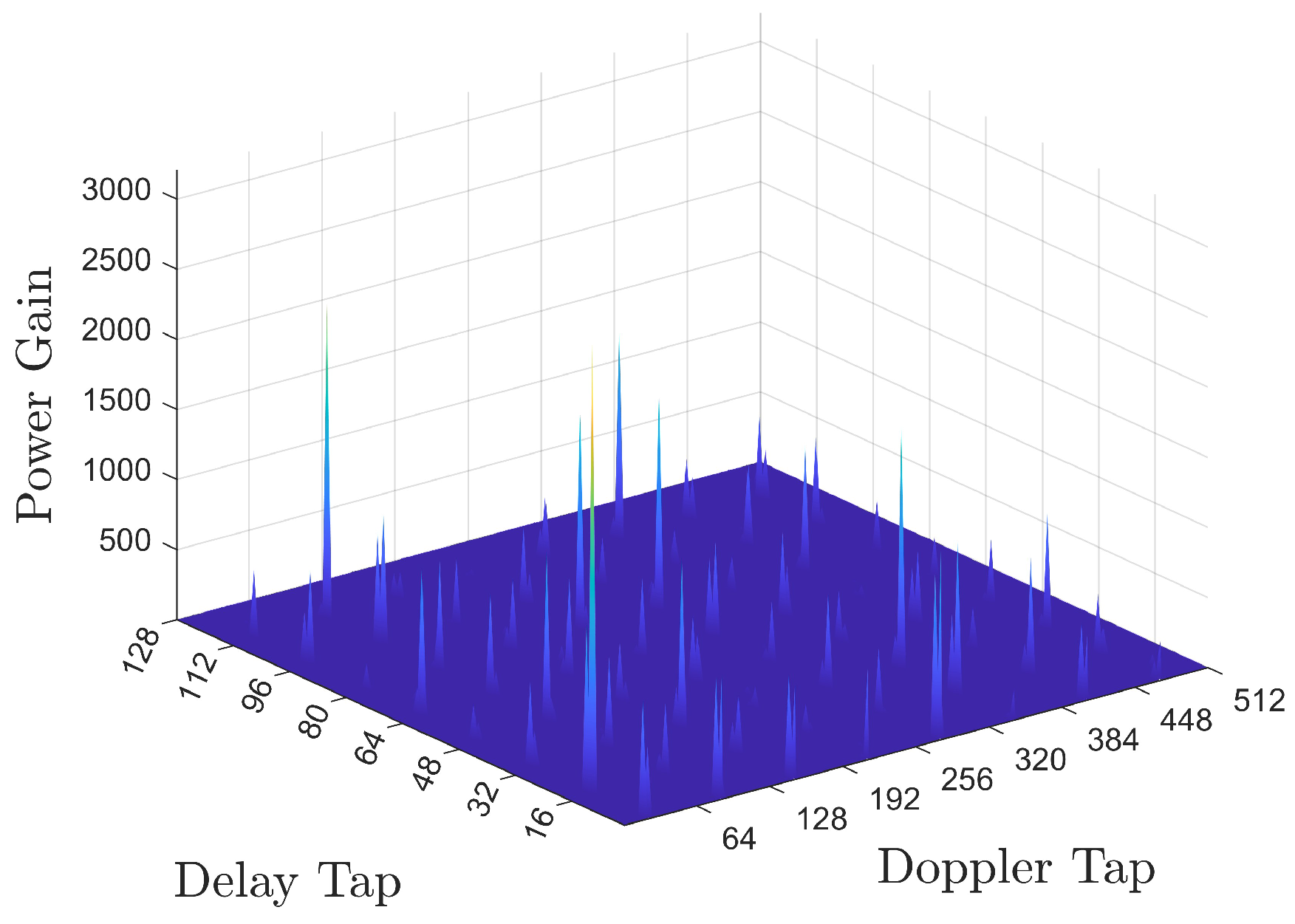


| Type | Taps | Normalized Delay | Power in [dB] | Fading Distribution |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NTN-TDL-A | 1 | 0 | 0 | Rayleigh |
| 2 | 1.0811 | −4.675 | Rayleigh | |
| 3 | 2.8416 | −6.482 | Rayleigh | |
| NTN-TDL-B | 1 | 0 | 0 | Rayleigh |
| 2 | 0.7249 | −1.973 | Rayleigh | |
| 3 | 0.7410 | −4.332 | Rayleigh | |
| 4 | 5.7392 | −11.914 | Rayleigh | |
| NTN-TDL-C | 1 | 0 | 0.394 | LOS path |
| 2 | 14.8124 | −23.373 | Rayleigh | |
| NTN-TDL-D | 1 | 0 | 0.284 | LOS path |
| 2 | 0.5596 | −9.887 | Rayleigh | |
| 3 | 7.3340 | −16.771 | Rayleigh |
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Altitude of LEO satellites, h | 1500 km |
| Velocity of LEO satellites, v | 7112.2 Km/s |
| Radius of the earth, | 6370 Km |
| Working frequency, | 2.2 GHz |
| Subcarrier spacing, | 15 KHz |
| Bandwidth, B | 960 KHz |
| Frame duration, D | 0.00107 s |
| The elevation angle between the satellite and the terminal, | 50° |
| The angle between the terminal’s movement direction and the satellite’s projection plane on earth, | 40° |
| Channel signal-to-noise ratio, | 0–18 dB |
| Modulation order, | 4/16-QAM |
| Speed of the terminal, | 500 km/h |
| Population size for the SSA, P | 10 |
| Maximum number of iterations for the SSA, | 20 |
| Safety values for the SSA, S | 0.6 |
| Proportion of discoverers for the SSA, | 0.7 |
| Proportion of monitors for the SSA, | 0.2 |
| Modulation Format/Size of Antenna Array | (2, 2) | (8, 8) | (16, 16) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4-QAM | 0.33 | 0.31 | 0.11 |
| 16-QAM | 0.43 | 0.42 | 0.39 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, M.; Zhang, Q.; Yao, H.; Gao, R.; Li, J.; Feng, W.; Wang, F.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Tian, F.; et al. Iterative Maximum Ratio Combining Detector for Satellite Multiple-Input Multiple-Output/Orthogonal Time–Frequency Space Systems Based on Soft-Symbol Interference Cancelation. Electronics 2025, 14, 521. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14030521
Sun M, Zhang Q, Yao H, Gao R, Li J, Feng W, Wang F, Li X, Liu X, Tian F, et al. Iterative Maximum Ratio Combining Detector for Satellite Multiple-Input Multiple-Output/Orthogonal Time–Frequency Space Systems Based on Soft-Symbol Interference Cancelation. Electronics. 2025; 14(3):521. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14030521
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Meng, Qi Zhang, Haipeng Yao, Ran Gao, Jiayuan Li, Weiying Feng, Fu Wang, Xiaohu Li, Xiangyu Liu, Feng Tian, and et al. 2025. "Iterative Maximum Ratio Combining Detector for Satellite Multiple-Input Multiple-Output/Orthogonal Time–Frequency Space Systems Based on Soft-Symbol Interference Cancelation" Electronics 14, no. 3: 521. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14030521
APA StyleSun, M., Zhang, Q., Yao, H., Gao, R., Li, J., Feng, W., Wang, F., Li, X., Liu, X., Tian, F., Tian, Q., Zhao, Y., Liu, L., & Wang, Y. (2025). Iterative Maximum Ratio Combining Detector for Satellite Multiple-Input Multiple-Output/Orthogonal Time–Frequency Space Systems Based on Soft-Symbol Interference Cancelation. Electronics, 14(3), 521. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14030521














