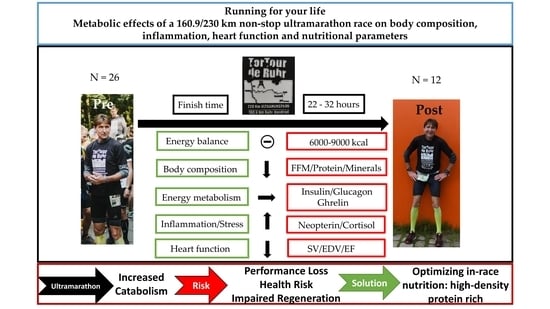
Running for Your Life: Metabolic Effects of a 160.9/230 km Non-Stop Ultramarathon Race on Body Composition, Inflammation, Heart Function, and Nutritional Parameters
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Entry Eligibility
2.2. Anthropometry and Body Composition
2.3. Study Group Characteristics
2.4. Environmental Conditions
2.5. Energy Intake and Expenditure
2.6. Energy Metabolism and Stress Response
2.7. Echocardiography
2.8. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Race Nutrition
3.2. Body Composition
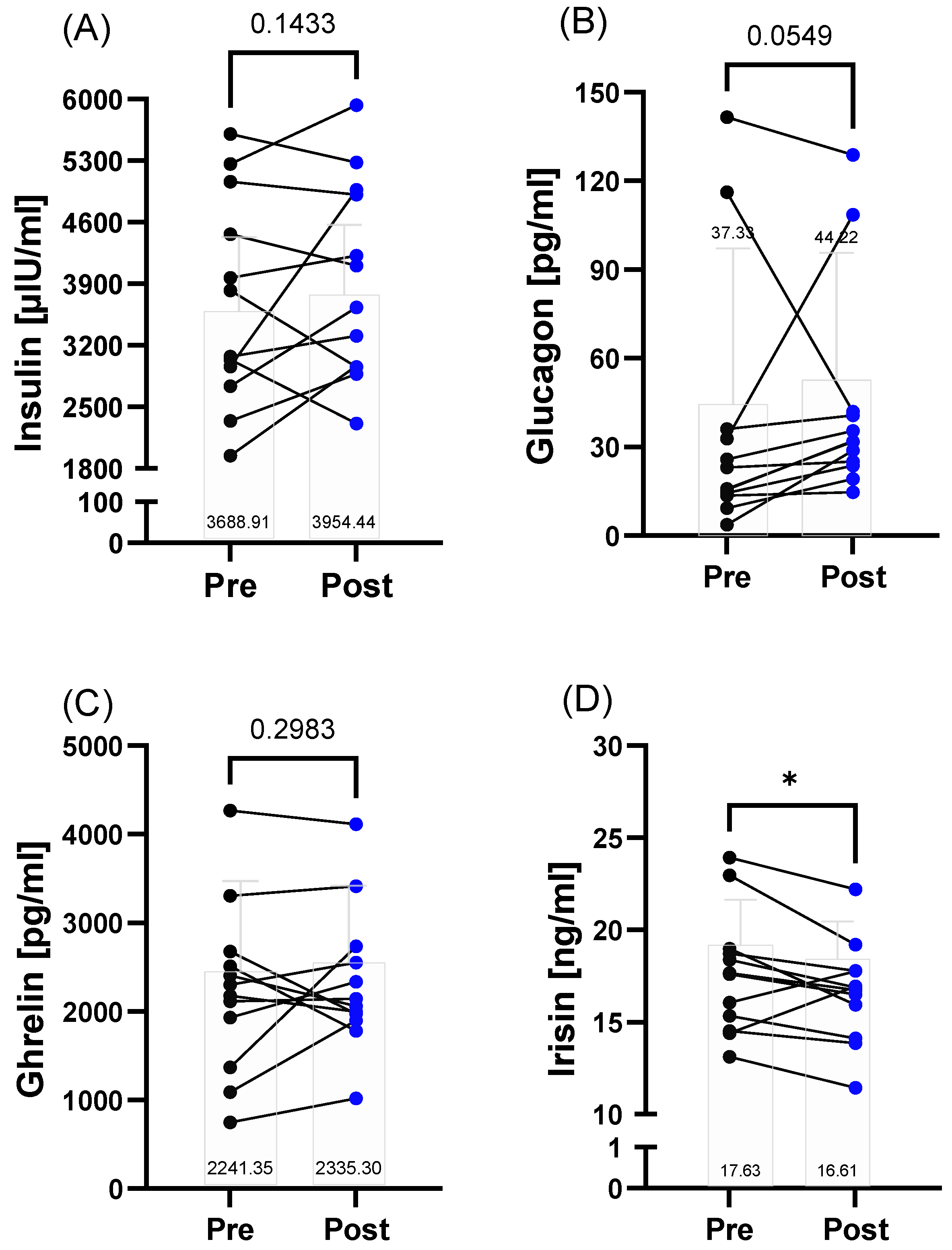
3.3. Energy Metabolism
3.4. Stress Response
3.5. Echocardiography
4. Discussion
4.1. Energy Metabolism and Nutritional Strategies
4.2. Inflammatory and Immunological (Stress) Response
4.3. Cardiac Considerations
4.4. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hunter, P. The evolution of human endurance. EMBO Rep. 2019, 20, e49396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knechtle, B. Ultramarathon runners: Nature or nurture? Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2012, 7, 310–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, M.D.; Khodaee, M.; Nudell, N.G.; Pasternak, A. Recommendations on the Appropriate Level of Medical Support at Ultramarathons. Sports Med. 2020, 50, 871–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teramoto, M.; Bungum, T.J. Mortality and longevity of elite athletes. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2010, 13, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemez, S.; Baker, J. Do Elite Athletes Live Longer? A Systematic Review of Mortality and Longevity in Elite Athletes. Sports Med. Open 2015, 1, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheer, V.; Tiller, N.B.; Doutreleau, S.; Khodaee, M.; Knechtle, B.; Pasternak, A.; Rojas-Valverde, D. Potential Long-Term Health Problems Associated with Ultra-Endurance Running: A Narrative Review. Sports Med. 2022, 52, 725–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knechtle, B.; Nikolaidis, P.T. Physiology and Pathophysiology in Ultra-Marathon Running. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansoni, V.; Vernillo, G.; Perego, S.; Barbuti, A.; Merati, G.; Schena, F.; La Torre, A.; Banfi, G.; Lombardi, G. Bone turnover response is linked to both acute and established metabolic changes in ultra-marathon runners. Endocrine 2017, 56, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiller, N.B.; Roberts, J.D.; Beasley, L.; Chapman, S.; Pinto, J.M.; Smith, L.; Wiffin, M.; Russell, M.; Sparks, S.A.; Duckworth, L.; et al. International Society of Sports Nutrition Position Stand: Nutritional considerations for single-stage ultra-marathon training and racing. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2019, 16, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagourelias, E.D.; Christou, G.A.; Sotiriou, P.G.; Anifanti, M.A.; Koutlianos, N.A.; Tsironi, M.P.; Christou, K.A.; Vassilikos, V.P.; Deligiannis, A.P.; Kouidi, E.J. Impact of a 246 Km ultra-marathon running race on heart: Insights from advanced deformation analysis. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2022, 22, 1287–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lord, R.; George, K.; Somauroo, J.; Stembridge, M.; Jain, N.; Hoffman, M.D.; Shave, R.; Haddad, F.; Ashley, E.; Jones, H.; et al. Alterations in Cardiac Mechanics Following Ultra-Endurance Exercise: Insights from Left and Right Ventricular Area-Deformation Loops. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2016, 29, 879–887.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sewry, N.; Schwellnus, M.; Boulter, J.; Seocharan, I.; Jordaan, E. Medical Encounters in a 90-km Ultramarathon Running Event: A 6-year Study in 103 131 Race Starters-SAFER XVII. Clin. J. Sport Med. 2022, 32, e61–e67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almekinders, L.C.; Engle, C.R. Common and Uncommon Injuries in Ultra-endurance Sports. Sports Med. Arthrosc. Rev. 2019, 27, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieman, D.C.; Dumke, C.L.; Henson, D.A.; McAnulty, S.R.; Gross, S.J.; Lind, R.H. Muscle damage is linked to cytokine changes following a 160-km race. Brain Behav. Immun. 2005, 19, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lucas, R.D.; Caputo, F.; Mendes de Souza, K.; Sigwalt, A.R.; Ghisoni, K.; Lock Silveira, P.C.; Remor, A.P.; Da Luz Scheffer, D.; Guglielmo, L.G.A.; Latini, A. Increased platelet oxidative metabolism, blood oxidative stress and neopterin levels after ultra-endurance exercise. J. Sports Sci. 2014, 32, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, J.E.; Hodges, N.J.; Bosch, J.A.; Aldred, S. Prolonged depletion of antioxidant capacity after ultraendurance exercise. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2011, 43, 1770–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, M.; Suzuki, Y. Alterations in intestinal microbiota in ultramarathon runners. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 6984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaidis, P.T.; Veniamakis, E.; Rosemann, T.; Knechtle, B. Nutrition in Ultra-Endurance: State of the Art. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavoué, C.; Siracusa, J.; Chalchat, É.; Bourrilhon, C.; Charlot, K. Analysis of food and fluid intake in elite ultra-endurance runners during a 24-h world championship. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2020, 17, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copeland, J.L.; Verzosa, M.L.S. Endocrine response to an ultra-marathon in pre- and post-menopausal women. Biol. Sport 2014, 31, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Holliday, A.; Blannin, A. Appetite, food intake and gut hormone responses to intense aerobic exercise of different duration. J. Endocrinol. 2017, 235, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, J.A.; King, J.A.; McFarlane, E.; Baker, L.; Bradley, C.; Crouch, N.; Hill, D.; Stensel, D.J. Appetite, appetite hormone and energy intake responses to two consecutive days of aerobic exercise in healthy young men. Appetite 2015, 92, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howe, C.C.F.; Alshehri, A.; Muggeridge, D.; Mullen, A.B.; Boyd, M.; Spendiff, O.; Moir, H.J.; Watson, D.G. Untargeted Metabolomics Profiling of an 80.5 km Simulated Treadmill Ultramarathon. Metabolites 2018, 8, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karstoft, K.; Solomon, T.P.; Laye, M.J.; Pedersen, B.K. Daily marathon running for a week--the biochemical and body compositional effects of participation. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2013, 27, 2927–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrotta, A.S.; Jeklin, A.T.; Bredin, S.S.D.; Shellington, E.M.; Kaufman, K.L.; de Faye, A.; Miles, R.M.; Warburton, D.E.R. Effect of an Ultra-Endurance Event on Cardiovascular Function and Cognitive Performance in Marathon Runners. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 838704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jörres, M.; Gunga, H.-C.; Steinach, M. Physiological Changes, Activity, and Stress During a 100-km-24-h Walking-March. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 640710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bizjak, D.A.; Treff, G.; Zügel, M.; Schumann, U.; Winkert, K.; Schneider, M.; Abendroth, D.; Steinacker, J.M. Differences in Immune Response During Competition and Preparation Phase in Elite Rowers. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 803863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trappe, S. Marathon runners: How do they age? Sports Med. 2007, 37, 302–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petek, B.J.; Gustus, S.K.; Wasfy, M.M. Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing in Athletes: Expect the Unexpected. Curr. Treat. Options Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 23, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gellish, R.L.; Goslin, B.R.; Olson, R.E.; McDonald, A.; Russi, G.D.; Moudgil, V.K. Longitudinal modeling of the relationship between age and maximal heart rate. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2007, 39, 822–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargreaves, M.; Spriet, L.L. Skeletal muscle energy metabolism during exercise. Nat. Metab. 2020, 2, 817–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakawa, K.; Hosono, A.; Shibata, K.; Ghadimi, R.; Fuku, M.; Goto, C.; Imaeda, N.; Tokudome, Y.; Hoshino, H.; Marumoto, M.; et al. Changes in blood biochemical markers before, during, and after a 2-day ultramarathon. Open Access J. Sports Med. 2016, 7, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Martinez Munoz, I.Y.; Del Camarillo Romero, E.S.; Garduno Garcia, J.d.J. Irisin a Novel Metabolic Biomarker: Present Knowledge and Future Directions. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 2018, 7816806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coker, R.H.; Weaver, A.N.; Coker, M.S.; Murphy, C.J.; Gunga, H.-C.; Steinach, M. Metabolic Responses to the Yukon Arctic Ultra: Longest and Coldest in the World. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2017, 49, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Venrooij, N.F.J.; Wardenaar, F.C.; Hoogervorst, D.; Senden, J.M.G.; van Dijk, J.-W.; Jonvik, K.L. The association between gastrointestinal injury, complaints, and food intake in 60-km ultramarathon runners. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2022, 47, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hohl, R.; Nazário de Rezende, F.; Millet, G.Y.; Da Ribeiro Mota, G.; Marocolo, M. Blood cardiac biomarkers responses are associated with 24 h ultramarathon performance. Heliyon 2019, 5, e01913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murr, C.; Widner, B.; Wirleitner, B.; Fuchs, D. Neopterin as a marker for immune system activation. Curr. Drug Metab. 2002, 3, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bizjak, D.A.; Stangl, M.; Börner, N.; Bösch, F.; Durner, J.; Drunin, G.; Buhl, J.-L.; Abendroth, D. Kynurenine serves as useful biomarker in acute, Long- and Post-COVID-19 diagnostics. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1004545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duclos, M.; Tabarin, A. Exercise and the Hypothalamo-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis. Front. Horm. Res. 2016, 47, 12–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittert, G.A.; Livesey, J.H.; Espiner, E.A.; Donald, R.A. Adaptation of the hypothalamopituitary adrenal axis to chronic exercise stress in humans. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1996, 28, 1015–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieman, D.C.; Pedersen, B.K. Exercise and Immune Function. Sports Med. 1999, 27, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vuorimaa, T.; Ahotupa, M.; Häkkinen, K.; Vasankari, T. Different hormonal response to continuous and intermittent exercise in middle-distance and marathon runners. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2008, 18, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jastrzębski, Z.; Żychowska, M.; Jastrzębska, M.; Prusik, K.; Prusik, K.; Kortas, J.; Ratkowski, W.; Konieczna, A.; Radzimiński, Ł. Changes in blood morphology and chosen biochemical parameters in ultra-marathon runners during a 100-km run in relation to the age and speed of runners. Int. J. Occup. Med. Environ. Health 2016, 29, 801–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiller, N.B.; Wheatley-Guy, C.M.; Fermoyle, C.C.; Robach, P.; Ziegler, B.; Gavet, A.; Schwartz, J.C.; Taylor, B.J.; Constantini, K.; Murdock, R.; et al. Sex-Specific Physiological Responses to Ultramarathon. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2022, 54, 1647–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavigli, L.; Zorzi, A.; Spadotto, V.; Mandoli, G.E.; Melani, A.; Fusi, C.; D’Andrea, A.; Focardi, M.; Valente, S.; Cameli, M.; et al. The Acute Effects of an Ultramarathon on Atrial Function and Supraventricular Arrhythmias in Master Athletes. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Anthropometry | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age [years] | Height [cm] | Body Mass [kg] | Body Mass Index [kg/m²] | ||||
| 160.9 km | 230 km | 160.9 km | 230 km | 160.9 km | 230 km | 160.9 km | 230 km |
| 50.20 (7.98) | 50.14 (9.74) | 174.80 (4.62) | 177.43 (8.74) | 71.14 (4.18) | 71.89 (11.30) | 23.30 (1.29) | 22.79 (2.93) |
| Finish time [hours] | |||||||
| 160.9 km | 22.56 (3.31) | ||||||
| 230 km | 32.28 (2.95) | ||||||
| Race Nutrition | |||||||
| Energy expenditure [kcal] | Energy intake [kcal] | Macronutrient distribution (%) | |||||
| 160.9 km | 230 km | 160.9 km | 230 km | Carbohydrates | Fat | Protein | Alcohol |
| 11,203.78 (1793.33) | 15,977.52 (2351.22) | 5379.10 (1460.69) | 6695.85 (3748.86) | 64.6 (17.5) | 24.4 (16.4) | 8.8 (4.1) | 2.2 (2.4) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bizjak, D.A.; Schulz, S.V.W.; John, L.; Schellenberg, J.; Bizjak, R.; Witzel, J.; Valder, S.; Kostov, T.; Schalla, J.; Steinacker, J.M.; et al. Running for Your Life: Metabolic Effects of a 160.9/230 km Non-Stop Ultramarathon Race on Body Composition, Inflammation, Heart Function, and Nutritional Parameters. Metabolites 2022, 12, 1138. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12111138
Bizjak DA, Schulz SVW, John L, Schellenberg J, Bizjak R, Witzel J, Valder S, Kostov T, Schalla J, Steinacker JM, et al. Running for Your Life: Metabolic Effects of a 160.9/230 km Non-Stop Ultramarathon Race on Body Composition, Inflammation, Heart Function, and Nutritional Parameters. Metabolites. 2022; 12(11):1138. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12111138
Chicago/Turabian StyleBizjak, Daniel A., Sebastian V. W. Schulz, Lucas John, Jana Schellenberg, Roman Bizjak, Jens Witzel, Sarah Valder, Tihomir Kostov, Jan Schalla, Jürgen M. Steinacker, and et al. 2022. "Running for Your Life: Metabolic Effects of a 160.9/230 km Non-Stop Ultramarathon Race on Body Composition, Inflammation, Heart Function, and Nutritional Parameters" Metabolites 12, no. 11: 1138. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12111138
APA StyleBizjak, D. A., Schulz, S. V. W., John, L., Schellenberg, J., Bizjak, R., Witzel, J., Valder, S., Kostov, T., Schalla, J., Steinacker, J. M., Diel, P., & Grau, M. (2022). Running for Your Life: Metabolic Effects of a 160.9/230 km Non-Stop Ultramarathon Race on Body Composition, Inflammation, Heart Function, and Nutritional Parameters. Metabolites, 12(11), 1138. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12111138