Expression and Clinical Significance of MDM2 in Non-Functioning PitNETs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients, Tissue Specimens and Cell Lines
2.2. Reverse Transcription and Quantitative PCR
2.3. TMA Construction and Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
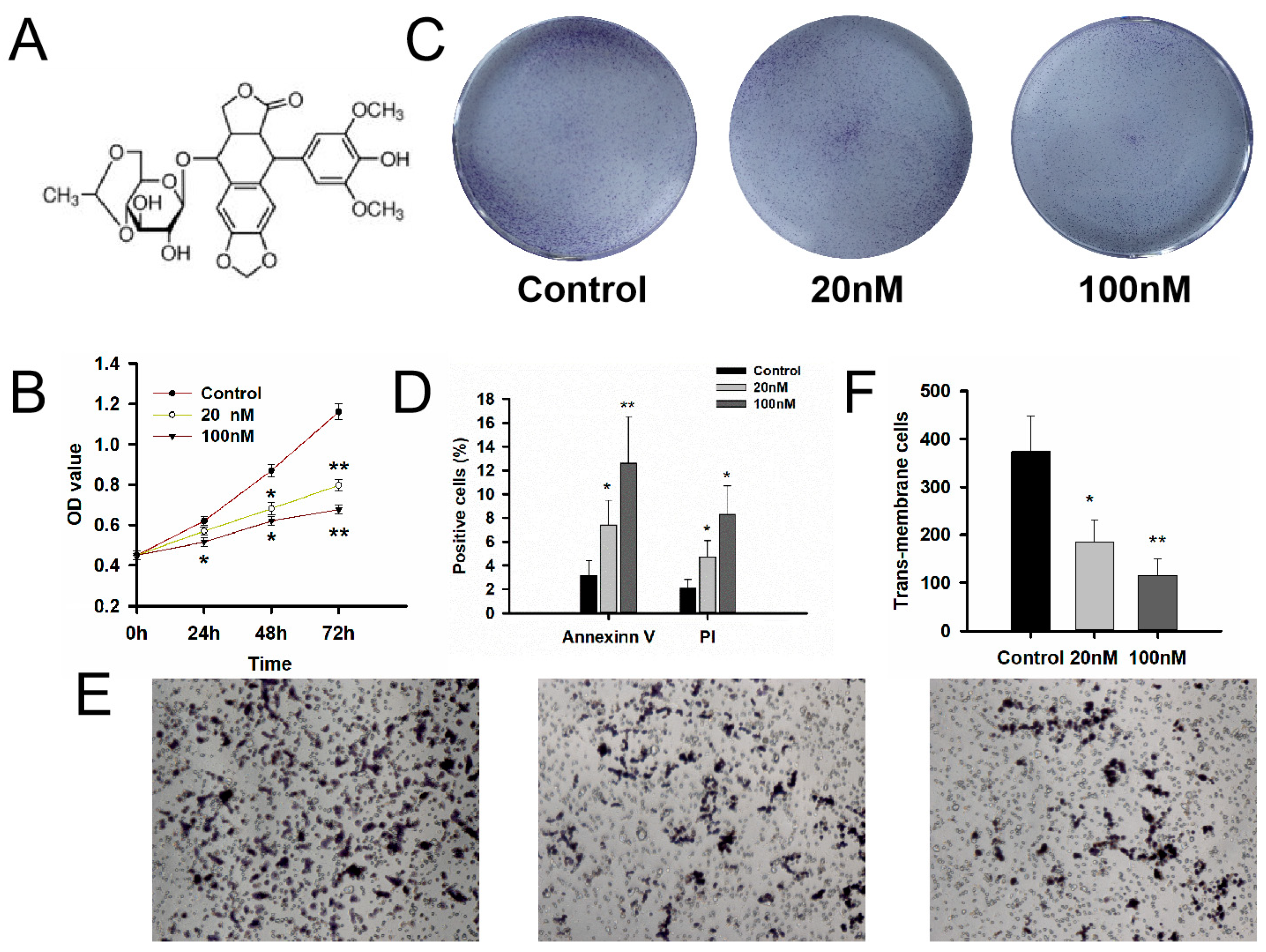
2.4. Cell Proliferation, Cell Colony Formation Assay, Cell Migration and Invasion Assays
2.5. SDS–PAGE and Western Blot Analyses
2.6. TUNEL Staining for Apoptosis Assay
2.7. Mouse Xenograft Model
2.8. Statistic
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Features of 103 NF-PitNET Patients
3.2. MDM2 and p53 Expression Profiles and Correlations with Clinicopathologic Parameters in NF-PitNET Patients
3.3. Evaluation of the MDM2 Inhibitors Etoposide on Cell Bioactivity of GT1-1 Cells
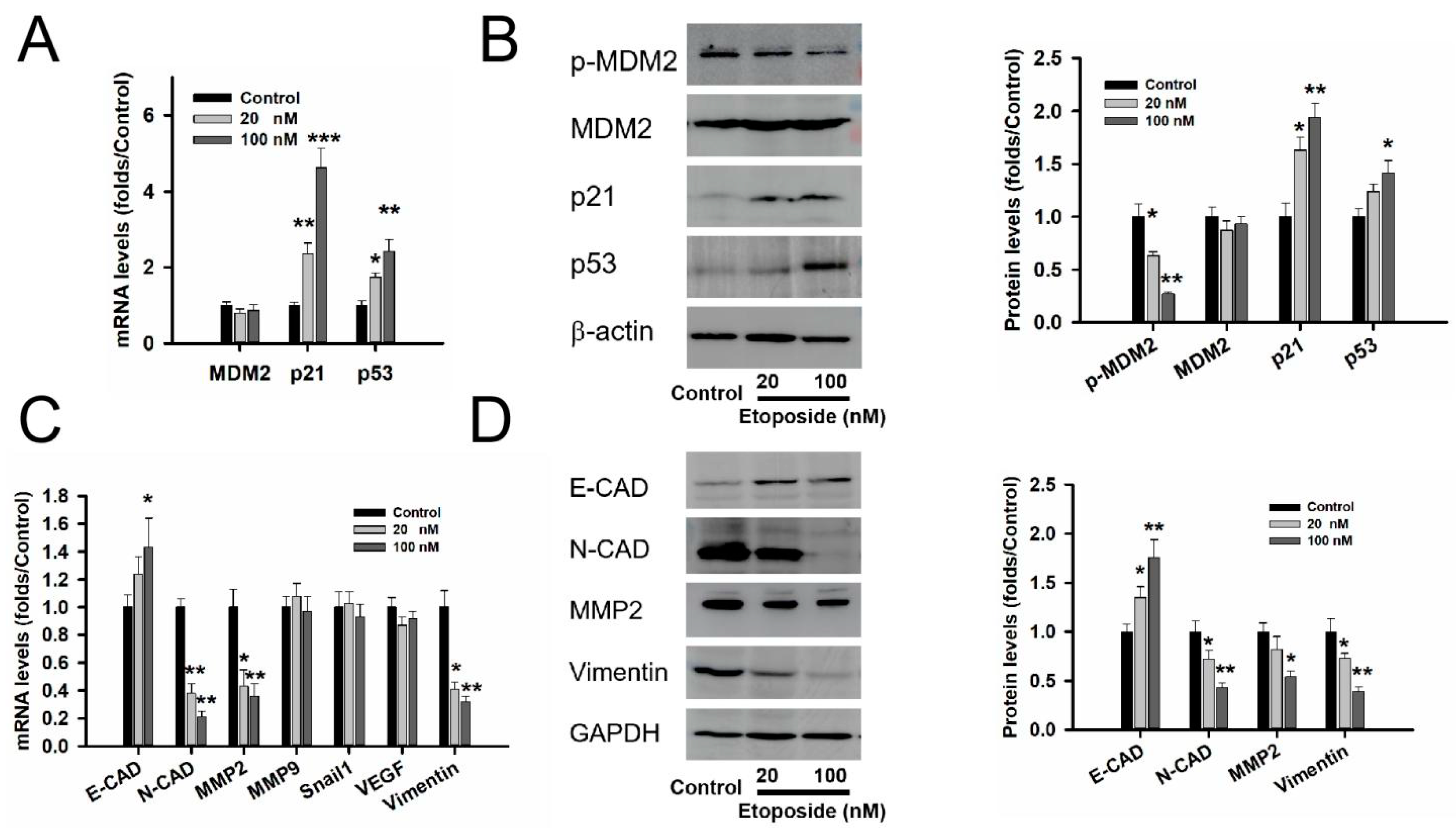
3.4. MDM2 Inhibitor Etoposide Regulated p53 Stability and Related to Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) in GT1-1 Cell Line
3.5. MDM2 Inhibitor Etoposide Showed the Anti-Proliferative Role in GT1-1 Xenograft Mouse Model
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Even-Zohar, N.; Greenman, Y. Management of NFAs: Medical treatment. Pituitary 2018, 21, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.W.; Sung, K.S.; Moon, J.H.; Kim, E.H.; Chang, W.S.; Jung, H.H.; Chang, J.W.; Park, Y.G.; Kim, S.H.; Chang, J.H. Hypopituitarism after Gamma Knife surgery for postoperative nonfunctioning pituitary adenoma. J. Neurosurg. 2018, 129, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- AlMalki, M.H.; Ahmad, M.M.; Brema, I.; AlDahmani, K.M.; Pervez, N.; Al-Dandan, S.; AlObaid, A.; Beshyah, S.A. Contemporary Management of Clinically Non-functioning Pituitary Adenomas: A Clinical Review. Clin. Med. Insights Endocrinol. Diabetes 2020, 13, 1179551420932921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neto, L.V.; Wildemberg, L.E.; Moraes, A.B.; Colli, L.M.; Kasuki, L.; Marques, N.V.; Gasparetto, E.L.; de Castro, M.; Takiya, C.M.; Gadelha, M.R. Dopamine receptor subtype 2 expression profile in nonfunctioning pituitary adenomas and in vivo response to cabergoline therapy. Clin. Endocrinol. 2015, 82, 739–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawada, N.B.; Kunert-Radek, J.; Pawlikowski, M.; Pisarek, H.; Radek, M. An evaluation of the effects of somatostatin analogue therapy in non-functioning pituitary adenomas in comparison to acromegaly. Endokrynol. Pol. 2016, 67, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karakostis, K.; López, I.; Peña-Balderas, A.M.; Fåhareus, R.; Olivares-Illana, V. Molecular and Biochemical Techniques for Deciphering p53-MDM2 Regulatory Mechanisms. Biomolecules 2020, 11, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karni-Schmidt, O.; Lokshin, M.; Prives, C. The Roles of MDM2 and MDMX in Cancer. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2016, 11, 617–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathinavelu, P.; Malavé, A.; Raney, S.R.; Hurst, J.; Roberson, C.T.; Rathinavelu, A. Expression of mdm-2 oncoprotein in the primary and metastatic sites of mammary tumor (GI-101) implanted athymic nude mice. Cancer Biochem. Biophys. 1999, 17, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lazo, P.A. Reverting p53 activation after recovery of cellular stress to resume with cell cycle progression. Cell Signal 2017, 33, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, C.; Wang, P.; Huang, C.; Peng, H. MDM2 promotes the proliferation and inhibits the apoptosis of pituitary adenoma cells by directly interacting with p53. Endokrynol. Pol. 2020, 71, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, X.; Gao, H.; Li, C.; Wu, L.; Bai, J.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y. Analysis of Ki67, HMGA1, MDM2, and RB expression in nonfunctioning pituitary adenomas. J. Neurooncol. 2017, 132, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeay, S.; Ferretti, S.; Holzer, P.; Fuchs, J.; Chapeau, E.A.; Wartmann, M.; Sterker, D.; Romanet, V.; Murakami, M.; Kerr, G.; et al. Dose and Schedule Determine Distinct Molecular Mechanisms Underlying the Efficacy of the p53-MDM2 Inhibitor HDM201. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 6257–6267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Erba, H.P.; Becker, P.S.; Shami, P.J.; Grunwald, M.R.; Flesher, D.L.; Zhu, M.; Rasmussen, E.; Henary, H.A.; Anderson, A.A.; Wang, E.S. Phase 1b study of the MDM2 inhibitor AMG 232 with or without trametinib in relapsed/refractory acute myeloid leukemia. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 1939–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wagner, A.J.; Banerji, U.; Mahipal, A.; Somaiah, N.; Hirsch, H.; Fancourt, C.; Johnson-Levonas, A.O.; Lam, R.; Meister, A.K.; Russo, G.; et al. Phase I Trial of the Human Double Minute 2 Inhibitor MK-8242 in Patients With Advanced Solid Tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 1304–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravandi, F.; Gojo, I.; Patnaik, M.M.; Minden, M.D.; Kantarjian, H.; Johnson-Levonas, A.O.; Fancourt, C.; Lam, R.; Jones, M.B.; Knox, C.D.; et al. A phase I trial of the human double minute 2 inhibitor (MK-8242) in patients with refractory/recurrent acute myelogenous leukemia (AML). Leuk. Res. 2016, 48, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, H.; Wang, F.; Lan, X.; Li, C.; Feng, J.; Bai, J.; Cao, L.; Gui, S.; Hong, L.; Zhang, Y. Temozolomide therapy for aggressive functioning pituitary adenomas refractory to surgery and radiation: A case series. Neurooncol. Pract. 2018, 5, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Wang, F.; Lan, X.; Li, C.; Feng, J.; Bai, J.; Cao, L.; Gui, S.; Hong, L.; Zhang, Y. Lower PRDM2 expression is associated with dopamine-agonist resistance and tumor recurrence in prolactinomas. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pabinger, S.; Rödiger, S.; Kriegner, A.; Vierlinger, K.; Weinhäusel, A. A survey of tools for the analysis of quantitative PCR (qPCR) data. Biomol. Detect. Quantif. 2014, 1, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.; Gao, H.; Cao, L.; Gui, S.; Liu, Q.; Li, C.; Li, D.; Gong, L.; Zhang, Y. The role of FSCN1 in migration and invasion of pituitary adenomas. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2016, 419, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zatelli, M.C. Pathogenesis of non-functioning pituitary adenomas. Pituitary 2018, 21, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, K.; Fry, E.A.; Frazier, D.P. Transcription factors that interact with p53 and Mdm2. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 138, 1577–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Deiry, W.S.; Tokino, T.; Velculescu, V.E.; Levy, D.B.; Parsons, R.; Trent, J.M.; Lin, D.; Mercer, W.E.; Kinzler, K.W.; Vogelstein, B. WAF1, a potential mediator of p53 tumor suppression. Cell 1993, 75, 817–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliner, J.D.; Kinzler, K.W.; Meltzer, P.S.; George, D.L.; Vogelstein, B. Amplification of a gene encoding a p53-associated protein in human sarcomas. Nature 1992, 358, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oliner, J.D.; Saiki, A.Y.; Caenepeel, S. The Role of MDM2 Amplification and Overexpression in Tumorigenesis. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2016, 6, a026336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grimm, F.; Maurus, R.; Beschorner, R.; Naros, G.; Stanojevic, M.; Gugel, I.; Giese, S.; Bier, G.; Bender, B.; Honegger, J. Ki-67 labeling index and expression of p53 are non-predictive for invasiveness and tumor size in functional and nonfunctional pituitary adenomas. Acta Neurochir. 2019, 161, 1149–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivas, R.; Satterlee, A.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Huang, L. Theranostic etoposide phosphate/indium nanoparticles for cancer therapy and imaging. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 18542–18551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tang, Y.; Xuan, Y.; Qiao, G.; Ou, Z.; He, Z.; Zhu, Q.; Liao, M.; Yin, G. MDM2 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition through activation of Smad2/3 signaling pathway in lung adenocarcinoma. Onco. Targets Ther. 2019, 12, 2247–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ingham, M.; Schwartz, G.K. Cell-Cycle Therapeutics Come of Age. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 2949–2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanjirband, M.; Rahgozar, S. Targeting p53-MDM2 Interaction Using Small Molecule Inhibitors and the Challenges Needed to be Addressed. Curr. Drug Targets 2019, 20, 1091–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, C.; Mondal, P.; Mukhopadhyay, M.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Ghosh, I.; Handral, A. Evaluation of prognostic utility of Ki-67, P53, and O-6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase expression in pituitary tumors. J. Lab. Physicians 2019, 11, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Deiry, W.S. p21(WAF1) Mediates Cell-Cycle Inhibition, Relevant to Cancer Suppression and Therapy. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 5189–5191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Variable | MDM2 | p Value | p53 | p Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| High (n = 51) | Low (n = 52) | High (n = 51) | Low (n = 52) | |||
| Gender | 0.012 | 0.012 | ||||
| Male | 32 | 38 | 46 | 24 | ||
| Female | 19 | 14 | 13 | 20 | ||
| Age | 48.8 ± 1.63 | 54.5 ± 1.24 | 0.007 | 53.01 ± 1.18 | 49.39 ± 1.86 | 0.088 |
| Tumor size (cm3) | 16.79 | 6.63 ± 1.15 | 0.018 | 6.86 ± 1.13 | 18.53 ± 4.75 | 0.008 |
| Recurrence | 0.012 | 0.012 | ||||
| Yes | 6 | 13 | 6 | 13 | ||
| No | 53 | 31 | 53 | 31 | ||
| Invasive behavior | ||||||
| Yes | 30 | 14 | 0.001 | 24 | ||
| No | 21 | 38 | 27 | |||
| Cavernous sinus compression | 0.061 | 0 | ||||
| Yes | 17 | 9 | 5 | 21 | ||
| no | 34 | 43 | 54 | 23 | ||
| Kinds | Univariate Cox | Multivariate Cox | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p Value | HR | 95%CI Down | 95%CI Up | p Value | HR | 95%CI Down | 95%CI Up | |
| MDM2 | 0.018 | 1.048 | 1.008 | 1.090 | 0.023 | 1.151 | 1.019 | 1.299 |
| TP53 | 0.066 | 1.100 | 0.994 | 1.217 | 0.281 | 1.079 | 0.940 | 1.240 |
| Age | 0.075 | 0.966 | 0.930 | 1.004 | 0.280 | 0.977 | 0.936 | 1.019 |
| Gender | 0.039 | 0.409 | 0.176 | 0.954 | 0.091 | 0.454 | 0.181 | 1.135 |
| Recurrence | 0.016 | 3.704 | 1.278 | 10.735 | 0.043 | 3.296 | 1.037 | 10.477 |
| Tumor size | 0.119 | 1.020 | 0.995 | 1.046 | 0.239 | 1.014 | 0.991 | 1.038 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yao, X.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, S.; Cheng, R.; Liu, C.; Zhang, G. Expression and Clinical Significance of MDM2 in Non-Functioning PitNETs. Medicina 2023, 59, 373. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59020373
Yao X, Liu Q, Zhao S, Cheng R, Liu C, Zhang G. Expression and Clinical Significance of MDM2 in Non-Functioning PitNETs. Medicina. 2023; 59(2):373. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59020373
Chicago/Turabian StyleYao, Xiaohui, Qian Liu, Sida Zhao, Rui Cheng, Chunhui Liu, and Gangli Zhang. 2023. "Expression and Clinical Significance of MDM2 in Non-Functioning PitNETs" Medicina 59, no. 2: 373. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59020373
APA StyleYao, X., Liu, Q., Zhao, S., Cheng, R., Liu, C., & Zhang, G. (2023). Expression and Clinical Significance of MDM2 in Non-Functioning PitNETs. Medicina, 59(2), 373. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina59020373





