A 4-mW Temperature-Stable 28 GHz LNA with Resistive Bias Circuit for 5G Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Analysis and Design
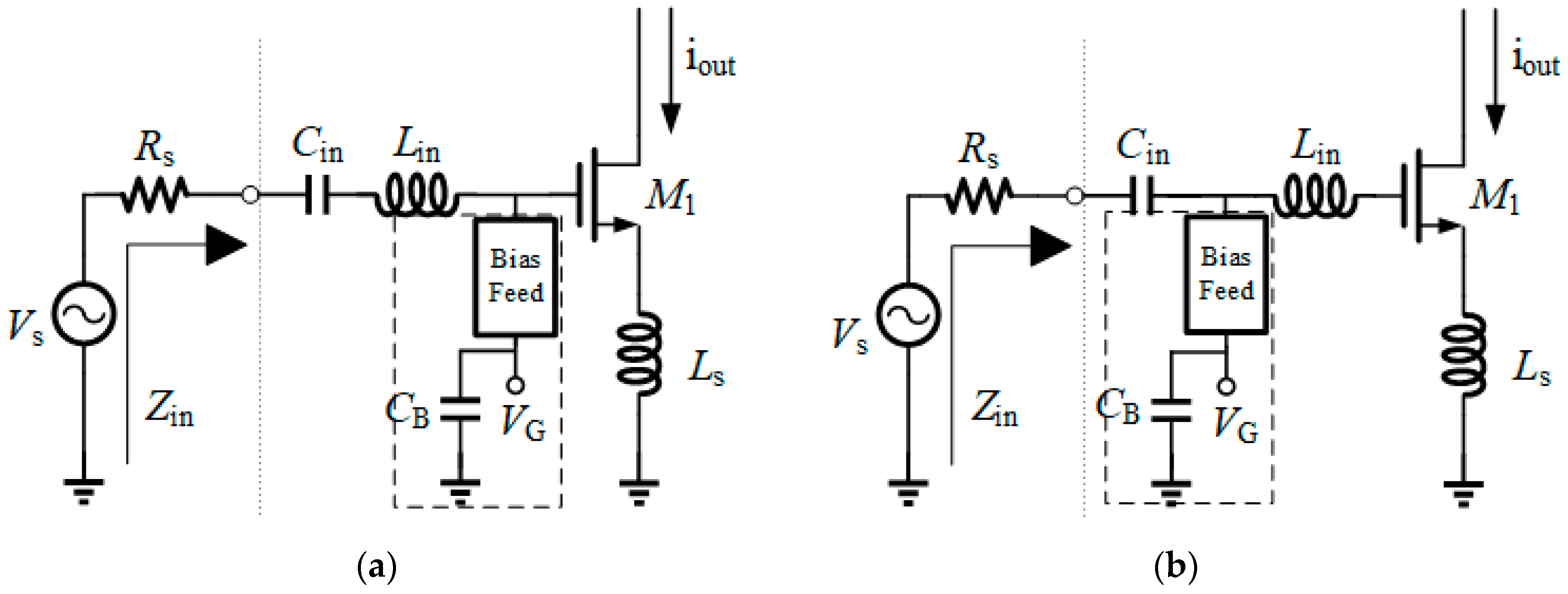
2.1. Bias Circuit Design
2.1.1. Bias Circuit with SNIM
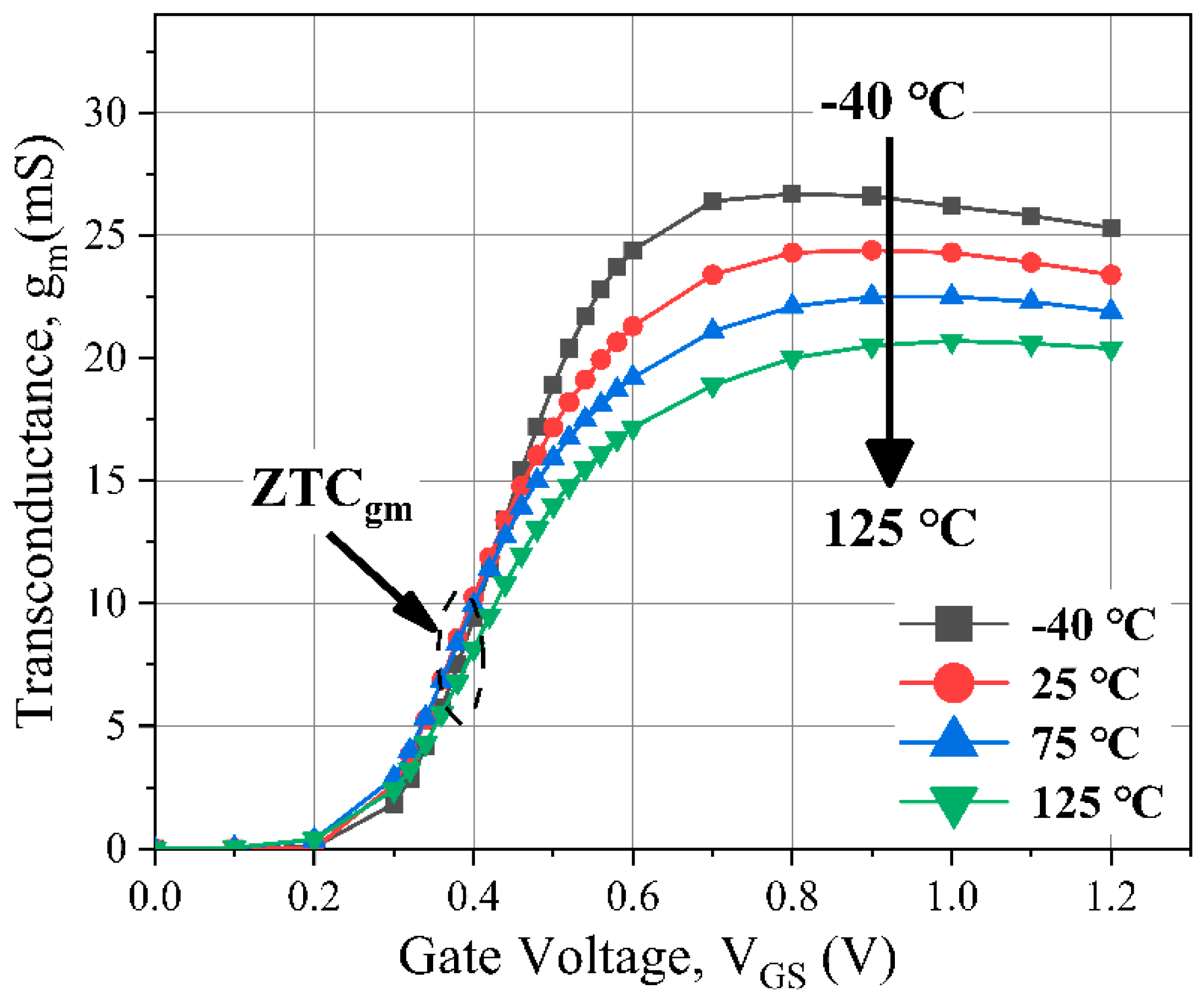
2.1.2. Bias Points Design
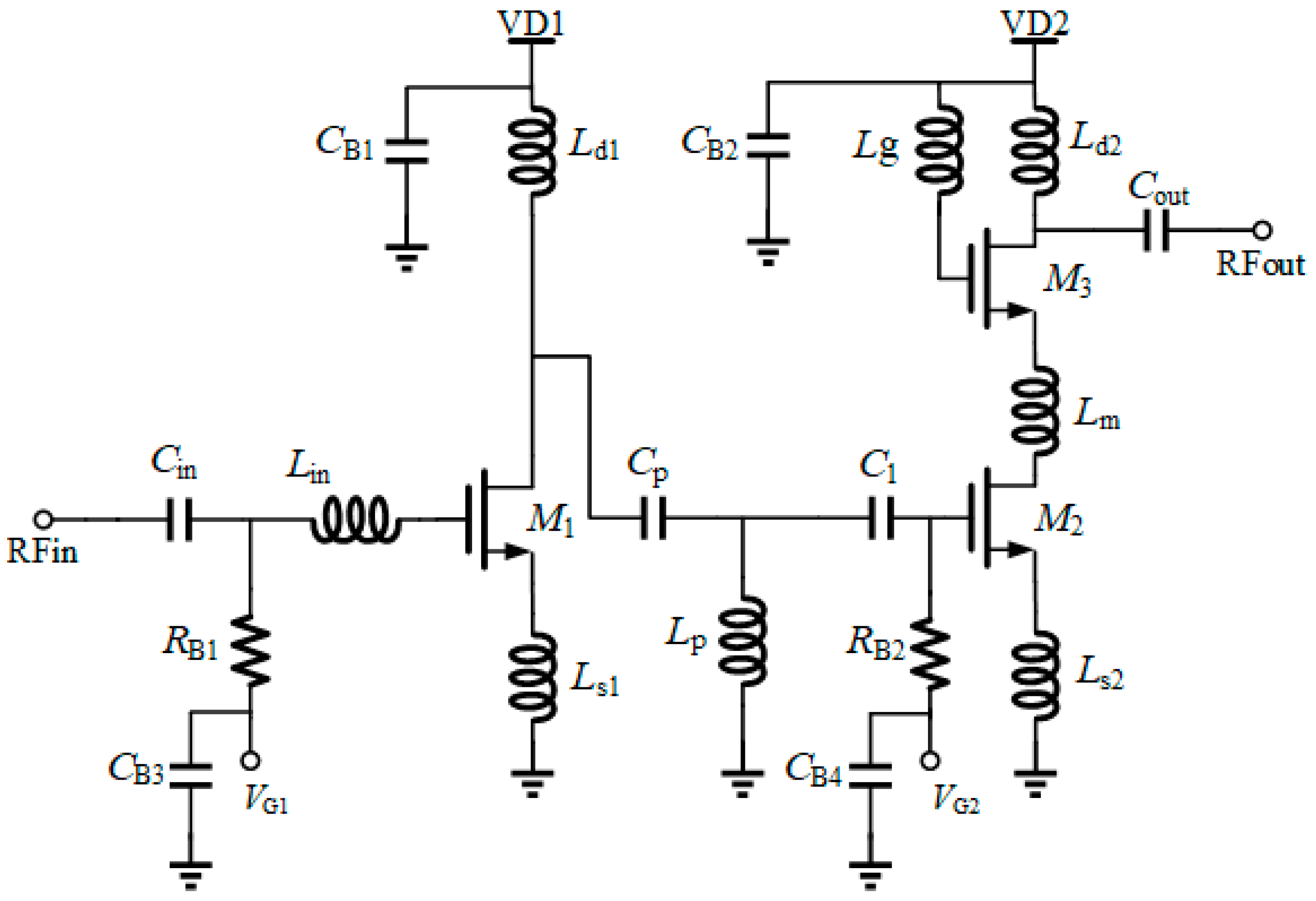
2.2. Two-Stage Single-End LNA Design
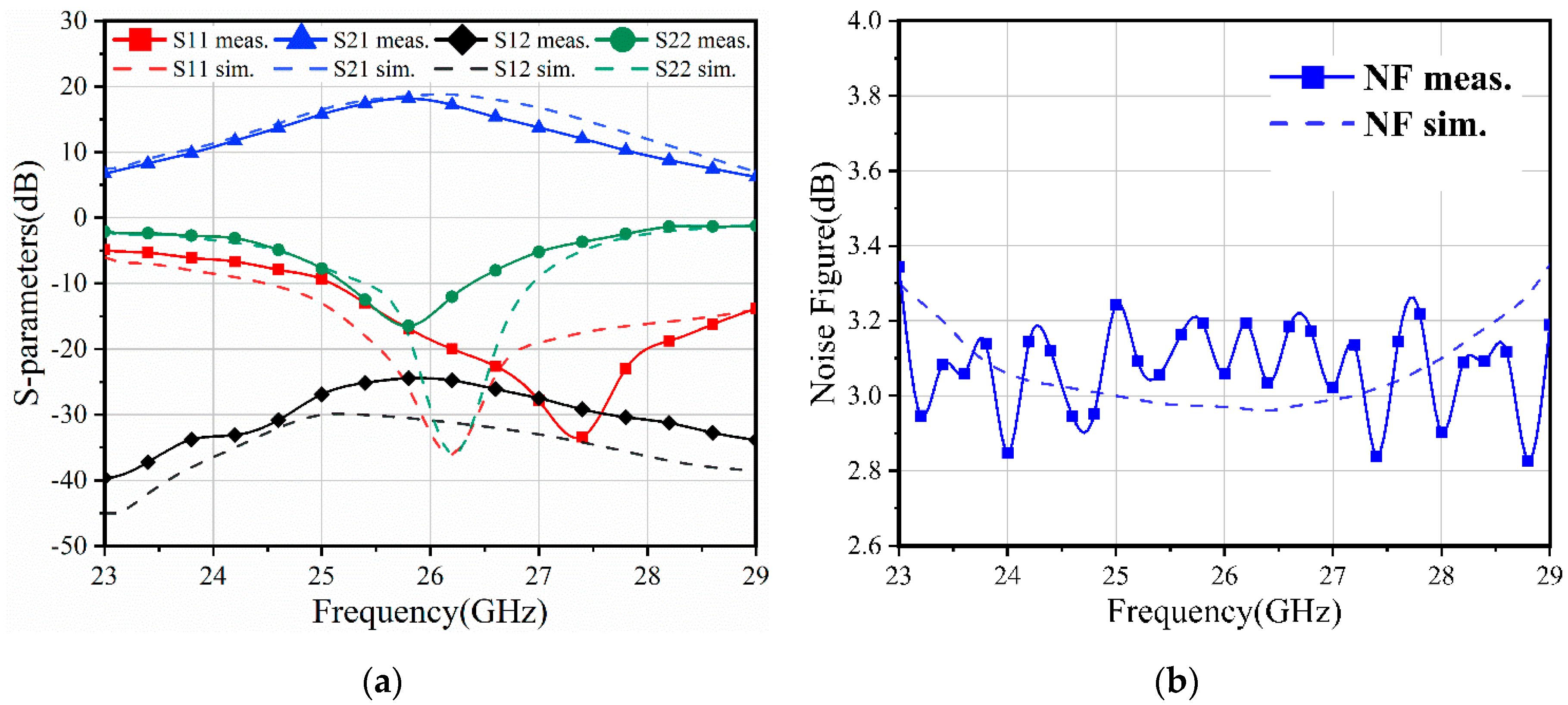
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sadhu, B.; Tousi, Y.; Hallin, J.; Sahl, S.; Reynolds, S.K.; Renstrom, O.; Sjogren, K.; Haapalahti, O.; Mazor, N.; Bokinge, B.; et al. A 28-GHz 32-Element TRX Phased-Array IC with Concurrent Dual-Polarized Operation and Orthogonal Phase and Gain Control for 5G Communications. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 2017, 52, 3373–3391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.T.; Park, B.S.; Oh, S.M.; Song, S.S.; Ho, Y.C. A 28GHz CMOS direct conversion transceiver with packaged antenna arrays for 5G cellular system. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits Symposium (RFIC), Honolulu, HI, USA, 4–6 June 2017; pp. 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibaroglu, K.; Sayginer, M.; Phelps, T.; Rebeiz, G.M. A 64-Element 28-GHz phased-array transceiver with 52-dBm EIRP and 8–12-Gb/s 5G link at 300 meters without any calibration. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2018, 66, 5796–5811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chettri, L.; Bera, R. A Comprehensive Survey on Internet of Things (IoT) Toward 5G Wireless Systems. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 7, 16–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Q.; Li, D.; Huang, J.; Li, J.; Chang, H.; Sun, B.; Liu, H. A 28 GHz Linear Power Amplifier Based on CPW Matching Networks with Series-Connected DC-Blocking Capacitors. Electronics 2020, 9, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkholy, M.; Shakib, S.; Dunworth, J.; Aparin, V.; Entesari, K. A Wideband Variable Gain LNA with High OIP3 for 5G Using 40-nm Bulk CMOS. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 2018, 28, 64–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, B.H.; Inac, O.; Chang, M.; Yang, H.H.; Rebeiz, G.M. A high-linearity 76–85-GHz 16-element 8-transmit/8-receive phased-array chip with high isolation and flip-chip packaging. Microw. Theory Tech. 2014, 62, 2337–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madan, A.; McPartlin, M.J.; Masse, C.; Vaillancourt, W.; Cressler, J.D. A 5 GHz 0.95 dB NF Highly Linear Cascode Floating-Body LNA in 180 nm SOI CMOS Technology. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 2012, 22, 200–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, H.J.; Chang, W.I.; Kim, S.M.; Park, B.J.; Yook, J.-M.; Eo, Y.-S. 28 GHz GaAs pHEMT MMICs and RF front-end module for 5G communication systems. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2019, 61, 878–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-C.; Lin, Y.-S.; Huang, G.-W.; Lu, S.-S. A 5.79-dB NF, 30-GHz-band monolithic LNA with 10 mW power consumption in standard 0.18-μm CMOS technology. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2009, 51, 933–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; He, J.; Wang, H.; Chang, S.; Huang, Q.; Yu, X.-P. A 28 GHz LNA using defected ground structure for 5G application. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2018, 60, 1067–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; El-Aassar, O.; Kumar, A.; Boenke, M.; Rebeiz, G.M. LNA Design with CMOS SOI Process-l.4dB NF K/Ka band LNA. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/MTT-S International Microwave Symposium—IMS, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 10–15 June 2018; pp. 1484–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, F.; Syed, S.; Otto, M.; Bellaouar, A. A Low Noise Figure 28GHz LNA in 22nm FDSOI Technology. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits Symposium (RFIC), Boston, MA, USA, 2–4 June 2019; pp. 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issakov, V.; Ciocoveanu, R. Low-Power K-Band LNA in 45 nm SOI CMOS. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Microwaves, Antennas, Communications and Electronic Systems (COMCAS), Tel-Aviv, Israel, 4–6 November 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Kaamouchi, M.; Moussa, M.S.; Raskin, J.-P.; Vanhoenacker-Janvier, D. Zero-temperature-coefficient biasing point of 2.4-GHz LNA in PD SOI CMOS technology. In Proceedings of the 2007 European Microwave Conference, Munich, Germany, 9–12 October 2007; pp. 1101–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, E.; Ikushima, T.; Itoh, K.; Suematsu, N. A dual bias-feed circuit design for SiGe HBT low-noise linear amplifier. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2003, 51, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickson, T.; Yau, K.; Chalvatzis, T.; Mangan, A.; Laskin, E.; Beerkens, R.; Westergaard, P.; Tazlauanu, M.; Yang, M.-T.; Voinigescu, S. The Invariance of Characteristic Current Densities in Nanoscale MOSFETs and Its Impact on Algorithmic Design Methodologies and Design Porting of Si(Ge) (Bi)CMOS High-Speed Building Blocks. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 2006, 41, 1830–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.-L.; Chang, S.-F.; Chen, K.-M.; Huang, G.-W.; Chang, J.-C. Temperature Effect on Kυ-Band Current-Reused Common-Gate LNA in 0.13-μm CMOS Technology. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2009, 57, 2131–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, A.; Osman, M.; Dogan, N.; Imam, M. Zero-temperature-coefficient biasing point of partially depleted SOI MOSFET’s. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 1995, 42, 1709–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.-K.; Kim, C.-H.; Ihm, G.-J.; Yang, M.-S.; Lee, S.-G. CMOS Low-Noise Amplifier Design Optimization Techniques. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2004, 52, 1433–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soyuer, M.; Plouchart, J.-O.; Ainspan, H.; Burghartz, J. A 5.8-GHz 1-V low-noise amplifier in SiGe bipolar technology. In Proceedings of the 1997 IEEE Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits (RFIC) Symposium. Digest of Technical Papers, Denver, CO, USA, 10 June 1997; pp. 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsay, J.; Lopez, J.; Lie, D. The impacts of base bias resistor and LTE 16QAM signal bandwidth on high-efficiency linear SiGe power amplifier design. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Bipolar/BiCMOS Circuits and Technology Meeting (BCTM), New Brunswick, NJ, USA, 25–27 September 2016; pp. 52–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.-J.; Lin, K.-Y.; Wang, H. Millimeter-Wave Low Power and Miniature CMOS Multicascode Low-Noise Amplifiers with Noise Reduction Topology. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2009, 57, 3049–3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Feng, J.; Guo, Y.; Li, Z. Analysis and design of a V-band low-noise amplifier in 90 nm CMOS for 60 GHz applications. IEICE Electron. Express 2015, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kodak, U.; Rebeiz, G.M. A 42mW 26–28 GHz phased-array receive channel with 12 dB gain, 4 dB NF and 0 dBm IIP3 in 45nm CMOS SOI. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits Symposium (RFIC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 22–24 May 2016; pp. 348–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, B.; Long, J.R.; Harame, D.L. A 1.7-dB Minimum NF, 22-32 GHz Low-Noise Feedback Amplifier with Multistage Noise Matching in 22-nm SOI-CMOS. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits Symposium (RFIC), Boston, MA, USA, 2–4 June 2019; pp. 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Kang, K. A Ku-band Miniaturized LNA in 0.18-µm CMOS Process for Low-cost Phased Array Application. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Symposium on Radio-Frequency Integration Technology (RFIT), Nanjing, China, 28–30 August 2019; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| M1–M3 | Cin/Cout | CB1-CB4 | RB1/RB2 | Cp | C1 | Lin |
| 30 um/90 nm | 1.25 pF | 2 pF | 1.2 kΩ | 110 fF | 1 pF | 680 pH |
| Ls1 | Ls2 | Ld1 | Ld2 | Lm | Lg | |
| 300 pH | 270 pH | 550 pH | 700 pH | 140 pH | 160 pH |
| This Work | [13] | [14] | [25] | [26] | [12] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Technology | 90 nm SOI | 22 nm SOI | 45 nm SOI | 45 nm SOI | 22 nm SOI | 45 nm SOI |
| Topology 1 | 2 SE | 1 SE | 1 SE | 1 SE | 2 SE | 1 SE |
| Bias circuit | resistive | off-chip | resistive | inductive | off-chip | resistive |
| Gain (dB) | 18.1 | 12.6 | 10.5 | 8.5 | 20.1 | 12.8 |
| NF 2 (dB) | 3.1 | 1.35 | 1.6 | 3 | 1.95 | 1.4 |
| IP1 dB (dBm) | –16 | –7.9 | –10.3 | 3.5 | NA | NA |
| IIP3 (dBm) | –6 | 1.4 | NA | NA | −14 | 5 |
| PDC (mW) | 4 | 13 | 6 | 12 | 17.3 | 7 |
| Area 3 (mm2) | 0.16 | 0.21 | 0.18 | NA | 0.05 | 0.3 |
| This Work | [15] | [27] | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Technology | 90 nm SOI CMOS | 130 nm SOI CMOS | 180 nm CMOS |
| Frequency (GHz) | 26 | 2.5 | 17 |
| Gain (dB) | 15.8–18.8 | 9.1–10 | 18.7–23 |
| Gain variation (dB) | 3 | 0.9 | 4.3 |
| NF (dB) | 2.3–4.2 | 3.4–5.7 | 2.2–4.3 |
| NF variation (dB) | 1.9 | 2.3 | 2.1 |
| Power consumption (mW) | 3.7–4.5 | 2.2–3.7 | 66 1 |
| Power variation (mW) | 0.8 | 1.5 | NA |
| Temperature range (°C) | −40–125 | 25–200 | −55–120 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, D.; Xia, Q.; Huang, J.; Li, J.; Chang, H.; Sun, B.; Liu, H. A 4-mW Temperature-Stable 28 GHz LNA with Resistive Bias Circuit for 5G Applications. Electronics 2020, 9, 1225. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9081225
Li D, Xia Q, Huang J, Li J, Chang H, Sun B, Liu H. A 4-mW Temperature-Stable 28 GHz LNA with Resistive Bias Circuit for 5G Applications. Electronics. 2020; 9(8):1225. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9081225
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Dongze, Qingzhen Xia, Jiawei Huang, Jinwei Li, Hudong Chang, Bing Sun, and Honggang Liu. 2020. "A 4-mW Temperature-Stable 28 GHz LNA with Resistive Bias Circuit for 5G Applications" Electronics 9, no. 8: 1225. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9081225
APA StyleLi, D., Xia, Q., Huang, J., Li, J., Chang, H., Sun, B., & Liu, H. (2020). A 4-mW Temperature-Stable 28 GHz LNA with Resistive Bias Circuit for 5G Applications. Electronics, 9(8), 1225. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9081225





