Cross-Omics: Integrating Genomics with Metabolomics in Clinical Diagnostics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
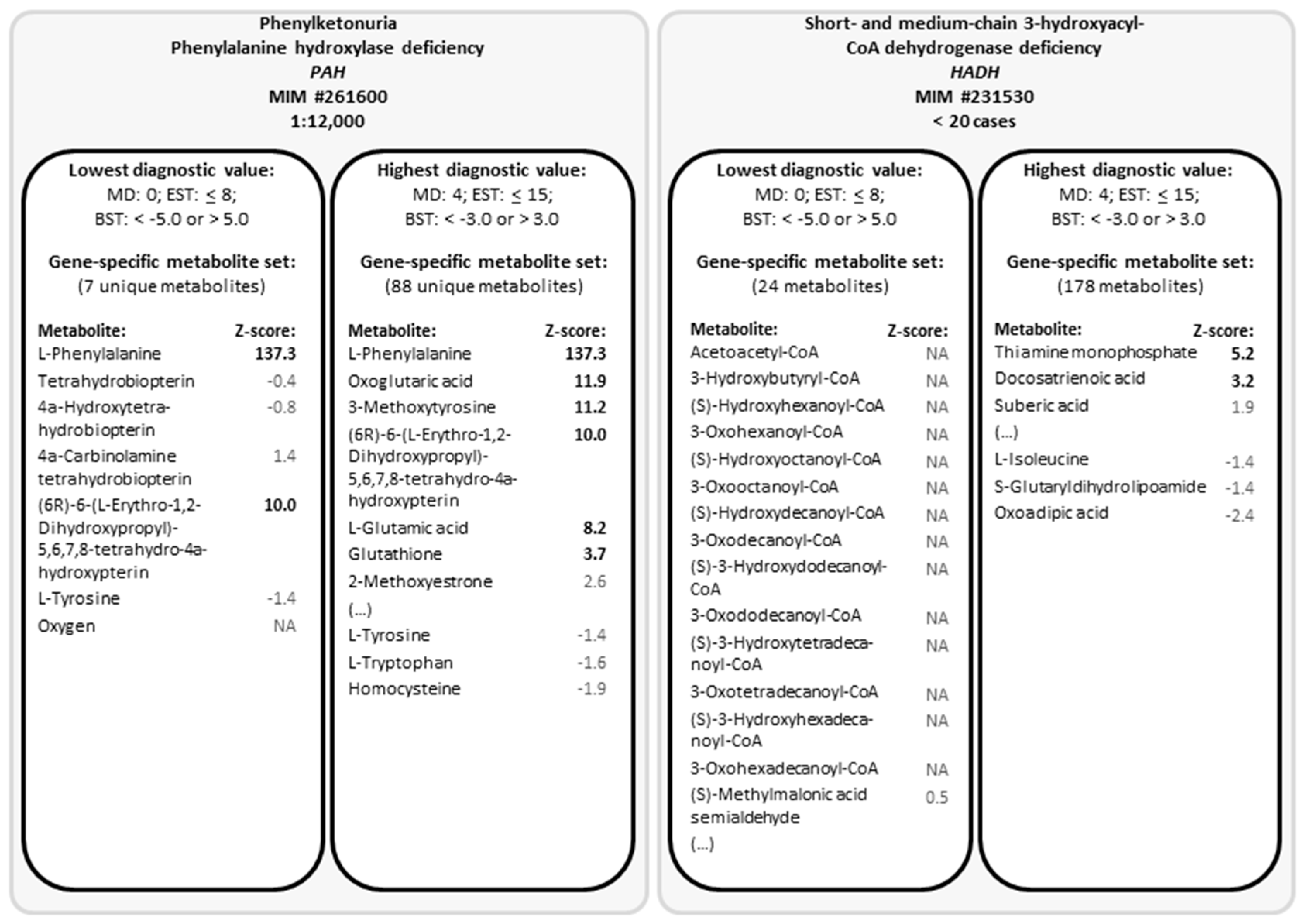
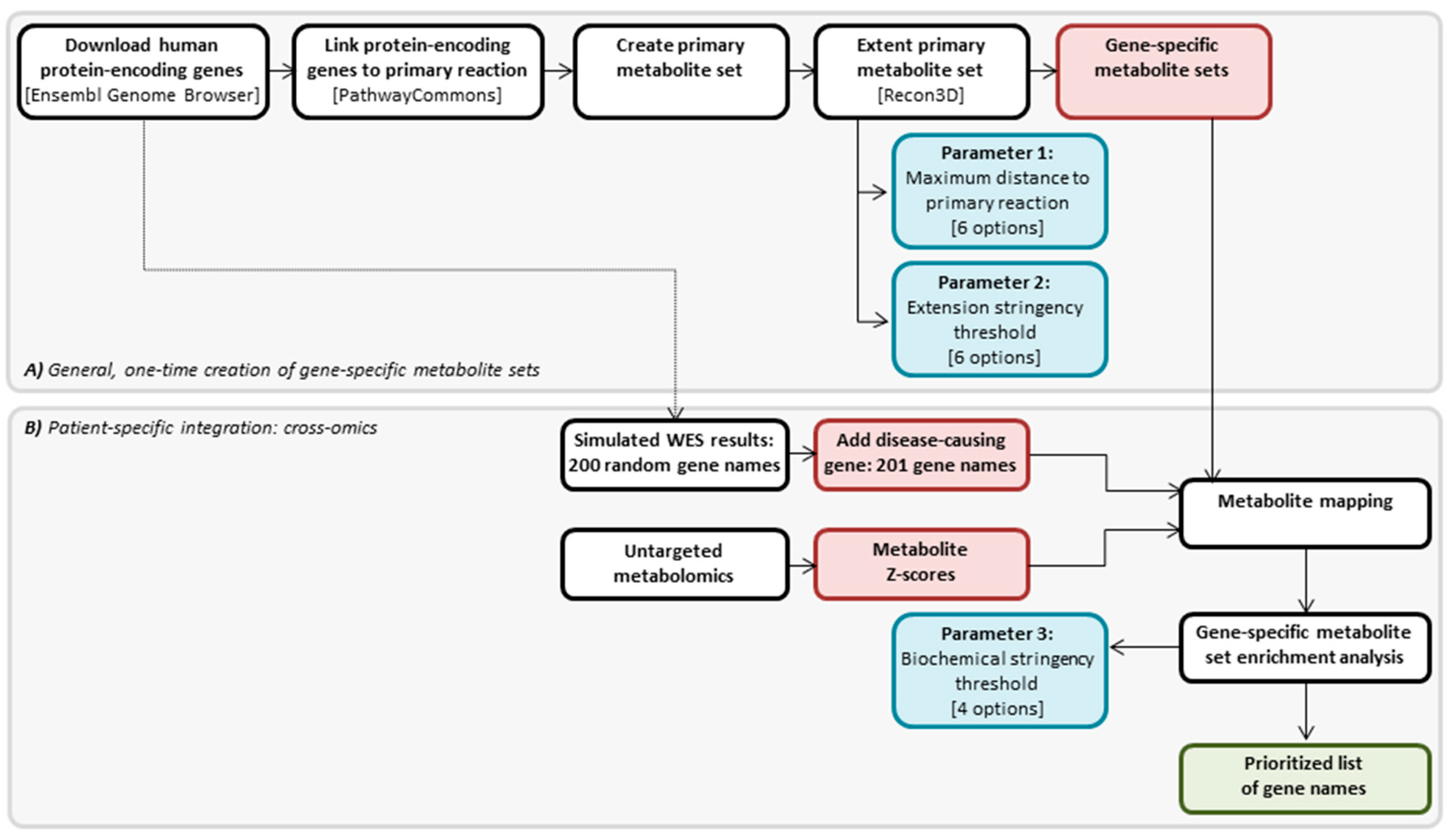
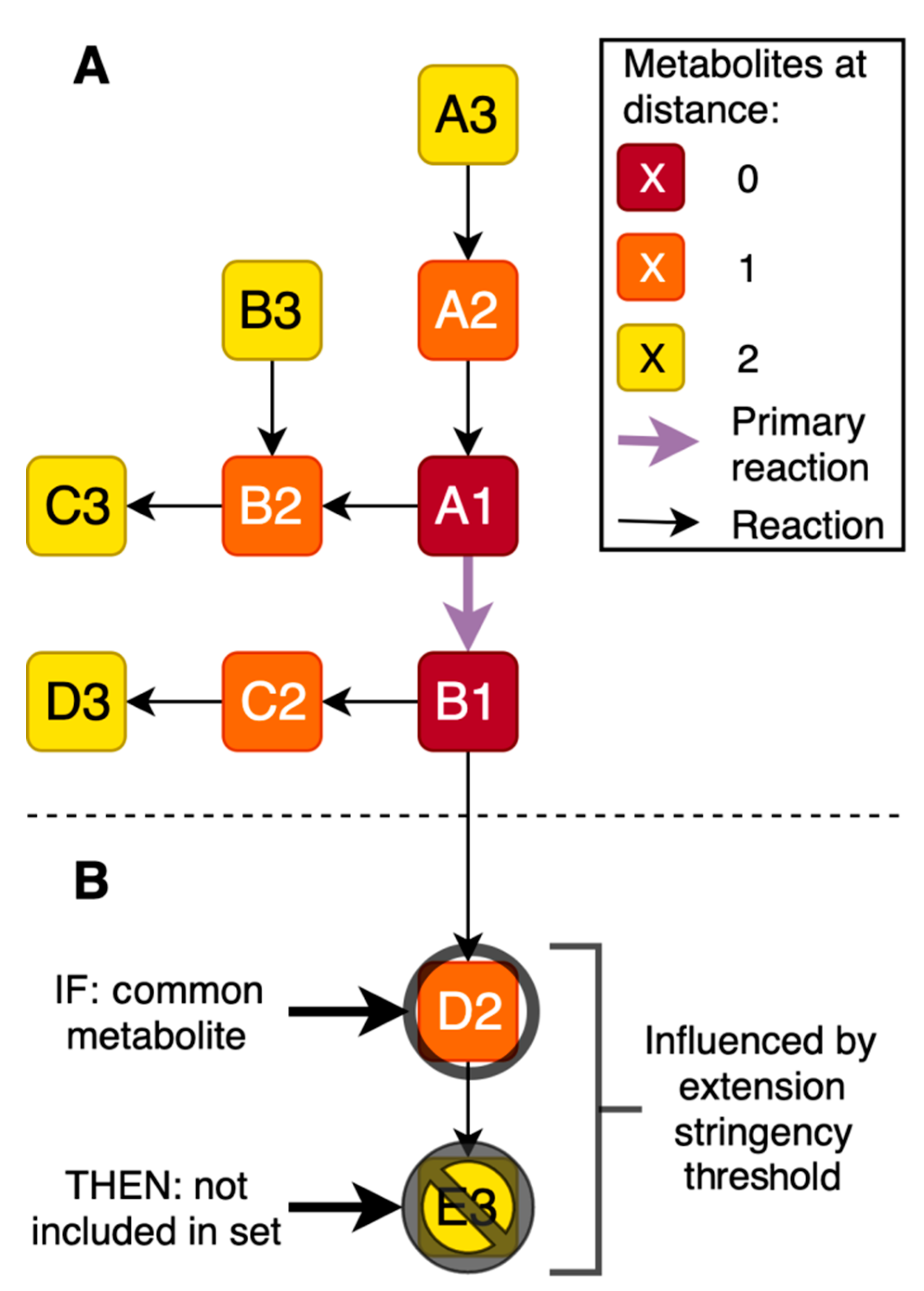
2.1. Generation of Gene-Specific Metabolite Sets
2.2. Assessment of the Most Favorable Parameter Combination for the Cross-Omics Method
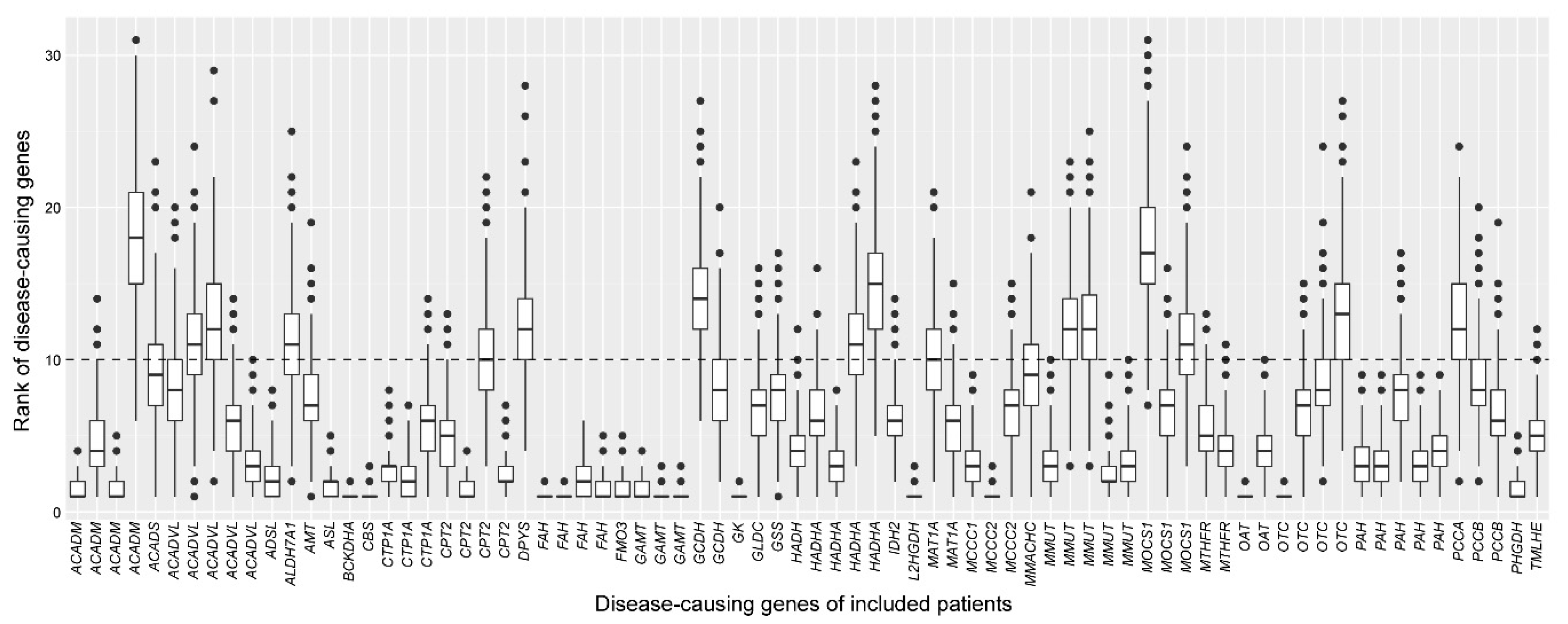
2.3. Assessment of the Robustness of the Cross-Omics Method
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sample Inclusion
4.2. Cross-Omics Method
4.3. Cross-Omics Method Part A: One-Time Generation of Gene-Specific Metabolite Sets
4.4. Cross-Omics Method Part B: Patient-Specific Integration: Cross-Omics
4.4.1. In Silico Simulation of WES Results
4.4.2. Direct-Infusion High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry
4.4.3. Metabolite Mapping
4.4.4. Gene-Specific Metabolite Set Enrichment Analysis
4.5. Assessment of the Most Favorable Parameter Combination for the Cross-Omics Method
4.6. Assessment of the Robustness of the Cross-Omics Method
4.7. Data Availability
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferreira, C.R.; van Karnebeek, C.D.; Vockley, J.; Blau, N. A proposed nosology of inborn errors of metabolism. Genet. Med. 2019, 21, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Waters, D.; Adeloye, D.; Woolham, D.; Wastnedge, E.; Patel, S.; Rudan, I. Global birth prevalence and mortality from inborn errors of metabolism: A systematic analysis of the evidence. J. Glob. Health 2018, 8, 021102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monroe, G.R.; Frederix, G.W.; Savelberg, S.M.; de Vries, T.I.; Duran, K.J.; van der Smagt, J.J.; Terhal, P.A.; van Hasselt, P.M.; Kroes, H.Y.; Verhoeven-Duif, N.M.; et al. Effectiveness of whole-exome sequencing and costs of the traditional diagnostic trajectory in children with intellectual disability. Genet. Med. 2016, 18, 949–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tabor, H.K.; Auer, P.L.; Jamal, S.M.; Chong, J.X.; Yu, J.H.; Gordon, A.S.; Graubert, T.A.; O’Donnell, C.J.; Rich, S.S.; Nickerson, D.A.; et al. Pathogenic variants for Mendelian and complex traits in exomes of 6,517 European and African Americans: Implications for the return of incidental results. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2014, 95, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, F.; Keinan, A. High burden of private mutations due to explosive human population growth and purifying selection. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, S3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; Voelkerding, K.; et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacArthur, D.G.; Balasubramanian, S.; Frankish, A.; Huang, N.; Morris, J.; Walter, K.; Jostins, L.; Habegger, L.; Pickrell, J.K.; Montgomery, S.B.; et al. A Systematic Survey of Loss-of-Function Variants in Human Protein-Coding Genes. Science 2012, 335, 823–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miller, M.J.; Kennedy, A.D.; Eckhart, A.D.; Burrage, L.C.; Wulff, J.E.; Miller, L.A.; Milburn, M.V.; Ryals, J.A.; Beaudet, A.L.; Sun, Q.; et al. Untargeted metabolomic analysis for the clinical screening of inborn errors of metabolism. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2015, 38, 1029–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coene, K.L.; Kluijtmans, L.A.; van der Heeft, E.; Engelke, U.F.; de Boer, S.; Hoegen, B.; Kwast, H.J.; van de Vorst, M.; Huigen, M.C.; Keularts, I.M.; et al. Next-generation metabolic screening: Targeted and untargeted metabolomics for the diagnosis of inborn errors of metabolism in individual patients. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2018, 41, 337–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Körver-Keularts, I.M.L.W.; Wang, P.; Waterval, H.W.A.H.; Kluijtmans, L.A.J.; Wevers, R.A.; Langhans, C.D.; Scott, D.; Habets, D.D.J.; Bierau, J. Fast and accurate quantitative organic acid analysis with LC-QTOF/MS facilitates screening of patients for inborn errors of metabolism. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2018, 41, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haijes, H.A.; Willemsen, M.; Van der Ham, M.; Gerrits, J.; Pras-Raves, M.L.; Prinsen, H.C.; Van Hasselt, P.M.; De Sain-van der Velden, M.G.; Verhoeven-Duif, N.M.; Jans, J.J. Direct Infusion Based Metabolomics Identifies Metabolic Disease in Patients’ Dried Blood Spots and Plasma. Metabolites 2019, 9, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haijes, H.A.; van der Ham, M.; Gerrits, J.; van Hasselt, P.M.; Prinsen, H.C.M.T.; de Sain-van der Velden, M.G.M.; Verhoeven-Duif, N.M.; Jans, J.J.M. Direct-infusion based metabolomics unveils biochemical profiles of inborn errors of metabolism in cerebrospinal fluid. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2019, 127, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonte, R.; Bongaerts, M.; Demirdas, S.; Langendonk, J.G.; Huidekoper, H.H.; Williams, M.; Onkenhout, W.; Jacobs, E.H.; Blom, H.J.; Ruijter, G.J.G. Untargeted metabolomics-based screening method for inborn errors of metabolism using semi-automatic sample preparation with an UHPLC-Orbitrap-MS platform. Metabolites 2019, 9, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haijes, H.A.; van der Ham, M.; Prinsen, H.C.; Broeks, M.H.; van Hasselt, P.M.; de Sain-van der Velden, M.G.; Verhoeven-Duif, N.M.; Jans, J.J.M. Untargeted Metabolomics for Metabolic Diagnostic Screening with Automated Data Interpretation Using a Knowledge-Based Algorithm. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Graham, E.; Lee, J.; Price, M.; Tarailo-Graovac, M.; Matthews, A.; Engelke, U.; Tang, J.; Kluijtmans, L.A.; Wevers, R.A.; Wasserman, W.W.; et al. Integration of genomics and metabolomics for prioritization of rare disease variants: A 2018 literature review. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2018, 41, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, H.; Deignan, J.L.; Dorrani, N.; Strom, S.P.; Kantarci, S.; Quintero-Rivera, F.; Das, K.; Toy, T.; Harry, B.; Yourshaw, M.; et al. Clinical exome sequencing for genetic identification of rare Mendelian disorders. JAMA 2014, 312, 1880–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillon, O.J.; Lunke, S.; Stark, Z.; Yeung, A.; Thorne, N.; Melbourne Genomics Health Alliance; Gaff, C.; White, S.M.; Tan, T.Y. Exome sequencing has higher diagnostic yield compared to simulated disease-specific panels in children with suspected monogenic disorders. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2018, 26, 644–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Marmiesse, A.; Gouveia, S.; Couce, M.L. NGS Technologies as a Turning Point in Rare Disease Research, Diagnosis and Treatment. Curr. Med. Chem. 2018, 25, 404–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vissers, L.E.; Gilissen, C.; Veltman, J.A. Genetic studies in intellectual disability and related disorders. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2016, 17, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thevenon, J.; Duffourd, Y.; Masurel-Paulet, A.; Lefebvre, M.; Feillet, F.; El Chehadeh-Djebbar, S.; St-Onge, J.; Steinmetz, A.; Huet, F.; Chouchane, M.; et al. Diagnostic odyssey in severe neurodevelopmental disorders: Toward clinical whole-exome sequencing as a first-line diagnostic test. Clin. Genet. 2016, 89, 700–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarailo-Graovac, M.; Shyr, C.; Ross, C.J.; Horvath, G.A.; Salvarinova, R.; Ye, X.C.; Zhang, L.H.; Bhavsar, A.P.; Lee, J.J.; Drögemöller, B.I.; et al. Exome sequencing and the management of neurometabolic disorders. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 2246–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McKusick-Nathans Institute of Genetic Medicine; Johns Hopkins University (Baltimore; MD). Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man, OMIM®. Available online: https://omim.org/ (accessed on 10 December 2019).
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Yates, A.; Akanni, W.; Amode, M.R.; Barrell, D.; Billis, K.; Carvalho-Silva, D.; Cummins, C.; Clapham, P.; Fitzgerald, S.; Gil, L.; et al. Ensembl 2016. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D710–D716. Available online: https://ensembl.org/ (accessed on 1 April 2019). [CrossRef]
- Luna, A.; Babur, O.; Aksoy, A.B.; Demir, E.; Sander, C. PaxtoolsR: Pathway Analysis in R Using Pathway Commons. Bioinformatics 2015, 32, 1262–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brunk, E.; Sahoo, S.; Zielinski, D.C.; Altunkaya, A.; Dräger, A.; Mih, N.; Gatto, F.; Nilsson, A.; Gonzalez, G.A.; Aurich, M.K.; et al. Recon3D enables a three-dimensional view of gene variation in human metabolism. Nat. Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wishart, D.S.; Jewison, T.; Guo, A.C.; Wilson, M.L.; Knox, C.; Liu, Y.; Djoumbou, Y.; Mandal, R.; Aziat, F.; Dong, E.; et al. HMDB 3.0-The Human Metabolome Database in 2013. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 801–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willemsen, A.M.; Pras-Raves, M.L.; van Unen, N. DIMS Pipeline (15 April 2020). Zenodo 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willemsen, A.M.; Kerkhofs, M.H.P.M. Cross-Omics Method (15 April 2020). Zenodo 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

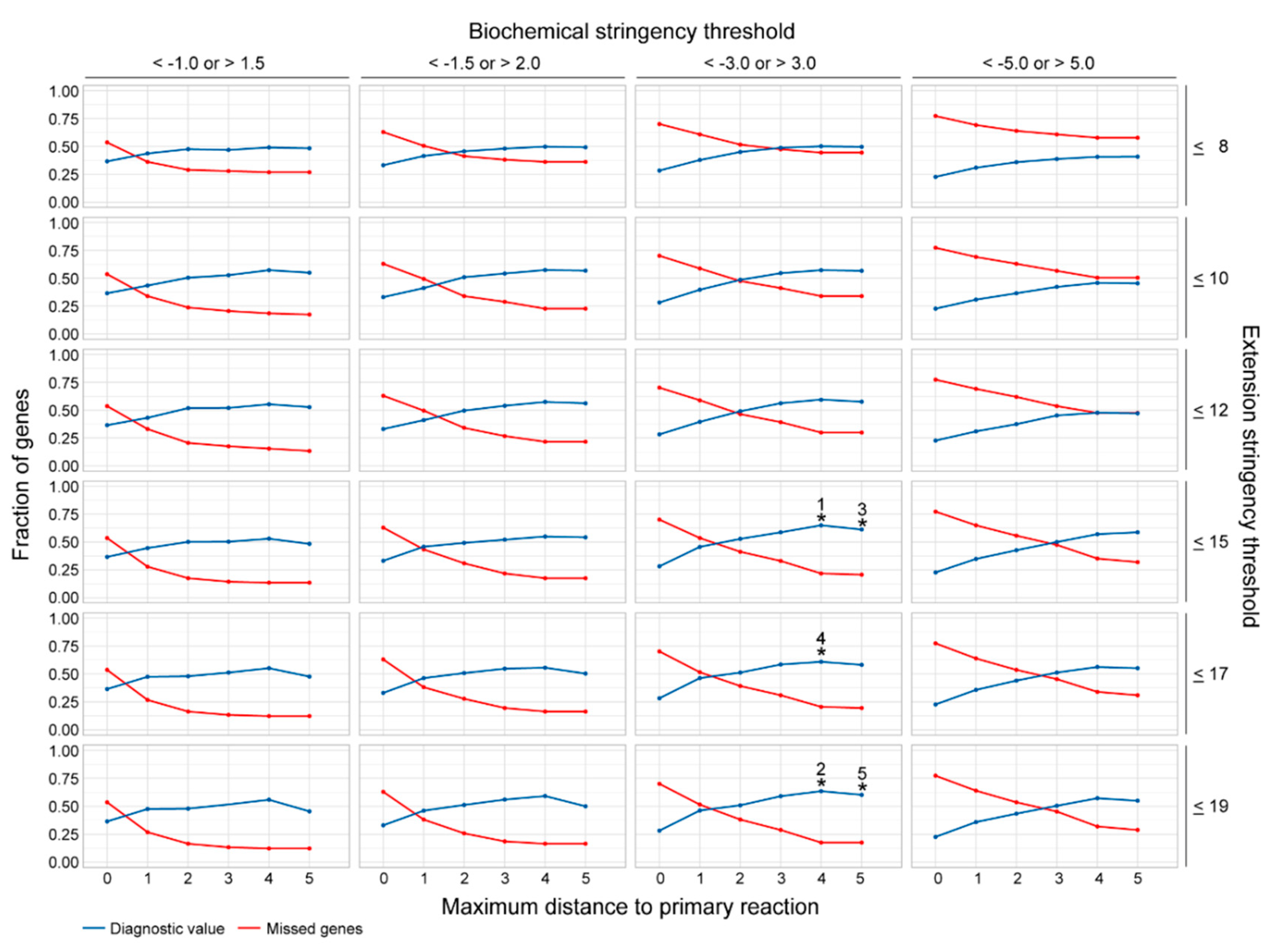
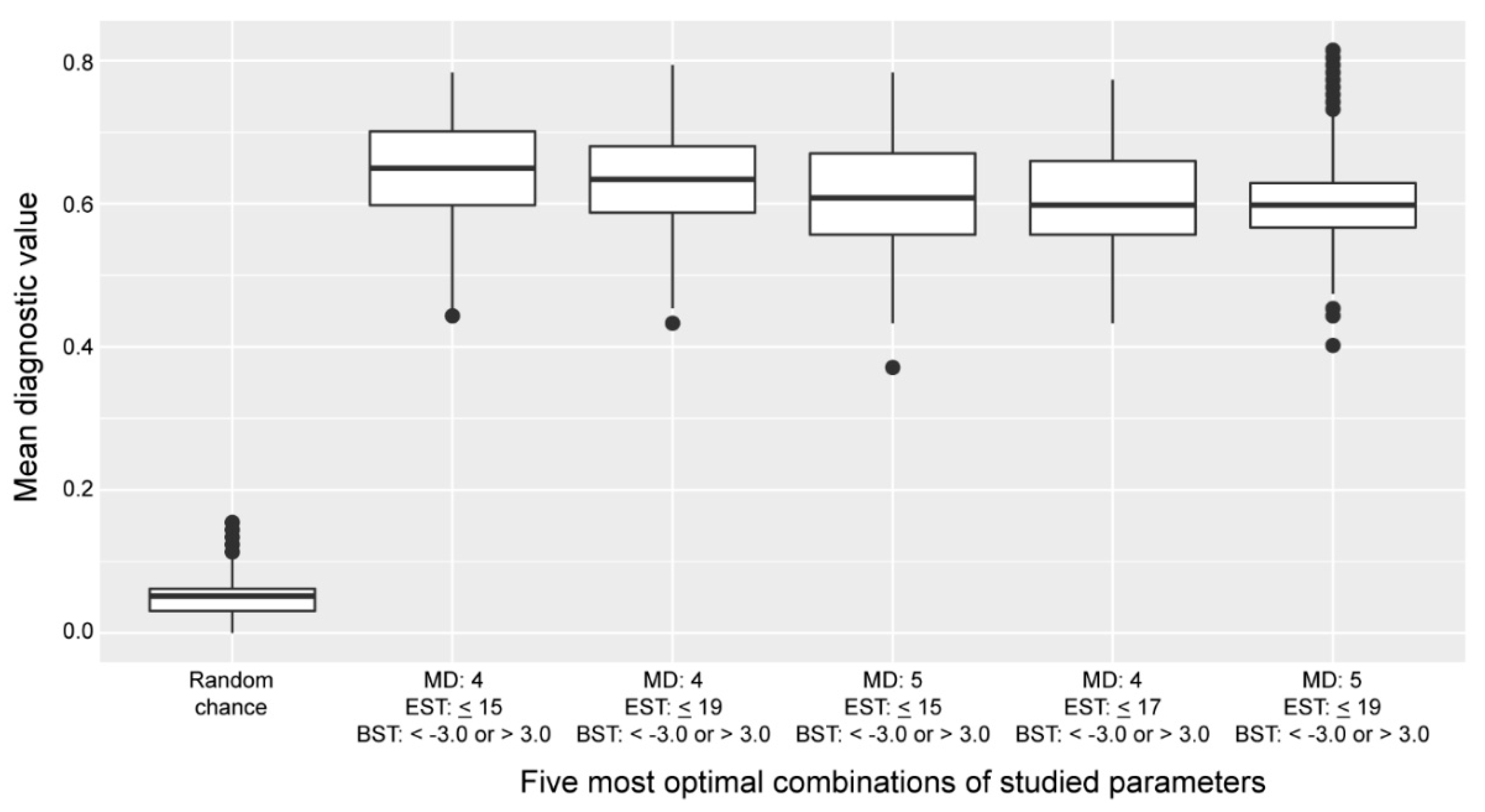
| Rank | Diagnostic Value | Missed Fraction | Maximum Distance | Extension Stringency | Biochemical Stringency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.65 | 0.22 | 4 | ≤15 | <−3.0; >3.0 |
| 2 | 0.64 | 0.18 | 4 | ≤19 | <−3.0; >3.0 |
| 3 | 0.61 | 0.21 | 5 | ≤15 | <−3.0; >3.0 |
| 4 | 0.61 | 0.21 | 4 | ≤17 | <−3.0; >3.0 |
| 5 | 0.60 | 0.18 | 5 | ≤19 | <−3.0; >3.0 |
| 6 | 0.59 | 0.30 | 4 | ≤12 | <−3.0; >3.0 |
| 7 | 0.59 | 0.17 | 4 | ≤19 | <−1.5; >2.0 |
| 8 | 0.59 | 0.29 | 3 | ≤19 | <−3.0; >3.0 |
| 9 | 0.59 | 0.33 | 3 | ≤15 | <−3.0; >3.0 |
| 10 | 0.59 | 0.32 | 5 | ≤15 | <−5.0; >5.0 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kerkhofs, M.H.P.M.; Haijes, H.A.; Willemsen, A.M.; van Gassen, K.L.I.; van der Ham, M.; Gerrits, J.; de Sain-van der Velden, M.G.M.; Prinsen, H.C.M.T.; van Deutekom, H.W.M.; van Hasselt, P.M.; et al. Cross-Omics: Integrating Genomics with Metabolomics in Clinical Diagnostics. Metabolites 2020, 10, 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10050206
Kerkhofs MHPM, Haijes HA, Willemsen AM, van Gassen KLI, van der Ham M, Gerrits J, de Sain-van der Velden MGM, Prinsen HCMT, van Deutekom HWM, van Hasselt PM, et al. Cross-Omics: Integrating Genomics with Metabolomics in Clinical Diagnostics. Metabolites. 2020; 10(5):206. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10050206
Chicago/Turabian StyleKerkhofs, Marten H. P. M., Hanneke A. Haijes, A. Marcel Willemsen, Koen L. I. van Gassen, Maria van der Ham, Johan Gerrits, Monique G. M. de Sain-van der Velden, Hubertus C. M. T. Prinsen, Hanneke W. M. van Deutekom, Peter M. van Hasselt, and et al. 2020. "Cross-Omics: Integrating Genomics with Metabolomics in Clinical Diagnostics" Metabolites 10, no. 5: 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10050206
APA StyleKerkhofs, M. H. P. M., Haijes, H. A., Willemsen, A. M., van Gassen, K. L. I., van der Ham, M., Gerrits, J., de Sain-van der Velden, M. G. M., Prinsen, H. C. M. T., van Deutekom, H. W. M., van Hasselt, P. M., Verhoeven-Duif, N. M., & Jans, J. J. M. (2020). Cross-Omics: Integrating Genomics with Metabolomics in Clinical Diagnostics. Metabolites, 10(5), 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10050206




_Verhoeven-Duif.png)


