Remdesivir—Bringing Hope for COVID-19 Treatment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Method
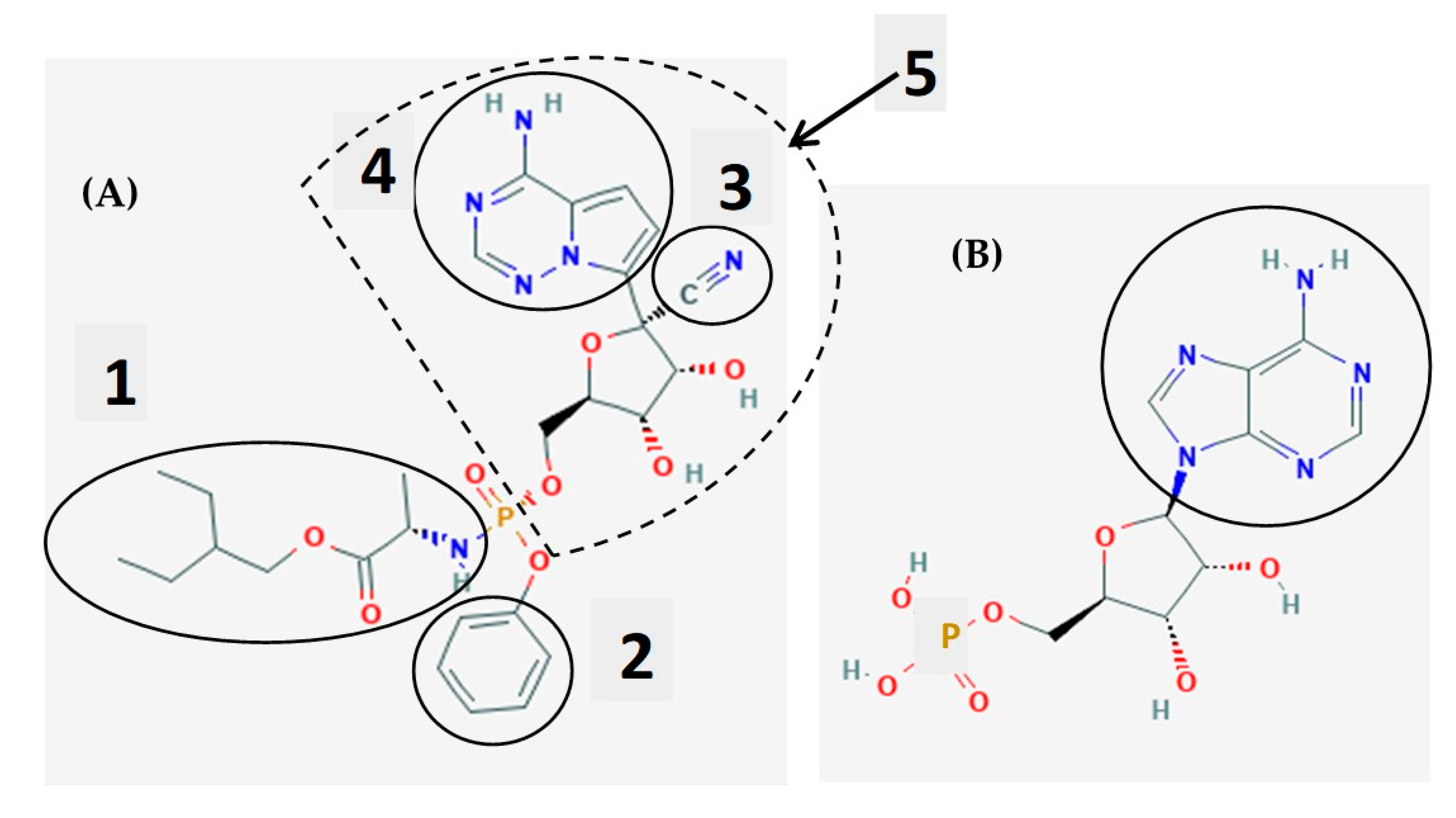
3. Remdesivir as a Chemical Molecule and a Prodrug
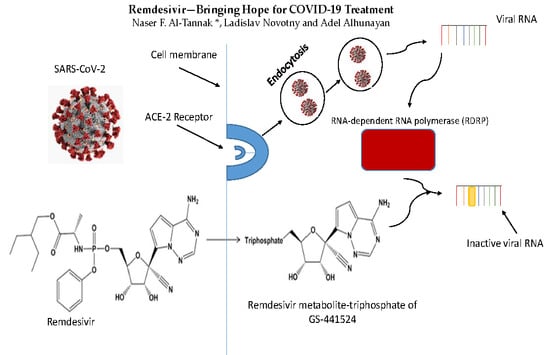
4. Mechanisms of Activity of Remdesivir
5. Basic Pharmacological Data of Remdesivir and Its Adverse Effects in Patients
6. Analytical Determinations of Remdesivir, Its Metabolite GS-441524, and Its Triphosphate
7. Therapeutic Uses of Remdesivir
7.1. The In Vitro and In Vivo Testing of Remdesivir
7.2. Ebola
7.3. Nipah Virus
7.4. Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS)
7.5. COVID-19—Clinical Trials Evaluating Remdesivir as a Treatment for COVID-19
8. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO (World Health Organization), Rolling Updates on Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19). 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/events-as-they-happen (accessed on 21 May 2020).
- CNN: Coronavirus Pandemic: Updates from around the World. 2020. Available online: https://edition.cnn.com/world/live-news/coronavirus-pandemic-05-16-20-intl/h_9114917ccbcb0340a6be8fc56b32baa3 (accessed on 21 May 2020).
- Scavone, C.; Brusco, S.; Bertini, M.; Sportiello, L.; Rafaniello, C.; Zoccoli, A.; Berrino, L.; Racagni, G.; Rossi, F.; Capuano, A. Current pharmacological treatments for COVID-19: What’s next? Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- PubChem, Remdesivir. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/121304016#section=2D-Structure (accessed on 25 May 2020).
- Ferner, R.E.; Aronson, J.K. Remdesivir in covid-19. BMJ 2020, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eastman, R.T.; Roth, J.S.; Brimacombe, K.R.; Simeonov, A.; Shen, M.; Patnaik, S.; Hall, M.D. Remdesivir: A review of its discovery and development leading to emergency use authorization for treatment of COVID-19. ACS Cent. Sci. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchesnokov, E.P.; Feng, J.Y.; Porter, D.P.; Gotte, M. Mechanism of inhibition of Ebola virus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase by remdesivir. Viruses 2019, 11, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gordon, C.J.; Tchesnokov, E.P.; Woolner, E.; Perry, J.K.; Feng, J.Y.; Porter, D.P.; Götte, M. Remdesivir is a direct-acting antiviral that inhibits RNA-dependent RNA polymerase from severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 with high potency. J. Biol. Chem. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiotos, K.; Hayes, M.; Kimberlin, D.W.; Jones, S.B.; James, S.H.; Pinninti, S.G.; Yarbrough, A.; Abzug, M.J.; MacBrayne, C.E.; Soma, V.L.; et al. Multicenter initial guidance on use of antivirals for children with COVID-19/SARS-CoV-2. J. Pediatr. Inf. Dis. Soc. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostini, M.L.; Andres, E.L.; Sims, A.C.; Graham, R.L.; Sheahan, T.P.; Lu, X.; Smith, E.C.; Case, J.B.; Feng, J.Y.; Jordan, R.; et al. Coronavirus susceptibility to the antiviral remdesivir (GS-5734) is mediated by the viral polymerase and the proofreading exoribonuclease. MBio 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sheahan, T.P.; Sims, A.C.; Graham, R.L.; Menachery, V.D.; Gralinski, L.E.; Case, J.B.; Leist, S.R.; Pyrc, K.; Feng, J.Y.; Trantcheva, I.; et al. Broad-spectrum antiviral GS-5734 inhibits both epidemic and zoonotic coronaviruses. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shannon, A.; Le, N.T.-T.; Selisko, B.; Alvarez, K.; Guillemot, J.C.; Decroly, E.; Peersen, O.; Ferron, F.; Canard, B. Remdesivir and SARS-CoV-2: Structural requirements at both nsp12 RdRp and nsp14 exonuclease active-sites. Antivir. Res. 2020, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, B.R.; Shin, B.; Choi, Y.; Park, S.; Kang, K. Predicting commercially available antiviral drugs that may act on the novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) through a Drug-Target Interaction Deep Learning Model. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 784–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, D.C.; Ji, H.-F. A search for medications to treat COVID-19 via in silico molecular docking models of the SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein and 3CL protease. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.A.; Zia, K.; Ashraf, S.; Uddin, R.; Ul-Haq, Z. Identification of chymotrypsin-like protease inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 via integrated computational approach. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2020, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Elfiky, A.A. Anti-HCV, nucleotide inhibitors, repurposing against COVID-19. Life Sci. 2020, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drug Bank, Remdesivir. 2020. Available online: http://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB14761 (accessed on 25 May 2020).
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Du, G.; Du, R.; Zhao, J.; Jin, Y.; Fu, S.; Gao, L.; Cheng, Z.; Lu, Q.; et al. Remdesivir in adults with severe COVID-19: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre trial. Lancet 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, N.; Mazer-Amirshahi, M.; Alkindi, N. Pharmacotherapy in COVID-19; A narrative review for emergency providers. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FDA, Frequently Asked Questions on the Emergency Use Authorization for Remdesivir for Certain Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients, 2020. (PDF). U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), 1 May 2020, Updated 16 May 2020. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/137574/download (accessed on 25 May 2020).
- Punyawudho, B.; Singkham, N.; Thammajaruk, N.; Dalodom, T.; Kerr, S.J.; Burger, D.M.; Ruxrungtham, K. Therapeutic drug monitoring of antiretroviral drugs in HIV-infected patients. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2016, 9, 1583–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Ma, Q.; Zhang, F. Therapeutic drug monitoring in highly active antiretroviral therapy. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2010, 9, 743–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarnoutse, R.E.; Schapiro, J.M.; Boucher, C.A.; Hekster, Y.A.; Burger, D.M. Therapeutic drug monitoring: An aid to optimising response to antiretroviral drugs? Drugs 2003, 63, 741–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avataneo, V.; de Nicolo, A.; Cusato, J.; Antonucci, M.; Manca, A.; Palermiti, A.; Waitt, C.; Walimbwa, S.; Lamorde, M.; di Perri, G.; et al. Development and validation of a UHPLC-MS/MS method for quantification of the prodrug remdesivir and its metabolite GS-441524: A tool for clinical pharmacokinetics of SARS-CoV-2/ COVID-19 and Ebola virus disease. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phenomenex. 2020. Available online: https://phenomenex.blob.core.windows.net/documents/1e92d611-4422-492b-bae9-696aa40a164b.pdf (accessed on 21 May 2020).
- Murphy, B.G.; Perron, M.; Murakami, E.; Bauer, K.; Park, Y.; Eckstrand, C.; Liepnieks, M.; Pedersen, N.C. The nucleoside analog GS-441524 strongly inhibits feline infectious peritonitis (FIP) virus in tissue culture and experimental cat infection studies. Vet. Microbiol. 2018, 219, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajapati, S.; Sharma, M.; Kumar, A.; Gupta, P.; Narasimha Kumar, G.V. An update on novel COVID-19 pandemic: A battle between humans and virus. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 5819–5829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, T.; Jordan, R.; Lo, M.; Soloveva, V.; Ray, A.; Bannister, R.; Mackman, R.; Perron, M.; Stray, K.; Feng, J.; et al. Nucleotide prodrug GS-5734 is a broad-spectrum filovirus inhibitor that provides complete therapeutic protection against the development of Ebola virus disease (EVD) in infected non-human primates. Open Forum Inf. Dis. 2015, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, T.K.; Jordan, R.; Lo, M.K.; Ray, A.S.; Mackman, R.L.; Soloveva, V.; Siegel, D.; Perron, M.; Bannister, R.; Hui, H.C.; et al. Therapeutic efficacy of the small molecule GS-5734 against Ebola virus in rhesus monkeys. Nature 2016, 531, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheahan, T.P.; Sims, A.C.; Leist, S.R.; Schäfer, A.; Won, J.; Brown, A.J.; Montgomery, S.A.; Hogg, A.; Babusis, D.; Clarke, M.O.; et al. Comparative therapeutic efficacy of remdesivir and combination lopinavir, ritonavir, and interferon beta against MERS-CoV. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Choy, K.-T.; Wong, A.Y.-L.; Kaewpreedee, P.; Sia, S.F.; Chen, D.; Hui, K.P.Y.; Chu, D.K.W.; Chan, M.C.W.; Cheung, P.P.; Huang, X.; et al. Remdesivir, lopinavir, emetine, and homoharringtonine inhibit SARS-Co-2 replication in vitro. Antivir. Res. 2020, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorgensen, S.C.; Kebriaei, R.; Dresser, L.D. Remdesivir: Review of pharmacology, pre-clinical data and emerging clinical experience for COVID-19. Pharmacotherapy 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasiou, I.A.; Eleftheriadou, I.; Tentolouris, A.; Tsilingiris, D.; Tentolouris, N. In vitro data of current therapies for SARS-CoV-2. Curr. Med. Chem. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulangu, S.; Dodd, L.E.; Davey, R.T., Jr.; Tshiani Mbaya, O.; Proschan, M.; Mukadi, D.; Lusakibanza Manzo, M.; Nzolo, D.; Tshomba Oloma, A.; Ibanda, A.; et al. A randomized, controlled trial of Ebola virus disease therapeutics. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 2293–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoenen, T.; Groseth, A.; Feldmann, H. Therapeutic strategies to target the Ebola virus life cycle. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 593–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, M.K.; Jordan, R.; Arvey, A.; Sudhamsu, J.; Shrivastava-Ranjan, P.; Hotard, A.L.; Flint, M.; McMullan, L.K.; Siegel, D.; Clarke, M.O.; et al. GS-5734 and Its Parent Nucleoside Analog Inhibit Filo-, Pneumo-, and Paramyxoviruses. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dornemann, J.; Burzio, C.; Ronsse, A.; Sprecher, A.; De Clerck, H.; Van Herp, M.; Kolié, M.C.; Yosifiva, V.; Caluwaerts, S.; McElroy, A.K.; et al. First newborn baby to receive experimental therapies survives Ebola virus disease. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 215, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Inungu, J.; Iheduru-Anderson, K.; Odio, O. Recurrent Ebola virus disease in the Democratic Republic of Congo: Update and challenges. AIMS Public Health 2019, 6, 502–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO (World Health Organization). Nipah Virus. 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/nipah-virus (accessed on 25 May 2020).
- Lo, M.K.; Feldmann, F.; Gary, J.M.; Jordan, R.; Bannister, R.; Cronin, J.; Patel, N.R.; Klena, J.D.; Nichol, S.T.; Cihlar, T.; et al. Remdesivir (GS-5734) protects African green monkeys from Nipah virus challenge. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, A.J.; Won, J.J.; Graham, R.L.; Dinnon, K.H., 3rd; Sims, A.C.; Feng, J.Y.; Cihlar, T.; Denison, M.R.; Baric, R.S.; Sheahan, T.P. Broad spectrum antiviral Remdesivir inhibits human endemic and zoonotic deltacoronaviruses with a highly divergent RNA dependent RNA polymerase. Antivir. Res. 2019, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wit, E.; Feldmann, F.; Cronin, J.; Jordan, R.; Okumura, A.; Thomas, T.; Scott, D.; Cihlar, T.; Feldmann, H. Prophylactic and therapeutic remdesivir (GS-5734) treatment in the rhesus macaque model of MERS-CoV Infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 6771–6776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gordon, C.J.; Tchesnokov, E.P.; Feng, J.Y.; Porter, D.P.; Gotte, M. The antiviral compound remdesivir potently inhibits RNA-dependent RNA polymerase form Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 4773–4779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grein, J.; Ohmagari, N.; Shin, D.; Diaz, G.; Asperges, E.; Castagna, A.; Feldt, T.; Green, G.; Green, M.L.; Lescure, F.X.; et al. Compassionate use of remdesivir for patients with severe Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNMC, Remdesivir Speeds up COVID-19 Recovery. 2020. Available online: https://www.nebraskamed.com/COVID/remdesivir-speeds-up-covid-19-recovery (accessed on 24 May 2020).
- ClinicalTrials.gov. 2020. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/results/NCT04280705 (accessed on 24 May 2020).
- ClinicalTrials.gov, Remdesivir & Covid. 2020. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/results/details?term=remdesivir&cond=COVID (accessed on 24 May 2020).
- ClinicalTrials.gov, Remdesivir & Covid. 2020. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/results?term=remdesivir&cond=COVID (accessed on 24 May 2020).
- Russell, B.; Moss, C.; George, G.; Santaolalla, A.; Cope, A.; Papa, S.; Van Hemelrijck, M. Associations between immune-suppressive and stimulating drugs and novel COVID-19—A systematic review of current evidence. Ecancermedicalscience 2020, 1410, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Q.; Li, T.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yan, X.; et al. The use of anti-inflammatory drugs in the treatment of people with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): The perspectives of clinical immunologists from China. Clin. Immunol. 2020, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seif, F.; Aazami, H.; Khoshmirsafa, M.; Kamali, M.; Mohsenzadegan, M.; Pornour, M.; Mansouri, D. JAK inhibition as a new treatment strategy for patients with COVID-19. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2020, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napolitano, M.; Fabbrocini, G.; Patruno, C. Reply: Potential role of Janus kinase inhibitors in COVID-19. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, D.; Damsky, W.; King, B. Reply: Calm before the storm: Understanding the role of Janus kinase inhibitors in COVID-19. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Wei, J.; Zou, L.; Jian, T.; Wang, G.; Chen, L.; Huang, L.; Meng, F.; Huang, L.; Wang, L.; et al. Ruxolitinib in treatment of severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A multicenter, single-blind, randomized controlled trial. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Tannak, N.F.; Novotny, L.; Alhunayan, A. Remdesivir—Bringing Hope for COVID-19 Treatment. Sci. Pharm. 2020, 88, 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm88020029
Al-Tannak NF, Novotny L, Alhunayan A. Remdesivir—Bringing Hope for COVID-19 Treatment. Scientia Pharmaceutica. 2020; 88(2):29. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm88020029
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Tannak, Naser F., Ladislav Novotny, and Adel Alhunayan. 2020. "Remdesivir—Bringing Hope for COVID-19 Treatment" Scientia Pharmaceutica 88, no. 2: 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm88020029
APA StyleAl-Tannak, N. F., Novotny, L., & Alhunayan, A. (2020). Remdesivir—Bringing Hope for COVID-19 Treatment. Scientia Pharmaceutica, 88(2), 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm88020029