Abstract
The last two decades have witnessed a rich variety of indoor positioning and localization research. Starting with Microsoft Research pioneering the fingerprint approach based RADAR, MIT’s Cricket, and then moving towards beacon-based localization are few among many others. In parallel, researchers looked into other appealing and promising technologies like radio frequency identification, ultra-wideband, infrared, and visible light-based systems. However, the proliferation of smartphones over the past few years revolutionized and reshaped indoor localization towards new horizons. The deployment of MEMS sensors in modern smartphones have initiated new opportunities and challenges for the industry and academia alike. Additionally, the demands and potential of location-based services compelled the researchers to look into more robust, accurate, smartphone deployable, and context-aware location sensing. This study presents a comprehensive review of the approaches that make use of data from one or more sensors to estimate the user’s indoor location. By analyzing the approaches leveraged on smartphone sensors, it discusses the associated challenges of such approaches and points out the areas that need considerable research to overcome their limitations.
1. Introduction
The current decade is marked by the inception and vast expansion of modern mobile devices. A majority of these mobile devices are smartphones which are replacing personal computers today. Equipped with increased processing capabilities, such smartphones can perform more complex tasks than those of personal computers a few decades ago. The vast proliferation of modern smartphones resulted in the commencement of many new domains and applications including online marketing, on-the-go services, etc. Smartphone related time spent of the users comprises of social, business, shopping and finance applications [1,2]. Additionally, the Location Based Services (LBS) industry accelerated the expansion of smartphone usage as well. LBS utilize smartphones to provide customer services relevant to their current location. The user’s current location estimation is an imperative element upon which LBS pivot on. Outdoor positioning is served using many technologies like Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS), GPS, etc. However, GPS is the most widely used, as it has the potential to give very accurate location information of up to a few meters [3] in the outdoors. Despite that, the GPS positioning capacity is crippled in the indoor environment where its frequency is attenuated by a variety of physical barriers like roofs, walls, and other similar interference sources. The benefit of using GNNS is access to multiple satellites that can increase accuracy, redundancy, and availability of localization at all times. If Line of Sight (LOS) is obstructed, the data from multiple satellites can be utilized to compensate for the localization error. However, unlike GPS or GNSS which provide accurate outdoor localization, we do not have any indoor technology which is well demonstrated and established as a standard.
Modern smartphones are now provided with a variety of sensors that can be adapted for indoor location estimation. A significant research effort has been dedicated towards indoor localization during the last decade which emphasizes its importance and potential. A wide range of applications like finding shops inside a mall, desired items in a store, and locating the people working in emergency response need precise location information. Smartphones can help achieve the level of localization, these services require. In addition, other systems that establish a position using installed specialized hardware (like IR, RF tags, UWB, iBeacon, etc.) can get a refined localization. Such systems involve the expansive placement of infrastructure in the area where localization service needs to be provided. The positive side of such systems is that they can provide cm level accuracy. On the other hand, many systems can be founded on the subsisting infrastructure (like Wi-Fi) and benefit from Commercial-Off-The-Shelf (COTS) hardware to estimate the user’s indoor position. They mainly rely on the fingerprinting approach and offers an inexpensive solution to the localization problem. The current study aims at the following objectives
- A brief description of the embedded sensors of a smartphone, their usage concerning localization, and relevant challenges.
- A comprehensive overview of the localization approaches for each smartphone sensor, operational procedure, limitations, and prospective trends for future research.
- A discussion on the accuracy of the localization approaches that utilize smartphone sensors, probable solutions for enhancing the accuracy, and description of the associated challenges.
The current study is centralized on the description of the sensors present in the smartphone and how can they be leveraged to find the user’s current location. Section 2 provides a brief introduction of sensors deployed in a smartphone. Section 3 discusses the localization approaches which are developed on each of these sensors separately. It also gives an account of the current limitations of these approaches and discusses possible areas for future research. In the end, Section 4 provides discussions about localization approaches and conclusion.
2. Smartphone Sensors
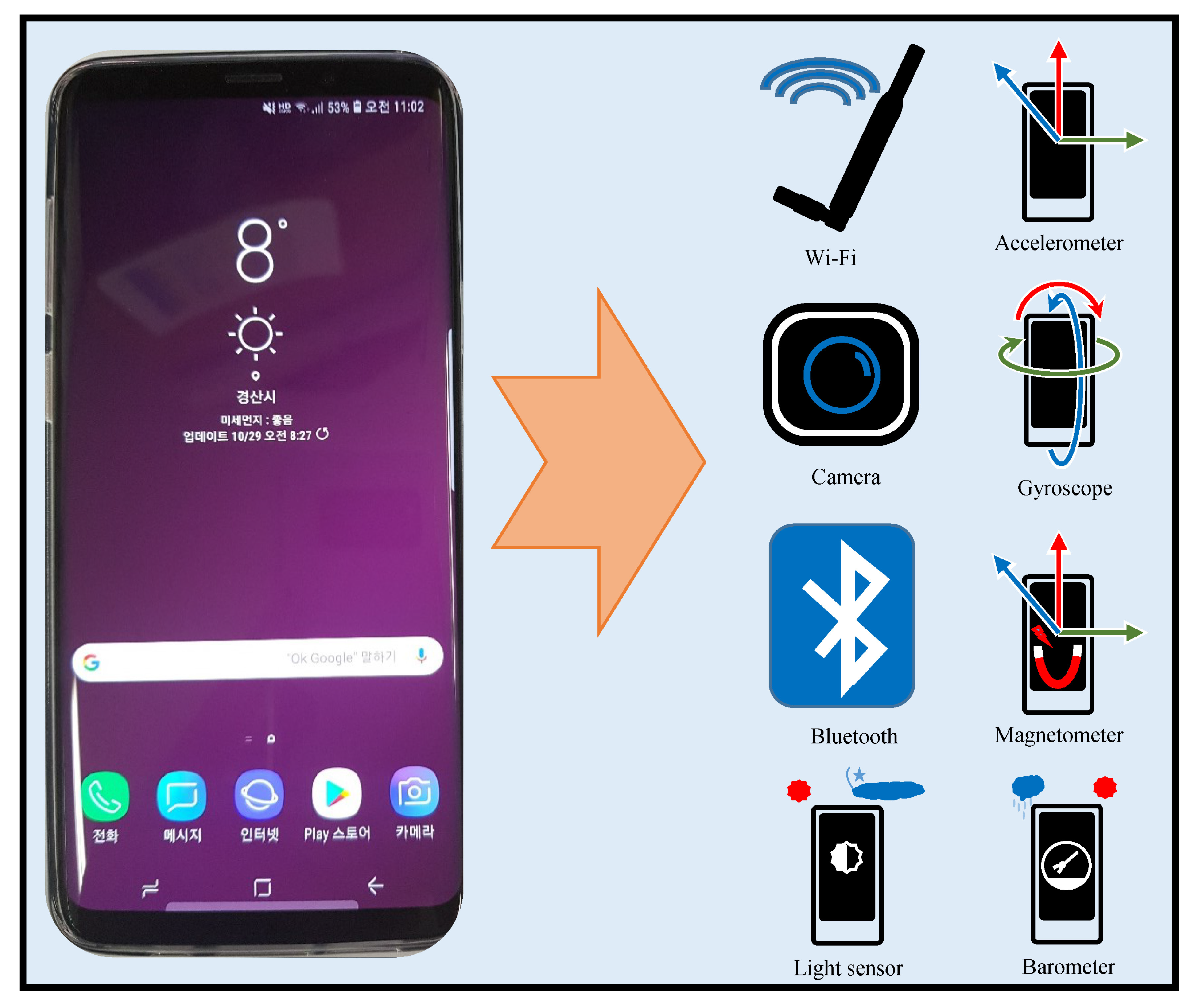
Modern smartphones are equipped with a variety of sensors including accelerometer, barometer, light sensor, etc. This section provides a brief description of sensors present in the smartphone with their importance to the localization problem. Figure 1 shows all the sensors present in modern smartphones.
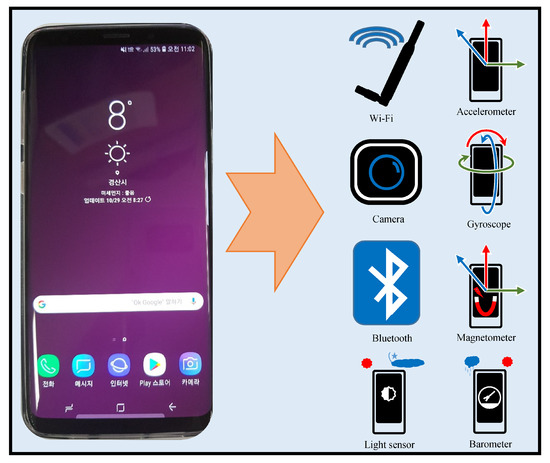
Figure 1.
Smartphone sensors embedded in modern smartphones.
Recent smartphones like Samsung Galaxy S10+, iPhone 11, etc. are provided with a 5G Wi-Fi gigabit transceiver which can implement IEEE 802.11 Wi-Fi standard. IEEE 802.11 is a Wi-Fi standard and represents a set of wireless standards developed by the IEEE LAN/MAN Standards Committee. Currently, this group contains six modulation techniques which follow the same protocol. Different parts of IEEE 802.11 standard have been presented over time like 802.11b, 802.11a, 802.11g, etc. for 1 to 6 GHz range and 802.11ad, 802.11ay, and 802.11aj for mmWave. The Wi-Fi sensor in the recent smartphones can implement 3-stream 802.11ac specification which enables speeds up to 1.3 Gb/s. A single-chip holds a dual-band transceiver that integrates the functional blocks including radio, baseband, and Media Access Control (MAC). They have a 256-QAM modulation scheme which increases the data transfer efficiency and possesses Low-Density Parity Check (LDPC) codes to increase the rate at the range. Android WifiManager Application Programming Interface (API) can provide information including Basic Services Support Identification (BSSID), Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI), state of the signal, etc. which can be used to formulate Radio Frequency (RF)-based database for localization.
The camera is another important sensor available in smartphones that can assist in may tasks including localization. Since the inception of CCD cameras in the 1990s, this technology has undergone a huge development. However, the big jump was made with the introduction of Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor (CMOS) sensor technology which paved the way for the low-cost and high volume camera phone market. The CMOS cameras are smaller in size, consume low power, possess lower sensitivity, and are appropriate to be used in small devices. Now CMOS has made its way into many areas including automotive and transport, medical systems, security and surveillance, and mobile phones especially. The smartphones are equipped with CMOS Backside illumination (BSI) cameras with new color filters which can do pixel isolation. These cameras possess High Dynamic Range (HDR), Extended Depth of Focus (eDoF), and Near IR Capability (NIR). Additionally, they can do the image stabilization using the Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS) based inertial systems present in the smartphones.
Bluetooth is another important sensor in smartphones which can be used for wireless Personal Area Networks (PAN). It is an industrial specification for wireless PANs also known as IEEE 802.15.1 Bluetooth makes it possible to connect and exchange information between different devices such as personal digital assistants (PDAs), mobile phones, etc. This communication is achieved via a secure, globally unlicensed short-range radio-frequency band. The Bluetooth communication is primarily based on low power consumption within a short range of 1 m to 100 m depending upon the power class and low-cost transceiver microchips.
The Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) consists of multiple sensors including accelerometer, gyroscope, light sensor, barometer, and magnetometer which are used to sense the inertial state of the smartphone. The accelerometer provides 3D digital readings of acceleration in m/s for x, y, and z directions [4]. An accelerometer is very helpful to determine the movements of a smartphone user. A gyroscope helps in determining the angular movement of a smartphone in x, y, and z directions. The gyroscope readings are given in radians/s and very helpful to determine the heading direction of a pedestrian. Accelerometer and gyroscope are often used together to get the short term location of a user. The magnetometer measures the ambient geomagnetic field value at a given point. It is used to determine the North and can help to remove discrepancies in the gyroscope readings. The smartphone’s magnetometer provides the magnetic value in x, y, and z directions which are further used to calculate inclination, declination, total horizontal intensity, and total magnetic intensity. The magnetometer is used along with the accelerometer to find the rotation vector of the smartphone as well. The barometer is an ultra-compact piezoresistive absolute pressure sensor and works as a digital output barometer. It comprises a sensing element and a communication interface. The sensing elements detect absolute pressure through a dedicated process. It works on an embedded First In First Out (FIFO) data output and provides 24-bit pressure data output [5]. The light sensor in the smartphone allows the accurate sensing of environment light in which the smartphone is currently operating. The latest light sensor package contains an integrated Ambient Light Sensing (ALS), proximity sensors, and IR LED which assist in proximity detection and light-sensing behind spectrally distorting materials [6]. These sensors can operate in a variety of environments including sunlight, night, and clouds. IMU sensors provided with the smartphones can operate between −40 °C to +85 °C and are becoming more accurate and reliable than before.
3. Application of Smartphone Sensor for Indoor Localization
3.1. Wi-Fi Localization
A growing research effort has been observed over the past few years in indoor localization techniques specifically the techniques that rely mainly on the in-building communication infrastructure (e.g., Wi-Fi) or the natural phenomenon (e.g., geomagnetism). The predominant techniques in this category operate on the fingerprinting technique. The fingerprinting technique leverages already available infrastructure but involves a laborious effort to construct the radio map during the training phase. The main contribution of the fingerprinting technique is the easy and inexpensive deployment for localization. It is low-cost because Wi-Fi communications are ubiquitous especially after large and dense deployment of Wi-Fi Access Points (APs) in buildings and the vast proliferation of smartphones over the past few years. Thereupon, a lot of research efforts are put in the same course for better and more stable accuracy results.
Wi-Fi-based localization systems have been researched extensively for the last few decades. Starting from Microsoft Research pioneering the fingerprint approach based RADAR, it led to the development of many similar systems which aim to solve positioning and localization problem. Two techniques broadly known as multilateration and fingerprinting are utilized in Wi-Fi-based indoor localization. Various fundamental wireless positioning techniques are explained in this regard. The concept of multilateration or trilateration is to use the signal strength transmitted by the APs to estimate the position of the receiving device. Time of Arrival (TOA) [7,8], Time Difference of Arrival (TDOA) [9,10], Angle of Arrival (AOA) [11,12], and their extended forms [13,14,15] are used for this purpose. The downside of such techniques is the low accuracy, and high energy consumption.
The fingerprinting techniques are simple and easily adaptable for smartphones and offer an average accuracy of 2 to 3 m without the need to install and configure expensive hardware. However, this accuracy is lower in comparison to those offered by Firefly, OPTOTRAK, Sonitor, and similar other commercially available systems which although expensive, offer a cm level accuracy. We focus here on Wi-Fi systems that use location fingerprinting as the backbone of the localization system.
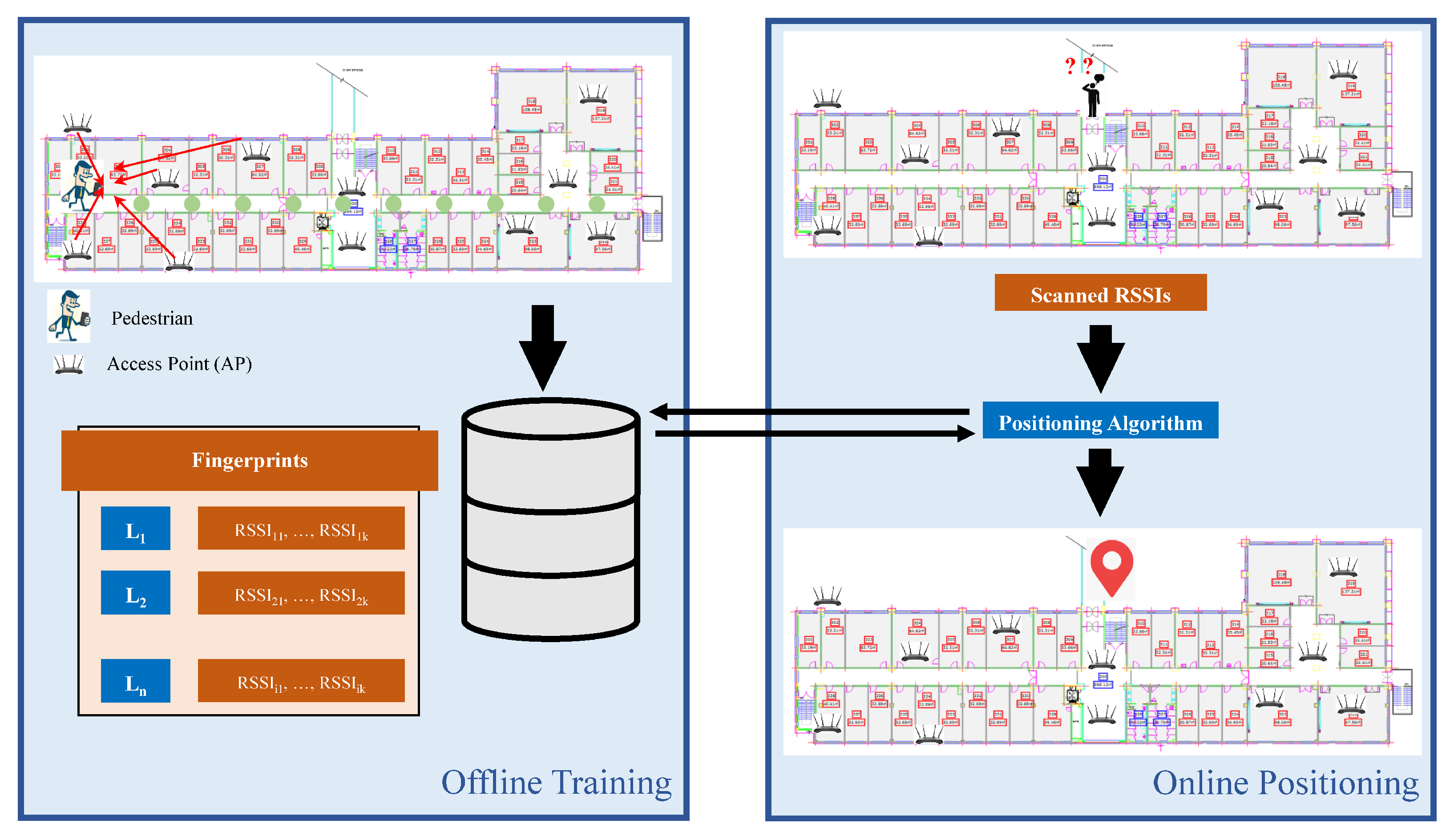
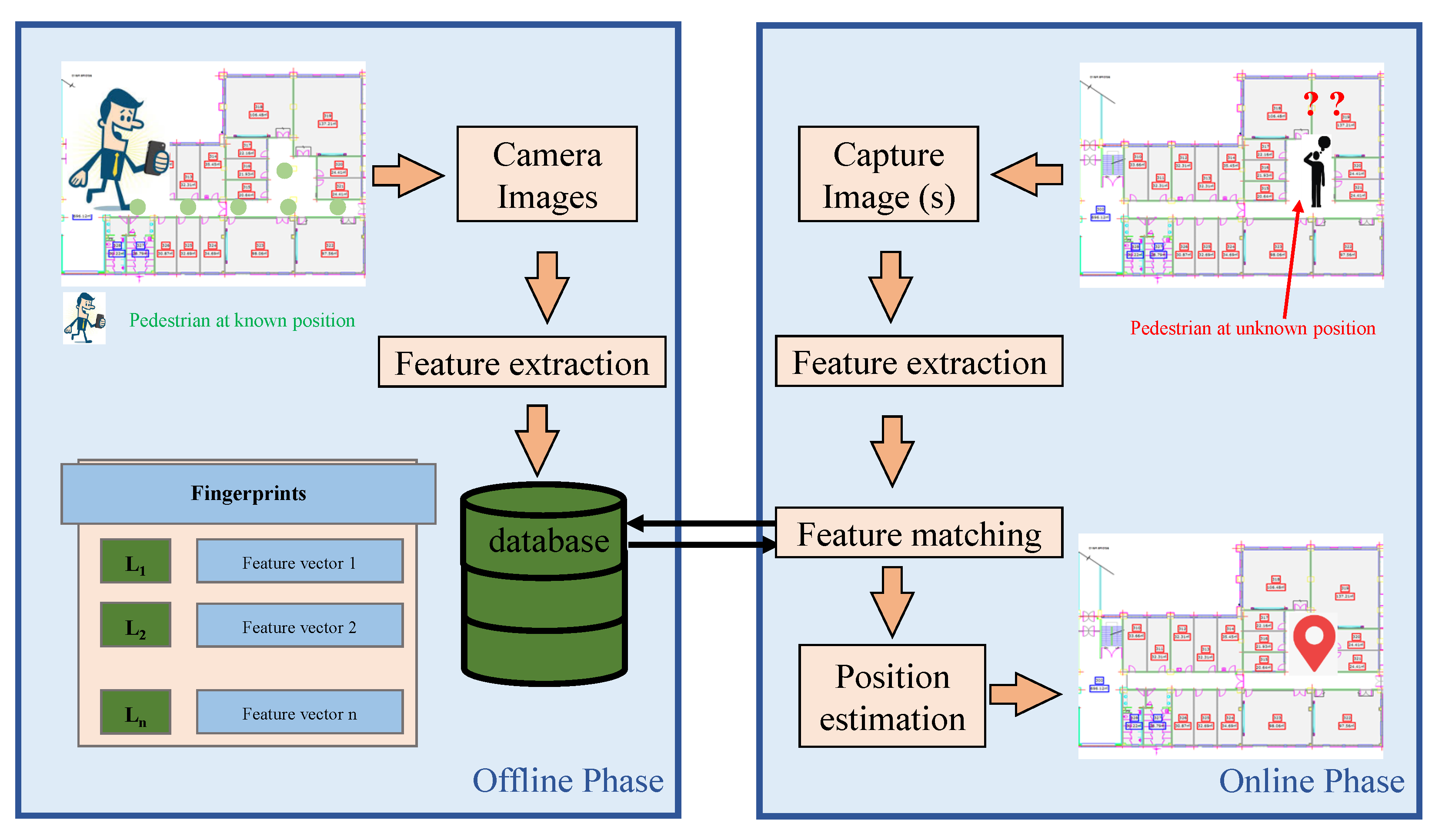
Microsoft RADAR [16] pioneered the idea of fingerprinting to utilize the Wi-Fi communications infrastructure for localization. After that, it has been investigated, refined, and used in many positioning systems [17,18,19]. Figure 2 shows the architecture of a Wi-Fi based indoor positioning system that is based on the fingerprinting approach. The fingerprinting can further be classified into two approaches: deterministic fingerprinting and probabilistic fingerprinting [18,20]. Location fingerprinting utilizes already available infrastructure, yet, involves tiresomely effort to build the fingerprint during the training phase. During this offline training phase, a radio map of the environment is built which involves measuring RSSI values at indexed locations. Multiple RSSI readings at fixed points are taken and then averaged RSSI for each scanned AP are stored with AP names and indexed locations. In addition to RSSI, other finger representations have also been investigated including Gaussian model [21,22] histogram [23,24] of an RSS and other complex distributions [18,25]. One difficulty in using an RSSI as the fingerprint is its varying magnitude from various phones for the same location. Consequently, other fingerprint variations including Received Signal Strength (RSS) [26], Hyperbolic Location Fingerprinting (HLF) [27], DIFF [28], an ordered sequence of RSSIs [29] have been proposed as well. The use of Wi-Fi APs coverage area to mitigate the impact of RSS change over time is reported as well in [30].
Figure 2.
Architecture of a Wi-Fi based indoor positioning system that is based on fingerprinting approach.
The online phase involves the collection of RSSI from the user’s devices and sending it to a server (or process locally) to match it with the pre-built fingerprint database. The matching process may involve simple matching techniques like distance measurement with Euclidean, Manhattan distance, cross-correlation, etc. However, Nearest Neighbor (NN) and its other variants like KNN and weighted KNN are quite popular as well [31,32]. Additionally, Maximum Likelihood Estimator (MLE) [33], machine learning techniques [34,35], and neural networks [36,37] have been applied as well. The probabilistic fingerprinting considers that storing the simple average of RSS values causes errors in position estimation. Instead, it is more logical to store the joint distribution of RSS samples as a fingerprint. The earliest work on the probabilistic approach was proposed by [38]. Once the fingerprint is made, the position which has a higher probability of resulting in the observed RSS vector is considered as the estimated position. Bayes’s rule is utilized for this purpose.
Current Challenges and Future Directions
Location fingerprinting is laborious and time-consuming. It becomes tiresomely, especially within huge buildings with tens of floors. The current accuracy of 2 m to 3 m offered by fingerprinting-based Wi-Fi systems is not sufficient enough for indoor LBS. One underlying assumption of such systems is that similar wireless conditions pertain during training and positioning phases which is hardly practical. The data collection and online location estimation circumstances may change drastically due to dynamic factors including the movement of heavy furniture. It is observed that the movement of people affects the accuracy of Wi-Fi systems immensely especially at airports, train stations, and similar other places with frequent and large movements. Signal’s absorption, fading, and multipath due to movement of other machinery at airports have a similar effect. The fingerprint databases need to be updated periodically to compensate for the impact of signal loss over time and signal change due to internal infrastructure. One future direction to mitigate such effects is the utilization of the Internet of Things (IoT) sensors that can be placed at fixed points to monitor APs and update the fingerprint database after a specified time. This way, the database never outdates and the impact of dynamic factors can also be handled. Another possibility is to use crowdsourcing for updating the database after a specified time. However, it has a few relevant issues to be investigated first. Crowdsourcing involves heterogeneous devices with different WLAN capacities which results in varying RSSI for the same place. Moreover, samples are collected with different phone orientations and in different directions which also affects RSSI value. Crowdsourcing with other sensors including gyroscope to estimate the relevant orientation would be a better choice. Throughput and latency are still not resolved for Wi-Fi-based positioning. When scanning Wi-Fi APs, a mobile device spends a considerable time scanning all APs which may be up to 100 in a university while it can go to a few hundred at airports. The longer scanning time increases latency and reduces accuracy too. With the introduction of 5G, new possibilities and directions can also be investigated to increase current accuracy as well.
3.2. Pedestrian Dead Reckoning
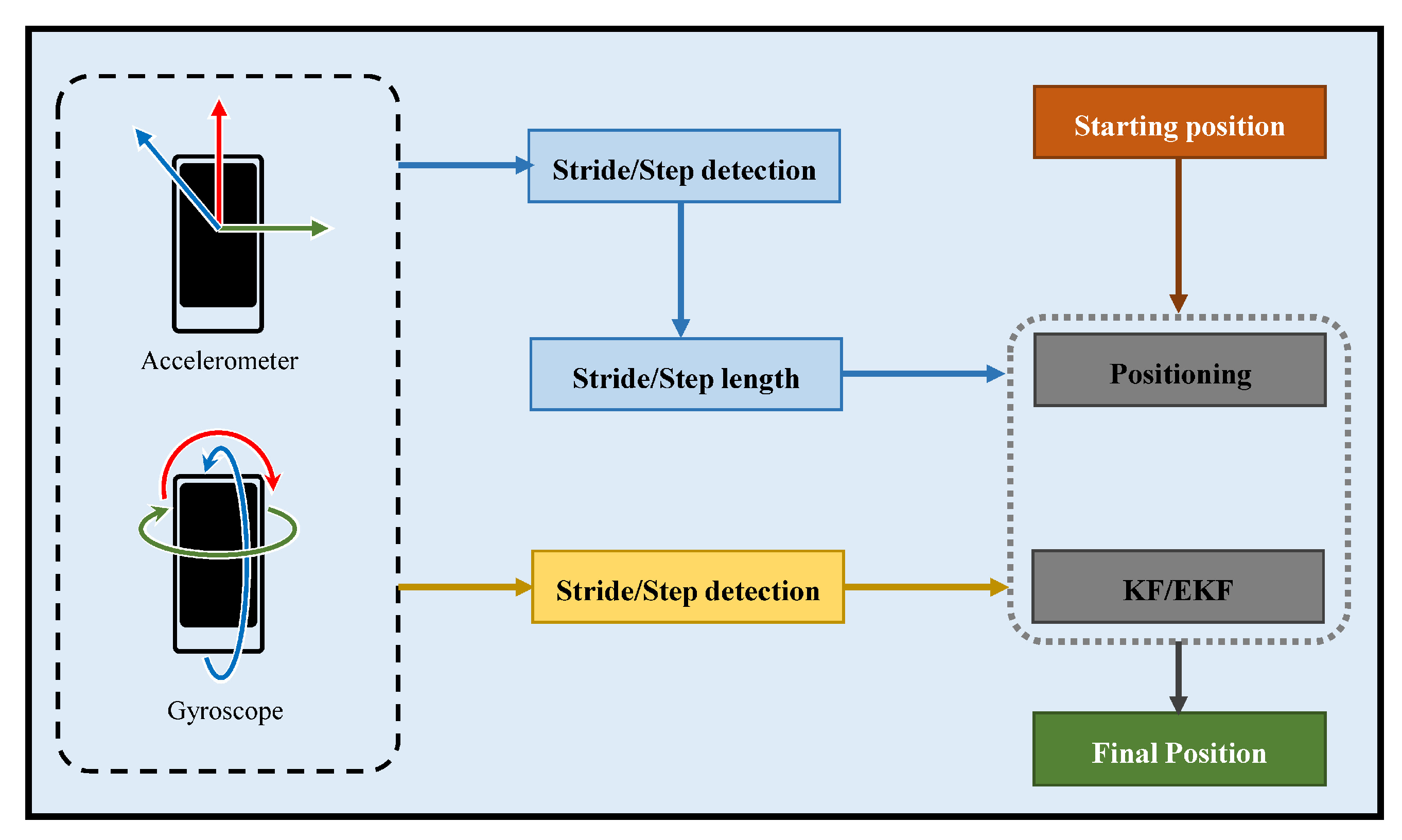
During the recent few years, we have seen a wide proliferation of smartphones that are equipped with a variety of sensors. These MEMS sensors have become very small in size yet inexpensive and more reliable to enable the tracking of the smartphone carrying individuals. The original challenge is now to manipulate these sensors to devise tracking systems that can provide reliable and robust location information like GPS does outdoors. The ubiquitous deployment of smartphone sensors has paved the way to utilize the Dead Reckoning (DR) using smartphones. The term DR is derived from “Deduced Reckoning” which is used to approximate the pedestrian’s relative position against a definite location which means that it estimates the change from the last known position. It infers that the Pedestrian Dead Reckoning (PDR) systems do not require any infrastructure to be installed in the indoor environment which makes it a very befitting solution for indoor localization. Instead, the inertial sensors like accelerometer, magnetometer, gyroscopes, etc. can be used as input devices to PDR systems. Figure 3 shows the architecture of a typical PDR based indoor positioning system.
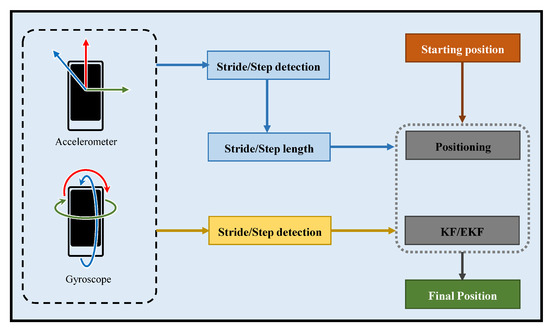
Figure 3.
The working architecture of pedestrian dead reckoning.
The PDR systems are categorized into two types: Inertial Navigation Systems (INS) and Step and Heading Systems (SHS) [39]. An INS usually trails the location of an individual by considering 3D trajectory information at a given time. This technique uses the measurements provided by the accelerometers and gyroscopes to track the position, orientation, and velocity of a moving object concerning its start/previous position. INSs are used to track a variety of objects including airplanes, missiles, space ships, vehicles, etc. An SHS on the other hand, is specifically related to the pedestrians and calculates the position by the change in the distance and heading with the help of steps. The working cycle of an SHS system includes three phases:
- The detection of a step/stride in a given data set,
- The calculation of the step length,
- The estimation of the heading of the detected step.
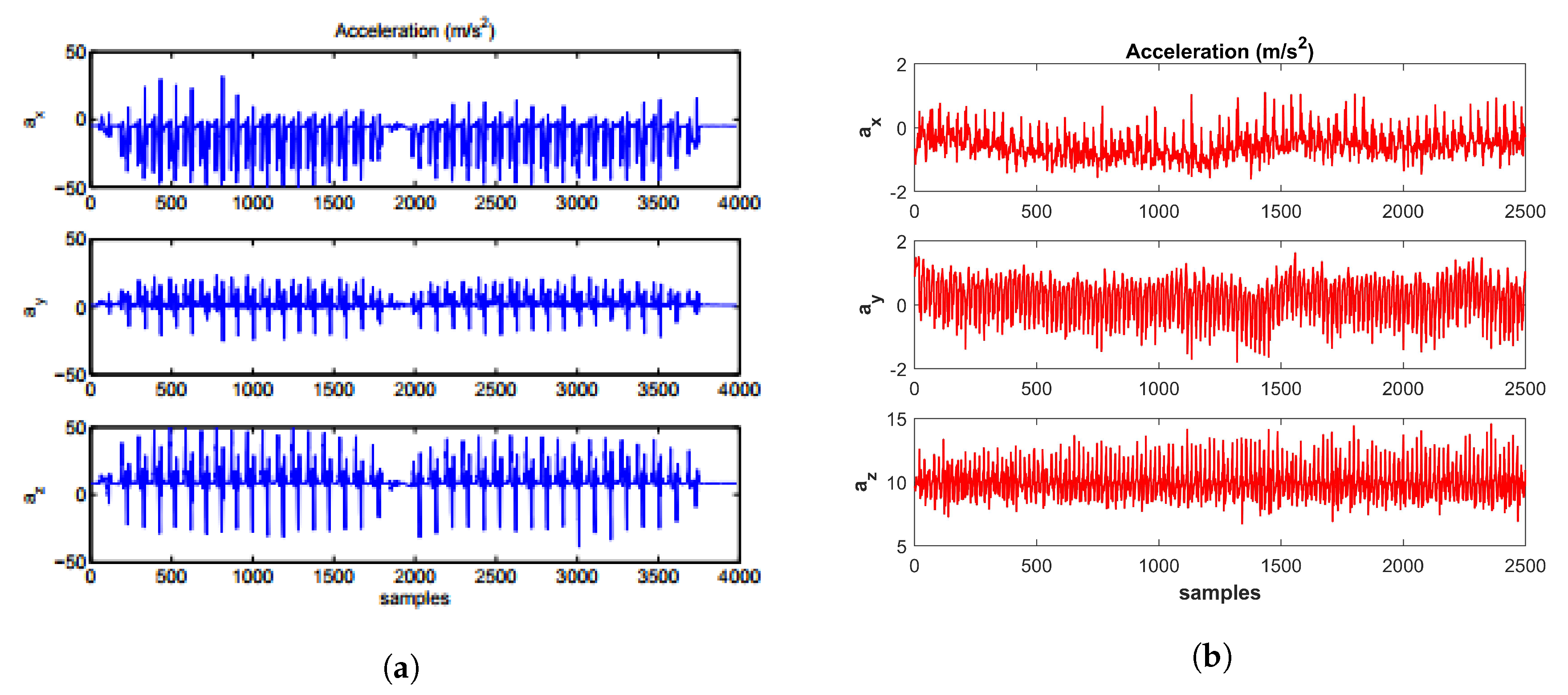
Although, many step detection techniques including particle filters [40,41] and zero velocity detectors [42] are used, however, the thresholding-based methods are most common in practice. Many algorithms which utilize the thresholding technique on accelerometer [43,44,45,46,47] and gyroscope [48,49,50,51] or both [52] exist in literature. In addition, magnetometer thresholding for step detection has also been tried and reported [53,54]. These methods are reported to have good results and show errors of 0.1% for accelerometer and 0.2% for gyroscope [53]. These results are, however, for SHS systems which are based on foot-mounted or waist belt striped systems and assume that at least one of the feet is striking on the ground. In such cases, it is easy to detect steps as the sensors’ data is very smooth as shown in Figure 4a.
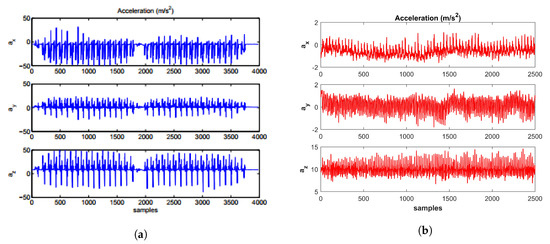
Figure 4.
Acceleration data from the Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU), (a) foot mounted [53], (b) smartphone.
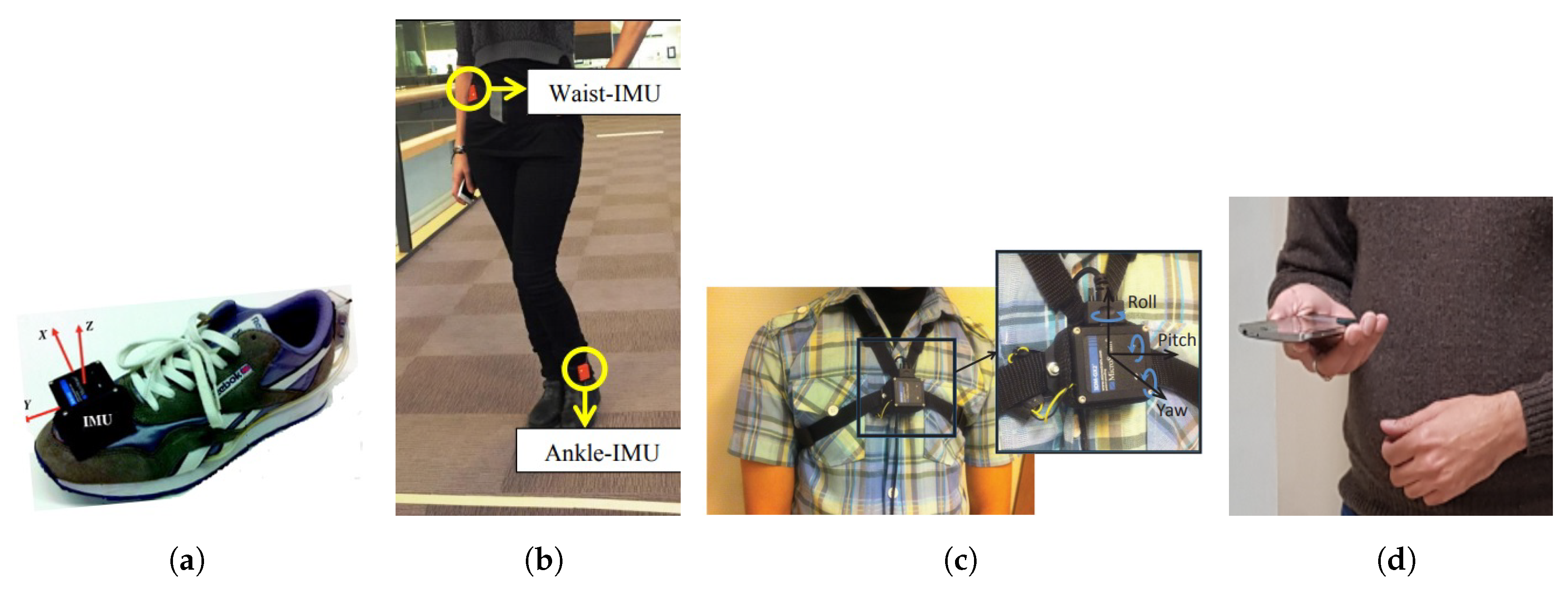
The SHS, which utilizes the smartphone sensors, does not comply with such assumptions. Since the pedestrian holds the smartphone in his hand, the sensor’s data is not smooth due to handshaking or the jitter caused by walking as shown in Figure 4b. In addition, there are no zero velocity cases like that of foot mounted SHS systems. With the smartphone, the pedestrian movements are more complex and users changing the orientation of the smartphone makes the step detection further difficult. The peak detection from accelerometer data is the most viable option and has been reported to generate good results [55,56,57,58]. Figure 5 shows the various positions where IMU is mounted in PDR systems [53,59,60].
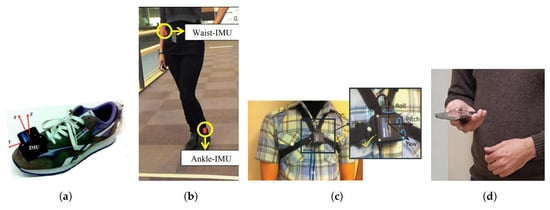
Figure 5.
Examples of IMU placement, (a) foot mounted [44], (b) waist and ankel mounted [59], (c) chest hung [60], and (d) smartphone embedded.
From the above-mentioned PDR system, the body-mounted sensors packages where the user mounts the sensors on foot or leg or ankle are easy and show very good performance in terms of both step detection and orientation measurement. Such deployments are easy and simplify the interpretation of data, yet not very practical by nature. The convenience lies in the fact that the attitude of the sensors is fixed and the transformation from the body sensor is constant and well known. Its practicality is questioned as the mounted sensors cannot remain on the body every time and they hinder the user’s other activities of work.
Contrary to mounted packages, the PDR systems which utilize smartphone are very practical, though complicated and difficult. Since the user attitude with the smartphone cannot be predicted, it is very difficult to cope with such situations. Moreover, the movements of the sensor in 3D fashion makes the sensor integration more difficult. Body-mounted packages show higher accuracy of positioning than that of systems that depend on smartphone sensors. Despite that, the PDR systems cannot function alone to determine the precise location of the pedestrian owing to many inherent limitations. First, since PDR systems need the starting/initial position at time to estimate the location at , this means that the error in the estimation of the starting position is inherent and cannot be compensated with later calculations unless we have other location correction measures. Periodic WiFi positioning after a few seconds to correct the PDR is often used to overcome this issue. Second, the location estimation is the iterative process and the error in localization accumulates over time. If the indoor path is long and straight, the user may deviate 5 to 10 m from the actual position after a few minutes. This error, however, can be mitigated using the environmental knowledge [61], map matching [62], or similar other techniques. Although the addition of other location correcting techniques can improve the localization accuracy, it may introduce some cost and infrastructure dependency as well.
Current Challenges and Future Directions
Pedestrian tracking based on accelerometer and gyroscope data facilitates continuous localization in the indoor environment, however, the drift/error is accumulated over time [63]. The foot and body-mounted PDR systems have shown good performance as the movements are smooth and controlled. However, PDR systems which utilize the smartphones are more vulnerable and show poor performance in complex environments. Most systems necessitate the user to hand-hold the smartphone in a navigation mode which is not very practical [39,64]. Such restrictions, however, prove to be more accurate in location estimation.
Most of the experiments for smartphone-based PDR are performed in simple indoor environments like university campuses and labs where the paths are somewhat straight with few turns. It shows better localization accuracy of PDR-based techniques. In real-life scenarios, on the other hand, the indoor environment is more complex like in the shopping malls where their efficacy is affected by many factors [65]. First of all, the navigation environment is complex and includes short spaces and more turns. Secondly, due to the dynamic and frequent movements of people, the pedestrians have to move quickly into various directions which can make smartphone sensors’ data noisy. Thirdly, although PDR systems show good performance in some scenarios, yet the complex walking styles of users severely affects their accuracy. Multifarious user movements make it very hard to perform localization. Additionally, slight errors in the PDR system results in error accrual over time and a major concern for their real-life implementation. Often they are corrected by opportunistic Wi-Fi localization to mitigate the error. Another possibility is to use map information of the building to reduce the error [66]. However, the map information of every building may not be available in many cases which poses an extra challenge. Research on the identification of user actions has also been underway [67] where first a user’s action is identified and then a PDR relevant to that action is applied. However, this task is complicated as well as time-consuming. Moreover, it is not possible to define and identify all the possible actions of a user and in many situations an action cannot be associated with a particular class as well.
3.3. Geomagnetic Indoor Localization
Regardless of the localization accuracy of the infrastructure-based systems like RF tags [68], Bluetooth beacon [69], ultrasound [70,71], etc., their infrastructure installation cost and systems dependency necessitated the exploration of other alternatives which are comparatively less accurate yet infrastructure-free and simple. This demand led the researchers to investigate the discipline of the magnetic field as various animals are reported to follow the earth’s magnetic field for navigation [72,73,74,75]. Animals like sea turtles, lobsters, and pigeons can sense the direction using a magnetic field when navigating to their homes.
The Earth’s geomagnetic field is the omnipresent phenomenon extending from the earth’s interior until it catches the solar wind. The magnitude of the earth’s magnetic field varies geographically from 25 Tesla to 65 Tesla. During the last few years, geomagnetism has enticed an ample consideration for indoor localization primarily because of its pervasiveness and secondly due to its infrastructure independence. Two different attributes of geomagnetism are discussed in the literature regarding its use for localization: magnetic field strength and magnetic flux density. They are represented by H and B and calculated in amps per meter (A/m) and Teslas (Tesla or G, 1T = 10 G), respectively.
The Earth’s magnetic field strength is uniform and does not commute abruptly over a small area of a few meters. However, the presence of ferromagnetic materials including steel-reinforced concrete, metallic doors, pillars, or steel walls interfere with the natural magnetic field and introduce disturbances also called anomalies [76,77]. Additionally, electric power lines and appliances are also reported to sway the geomagnetic field [78]. Such anomalies can be captured using a magnetometer and can serve as signatures/fingerprints to identify various locations [79]. The magnetic influences can be measured using a separate magnetometer or a smartphone built-in magnetometer. Traditionally, two types of magnetometers are used to capture the magnetic field: vector magnetometers and total field magnetometers [80]. The former measures a single component which contains , , and while the latter measures only the magnetic magnitude and no direction. The captured signatures are stored in the database as a unique fingerprint for each indexed location and later used to identify the location by matching against the user sent magnetic measurements. Both the natural magnetic field as well as the artificially generated magnetic fields are reported to be used for localization [81]. A pre-deployed artificially generated magnetic field using the electric coils is used for localization [82,83] via the traditional trilateration or proximity detection [84].
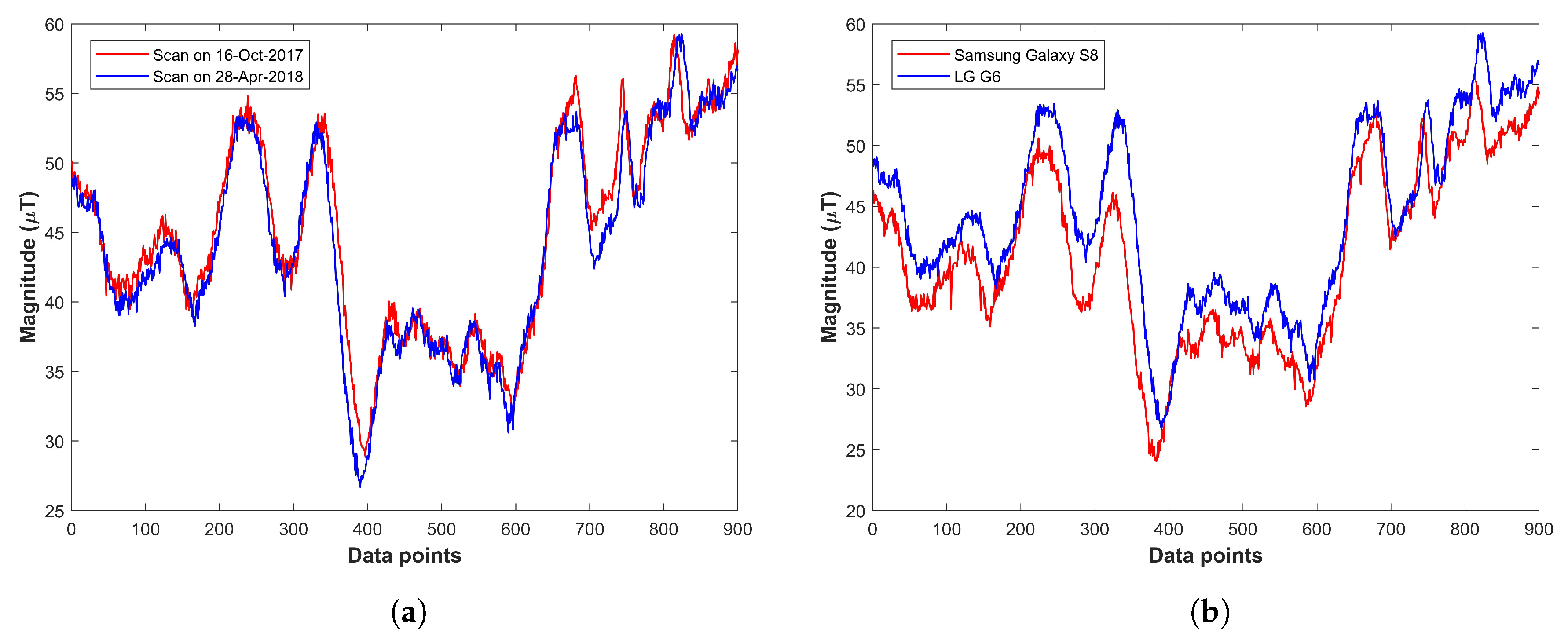
A good signature/fingerprint of a location must possess two essential characteristics: spatial differentiation and temporal stability [85,86]. A large body of research work can be found that studies the feasibility of using a geomagnetic field for localization [79,87]. This research demonstrates that the magnetic field exhibits discernible spatial variation and temporal stable deviations that can serve as location signatures [77,88]. Similarly, research works [58,78] study the long-term behavior of the magnetic field by analyzing the changes over months and validate that temporal stability has very fewer mutations over time and the magnetic field is stable as shown in Figure 6a.
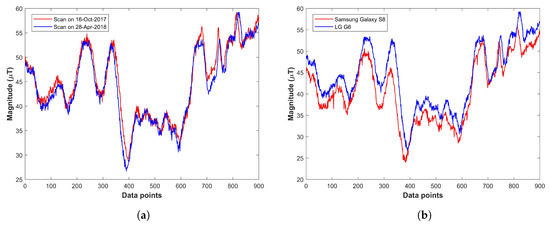
Figure 6.
Magnetic field attitude over various time and smartphones, (a) on different dates with the same smartphone, (b) various smartphones at the same time.
Despite being pervasive, inexpensive, infrastructure-independent, and stable over time, the magnetic field has numerous inherent challenges we need to investigate before it can serve as a standardized indoor localization technology. The magnetic field experiences sudden temporal changes while walking between metallic objects like moving elevators. The moving vehicles close by also affects its attitude likewise. This effect mainly depends upon the size of the moving metallic object and its distance from the observer.
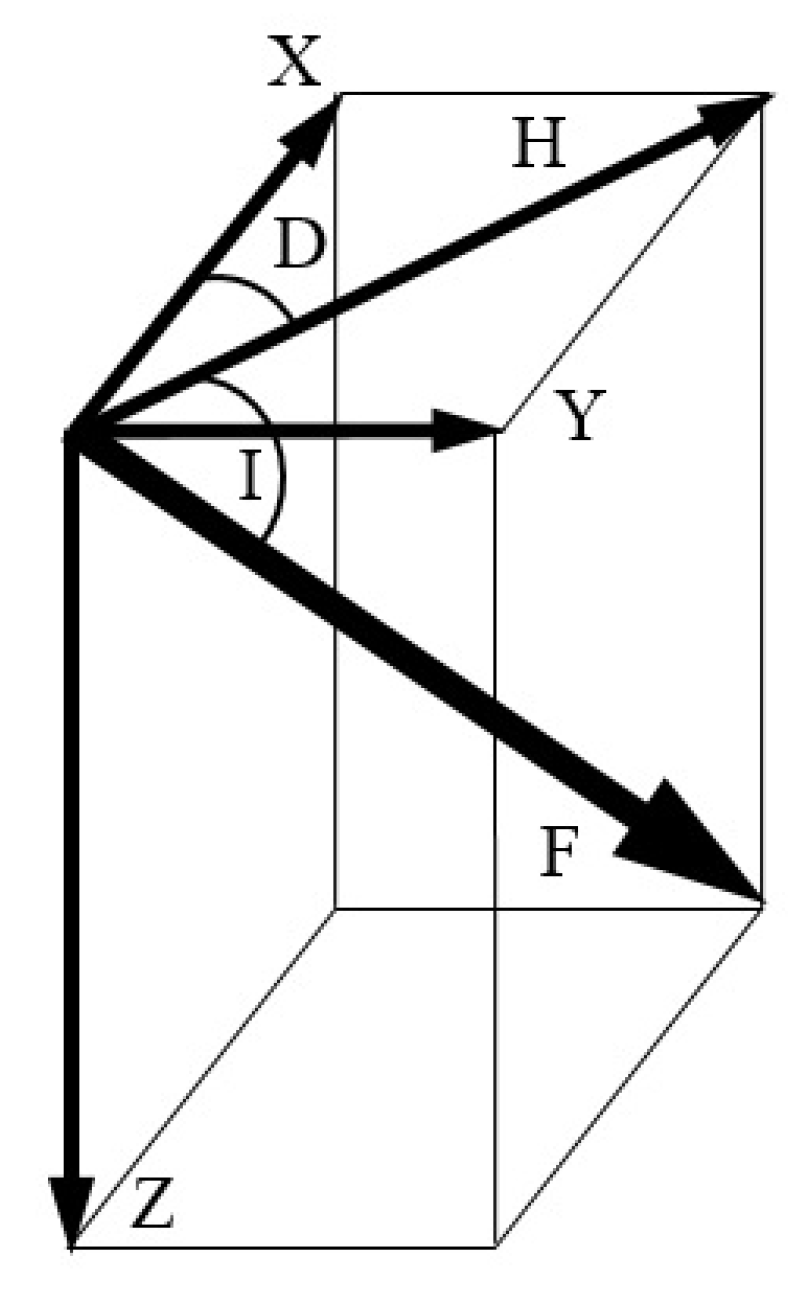
Another challenge is the varying measurement readings as shown in Figure 6b. Use of various magnetometers or various smartphones leads to device dependency. Most studies use device calibration to cope with device dependency [78,89]. Offline calibration also helps to mitigate device heterogeneity. Recent studies [90] also focus to use the sequential measurements instead of taking absolute values as the fingerprints. A different approach is to leverage the patterns formed by the magnetic field strength to use a unique signature for each location. The pattern matching technique has already been tested in a few studies [58,78,91,92] and proves to be more accurate than the raw values. The use of magnetic patterns from multiple smartphones is reported in [93] to provide higher accuracy than that of using the magnetic field data from a single smartphone. In addition to device dependency, another problem that needs attention is the varying geomagnetic readings at the same place even by the same smartphone. The nearby metallic objects pose a soft iron effect threat which may lead to these deviations for the mobile devices, so we need to perform the calibration for each environment we intend to use the mobile device in. The compass swinging calibration is widely used for such calibration where the smartphone is rotated around three orientations [94]. One basic approach to use geomagnetism for indoor localization is through the fingerprinting database approach. Although three kinds of magnetic field values are used to build the fingerprint database including 3D vector readings, magnetic field magnitude, and horizontal and vertical magnitudes, the latter two are the most frequent. The geomagnetic field is comprised of seven components in total as shown in Figure 7. The X, Y, and Z show the magnetic field components for North, South, and vertical intensities, while H is the total horizontal intensity and F represents the total intensity or magnitude of the magnetic field at a given point. The D and I are measured in degrees and they represent the declination and inclination respectively.
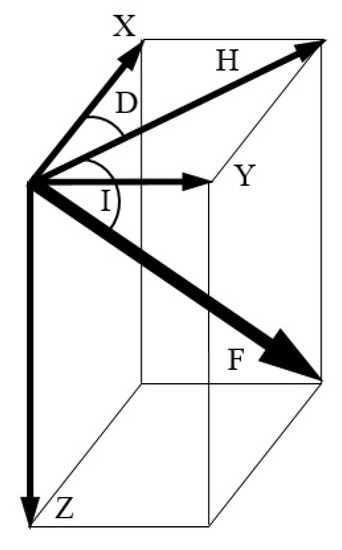
Figure 7.
The components of magnetic field.
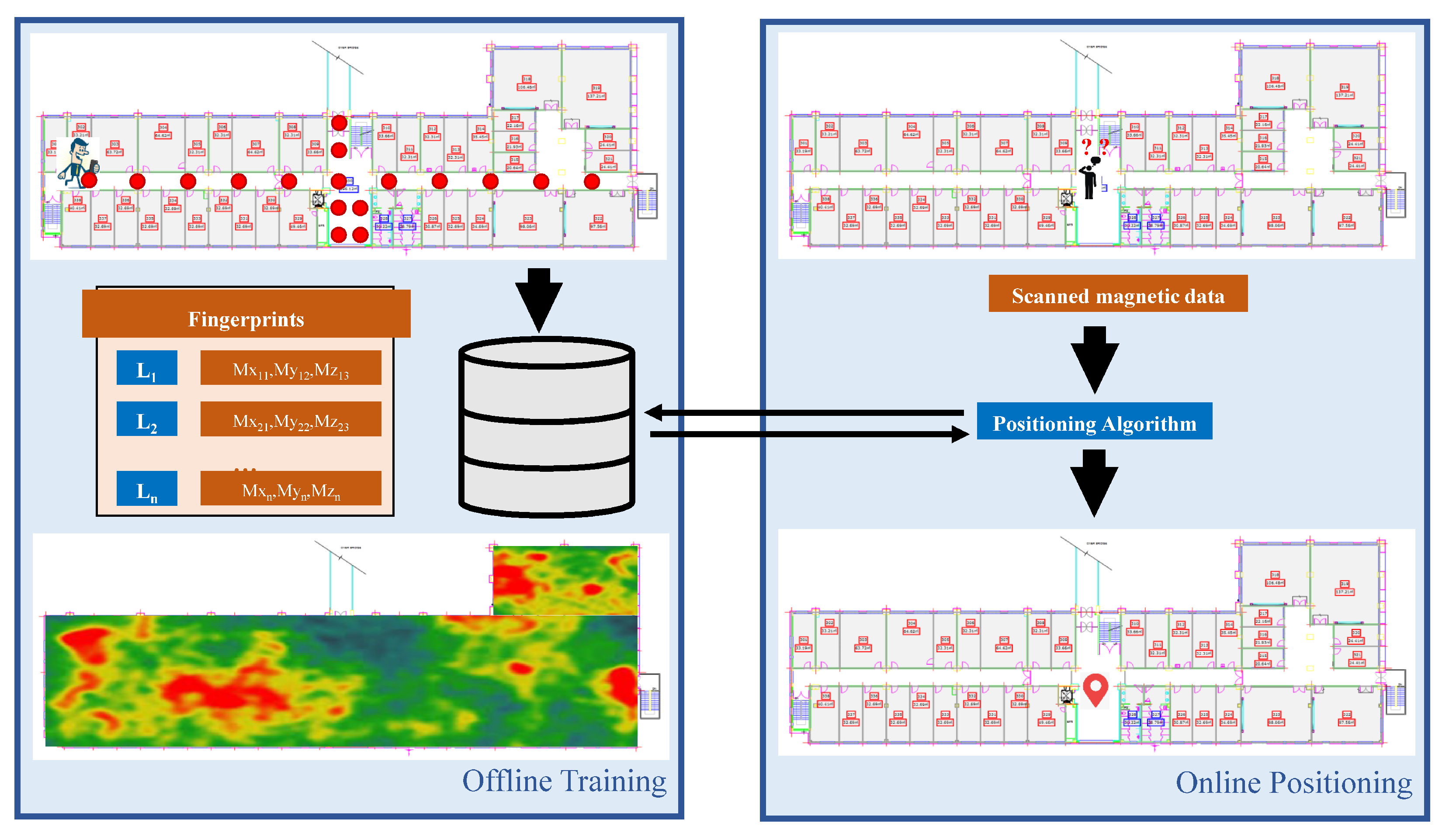
The magnetic field data-based fingerprinting localization systems work analogous to Wi-Fi-based systems. However, the fingerprint database making approach is different. Figure 8 shows the architecture of a typical magnetic field data-based fingerprint approach for positioning. The magnetic fingerprint database can be prepared by either taking continuous scans of the intended area of localization or dividing the area into equally spaced grids and taking samples at each grid point. Both techniques involve several samples and then storing the normalized values of each point. Grid-based fingerprinting has less labor as compared to continuous scans. The change in phone orientation results in the various magnitude of the magnetic sample, so, traditionally the normalized total magnetic intensity is stored as a fingerprint. Research [95] used 3D readings of the magnetic field for localization however using 3D readings is convenient for localization of a robot due to its fixed orientation, but the smartphone encounters variations in its orientation during navigation, hence, the use of 3D readings in smartphone localization is complicated. One solution though is to work with a fixed orientation where the pedestrian can change the x plane (directions) but not y and z planes. Alternatively, the coordinate transformation can also be performed from smartphone to earth coordinate systems which are however error-prone and difficult [96].
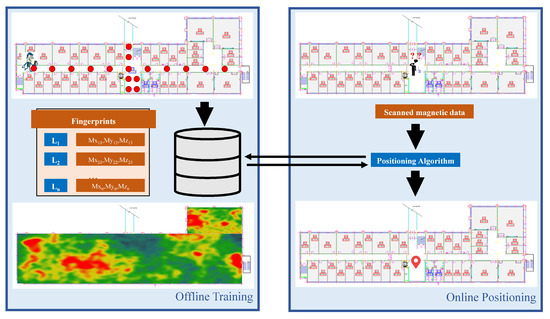
Figure 8.
The architecture of a magnetic localization system.
Even so, the use of magnetic field magnitude |B| is more suitable for the fingerprint database instead of using the 3D vector [77] and is used in recent research works [89,97]. This is not advantageous over 3D readings because of less dimensionality and proves to be less accurate as a consequence. Yet, it can serve as a complementary measure with other systems like WiFi systems to enhance the accuracy of such systems [86]. Another fingerprint is to take into account the horizontal and vertical components, as it is reported [79] that it provides more positional features than the magnitude alone. However, it requires the orientation information of the smartphone, and the gravity readings must be considered as they may influence these components. In the same vein, other studies consider the use of international geomagnetic reference field (IGRF) as a fingerprint which includes the magnitude, horizontal component, and inclination angle [98,99]. Apart from fingerprinting approaches, various filters including particle filters and machine learning approaches are used as well to perform localization with the magnetic field data [100,101].
Current Challenges and Future Directions
Magnetic field data gathering and making the magnetic map is the key part in the magnetic field-based indoor localization systems. However, this process can easily be affected due to many factors. First, the proximity of ferromagnetic materials like iron and nickel may lead to anomalous readings. Second, device calibration plays an important role during the map-making part. If the device is not calibrated, the collected magnetic data can be different than when the devices are calibrated [102,103]. It is important to mention that device calibration involves orientation calibration as well. MEMS-based smartphone sensors can easily be uncalibrated by the proximity of magnets and close placements of multiple smartphones. One of the biggest challenges in magnetic field-based localization is the signal map construction, for which the wardriving is utilized. Although several techniques [104,105,106] including crowdsourcing have been proposed, the efficacy of such solutions is limited. One reason is the diverse nature of the devices used to build the map. The magnetic data collected from various mobile devices is different depending upon the quality, and sensitivity of the sensors used in the devices. The MEMS sensors deployed in mobile devices are sensitive and can easily get noisy. The same mobile device may behave very differently during a different time of data collection [58,78]. Similarly, the locations from where the magnetic data is crowdsourced needs to be annotated. The annotations can be done by the user (active fingerprint crowdsourcing) or by exploiting smartphone built-in sensors (passive fingerprint crowdsourcing) [107]. The location inference can be inaccurate/wrong due to non-professional surveyors collecting the magnetic data. Another critical limitation of the magnetic field is its low dimensional/resolution data. Traditionally, the total magnetic intensity is used to make the magnetic map. Several studies, however, have tried to use the magnetic field intensity in x, y, and z directions. This, in turn, puts the limit to the device orientation. Hybrid techniques including inertial measurement and Wi-Fi have also been worked upon which can refine the position estimation. These techniques, on the other hand, have limitations of their own.
3.4. Camera Based Localization
The upsurge of smartphones during the last few years initiated many new possibilities for indoor localization primarily due to the availability of a wide range of smartphone embedded sensors that can be exploited to record a variety of data. The smartphone’s ability to transmit the captured images imparts the feasibility of utilizing the camera for localization. The robot localization using vision camera in Artificial Intelligence (AI) has been performed for quite a long time and vision is a well-studied field as well [108,109,110,111,112,113,114]. The adaptation of camera for localization of individuals bearing smartphones is no surprise. The images can be captured and sent to the server by individuals using a smartphone just like the robots do. We divide the vision-based research into two broad categories concerning indoor localization: cameras used for tagged objects and smartphone camera for scene capturing. Many research works are presented which make the use of physical objects tagged with visual codes [115,116,117,118,119]. Such objects, when scanned with the camera, provide the information stored including the location information as well [120].
The smartphone camera-based indoor localization is a very promising approach as discussed in [121]. Since the smartphone camera can capture good quality images, these images can be used for visual location recognition. Contrary to other approaches like WiFi, RFID, etc. it does not require the addition of expensive infrastructure installment. Predominantly, smartphone camera-based localization is based on the fingerprinting technique where during the offline phase images from reference points are captured to make the database. Images require a substantial amount of space to be kept on the computer, so various features like edges, corners, blobs, ridges, etc., are extracted from images and stored as the database. Figure 9 shows an example of a traditional smartphone camera-based localization approach.
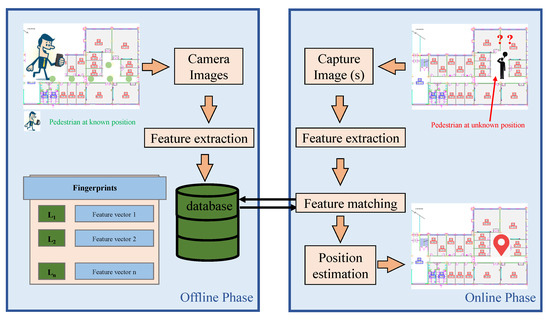
Figure 9.
The architecture of a smartphone camera-based localization system.
Localization methods that perform image analysis rely on the scene analysis captured by the smartphone camera. Such methods consist of four main stages [122]
- The First step is image acquisition using the smartphone camera.
- The acquired image is segmented to extract features.
- Finding the closest match of extracted features against the database features.
Once an image is captured from the user, feature extraction takes place as a precursor to the matching process. Feature extraction involves the processing of an image using mathematical formulation to extract a set of numerical values that can uniquely describe an image. Often image histograms, edges, blobs, and their spatial relationship can represent an image [122,123]. The selection of efficient feature extraction technique and an appropriate feature matching measure serves as the basic components of a good vision-based localization system. Image matching is the process where the similarity between two images is computed. A large variety of image matching techniques have been proposed including Scale Invariant Feature Transform (SIFT) [124], Speed up Robust Feature (SURF) [125], Binary Robust Independent Elementary Features (BRIEF) [126], Oriented FAST and Rotated BRIEF (ORB) [127], etc., to enhance image matching accuracy. A small change in camera angle may largely change the captured image which can potentially influence the localization performance for vision systems. Hence, adding camera angle and orientation in the database and its matching with the user captured image is often fruitful to enhance the localization accuracy.
The radio frequency band which occupies 3 kHz to 300 GHz is becoming scarce due to the excessive increase of wireless network traffic and requires optimal management of the spectrum to cope with the problem. The other option, the research community is currently working on is the utilization of appropriate alternatives like Visible Light Communication (VLC). VLC occupies the spectral band from 400 THz to 800 THz and possesses a great potential to be used for the communication. VLC systems make use of the modulating scheme of optical source intensity to transmit the information. Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) are the most suitable candidate for VLC systems due to a variety of reasons. LEDs have a very high switching rate which predominates other light sources to be used in VLC. LEDs are energy efficient whose light sources can be controlled [128] which makes it very suitable to achieve eco-friendly communication [129,130]. Additionally, since LEDs are energy efficient, replacing traditional light sources with LEDs would save a substantial amount of energy. Moreover, the deployment of LEDs is easy and comparatively cheap and a further reduction in cost is expected as well. For a detailed list of LED features over traditional lighting sources please refer to [131]. Many survey papers are presented which discuss the basic theory, system components, architecture of VLC [132], the propagation model [133], indoor and outdoor applications of VLC [134] and development of VLC for indoor broadband communication [131]. Localization systems that leverage VLC are grouped into two categories: those who require customized LEDs and those who function on already deployed LEDs inside the buildings. The latter makes use of LEDs that are densely put to illuminate large buildings today, so they do not incur an extra cost. The former, on the other hand, functions with customized LEDs with a high sample rate and incur extra infrastructure costs. Both techniques use the Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor (CMOS) camera as a receiver that receives data encoded in the optical transmissions. Many VLC localization approaches using smartphone cameras have been presented and can be put under two categories: that work with RSS (light intensity in VLC case) [135,136], and multilateration [133,137]. VLC is preferred because contrary to Radio Frequency (RF) signals, the light signal is less affected by multi-path effect and recently built buildings with large LEDs deployment provide a potential opportunity to be utilized for localization.
The smartphone camera-based visual localization, though not expensive, has other several affiliated challenges that can undermine the accuracy of the system. In many situations visual localization performs very poorly, e.g., in corridors, the features are often indistinguishable and repetitive which makes it very difficult to find the correct location. The extraction of good and distinct features is very important to achieve high accuracy [138]. One option is the fusion with other motion models or sensors to compensate for the error. In addition to that the indoor environment is dynamic and objects like tables, trash bins may move and doors may be opened or closed during the database generation and localization which further complicates the visual localization process. One disadvantage of the vision-based system is the storage capacity required to build the database of the image that are annotated with the environment map. Additionally, significant computational resources are also required to do the image matching during the localization process [139]. This makes it very difficult to implement the system on smartphones and in case of computation on the server, a good speed network is required to overcome latency issues. Another big challenge for vision systems is to cope with the problem of low light or dark scenarios as it is reported that a vision-based system performs poorly in a dark environment [140].
Current Challenges and Future Directions
Efficient feature extraction and a suitable image matching strategy are the two key components of vision-based localization systems that greatly improve the localization performance. However, these methods are exposed to many factors. Complex indoor environments that contain narrow corners and corridors without prominent features make distinct feature extraction and matching very difficult. Moreover, dynamic indoor environments like shopping malls, train stations, and airports further complicate this process due to high human mobility. Although a large body of literature is available that focuses on vision-based robot localization [141,142,143], its adaptation for human-centric smartphone-based localization has numerous challenges that require a substantial effort on both academia and industry. Contrary to robots with a fixed camera position, user activities with the smartphone are multifarious which makes the image matching very difficult. With the rise of deep learning during the last few years, many research works focusing on the use of Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) for image matching have been proposed [144,145]. However, the use of a camera image with MEMS sensors has proven to perform better than using it alone. Consequently, it has been used to identify indoor scene which helps to reduce the database search space and enhance the overall performance of the system [140,146,147]. Despite the enhanced accuracy of deep learning models, the computational resources required for such models are high, so they need to reside on the server-side. User captured images are sent to the server, where the processing takes place and results are sent back. It requires a communication link between the server and the smartphone and often introduces latency for real-time systems. VLC localization with smartphone cameras often requires close contact with LEDs and obstruction and clutter pose a real challenge to the performance of such approaches as they have to rely on a line-of-sight link between the transmitter and receiver. Although offering sub-meter accuracy, such approaches are easily affected by the pose and orientation of smartphones and require a substantial research effort to overcome these issues.
3.5. Indoor Localization Using Bluetooth
Bluetooth was designed for low power consumption wireless communication that operates in the Industrial, Scientific, and Medical(ISM) band between 2.402 GHz and 2.480 GHz. Although, Bluetooth has three categories based on the range: class 1 with a range of 100 m, class 2 with a range of 10 m, and class three with a range of 5 m, the majority of available devices have a short range of typically 10–15 m. Bluetooth is lighter and ubiquitous to be embedded in mobile devices like smartphones. It is easy to utilize smartphones for Bluetooth-based indoor localization. Bluetooth is based on low-cost transceiver microchips so it is not expensive to design an indoor localization system that utilizes Bluetooth [148]. Bluetooth technology leverages two approaches for positioning: triangulation and fingerprinting. Various signal parameters like Link Quality (LQ), RSSI, Transmit Power Level (TPL), and Inquiry Result with RSSI are used for this purpose [149]. Fingerprinting is, however, preferred over the triangulation method that follows a two-phase approach like the Wi-Fi.
One critical factor to be considered for real-time localization technologies is the latency that can dramatically change the importance and influence of a particular approach and thus be given special consideration. Bluetooth requires an inquiry phase to discover visible devices within a range before setting up the network. The delay that is caused by device discovery is called discovery latency. This introduces the latency and reduces the responsiveness of Bluetooth-based localization. Improvements to Bluetooth came as Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) also called Bluetooth 4 or Bluetooth Smart. In BLE the slave can advertise on any of the three allowed channels to perform discovery of other devices. The master, on the other hand, scans periodically. Data transfer is in periodic connections that save energy. As described previously, the Bluetooth inquiry phase takes a relatively long period for its discovery of Bluetooth beacons, several researchers have investigated BLE for latency [150]. The discovery latency can take 10.24 s on average [151]. Various approaches have been proposed to reduce discovery latency. For example, authors in [152] proposes an approach to get the optimal parameter setting to reduce the discovery latency for BLE. The discovery latency can be reduced by decreasing the collisions and unsuccessful discoveries [153]. Similarly, it can be reduced by changing the advertising and scanning parameters [154].
Due to ease of use, low-power consumption, and low-cost, many BLE-based methods can be found. For example authors in [155] use a set of BLE beacons to track the patients in a hospital. BLE systems have been proposed for people detection [156], route guidance [157], and indoor localization [158]. Concerning the technique used for localization, BLE approaches can be divided into range-based [159], angle-based [158], and hybrid approaches [160]. Range-based approaches for BLE are based on RSSI measurement where the value of the wireless channel is estimated. However, such estimation is crippled by the multipath effect. The fingerprinting approach can be adopted for RSSI measurement at specified locations to make the fingerprint but the multipath effect still impacts it severely. The adaptive range-based approach can be utilized as well to improve the performance of range estimation with RSSI [161]. An alternative option would be to use Channel State Information (CSI) from BLE beacons to perform localization [162]. Contrary to range-based estimation, angle-based BLE localization can provide sub-meter accuracy at room level as reported in [163]. Hybrid approaches that utilized BLE with either Wi-Fi or smartphone sensors prove more accurate for indoor localization [164,165].
Above-cited works have investigated BLE indoor localization and reported a localization accuracy of 2 m to 3 m. Despite the provided accuracy, BLE localization systems are degraded because of the drawbacks of radio frequency propagation, especially in complex and dynamic environments. The effect of such limitations can be mitigated by increasing the number of BLE tags in the localization intended area. Research proves that an increase in BLE tags increases the localization accuracy [166], however, this will enhance the accuracy until there is the saturation of iBeacons. Moreover, a large number of BLE tags in an environment can potentially increase the discovery latency. Another option is to install the tags on appropriate heights to avoid interference from obstacles and human mobility.
Limitations and Future Directions
Contrary to Wi-Fi systems, BLE-based localization is light, low-cost, and low-power consuming that makes it preferable. However, it suffers from radiofrequency propagation drawbacks just like the Wi-Fi. Moreover, it requires the installation of BLE tags in the localization intended area. Despite the tags inexpensiveness, BLE systems cannot work properly or cannot provide the threshold of localization accuracy required for indoor LBS, without additional infrastructure. However, owing to the rapid increase in Internet of Things (IoT) devices, a large number of devices are expected to be installed inside soon that makes BLE systems favorable over other localization technologies. Advent approaches are needed to perform more accurate localization with BLE.
Research provides exhaustive results regarding the discovery latency in BLEs and it is estimated that it is still a challenging issue that needs to be coped with to visualize the localization accuracy that the BLE can assure. BLE energy consumption, on the other hand, is not fully investigated yet and requires a comprehensive evaluation as a trade-off is required between energy consumption and device discovery in BLE localization.
3.6. Lux Meter and Barometer
Luxmeter is the device that is used to measure the intensity of light. Smartphones have embedded lux meter that measures the light intensity and automatically adjusts the screen brightness to optimize the battery usage [167]. Lux meter provides the intensities of Red, Green, Blue (RGB), as well as, the white light at any point in lux. Lux meter has been used in many works for indoor to outdoor transition detection and vice versa as there is a large difference in light intensity for both environments [168,169]. Similarly, day and night time can be separated based on the light intensity. Apart from that, recently lux meter has been employed for indoor localization as well. Contrary to VLC that utilizes LEDs, lux meter adopting approaches are based on the uneven light distribution in a given environment. Although not customary, building insides are not illuminated evenly and often have low and highly deployed lighting resources. It leads to uneven light distribution in an environment that causes the varied light intensity at various indoor locations that can be used as fingerprints for localization. However, such fingerprints are not unique enough to be used solely for localization and instead serve as a complementing module to INS or Wi-Fi systems to enhance their accuracy. For example, research works [170,171] make use of a smartphone light sensor to measure light at various locations that serve as landmarks that help to elevate the performance in case of sparse APs distribution.
Barometer, though it cannot be deployed as an individual sensor for localization, often proves to be very influential to determine the change in altitude for PDR localization. It measures the atmospheric pressure and uses the hypsometeric equation to measure the altitude [172]:
where P shows the current atmospheric pressure, is the sea-level pressure i.e., 1013.25 hectopascals (hPa), h is the altitude, and T is the current temperature. When a user moves upward or downward, the change in atmospheric pressure helps to determine the change in altitude. Along with user movement, change in altitude can help in localizing the user on a particular floor. Predominantly, the barometer is used to identify a specific floor in a given indoor environment. For this purpose, largely two approaches have been utilized. The first approach is to install barometers at each floor that can measure and transmit the atmospheric pressure to a server at regular intervals or on-demand [173,174]. The localization device can send its reading to the server that can determine the current floor by comparing the reading with that of the barometers. Such updating of data is essential because the atmospheric data can change approximately 1.68 hPa in a short time as 15 m only [175]. The second approach is to put a barometer at any particular floor and use it as a standard to measure the relative change [176]. For this approach, however, the exact height of each floor should be known in advance to identify the floors. However, the exact height information of each floor may not be available in many cases.
There are other alternatives as well to maximize the floor detection accuracy. For example, it is also possible to use the knowledge of user initial floor information and its barometer data and then estimate the floor concerning the change in the pressure but it reduces the usability of such systems as determining the initial floor has its challenges and limitations. Hybrid approaches have proven to be highly precise and can provide an accuracy of higher than 95% for correct floor detection [175,177,178]. In addition, machine learning approaches including Support Vector Machine (SVM) [179], K Nearest Neighbor (KNN), and Back Propagation Neural Network (BPNN) [180] have been employed as well for floor detection. Both hybrid and machine learning approaches need a large data collection for the training phase that adds laborious work to such approaches. Albeit crowd-sourcing data collection can be utilized to mitigate or overcome this issue [173], calibration and integration of such data requires a lot of work.
Current Challenges and Future Directions
Currently, smartphone embedded lux meter is not used as a standalone localization sensor but may prove very influential. In future buildings, the illumination resources may be deliberately designed to cause varying illumination to support light-based localization. As we have witnessed the addition of more and more sensors in recent smartphones, e.g., an increase in cameras from 1 to 4 in iPhone and Samsung Galaxy, the addition of multiple lux meter may prove helpful to overcome the limitations of obstruction, angle of incidence measurement, etc. Hybrid barometer and Wi-Fi approaches are not suitable for floor detection where the floor structure is uneven. However, with the wide proliferation of IoT devices, barometers will become cheap, energy-efficient, and densely deployed which can help to elevate the performance of indoor localization.
3.7. Indoor Localization Using Multi-Sensor Fusion
Above discussed approaches reveal that no single technology is capable to serve desired indoor localization accuracy. Hybrid approaches, on the other hand, take advantage of the data from multiple sensors to mitigate their deficiencies and enhance the performance. The choice of sensors for fusion depends on a large number of factors like desired accuracy, localization environment, available computing resources, latency requirements, etc. For example, higher accuracy is possible when a smartphone camera, accelerometer, gyroscope, magnetometer, BLE, and Wi-Fi data is used for indoor localization [140,147]. However, image processing techniques to process the images from the smartphone camera requires substantial computing resources. For multi-floor buildings where the user can move between the floors, floor identification can substantially increase the localization accuracy [181]. Sensor fusion helps to increase the reliability and accuracy of localization systems. One challenge to achieving higher accuracy from multi-sensor approaches is the fusion process than often involves the use of filters like particle filter and extended Kalman filter [182]. The accuracy of a multi-sensor localization system depends on the sensor fusion algorithm [183]. Machine and deep learning approaches can be adopted as well, however, it is not possible to deploy the trained models on the smartphone [101]. Moreover, such techniques require a large amount of annotated data. Knowledge transfer frameworks can be adapted to transfer knowledge from one context to another for sensor fusion [184]. However, machine and deep learning models reside in the server and a communication link is used for communication between the smartphone and the server. It increases latency and raises concerns for real-time positioning systems. Sensor fusion is an active research area and holds the potential to enhance the localization accuracy by using the data from multiple sensors embedded in the smartphone.
3.8. Enhanced GPS Based Indoor Localization
GPS technology suffers accuracy degradation for indoor localization due to signal attenuation by roofs, walls, and similar other obstacles. GPS provided location accuracy does not fulfill the indoor localization accuracy set for E911 calls. It is because GPS can not provide accurate location information in severe signal-degraded complex indoor environments. Consequently, improvements to GPS technology are made to enhance its capability for indoor localization. For example, Assisted-GPS (A-GPS) is often used to increase GPS location accuracy by improving Time-To-First-Fix (TTFF) of GPS positioning system [185]. A-GPS enhances location accuracy by augmenting satellite data from cell tower data and helps to reduce TTFF for GPS [186]. Enhanced-GPS (E-GPS ) augments GPS signals and ensures faster location fixes. Its implementation cost, as well as power and processing requirements, are lower than that of A-GPS. It uses cell tower data to provide a coarse location that can be used to search for GPS signals and acquire satellite information. It can operate in all environments and shows better location accuracy than that of both GPS and A-GPS [187].
4. Discussion and Conclusions
The rapid expansion and wide acceptance of smartphones led to the inception and introduction of new service industries during the last decade or so. With an increase in the number and processing capabilities of the embedded sensors, smartphones can perform the tasks that personal computers could do a couple of decades ago. Consequently, the smartphone industry with its affiliated services lay on the center of the consumer market today and many new application areas have commenced that focus on this market like online marketing, on-the-go services, telemedicine, etc. One of the biggest services that center around the smartphone is LBS, a group of a variety of customer-oriented services pivoting on the user’s location. Since the location is the first and foremost component of LBS, accurate location information helps to provide the right service within the user’s vicinity and increase the quality of service and user satisfaction.
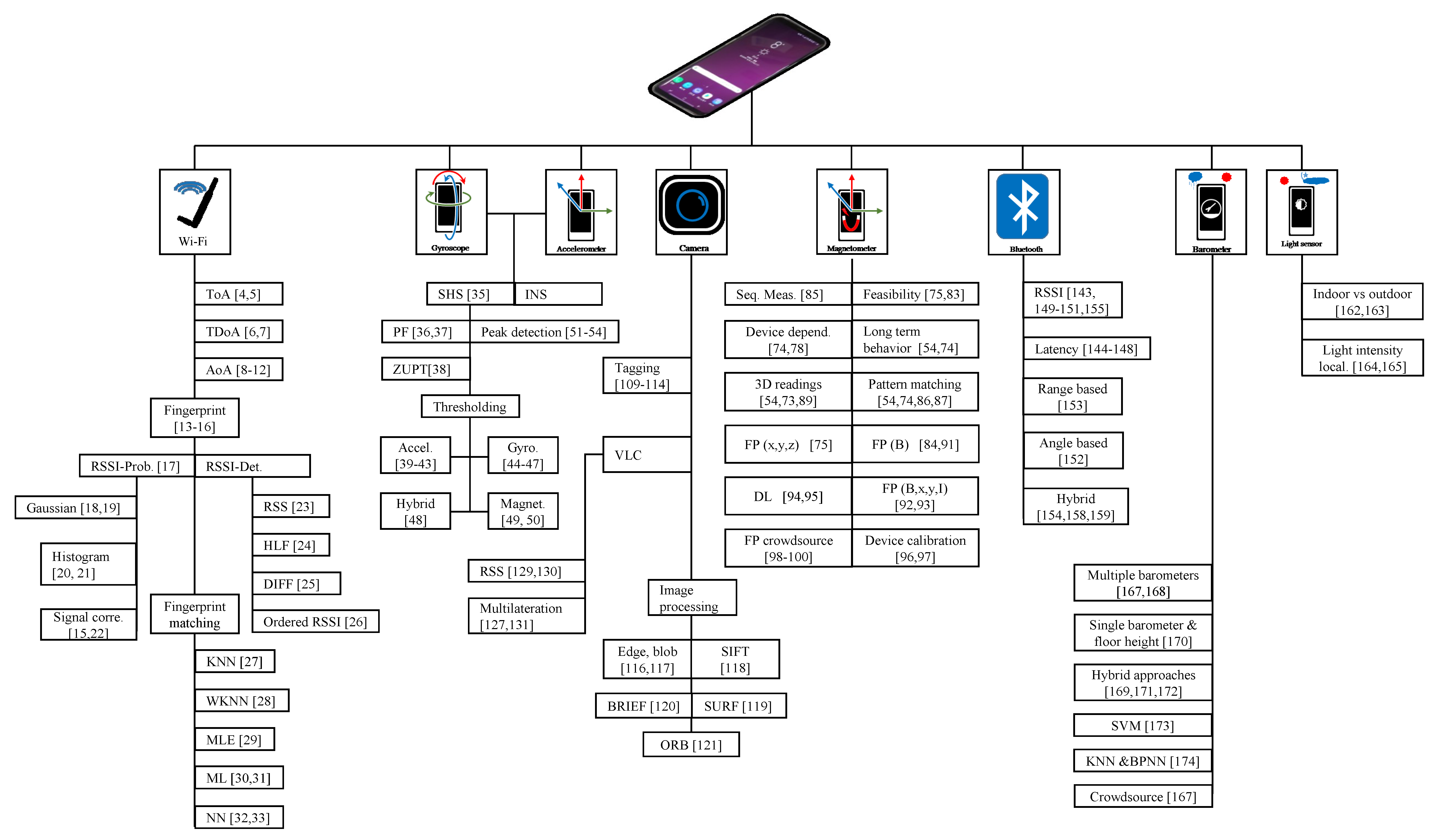
Unlike the outdoor environments where GPS can provide location information within a few meters, the indoor environment has no such counterpart to do so. Recent years have seen enhancements to the GPS positioning for indoor positioning. Assisted-GPS and Enhanced-GPS positioning have been introduced that aid to minimize time-to-first-fix and enhances the performance of GPS for indoor environments. These techniques utilize cellular data to augment GPS signals in severely attenuated satellite signal environments. They provide a coarse position to look for GPS signals and thus reduce positioning time and increase accuracy. Pervasiveness and infrastructure independence are two most favorable attributes required from a ubiquitous location perspective and smartphone sensors can be utilized to achieve this. Many approaches employing the smartphone sensors are in the limelight and can be utilized to meet the location standards required for LBS. Despite that, each of these approaches comes up with their advantages and disadvantages that should be studied well to overcome the week points and exploit the benefits. The current study discusses the approaches that make use of smartphone sensors and doing so elaborates on the current challenges of such approaches and discusses the possible future directions. Figure 10 shows a comprehensive overview of the discussed approaches for each smartphone sensor.
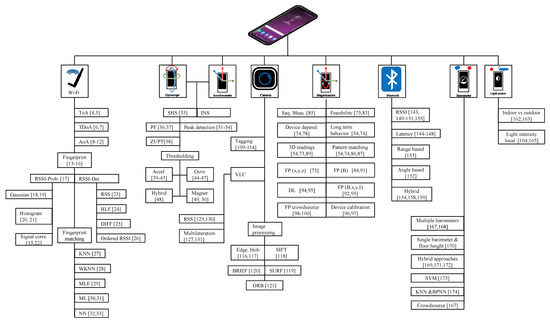
Figure 10.
List of the approaches discussed in the paper against each smartphone sensor.
Wi-Fi has been extensively investigated for indoor localization owing to the large and dense deployment of Wi-Fi APs in the majority of the buildings. Fingerprinting serves as a potential solution for complex indoor environments and more attractive than those of AoA, ToA, and TDoA approaches. However, the Wi-Fi scan throttle introduced in Android 9 and iPhone’s restriction on providing the APs information put a question mark on its future usage for indoor localization. Consequently, PDR, magnetic systems and BLE-based location emerge as its substitutes for localization. In principle, PDR systems need a starting or recent position of the user to locate its current position as they offer only a relative change in position; hence cannot be used as an independent system. Moreover, based on MEMS sensors which offer a limited accuracy in data measurement, PDR offers acceptable accuracy for short time localization as the drift and error in PDR are accumulated over time if not periodically corrected. Magnetic field-based localization has been examined recently as an appealing candidate for indoor localization on account of its infrastructure independence, pervasiveness, and magnetic sensor availability in smartphones. It is still in its infancy and requires a substantial amount of effort in academia and industry to devise novel approaches to utilize its full potential. The major challenge is handling the device diversity as a rich variety of smartphones are used today and the precision of smartphone sensors. BLE has emerged as a low-power, low-cost, and easy to deploy solution for indoor localization. BLE tags are cheap, small in size, and can be easily adapted for smartphones. Although it relies on the added infrastructure, yet in the future, more and more IoT sensors are envisioned to be deployed in the indoor environment which can be leveraged for indoor localization using BLE. The most noteworthy fact, however, is that the hybrid solutions that combine multiple localization techniques have proven to perform superior and offer higher accuracy than the use of individual technology. Multi-sensor fusion approaches can increase the accuracy of indoor localization techniques as the data from multiple sensors can compensate for the deficiencies of other sensors. However, the accuracy of multi-sensor approaches depends on the fusion algorithm. Owing to the benefits of sensor fusion, more hybrid approaches are foreseen as we expect more sensors to be introduced in the future smartphones for distance and angle measurement. Deep learning approaches provide elevated accuracy, the computational power they require is not supported yet on the smartphones, nor it is possible to deploy the trained models on Android or ios; however, it may become possible soon. Additionally, the launch of 5G with its reduced latency may yet have to show its potential for indoor localization.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.A.; data curation, S.H.; methodology, I.A. and S.H.; formal analysis, I.A.; resources, S.H. and Y.P.; writing—original draft preparation, I.A.; writing—review and editing, Y.P.; funding acquisition, Y.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the MSIT (Ministry of Science and ICT), Korea, under the ITRC (Information Technology Research Center) support program (IITP-2019-2016-0-00313) supervised by the IITP (Institute for Information & communication Technology Promotion).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results’.
References
- Falaki, H.; Mahajan, R.; Kandula, S.; Lymberopoulos, D.; Govindan, R.; Estrin, D. Diversity in smartphone usage. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Mobile Systems, Applications, and Services, San Francisco, CA, USA, 15–18 June 2010; pp. 179–194. [Google Scholar]
- Salesforce Blog. What Are Conumsers Doing on Their Smartphones Anyway. Available online: https://www.salesforce.com/blog/2018/02/consumer-smartphone-use.html (accessed on 19 May 2020).
- Karimi, H.A. Advanced Location-Based Technologies and Services; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Microelectronics, S. LSM6DSM, iNEMO Inertial Module: Always-on 3D Accelerometer and 3D Gyroscope, Product Datasheet. 2017. Available online: https://www.st.com/resource/en/datasheet/lsm6dsl.pdf (accessed on 25 May 2020).
- Microelectronics, S. LPS22HB MEMS Nano Pressure Sensor: 260–1260 hPa Absolute Digital Output Barometer. 2017. Available online: https://www.st.com/resource/en/datasheet/dm00140895.pdf (accessed on 25 May 2020).
- AG, A. TSL27713 Ambient Light Sensor Light-To-Digital Converter with Proximity Sensing. Available online: https://ams.com/tsl27713 (accessed on 29 October 2019).
- Miao, H. Channel Estimation and Positioning for Multiple Antenna Systems. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Oulu, Oulu, Finland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Vossiek, M.; Wiebking, L.; Gulden, P.; Wieghardt, J.; Hoffmann, C.; Heide, P. Wireless local positioning. IEEE Microw. Mag. 2003, 4, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukerche, A.; Oliveira, H.A.; Nakamura, E.F.; Loureiro, A.A. Localization systems for wireless sensor networks. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2007, 14, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafsson, F.; Gunnarsson, F. Positioning using time-difference of arrival measurements. In Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Hong Kong, China, 6–10 April 2003; Volume 6, p. VI-553. [Google Scholar]
- Malajner, M.; Planinsic, P.; Gleich, D. Angle of arrival estimation using RSSI and omnidirectional rotatable antennas. IEEE Sens. J. 2011, 12, 1950–1957. [Google Scholar]
- Patwari, N.; Ash, J.N.; Kyperountas, S.; Hero, A.O.; Moses, R.L.; Correal, N.S. Locating the nodes: Cooperative localization in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2005, 22, 54–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zekavat, S. Comparison of semidistributed multinode TOA-DOA fusion localization and GPS-Aided TOA (DOA) fusion localization for MANETs. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2008, 2008, 439523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, G.; Fidan, B.; Anderson, B.D. Wireless sensor network localization techniques. Comput. Netw. 2007, 51, 2529–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.A.; Ni, W.; Cheng, P.; Lu, Y. Angle-of-arrival estimation using different phase shifts across subarrays in localized hybrid arrays. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2016, 20, 2205–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahl, P.; Padmanabhan, V.N. RADAR: An in-building RF-based user location and tracking system. In Proceedings of the IEEE INFOCOM 2000, Conference on Computer Communications, Nineteenth Annual Joint Conference of the IEEE Computer and Communications Societies (Cat. No. 00CH37064), Tel Aviv, Israel, 26–30 March 2000; Volume 2, pp. 775–784. [Google Scholar]
- Castro, P.; Chiu, P.; Kremenek, T.; Muntz, R. A probabilistic room location service for wireless networked environments. In International Conference on Ubiquitous Computing; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2001; pp. 18–34. [Google Scholar]
- Youssef, M.; Agrawala, A. The Horus WLAN location determination system. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Mobile Systems, Applications, and Services, Seattle, WA, USA, 6–8 June 2005; pp. 205–218. [Google Scholar]
- Ekahau, I. The Ekahau Real-Time Location System. Available online: https://www.optrics.com/downloads/ekahau/Ekahau-RFID-over-WiFi-RTLS-Solutions.pdf (accessed on 25 May 2020).
- Madigan, D.; Einahrawy, E.; Martin, R.P.; Ju, W.H.; Krishnan, P.; Krishnakumar, A. Bayesian indoor positioning systems. In Proceedings of the IEEE 24th Annual Joint Conference of the IEEE Computer and Communications Societies, Miami, FL, USA, 13–17 March 2005; Volume 2, pp. 1217–1227. [Google Scholar]
- Haeberlen, A.; Flannery, E.; Ladd, A.M.; Rudys, A.; Wallach, D.S.; Kavraki, L.E. Practical robust localization over large-scale 802.11 wireless networks. In Proceedings of the 10th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 26 September–1 October 2004; pp. 70–84. [Google Scholar]
- Kaemarungsi, K.; Krishnamurthy, P. Properties of indoor received signal strength for WLAN location fingerprinting. In Proceedings of the The First Annual International Conference on Mobile and Ubiquitous Systems: Networking and Services, Boston, MA, USA, 26 August 2004; pp. 14–23. [Google Scholar]
- Roos, T.; Myllymäki, P.; Tirri, H.; Misikangas, P.; Sievänen, J. A probabilistic approach to WLAN user location estimation. Int. J. Wirel. Inf. Netw. 2002, 9, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, T.; Kopf, S.; Haenselmann, T.; Lubberger, C.; Effelsberg, W. COMPASS: A probabilistic indoor positioning system based on 802.11 and digital compasses. In Proceedings of the 1st International Workshop on Wireless Network Testbeds, Experimental Evaluation & Characterization, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 26 September–1 October 2006; pp. 34–40. [Google Scholar]
- Ladd, A.M.; Bekris, K.E.; Rudys, A.; Kavraki, L.E.; Wallach, D.S. Robotics-based location sensing using wireless ethernet. Wirel. Netw. 2005, 11, 189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonitor. Sonitor Technologies. Available online: https://www.sonitor.com/ (accessed on 25 May 2020).
- Kjærgaard, M.B. Indoor location fingerprinting with heterogeneous clients. Pervas. Mob. Comput. 2011, 7, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; Chen, Y.; Liu, J.; Ning, Q.; Piao, S. A calibration-free localization solution for handling signal strength variance. In International Workshop on Mobile Entity Localization and Tracking in GPS-less Environments; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2009; pp. 79–90. [Google Scholar]
- Yedavalli, K.; Krishnamachari, B.; Ravula, S.; Srinivasan, B. Ecolocation: A sequence based technique for RF localization in wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of the IPSN 2005 Fourth International Symposium on Information Processing in Sensor Networks, Boise, ID, USA, 15 April 2005; pp. 285–292. [Google Scholar]
- Ashraf, I.; Hur, S.; Park, Y. Indoor positioning on disparate commercial smartphones using Wi-Fi access points coverage area. Sensors 2019, 19, 4351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yigit, H. A weighting approach for KNN classifier. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference on Electronics, Computer And Computation (ICECCO), Ankara, Turkey, 7–9 November 2013; pp. 228–231. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, B.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, T.; Kim, H.S. Enhanced weighted K-nearest neighbor algorithm for indoor Wi-Fi positioning systems. In Proceedings of the 2012 8th International Conference on Computing Technology and Information Management (NCM and ICNIT), Seoul, South Korea, 24–26 April 2012; Volume 2, pp. 574–577. [Google Scholar]
- Bialer, O.; Raphaeli, D.; Weiss, A.J. Maximum-likelihood direct position estimation in dense multipath. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2012, 62, 2069–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Gao, Z.; He, Z.; Zhuang, Y.; Radi, A.; Chen, R.; El-Sheimy, N. Wireless fingerprinting uncertainty prediction based on machine learning. Sensors 2019, 19, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsheikh, M.A.; Lin, S.; Niyato, D.; Tan, H.P. Machine learning in wireless sensor networks: Algorithms, strategies, and applications. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2014, 16, 1996–2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, K.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, J. Deep neural networks for wireless localization in indoor and outdoor environments. Neurocomputing 2016, 194, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Gao, L.; Mao, S.; Pandey, S. DeepFi: Deep learning for indoor fingerprinting using channel state information. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), New Orleans, LA, USA, 9–12 March 2015; pp. 1666–1671. [Google Scholar]
- Youssef, M.A.; Agrawala, A.; Shankar, A.U. WLAN location determination via clustering and probability distributions. In Proceedings of the First IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications, Fort Worth, TX, USA, 26 March 2003; pp. 143–150. [Google Scholar]
- Harle, R. A survey of indoor inertial positioning systems for pedestrians. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2013, 15, 1281–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinchin, J.; Hide, C.; Moore, T. A particle filter approach to indoor navigation using a foot mounted inertial navigation system and heuristic heading information. In Proceedings of the 2012 International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation (IPIN), Sydney, NSW, Australia, 13–15 November 2012; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez, A.R.; Seco, F.; Prieto, J.C.; Guevara, J. Indoor pedestrian navigation using an INS/EKF framework for yaw drift reduction and a foot-mounted IMU. In Proceedings of the 2010 7th Workshop on Positioning, Navigation and Communication, Dresden, Germany, 11–12 March 2010; pp. 135–143. [Google Scholar]
- Skog, I.; Nilsson, J.O.; Händel, P. Evaluation of zero-velocity detectors for foot-mounted inertial navigation systems. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation, Zurich, Switzerland, 15–17 September 2010; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Krach, B.; Roberston, P. Cascaded estimation architecture for integration of foot-mounted inertial sensors. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE/ION Position, Location and Navigation Symposium, Monterey, CA, USA, 5–8 May 2008; pp. 112–119. [Google Scholar]
- Castaneda, N.; Lamy-Perbal, S. An improved shoe-mounted inertial navigation system. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation, Zurich, Switzerland, 15–17 September 2010; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Godha, S.; Lachapelle, G. Foot mounted inertial system for pedestrian navigation. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2008, 19, 075202. [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson, J.O.; Gupta, A.K.; Händel, P. Foot-mounted inertial navigation made easy. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation (IPIN), Busan, South Korea, 27–30 October 2014; pp. 24–29. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.W.; Jang, H.J.; Hwang, D.H.; Park, C. A step, stride and heading determination for the pedestrian navigation system. J. Glob. Position. Syst. 2004, 3, 273–279. [Google Scholar]
- Woodman, O.; Harle, R. Pedestrian localisation for indoor environments. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Ubiquitous Computing, Seoul, South Korea, 21–24 September 2008; pp. 114–123. [Google Scholar]
- Ojeda, L.; Borenstein, J. Non-GPS navigation with the personal dead-reckoning system. In Unmanned Systems Technology IX; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2007; Volume 6561, p. 65610C. [Google Scholar]
- Ladetto, Q.; Gabaglio, V.; Merminod, B. Combining gyroscopes, magnetic compass and GPS for pedestrian navigation. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Kinematic Systems in Geodesy, Geomatics, and Navigation, Lausanne, Switzerland, 29 May–1 June 2001; pp. 205–213. [Google Scholar]
- Feliz Alonso, R.; Zalama Casanova, E.; Gómez García-Bermejo, J. Pedestrian Tracking Using Inertial Sensors. J. Phys. Agents 2009, 3, 35–43. [Google Scholar]
- Foxlin, E. Pedestrian tracking with shoe-mounted inertial sensors. IEEE Comput. Graph. Appl. 2005, 25, 38–46. [Google Scholar]
- Jimenez, A.R.; Seco, F.; Prieto, C.; Guevara, J. A comparison of pedestrian dead-reckoning algorithms using a low-cost MEMS IMU. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Symposium on Intelligent Signal Processing, Budapest, Hungary, 26–28 August 2009; pp. 37–42. [Google Scholar]
- Bird, J.; Arden, D. Indoor navigation with foot-mounted strapdown inertial navigation and magnetic sensors [emerging opportunities for localization and tracking]. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2011, 18, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brajdic, A.; Harle, R. Walk detection and step counting on unconstrained smartphones. In Proceedings of the 2013 ACM International Joint Conference On Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing, Zurich, Switzerland, 8–12 September 2013; pp. 225–234. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Zhao, C.; Ding, G.; Gong, J.; Liu, C.; Zhao, F. A reliable and accurate indoor localization method using phone inertial sensors. In Proceedings of the 2012 ACM Conference on Ubiquitous Computing, Hammerla, NY, USA, 5–8 September 2012; pp. 421–430. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, W.; Han, Y. SmartPDR: Smartphone-based pedestrian dead reckoning for indoor localization. IEEE Sens. J. 2014, 15, 2906–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, I.; Hur, S.; Park, Y. mPILOT-magnetic field strength based pedestrian indoor localization. Sensors 2018, 18, 2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zihajehzadeh, S.; Park, E.J. Experimental evaluation of regression model-based walking speed estimation using lower body-mounted IMU. In Proceedings of the 2016 38th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Orlando, FL, USA, 16–20 August 2016; pp. 243–246. [Google Scholar]
- Panahandeh, G.; Mohammadiha, N.; Leijon, A.; Händel, P. Chest-mounted inertial measurement unit for pedestrian motion classification using continuous hidden Markov model. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference Proceedings, Graz, Austria, 13–16 May 2012; pp. 991–995. [Google Scholar]
- Höllerer, T.; Hallaway, D.; Tinna, N.; Feiner, S. Steps toward accommodating variable position tracking accuracy in a mobile augmented reality system. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Workshop on Artificial Intelligence in Mobile Systems (AIMS’01), Citeseer, Graz, Austria, 13–16 May 2001; pp. 31–37. [Google Scholar]
- Koide, S.; Kato, M. 3-d human navigation system considering various transition preferences. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 12 October 2005; Volume 1, pp. 859–864. [Google Scholar]
- Ojeda, L.; Borenstein, J. Personal dead-reckoning system for GPS-denied environments. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Workshop on Safety, Security and Rescue Robotics, Rome, Italy, 27–29 September 2007; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher, T.; Wise, E.; Li, B.; Dempster, A.G.; Rizos, C.; Ramsey-Stewart, E. Indoor positioning system based on sensor fusion for the blind and visually impaired. In Proceedings of the 2012 International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation (IPIN), Sydney, NSW, Australia, 13–15 November 2012; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Radu, V.; Marina, M.K. HiMLoc: Indoor smartphone localization via activity aware pedestrian dead reckoning with selective crowdsourced WiFi fingerprinting. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation, Montbeliard-Belfort, France, 28–31 October 2013; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Link, J.A.B.; Smith, P.; Viol, N.; Wehrle, K. Footpath: Accurate map-based indoor navigation using smartphones. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation, Guimaraes, Portugal, 21–23 September 2011; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, B.; Kim, C.; Kim, J.; Lee, S.; Kee, C.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, T. Motion recognition-based 3D pedestrian navigation system using smartphone. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 16, 6977–6989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, L.M.; Liu, Y.; Lau, Y.C.; Patil, A.P. LANDMARC: Indoor location sensing using active RFID. In Proceedings of the First IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications, Fort Worth, TX, USA, 26 March 2003; pp. 407–415. [Google Scholar]
- Bruno, R.; Delmastro, F. Design and analysis of a bluetooth-based indoor localization system. In IFIP International Conference on Personal Wireless Communications; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2003; pp. 711–725. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, A.; Jones, A.; Hopper, A. A new location technique for the active office. IEEE Pers. Commun. 1997, 4, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyantha, N.B.; Chakraborty, A.; Balakrishnan, H. The cricket location-support system. In Proceedings of the 6th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking, Boston, MA USA, 6–11 August 2000; pp. 32–43. [Google Scholar]
- Maugh, T.H. Magnetic navigation an attractive possibility. Science 1982, 215, 1492–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boles, L.C.; Lohmann, K.J. True navigation and magnetic maps in spiny lobsters. Nature 2003, 421, 60–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, C.V.; Davison, M.; Wild, J.M.; Walker, M.M. Magnetoreception and its trigeminal mediation in the homing pigeon. Nature 2004, 432, 508–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohmann, K.J.; Lohmann, C.M.; Ehrhart, L.M.; Bagley, D.A.; Swing, T. Geomagnetic map used in sea-turtle navigation. Nature 2004, 428, 909–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Wang, G.; Wu, K.; Ni, L.M. SmartScanner: Know more in walls with your smartphone! IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2015, 15, 2865–2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbu, K.P.; Gozick, B.; Dantu, R. LocateMe: Magnetic-fields-based indoor localization using smartphones. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. (TIST) 2013, 4, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Y.; Bo, C.; Shen, G.; Zhao, C.; Li, L.; Zhao, F. Magicol: Indoor localization using pervasive magnetic field and opportunistic WiFi sensing. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2015, 33, 1443–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Gallagher, T.; Dempster, A.G.; Rizos, C. How feasible is the use of magnetic field alone for indoor positioning? In Proceedings of the 2012 International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation (IPIN), Sydney, NSW, Australia, 13–15 November 2012; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Lenz, J.; Edelstein, S. Magnetic sensors and their applications. IEEE Sens. J. 2006, 6, 631–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Angelis, G.; Pasku, V.; De Angelis, A.; Dionigi, M.; Mongiardo, M.; Moschitta, A.; Carbone, P. An indoor AC magnetic positioning system. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2014, 64, 1267–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasku, V.; De Angelis, A.; De Angelis, G.; Arumugam, D.D.; Dionigi, M.; Carbone, P.; Moschitta, A.; Ricketts, D.S. Magnetic field-based positioning systems. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2017, 19, 2003–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markham, A.; Trigoni, N.; Macdonald, D.W.; Ellwood, S.A. Underground localization in 3-D using magneto-inductive tracking. IEEE Sens. J. 2011, 12, 1809–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blankenbach, J.; Norrdine, A. Position estimation using artificial generated magnetic fields. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation, Zurich, Switzerland, 15–17 September 2010; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Angermann, M.; Frassl, M.; Doniec, M.; Julian, B.J.; Robertson, P. Characterization of the indoor magnetic field for applications in localization and mapping. In Proceedings of the 2012 International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation (IPIN), Sydney, NSW, Australia, 13–15 November 2012; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Frassl, M.; Angermann, M.; Lichtenstern, M.; Robertson, P.; Julian, B.J.; Doniec, M. Magnetic maps of indoor environments for precise localization of legged and non-legged locomotion. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Tokyo, Japan, 3–7 November 2013; pp. 913–920. [Google Scholar]
- Haverinen, J.; Kemppainen, A. Global indoor self-localization based on the ambient magnetic field. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2009, 57, 1028–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, I.; Hur, S.; Park, Y. BLocate: A building identification scheme in GPS denied environments using smartphone sensors. Sensors 2018, 18, 3862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Shen, G.; Li, L.; Zhao, C.; Li, M.; Zhao, F. Travi-navi: Self-deployable indoor navigation system. IEEE/ACM Trans. Netw. 2017, 25, 2655–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Gu, T.; Tao, X.; Ye, H.; Lu, J. A reliability-augmented particle filter for magnetic fingerprinting based indoor localization on smartphone. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2015, 15, 1877–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, I.; Hur, S.; Shafiq, M.; Kumari, S.; Park, Y. GUIDE: Smartphone sensors-based pedestrian indoor localization with heterogeneous devices. Int. J. Commun. Syst. 2019, 32, e4062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rallapalli, S.; Dong, W.; Qiu, L.; Zhang, Y. WaveLoc: Wavelet signatures for ubiquitous localization. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 13th International Conference on Mobile Ad Hoc and Sensor Systems (MASS), Brasilia, Brazil, 10–13 October 2016; pp. 219–227. [Google Scholar]
- Ashraf, I.; Hur, S.; Park, Y. Enhancing Performance of Magnetic Field Based Indoor Localization Using Magnetic Patterns from Multiple Smartphones. Sensors 2020, 20, 2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apple, I. Developer Library. Manage 2016, 26, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, J.; Donahoe, M.; Schmandt, C.; Kim, I.J.; Razavai, P.; Wiseman, M. Indoor location sensing using geo-magnetism. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Mobile Systems, Applications, and Services, Bethesda, MD, USA, 28 June–1 July 2011; pp. 141–154. [Google Scholar]
- Brzozowski, B.; Kaźmierczak, K.; Rochala, Z.; Wojda, M.; Wojtowicz, K. A concept of UAV indoor navigation system based on magnetic field measurements. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Metrology for Aerospace (MetroAeroSpace), Florence, Italy, 22–23 June 2016; pp. 636–640. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Chen, Y.; Gruteser, M.; Yang, J.; Liu, H. E-eyes: Device-free location-oriented activity identification using fine-grained wifi signatures. In Proceedings of the 20th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking, Maui, HI, USA, 7–11 September 2014; pp. 617–628. [Google Scholar]
- Abadi, M.J.; Luceri, L.; Hassan, M.; Chou, C.T.; Nicoli, M. A collaborative approach to heading estimation for smartphone-based PDR indoor localisation. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation (IPIN), Busan, South Korea, 27–30 October 2014; pp. 554–563. [Google Scholar]
- Thébault, E.; Finlay, C.C.; Beggan, C.D.; Alken, P.; Aubert, J.; Barrois, O.; Bertrand, F.; Bondar, T.; Boness, A.; Brocco, L.; et al. International geomagnetic reference field: The 12th generation. Earth Planets Space 2015, 67, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, I.; Hur, S.; Park, S.; Park, Y. DeepLocate: Smartphone Based Indoor Localization with a Deep Neural Network Ensemble Classifier. Sensors 2020, 20, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, I.; Kang, M.; Hur, S.; Park, Y. MINLOC: Magnetic Field Patterns-Based Indoor Localization Using Convolutional Neural Networks. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 66213–66227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, N.; Wang, H.; Roy Choudhury, R. I am a smartphone and i can tell my user’s walking direction. In Proceedings of the 12th Annual International Conference on Mobile Systems, Applications, and Services, Woods, NH, USA, 16–19 June 2014; pp. 329–342. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, P.; Li, M.; Shen, G. Use it free: Instantly knowing your phone attitude. In Proceedings of the 20th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking, Maui, HI, USA, 7–11 September 2014; pp. 605–616. [Google Scholar]
- Wahlström, N.; Kok, M.; Schön, T.B.; Gustafsson, F. Modeling magnetic fields using Gaussian processes. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 26–31 May 2013; pp. 3522–3526. [Google Scholar]
- Solin, A.; Kok, M.; Wahlström, N.; Schön, T.B.; Särkkä, S. Modeling and interpolation of the ambient magnetic field by Gaussian processes. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2018, 34, 1112–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wen, H.; Clark, R.; Trigoni, N. Keyframe based large-scale indoor localisation using geomagnetic field and motion pattern. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Daejeon, South Korea, 9–14 October 2016; pp. 1910–1917. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Chen, Q.; Yang, L.T.; Chao, H.C. Indoor smartphone localization via fingerprint crowdsourcing: Challenges and approaches. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2016, 23, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thrun, S.; Fox, D.; Burgard, W.; Dellaert, F. Robust Monte Carlo localization for mobile robots. Artif. Intell. 2001, 128, 99–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rofer, T.; Jungel, M. Vision-based fast and reactive monte-carlo localization. In Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (Cat. No. 03CH37422), Taipei, Taiwan, 14–19 September 2003; Volume 1, pp. 856–861. [Google Scholar]
- Gutmann, J.S.; Fox, D. An experimental comparison of localization methods continued. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Lausanne, Switzerland, 30 September–4 October 2002; Volume 1, pp. 454–459. [Google Scholar]
- Sim, R.; Dudek, G. Mobile robot localization from learned landmarks. In Proceedings of the 1998 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Innovations in Theory, Practice and Applications (Cat. No. 98CH36190), Victoria, BC, Canada, 17 October 1998; Volume 2, pp. 1060–1065. [Google Scholar]
- Wolf, J.; Burgard, W.; Burkhardt, H. Robust vision-based localization by combining an image-retrieval system with Monte Carlo localization. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2005, 21, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quigley, M.; Stavens, D.; Coates, A.; Thrun, S. Sub-meter indoor localization in unmodified environments with inexpensive sensors. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots And Systems, Taipei, Taiwan, 18–22 October 2010; pp. 2039–2046. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.Y.; Jung, S.C.; Song, Y.S.; Kim, H.J. Mobile robot localization in indoor environment using scale-invariant visual landmarks. In Proceedings of the 18th IAPR International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Hong Kong, China, 20–24 August 2008; pp. 159–163. [Google Scholar]
- Rohs, M.; Zweifel, P. A conceptual framework for camera phone-based interaction techniques. In International Conference on Pervasive Computing; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2005; pp. 171–189. [Google Scholar]
- Ballagas, R.; Rohs, M.; Sheridan, J.G. Sweep and point and shoot: Phonecam-based interactions for large public displays. In Proceedings of the CHI’05 Extended Abstracts on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Austin, TX, USA, 25–30 April 2005; pp. 1200–1203. [Google Scholar]
- Rohs, M. Real-world interaction with camera phones. In International Symposium on Ubiquitious Computing Systems; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2004; pp. 74–89. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, D.; Sharp, R.; Madhavapeddy, A.; Upton, E. Using visual tags to bypass Bluetooth device discovery. ACM SIGMOBILE Mob. Comput. Commun. Rev. 2005, 9, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toye, E.; Sharp, R.; Madhavapeddy, A.; Scott, D. Using smart phones to access site-specific services. IEEE Pervas. Comput. 2005, 4, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjan, B.S.; Beckmann, P.J.; Roy, R.; Giudice, N.; Legge, G.E. Digital sign system for indoor wayfinding for the visually impaired. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR’05)-Workshops, San Diego, CA, USA, 21–23 September 2005; p. 30. [Google Scholar]
- Schroth, G.; Huitl, R.; Chen, D.; Abu-Alqumsan, M.; Al-Nuaimi, A.; Steinbach, E. Mobile visual location recognition. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2011, 28, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Aider, O.A.; Hoppenot, P.; Colle, E. A model-based method for indoor mobile robot localization using monocular vision and straight-line correspondences. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2005, 52, 229–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frontoni, E.; Zingaretti, P. An efficient similarity metric for omnidirectional vision sensors. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2006, 54, 750–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, D.G. Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2004, 60, 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bay, H.; Ess, A.; Tuytelaars, T.; Van Gool, L. Speeded-up robust features (SURF). Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2008, 110, 346–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calonder, M.; Lepetit, V.; Strecha, C.; Fua, P. Brief: Binary robust independent elementary features. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2010; pp. 778–792. [Google Scholar]
- Rublee, E.; Rabaud, V.; Konolige, K.; Bradski, G. ORB: An efficient alternative to SIFT or SURF. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Computer Vision, Barcelona, Spain, 6–13 November 2011; pp. 2564–2571. [Google Scholar]
- Kavehrad, M. Sustainable energy-efficient wireless applications using light. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2010, 48, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pujapanda, K.P. LiFi integrated to power-lines for smart illumination cum communication. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference on Communication Systems and Network Technologies, Gwalior, India, 6–8 April 2013; pp. 875–878. [Google Scholar]
- Uddin, M.S.; Chowdhury, M.Z.; Jang, Y.M. Priority-based resource allocation scheme for visible light communication. In Proceedings of the 2010 Second International Conference on Ubiquitous and Future Networks (ICUFN), Jeju, South Korea, 16–18 June 2010; pp. 247–250. [Google Scholar]
- Karunatilaka, D.; Zafar, F.; Kalavally, V.; Parthiban, R. LED based indoor visible light communications: State of the art. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2015, 17, 1649–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Lampe, L.; Hranilovic, S. Integration of indoor visible light and power line communication systems. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE 17th International Symposium on Power Line Communications and Its Applications, Johannesburg, South Africa, 24–27 March 2013; pp. 291–296. [Google Scholar]
- Sevincer, A.; Bhattarai, A.; Bilgi, M.; Yuksel, M.; Pala, N. LIGHTNETs: Smart LIGHTing and mobile optical wireless NETworks—A survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2013, 15, 1620–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Lourenco, N.R. Led-based visible light communication system: A brief survey and investigation. J. Eng. Appl. Sci 2010, 5, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, Y.S.; Pannuto, P.; Hsiao, K.J.; Dutta, P. Luxapose: Indoor positioning with mobile phones and visible light. In Proceedings of the 20th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking, Maui, HI, USA, 7–11 September 2014; pp. 447–458. [Google Scholar]
- Rajagopal, N.; Lazik, P.; Rowe, A. Visual light landmarks for mobile devices. In Proceedings of the 13th International Symposium On Information Processing in Sensor Networks, Berlin, Germany, 15–17 April 2014; pp. 249–260. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Hu, P.; Peng, C.; Shen, G.; Zhao, F. Epsilon: A visible light based positioning system. In Proceedings of the 11th USENIX Symposium on Networked Systems Design and Implementation (NSDI 14), Seattle, WA, USA, 10 January 2014; pp. 331–343. [Google Scholar]
- Coates, A.; Ng, A.; Lee, H. An analysis of single-layer networks in unsupervised feature learning. In Proceedings of the Fourteenth International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, Lauderdale, FL, USA, 11–13 April 2011; pp. 215–223. [Google Scholar]
- Hightower, J.; Borriello, G. Location systems for ubiquitous computing. Computer 2001, 34, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Chen, R.; Li, D.; Chen, Y.; Guo, G.; Cao, Z.; Pan, Y. Scene recognition for indoor localization using a multi-sensor fusion approach. Sensors 2017, 17, 2847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giovannangeli, C.; Gaussier, P.; Banquet, J. Robustness of visual place cells in dynamic indoor and outdoor environment. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2006, 3, 19. [Google Scholar]
- Ido, J.; Shimizu, Y.; Matsumoto, Y.; Ogasawara, T. Indoor navigation for a humanoid robot using a view sequence. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2009, 28, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo, R.; Zouqi, M.; Chen, Z.; Samarabandu, J. Robust and efficient feature tracking for indoor navigation. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part B (Cybernetics) 2009, 39, 658–671. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, J.; Li, F.; Deng, Z.; Ma, W. A smartphone camera-based indoor positioning algorithm of crowded scenarios with the assistance of deep CNN. Sensors 2017, 17, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, J.; Deng, Z. Deep combining of local phase quantization and histogram of oriented gradients for indoor positioning based on smartphone camera. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 2017, 13, 1550147716686978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Wu, R.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, X. Deep learning scene recognition method based on localization enhancement. Sensors 2018, 18, 3376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, I.; Hur, S.; Park, Y. Application of Deep Convolutional Neural Networks and Smartphone Sensors for Indoor Localization. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Lo, A.; Niemegeers, I. A survey of indoor positioning systems for wireless personal networks. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2009, 11, 13–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, A.M.; Soh, W.S. A comprehensive study of bluetooth signal parameters for localization. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE 18th International Symposium on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications, Athens, Greece, 3–7 September 2007; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, K.; Jung, C.; Kim, J.; Yoon, Y.; Han, K. Modeling and analysis of performance based on Bluetooth Low Energy. In Proceedings of the 2015 7th IEEE Latin-American Conference on Communications (LATINCOM), Arequipa, Peru, 4–6 November 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, A.M.; Soh, W.S. A survey of calibration-free indoor positioning systems. Comput. Commun. 2015, 66, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Jeon, W.S.; Dwijaksara, M.H.; Jeong, D.G. Performance analysis of neighbor discovery process in bluetooth low-energy networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2016, 66, 1865–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Han, K. Backoff scheme for crowded Bluetooth low energy networks. IET Commun. 2017, 11, 548–557. [Google Scholar]
- Contreras, D.; Castro, M.; de la Torre, D.S. Performance evaluation of bluetooth low energy in indoor positioning systems. Trans. Emerg. Telecommun. Technol. 2017, 28, e2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.Y.; Ho, T.W.; Fang, C.C.; Yen, Z.S.; Yang, B.J.; Lai, F. A mobile indoor positioning system based on iBeacon technology. In Proceedings of the 2015 37th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Milan, Italy, 25–29 August 2015; pp. 4970–4973. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, M.; Park, W.K.; Lee, I. Smart office energy management system using bluetooth low energy based beacons and a mobile app. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics (ICCE), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 9–12 January 2015; pp. 501–502. [Google Scholar]
- Fujihara, A.; Yanagizawa, T. Proposing an extended iBeacon system for indoor route guidance. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Intelligent Networking and Collaborative Systems, Taipei, Taiwan, 2–4 September 2015; pp. 31–37. [Google Scholar]
- Subhan, F.; Hasbullah, H.; Rozyyev, A.; Bakhsh, S.T. Indoor positioning in Bluetooth networks using fingerprinting and lateration approach. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Information Science and Applications, Jeju Island, South Korea, 26–29 April 2011; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, X.; Song, J.; Gurrin, C.; Zhu, Z. A comprehensive study of bluetooth fingerprinting-based algorithms for localization. In Proceedings of the 2013 27th International Conference on Advanced Information Networking and Applications Workshops, Barcelona, Spain, 25–28 March 2013; pp. 300–305. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Cuthbert, L. Bluetooth positioning using RSSI and triangulation methods. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE 10th Consumer Communications and Networking Conference (CCNC), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 11–14 January 2013; pp. 837–842. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, J.W.; Lin, C.P.; Tseng, Y.C. BLE-based collaborative indoor localization with adaptive multi-lateration and mobile encountering. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference, Doha, Qatar, 3–6 April 2016; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Ayyalasomayajula, R.; Vasisht, D.; Bharadia, D. BLoc: CSI-based accurate localization for BLE tags. In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Emerging Networking EXperiments and Technologies, Heraklion, Greece, 4–7 December 2018; pp. 126–138. [Google Scholar]
- Monfared, S.; Nguyen, T.H.; Petrillo, L.; De Doncker, P.; Horlin, F. Experimental demonstration of BLE transmitter positioning based on AOA estimation. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 29th Annual International Symposium on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications (PIMRC), Bologna, Italy, 9–12 September 2018; pp. 856–859. [Google Scholar]
- Röbesaat, J.; Zhang, P.; Abdelaal, M.; Theel, O. An improved BLE indoor localization with Kalman-based fusion: An experimental study. Sensors 2017, 17, 951. [Google Scholar]
- Antevski, K.; Redondi, A.E.; Pitic, R. A hybrid BLE and Wi-Fi localization system for the creation of study groups in smart libraries. In Proceedings of the 2016 9th IFIP Wireless and Mobile Networking Conference (WMNC), Colmar, France, 11–13 July 2016; pp. 41–48. [Google Scholar]
- Zafari, F.; Papapanagiotou, I. Enhancing ibeacon based micro-location with particle filtering. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), San Diego, CA, USA, 6–10 December 2015; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Spreitzer, R. Pin skimming: Exploiting the ambient-light sensor in mobile devices. In Proceedings of the 4th ACM Workshop on Security and Privacy in Smartphones & Mobile Devices, Raleigh, NC, USA, 19 October 2014; pp. 51–62. [Google Scholar]
- Gutierrez-Martinez, J.M.; Castillo-Martinez, A.; Medina-Merodio, J.A.; Aguado-Delgado, J.; Martinez-Herraiz, J.J. Smartphones as a light measurement tool: Case of study. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, I.; Hur, S.; Park, Y. MagIO: Magnetic field strength based indoor-outdoor detection with a commercial smartphone. Micromachines 2018, 9, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Huang, W.; Li, X.Y.; Yang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Mao, X. Lightitude: Indoor positioning using uneven light intensity distribution. Proc. ACM Int. Mob. Wearable Ubiquitous Technol. 2018, 2, 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, E. A Low-Infrastructure Approach to Indoor Localization and Tracking Using Lighting Information. Ph.D. Thesis, Electrical and Computer Engineering Department, Hamilton, ON, Canada, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Burton, B. Atmospheric pressure, and temperature aloft. Weather 1993, 48, 141–147. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, H.; Gu, T.; Tao, X.; Lu, J. Scalable floor localization using barometer on smartphone. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2016, 16, 2557–2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Gao, Z.; He, Z.; Zhang, P.; Chen, R.; El-Sheimy, N. Multi-sensor multi-floor 3D localization with robust floor detection. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 76689–76699. [Google Scholar]
- Muralidharan, K.; Khan, A.J.; Misra, A.; Balan, R.K.; Agarwal, S. Barometric phone sensors: More hype than hope! In Proceedings of the 15th Workshop on Mobile Computing Systems and Applications, Santa Barbara, CA, USA, 26–27 February 2014; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Haque, F.; Dehghanian, V.; Fapojuwo, A.O. Sensor fusion for floor detection. In Proceedings of the 2017 8th IEEE Annual Information Technology, Electronics and Mobile Communication Conference (IEMCON), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 3–5 October 2017; pp. 134–140. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Lenz, H.; Szabo, A.; Hanebeck, U.D.; Bamberger, J. Fusion of barometric sensors, wlan signals and building information for 3-d indoor/campus localization. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Multisensor Fusion and Integration for Intelligent Systems (MFI 2006), Heidelberg, Germany, 3–6 September 2006; pp. 426–432. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Guo, J.; Wang, W.; Hu, J. Floor recognition based on SVM for WiFi indoor positioning. In China Satellite Navigation Conference; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2018; pp. 725–735. [Google Scholar]
- Tiwari, S.; Jain, V.K. Smartphone based improved floor determination technique for multi-floor buildings. In Proceedings of the World Congress on Engineering, London, UK, 4–6 July 2018; pp. 4–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ai, H.; Liu, M.; Shi, Y.; Zhao, J. Floor Identification with Commercial Smartphones in Wifi-Based Indoor Localization System. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2016, 41, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, I.; Hur, S.; Shafiq, M.; Park, Y. Floor identification using magnetic field data with smartphone sensors. Sensors 2019, 19, 2538. [Google Scholar]
- Ashraf, I.; Hur, S.; Park, Y. MDIRECT-Magnetic field strength and peDestrIan dead RECkoning based indoor localizaTion. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation (IPIN), Nantes, France, 24–27 September 2018; pp. 24–27. [Google Scholar]
- Elmenreich, W. An introduction to sensor fusion. Vienna Univ. Technol. Austria 2002, 502, 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Gravina, R.; Alinia, P.; Ghasemzadeh, H.; Fortino, G. Multi-sensor fusion in body sensor networks: State-of-the-art and research challenges. Inf. Fusion 2017, 35, 68–80. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S. Comparison of assisted GPS (AGPS) performance using simulator and field tests. In Proceedings of the ION GNSS, Citeseer, Fort Worth, TX, USA, 26–29 September 2006; pp. 26–29. [Google Scholar]
- Van Diggelen, F. A-Gps: Assisted Gps, Gnss, and Sbas; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Rowe, R.W.; Duffett-Smith, P.J.; Jarvis, M.R.; Graube, N.G. Enhanced GPS: The tight integration of received cellular timing signals and GNSS receivers for ubiquitous positioning. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE/ION Position, Location and Navigation Symposium, Monterey, CA, USA, 5–8 May 2008; pp. 838–845. [Google Scholar]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).