Identification of Salivary Microorganisms and Metabolites Associated with Halitosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Demographic and Clinical Characteristics of the Study Subjects
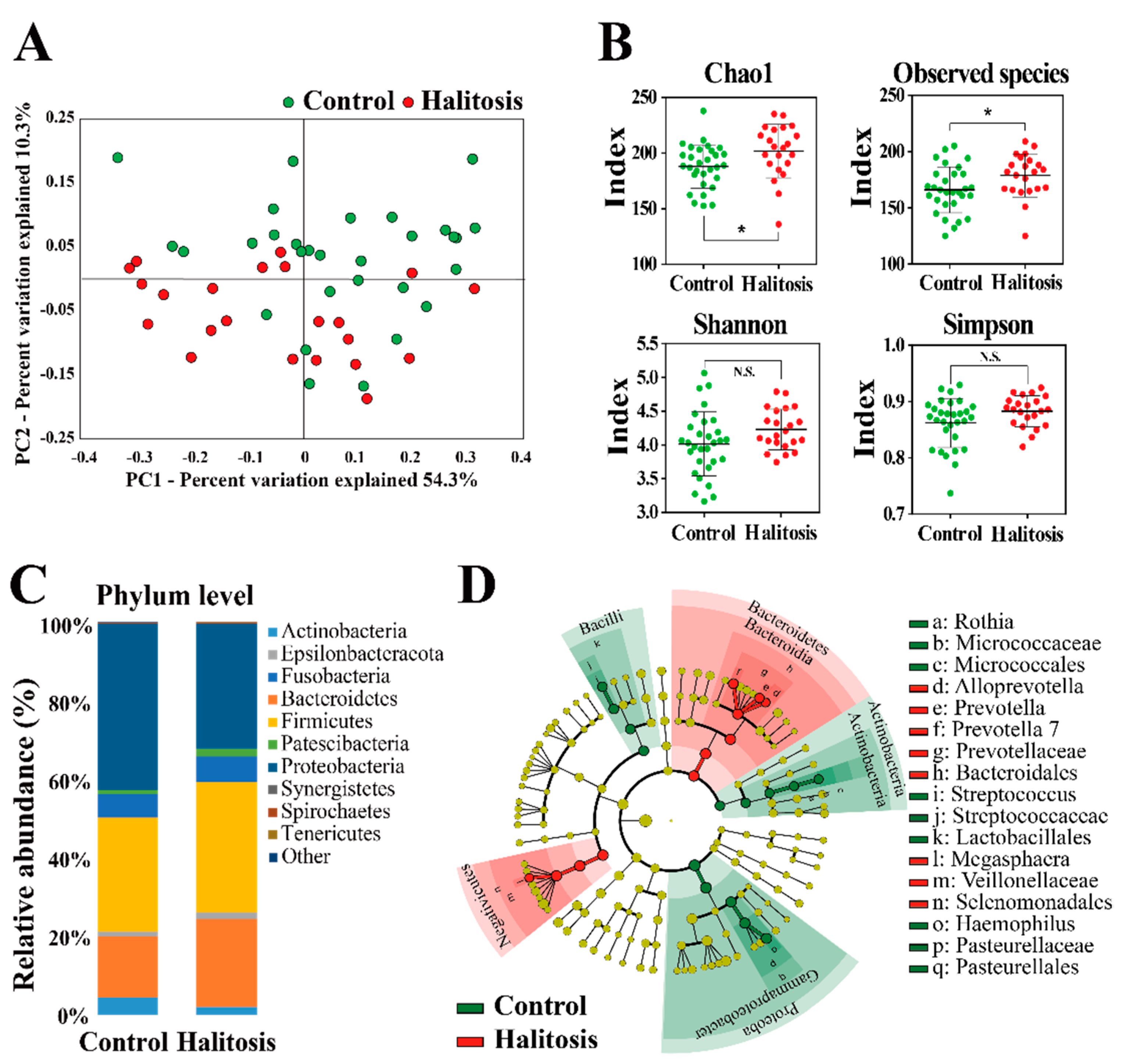
2.2. Profiling of Salivary Bacterial Microbiome
2.3. Profiling of Saliva Metabolites
2.4. Correlation between Microbiome and Metabolome
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Ethics Statement
3.2. Halitosis Assessment
3.3. Exclusion Criteria
3.4. Inclusion Criteria
3.5. Collection of Saliva
3.6. DNA Extraction and 16S rRNA Gene Amplicon Sequencing
3.7. Sample Derivatization and GC–MS Analysis
3.8. Data Processing and Multivariate Analysis
3.9. Correlation Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Armstrong, B.L.; Sensat, M.L.; Stoltenberg, J.L. Halitosis: A review of current literature. J. Dent. Hyg. 2010, 84, 65–74. [Google Scholar]
- Van den Broek, A.M.W.T.; Feenstra, L.; de Baat, C. A review of the current literacture on aetiology and measurement methods of halitosis. J. Dent. 2007, 35, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tangerman, A. Halitosis in medicine: A review. Int. Dent. J. 2002, 52, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mok, S.F.; Chinna, K.; Cheah, Y.K.; Ngeow, W.C.; Zain, R.B.; Yap, S.F.; Ong, H. The oral microbiome community variations associated with normal, potentially malignant disorders and malignant lesions of the oral cavity. Malays. J. Pathol. 2017, 39, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Amou, T.; Hinode, D.; Yoshioka, M.; Grenier, D. Relationship between halitosis and periodontal disease–associated oral bacteria in tongue coatings. Int. J. Dent. Hyg. 2014, 12, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleinberg, I.; Codipilly, M. Modeling of the oral malodor system and methods of analysis. Quintessence Int. 1999, 30, 357–369. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, H.X.; Tang, C.; Chen, X.; Wong, M.; Ye, W. Characteristics of patients complaining of halitosis and factors associated with halitosis. Oral. Dis. 2014, 20, 787–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyrrell, K.L.; Citron, D.M.; Warren, Y.A.; Nachnani, S.; Goldstein, E.J. Anaerobic bacteria cultured from the tongue dorsum of subjects with oral malodor. Anaerobe 2003, 9, 243–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazor, C.; Mitchell, P.; Lee, A.; Stokes, L.; Loesche, W.; Dewhirst, F.; Paster, B. Diversity of bacterial populations on the tongue dorsa of patients with halitosis and healthy patients. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 558–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haraszthy, V.I.; Zambon, J.J.; Sreenivasan, P.K.; Zambon, M.M.; Gerber, D.; Rego, R.; Parker, C. Identification of oral bacterial species associated with halitosis. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 2007, 138, 1113–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampelska, K.; Jaworska, M.M.; Babalska, Z.Ł.; Karpiński, T.M. The role of oral microbiota in intra-oral halitosis. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awano, S.; Gohara, K.; Kurihara, E.; Ansai, T.; Takehara, T. The relationship between the presence of periodontopathogenic bacteria in saliva and halitosis. Int. Dent. J. 2002, 52, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetz, G.; Vikina, D.; Brown, S.; Zappile, P.; Dolgalev, I.; Tsirigos, A.; Heguy, A.; Tetz, V. Draft Genome Sequence of Streptococcus halitosis sp. nov., Isolated from the Dorsal Surface of the Tongue of a Patient with Halitosis. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2019, 8, e01704–e01718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tonzetich, J. Production and origin of oral malodor: A review of mechanisms and methods of analysis. J. Periodontol. 1977, 48, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bornstein, M.M.; Kislig, K.; Hoti, B.B.; Seemann, R.; Lussi, A. Prevalence of halitosis in the population of the city of Bern, Switzerland: A study comparing self-reported and clinical data. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 2009, 117, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, M.; Kulkarni, G.; Bosy, A.; Mcculloch, C. Reproducibility and sensitivity of oral malodor measurements with a portable sulphide monitor. J. Dent. Res. 1991, 70, 1436–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Cannon, R.; Ji, P.; Farella, M.; Mei, L. Halitosis: Prevalence, risk factors, sources, measurement and treatment–a review of the literature. Aust. Dent. J. 2020, 65, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talebian, A.; Tazhibi, M.; Semyari, H.; Iranpoor, R.; Talebian, H.; Oreizy, S.M.; Khansari, M. Clinical evaluation of 222 Iranian patients with halitosis. J. Breath. Res. 2008, 2, 017015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Velde, S.; van Steenberghe, D.; Van Hee, P.; Quirynen, M. Detection of odorous compounds in breath. J. Dent. Res. 2009, 88, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Den Velde, S.; Quirynen, M.; van Steenberghe, D. Halitosis associated volatiles in breath of healthy subjects. J. Chromatogr. B 2007, 853, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monedeiro, F.; Milanowski, M.; Ratiu, I.-A.; Zmysłowski, H.; Ligor, T.; Buszewski, B. VOC profiles of saliva in assessment of halitosis and submandibular abscesses using HS-SPME-GC/MS technique. Molecules 2019, 24, 2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beale, D.J.; Pinu, F.R.; Kouremenos, K.A.; Poojary, M.M.; Narayana, V.K.; Boughton, B.A.; Kanojia, K.; Dayalan, S.; Jones, O.A.; Dias, D.A. Review of recent developments in GC–MS approaches to metabolomics-based research. Metabolomics 2018, 14, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanani, H.; Chrysanthopoulos, P.K.; Klapa, M.I. Standardizing GC-MS metabolomics. J. Chromatogr. B 2008, 871, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scully, C.; Porter, S.; Greenman, J. What to do about halitosis. BMJ 1994, 308, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, N. Oral microbiome metabolism: From “who are they?” to “what are they doing?”. J. Dent. Res. 2015, 94, 1628–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, S.; Claesson, R.; Carlsson, J. The capacity of subgingival microbiotas to produce volatile sulfur compounds in human serum. Oral. Microbiol. Immunol. 1989, 4, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterer, N.; Shaharabany, M.; Rosenberg, M. β-Galactosidase activity and H2S production in an experimental oral biofilm. J. Breath. Res. 2009, 3, 016006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanos, V.; Pintus, M.C.; Pintus, R.; Marcialis, M.A. Lung microbiota in the acute respiratory disease: From coronavirus to metabolomics. J. Pediatric. Neonatal. Individ. Med. 2020, 9, e090139. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.; Ji, G.; Jia, W.; Li, H. Gut microbiota and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Insights on mechanism and application of metabolomics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gower, J.C. Principal coordinates analysis. In Wiley StatsRef: Statistics Reference Online; American Cancer Society: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2015; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Oshiro, A.; Zaitsu, T.; Ueno, M.; Kawaguchi, Y. Characterization of oral bacteria in the tongue coating of patients with halitosis using 16S rRNA analysis. Acta Odontol. Scand. 2020, 78, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ye, W.; Zhang, Y.; He, M.; Zhu, C.; Feng, X.-P. Relationship of tongue coating microbiome on volatile sulfur compounds in healthy and halitosis adults. J. Breath Res. 2019, 14, 016005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeshita, T.; Suzuki, N.; Nakano, Y.; Yasui, M.; Yoneda, M.; Shimazaki, Y.; Hirofuji, T.; Yamashita, Y. Discrimination of the oral microbiota associated with high hydrogen sulfide and methyl mercaptan production. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, N.; Yoneda, M.; Takeshita, T.; Hirofuji, T.; Hanioka, T. Induction and inhibition of oral malodor. Mol. Oral. Microbiol. 2019, 34, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seerangaiyan, K.; van Winkelhoff, A.J.; Harmsen, H.J.; Rossen, J.W.; Winkel, E.G. The tongue microbiome in healthy subjects and patients with intra-oral halitosis. J. Breath Res. 2017, 11, 036010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Codipilly, D.; Kleinberg, I. Generation of indole/skatole during malodor formation in the salivary sediment model system and initial examination of the oral bacteria involved. J. Breath Res. 2008, 2, 017017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardi, S.; Karygianni, L.; Filippi, A.; Anderson, A.C.; Zürcher, A.; Hellwig, E.; Vach, K.; Macchiarelli, G.; Al-Ahmad, A. Combining culture and culture-independent methods reveals new microbial composition of halitosis patients’ tongue biofilm. Microbiologyopen 2020, 9, e958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardi, S.; Continenza, M.A.; Al-Ahmad, A.; Karygianni, L.; Follo, M.; Filippi, A.; Macchiarelli, G. Streptococcus spp. and Fusobacterium nucleatum in tongue dorsum biofilm from halitosis patients: A fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) and confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) study. New Microbiol. 2019, 42, 108–113. [Google Scholar]
- Liebsch, C.; Pitchika, V.; Pink, C.; Samietz, S.; Kastenmüller, G.; Artati, A.; Suhre, K.; Adamski, J.; Nauck, M.; Völzke, H. The saliva metabolome in association to oral health status. J. Dent. Res. 2019, 98, 642–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustamante, M.; Oomah, B.D.; Mosi-Roa, Y.; Rubilar, M.; Burgos-Díaz, C. Probiotics as an adjunct therapy for the treatment of halitosis, dental caries and periodontitis. Probiotics. Antimicrob. Proteins 2020, 12, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, H.T.; Li, J.-Y.; Peng, Y.-C.; Lu, C.-D. Molecular characterization of PauR and its role in control of putrescine and cadaverine catabolism through the γ-glutamylation pathway in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. J. Bacteriol. 2013, 195, 3906–3913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ye, W.; Li, Y.; Feng, X. Correlation study between cadaverine level in saliva and halitosis. Shanghai Kou Qiang Yi Xue 2007, 16, 347–350. [Google Scholar]
- Morizono, H.; Cabrera-Luque, J.; Shi, D.; Gallegos, R.; Yamaguchi, S.; Yu, X.; Allewell, N.M.; Malamy, M.H.; Tuchman, M. Acetylorinithine transcarbamylase: A novel enzyme in arginine biosynthesis. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 2974–2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Medina-Enríquez, M.M.; Alcantara-Farfan, V.; Aguilar-Faisal, L.; Trujillo-Ferrara, J.G.; Rodriguez-Paez, L.; Vargas-Ramírez, A.L. N-ω-chloroacetyl-l-ornithine, a new competitive inhibitor of ornithine decarboxylase, induces selective growth inhibition and cytotoxicity on human cancer cells versus normal cells. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2015, 30, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moye, L.M.; Liu, Y.; Coarfa, C.; Putluri, N.; Rhoads, J.M. Plasma urea cycle metabolites may be useful biomarkers in children with eosinophilic esophagitis. Front. Pediatr. 2019, 6, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhu, C.; Cao, G.; Zhan, J.; Feng, X.; Chen, X. Dynamic Alterations of Oral Microbiota Related to Halitosis in Preschool Children. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, S.; Kozlovsky, A.; Gordon, D.; Gelernter, I.; Sintov, A.; Rosenberg, M. Cadaverine as a putative component of oral malodor. J. Dent. Res. 1994, 73, 1168–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, W.; Chen, K.; Li, Y.; Hao, N.; Wang, X.; Ouyang, P. Advances in cadaverine bacterial production and its applications. Engineering 2017, 3, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-L.; Nascimento, M.; Burne, R.A. Progress toward understanding the contribution of alkali generation in dental biofilms to inhibition of dental caries. Int. J. Oral. Sci. 2012, 4, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jorge, J.M.; Pérez-García, F.; Wendisch, V.F. A new metabolic route for the fermentative production of 5-aminovalerate from glucose and alternative carbon sources. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 245, 1701–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.G.; Moon, Y.M.; Hong, J.W.; No, S.Y.; Choi, T.R.; Jung, H.R.; Yang, S.Y.; Bhatia, S.K.; Ahn, J.O.; Park, K.M. Production of glutaric acid from 5-aminovaleric acid using Escherichia coli whole cell bio-catalyst overexpressing GabTD from Bacillus subtilis. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2018, 118, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Z.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Xiang, C. Pyrosequencing analysis of the salivary microbiota of healthy Chinese children and adults. Microb. Ecol. 2013, 65, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tangerman, A.; Winkel, E.G. Intra-and extra-oral halitosis: Finding of a new form of extra-oral blood-borne halitosis caused by dimethyl sulphide. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2007, 34, 748–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Xun, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, X.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wu, C.; et al. Tongue Coating and the Salivary Microbial Communities Vary in Children with Halitosis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sakamoto, M.; Umeda, M.; Ishikawa, I.; Benno, Y. Comparison of the oral bacterial flora in saliva from a healthy subject and two periodontitis patients by sequence analysis of 16S rDNA libraries. Microbiol. Immunol. 2000, 44, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parada, A.E.; Needham, D.M.; Fuhrman, J.A. Every base matters: Assessing small subunit rRNA primers for marine microbiomes with mock communities, time series and global field samples. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 1403–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rognes, T.; Flouri, T.; Nichols, B.; Quince, C.; Mahé, F. VSEARCH: A versatile open source tool for metagenomics. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lommen, A. MetAlign: Interface-driven, versatile metabolomics tool for hyphenated full-scan mass spectrometry data preprocessing. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 3079–3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsugawa, H.; Bamba, T.; Shinohara, M.; Nishiumi, S.; Yoshida, M.; Fukusaki, E. Practical non-targeted gas chromatography/mass spectrometry-based metabolomics platform for metabolic phenotype analysis. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2011, 112, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Clinical Parameters | Control (n = 30) | Intra-Oral Halitosis (n = 22) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 38.50 ± 11.94 | 43.43 ± 15.73 | |
| Sex | Female | 20 | 13 |
| Male | 10 | 9 | |
| H2S 1 | 27.50 ± 25.81 | 806.77 ± 866.08 *** 1 | |
| CH3SH | 7.10 ± 6.14 | 213.41 ± 217.14 *** | |
| (CH3)2S | 39.73 ± 49.74 | 82.77 ± 71.20 * | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jo, J.-k.; Seo, S.-H.; Park, S.-E.; Kim, H.-W.; Kim, E.-J.; Na, C.-S.; Cho, K.-M.; Kwon, S.-J.; Moon, Y.-H.; Son, H.-S. Identification of Salivary Microorganisms and Metabolites Associated with Halitosis. Metabolites 2021, 11, 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11060362
Jo J-k, Seo S-H, Park S-E, Kim H-W, Kim E-J, Na C-S, Cho K-M, Kwon S-J, Moon Y-H, Son H-S. Identification of Salivary Microorganisms and Metabolites Associated with Halitosis. Metabolites. 2021; 11(6):362. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11060362
Chicago/Turabian StyleJo, Jae-kwon, Seung-Ho Seo, Seong-Eun Park, Hyun-Woo Kim, Eun-Ju Kim, Chang-Su Na, Kwang-Moon Cho, Sun-Jae Kwon, Young-Ho Moon, and Hong-Seok Son. 2021. "Identification of Salivary Microorganisms and Metabolites Associated with Halitosis" Metabolites 11, no. 6: 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11060362
APA StyleJo, J.-k., Seo, S.-H., Park, S.-E., Kim, H.-W., Kim, E.-J., Na, C.-S., Cho, K.-M., Kwon, S.-J., Moon, Y.-H., & Son, H.-S. (2021). Identification of Salivary Microorganisms and Metabolites Associated with Halitosis. Metabolites, 11(6), 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11060362






