Exploring the Link between Leaky-Gut-Related Markers and Metabolic Health in a Large Dutch Adult Population
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Characteristics of the Study Population
2.2. Measurement of LGMs
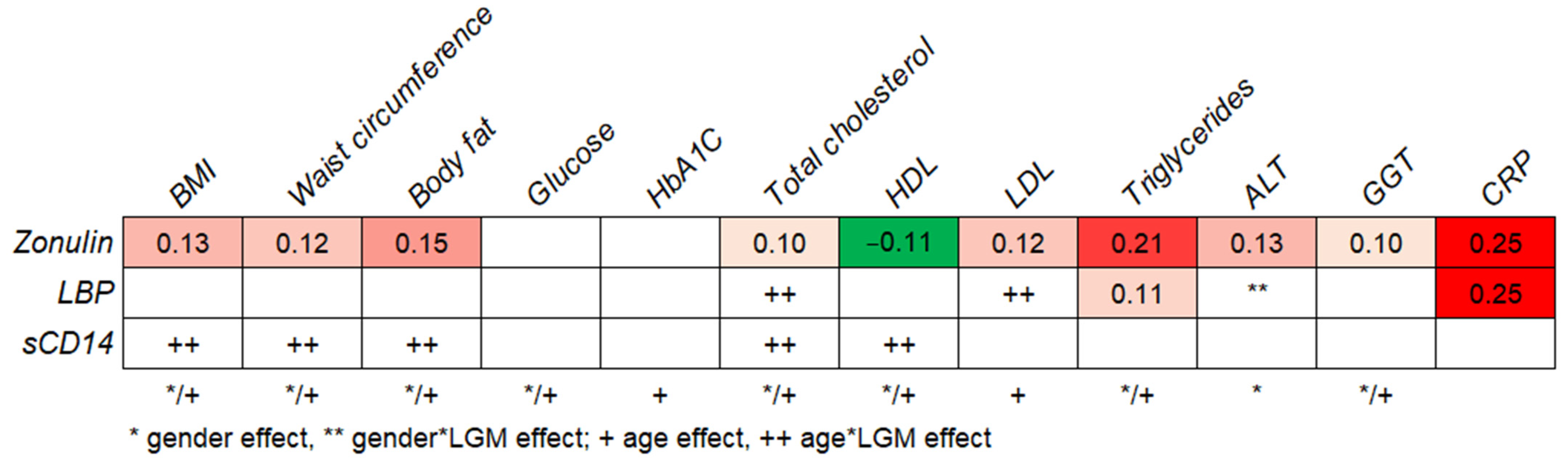
2.3. Relationship between LGMs and Metabolic Health
2.4. Quartile Analyses
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
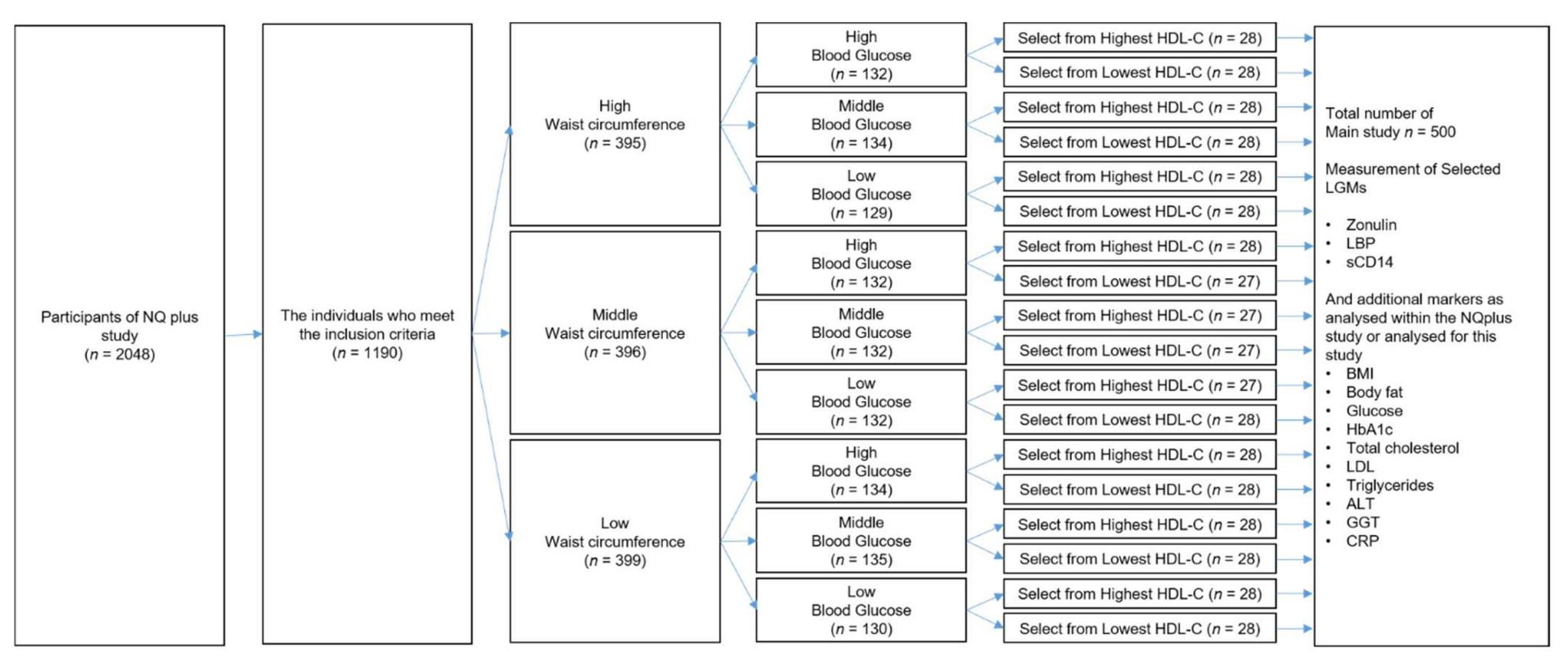
4.1. Study Participants
4.2. Measurement of the Markers
4.3. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shen, W.; Punyanitya, M.; Chen, J.; Gallagher, D.; Albu, J.; Pi-Sunyer, X.; Lewis, C.E.; Grunfeld, C.; Heshka, S.; Heymsfield, S.B. Waist circumference correlates with metabolic syndrome indicators better than percentage fat. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2006, 14, 727–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hinnouho, G.M.; Czernichow, S.; Dugravot, A.; Batty, G.D.; Kivimaki, M.; Singh-Manoux, A. Metabolically healthy obesity and risk of mortality: Does the definition of metabolic health matter? Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 2294–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fuentes, E.; Fuentes, F.; Vilahur, G.; Badimon, L.; Palomo, I. Mechanisms of chronic state of inflammation as mediators that link obese adipose tissue and metabolic syndrome. Mediators Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 136584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoshiko, H.; Feskens, E.J.M.; Oosterink, E.; Ariens, R.M.C.; Mes, J.J.; de Wit, N.J.W. Identification of leaky gut-related markers as indicators of metabolic health in Dutch adults: The Nutrition Questionnaires plus (NQplus) study. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0252936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, A.L.; Coelho, J.; Couto, L.; Leite-Moreira, A.; Roncon-Albuquerque, R., Jr. Metabolic endotoxemia: A molecular link between obesity and cardiovascular risk. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2013, 51, R51–R64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maeshima, N.; Fernandez, R.C. Recognition of lipid A variants by the TLR4-MD-2 receptor complex. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2013, 3, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Awoyemi, A.; Troseid, M.; Arnesen, H.; Solheim, S.; Seljeflot, I. Markers of metabolic endotoxemia as related to metabolic syndrome in an elderly male population at high cardiovascular risk: A cross-sectional study. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2018, 10, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scarpellini, E.; Lupo, M.; Iegri, C.; Gasbarrini, A.; De Santis, A.; Tack, J. Intestinal permeability in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: The gut-liver axis. Rev. Recent Clin. Trials 2014, 9, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshiko, H.; Zeinstra, G.G.; Lenaerts, K.; Oosterink, E.; Ariens, R.M.C.; Mes, J.J.; de Wit, N.J.W. An Observational Study to Evaluate the Association between Intestinal Permeability, Leaky Gut Related Markers, and Metabolic Health in Healthy Adults. Healthcare 2021, 9, 1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-Navarrete, J.M.; Sabater, M.; Ortega, F.; Ricart, W.; Fernandez-Real, J.M. Circulating zonulin, a marker of intestinal permeability, is increased in association with obesity-associated insulin resistance. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yuan, J.H.; Xie, Q.S.; Chen, G.C.; Huang, C.L.; Yu, T.; Chen, Q.K.; Li, J.Y. Impaired intestinal barrier function in type 2 diabetic patients measured by serum LPS, Zonulin, and IFABP. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2021, 35, 107766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Diabetes Federation: The IDF Consensus Worldwide Definition of the Metabolic Syndrome. 2006. Available online: https://www.idf.org/component/attachments/attachments.html?id=705&task=download (accessed on 17 November 2021).
- Fasano, A. Intestinal permeability and its regulation by zonulin: Diagnostic and therapeutic implications. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 10, 1096–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ohlsson, B.; Orho-Melander, M.; Nilsson, P.M. Higher Levels of Serum Zonulin May Rather Be Associated with Increased Risk of Obesity and Hyperlipidemia, Than with Gastrointestinal Symptoms or Disease Manifestations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fasano, A. All disease begins in the (leaky) gut: Role of zonulin-mediated gut permeability in the pathogenesis of some chronic inflammatory diseases. F1000Res 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laugerette, F.; Alligier, M.; Bastard, J.P.; Drai, J.; Chanséaume, E.; Lambert-Porcheron, S.; Laville, M.; Morio, B.; Vidal, H.; Michalski, M.C. Overfeeding increases postprandial endotoxemia in men: Inflammatory outcome may depend on LPS transporters LBP and sCD14. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2014, 58, 1513–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Yu, Z.; Ye, X.; Zou, S.; Li, H.; Yu, D.; Wu, H.; Chen, Y.; Dore, J.; Clement, K.; et al. A marker of endotoxemia is associated with obesity and related metabolic disorders in apparently healthy Chinese. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 1925–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghoshal, S.; Witta, J.; Zhong, J.; de Villiers, W.; Eckhardt, E. Chylomicrons promote intestinal absorption of lipopolysaccharides. J. Lipid. Res. 2009, 50, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clemente-Postigo, M.; Queipo-Ortuno, M.I.; Murri, M.; Boto-Ordonez, M.; Perez-Martinez, P.; Andres-Lacueva, C.; Cardona, F.; Tinahones, F.J. Endotoxin increase after fat overload is related to postprandial hypertriglyceridemia in morbidly obese patients. J. Lipid. Res. 2012, 53, 973–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Michalski, M.-C.; Vors, C.; Lecomte, M.; Laugerette, F. Dietary lipid emulsions and endotoxemia. Oilseeds Fats Crops Lipids 2016, 23, D306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mani, V.; Hollis, J.H.; Gabler, N.K. Dietary oil composition differentially modulates intestinal endotoxin transport and postprandial endotoxemia. Nutr. Metab. (Lond.) 2013, 10, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schütt, C. CD14. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1999, 31, 545–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Courten, B.; Moreno-Navarrete, J.M.; Lyons, J.; Soldatos, G.; de Courten, M.; Dougherty, S.; Forbes, J.; Fernández-Real, J.M. Contrasting association of circulating sCD14 with insulin sensitivity in non-obese and morbidly obese subjects. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2016, 60, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brouwer-Brolsma, E.M.; van Lee, L.; Streppel, M.T.; Sluik, D.; van de Wiel, A.M.; de Vries, J.H.M.; Geelen, A.; Feskens, E.J.M. Nutrition Questionnaires plus (NQplus) study, a prospective study on dietary determinants and cardiometabolic health in Dutch adults. BMJ Open 2018, 8, e020228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| Metabolic Parameter | Minimum | Maximum | Mean (SD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) * | 20 | 77 | 52 (11.7) |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 16.6 | 40.5 | 24.7 (3.4) |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 64.0 | 124.0 | 89.4 (10.9) |
| Body fat (%) | 5.1 | 54.0 | 29.2 (8.5) |
| Glucose (mmol/L) | 3.9 | 8.9 | 5.4 (0.6) |
| HbA1c (mmol/mol) | 22.0 | 49.7 | 35.7 (3.2) |
| Total cholesterol (mmol/L) | 2.0 | 8.6 | 5.52 (1.1) |
| HDL (mmol/L) | 0.7 | 3.7 | 1.7 (0.6) |
| LDL (mmol/L) | 0.7 | 6.0 | 3.3 (0.9) |
| Triglycerides (mmol/L) | 0.3 | 4.9 | 1.2 (0.7) |
| ALT (U/L) | 9.2 | 209.0 | 26.8 (14.6) |
| GGT (U/L) | 5.2 | 253.6 | 23.9 (23.0) |
| CRP (mg/mL) | 0.001 | 129.9 | 2.57 (7.4) |
| LGM | Minimum | Maximum | Mean (SD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zonulin (ng/mL) | 14.7 | 227.9 | 32.0 (13.4) |
| LBP (µg/mL) | 0.7 | 26.0 | 9.6 (3.5) |
| sCD14 (µg/mL) | 0.7 | 2.7 | 1.4 (0.3) |
| LGM | Male | Female | p-Value * |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zonulin (ng/mL) | 32.4 (12.0) | 31.6 (14.7) | 0.12 |
| LBP (µg/mL) | 9.8 (3.2) | 9.5 (3.8) | 0.37 |
| sCD14 (µg/mL) | 1.37 (0.3) | 1.52 (0.3) | <0.001 |
| LGM | Younger (<54 y) | Older (≥54 y) | p-Value * |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zonulin (ng/mL) | 31.0 (8.8) | 33.0 (16.7) | 0.84 |
| LBP (µg/mL) | 9.4 (3.6) | 9.9 (3.4) | 0.29 |
| sCD14 (µg/mL) | 1.39 (0.3) | 1.50 (0.3) | 0.02 |
| Metabolic Parameter | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | p-Value * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BMI (kg/m2) | 23.9 (2.9) | 24.2 (3.0) | 25.2 (3.4) | 25.9 (3.9) | <0.001 |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 87.3 (10.0) | 88.9 (10.4) | 91.1 (10.5) | 94.3 (10.6) | <0.001 |
| Body fat (%) | 27.2 (8.0) | 28.8 (8.3) | 31.4 (9.0) | 29.6 (7.9) | 0.004 |
| Glucose (mmol/L) | 5.4 (0.5) | 5.4 (0.5) | 5.5 (0.6) | 5.5 (0.6) | 0.10 |
| HbA1c (mmol/mol) | 35.3 (3.0) | 35.6 (3.2) | 36.1 (3.5) | 35.9 (3.0) | 0.15 |
| Total cholesterol (mmol/L) | 5.4 (1.0) | 5.4 (1.1) | 5.6 (1.0) | 5.6 (1.1) | 0.09 |
| HDL (mmol/L) | 1.74 (0.6) | 1.70 (0.6) | 1.65 (0.6) | 1.44 (0.5) | 0.002 |
| LDL (mmol/L) | 3.2 (0.9) | 3.2 (1.0) | 3.3 (0.8) | 3.5 (0.9) | 0.02 |
| Triglycerides (mmol/L) | 1.00 (0.5) | 1.04 (0.5) | 1.25 (0.6) | 1.50 (0.8) | <0.001 |
| ALT (U/L) | 23.9 (8.7) | 25.6 (9.6) | 25.9 (13.2) | 31.4 (13.4) | <0.001 |
| GGT (U/L) | 21.5 (18.2) | 20.2 (8.3) | 24.2 (26.1) | 29.6 (26.7) | 0.001 |
| CRP (mg/mL) | 1.3 (3.4) | 1.6 (2.4) | 2.4 (3.8) | 3.9 (6.7) | <0.001 |
| Zonulin (ng/mL) | 23.2 (2.4) | 28.1 (1.1) | 32.3 (1.5) | 44.5 (21.8) |
| Metabolic Parameter | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | p-Value * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BMI (kg/m2) | 24.3 (3.6) | 24.2 (2.9) | 25.0 (2.9) | 25.6 (3.9) | 0.004 |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 88.3 (10.4) | 88.4 (10.5) | 92.6 (9.9) | 92.4 (11.3) | 0.003 |
| Body fat (%) | 28.0 (9.1) | 28.7 (8.1) | 29.2 (7.9) | 31.1 (8.4) | 0.06 |
| Glucose (mmol/L) | 5.4 (0.6) | 5.4 (0.5) | 5.5 (0.5) | 5.5 (0.6) | 0.33 |
| HbA1c (mmol/mol) | 35.3 (3.2) | 35.7 (3.5) | 35.7 (3.0) | 36.2 (3.0) | 0.25 |
| Total cholesterol (mmol/L) | 5.3 (1.1) | 5.5 (1.0) | 5.6 (1.0) | 5.5 (1.0) | 0.14 |
| HDL (mmol/L) | 1.63 (0.6) | 1.88 (0.7) | 1.54 (0.5) | 1.47 (0.6) | <0.001 |
| LDL (mmol/L) | 3.2 (0.9) | 3.2 (0.9) | 3.5 (0.9) | 3.4 (0.9) | 0.03 |
| Triglycerides (mmol/L) | 1.08 (0.6) | 1.03 (0.5) | 1.26 (0.7) | 1.42 (0.8) | <0.001 |
| ALT (U/L) | 25.7 (11.0) | 24.4 (8.0) | 29.1 (12.1) | 27.7 (14.5) | 0.004 |
| GGT (U/L) | 20.3 (13.4) | 23.0 (21.1) | 26.3 (24.4) | 26.1 (24.9) | 0.01 |
| CRP (mg/mL) | 1.5 (2.7) | 1.6 (5.6) | 1.9 (2.8) | 4.2 (5.5) | <0.001 |
| LBP (µg/mL) | 5.7 (2.0) | 8.8 (0.5) | 10.3 (0.5) | 13.7 (2.8) |
| Metabolic Parameter | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | p-Value * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BMI (kg/m2) | 24.8 (3.2) | 24.7 (3.5) | 25.2 (3.5) | 24.3 (3.4) | 0.31 |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 90.3 (10.5) | 91.0 (11.2) | 91.8 (11.0) | 88.6 (9.9) | 0.36 |
| Body fat (%) | 28.0 (8.1) | 27.6 (8.1) | 30.9 (8.8) | 30.6 (8.3) | 0.01 |
| Glucose (mmol/L) | 5.4 (0.5) | 5.4 (0.6) | 5.4 (0.5) | 5.5 (0.6) | 0.14 |
| HbA1C (mmol/mol) | 35.1 (3.2) | 35.7 (2.8) | 36.0 (2.9) | 36.2 (3.7) | 0.01 |
| Total cholesterol (mmol/L) | 5.2 (1.0) | 5.5 (1.0) | 5.6 (1.0) | 5.7 (1.1) | 0.007 |
| HDL (mmol/L) | 1.51 (0.6) | 1.62 (0.6) | 1.68 (0.6) | 1.72 (0.6) | 0.08 |
| LDL (mmol/L) | 3.1 (0.9) | 3.3 (1.0) | 3.4 (0.9) | 3.4 (0.9) | 0.05 |
| Triglycerides (mmol/L) | 1.27 (0.7) | 1.26 (0.8) | 1.13 (0.5) | 1.14 (0.6) | 0.65 |
| ALT (U/L) | 27.3 (9.6) | 27.9 (12.1) | 24.9 (8.7) | 26.7 (15.3) | 0.43 |
| GGT (U/L) | 22.8 (14.8) | 27.3 (29.5) | 22.9 (22.1) | 22.8 (16.9) | 0.54 |
| CRP (mg/mL) | 1.3 (1.5) | 2.0 (3.3) | 2.6 (4.1) | 3.1 (7.0) | 0.04 |
| sCD14 (µg/mL) | 1.1 (0.1) | 1.3 (0.1) | 1.5 (0.1) | 1.9 (0.2) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hoshiko, H.; Feskens, E.J.M.; Oosterink, E.; Ariens, R.M.C.; Mes, J.J.; de Wit, N.J.W. Exploring the Link between Leaky-Gut-Related Markers and Metabolic Health in a Large Dutch Adult Population. Metabolites 2021, 11, 877. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11120877
Hoshiko H, Feskens EJM, Oosterink E, Ariens RMC, Mes JJ, de Wit NJW. Exploring the Link between Leaky-Gut-Related Markers and Metabolic Health in a Large Dutch Adult Population. Metabolites. 2021; 11(12):877. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11120877
Chicago/Turabian StyleHoshiko, Hiroyuki, Edith J. M. Feskens, Els Oosterink, Renata M. C. Ariens, Jurriaan J. Mes, and Nicole J. W. de Wit. 2021. "Exploring the Link between Leaky-Gut-Related Markers and Metabolic Health in a Large Dutch Adult Population" Metabolites 11, no. 12: 877. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11120877
APA StyleHoshiko, H., Feskens, E. J. M., Oosterink, E., Ariens, R. M. C., Mes, J. J., & de Wit, N. J. W. (2021). Exploring the Link between Leaky-Gut-Related Markers and Metabolic Health in a Large Dutch Adult Population. Metabolites, 11(12), 877. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11120877






