Nonuniformity-Immune Read-In Integrated Circuit for Infrared Sensor Testing Systems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
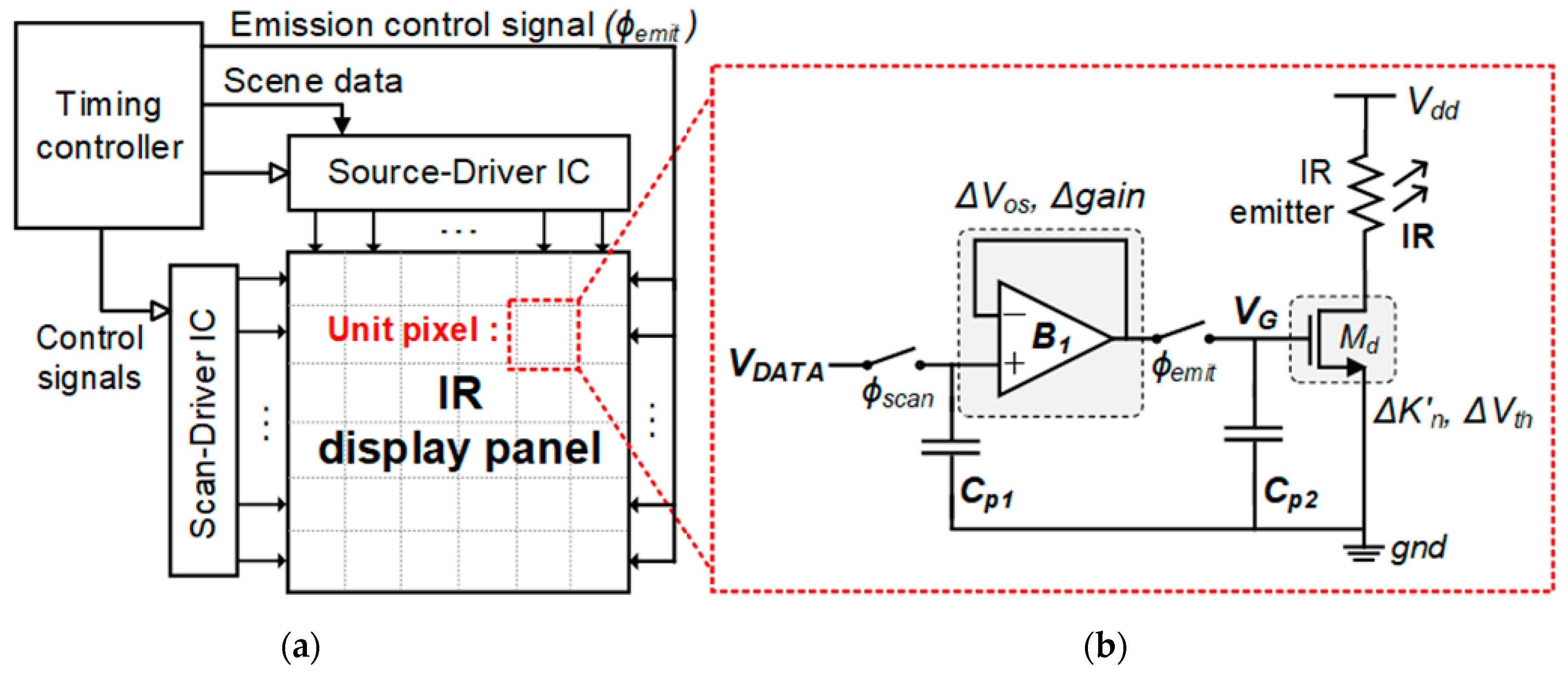
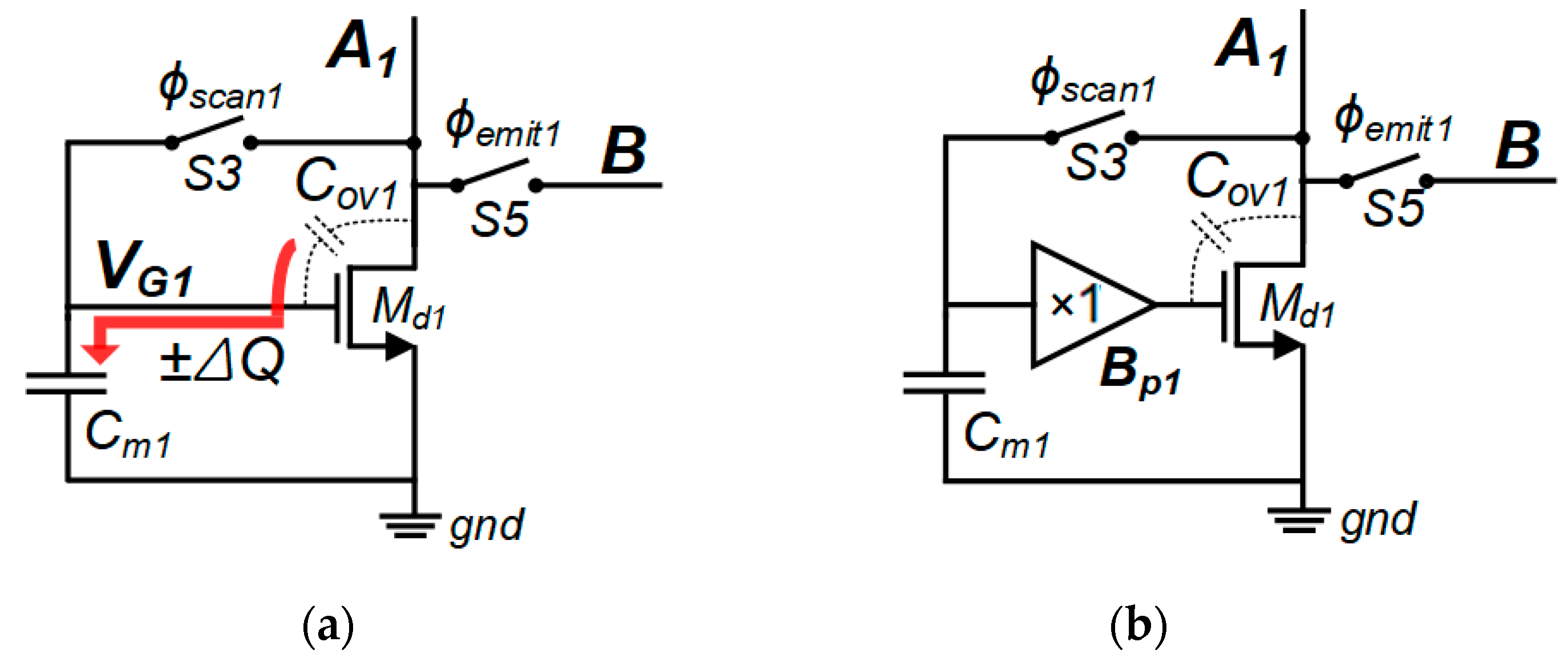
2. Proposed Nonuniformity-Immune RIIC
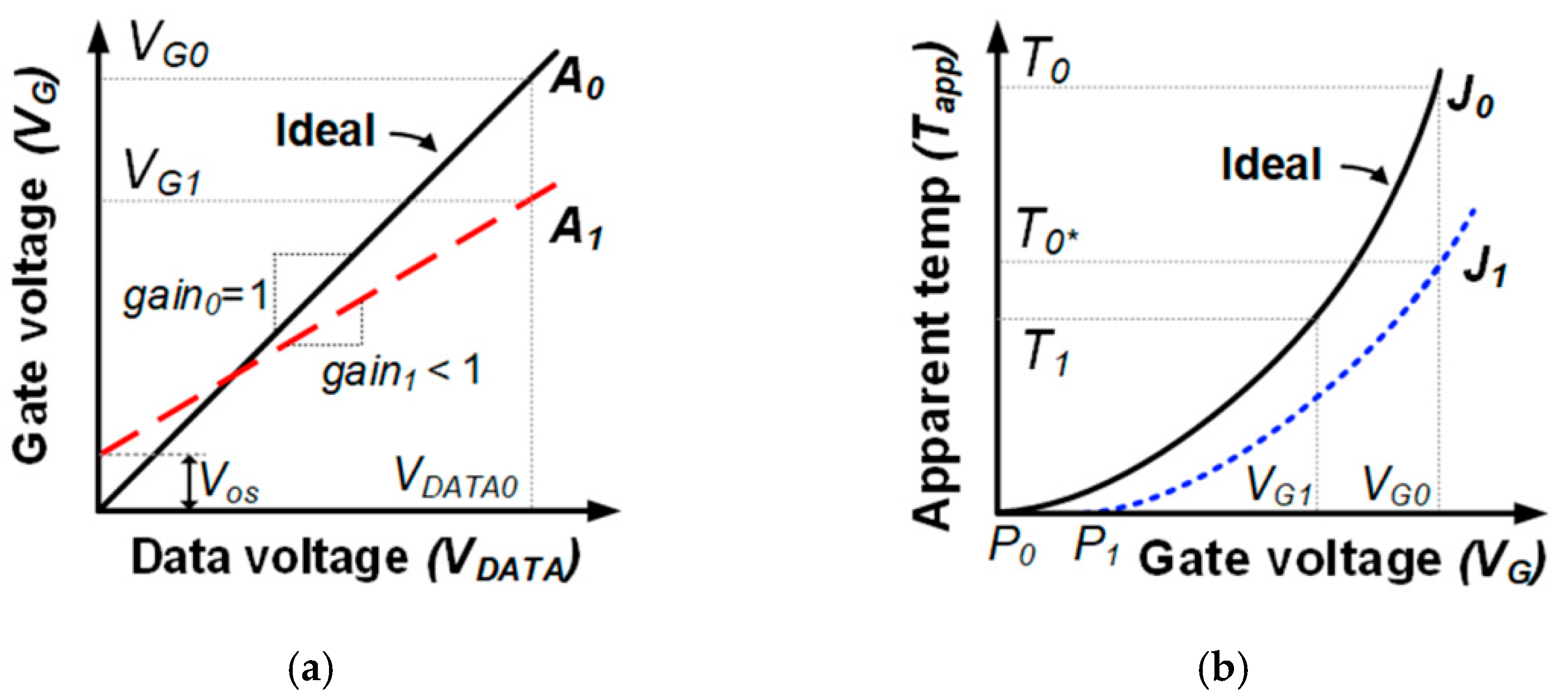
2.1. Nonuniformity Influences of the Conventional RIIC
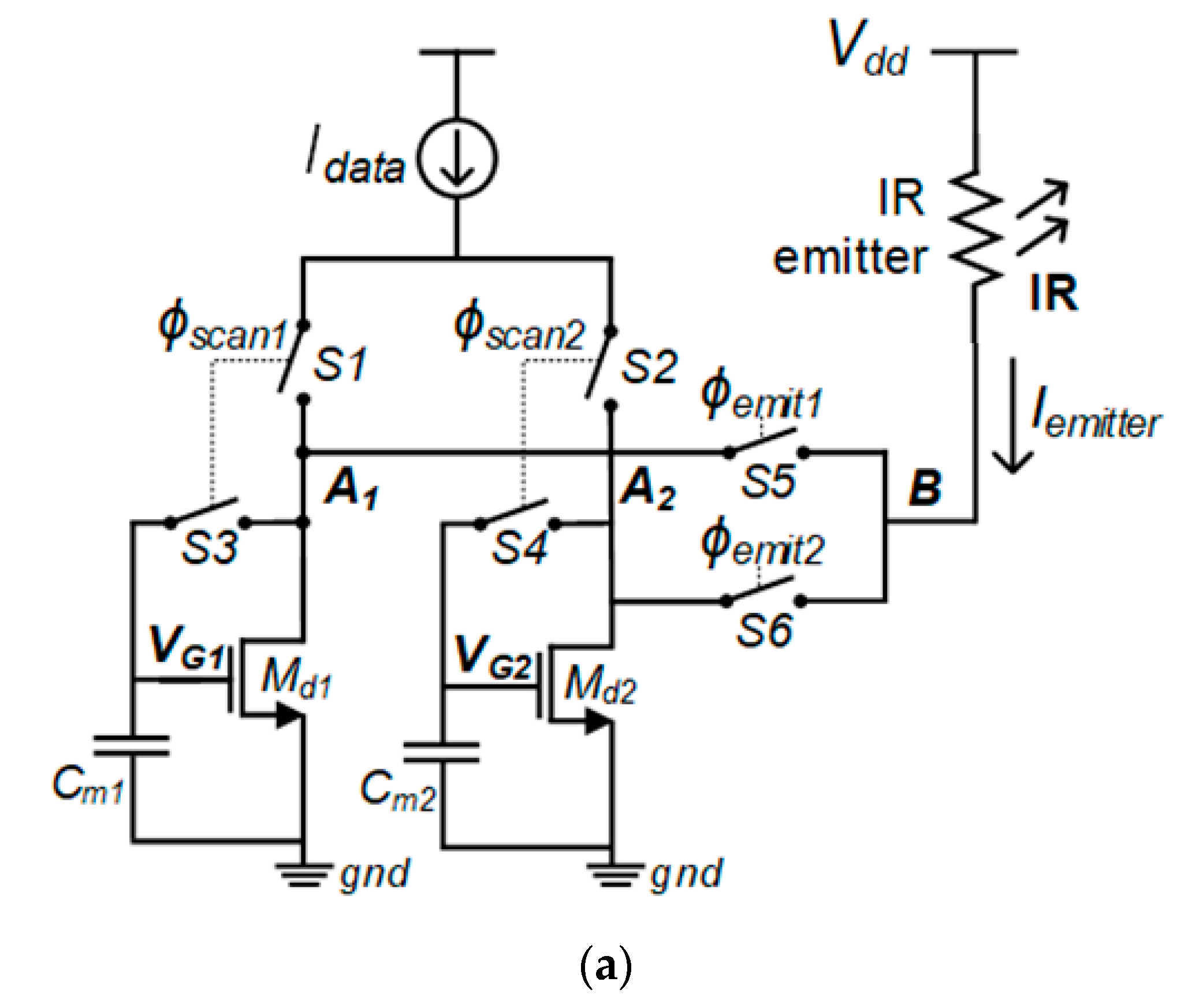
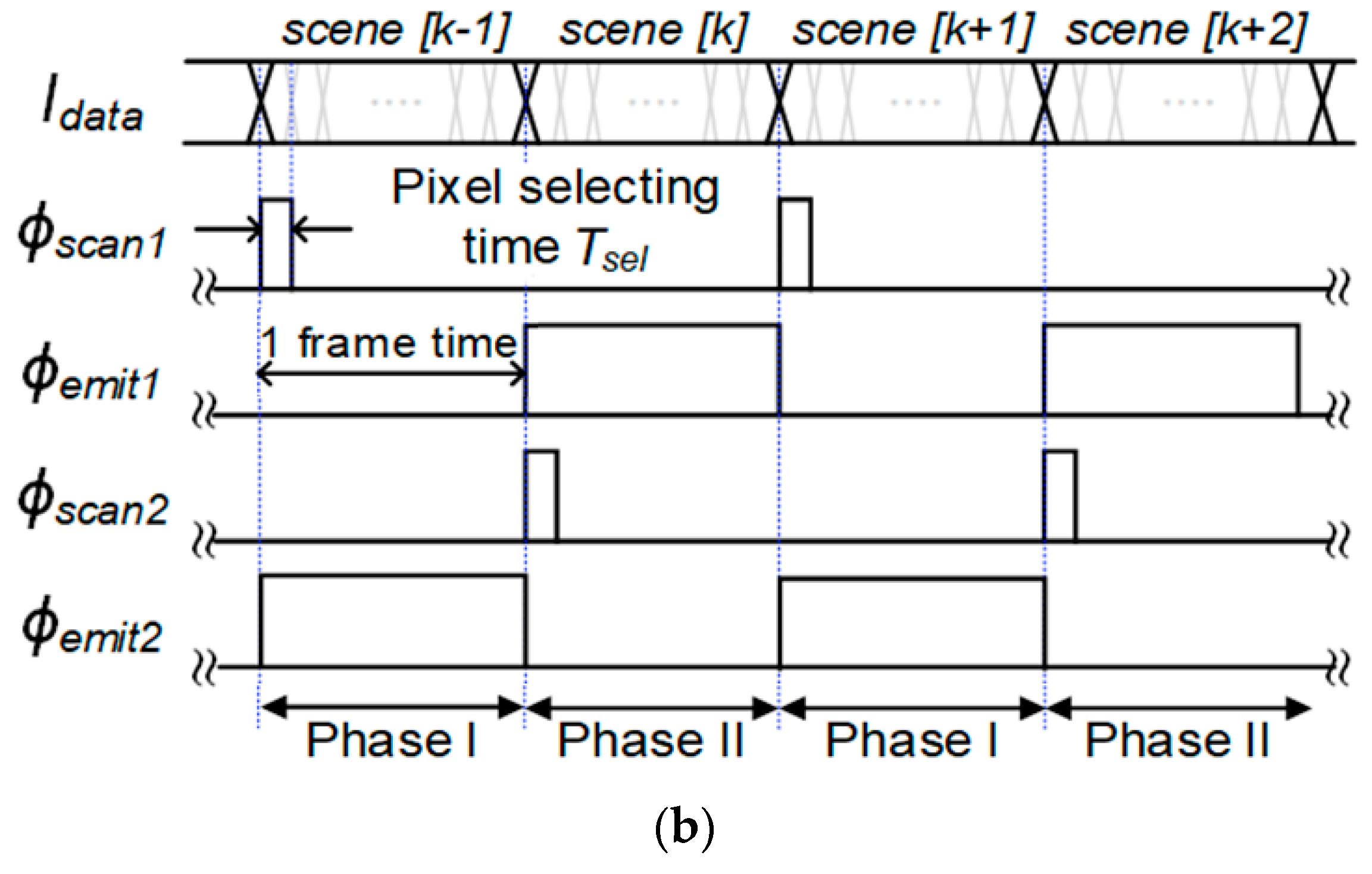
2.2. Proposed Nonuniformity-Immune RIIC
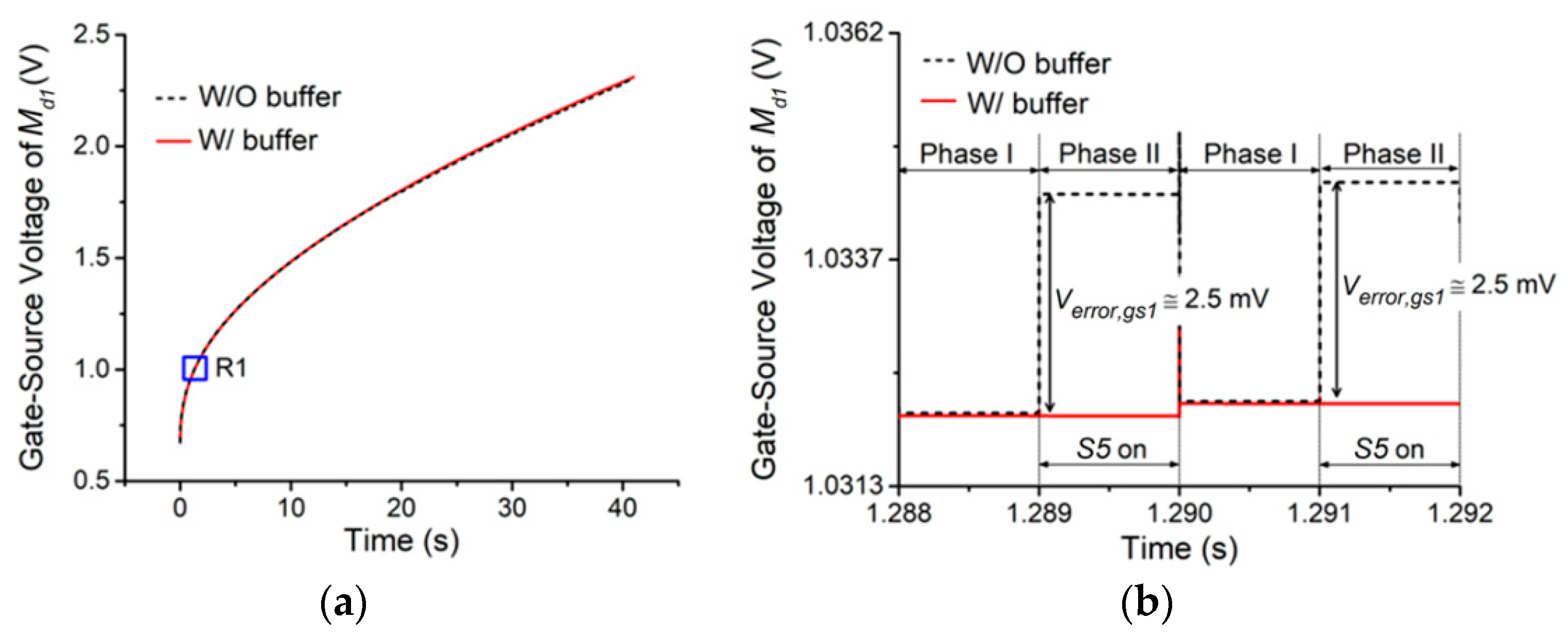
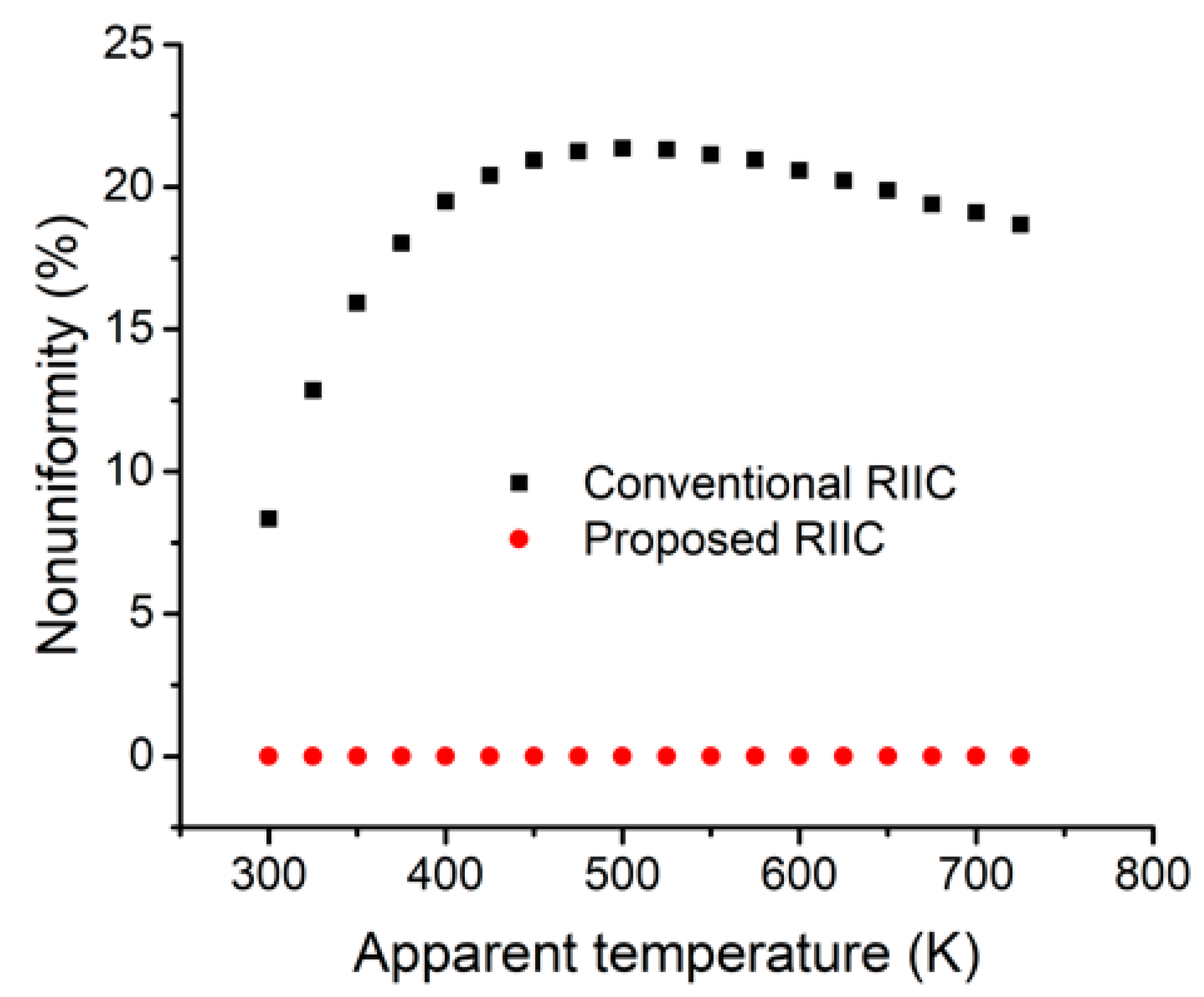
3. Simulation Results and Analysis
3.1. Data Sampling Accuracy
3.2. Evaluation of Nonuniformity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Franks, G.; Laveigne, J.; Danielson, T.; McHugh, S.; Lannon, J.; Goodwin, S. Development of an ultra-high Temperature infrared scene projector at Santa Barbara Infrared Inc. Proc. SPIE 2015, 9452, 94520W. [Google Scholar]
- Norton, D.T.; LaVeigne, J.; Franks, G.; McHugh, S.; Vengel, T.; Oleson, J.; MacDougal, M.; Westerfeld, D. Development of a high-definition IR LED scene projector. Proc. SPIE 2016, 9820, 98200X. [Google Scholar]
- McHugh, S.; Franks, G.; LaVeigne, J. High-temperature MIRAGE XL (LFRA) IRSP system development. Proc. SPIE 2017, 10178, 1017809. [Google Scholar]
- Sparkman, K.; LaVeigne, J.; McHugh, S.; Lannon, J.; Goodwin, S. Ultrahigh-temperature emitter pixel development for scene projectors. Proc. SPIE 2014, 9071, 90711H. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, M.J.; Woo, D.H.; Lee, H.C. Triple-Mode Read-In Integrated Circuit for Infrared Sensor Evaluation System. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 5014–5021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, P.; Solomon, S.; James, J. Bolometers running backward: The synergy between uncooled IR sensors and dynamic IR scene projectors. Proc. SPIE 2006, 6207, 62070J. [Google Scholar]
- Stauffer, D.; Haas, B.; Cole, B. Performance of A Thermal Scene Generator. Proc. SPIE 1989, 1050, 156. [Google Scholar]
- LaVeigne, J.; Prewarski, M.; Franks, G.; McHugh, S. A hybrid approach to non-uniformity correction of large format emitter arrays. Proc. SPIE 2012, 8356, 83560D. [Google Scholar]
- Danielson, T.; Franks, G.; LaVeigne, J.; Prewarski, M.; Nehring, B. Advances in iterative non-uniformity correction techniques for infrared scene projection. Proc. SPIE 2015, 9452, 945210. [Google Scholar]
- LaVeigne, J.; Franks, G.; Sparkman, K.; Prewarski, M.; Nehring, B. Enhanced LWIR NUC using an uncooled microbolometer camera. Proc. SPIE 2011, 8015, 801508. [Google Scholar]
- Oleson, J.; Greer, D. IR emitter non-uniformity correction (NUC): Making sense of the data. Proc. SPIE 2011, 8015, 801502. [Google Scholar]
- Swierkowski, L.; Joyce, R.A.; Williams, O. Resistor array infrared projector nonuniformity correction: Search for performance improvement IV. Proc. SPIE 2009, 7301, 73010M. [Google Scholar]
- Olson, E.M.; Murrer, R.L. Nonuniformity correction of a resistor array infrared scene projector. Proc. SPIE 1999, 3697, 403. [Google Scholar]
- Joyce, R.A.; Swierkowski, L.; Williams, O.M. Resistor array infrared projector nonuniformity correction: Search for performance improvement. Proc. SPIE 2006, 6208, 62081A. [Google Scholar]
- Cole, B.; Johnson, W. Infrared Scene Projector with Current-Mirror Control Electronics. US Patent 6,627,907, 30 September 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, U.S.; Cho, M.J.; Lee, H.C. Mismatch-tolerant read-in IC with voltage-drop compensation for infrared scene projectors. IEICE Electron. Express 2018, 15, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, J.B.; Oleson, J.; Bryant, P.T.; Sparkman, K.; Irwin, A.; McHugh, S.W.; Solomon, S.L. MIRAGE: Developments in emitter array fabrication and performance. Proc. SPIE 2002, 4717, 91. [Google Scholar]
- LaVeigne, J.D.; Kiamilev, F.; McGee, R.; Waite, N. Extended Dynamic Range Drive Circuit for Emitter Arrays. US Patent 9,078,333, 7 July 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Parrish, W.J.; Aziz, N.Y.; Heath, J.L.; Hoelter, T.R. Constant Power Snapshot Microemitter Array with Integral Digital Interface, Isolated Substrate Current Return, and Linearized Signal Response. US Patent 6,316,777, 13 November 2001. [Google Scholar]
- McHugh, S.W.; Warner, J.A.; Pollack, M.; Irwin, A.; Hoelter, T.R.; Parrish, W.J.; Woolaway, J.T. MIRAGE dynamic IR scene projector overview and status. Proc. SPIE 1999, 3697, 209. [Google Scholar]
- Cole, B.E.; Higashi, B.; Ridley, J.A.; Holmen, J.; Newstrom, K.; Zins, C.; Nguyen, K.; Weeres, S.R.; Johnson, B.R.; Stockbridge, R.G.; et al. Innovations in IR projector arrays. Proc. SPIE 2000, 4027, 350. [Google Scholar]
- Ashtiani, S.J.; Servati, P.; Striakhilev, D.; Nathan, A. A 3-TFT current-programmed pixel circuit for AMOLEDs. IEEE Trans. Electron. Devices 2005, 52, 1514–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHugh, S.W.; Robinson, R.M.; Parish, B.; Woolaway, J.T. MIRAGE: Large-format emitter arrays 1024 × 1024 and 1024 × 2048. Proc. SPIE 2000, 4027, 399. [Google Scholar]
- Nathan, A.; Chaji, G.R.; Ashtiani, S.J. Driving schemes for a-Si and LTPS AMOLED displays. J. Disp. Technol. 2005, 1, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, S.; Kobayashi, Y. An accelerative current-programming method for AM-OLED. IEICE Trans. Electron. 2005, E88-C, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, J.S.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, K.D.; Kwon, O.J.; Shin, C.S.; Lee, J.H.; Cho, G.H. A hybrid AMOLED driver IC for real-time TFT nonuniformity compensation. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2016, 51, 966–978. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, C.W.; Huang, L.C. A 10-bit LCD column driver with piecewise linear digital-to-analog converters. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2008, 43, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Yang, J.; Park, S.; Ryu, S.; Cho, G. A 10-Bit Column-Driver IC With Parasitic-Insensitive Iterative Charge-Sharing Based Capacitor-String Interpolation for Mobile Active-Matrix LCDs. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2014, 49, 766–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, Y.J.; Son, Y.S.; Jeon, J.Y.; Lee, G.H.; Lee, H.M.; Jung, S.C.; Cho, G.H. A cascaded-dividing current DAC with fine pitch for high-resolution AMOLED display drivers. Sid Symp. Dig. Tech. Pap. 2007, 1644–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.W.; Lee, P.; Chang, Y.G.; Huang, X.W.; Cheng, J.S.; Tseng, P.Y.; Chou, C.H.; Chen, P.; Chang, T.Y.; Liu, J. A 10-bit 1026-Channel Column Driver IC With Partially Segmented Piecewise Linear Digital-to-Analog Converters for UHD TFT-LCDs with One Billion Color Display. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2019, 54, 2703–2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Properties | Value |
|---|---|
| Operating speed | 100 Hz |
| Array size | 64 × 64 |
| Pixel size | 56 µm × 56 µm |
| Digital input depth | 12 bits |
| Apparent temperature range | 275–700 K |
| Nonuniformity | <3% |
| Properties | Value |
|---|---|
| Resistance | 15 kΩ |
| ɛ ∙ ff | 0.47 |
| G | 1.0 µW/K |
| λ1, λ2 | 3 µm, 5 µm |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cho, M.; Lee, H.; Woo, D. Nonuniformity-Immune Read-In Integrated Circuit for Infrared Sensor Testing Systems. Electronics 2020, 9, 1603. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9101603
Cho M, Lee H, Woo D. Nonuniformity-Immune Read-In Integrated Circuit for Infrared Sensor Testing Systems. Electronics. 2020; 9(10):1603. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9101603
Chicago/Turabian StyleCho, Minji, Heechul Lee, and Doohyung Woo. 2020. "Nonuniformity-Immune Read-In Integrated Circuit for Infrared Sensor Testing Systems" Electronics 9, no. 10: 1603. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9101603
APA StyleCho, M., Lee, H., & Woo, D. (2020). Nonuniformity-Immune Read-In Integrated Circuit for Infrared Sensor Testing Systems. Electronics, 9(10), 1603. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9101603





