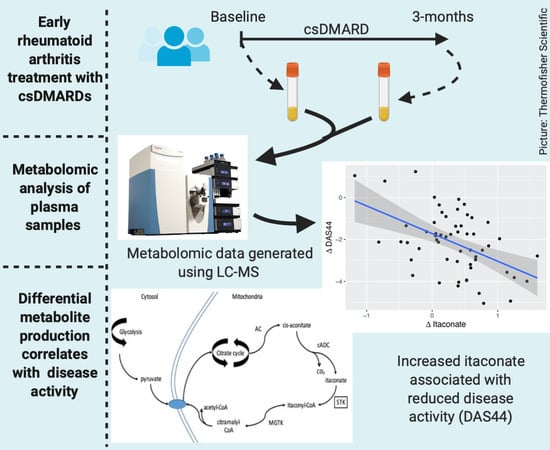
Changes in Plasma Itaconate Elevation in Early Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Elucidates Disease Activity Associated Macrophage Activation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Metabolomic Analysis
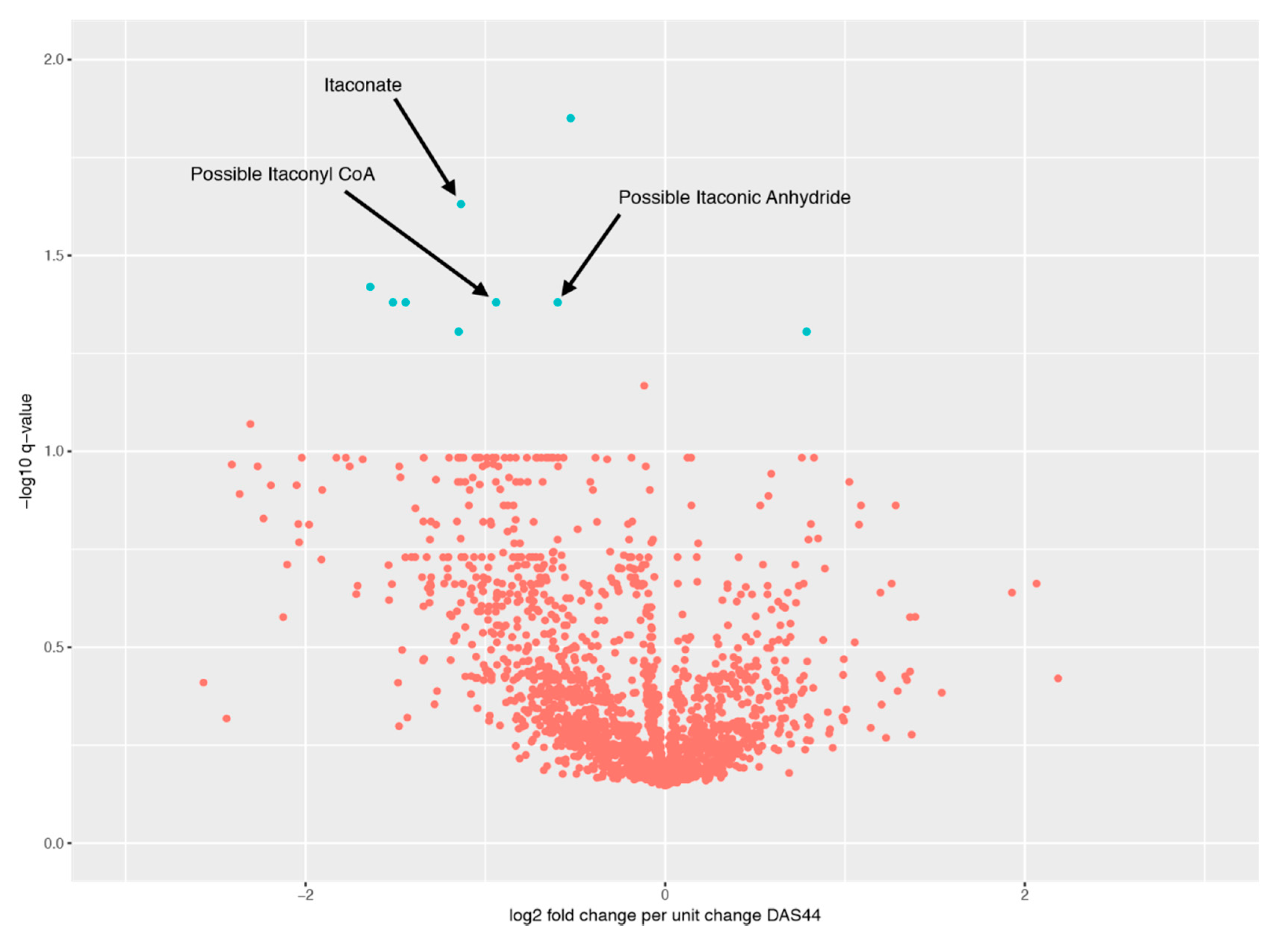
2.3. Metabolite Comparisons
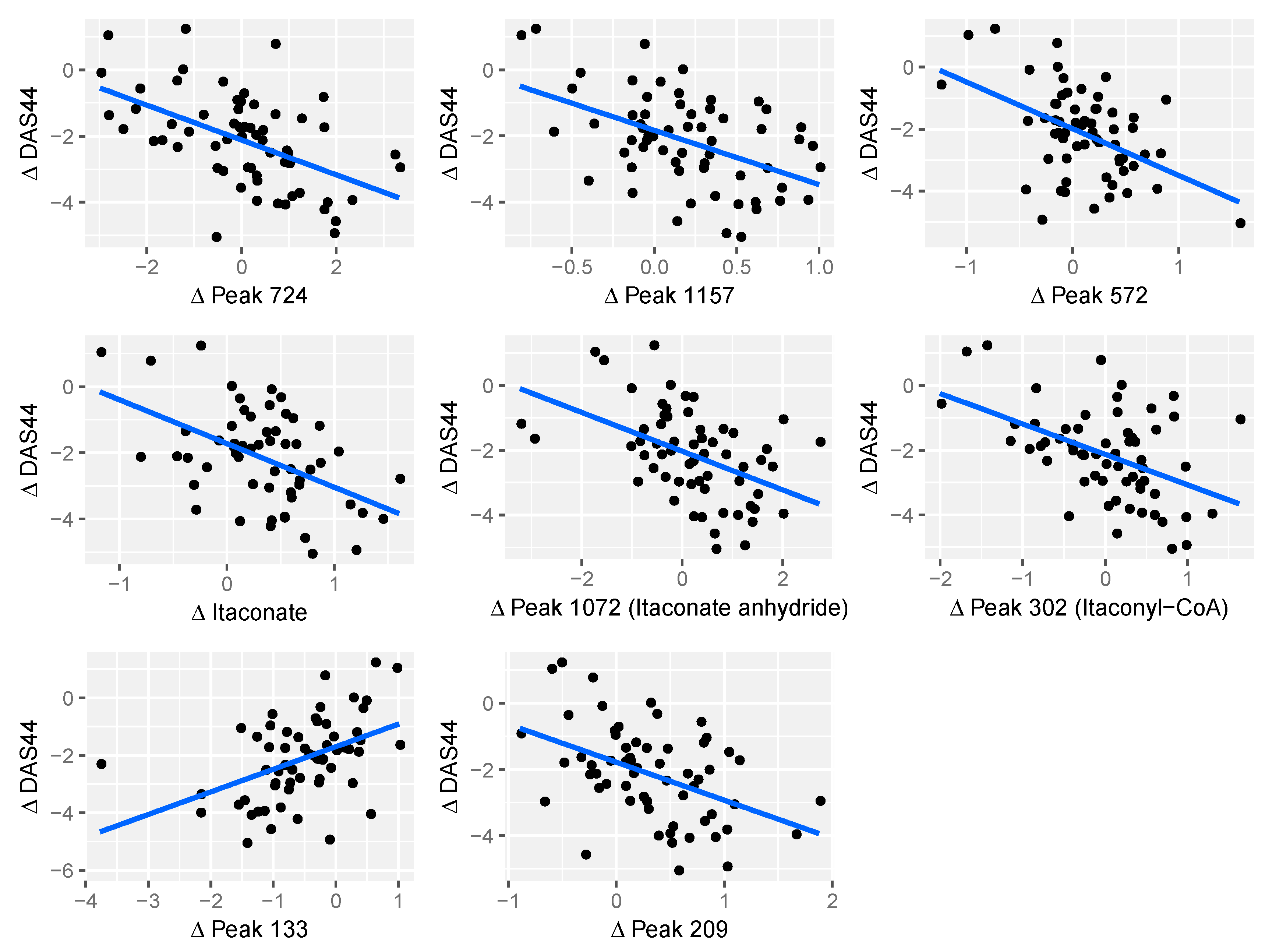
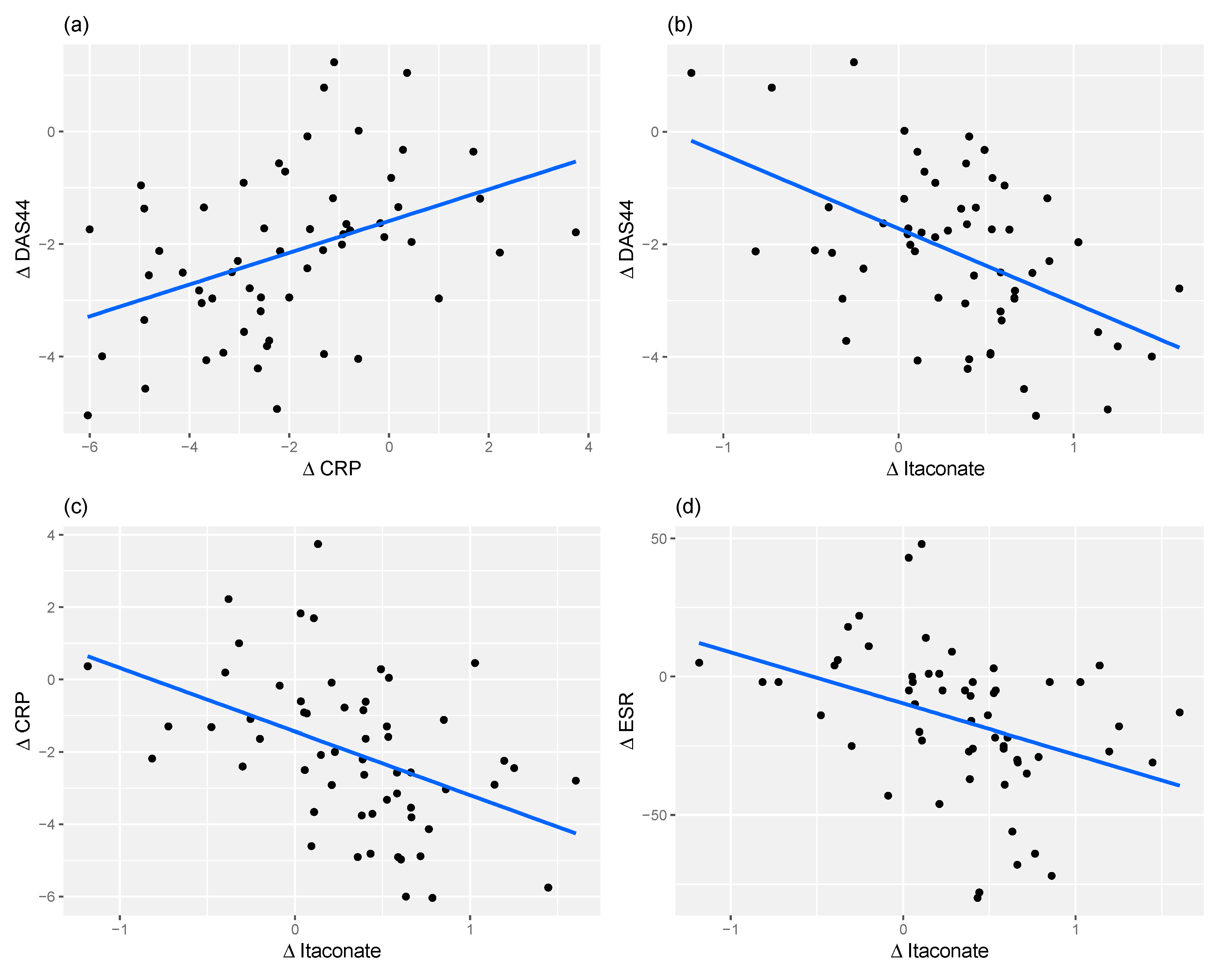
2.4. Relationship between Changes in Metabolite Levels and Changes in DAS44
2.5. Itaconate and CRP Level Have Similar Predictive Power for Response
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Population
4.2. Sample Collection and Preparation
4.3. Metabolomics
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McInnes, I.B.; Schett, G. The Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 2205–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Metsios, G.S.; Stavropoulos-Kalinoglou, A.; Nevill, A.M.; Douglas, K.M.J.; Koutedakis, Y.; Kitas, G.D. Cigarette smoking significantly increases basal metabolic rate in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2008, 67, 70–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Elmesmari, A.; Fraser, A.R.; Wood, C.; Gilchrist, D.; Vaughan, D.; Stewart, L.; McSharry, C.; McInnes, I.B.; Kurowska-Stolarska, M. MicroRNA-155 regulates monocyte chemokine and chemokine receptor expression in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Rheumatology 2016, 55, 2056–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Robertson, J.; Porter, D.; Sattar, N.; Packard, C.J.; Caslake, M.; McInnes, I.; McCarey, D. Interleukin-6 blockade raises LDL via reduced catabolism rather than via increased synthesis: A cytokine—specific mechanism for cholesterol changes in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 1949–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Semerano, L.; Roméo, P.-H.; Boissier, M.-C. Metabolomics for rheumatic diseases: Has the time come? Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 1325–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Young, S.P.; Kapoor, S.R.; Viant, M.R.; Byrne, J.J.; Filer, A.; Buckley, C.D.; Kitas, G.D.; Raza, K. The Impact of Inflammation on Metabolomic Profiles in Patients with Arthritis. Arthritis. Rheum. 2013, 65, 2015–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Newgard, C.B. Metabolomics and Metabolic Diseases: Where Do We Stand? Cell Metab. 2017, 25, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jutley, G.S.; Young, S.P. Metabolomics to identify biomarkers and as a predictive tool in inflammatory diseases. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2015, 29, 770–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapoor, S.R.; McGrath, C.M.; Fitzpatrick, M.A.; Young, S.P. Metabolomics in rheumatology. Rheumatology 2015, 54, 2124–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smoleńska, Z.; Zdrojewski, Z. Metabolomics and its potential in diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of rheumatic diseases. Reumatologia 2015, 53, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guma, M.; Tiziani, S.; Firestein, G.S. Metabolomics in rheumatic diseases: Desperately seeking biomarkers. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2016, 12, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priori, R.; Scrivo, R.; Brandt, J.E.; Valerio, M.; Casadei, L.; Valesini, G.; Manetti, C. Metabolomics in rheumatic diseases: The potential of an emerging methodology for improved patient diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment efficacy. Autoimmun. Rev. 2013, 12, 1022–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madsen, R.K.; Lundstedt, T.; Gabrielsson, J.; Sennbro, C.-J.; Alenius, G.-M.; Moritz, T.; Rantapää-Dahlqvist, S.; Trygg, J. Diagnostic properties of metabolic perturbations in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis. Res. Ther. 2011, 13, R19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, M.; Chen, T.; Feng, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, L.; Zhao, A.; Niu, X.; Liang, F.; Wang, M.; Zhan, J.; et al. Serum Metabolic Signatures of Four Types of Human Arthritis. J. Proteome. Res. 2013, 12, 3769–3779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapoor, S.R.; Filer, A.; Fitzpatrick, M.; Fisher, B.A.; Taylor, P.C.; Buckley, C.D.; McInnes, I.; Raza, K.; Young, S.P. Metabolic Profiling Predicts Response to Anti-Tumor Necrosis Factor α Therapy in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis. Rheum. 2013, 65, 1448–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuppen, B.V.J.; Fu, J.; Van Wietmarschen, H.A.; Harms, A.C.; Koval, S.; Marijnissen, A.C.A.; Peeters, J.J.W.; Bijlsma, J.W.J.; Tekstra, J.; Van Laar, J.M.; et al. Exploring the Inflammatory Metabolomic Profile to Predict Response to TNF-α Inhibitors in Rheumatoid Arthritis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Yang, S.; Wang, Y.; Yu, L.; Zhang, B.; Rao, Z.; Gao, J.; Tu, S. 1H NMR-based metabolomic analysis for identifying serum biomarkers to evaluate methotrexate treatment in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2012, 4, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Creek, D.J.; Jankevics, A.; Breitling, R.; Watson, D.G.; Barrett, M.P.; Burgess, K.E.V. Toward Global Metabolomics Analysis with Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry: Improved Metabolite Identification by Retention Time Prediction. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 8703–8710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Keller, B.O.; Sui, J.; Young, A.B.; Whittal, R.M. Interferences and contaminants encountered in modern mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 627, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.-F.; Adler, J.; Lardy, H.A. The pathway of itaconate metabolism by liver mitochondria. J. Biol. Chem. 1961, 236, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vernon, H.J. Inborn Errors of Metabolism: Advances in Diagnosis and Therapy. JAMA Pediatr. 2015, 169, 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, L.D.; Koulman, A.; Griffin, J.L. Towards metabolic biomarkers of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes: Progress from the metabolome. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014, 2, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatar, Z.; Migné, C.; Pétéra, M.; Gaudin, P.; Lequerré, T.; Marotte, H.; Tebib, J.; Pujos-Guillot, E.; Soubrier, M. Variations in the metabolome in response to disease activity of rheumatoid arthritis. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2016, 17, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van der Hooft, J.J.J.; Wandy, J.; Barrett, M.P.; Burgess, K.E.V.; Rogers, S. Topic modeling for untargeted substructure exploration in metabolomics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 13738–13743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lampropoulou, V.; Sergushichev, A.; Bambouskova, M.; Nair, S.; Vincent, E.E.; Loginicheva, E.; Cervantes-Barragan, L.; Ma, X.; Huang, S.C.-C.; Griss, T.; et al. Itaconate Links Inhibition of Succinate Dehydrogenase with Macrophage Metabolic Remodeling and Regulation of Inflammation. Cell Metab. 2016, 24, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mills, E.L.; Ryan, D.G.; Prag, H.A.; Dikovskaya, D.; Menon, D.; Zaslona, Z.; Jedrychowski, M.P.; Costa, A.S.H.; Higgins, M.; Hams, E.; et al. Itaconate is an anti-inflammatory metabolite that activates Nrf2 via alkylation of KEAP1. Nature 2018, 556, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bambouskova, M.; Gorvel, L.; Lampropoulou, V.; Sergushichev, A.; Loginicheva, E.; Johnson, K.; Korenfeld, D.; Mathyer, M.E.; Kim, H.; Huang, L.-H.; et al. Electrophilic properties of itaconate and derivatives regulate the IκBζ–ATF3 inflammatory axis. Nature 2018, 556, 501–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michopoulos, F.; Karagianni, N.; Whalley, N.M.; Firth, M.A.; Nikolaou, C.; Wilson, I.D.; Critchlow, S.E.; Kollias, G.; Theodoridis, G.A. Targeted Metabolic Profiling of the Tg197 Mouse Model Reveals Itaconic Acid as a Marker of Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Proteome Res. 2016, 15, 4579–4590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luan, H.H.; Medzhitov, R. Food Fight: Role of Itaconate and Other Metabolites in Antimicrobial Defense. Cell Metab. 2016, 24, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, J.; Purves, D.; McConnachie, A.; McInnes, I.; Porter, D. Tightening Up? Impact of Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Disease Activity Assessment on Early Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Treated Using a Treat to Target Strategy. Arthritis Care Res. (Hoboken) 2014, 66, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, J.; Stirling, A.; Zhang, R.; Purves, D.; Foley, J.; Sambrook, M.; Conaghan, P.G.; Van Der Heijde, D.; McConnachie, A.; McInnes, I.; et al. Targeting ultrasound remission in early rheumatoid arthritis: The results of the TaSER study, a randomised clinical trial. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 1043–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holman, J.D.; Tabb, D.L.; Mallick, P.; Holman, J.D.; Tabb, D.L.; Mallick, P. Employing ProteoWizard to Convert Raw Mass Spectrometry Data. In Current Protocols in Bioinformatics; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 13.24.1–13.24.9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheltema, R.A.; Jankevics, A.; Jansen, R.C.; Swertz, M.A.; Breitling, R. PeakML/mzMatch: A File Format, Java Library, R Library, and Tool-Chain for Mass Spectrometry Data Analysis. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 2786–2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Creek, D.J.; Jankevics, A.; Burgess, K.E.V.; Breitling, R.; Barrett, M.P. IDEOM: An excel interface for analysis of LC-MS-based metabolomics data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1048–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Demographics | ||
|---|---|---|
| Female Sex, n (%) | 54 (68%) | |
| Age (y) | 56 ± 13 | |
| Disease Duration (months) | 5.3 ± 3.1 | |
| Rheumatoid Factor Positive, n (%) | 51 (65%) | |
| Anti-CCP Positive, n (%) | 43 (53%) | |
| Plain X-ray Erosions, n (%) | 26 (33%) | |
| Disease Activity Outcomes | Baseline | 3 Months |
| DAS44 | 4.5 ± 1.2 | 2.3 ± 1.3 |
| HAQ | 1.5 ± 0.8 | 0.9 ± 0.9 |
| ESR | 36 ± 26 | 21 ± 21 |
| CRP | 42 ± 55 | 14 ± 25 |
| Peak ID | Peak Change q-Value | m/z | RT (s) | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peak.n.724 | 0.0141 | 134.0579 | 477 | Peak check passed. No ID |
| Peak.n.1157 | 0.0364 | 281.7499 | 204 | Peak check passed. No ID |
| Peak.n.572 | 0.0364 | 466.3118 | 208 | Peak check passed. Putative ID: cholesterol sulphate |
| Peak.n.302 | 0.0364 | 130.0267 | 435 | Peak check passed. Putative ID: Itaconyl-CoA fragment, based on not matching standards for itaconic acid or isomers |
| Peak.n.1072 | 0.0364 | 112.0161 | 429 | Peak check passed. Putative ID: ITACONIC-ANHYDRIDE |
| Peak.n.255 | 0.0234 | 130.0266 | 658 | Peak check passed. Multiple peaks. Putative ID: Itaconate, Metabolomics Standards Initiative level 1, based on retention time and monoisotopic mass |
| Peak.n.1082 | 0.0364 | 467.3151 | 208 | Peak check passed. Isotope of 572 |
| Peak.p.133 | 0.0444 | 263.1115 | 616 | Peak check passed. PEPTIDE_856, PEPTIDE_1100 |
| Peak.p.209 | 0.004 | 481.3169 | 279 | Peak check passed. Putative ID: lysoPC(15:0) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Daly, R.; Blackburn, G.; Best, C.; Goodyear, C.S.; Mudaliar, M.; Burgess, K.; Stirling, A.; Porter, D.; McInnes, I.B.; Barrett, M.P.; et al. Changes in Plasma Itaconate Elevation in Early Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Elucidates Disease Activity Associated Macrophage Activation. Metabolites 2020, 10, 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10060241
Daly R, Blackburn G, Best C, Goodyear CS, Mudaliar M, Burgess K, Stirling A, Porter D, McInnes IB, Barrett MP, et al. Changes in Plasma Itaconate Elevation in Early Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Elucidates Disease Activity Associated Macrophage Activation. Metabolites. 2020; 10(6):241. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10060241
Chicago/Turabian StyleDaly, Rónán, Gavin Blackburn, Cameron Best, Carl S. Goodyear, Manikhandan Mudaliar, Karl Burgess, Anne Stirling, Duncan Porter, Iain B. McInnes, Michael P. Barrett, and et al. 2020. "Changes in Plasma Itaconate Elevation in Early Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Elucidates Disease Activity Associated Macrophage Activation" Metabolites 10, no. 6: 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10060241
APA StyleDaly, R., Blackburn, G., Best, C., Goodyear, C. S., Mudaliar, M., Burgess, K., Stirling, A., Porter, D., McInnes, I. B., Barrett, M. P., & Dale, J. (2020). Changes in Plasma Itaconate Elevation in Early Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Elucidates Disease Activity Associated Macrophage Activation. Metabolites, 10(6), 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10060241