Early Perturbations in Glucose Utilization in Malaria-Infected Murine Erythrocytes, Liver and Brain Observed by Metabolomics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. NMR Spectroscopy of Organ and Cellular Extracts
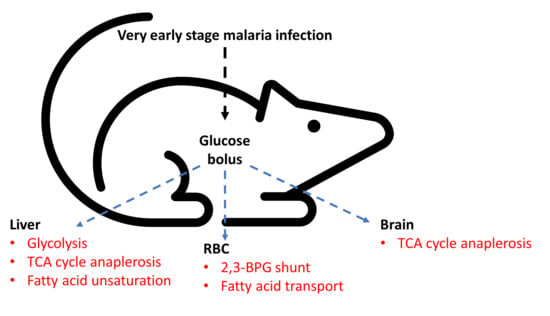
2.2. Alteration in Glucose Utilization of RBC
2.3. Alteration in Glucose Utilization of Liver
2.4. Alteration in Glucose Utilization of Brain
3. Discussion
4. Limitations of the Study
5. Material and Methods
5.1. Animal Experiments
5.2. Preparation of RBC, Liver and Brain Extracts
5.3. NMR Spectroscopy of Organ and RBC Extracts
5.4. Multivariate Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miller, L.H.; Baruch, D.I.; Marsh, K.; Doumbo, O.K. The pathogenic basis of malaria. Nature 2002, 415, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penet, M.F.; Kober, F.; Confort-Gouny, S.; Le Fur, Y.; Dalmasso, C.; Coltel, N.; Liprandi, A.; Gulian, J.M.; Grau, G.E.; Cozzone, P.J.; et al. Magnetic resonance spectroscopy reveals an impaired brain metabolic profile in mice resistant to cerebral malaria infected with Plasmodium berghei ANKA. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 14505–14514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dondorp, A.M.; Kager, P.A.; Vreeken, J.; White, N.J. Abnormal blood flow and Red Blood Cell deformability in severe malaria. Parasitol. Today 2000, 16, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macpherson, G.G.; Warrell, M.J.; White, N.J.; Looareesuwan, S.; Warrell, D.A. Human Cerebral malaria—A quantitative ultrastructural analysis of parasitized erythrocyte sequestration. Am. J. Pathol. 1985, 119, 385–401. [Google Scholar]
- Dondorp, A.M.; Pongponratn, E.; White, N.J. Reduced microcirculatory flow in severe falciparum malaria: Pathophysiology and electron-microscopic pathology. Acta Trop. 2004, 89, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haldar, K.; Murphy, S.C.; Milner, D.A.; Taylor, T.E. Malaria: Mechanisms of erythrocytic infection and pathological correlates of severe disease. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2007, 2, 217–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planche, T.; Krishna, S. Severe malaria: Metabolic complications. Curr. Mol. Med. 2006, 6, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trampuz, A.; Jereb, M.; Muzlovic, I.; Prabhu, R.M. Clinical review: Severe malaria. Crit. Care 2003, 7, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roe, J.K.; Pasvol, G. New developments in the management of malaria in adults. Q. J. Med. 2009, 102, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- English, M.; Sauerwein, R.; Waruiru, C.; Mosobo, M.; Obiero, J.; Lowe, B.; Marsh, K. Acidosis in severe childhood malaria. Q. J. Med. 1997, 90, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbenyega, T.; Angus, B.J.; Bedu-Addo, G.; Baffoe-Bonnie, B.; Guyton, T.; Stacpoole, P.W.; Krishna, S. Glucose and lactate kinetics in children with severe malaria. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2000, 85, 1569–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joet, T.; Eckstein-Ludwig, U.; Morin, C.; Krishna, S. Validation of hexose transporter of Plasmodium falciparum as a novel drug target. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 7476–7479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deslauriers, R.; Ekiel, I.; Kroft, T.; Léveillé, L.; Smith, I.C. NMR studies of malaria: Glycolysis in red cells of mice infected with Plasmodium bergheii and the effects thereon on antimalarial drugs. Tetrahedron 1983, 39, 3543–3548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, M.; Sonawat, H.M.; Sharma, S. Malaria parasite infected erythrocytes inhibit glucose utilization in uninfected red cells. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 6151–6158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Thien, H.; Ackermans, M.T.; Weverling, G.J.; Vinh, T.D.; Endert, E.; Kager, P.A.; Sauerwein, H.P. Gluconeogenesis and fasting in cerebral malaria. Neth. J. Med. 2004, 62, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Basant, A.; Rege, M.; Sharma, S.; Sonawat, H.M. Alterations in urine, serum and brain metabolomic profiles exhibit sexual dimorphism during malaria disease progression. Malar. J. 2010, 9, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sengupta, A.; Ghosh, S.; Pathak, S.; Gogtay, N.; Thatte, U.; Doshi, M.; Sharma, S.; Sonawat, H.M. Metabolomic analysis of urine samples of vivax malaria in-patients for biomarker identification. Metabolomics 2015, 11, 1351–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Pathak, S.; Sonawat, H.M.; Sharma, S.; Sengupta, A. Metabolomic changes in vertebrate host during malaria disease progression. Cytokine 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sengupta, A.; Basant, A.; Ghosh, S.; Sharma, S.; Sonawat, H.M. Liver metabolic alterations and changes in host intercompartmental metabolic correlation during progression of malaria. J. Parasitol. Res. 2011, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sengupta, A.; Ghosh, S.; Sharma, S.; Sonawat, H.M. 1H NMR Metabonomics Indicates Continued Metabolic Changes and Sexual Dimorphism Post-Parasite Clearance in Self-Limiting Murine Malaria Model. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghosh, S.; Sengupta, A.; Sharma, S.; Sonawat, H.M. Early prediction of cerebral malaria by 1H NMR based metabolomics. Malar. J. 2016, 15, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ghosh, S.; Sengupta, A.; Sharma, S.; Sonawat, H.M. Metabolic fingerprints of serum, brain, and liver are distinct for mice with cerebral and noncerebral malaria: A 1H NMR spectroscopy-based metabonomic study. J. Proteome Res. 2012, 11, 4992–5004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.; Sengupta, A.; Sharma, S.; Sonawat, H.M. Metabolic Perturbations of Kidney and Spleen in Murine Cerebral Malaria: 1H NMR-Based Metabolomic Study. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sengupta, A.; Ghosh, S.; Basant, A.; Malusare, S.; Johri, P.; Pathak, S.; Sharma, S.; Sonawat, H.M. Global host metabolic response to Plasmodium vivax infection: A 1H NMR based urinary metabonomic study. Malar. J. 2011, 10, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sengupta, A.; Ghosh, S.; Das, B.K.; Panda, A.; Tripathy, R.; Pied, S.; Ravindran, B.; Pathak, S.; Sharma, S.; Sonawat, H.M. Host metabolic responses to: Plasmodium falciparum infections evaluated by 1H NMR metabolomics. Mol. Biosyst. 2016, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.; Sengupta, A.; Sharma, S.; Sonawat, H.M. Brain and Hepatic Glucose Utilization in Malarial Infection Does Not Depend on Cerebral Symptoms of the Disease. Concepts Magn. Reson. Part A 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, M.; Sonawat, H.M.; Sharma, S. Glycolysis in Plasmodium falciparum results in modulation of host enzyme activities. J. Vector Borne Dis. 2006, 43, 95–103. [Google Scholar]
- Siesjo, B.K. Brain Energy Metabolism; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Schubert, D. Glucose metabolism and Alzheimer’s disease. Age Res. Rev. 2005, 4, 240–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polinsky, R.J.; Noble, H.; Di Chiro, G.; Nee, L.E.; Feldman, R.G.; Brown, R.T. Dominantly inherited Alzheimer’s disease: Cerebral glucose metabolism. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1987, 50, 752–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shah, K.; De Silva, S.; Abbruscato, T. The role of glucose transporters in brain disease: Diabetes and Alzheimer’s disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 12629–12655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rae, C.; McQuillan, J.A.; Parekh, S.B.; Bubb, W.A.; Weiser, S.; Balcar, V.J.; Hansen, A.M.; Ball, H.J.; Hunt, N.H. Brain gene expression, metabolism and bioenergetics: Interrelationships in murine models of cerebral and noncerebral malaria. FASEB J. 2004, 18, 499–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyelade, J.; Isewon, I.; Aromolaran, O.; Uwoghiren, E.; Dokunmu, T.; Rotimi, S.; Aworunse, O.; Obembe, O.; Adebiyi, E. Computational Identification of Metabolic Pathways of Plasmodium falciparum using the k-Shortest Path Algorithm. Int. J. Genom. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kinoshita, A.; Tsukada, K.; Soga, T.; Hishiki, T.; Ueno, Y.; Nakayama, Y.; Tomita, M.; Suematsu, M. Roles of hemoglobin allostery in hypoxia induced metabolic alterations in erythrocytes: Simulation and its verification by metabolome analysis. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 10731–10741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mackintosh, C.L.; Beeson, J.G.; Marsh, K. Clinical features and pathogenesis of severe malaria. Trends Parasitol. 2004, 20, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, M.L.; Hegde, R.; Ganguly, N.K.; Mahajan, R.C. Decreased level of 2,3-diphosphoglycerate and alteration of structural integrity in erythrocytes infected with Plasmodium falciparum in vitro. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2003, 246, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemaitre, R.N.; King, I.B.; Sotoodehnia, N.; Knopp, R.H.; Mozaffarian, D.; McKnight, B.; Rea, T.D.; Rice, K.; Friedlander, Y.; Lumleyd, T.S.; et al. Endogenous red blood cell membrane fatty acids and sudden cardiac arrest. Metabolism 2010, 59, 1029–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lehane, A.M.; Saliba, K.J.; Allen, R.J.; Kirk, K. Choline uptake by the malaria parasite is energized by the membrane potential. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 23, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanamatsu, T.; Tsukada, Y. Effects of ammonia on the anaplerotic pathway and amino acid metabolism in the brain: An ex vivo 13C NMR spectroscopic study of rats after administering [2-13C] glucose with or without ammonium acetate. Brain Res. 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGill, M.R. The past and present of serum aminotransferases and the future of liver injury biomarkers. EXCLI J. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandri, E.; Ahmed, R.; Siddiqui, H.; Choudhary, M.I.; Tsiafoulis, C.G.; Gerothanassis, I.P. High resolution NMR spectroscopy as a structural and analytical tool for unsaturated lipids in solution. Molecules 2017, 22, 1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumaratilake, L.M.; Robinson, B.S.; Ferrante, A.; Poulos, A. Antimalaria properties of n-3 and n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids: In vitro effects on Plasmodium falciparum and in vivo effects on Plasmodium bergheii. J. Clin. Investig. 1992, 89, 961–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Das, U.N. Antibiotic-like actions of essential fatty acids. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 1985, 132, 1350–1352. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jitrapakdee, S.; St Maurice, M.; Rayment, I.; Cleland, W.W.; Wallace, J.C.; Attwood, P.V. Structure, mechanism and regulation of pyruvate carboxylase. Biochem. J. 2008, 413, 369–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]





© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sengupta, A.; Ghosh, S.; Sharma, S.; Sonawat, H.M. Early Perturbations in Glucose Utilization in Malaria-Infected Murine Erythrocytes, Liver and Brain Observed by Metabolomics. Metabolites 2020, 10, 277. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10070277
Sengupta A, Ghosh S, Sharma S, Sonawat HM. Early Perturbations in Glucose Utilization in Malaria-Infected Murine Erythrocytes, Liver and Brain Observed by Metabolomics. Metabolites. 2020; 10(7):277. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10070277
Chicago/Turabian StyleSengupta, Arjun, Soumita Ghosh, Shobhona Sharma, and Haripalsingh M. Sonawat. 2020. "Early Perturbations in Glucose Utilization in Malaria-Infected Murine Erythrocytes, Liver and Brain Observed by Metabolomics" Metabolites 10, no. 7: 277. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10070277
APA StyleSengupta, A., Ghosh, S., Sharma, S., & Sonawat, H. M. (2020). Early Perturbations in Glucose Utilization in Malaria-Infected Murine Erythrocytes, Liver and Brain Observed by Metabolomics. Metabolites, 10(7), 277. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10070277