Assessment of Physiological Rat Kidney Ageing—Implications for the Evaluation of Allograft Quality Prior to Renal Transplantation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Vital and Serum Parameters
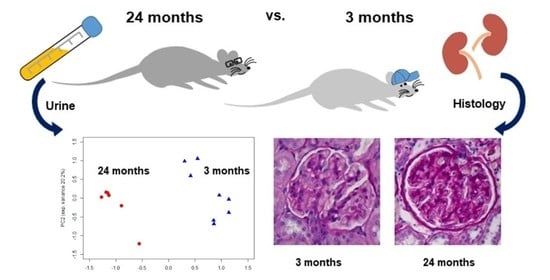
2.2. Urine Parameters
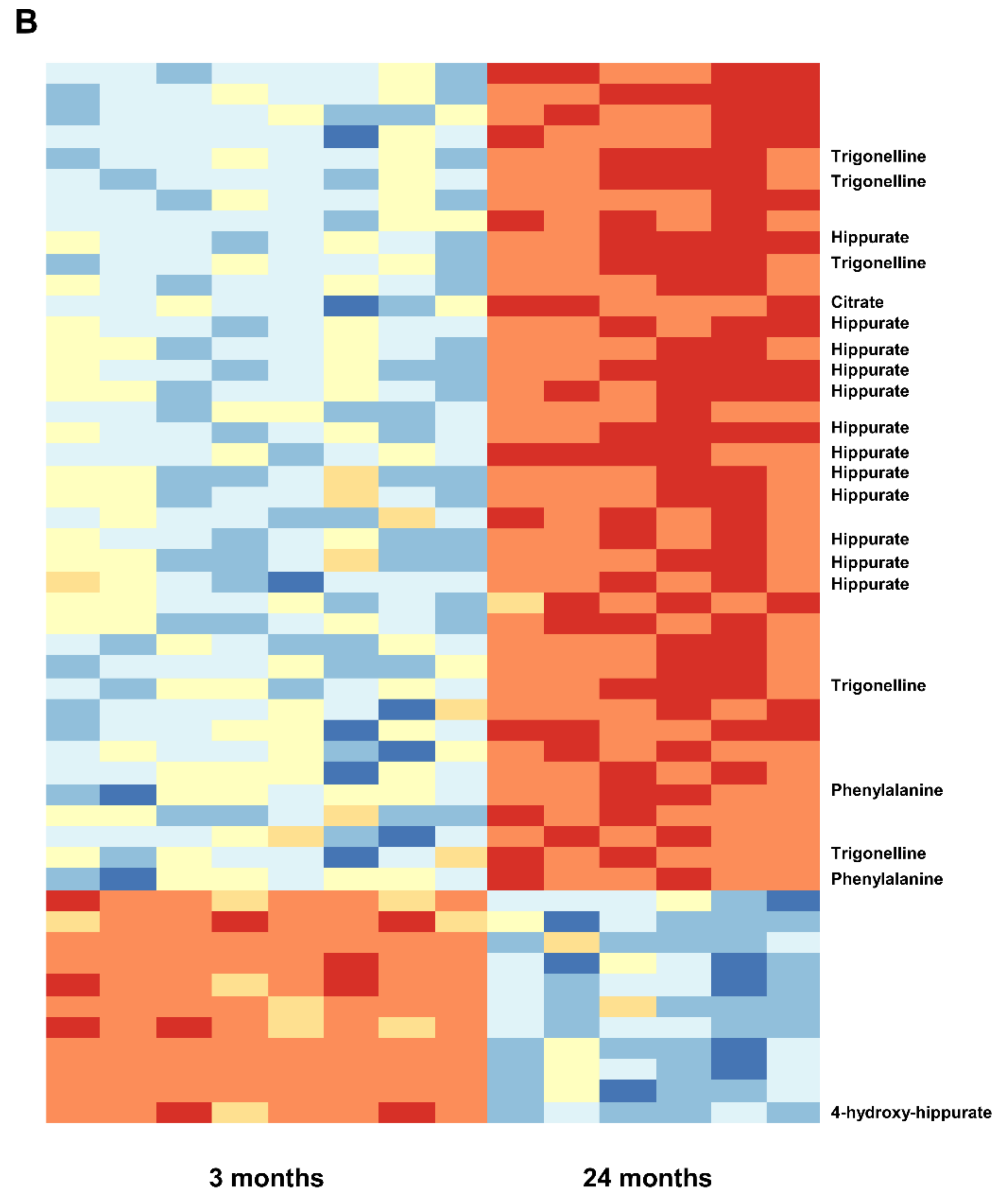
2.3. Urine Metabolomics
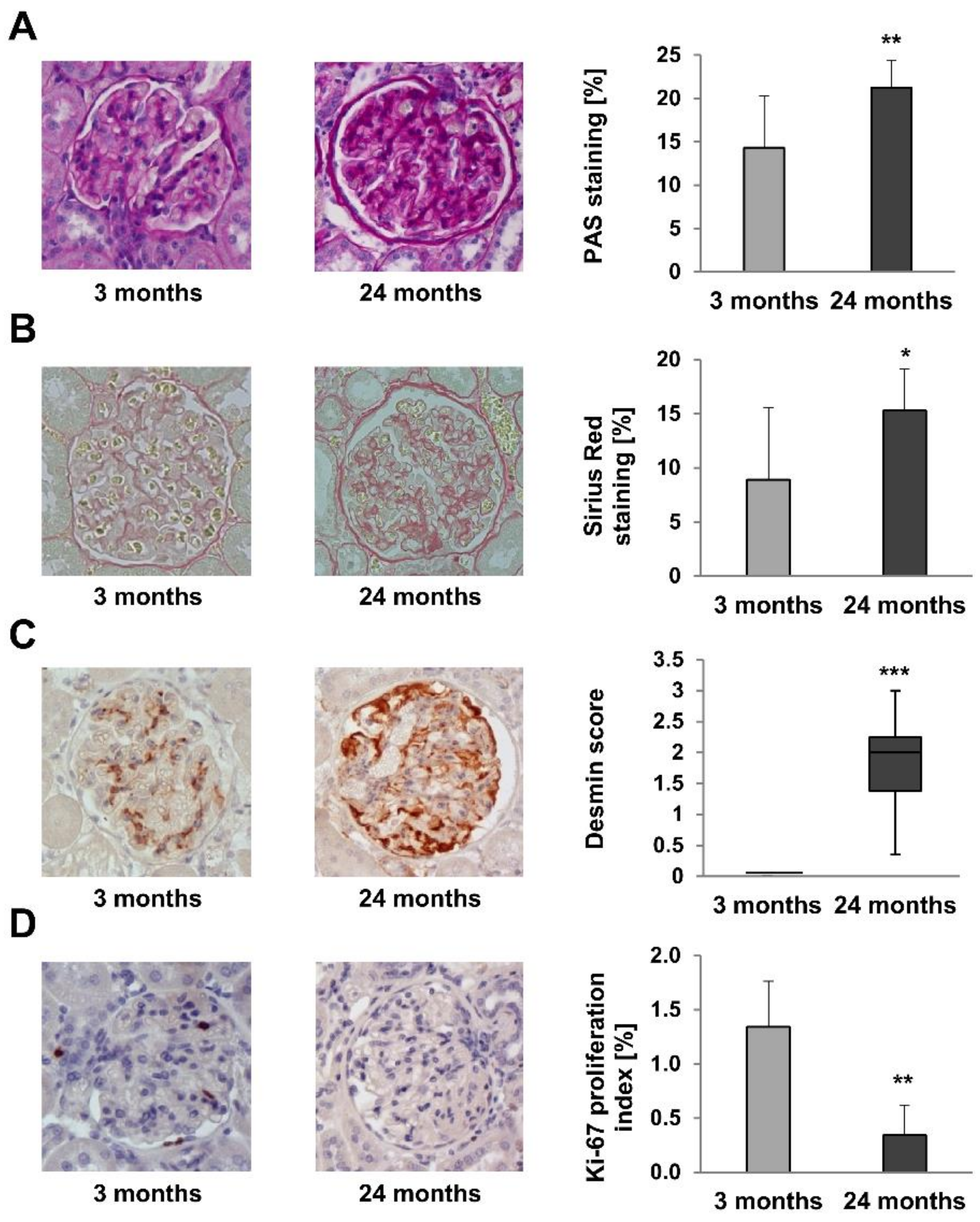
2.4. Renal Structure Alterations
2.5. Renal Fibrosis Markers
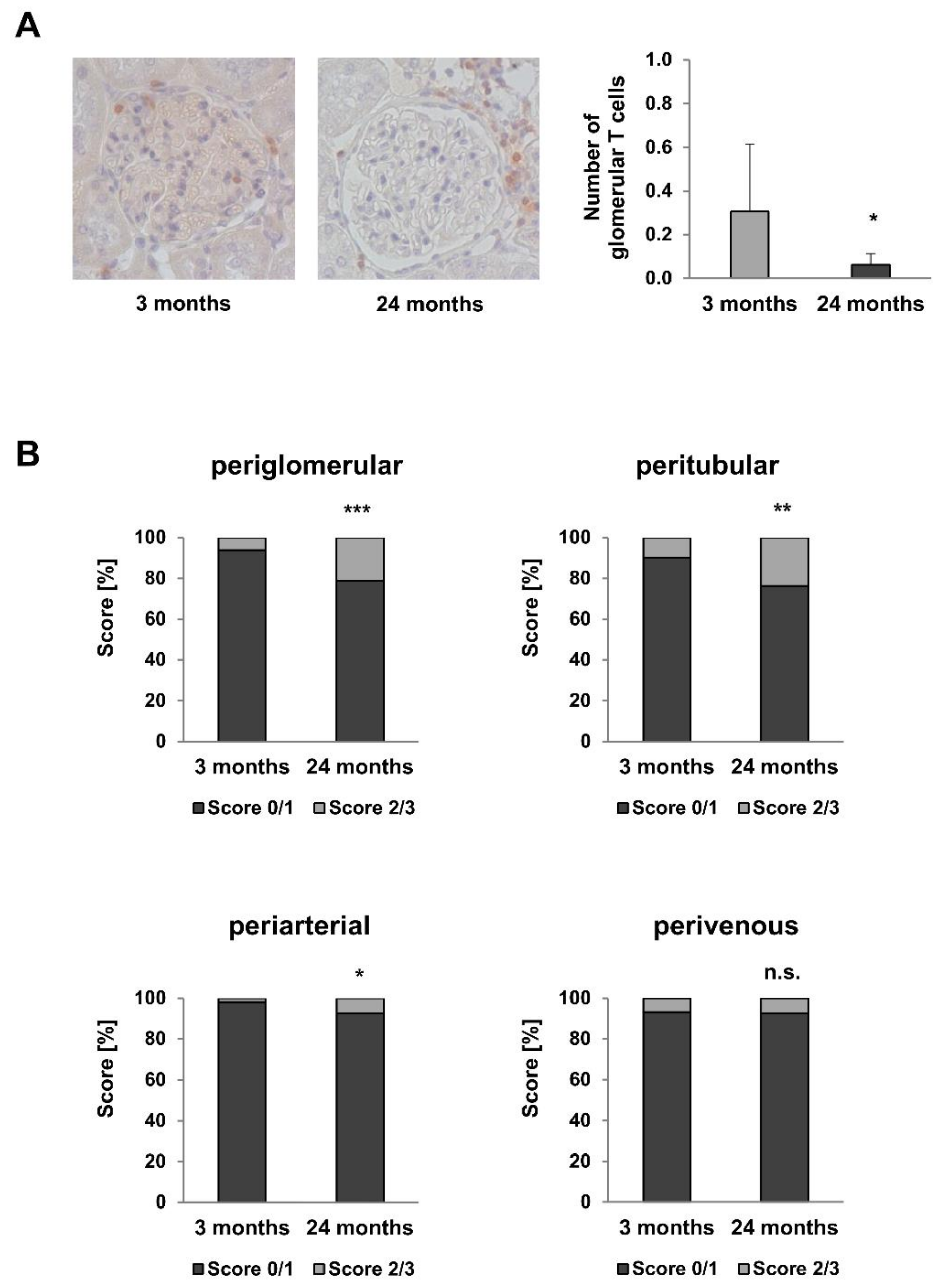
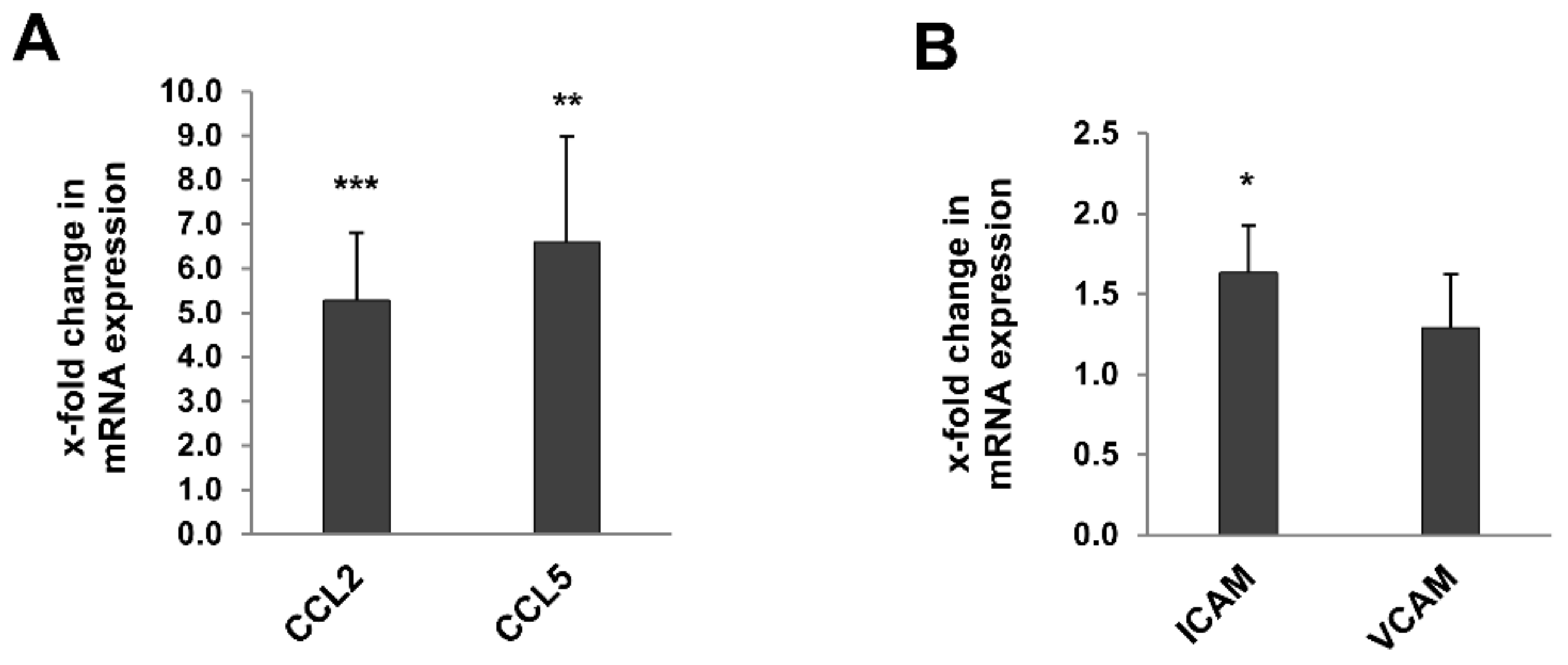
2.6. Inflammaging Markers
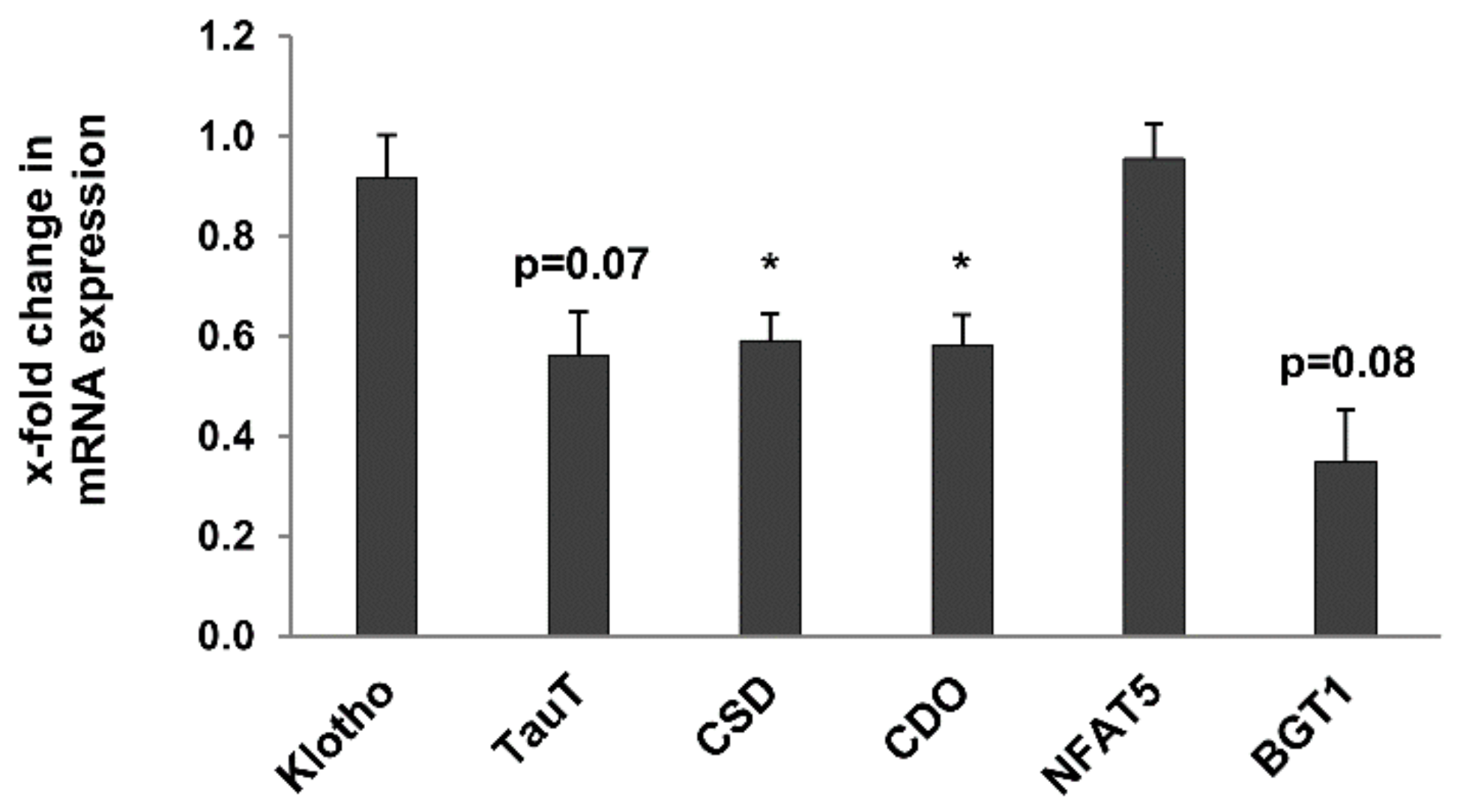
2.7. Other Age-Related Renal Metabolic Markers
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals and Tissues
4.2. Blood Pressure and Heart Rate
4.3. Serum Analyses
4.4. Analyses in Urine
4.5. NMR-Spectroscopy
4.6. Tissue Preparation and Histologic Staining
4.7. Immunohistochemistry and Morphometric Analyses
4.8. Electron Microscopy
4.9. RNA Isolation and Quantitative RT-PCR
4.10. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Available online: https://www.eurotransplant.org/organs/kidney/ (accessed on 15 October 2021).
- Ferguson, M.A.; Waikar, S.S. Established and emerging markers of kidney function. Clin. Chem. 2012, 58, 680–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Von Moos, S.; Akalin, E.; Mas, V.; Mueller, T.F. Assessment of Organ Quality in Kidney Transplantation by Molecular Analysis and Why It May Not Have Been Achieved, Yet. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dayoub, J.C.; Cortese, F.; Anžič, A.; Grum, T.; de Magalhães, J.P. The effects of donor age on organ transplants: A review and implications for aging research. Exp. Gerontol. 2018, 110, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, J.C.; Muzaale, A.D.; James, N.; Hoque, M.; Wang, J.M.G.; Montgomery, R.A.; Massie, A.B.; Hall, E.C.; Segev, D.L. Living kidney donors ages 70 and older: Recipient and donor outcomes. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 6, 2887–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keith, D.S.; Demattos, A.; Golconda, M.; Prather, J.; Norman, D. Effect of donor recipient age match on survival after first deceased donor renal transplantation. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2004, 15, 1086–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fassett, R.G.; Venuthurupalli, S.K.; Gobe, G.C.; Coombes, J.S.; Cooper, M.A.; Hoy, W.E. Biomarkers in chronic kidney disease: A review. Kidney Int. 2011, 80, 806–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Land, W.G. Ageing and immunosuppression in kidney transplantation. Exp. Clin. Transplant. 2004, 2, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dodig, S.; Čepelak, I.; Pavić, I. Hallmarks of senescence and aging. Biochem. Med. 2019, 29, 30501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, K.-H.; Cameron-Smith, D.; Wessner, B.; Franzke, B. Biomarkers of Aging: From Function to Molecular Biology. Nutrients 2016, 8, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Banas, M.C.; Banas, B.; Hudkins, K.L.; Wietecha, T.A.; Iyoda, M.; Bock, E.; Hauser, P.; Pippin, J.W.; Shankland, S.J.; Smith, K.D.; et al. TLR4 links podocytes with the innate immune system to mediate glomerular injury. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2008, 19, 704–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bergler, T.; Hoffmann, U.; Bergler, E.; Jung, B.; Banas, M.C.; Reinhold, S.W.; Krämer, B.K.; Banas, B. Toll-like receptor 4 in experimental kidney transplantation: Early mediator of endogenous danger signals. Nephron Exp. Nephrol. 2012, 121, e59–e70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, H.; Noordmans, G.A.; O’Brien, M.R.; Ma, J.; Zhao, C.Y.; Zhang, G.Y.; Kwan, T.K.T.; Alexander, S.I.; Chadban, S.J. Absence of MyD88 signaling induces donor-specific kidney allograft tolerance. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 23, 1701–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xi, Y.; Shao, F.; Bai, X.-Y.; Cai, G.; Lv, Y.; Chen, X. Changes in the Expression of the Toll-Like Receptor System in the Aging Rat Kidneys. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Franceschi, C.; Bonafè, M.; Valensin, S.; Olivieri, F.; de Luca, M.; Ottaviani, E.; de Benedictis, G. Inflamm-aging. An evolutionary perspective on immunosenescence. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 2000, 908, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, S.; Khanabdali, R.; Kalionis, B.; Wu, J.; Wan, W.; Tai, X. An Update on Inflamm-Aging: Mechanisms, Prevention, and Treatment. J. Immunol. Res. 2016, 2016, 8426874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamińska, J.; Dymicka-Piekarska, V.; Tomaszewska, J.; Matowicka-Karna, J.; Koper-Lenkiewicz, O.M. Diagnostic utility of protein to creatinine ratio (P/C ratio) in spot urine sample within routine clinical practice. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2020, 57, 345–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Baena, G.; Armstrong, S.D.; Phelan, M.M.; Hurst, J.L.; Beynon, R.J. The major urinary protein system in the rat. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2014, 42, 886–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vleming, L.J.; Baelde, J.J.; Westendorp, R.G.; Daha, M.R.; van Es, L.A.; Bruijn, J.A. The glomerular deposition of PAS positive material correlates with renal function in human kidney diseases. Clin. Nephrol. 1997, 47, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Farris, A.B.; Adams, C.D.; Brousaides, N.; Della Pelle, P.A.; Collins, A.B.; Moradi, E.; Smith, R.N.; Grimm, P.C.; Colvin, R.B. Morphometric and visual evaluation of fibrosis in renal biopsies. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 22, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Phillips, A.O.; Baboolal, K.; Riley, S.; Gröne, H.; Janssen, U.; Steadman, R.; Williams, J.; Floege, J. Association of prolonged hyperglycemia with glomerular hypertrophy and renal basement membrane thickening in the Goto Kakizaki model of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2001, 37, 400–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funk, J.; Ott, V.; Herrmann, A.; Rapp, W.; Raab, S.; Riboulet, W.; Vandjour, A.; Hainaut, E.; Benardeau, A.; Singer, T.; et al. Semiautomated quantitative image analysis of glomerular immunohistochemistry markers desmin, vimentin, podocin, synaptopodin and WT-1 in acute and chronic rat kidney disease models. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2016, 145, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, R.J.; Iida, H.; Alpers, C.E.; Majesky, M.W.; Schwartz, S.M.; Pritzi, P.; Gordon, K.; Gown, A.M. Expression of smooth muscle cell phenotype by rat mesangial cells in immune complex nephritis. Alpha-smooth muscle actin is a marker of mesangial cell proliferation. J. Clin. Investig. 1991, 87, 847–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romano, L.A.; Ferder, L.; Inserra, F.; Ercole, L.; Gomez, R.A. Intraglomerular expression of alpha-smooth muscle actin in aging mice. Hypertension 1994, 23, 889–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sureshbabu, A.; Muhsin, S.A.; Choi, M.E. TGF-β signaling in the kidney: Profibrotic and protective effects. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2016, 310, F596–F606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Manavalan, B.; Basith, S.; Choi, S. Similar Structures but Different Roles—An Updated Perspective on TLR Structures. Front. Physiol. 2011, 2, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Izquierdo, M.C.; Perez-Gomez, M.V.; Sanchez-Niño, M.D.; Sanz, A.B.; Ruiz-Andres, O.; Poveda, J.; Moreno, J.A.; Egido, J.; Ortiz, A. Klotho, phosphate and inflammation/ageing in chronic kidney disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant 2012, 27 (Suppl. 4), iv6–iv10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hao, S.; Bellner, L.; Zhao, H.; Ratliff, B.B.; Darzynkiewicz, Z.; Vio, C.P.; Ferreri, N.R. NFAT5 is protective against ischemic acute kidney injury. Hypertension 2014, 63, e46–e52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruiz-Torres, M.P.; Bosch, R.J.; O’Valle, F.; Del Moral, R.G.; Ramírez, C.; Masseroli, M.; Pérez-Caballero, C.; Iglesias, M.C.; Rodríguez-Puyol, M.; Rodríguez-Puyol, D. Age-related increase in expression of TGF-beta1 in the rat kidney: Relationship to morphologic changes. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1998, 9, 782–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feinfeld, D.A.; Keller, S.; Somer, B.; Wassertheil-Smoller, S.; Carvounis, C.P.; Aronson, M.; Nelson, M.; Frishman, W.H. Serum creatinine and blood urea nitrogen over a six-year period in the very old. Creatinine and BUN in the very old. Geriatr. Nephrol. Urol. 1998, 8, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elahi, D.; Muller, D.C. Carbohydrate metabolism in the elderly. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2000, 54 (Suppl. 3), S112–S120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Melk, A.; Schmidt, B.M.W.; Takeuchi, O.; Sawitzki, B.; Rayner, D.C.; Halloran, P.F. Expression of p16INK4a and other cell cycle regulator and senescence associated genes in aging human kidney. Kidney Int. 2004, 65, 510–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Albano, L.; Banas, B.; Klempnauer, J.L.; Glyda, M.; Viklicky, O.; Kamar, N. OSAKA Trial: A Randomized, Controlled Trial Comparing Tacrolimus QD and BD in Kidney Transplantation. Transplantation 2013, 96, 897–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincenti, F.; Charpentier, B.; Vanrenterghem, Y.; Rostaing, L.; Bresnahan, B.; Darji, P.; Massari, P.; Mondragon-Ramirez, G.A.; Agarwal, M.; Di Russo, G.; et al. A phase III study of belatacept-based immunosuppression regimens versus cyclosporine in renal transplant recipients (BENEFIT study). Am. J. Transplant 2010, 10, 535–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekberg, H.; Tedesco-Silva, H.; Demirbas, A.; Vítko, S.; Nashan, B.; Gürkan, A.; Margreiter, R.; Hugo, C.; Grinyó, J.M.; Frei, U.; et al. Reduced exposure to calcineurin inhibitors in renal transplantation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 2562–2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Albano, L.; Banas, B.; Lehner, F.; Glyda, M.; Viklicky, O.; Schleibner, S.; Brown, M.; Kamar, N. Outcomes with Tacrolimus-Based Immunosuppression After Kidney Transplantation from Standard- and Extended-Criteria Donors—A Post Hoc Analysis of the Prospective OSAKA Study. Ann. Transplant. 2020, 25, e920041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Pan, Z.; Xi, B.; Hainline, B.E.; Shanaiah, N.; Asiago, V.; Gowda, G.A.N.; Raftery, D. 1H NMR metabolomics study of age profiling in children. NMR Biomed. 2009, 22, 826–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Akira, K.; Masu, S.; Imachi, M.; Mitome, H.; Hashimoto, T. A metabonomic study of biochemical changes characteristic of genetically hypertensive rats based on (1)H NMR spectroscopic urinalysis. Hypertens. Res. 2012, 35, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Williams, R.E.; Lenz, E.M.; Lowden, J.S.; Rantalainen, M.; Wilson, I.D. The metabonomics of aging and development in the rat: An investigation into the effect of age on the profile of endogenous metabolites in the urine of male rats using 1H NMR and HPLC-TOF MS. Mol. Biosyst. 2005, 1, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, J.D.; Sadler, P.J.; Morris, V.C.; Levander, O.A. Effect of aging and diet on proton NMR spectra of rat urine. Magn. Reson. Med. 1991, 17, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaglia, J.L.; Wyckoff, J.; Abrahamson, M.J. Acute hyperglycemic crisis in the elderly. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2004, 88, 1063–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjölin, J.; Stjernström, H.; Henneberg, S.; Hambraeus, L.; Friman, G. Evaluation of urinary 3-methylhistidine excretion in infection by measurements of 1-methylhistidine and the creatinine ratios. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1989, 49, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Slupsky, C.M.; Rankin, K.N.; Wagner, J.; Fu, H.; Chang, D.; Weljie, A.M.; Saude, E.J.; Lix, B.; Adamko, D.J.; Shah, S.; et al. Investigations of the effects of gender, diurnal variation, and age in human urinary metabolomic profiles. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 6995–7004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gronwald, W.; Klein, M.S.; Kaspar, H.; Fagerer, S.R.; Nürnberger, N.; Dettmer, K.; Bertsch, T.; Oefner, P.J. Urinary metabolite quantification employing 2D NMR spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 9288–9297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gronwald, W.; Klein, M.S.; Zeltner, R.; Schulze, B.-D.; Reinhold, S.W.; Deutschmann, M.; Immervoll, A.-K.; Böger, C.A.; Banas, B.; Eckardt, K.-U.; et al. Detection of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease by NMR spectroscopic fingerprinting of urine. Kidney Int. 2011, 79, 1244–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Society. Ser. B (Methodol.) 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Parameters | 3 Months | 24 Months | p-Value (MWU) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vital parameters | |||
| Systolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 159 (±14) | 154 (±24) | 0.721 |
| Diastolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 111 (±15) | 105 (±19) | 0.674 |
| Heart rate (beats/min) | 490 (±38) | 499 (±47) | 0.721 |
| Serum parameters | |||
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.32 (±0.03) | 0.28 (±0.03) | 0.051 |
| Albumin (g/L) | 12.5± (1.4) | 11.9 (±1.3) | 0.598 |
| Total protein (g/L) | 58.6 (±4.3) | 68.3 (±1.8) | 0.793 |
| Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) (mg/dL) | 50 (±5.8) | 21 (±4.4) | 0.001 |
| Uric acid (mg/dL) | 3.4 (±0.5) | 0.4 (±0.1) | 0.002 |
| C-reactive protein (CRP) (mg/dL) | <2.9 | <2.9 | - |
| ASAT (mg/dL) | 143 (±44.5) | 103 (±20.3) | 0.065 |
| ALAT (mg/dL) | 62.5 (±7.6) | 43.3 (±22.8) | 0.052 |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 151 (±37.4) | 80 (±20.6) | 0.001 |
| Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 92 (±12.7) | 105 (±38.1) | 0.753 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 139 (±52.9) | 156 (±92.1) | 0.958 |
| TLR | Kidney | Liver | Spleen | Lung |
| FC at 24 Months Relative to 3 Months | FC at 24 Months Relative to 3 Months | FC at 24 Months Relative to 3 Months | FC at 24 Months Relative to 3 Months | |
| TLR1 | 2.02 (±1.07) p = 0.0023 ** | 0.85 (±0.64) p = 0.8785 | 0.78 (±0.58) p = 0.3357 | 0.78 (±0.51) p = 0.4634 |
| TLR2 | 1.74 (±1.17) p = 0.0728 | 1.93 (±0.80) p = 0.0019 ** | 1.01 (±0.57) p = 0.2319 | 1.15 (±0.41) p = 0.3969 |
| TLR3 | 0.96 (±0.36) p = 0.9015 | 2.64 (±0.96) p = 0.0002 *** | 1.10 (±0.69) p = 0.6126 | 1.07 (±0.48) p = 0.6943 |
| TLR4 | 1.72 (±0.73) p = 0.0041 ** | 1.64 (±0.63) p = 0.0047 ** | 1.10 (±0.73) p = 0.0541 | 0.99 (±0.28) p = 0.6943 |
| TLR5 | 3.78 (±6.05) p = 0.0379 * | 2.19 (±3.46) p = 0.4005 | 1.23 (±1.56) p = 0.6126 | 1.14 (±1.31) p = 0.7789 |
| TLR6 | 1.45 (±0.42) p = 0.0023 ** | 1.86 (±0.69) p = 0.0019 ** | 0.80 (±0.51) p = 0.8665 | 1.10 (±0.35) p = 0.6943 |
| TLR7 | 1.95 (±1.23) p = 0.0379 * | 2.40 (±1.02) p = 0.0002 *** | 1.43 (±0.55) p = 0.0939 | 1.01 (±0.34) p = 0.8665 |
| TLR8 | 2.72 (±2.14) p = 0.0041 ** | 1.34 (±0.56) p = 0.0830 | 1.48 (±0.49) p = 0.0140 * | 1.07 (±0.44) p = 0.6126 |
| TLR9 | 2.01 (±3.69) p = 0.1282 | 2.80 (±7.56) p = 0.1949 | 1.05 (±2.39) p = 0.8665 | 1.01 (±2.38) p = 0.8665 |
| TLR10 | 3.89 (±3.40) p = 0.0006 *** | 1.04 (±0.55) p = 0.8785 | 0.89 (±0.78) p = 0.3357 | 0.75 (±0.70) p = 0.5358 |
| TLR11 | 2.73 (±1.80) p = 0.0012 ** | 1.00 (±0.58) p = 0.9591 | 0.77 (±0.56) p = 0.3969 | 0.57 (±0.50) p = 0.1520 |
| TLR12 | 5.09 (±4.66) p = 0.0070 ** | 1.07 (±0.67) p = 0.8785 | 0.73 (±0.58) p = 0.4634 | 0.74 (±0.55) p = 0.3969 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baumgartner, A.; Reichelt-Wurm, S.; Gronwald, W.; Samol, C.; Schröder, J.A.; Fellner, C.; Holler, K.; Steege, A.; Putz, F.J.; Oefner, P.J.; et al. Assessment of Physiological Rat Kidney Ageing—Implications for the Evaluation of Allograft Quality Prior to Renal Transplantation. Metabolites 2022, 12, 162. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12020162
Baumgartner A, Reichelt-Wurm S, Gronwald W, Samol C, Schröder JA, Fellner C, Holler K, Steege A, Putz FJ, Oefner PJ, et al. Assessment of Physiological Rat Kidney Ageing—Implications for the Evaluation of Allograft Quality Prior to Renal Transplantation. Metabolites. 2022; 12(2):162. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12020162
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaumgartner, Andreas, Simone Reichelt-Wurm, Wolfram Gronwald, Claudia Samol, Josef A. Schröder, Claudia Fellner, Kathrin Holler, Andreas Steege, Franz Josef Putz, Peter J. Oefner, and et al. 2022. "Assessment of Physiological Rat Kidney Ageing—Implications for the Evaluation of Allograft Quality Prior to Renal Transplantation" Metabolites 12, no. 2: 162. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12020162
APA StyleBaumgartner, A., Reichelt-Wurm, S., Gronwald, W., Samol, C., Schröder, J. A., Fellner, C., Holler, K., Steege, A., Putz, F. J., Oefner, P. J., Banas, B., & Banas, M. C. (2022). Assessment of Physiological Rat Kidney Ageing—Implications for the Evaluation of Allograft Quality Prior to Renal Transplantation. Metabolites, 12(2), 162. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12020162