An Overview of Ovarian Cancer: The Role of Cancer Stem Cells in Chemoresistance and a Precision Medicine Approach Targeting the Wnt Pathway with the Antagonist sFRP4
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Types of Ovarian Cancers
3. Existing Markers of Ovarian Cancer
4. Current Treatment Methods
4.1. PARP (Poly(ADPribose) Polymerase) Inhibitors
4.2. Anti-Angiogenic Therapy
4.3. Immunomodulators (Pembrolizumab, Dostarlimab)
4.4. Radiotherapy
5. Chemoresistance and Cancer Stem Cells in Ovarian Cancer
6. Circulating Tumor Cells
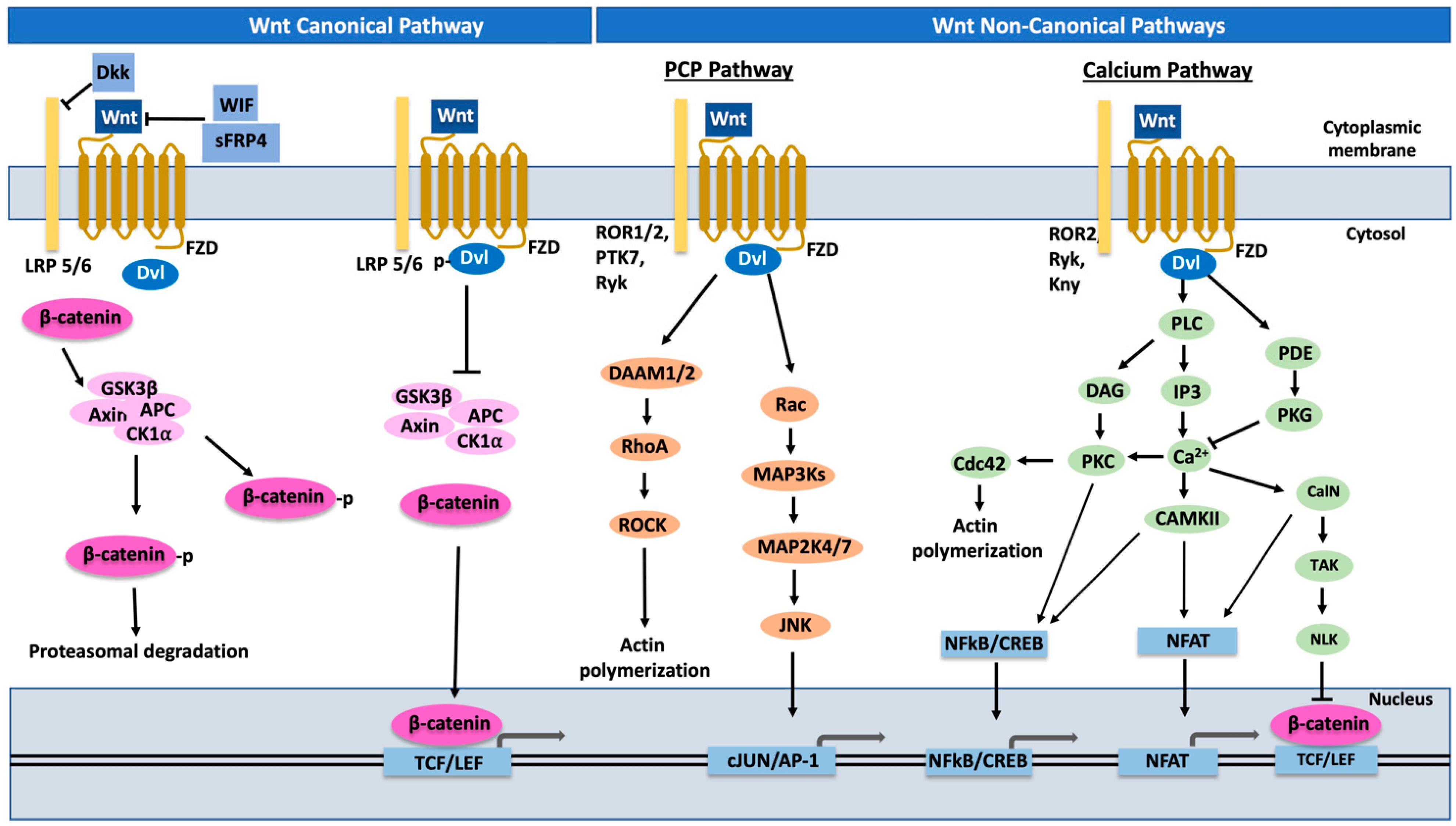
7. Role of Wnt Pathway and EMT in Ovarian Metastasis
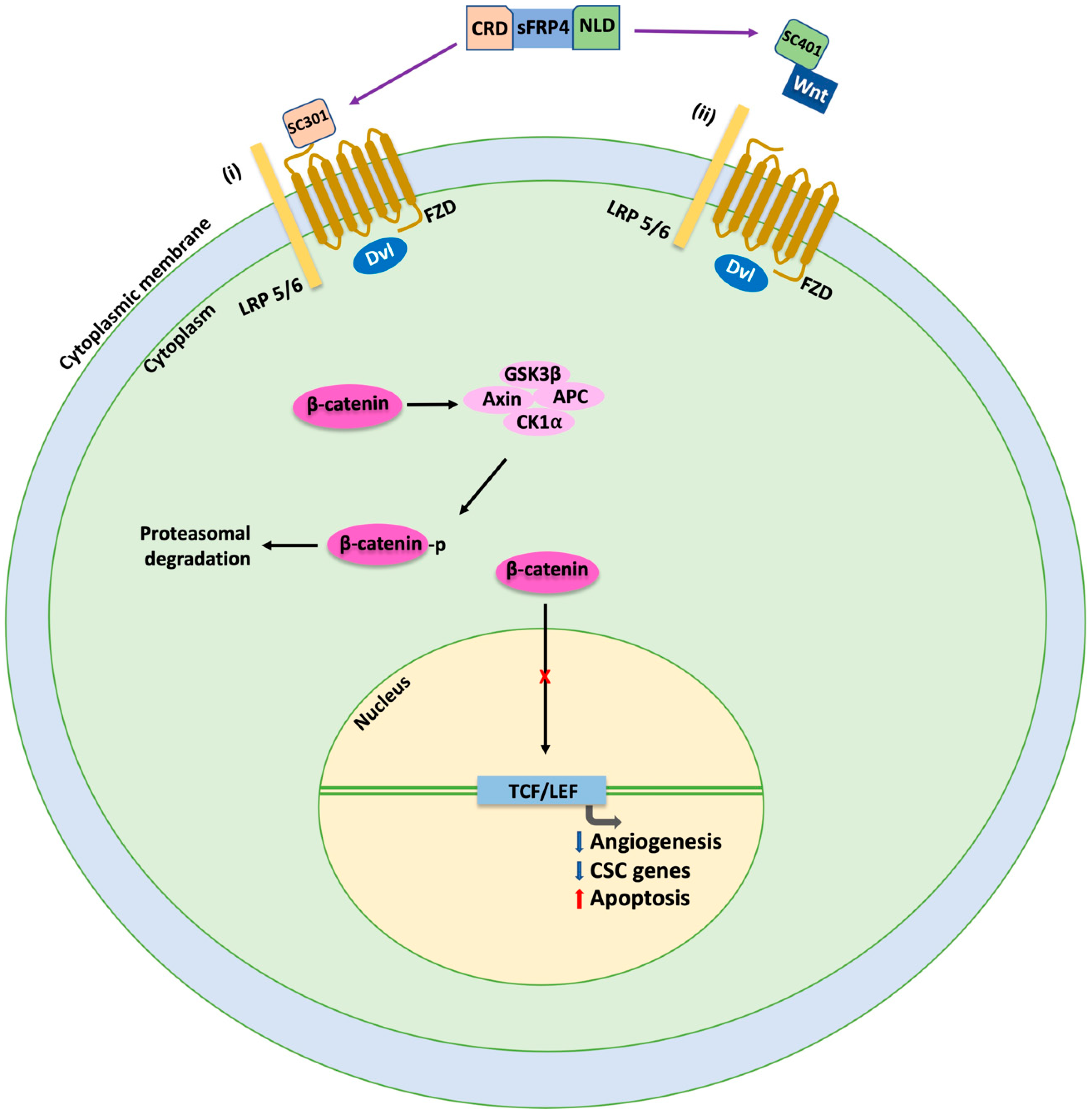
8. Wnt Inhibition by sFRP4 Micropeptides: Potential Breakthrough in Ovarian Cancer Treatment?
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, J.; Chan, W.C.; Ngai, C.H.; Lok, V.; Zhang, L.; Lucero-Prisno, D.E., 3rd; Xu, W.; Zheng, Z.J.; Elcarte, E.; Withers, M.; et al. Worldwide Burden, Risk Factors, and Temporal Trends of Ovarian Cancer: A Global Study. Cancers 2022, 14, 2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaitskell, K.; Hermon, C.; Barnes, I.; Pirie, K.; Floud, S.; Green, J.; Beral, V.; Reeves, G.K. Ovarian cancer survival by stage, histotype, and pre-diagnostic lifestyle factors, in the prospective UK Million Women Study. Cancer Epidemiol. 2022, 76, 102074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortés-Guiral, D.; Hübner, M.; Alyami, M.; Bhatt, A.; Ceelen, W.; Glehen, O.; Lordick, F.; Ramsay, R.; Sgarbura, O.; Van Der Speeten, K.; et al. Primary and metastatic peritoneal surface malignancies. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2021, 7, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchetti, C.; De Felice, F.; Romito, A.; Iacobelli, V.; Sassu, C.M.; Corrado, G.; Ricci, C.; Scambia, G.; Fagotti, A. Chemotherapy resistance in epithelial ovarian cancer: Mechanisms and emerging treatments. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2021, 77, 144–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, F.; Zhu, T.; Pan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, H.; Wang, X.; Hu, J.; Han, H.; Mei, L.; Chen, D.; et al. Comprehensive genomic profiling of high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma from Chinese patients identifies co-occurring mutations in the Ras/Raf pathway with TP53. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 3928–3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vang, R.; Shih Ie, M.; Kurman, R.J. Ovarian low-grade and high-grade serous carcinoma: Pathogenesis, clinicopathologic and molecular biologic features, and diagnostic problems. Adv. Anat. Pathol. 2009, 16, 267–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, K.-L.; Lee, M.-Y.; Chao, W.-R.; Han, C.-P. The status of Her2 amplification and Kras mutations in mucinous ovarian carcinoma. Human Genom. 2016, 10, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kurman, R.J.; Shih Ie, M. Molecular pathogenesis and extraovarian origin of epithelial ovarian cancer--shifting the paradigm. Human Pathol. 2011, 42, 918–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ackroyd, S.A.; Arguello, D.; Ramos, P.; Mahdi, H.; ElNaggar, A.; Winer, I.; Holloway, R.; Krivak, T.; Jones, N.; Turner, V.G.; et al. Molecular portraits of clear cell ovarian and endometrial carcinoma with comparison to clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Gynecol. Oncol. 2022, 169, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casagrande, J.T.; Louie, E.W.; Pike, M.C.; Roy, S.; Ross, R.K.; Henderson, B.E. “Incessant ovulation” and ovarian cancer. Lancet 1979, 2, 170–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yachida, N.; Yoshihara, K.; Yamaguchi, M.; Suda, K.; Tamura, R.; Enomoto, T. How Does Endometriosis Lead to Ovarian Cancer? The Molecular Mechanism of Endometriosis-Associated Ovarian Cancer Development. Cancers 2021, 13, 1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atallah, G.A.; Abd Aziz, N.H.; Teik, C.K.; Shafiee, M.N.; Kampan, N.C. New Predictive Biomarkers for Ovarian Cancer. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinberger, V.; Bednarikova, M.; Cibula, D.; Zikan, M. Serous tubal intraepithelial carcinoma (STIC)—Clinical impact and management. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2016, 16, 1311–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vercellini, P.; Crosignani, P.; Somigliana, E.; Viganò, P.; Buggio, L.; Bolis, G.; Fedele, L. The ‘incessant menstruation’ hypothesis: A mechanistic ovarian cancer model with implications for prevention. Human Reprod. 2011, 26, 2262–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koshiyama, M.; Matsumura, N.; Konishi, I. Recent concepts of ovarian carcinogenesis: Type I and type II. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 934261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Dowdy, S.; Tipton, T.; Podratz, K.; Lu, W.G.; Xie, X.; Jiang, S.W. HE4 as a biomarker for ovarian and endometrial cancer management. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2009, 9, 555–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bast, R.C., Jr.; Feeney, M.; Lazarus, H.; Nadler, L.M.; Colvin, R.B.; Knapp, R.C. Reactivity of a monoclonal antibody with human ovarian carcinoma. J. Clin. Investig. 1981, 68, 1331–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Terry, K.L.; Sluss, P.M.; Skates, S.J.; Mok, S.C.; Ye, B.; Vitonis, A.F.; Cramer, D.W. Blood and urine markers for ovarian cancer: A comprehensive review. Dis. Markers 2004, 20, 53–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galgano, M.T.; Hampton, G.M.; Frierson, H.F., Jr. Comprehensive analysis of HE4 expression in normal and malignant human tissues. Mod. Pathol. 2006, 19, 847–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dochez, V.; Caillon, H.; Vaucel, E.; Dimet, J.; Winer, N.; Ducarme, G. Biomarkers and algorithms for diagnosis of ovarian cancer: CA125, HE4, RMI and ROMA, a review. J. Ovarian Res. 2019, 12, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yanaranop, M.; Anakrat, V.; Siricharoenthai, S.; Nakrangsee, S.; Thinkhamrop, B. Is the Risk of Ovarian Malignancy Algorithm Better Than Other Tests for Predicting Ovarian Malignancy in Women with Pelvic Masses? Gynecol. Obstet. Investig. 2017, 82, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, R.G.; McMeekin, D.S.; Brown, A.K.; DiSilvestro, P.; Miller, M.C.; Allard, W.J.; Gajewski, W.; Kurman, R.; Bast, R.C., Jr.; Skates, S.J. A novel multiple marker bioassay utilizing HE4 and CA125 for the prediction of ovarian cancer in patients with a pelvic mass. Gynecol. Oncol. 2009, 112, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Montagnana, M.; Danese, E.; Ruzzenente, O.; Bresciani, V.; Nuzzo, T.; Gelati, M.; Salvagno, G.L.; Franchi, M.; Lippi, G.; Guidi, G.C. The ROMA (Risk of Ovarian Malignancy Algorithm) for estimating the risk of epithelial ovarian cancer in women presenting with pelvic mass: Is it really useful? Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2011, 49, 521–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, F.P.; Batista, E.L., Jr.; Zelmanowicz, A.; Svedman, C.; Devenz, G.; Alves, S.; Silva, A.S.; Garicochea, B. Prostasin, a potential tumor marker in ovarian cancer--a pilot study. Clinics 2009, 64, 641–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walentowicz, P.; Krintus, M.; Sadlecki, P.; Grabiec, M.; Mankowska-Cyl, A.; Sokup, A.; Walentowicz-Sadlecka, M. Serum inhibin A and inhibin B levels in epithelial ovarian cancer patients. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trimbos, J.B.; Vergote, I.; Bolis, G.; Vermorken, J.B.; Mangioni, C.; Madronal, C.; Franchi, M.; Tateo, S.; Zanetta, G.; Scarfone, G.; et al. Impact of adjuvant chemotherapy and surgical staging in early-stage ovarian carcinoma: European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer-Adjuvant ChemoTherapy in Ovarian Neoplasm trial. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2003, 95, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.; Han, Y.; Kim, S.I.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, S.J.; Song, Y.S. Tumor evolution and chemoresistance in ovarian cancer. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2018, 2, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pomel, C.; Jeyarajah, A.; Oram, D.; Shepherd, J.; Milliken, D.; Dauplat, J.; Reynolds, K. Cytoreductive surgery in ovarian cancer. Cancer Imaging 2007, 7, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chandra, A.; Pius, C.; Nabeel, M.; Nair, M.; Vishwanatha, J.K.; Ahmad, S.; Basha, R. Ovarian cancer: Current status and strategies for improving therapeutic outcomes. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 7018–7031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riggs, M.J.; Pandalai, P.K.; Kim, J.; Dietrich, C.S. Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy in Ovarian Cancer. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bristow, R.E.; Tomacruz, R.S.; Armstrong, D.K.; Trimble, E.L.; Montz, F.J. Survival effect of maximal cytoreductive surgery for advanced ovarian carcinoma during the platinum era: A meta-analysis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2002, 20, 1248–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, A.; Ueda, Y.; Naka, T.; Enomoto, T. Therapeutic strategies in epithelial ovarian cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 31, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gadducci, A.; Guarneri, V.; Peccatori, F.A.; Ronzino, G.; Scandurra, G.; Zamagni, C.; Zola, P.; Salutari, V. Current strategies for the targeted treatment of high-grade serous epithelial ovarian cancer and relevance of BRCA mutational status. J. Ovarian Res. 2019, 12, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drew, Y. The development of PARP inhibitors in ovarian cancer: From bench to bedside. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 113 (Suppl. 1), S3–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Redelico, T. Rucaparib and Niraparib in Advanced Ovarian Cancer. J. Adv. Pract. Oncol. 2019, 10, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Feng, Y.; Li, J.; Deng, T.; Yin, A.; Yan, L.; Zheng, M.; Xiong, Y.; Li, J.; Huang, Y.; et al. A novel combination of niraparib and anlotinib in platinum-resistant ovarian cancer: Efficacy and safety results from the phase II, multi-center ANNIE study. EClinicalMedicine 2022, 54, 101767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, J.; Hurwitz, H.I.; Sandler, A.B.; Miles, D.; Coleman, R.L.; Deurloo, R.; Chinot, O.L. Bevacizumab (Avastin®) in cancer treatment: A review of 15 years of clinical experience and future outlook. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2020, 86, 102017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.J.; Armaiz Pena, G.N.; Pradeep, S.; Cho, M.S.; Coleman, R.L.; Sood, A.K. Anti-vascular therapies in ovarian cancer: Moving beyond anti-VEGF approaches. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2015, 34, 19–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palaia, I.; Tomao, F.; Sassu, C.M.; Musacchio, L.; Benedetti Panici, P. Immunotherapy for Ovarian Cancer: Recent Advances And Combination Therapeutic Approaches. Onco Targets Ther. 2020, 13, 6109–6129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamanishi, J.; Mandai, M.; Iwasaki, M.; Okazaki, T.; Tanaka, Y.; Yamaguchi, K.; Higuchi, T.; Yagi, H.; Takakura, K.; Minato, N.; et al. Programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 and tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T lymphocytes are prognostic factors of human ovarian cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 3360–3365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fields, E.C.; McGuire, W.P.; Lin, L.; Temkin, S.M. Radiation Treatment in Women with Ovarian Cancer: Past, Present, and Future. Front. Oncol. 2017, 7, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Durno, K.; Powell, M.E. The role of radiotherapy in ovarian cancer. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2022, 32, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemp, Z.; Ledermann, J. Update on first-line treatment of advanced ovarian carcinoma. Int. J. Women’s Health 2013, 5, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miller, R.E.; Lewis, A.J.; Powell, M.E. PARP inhibitors and immunotherapy in ovarian and endometrial cancers. Br. J. Radiol. 2021, 94, 20210002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitiyarachchi, O.; Friedlander, M.; Java, J.J.; Chan, J.K.; Armstrong, D.K.; Markman, M.; Herzog, T.J.; Monk, B.J.; Backes, F.; Secord, A.A.; et al. What proportion of patients with stage 3 ovarian cancer are potentially cured following intraperitoneal chemotherapy? Analysis of the long term (≥10 years) survivors in NRG/GOG randomized clinical trials of intraperitoneal and intravenous chemotherapy in stage III ovarian cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2022, 166, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Pestell, T.G.; Lisanti, M.P.; Pestell, R.G. Cancer stem cells. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2012, 44, 2144–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Parte, S.; Bhartiya, D.; Telang, J.; Daithankar, V.; Salvi, V.; Zaveri, K.; Hinduja, I. Detection, characterization, and spontaneous differentiation in vitro of very small embryonic-like putative stem cells in adult mammalian ovary. Stem Cells Dev. 2011, 20, 1451–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skvortsova, I.; Debbage, P.; Kumar, V.; Skvortsov, S. Radiation resistance: Cancer stem cells (CSCs) and their enigmatic pro-survival signaling. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2015, 35, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapidot, T.; Sirard, C.; Vormoor, J.; Murdoch, B.; Hoang, T.; Caceres-Cortes, J.; Minden, M.; Paterson, B.; Caligiuri, M.A.; Dick, J.E. A cell initiating human acute myeloid leukaemia after transplantation into SCID mice. Nature 1994, 367, 645–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, X.; Nephew, K.P. Ovarian Cancer Stem Cells: Role in Metastasis and Opportunity for Therapeutic Targeting. Cancers 2019, 11, 934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, J.; Zheng, T.; Hong, W.; Ye, H.; Hu, C.; Zheng, Y. Mechanism for the Decision of Ovarian Surface Epithelial Stem Cells to Undergo Neo-Oogenesis or Ovarian Tumorigenesis. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 50, 214–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, K.; Terai, Y.; Tanabe, A.; Ono, Y.J.; Hayashi, M.; Maeda, K.; Fujiwara, S.; Ashihara, K.; Nakamura, M.; Tanaka, Y.; et al. CD24 expression is a marker for predicting clinical outcome and regulates the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in ovarian cancer via both the Akt and ERK pathways. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 37, 3189–3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gao, M.Q.; Choi, Y.P.; Kang, S.; Youn, J.H.; Cho, N.H. CD24+ cells from hierarchically organized ovarian cancer are enriched in cancer stem cells. Oncogene 2010, 29, 2672–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burgos-Ojeda, D.; Wu, R.; McLean, K.; Chen, Y.C.; Talpaz, M.; Yoon, E.; Cho, K.R.; Buckanovich, R.J. CD24+ Ovarian Cancer Cells Are Enriched for Cancer-Initiating Cells and Dependent on JAK2 Signaling for Growth and Metastasis. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2015, 14, 1717–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, J.; Du, Y.; Lu, Y.; Luan, B.; Xu, C.; Yu, Y.; Zhao, H. CD44 Expression Predicts Prognosis of Ovarian Cancer Patients Through Promoting Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) by Regulating Snail, ZEB1, and Caveolin-1. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Yuan, B.; Zhang, H.; Li, H. Human epithelial ovarian cancer cells expressing CD105, CD44 and CD106 surface markers exhibit increased invasive capacity and drug resistance. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 17, 5351–5360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Motohara, T.; Fujimoto, K.; Tayama, S.; Narantuya, D.; Sakaguchi, I.; Tashiro, H.; Katabuchi, H. CD44 Variant 6 as a Predictive Biomarker for Distant Metastasis in Patients with Epithelial Ovarian Cancer. Obstet. Gynecol. 2016, 127, 1003–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stemberger-Papić, S.; Vrdoljak-Mozetic, D.; Ostojić, D.V.; Rubesa-Mihaljević, R.; Krigtofić, I.; Brncić-Fisher, A.; Kragević, M.; Eminović, S. Expression of CD133 and CD117 in 64 Serous Ovarian Cancer Cases. Coll. Antropol. 2015, 39, 745–753. [Google Scholar]
- Curley, M.D.; Therrien, V.A.; Cummings, C.L.; Sergent, P.A.; Koulouris, C.R.; Friel, A.M.; Roberts, D.J.; Seiden, M.V.; Scadden, D.T.; Rueda, B.R.; et al. CD133 expression defines a tumor initiating cell population in primary human ovarian cancer. Stem Cells 2009, 27, 2875–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagare, R.P.; Sneha, S.; Sidhanth, C.; Roopa, S.; Murhekar, K.; Shirley, S.; Swaminathan, R.; Sridevi, V.; Ganesan, T.S. Expression of cancer stem cell markers CD24, EPHA1 and CD9 and their correlation with clinical outcome in epithelial ovarian tumours. Cancer Biomark. 2020, 28, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.R.; Jo, K.; Lee, Y.; Sung, B.J.; Park, Y.W.; Lee, J.H. Upregulation of CD9 in ovarian cancer is related to the induction of TNF-α gene expression and constitutive NF-κB activation. Carcinogenesis 2012, 33, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, S.; Zhu, W.; Coffman, L.; Vlad, A.; Schwartz, L.E.; Elishaev, E.; Drapkin, R.; Buckanovich, R.J. CD105 Is Expressed in Ovarian Cancer Precursor Lesions and Is Required for Metastasis to the Ovary. Cancers 2019, 11, 1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meng, E.; Mitra, A.; Tripathi, K.; Finan, M.A.; Scalici, J.; McClellan, S.; Madeira da Silva, L.; Reed, E.; Shevde, L.A.; Palle, K.; et al. ALDH1A1 maintains ovarian cancer stem cell-like properties by altered regulation of cell cycle checkpoint and DNA repair network signaling. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Cui, B.; Lai, H.; Liu, G.; Ghia, E.M.; Widhopf, G.F., 2nd; Zhang, Z.; Wu, C.C.; Chen, L.; Wu, R.; et al. Ovarian cancer stem cells express ROR1, which can be targeted for anti-cancer-stem-cell therapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 17266–17271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruan, Z.; Yang, X.; Cheng, W. OCT4 accelerates tumorigenesis through activating JAK/STAT signaling in ovarian cancer side population cells. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, D.; Xie, W.; Wang, H.; Chen, W.; Chen, X.; Sun, H. OCT4 Promotes Ovarian Cancer Cell Metastasis and Angiogenesis via Modulating VEGFR2/LRPPRC Pathway. Res. Sq. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Hou, Y.; Huang, Z.; Cai, J.; Wang, Z. SOX2 is required to maintain cancer stem cells in ovarian cancer. Cancer Sci. 2017, 108, 719–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robinson, M.; Gilbert, S.F.; Waters, J.A.; Lujano-Olazaba, O.; Lara, J.; Alexander, L.J.; Green, S.E.; Burkeen, G.A.; Patrus, O.; Sarwar, Z.; et al. Characterization of SOX2, OCT4 and NANOG in Ovarian Cancer Tumor-Initiating Cells. Cancers 2021, 13, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Nam, E.J.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, S.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, Y.T. Prognostic impact of the cancer stem cell-related marker NANOG in ovarian serous carcinoma. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2012, 22, 1489–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siu, M.K.; Wong, E.S.; Kong, D.S.; Chan, H.Y.; Jiang, L.; Wong, O.G.; Lam, E.W.; Chan, K.K.; Ngan, H.Y.; Le, X.F.; et al. Stem cell transcription factor NANOG controls cell migration and invasion via dysregulation of E-cadherin and FoxJ1 and contributes to adverse clinical outcome in ovarian cancers. Oncogene 2013, 32, 3500–3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karvonen, H.; Arjama, M.; Kaleva, L.; Niininen, W.; Barker, H.; Koivisto-Korander, R.; Tapper, J.; Pakarinen, P.; Lassus, H.; Loukovaara, M.; et al. Glucocorticoids induce differentiation and chemoresistance in ovarian cancer by promoting ROR1-mediated stemness. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, J.; Jiang, C.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, F.; Hu, W.; He, X.; Li, X.; Zou, D.; Gu, N. Using ABCG2-molecule-expressing side population cells to identify cancer stem-like cells in a human ovarian cell line. Cell Biol. Int. 2011, 35, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagnoli, M.; Beretta, G.L.; Gatti, L.; Pilotti, S.; Alberti, P.; Tarantino, E.; Barbareschi, M.; Canevari, S.; Mezzanzanica, D.; Perego, P. Clinicopathological impact of ABCC1/MRP1 and ABCC4/MRP4 in epithelial ovarian carcinoma. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 143202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jung, M.; Gao, J.; Cheung, L.; Bongers, A.; Somers, K.; Clifton, M.; Ramsay, E.E.; Russell, A.J.; Valli, E.; Gifford, A.J.; et al. ABCC4/MRP4 contributes to the aggressiveness of Myc-associated epithelial ovarian cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 147, 2225–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onisim, A.; Iancu, M.; Vlad, C.; Kubelac, P.; Fetica, B.; Fulop, A.; Achimas-Cadariu, A.; Achimas-Cadariu, P. Expression of Nestin and CD133 in serous ovarian carcinoma. J. BUON 2016, 21, 1168–1175. [Google Scholar]
- Osman, W.M.; Shash, L.S.; Ahmed, N.S. Emerging Role of Nestin as an Angiogenesis and Cancer Stem Cell Marker in Epithelial Ovarian Cancer: Immunohistochemical Study. Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. 2017, 25, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzoldi, E.L.; Pavan, S.; Pilotto, G.; Leone, K.; Pagotto, A.; Frezzini, S.; Nicoletto, M.O.; Amadori, A.; Pastò, A. A juxtacrine/paracrine loop between C-Kit and stem cell factor promotes cancer stem cell survival in epithelial ovarian cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oktem, G.; Sanci, M.; Bilir, A.; Yildirim, Y.; Kececi, S.D.; Ayla, S.; Inan, S. Cancer stem cell and embryonic development-associated molecules contribute to prognostic significance in ovarian cancer. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2012, 22, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, E.J.; Kim, D.K.; Jang, I.H.; Choi, E.J.; Shin, S.H.; Lee, S.I.; Kwon, S.M.; Kim, K.H.; Suh, D.S.; Kim, J.H. Hypoxia-NOTCH1-SOX2 signaling is important for maintaining cancer stem cells in ovarian cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 55624–55638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abd El hafez, A.; El-Hadaad, H.A. Immunohistochemical expression and prognostic relevance of Bmi-1, a stem cell factor, in epithelial ovarian cancer. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2014, 18, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Qian, Q.; Cao, D.; Yang, J.; Gui, T.; Shen, K. Role of BMI1 in epithelial ovarian cancer: Investigated via the CRISPR/Cas9 system and RNA sequencing. J. Ovarian Res. 2018, 11, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, M.; Komorowski, M.P.; Seshadri, M.; Rokita, H.; McGray, A.J.; Opyrchal, M.; Odunsi, K.O.; Kozbor, D. CXCL12/CXCR4 blockade by oncolytic virotherapy inhibits ovarian cancer growth by decreasing immunosuppression and targeting cancer-initiating cells. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 5327–5337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sekiya, R.; Kajiyama, H.; Sakai, K.; Umezu, T.; Mizuno, M.; Shibata, K.; Yamamoto, E.; Fujiwara, S.; Nagasaka, T.; Kikkawa, F. Expression of CXCR4 indicates poor prognosis in patients with clear cell carcinoma of the ovary. Human Pathol. 2012, 43, 904–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tayama, S.; Motohara, T.; Narantuya, D.; Li, C.; Fujimoto, K.; Sakaguchi, I.; Tashiro, H.; Saya, H.; Nagano, O.; Katabuchi, H. The impact of EpCAM expression on response to chemotherapy and clinical outcomes in patients with epithelial ovarian cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 44312–44325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Spizzo, G.; Fong, D.; Wurm, M.; Ensinger, C.; Obrist, P.; Hofer, C.; Mazzoleni, G.; Gastl, G.; Went, P. EpCAM expression in primary tumour tissues and metastases: An immunohistochemical analysis. J. Clin. Pathol. 2011, 64, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Motohara, T.; Masuko, S.; Ishimoto, T.; Yae, T.; Onishi, N.; Muraguchi, T.; Hirao, A.; Matsuzaki, Y.; Tashiro, H.; Katabuchi, H.; et al. Transient depletion of p53 followed by transduction of c-Myc and K-Ras converts ovarian stem-like cells into tumor-initiating cells. Carcinogenesis 2011, 32, 1597–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ye, F.; Li, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhou, C.; Hu, Y.; Chen, H. Stage-specific embryonic antigen 4 expression in epithelial ovarian carcinoma. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2010, 20, 958–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Wu, B.O.; Flamini, V.; Evans, B.A.J.; Zhou, D.; Jiang, W.G. Knockdown of EPHA1 Using CRISPR/CAS9 Suppresses Aggressive Properties of Ovarian Cancer Cells. Anticancer Res. 2017, 37, 4415–4424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castellarin, M.; Milne, K.; Zeng, T.; Tse, K.; Mayo, M.; Zhao, Y.; Webb, J.R.; Watson, P.H.; Nelson, B.H.; Holt, R.A. Clonal evolution of high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma from primary to recurrent disease. J. Pathol. 2013, 229, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashashati, A.; Ha, G.; Tone, A.; Ding, J.; Prentice, L.M.; Roth, A.; Rosner, J.; Shumansky, K.; Kalloger, S.; Senz, J.; et al. Distinct evolutionary trajectories of primary high-grade serous ovarian cancers revealed through spatial mutational profiling. J. Pathol. 2013, 231, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takahashi-Yanaga, F.; Kahn, M. Targeting Wnt signaling: Can we safely eradicate cancer stem cells? Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 3153–3162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Borah, A.; Raveendran, S.; Rochani, A.; Maekawa, T.; Kumar, D.S. Targeting self-renewal pathways in cancer stem cells: Clinical implications for cancer therapy. Oncogenesis 2015, 4, e177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arend, R.C.; Londoño-Joshi, A.I.; Straughn, J.M., Jr.; Buchsbaum, D.J. The Wnt/β-catenin pathway in ovarian cancer: A review. Gynecol. Oncol. 2013, 131, 772–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, T.; Long, H.; He, L.; Han, X.; Lin, K.; Liang, Z.; Zhuo, W.; Xie, R.; Zhu, B. Interleukin-17 produced by tumor microenvironment promotes self-renewal of CD133+ cancer stem-like cells in ovarian cancer. Oncogene 2015, 34, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.Y.; Zhang, X.L.; Du, P.; Zheng, J.H. γ-Secretase Inhibitor, DAPT Inhibits Self-renewal and Stemness Maintenance of Ovarian Cancer Stem-like Cells In Vitro. Chin. J. Cancer Res. 2011, 23, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le, P.N.; McDermott, J.D.; Jimeno, A. Targeting the Wnt pathway in human cancers: Therapeutic targeting with a focus on OMP-54F28. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 146, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boone, J.D.; Arend, R.C.; Johnston, B.E.; Cooper, S.J.; Gilchrist, S.A.; Oelschlager, D.K.; Grizzle, W.E.; McGwin, G., Jr.; Gangrade, A.; Straughn, J.M., Jr.; et al. Targeting the Wnt/β-catenin pathway in primary ovarian cancer with the porcupine inhibitor WNT974. Lab. Investig. 2016, 96, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doo, D.W.; Meza-Perez, S.; Londoño, A.I.; Goldsberry, W.N.; Katre, A.A.; Boone, J.D.; Moore, D.J.; Hudson, C.T.; Betella, I.; McCaw, T.R.; et al. Inhibition of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway enhances antitumor immunity in ovarian cancer. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2020, 12, 1758835920913798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagaraj, A.B.; Joseph, P.; Kovalenko, O.; Singh, S.; Armstrong, A.; Redline, R.; Resnick, K.; Zanotti, K.; Waggoner, S.; DiFeo, A. Critical role of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in driving epithelial ovarian cancer platinum resistance. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 23720–23734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diamond, J.R.; Becerra, C.; Richards, D.; Mita, A.; Osborne, C.; O’Shaughnessy, J.; Zhang, C.; Henner, R.; Kapoun, A.M.; Xu, L.; et al. Phase Ib clinical trial of the anti-frizzled antibody vantictumab (OMP-18R5) plus paclitaxel in patients with locally advanced or metastatic HER2-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2020, 184, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, M.; Rajaie, S.; Keyvani, V.; Bolandi, S.; Hasanzadeh, M.; Pasdar, A. Clinical significance of circulating tumor cell related markers in patients with epithelial ovarian cancer before and after adjuvant chemotherapy. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradeep, S.; Kim, S.W.; Wu, S.Y.; Nishimura, M.; Chaluvally-Raghavan, P.; Miyake, T.; Pecot, C.V.; Kim, S.J.; Choi, H.J.; Bischoff, F.Z.; et al. Hematogenous metastasis of ovarian cancer: Rethinking mode of spread. Cancer Cell 2014, 26, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abreu, M.; Cabezas-Sainz, P.; Alonso-Alconada, L.; Ferreirós, A.; Mondelo-Macía, P.; Lago-Lestón, R.M.; Abalo, A.; Díaz, E.; Palacios-Zambrano, S.; Rojo-Sebastian, A.; et al. Circulating Tumor Cells Characterization Revealed TIMP1 as a Potential Therapeutic Target in Ovarian Cancer. Cells 2020, 9, 1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Yang, Y.; Zeng, Y.; He, M. A microfluidic ExoSearch chip for multiplexed exosome detection towards blood-based ovarian cancer diagnosis. Lab A Chip 2016, 16, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Teeuwssen, M.; Fodde, R. Wnt Signaling in Ovarian Cancer Stemness, EMT, and Therapy Resistance. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niehrs, C. The complex world of WNT receptor signalling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 13, 767–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, X.; Wang, X. Role of Wnt canonical pathway in hematological malignancies. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2010, 3, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pai, S.G.; Carneiro, B.A.; Mota, J.M.; Costa, R.; Leite, C.A.; Barroso-Sousa, R.; Kaplan, J.B.; Chae, Y.K.; Giles, F.J. Wnt/beta-catenin pathway: Modulating anticancer immune response. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2017, 10, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, X. Targeting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukamoto, A.S.; Grosschedl, R.; Guzman, R.C.; Parslow, T.; Varmus, H.E. Expression of the int-1 gene in transgenic mice is associated with mammary gland hyperplasia and adenocarcinomas in male and female mice. Cell 1988, 55, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, T.; Rindtorff, N.; Boutros, M. Wnt signaling in cancer. Oncogene 2017, 36, 1461–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, T.W.; Neufeld, K.L. APC controls Wnt-induced β-catenin destruction complex recruitment in human colonocytes. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jeays-Ward, K.; Hoyle, C.; Brennan, J.; Dandonneau, M.; Alldus, G.; Capel, B.; Swain, A. Endothelial and steroidogenic cell migration are regulated by WNT4 in the developing mammalian gonad. Development 2003, 130, 3663–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aiello, N.M.; Maddipati, R.; Norgard, R.J.; Balli, D.; Li, J.; Yuan, S.; Yamazoe, T.; Black, T.; Sahmoud, A.; Furth, E.E.; et al. EMT Subtype Influences Epithelial Plasticity and Mode of Cell Migration. Dev. Cell 2018, 45, 681–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hudson, L.G.; Zeineldin, R.; Stack, M.S. Phenotypic plasticity of neoplastic ovarian epithelium: Unique cadherin profiles in tumor progression. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2008, 25, 643–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, R.Y.; Wong, M.K.; Tan, T.Z.; Kuay, K.T.; Ng, A.H.; Chung, V.Y.; Chu, Y.S.; Matsumura, N.; Lai, H.C.; Lee, Y.F.; et al. An EMT spectrum defines an anoikis-resistant and spheroidogenic intermediate mesenchymal state that is sensitive to e-cadherin restoration by a src-kinase inhibitor, saracatinib (AZD0530). Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hojo, N.; Huisken, A.L.; Wang, H.; Chirshev, E.; Kim, N.S.; Nguyen, S.M.; Campos, H.; Glackin, C.A.; Ioffe, Y.J.; Unternaehrer, J.J. Snail knockdown reverses stemness and inhibits tumour growth in ovarian cancer. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Z.Q.; Li, X.Y.; Hu, C.Y.; Ford, M.; Kleer, C.G.; Weiss, S.J. Canonical Wnt signaling regulates Slug activity and links epithelial-mesenchymal transition with epigenetic Breast Cancer 1, Early Onset (BRCA1) repression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 16654–16659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jacob, F.; Ukegjini, K.; Nixdorf, S.; Ford, C.E.; Olivier, J.; Caduff, R.; Scurry, J.P.; Guertler, R.; Hornung, D.; Mueller, R.; et al. Loss of secreted frizzled-related protein 4 correlates with an aggressive phenotype and predicts poor outcome in ovarian cancer patients. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saran, U.; Arfuso, F.; Zeps, N.; Dharmarajan, A. Secreted frizzled-related protein 4 expression is positively associated with responsiveness to cisplatin of ovarian cancer cell lines in vitro and with lower tumour grade in mucinous ovarian cancers. BMC Cell Biol. 2012, 13, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Y, K.N.; Perumalsamy, N.K.; Warrier, S.; Perumalsamy, L.R.; Dharmarajan, A. Wnt antagonist as therapeutic targets in ovarian cancer. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2022, 145, 106191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohl, S.; Scott, R.; Arfuso, F.; Perumal, V.; Dharmarajan, A. Secreted frizzled-related protein 4 and its implications in cancer and apoptosis. Tumour Biol. 2015, 36, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshmukh, A.; Kumar, S.; Arfuso, F.; Newsholme, P.; Dharmarajan, A. Secreted Frizzled-related protein 4 (sFRP4) chemo-sensitizes cancer stem cells derived from human breast, prostate, and ovary tumor cell lines. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Belur Nagaraj, A.; Knarr, M.; Sekhar, S.; Connor, R.S.; Joseph, P.; Kovalenko, O.; Fleming, A.; Surti, A.; Nurmemmedov, E.; Beltrame, L.; et al. The miR-181a-SFRP4 Axis Regulates Wnt Activation to Drive Stemness and Platinum Resistance in Ovarian Cancer. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 2044–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundaram, S.M.; Varier, L.; Fathima, K.Z.; Dharmarajan, A.; Warrier, S. Short peptide domains of the Wnt inhibitor sFRP4 target ovarian cancer stem cells by neutralizing the Wnt β-catenin pathway, disrupting the interaction between β-catenin and CD24 and suppressing autophagy. Life Sci. 2023, 316, 121384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharif, T.; Martell, E.; Dai, C.; Kennedy, B.E.; Murphy, P.; Clements, D.R.; Kim, Y.; Lee, P.W.; Gujar, S.A. Autophagic homeostasis is required for the pluripotency of cancer stem cells. Autophagy 2017, 13, 264–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| Category | High-Grade Serous | Low-Grade Serous | Mucinous | Endometrioid | Clear Cell |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % in population | 70–74 | 3–5 | 2–6 | 7–24 | 10–26 |
| Origin | Fallopian tube epithelium | Fallopian tube epithelium | Unknown | Endometriosis | Endometriosis |
| Associated mutations | TP53, PIK3CA, BRCA1/2 | KRAS, BRAF, ERB2 | KRAS, HER 2 amplification | CTNNB1, PTEN | ARID1A, PIKC3A, CTNNB1, MSI |
| Ovarian CSC Markers | Protein Type | Role in Ovarian CSCs | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| CD24 | Mucin type glycoprotein | Poor prognosis, EMT, self-renewal, quiescence, resistance, sphere-forming capacity | [52,53,54] |
| CD44 | Cell-surface glycoprotein | Poor prognosis, migration, invasion, drug resistance, poor differentiation, high rate of recurrence, predictive marker for distant metastasis | [55,56,57] |
| CD117 | Receptor tyrosine kinase | Poor prognosis | [58] |
| CD133 | Pentaspan transmembrane glycoprotein | Sphere-forming capacity, increased tumorigenic capacity | [54,59] |
| CD9 | Tetraspanins | Poor prognosis, induces cell growth, activates NF-κB-signaling pathway | [60,61] |
| CD105 | Endoglin (ENG)- Type I membrane glycoprotein | Drug resistance, advanced disease stage, poor differentiation, high rate of recurrence, metastasis | [56,62] |
| CD106 | Vascular cell adhesion molecule | Drug resistance, advanced disease stage, poor differentiation, high rate of recurrence | [56] |
| ALDH1 | Cytosolic isoform of acetaldehyde dehydrogenase | Chemoresistance, invasion, colony formation | [63,64] |
| OCT4 | Transcription factor | Drug resistance, proliferation, activates JAK/STAT signaling pathway, angiogenesis, metastasis | [65,66] |
| SOX2 | Transcription factor | Spheroid formation, cell proliferation, cell migration, chemoresistance, tumorigenicity, stemness, relapse | [67,68] |
| NANOG | Transcription factor | Poor prognosis, migration, invasion | [69,70] |
| ROR1 | Receptor tyrosine kinases | Self-renewal, chemoresistance | [64,71] |
| ABCG2 | ATP-binding cassette transporter | Drug resistance, self-renewal, proliferation | [72] |
| ABCC1 | ATP-binding cassette transporter | Grading of cancer | [73] |
| ABCC4 | ATP-binding cassette transporter | Relapse, chemoresistance | [73,74] |
| NESTIN | Type VI intermediate filament protein | Chemoresistance, poor prognosis, angiogenesis | [75,76] |
| SCF | Ubiquitin ligases | Promote stemness properties | [77] |
| NOTCH1 | Type 1 transmembrane protein | Prognosis, Sphere formation, drug resistance, modulates expression of genes such as SOX2, ALDH and ABC transporters | [78,79] |
| Bmi-1 | Member of the Polycomb repressor complex 1 | Prognosis, cell growth, metastasis, anti-apoptotic function, chemoresistance | [80,81] |
| CXCR4 | G-coupled chemokine receptor | Maintaining stemness, prognosis | [82,83] |
| EpCAM | Epithelial cell adhesion/activating molecule | Chemoresistance, metastasis, maintenance of stemness, tumor initiation | [84,85,86] |
| SSEA4 | Sialyl-glycolipid | Advanced tumor stage, poorer tumor cell differentiation | [87] |
| EPHA1 | Receptor tyrosine kinase | Tumor aggressiveness, proliferation, invasion, migration | [60,88] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Varier, L.; Sundaram, S.M.; Gamit, N.; Warrier, S. An Overview of Ovarian Cancer: The Role of Cancer Stem Cells in Chemoresistance and a Precision Medicine Approach Targeting the Wnt Pathway with the Antagonist sFRP4. Cancers 2023, 15, 1275. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15041275
Varier L, Sundaram SM, Gamit N, Warrier S. An Overview of Ovarian Cancer: The Role of Cancer Stem Cells in Chemoresistance and a Precision Medicine Approach Targeting the Wnt Pathway with the Antagonist sFRP4. Cancers. 2023; 15(4):1275. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15041275
Chicago/Turabian StyleVarier, Lavanya, S. Mohana Sundaram, Naisarg Gamit, and Sudha Warrier. 2023. "An Overview of Ovarian Cancer: The Role of Cancer Stem Cells in Chemoresistance and a Precision Medicine Approach Targeting the Wnt Pathway with the Antagonist sFRP4" Cancers 15, no. 4: 1275. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15041275
APA StyleVarier, L., Sundaram, S. M., Gamit, N., & Warrier, S. (2023). An Overview of Ovarian Cancer: The Role of Cancer Stem Cells in Chemoresistance and a Precision Medicine Approach Targeting the Wnt Pathway with the Antagonist sFRP4. Cancers, 15(4), 1275. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15041275





