Abstract
The weighted K-nearest neighbor (WKNN) algorithm is the most commonly used algorithm for indoor localization. Traditional WKNN algorithms adopt received signal strength (RSS) spatial distance (usually Euclidean distance and Manhattan distance) to select reference points (RPs) for position determination. It may lead to inaccurate position estimation because the relationship of received signal strength and distance is exponential. To improve the position accuracy, this paper proposes an improved weighted K-nearest neighbor algorithm. The spatial distance and physical distance of RSS are used for RP selection, and a fusion weighted algorithm based on these two distances is used for position calculation. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm outperforms traditional algorithms, such as K-nearest neighbor (KNN), Euclidean distance-based WKNN (E-WKNN), and physical distance-based WKNN (P-WKNN). Compared with the KNN, E-WKNN, and P-WKNN algorithms, the positioning accuracy of the proposed method is improved by about 29.4%, 23.5%, and 20.7%, respectively. Compared with some recently improved WKNN algorithms, our proposed algorithm can also obtain a better positioning performance.
1. Introduction
Positioning technology is one of the key technologies of location service, the Internet of Things, and artificial intelligence, and the indoor positioning system has attracted much attention. The global navigation satellite system (GNSS) [1] can meet most of the needs of positioning in the outdoor environment, but it does not work in indoor environments because there is no GNSS signal in the interior of buildings. To overcome this shortcoming, some indoor positioning technologies have been proposed. Ultra-wideband (UWB) positioning technology [2] is a promising technology; it can obtain high positioning accuracy, but it is costly, because it needs specialized infrastructures. Radio frequency identifier (RFID) positioning technology [3] uses two-way communication and data exchange of radio frequency (RF) signals for positioning; it is low-cost, but the transmission distance of the RF signals is short. With visible light positioning technology [4], a modulated white light-emitting diode (LED) can provide location information to obtain a high accuracy position, but it does not work if the light is blocked out. Visual positioning [5] is a popular positioning technology; it locates a camera by estimating its posture or matching a captured photo with stored images associated with known locations. However, it requires an accurate image database, which is challenging and impractical. Bluetooth positioning technology [6] has the advantages of high security, low power consumption, and low cost, but the signal stability of Bluetooth is poor and the communication range is quite short. Pedestrian dead reckoning (PDR) [7,8] is a relative positioning technology. It uses the phone’s built-in accelerometer to detect steps and uses the magnetometer and gyroscope to determine the direction, then calculate the personal moved distance by steps and direction. The disadvantage of PDR is that the positioning error will accumulate with the increase in walking time. The most frequently used indoor positioning technology is Wi-Fi positioning technology [9,10]. The Wi-Fi access points (APs) are widely deployed in buildings such as shopping malls, office buildings, factories, and so on, and the Wi-Fi signal is easily received by mobile devices, such as smartphones. The main positioning methods of Wi-Fi positioning technology include the time of arrival (TOA) [11], time difference of arrival (TDOA) [12], round-trip time of flight (RTOF) [13], angle of arrival (AOA) [13], and received signal strength (RSS) [14]. The TOA method is costly because it requires precise clock synchronization between all receivers and transmitters. TDOA has no requirement of clock synchronization between receivers and transmitters but requires clock synchronization between the transmitters. The RTOF method requires obtaining the exact delay or processing time caused by the transmitter, which requires a larger distance between the receiver and transmitter. AOA method has no requirement for clock synchronization but it needs special and expensive hardware.
The Wi-Fi RSS positioning method has no requirement for clock synchronization or additional hardware, it includes fingerprinting and triangulation methods. In the triangulation method, the received RSS values are converted into distances between receivers and transmitters by the signal attenuation model, and more than three APs’ coordinates must be known. Fingerprinting is the most commonly used method [15]; it has no requirement for the locations of APs or the signal attenuation model. Fingerprinting includes offline training and online matching phases [16,17]. In the offline training phase, reference points (RPs) are selected, and the RSS values are collected at each RP; then, the fingerprint database is established. The task of the online phase is to calculate the coordinates of the test point (TP); the commonly used matching algorithms are the K-nearest neighbor (KNN) [18,19] algorithm and the weighted K-nearest neighbor (WKNN) [20] algorithm.
Traditional KNN and WKNN algorithms adopt spatial distance (SD) of RSS between the reference points and test point to select the K-nearest RPs for position calculation; Euclidean distance and Manhattan distance are the most used spatial distances. The spatial distances from RPs to the TP can be calculated by:
In Formula (1), is the measured RSS value from the -th AP at the TP; is the measured RSS value from the -th AP at the -th RP; is the total number of APs that can be simultaneously detected at TP and RP; represents the Manhattan distance if the value of is one, whereas it represents the Euclidean distance if the value of is two.
In the KNN algorithm, RPs with the smallest spatial distances are selected; by Formula (2), the average of these RPs’ coordinates is calculated as the TP’s coordinates.
In the WKNN algorithm, RPs with the smallest spatial distances are selected as well, but with weighted average. Considering that the distances from the selected reference points to the test point are different, the weights assigned to the reference points are different. The weights of the selected reference points can be calculated by Formula (3); the weight is inversely proportional to the spatial distance . The WKNN algorithm obtains a better positioning accuracy than the KNN algorithm, and it is the most frequently used matching algorithm [20].
The coordinates of the test point are calculated by Formula (4):
In Formulas (2) and (4), is the RP’s coordinates.
In the real indoor environment, reflection, occlusion, and personnel movement may cause non-line-of-sight (NLOS) propagation and multipath effects on the radio signal propagation process. The received RSS values are influenced by the devices and the real environments; therefore, in different environments, the distributions of the RSS values varied [21]. Ashraf [22] compared the impact of different devices and different orientations of the devices on measured RSS values, and a method with the help of APs’ intersections based on AP coverage area uniqueness and overlap is proposed to calculate the user’s position. Instead of only basing on the RSS similarity measure, Muhammad [23] exploits other important features of the RSS vector and their weights to estimate the positions; this proposed approach can obtain quite high accuracy and robustness. The collected RSS may have some degree of spatial correlation [24], and the RSSs from different APs can also interfere with each other. The spatial resolution of the RSS is uneven [25] because the relationship of the RSS and the actual distance is exponential. The experimental result in [26] demonstrated that it is improper to calculate RPs’ weights only based on spatial distance because of the uneven spatial resolution of RSSs. Therefore, the traditional KNN and WKNN algorithms that only adopt spatial distance are not accurate enough. To further improve the positioning accuracy, an improved WKNN algorithm based on the spatial distance and physical distance (PD) of the RSS is proposed. Different from spatial distance, physical distance is calculated by the signal attenuation model. In addition to spatial distance, the physical distance is adopted to select RPs, and then the weighted matching algorithm based on the fusion of weights of these two distances is used for position determination. Experimental results demonstrate that compared with traditional KNN and WKNN algorithms, the proposed algorithm can considerably improve positioning accuracy.
Some researchers have recently proposed improved WKNN algorithms to improve positioning accuracy. Hu [27] proposed the self-adaptive weighted K-nearest neighbor (SAWKNN) algorithm, SAWKNN dynamically selects RPs for position calculation in the online matching phase; the value of may vary for different TPs. Ma [28] proposed a fusion algorithm based on the WKNN algorithm and the probability algorithm. It first calculates two intermediate coordinates of the test point through the WKNN algorithm and the probability algorithm. Then, the final coordinates of the test points are calculated by the weighted fusion of these two coordinates. Xue [26] proposed a new weighted K-nearest neighbor algorithm (Two-P-WKNN) based on two different physical distances of the RSS; the weights of the selected RPs are generated by these two physical distances. Compared with the traditional WKNN algorithm, these recently improved algorithms improve the positioning accuracy to some extent. The positioning performances of some improved algorithms and our proposed algorithm are compared.
The RSS value measured by the receiver gradually weakens [29,30,31,32] with the distance between the receiver and transmitter increasing. Equation (5) is the signal attenuation model [33,34].
In Equation (5), is the path loss exponent of signal propagation in the real space; is the distance between the receiver and transmitter; is the RSS value received by a receiver at the distance to the transmitter, and is the RSS value received at the distance of . is the distance benchmark—it is usually set the value of 1 m.
The signal attenuation model indicates the relationship of the RSS received by the receiver and the distance from the receiver to the transmitter; according to Formula (5), the distance from the receiver to the transmitter can be calculated by:
The value of varies in different environments; it is about 3 [35] in complex indoor environments, such as a building with many walls and other obstacles, while in free space, it is about 2 [36,37]. Seidel [38] demonstrated that can be set to 2.76 and the is −31.7 dBm where the receiver and transmitter are on the same floor. In this paper, the values of and are fitted by the measured RSS data from the APs whose positions are known in the experimental area; the fitting values of and are 3.32 and −36.5 dBm, respectively.
2. The Proposed Algorithm
2.1. The Improved Weighted K-Nearest Neighbor Algorithm Based on Spatial Distance and Physical Distance of RSS
This section presents the improved weight K-nearest neighbor algorithm based on spatial distance and physical distance of the RSS proposed in this paper.
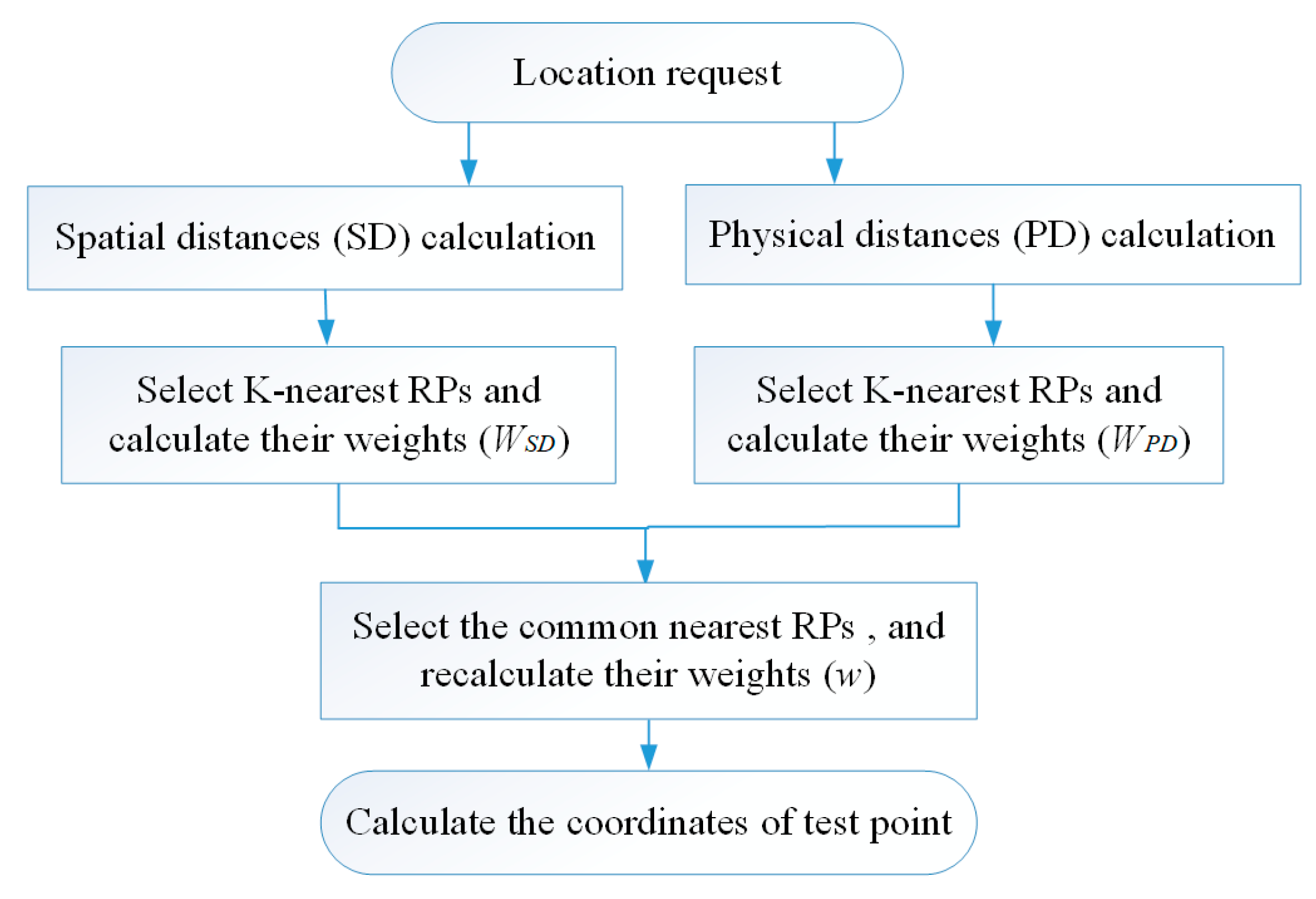
Figure 1 is the framework of our proposed algorithm. As Figure 1 displays, first the spatial distance and physical distances of all RPs are calculated, so two groups of K-nearest RPs are selected by the two distances, and their weights are assigned by the inverse proportional to the spatial distance and physical distance, respectively. Then, the common RPs among the K-nearest RPs of the two distances are selected; these common RPs are used to calculate the TP’s coordinates, and their weights are recalculated by their original weights. Finally, the TP’s estimated coordinates are calculated.
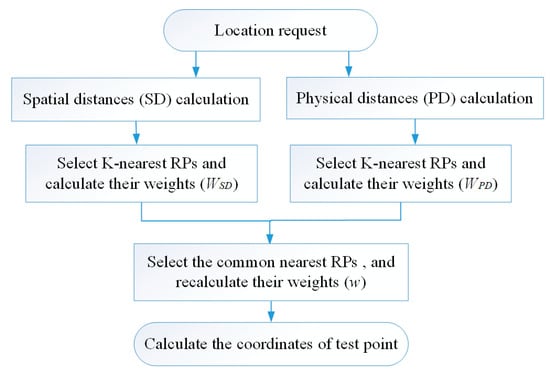
Figure 1.
The framework of the proposed algorithm.
The proposed algorithm is described as follows.
- (1)
- Distances and original weights calculation
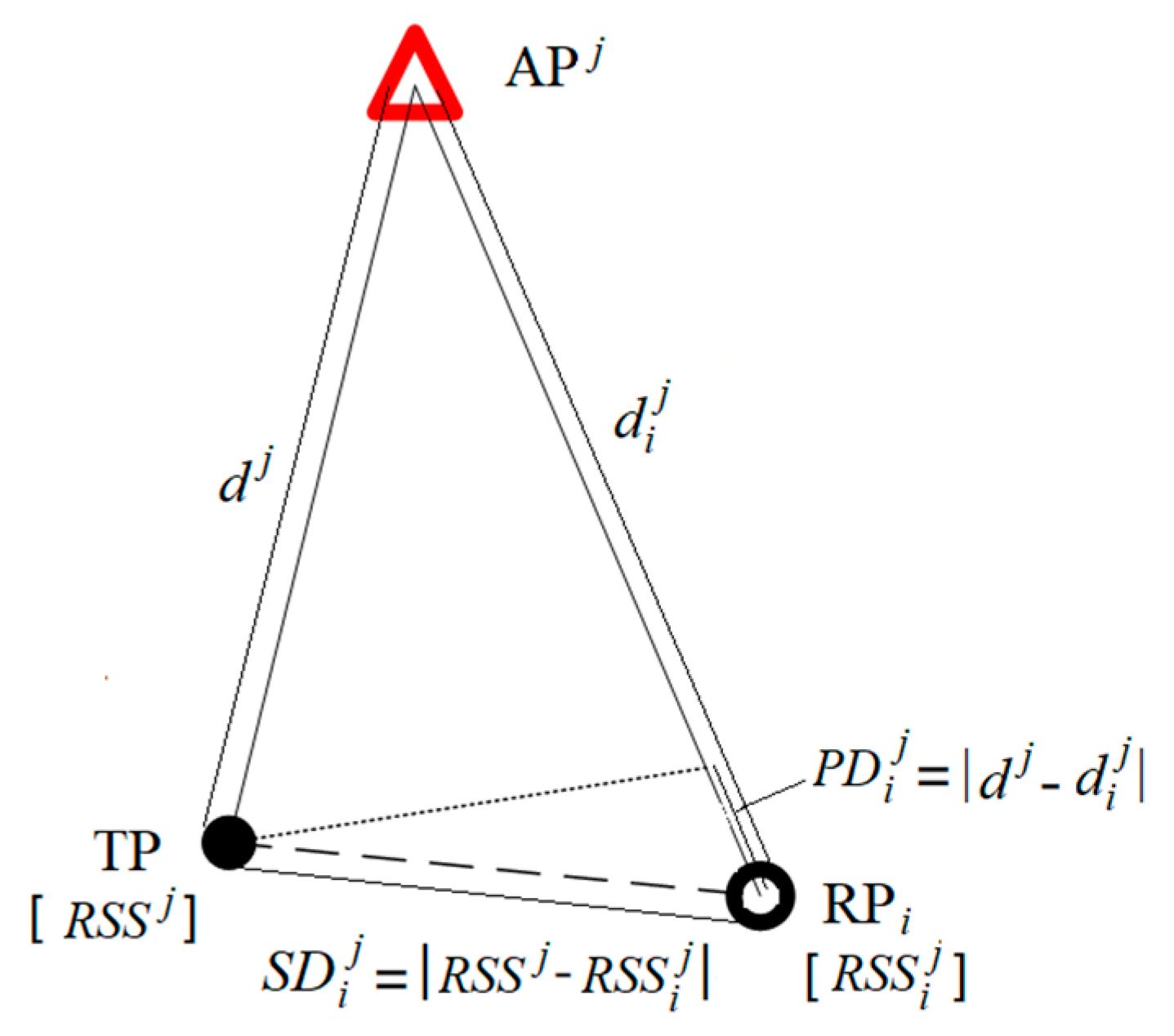
In this paper, the physical distance of the RSS is defined as the mean differential distance from the TP to APs and from RPs to the same APs.
Figure 2 indicates the physical distance and spatial distance (take one of the APs, for instance). Physical distance and spatial distance are calculated by the RSS values; physical distance and spatial distance both reflect the degree of distance from RPs to the TP. The main difference between these two distances is the calculation method; spatial distance has a linear relationship with the RSS value, whereas physical distance has an exponential relationship with the RSS value.
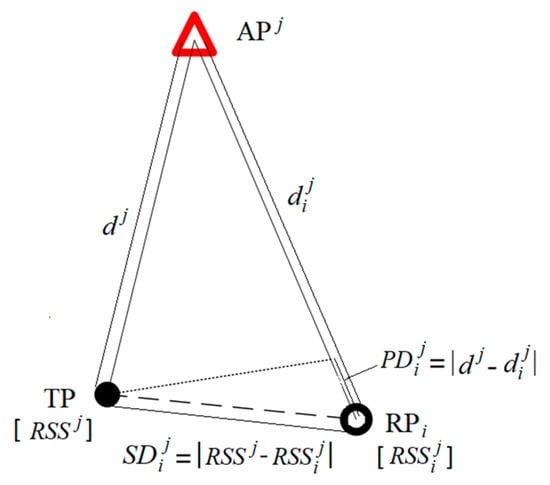
Figure 2.
Sketch of physical distance and spatial distance.
RPs’ physical distance is calculated by:
In Formula (7), is the physical distance of -th RP; is the number of APs that can be simultaneously detected at TP and RP; the value of may vary between different RPs.
is the distance from TP to -th AP calculated by the signal attenuation model; according to Formula (6), it can be calculated by:
In Formula (8), is the RSS value measured at the distance from the -th AP; is the RSS value measured at the TP from the -th AP.
is the distance from -th RP to -th AP calculated by the signal attenuation model; it can be calculated by:
In Formula (9), is the RSS value measured at the -th RP from the -th AP.
All RPs’ physical distances are calculated by Formula (7) and sorted in ascending order, and then the RPs with the smallest PD values are selected. The weight of the selected RP based on physical distance is denoted by , which is calculated by:
The spatial distance (Euclidean distance is adopted) from the -th RP to the TP is denoted by , which is calculated by:
All RPs’ spatial distances are calculated by Formula (11) and sorted in ascending order, and then the RPs with the smallest SD values are selected. The weight of the selected RP based on spatial distance is denoted by , which is calculated by:
- (2)
- RPs’ selection and weights recalculation
As shown in Table 1 (take a random test point, for instance), the common RPs from the RPs selected by physical distance and the RPs selected by spatial distance are selected and the number of the common RPs is denoted as (); these RPs are used to calculate the TP’s coordinates.

Table 1.
The selection of the common reference points (RPs).
The weights of the selected RPs are recalculated based on and ; there are two methods to recalculate the weight: weights addition (13) and weights multiplication (14).
- (3)
- Position calculation
The TP’s estimated coordinates are calculated by:
In Formula (15), are RPs’ coordinates.
2.2. Evaluation Indicators of Positioning Performance
In this section, some evaluation criteria of positioning performance are introduced. The mean position error (ME) is the quotient of the sum of all test points’ position errors and the total number of test points; it is calculated by Formula (17). The root mean square error (RMSE) reflects the deviation of the estimated results and the real values; it is calculated by Formula (18). Standard deviation (STD) is an indicator to evaluate the dispersion degree of the estimated results’ errors; it is calculated by Formula (19). The 90th percentile error is also adopted. The cumulative distribution function (CDF) represents the proportion of errors below a certain threshold.
In Formulas (16)–(19), is the position estimation error of test point, is the estimated coordinates of the test point, its real coordinates are , and is the number of test points.
3. Experiments and Results
3.1. Experimental Setup
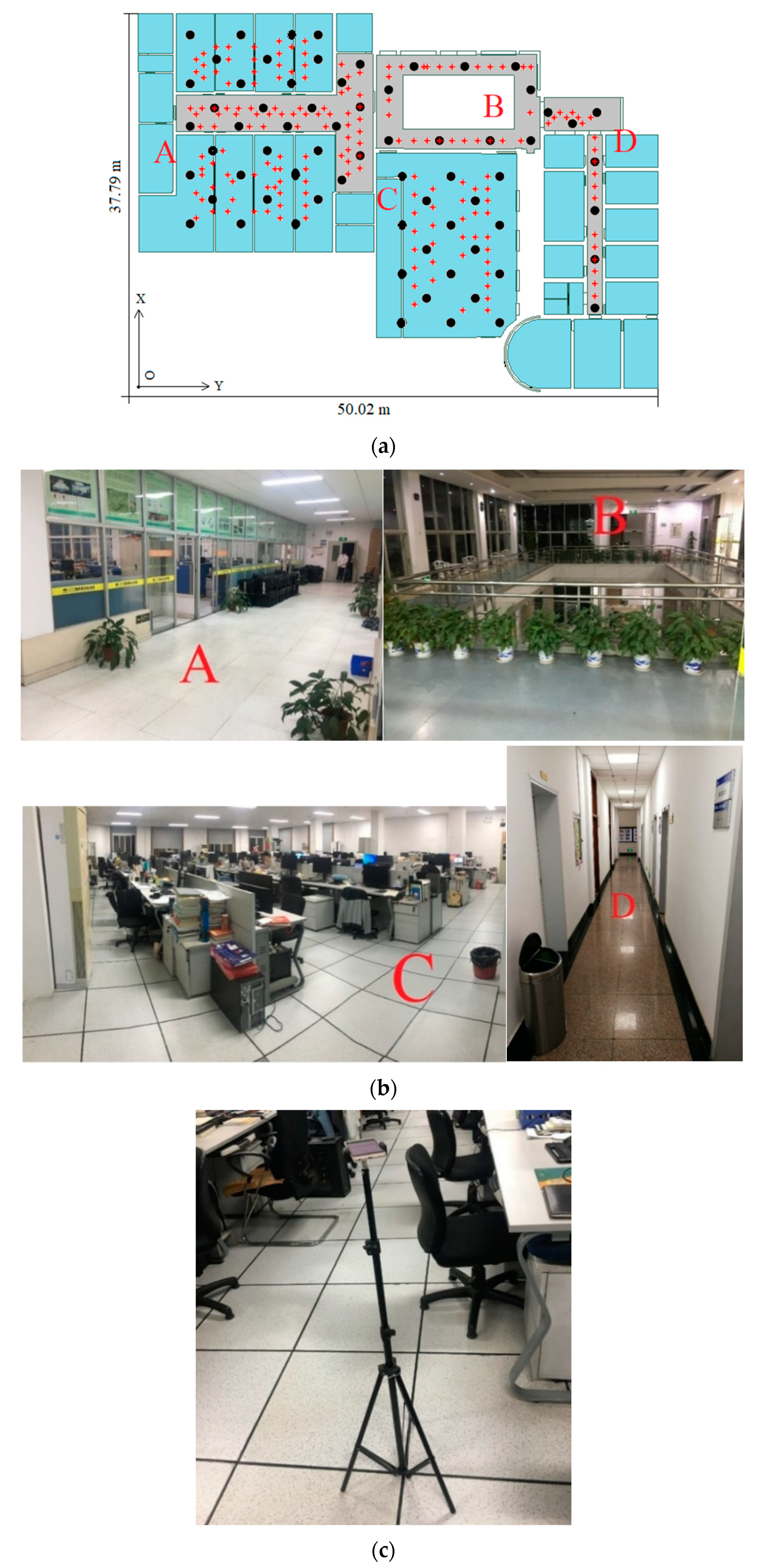
To test the proposed algorithm, the experiment was carried out on one floor of an office building. Figure 3 displays the experimental environment with dimensions of about 38 m × 50 m, including offices, corridors, a lobby, and postgraduate student workplaces. Figure 3a is the distribution diagram of the experimental points; 68 RPs and 180 TPs were selected. Each RP was measured 60 times, and each TP was measured 40 times; at most 60 RSSs were collected at each RP and 40 RSSs at each TP from one AP; then, the mean RSS value was computed and used to calculate spatial distance and physical distance. The corresponding real environments are displayed in Figure 3b. In the experimental environment, the mobile could receive Wi-Fi signals from more than 100 hotspots. To reduce the computation and obtain good accuracy, a quarter of APs (about 30 APs) with the largest mean RSS values were selected for calculation.

Figure 3.
Schematic diagram of the experimental environment. (a) The distribution of reference points (black dots) and test points (red dots); (b) the corresponding real experimental environments; (c) the placement of the smartphone.
The structures of different devices were heterogeneous; the received signals from the same access point may have been variable. To avoid this phenomenon, the same one smartphone (HUAWEI P9) was used to collect the Wi-Fi RSS data. The sampling rate of the RSS acquisition APP was set as 2 s for both reference points and test points. The orientation of the smartphone was random; to keep the device steady, the smartphone was placed on a tripod, as shown in Figure 3c. As displayed in Figure 3a, an independent plane Cartesian coordinate system was established for convenience; O is the origin, and the horizontal axis and the vertical axis are the X-axis and the Y-axis, respectively.
3.2. Experimental Result Analysis
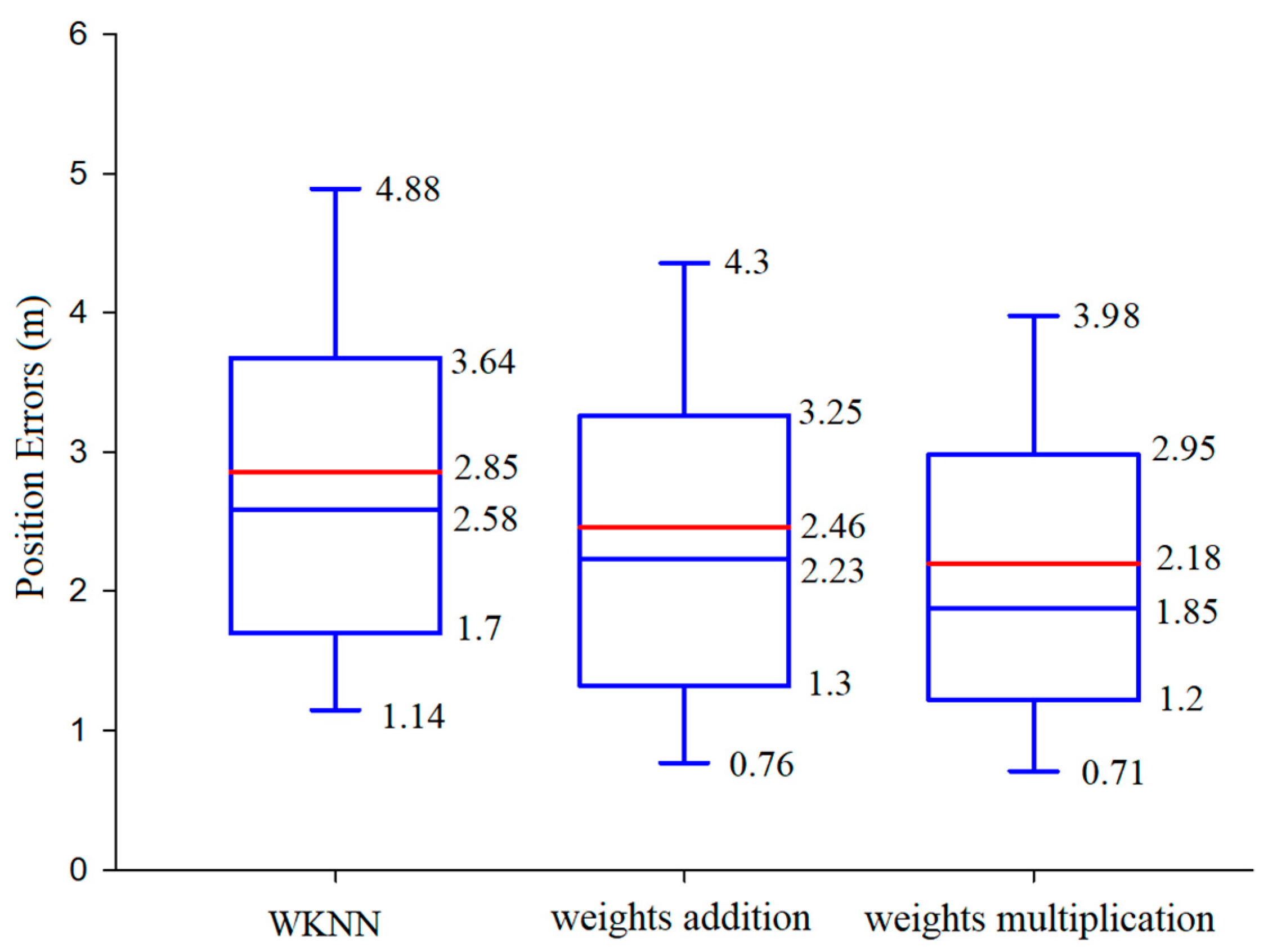
The recalculation of the weights of the selected RPs may affect positioning accuracy; the two methods of weight recalculation mentioned earlier are examined in this section.
Figure 4 displays the position error boxplots of the three algorithms (WKNN algorithm and the proposed algorithm using different weight calculation methods). The boxplot includes some position error statistics; in order, from top to bottom, they are 90th, 75th, mean error (the red line), median, 25th, and 10th percentile errors. As can be seen, the mean position error of the improved WKNN algorithm adopting the weights multiplication method is 2.18 m, which is better than the 2.46 m of the weights addition method and the 2.85 m of the traditional WKNN algorithm. The boxplots in Figure 4 demonstrate that the positioning performance of the improved WKNN algorithm is better than that of the traditional WKNN algorithm. For the improved WKNN algorithm, adopting the weights multiplication method outperforms adopting the weights addition method. The reason for this superiority is that the weights multiplication method can enlarge the weight of the high-quality RPs’ weights, thus improving the positioning accuracy. Therefore, the weights multiplication method is adopted.
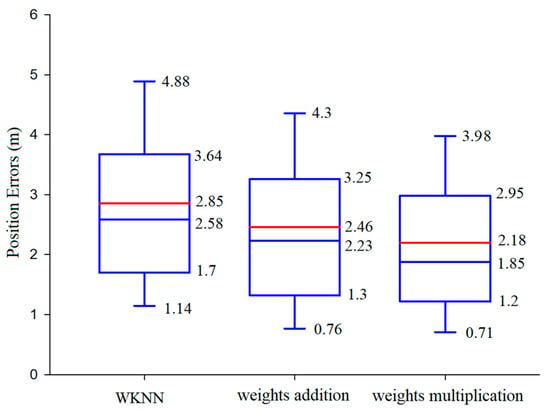
Figure 4.
Comparison of the positioning performance represented by boxplots.
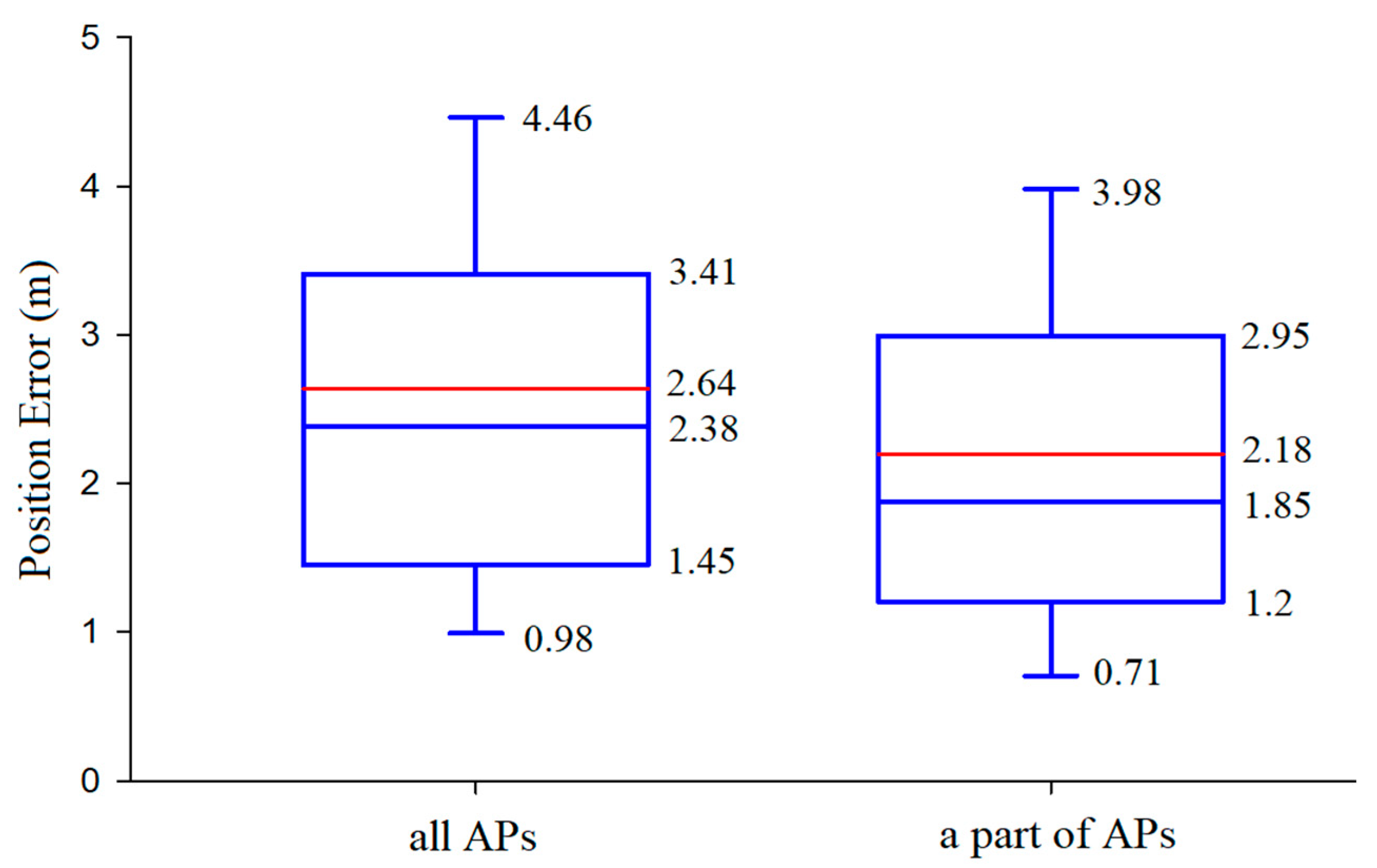
To reduce the computation, a number of APs with the largest RSS values were selected for localization, as mentioned earlier. The physical and spatial distances were calculated, then the weights were calculated, and finally, the coordinates of the TPs were estimated. Accordingly, the positioning performance is examined.
Figure 5 displays the boxplots of the position errors by the proposed positioning algorithm but adopting different amount of APs. The boxplots demonstrate that all error statistics of adopting a part of APs are better than those of adopting all APs. It can be concluded that the method of adopting a number of APs with the largest RSS values is more accurate and more practicable.
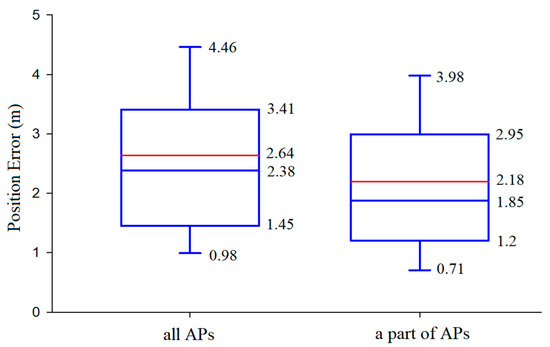
Figure 5.
Comparison of the positioning performance shown in boxplots.
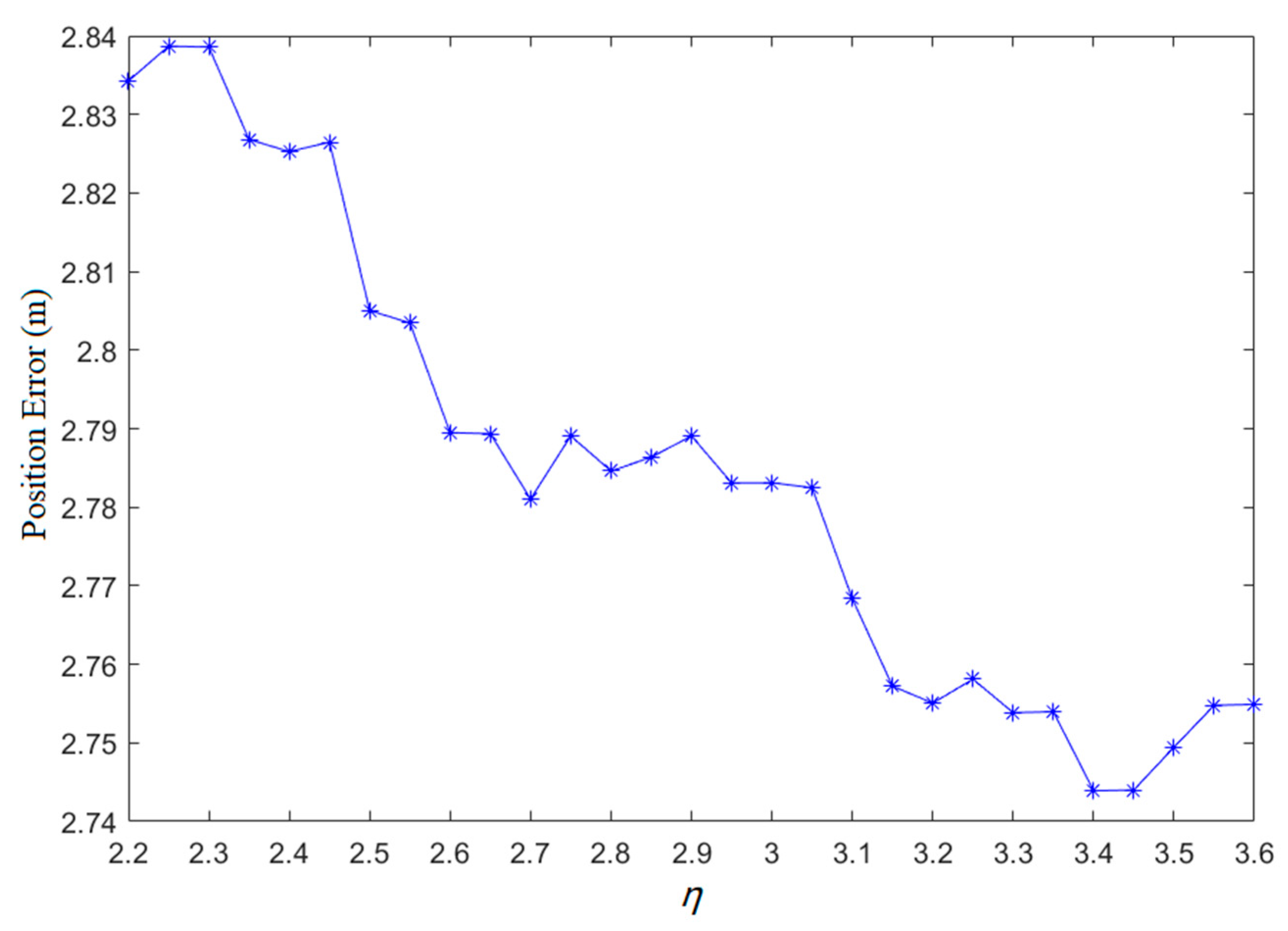
The value of the path loss exponent () of the signal attenuation model affects the accuracy of the physical distance calculation, which can impact the final positioning result. Now, the impact of the parameter on the positioning accuracy is examined.
Figure 6 displays the positioning accuracy with different values of . As can be seen, as increases, the positioning error first decreases and then increases; the best positioning accuracy is obtained when is from 3.4 to 3.45. The obtained by fitting is 3.32, rather than 3.4 or 3.5; the reason is that when fitting for , some APs with known positions are used instead of all APs in the localization area. Figure 6 indicates that the gap between the highest position error and the lowest position error is 9.5 cm with different values of . The impact of on the positioning accuracy of the improved WKNN algorithm is rather minor; is set to 3.32 in our experiments.
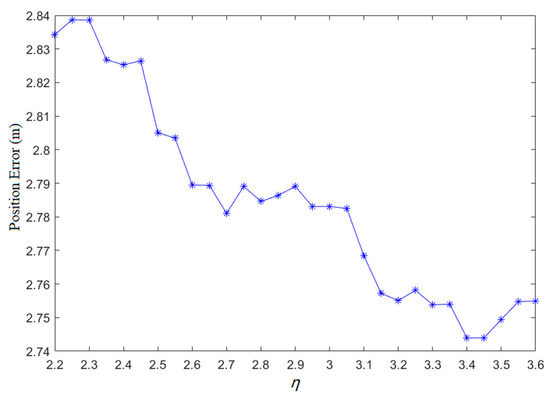
Figure 6.
Positioning accuracy with different values of .
Now, the performance of the proposed algorithm against those of the KNN, E-WKNN (Euclidean distance-based WKNN), M-WKNN (Manhattan distance-based WKNN), and P-WKNN (physical distance-based WKNN) algorithms is compared. The preprocessing of RSS data of the five algorithms is the same, and RSS mean value is adopted.
It can be observed from the error statistics shown in Table 2 that the positioning performance of our proposed improved WKNN algorithm is better than the other four algorithms. The ME of the proposed algorithm is 2.18 m, which is 0.91 m, 0.67 m, 0.82 m, and 0.57 m better than that of the KNN, E-WKNN, M-WKNN, and P-WKNN algorithms, respectively. The RMSE of the proposed algorithm is 2.59 m, which is better than the 3.60 m, 3.25 m, 3.47 m, and 3.16 m of the KNN, E-WKNN, M-WKNN, and P-WKNN, respectively. The 90th percentile error of the proposed algorithm is 3.98 m, w is better than the 5.23 m, 4.88 m, 5.55 m, and 4.77 m of the KNN, E-WKNN, M-WKNN, and P-WKNN algorithms, respectively.

Table 2.
Positioning performance comparison of the five algorithms.
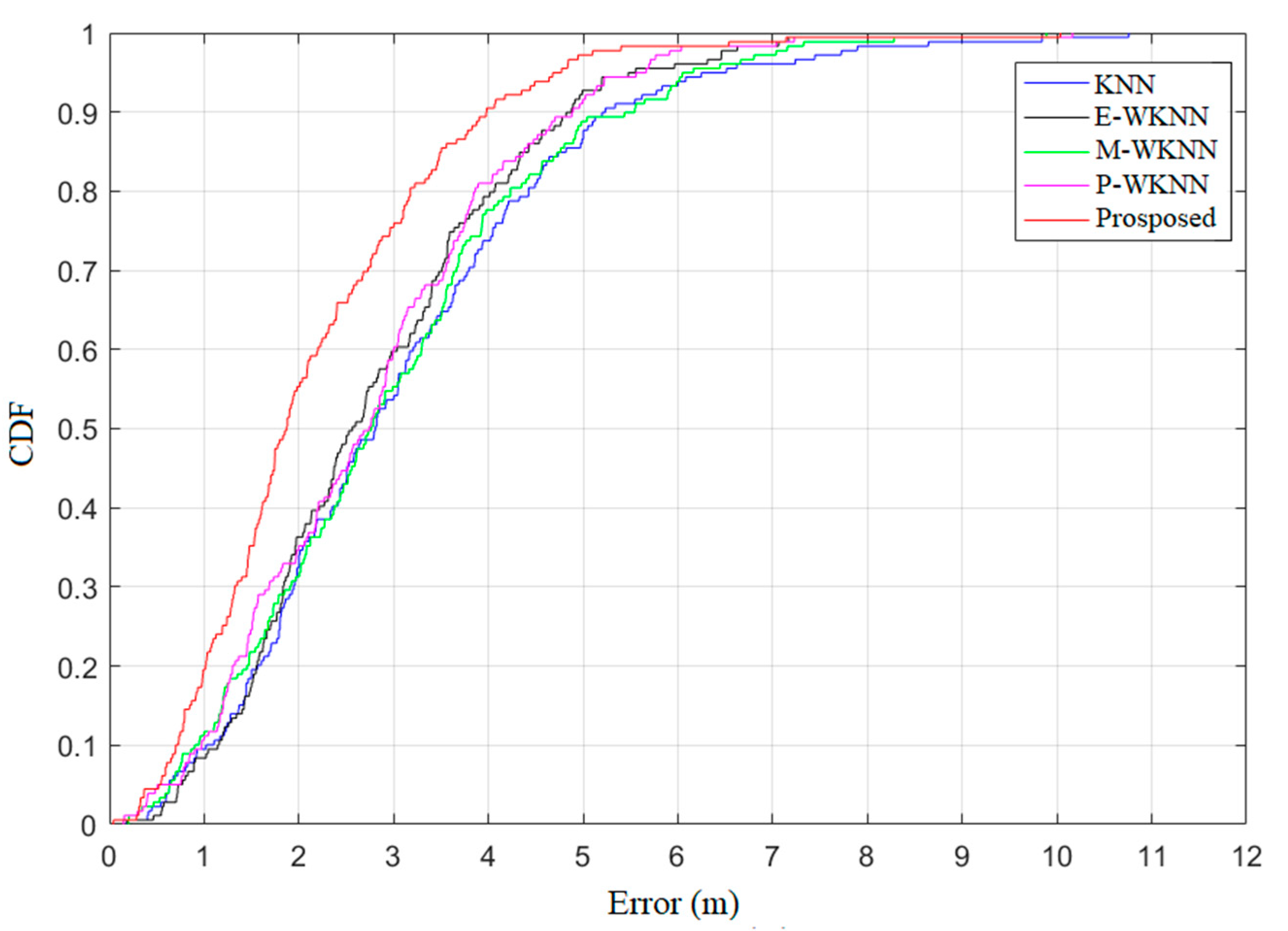
Figure 7 displays the position errors’ CDF of the five algorithms. Three error thresholds were selected; when the thresholds are set to 1, 3, and 5 m, the CDF values of the proposed algorithm are 20%, 75.6%, and 97.2%, respectively, which are considerably higher than the 9.4%, 53.9%, and 87.2% of the KNN, the 8.3%, 59.4%, and 92.2% of the E-WKNN, the 11.7%, 55%, and 88.3% of the M-WKNN, and the 11.7%, 60%, and 90.6% of the P-WKNN, respectively. The error statistics and the CDF of position errors demonstrate that the proposed algorithm is superior to the traditional KNN and WKNN algorithms.
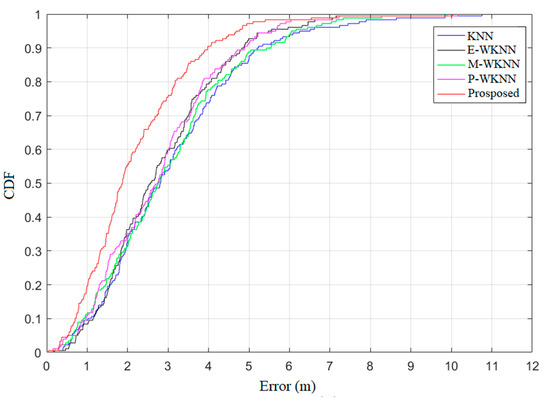
Figure 7.
Position errors’ cumulative distribution function (CDF) of the five algorithms.
Now, the positioning performance of the proposed algorithm against the recently improved WKNN algorithms (SAWKNN and Two-P-WKNN) are compared.
It can be observed from the error statistics shown in Table 3 that the ME of the proposed algorithm is 0.18 m and 0.62 m better than that of the SAWKNN and Two-P-WKNN algorithms, respectively. The RMSE of the proposed algorithm is 0.34 m and 0.62 m better than that of the SAWKNN and Two-P-WKNN algorithms, respectively. The STD and 90th percentile error of the proposed algorithm are better than the other two algorithms.

Table 3.
Positioning performance comparison of the three algorithms.
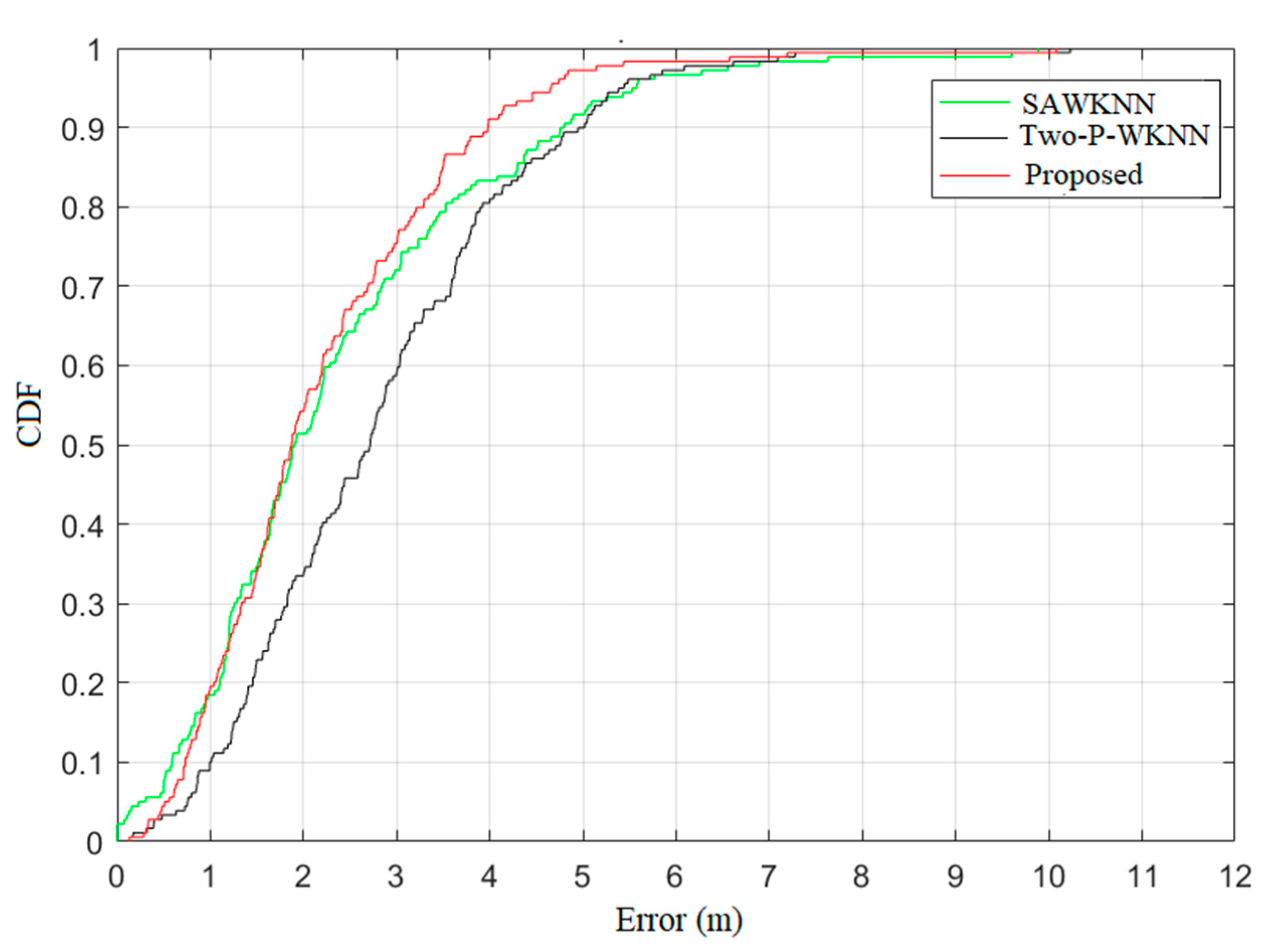
The position errors’ CDF of these three algorithms is displayed in Figure 8. When the threshold is 1 m, 3 m, and 5 m, the CDF values of the proposed algorithm are 20%, 75.6%, and 97.2%, respectively, which are higher than the 18.9%, 72.2%, and 91.7% of the SAWKNN and the 10.6%, 59.4%, and 90% of the Two-P-WKNN, respectively. The error statistics and the CDF of position errors demonstrate that our proposed algorithm outperforms some recently improved WKNN algorithms.
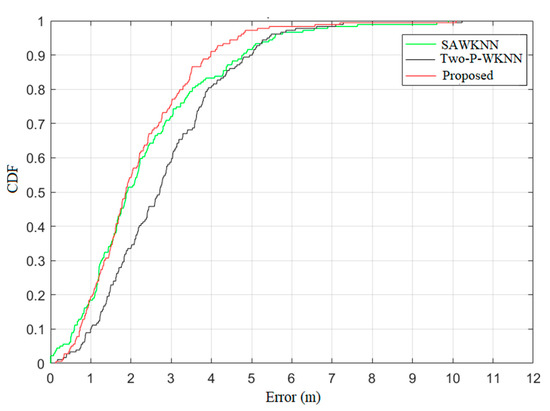
Figure 8.
Position errors’ CDF of the three algorithms.
4. Discussion and Conclusions
This paper proposed an improved weighted K-nearest neighbor algorithm. The proposed algorithm adopted both spatial distance and physical distance to select RPs for position determination; then, a weighted algorithm based on the fusion of weights of these two distances was used for position calculation.
The experiment was conducted in a real indoor environment, and the experimental results indicated that the positioning performance of the proposed algorithm is considerably better than the traditional WKNN algorithm and some recent improved WKNN algorithms, such as the SAWKNN algorithm and the Two-P-WKNN algorithm. Compared with the traditional WKNN algorithm, the SAWKNN algorithm, and the Two-P-WKNN algorithm, the positioning accuracy of this algorithm is improved from 2.85 m, 2.36 m, and 2.80 m to 2.18 m, respectively. The reason for the improvement is that (a) compared with adopting a single spatial distance or physical distance to select RPs, the proposed algorithm can exclude RPs with poor quality through twice selection. In addition to spatial distance, physical distance is adopted as an additional evaluation criterion to select RPs which can help to select high-quality RPs for position calculation. (b) The RPs assigned large weights by both spatial distance and physical distance are considered to be of high quality, and the recalculation of the selected RPs’ weights by the weights multiplication method can enlarge the high-quality RPs’ weights, so the accuracy of the position is further improved.
The proposed algorithm can considerably improve indoor positioning accuracy, so it is useful for Wi-Fi RSS-based indoor positioning technology. As mentioned in this paper, a mass of APs can be detected by mobile devices in the indoor environment, resulting in a heavy calculation burden, and the positioning may be affected because the signals between different APs may interfere with each other. A simple AP selection method is adopted in this work; a better selection of APs should be further researched for calculation burden reduction and better positioning accuracy.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.P., R.C. and W.X.; Data curation, X.P.; Formal analysis, X.P., K.Y. and W.X.; Funding acquisition, R.C.; Investigation, X.P.; Methodology, X.P., K.Y. and W.X.; Software, X.P.; Validation, X.P. and R.C.; Visualization, X.P., F.Y. and W.X.; Writing—original draft preparation, X.P.; Writing—review and editing, R.C., K.Y., F.Y. and W.X. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China, with grant numbers 2016YFB0502200 and 2016YFB0502201, and by the Natural Science Fund of China, with grant number 91638203.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Liu, D.; Wang, H.; Xia, Q.; Jiang, C. A Low-Cost Method of Improving the GNSS/SINS Integrated Navigation System Using Multiple Receivers. Electronics 2020, 9, 1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahfouz, M.R.; Fathy, A.E.; Kuhn, M.J.; Wang, Y. Recent trends and advances in UWB positioning. In Proceedings of the IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Workshop on Wireless Sensing, Local Positioning, and RFID (IMWS 2009-Croatia), Cavtat, Croatia, 1–4 November 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Lee, L.; Ho, C.; Wu, L.; Lai, Z. Real-time RFID indoor positioning system based on Kalman-filter drift removal and heron-bilateration location estimation. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2015, 64, 728–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.; Ha, C. Fingerprint-Based Indoor Positioning System Using Visible Light Communication—A Novel Method for Multipath Reflections. Electronics 2019, 8, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piasco, N.; Sidibé, D.; Demonceaux, C.; Gouet-Brunet, V. A survey on Visual-Based Localization: On the benefit of heterogeneous data. Pattern Recognit. 2018, 74, 90–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Cuthbert, L. Bluetooth positioning using RSSI and triangulation methods. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE 10th Consumer Communications and Networking Conference (CCNC), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 837–842 March 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Chen, W.; Chen, X.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.W. Sensing strides using EMG signal for pedestrian navigation. GPS Solut. 2010, 15, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Chen, R.; Chen, X.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Fu, Z. Comparison of EMG-based and accelerometer-based speed estimation methods in pedestrian dead reckoning. J. Navig. 2011, 64, 265–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, A.; Silva, I.; Meneses, F.; Nicolau, M.J.; Pendão, C.; Torres-Sospedra, J. Multiple simultaneous WiFi measurements in fingerprinting indoor positioning. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation (IPIN), Sapporo, Japan, 18–21 September 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, J.; Yang, F.; Niu, X.; Li, L.; Wang, Z.; Chen, R. A Bayesian Density Model Based Radio Signal Fingerprinting Positioning Method for Enhanced Usability. Sensors 2018, 18, 4063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, B.; Kmiecik, C.; Hartnett, R.; Thompson, P.; Mendoza, J.; Nguyen, H. Spread Spectrum Indoor Geolocation. Navigation 1998, 45, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, R.; Ogino, A.; Tamaki, T.; Uta, T.; Matsuzawa, N.; Kato, T. TDOA location system for IEEE 802.11b WLAN. In Proceedings of the IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference, New Orleans, LA, USA, 13–17 March 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H. Double-sided two-way ranging algorithm to reduce ranging time. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2009, 13, 486–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Guo, Y. Statistical NLOS Identification Based on AOA, TOA, and Signal Strength. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2009, 58, 274–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Shen, R.; Liu, D.; Wen, Y.; Wang, X. Performance analysis of RSS fingerprinting based indoor localization. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2017, 16, 2847–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Dortz, N.; Gain, F.; Zetterberg, P. Wi-Fi Fingerprint Indoor Positioning System Using Probability Distribution Comparison. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Kyoto, Japan, 25–30 March 2012; pp. 2301–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkvens, R.; Peremans, H.; Weyn, M. Conditional Entropy and Location Error in Indoor Localization Using Probabilistic Wi-Fi Fingerprinting. Sensors 2016, 16, 1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahl, P.; Padmanabhan, V.N. Radar: An in-building RF-based user location, and tracking system. In Proceedings of the IEEE INFOCOM 2000, Tel Aviv, Israel, 775–784 August 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhou, M.; Meng, W.; Ma, L. Optimal KNN positioning algorithm via theoretical accuracy criterion in WLAN indoor environment. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Global Telecommunications Conference GLOBECOM 2010, Miami, FL, USA, 6–10 December 2010; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunato, M.; Battiti, R. Statistical learning theory for location fingerprinting in wireless lans. Comput. Netw. 2005, 47, 825–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaemarungsi, K.; Krishnamurthy, P. Analysis of WLAN’s received signal strength indication for indoor location fingerprinting. Pervasive Mob. Comput. 2012, 8, 292–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, I.; Hur, S.; Park, Y. Indoor Positioning on Disparate Commercial Smartphones Using Wi-Fi Access Points Coverage Area. Sensors 2019, 19, 4351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, U.; Hur, S.; Park, S.; Park, Y. Harvesting Indoor Positioning Accuracy by Exploring Multiple Features from Received Signal Strength Vector. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 52110–52121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, Q.; Lin, X. A novel approach for fingerprint positioning based on spatial diversity. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Advanced Computer Theory and Engineering, Chengdu, China, 20–22 August 2010; pp. 441–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, W.; Qiu, W.; Hua, X.; Yu, K. Improved Wi-Fi RSSI measurement for indoor localization. IEEE Sens. J. 2017, 17, 2224–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, W.; Hua, X.; Li, Q.; Yu, K. A new weighted algorithm based on the uneven spatial resolution of RSSI for indoor localization. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 26588–26595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Liu, D.; Yan, Z.; Liu, H. Experimental analysis on weight k-nearest neighbor indoor fingerprint positioning. IEEE Internet Things J. 2018, 6, 891–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Guo, Q.; Hu, C.; Xue, J. An improved Wi-Fi indoor positioning algorithm by weighted fusion. Sensors 2015, 15, 21824–21843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, G.; Chen, R.; Ye, F.; Chen, L.; Pan, Y.; Liu, M.; Cao, Z. A pose awareness solution for estimating pedestrian walking speed. Remote. Sens. 2018, 11, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monica, S.; Bergenti, F. An Algorithm for Accurate and Robust Indoor Localization Based on Nonlinear Programming. Electronics 2020, 9, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Sospedra, J.; Montoliu, R.; Trilles, G.; Belmonte, O.; Huerta, J. Comprehensive analysis of distance and similarity measures for Wi-Fi fingerprinting indoor positioning systems. Expert Syst. Appl. 2015, 42, 9263–9278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, I.; Yu, K. Wireless Positioning: Principles and Practice; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 225–239. ISBN 978-981-10-8791-2. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, K.; Guo, Y. Improved positioning algorithms for nonline-of-sight environments. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2008, 57, 2342–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, C.L.; Georgiou, O.; Yonezawa, Y.; Doi, Y. The wireless localization matching problem. IEEE Internet Things J. 2017, 4, 1312–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, J.; Rappaport, T.; Yoshida, S. Propagation measurements and models for wireless communications channels. IEEE Commun. Mag. 1995, 33, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, P.; Colombi, D.; Thors, B.; Larsson, L.; Törnevik, C. Output power levels of 4G user equipment and implications on realistic RF EMF exposure assessments. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 4545–4550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, A.; Valenzuela, R. A Statistical. Model for Indoor Multipath Propagation. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 1987, 5, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidel, S.; Rappaport, T. 914 MHz Path Loss Prediction Models for Indoor Wireless Communications in Multifloored Buildings. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1992, 40, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).