Novel Plasma Metabolomic Markers Associated with Diabetes Progression in Older Puerto Ricans
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
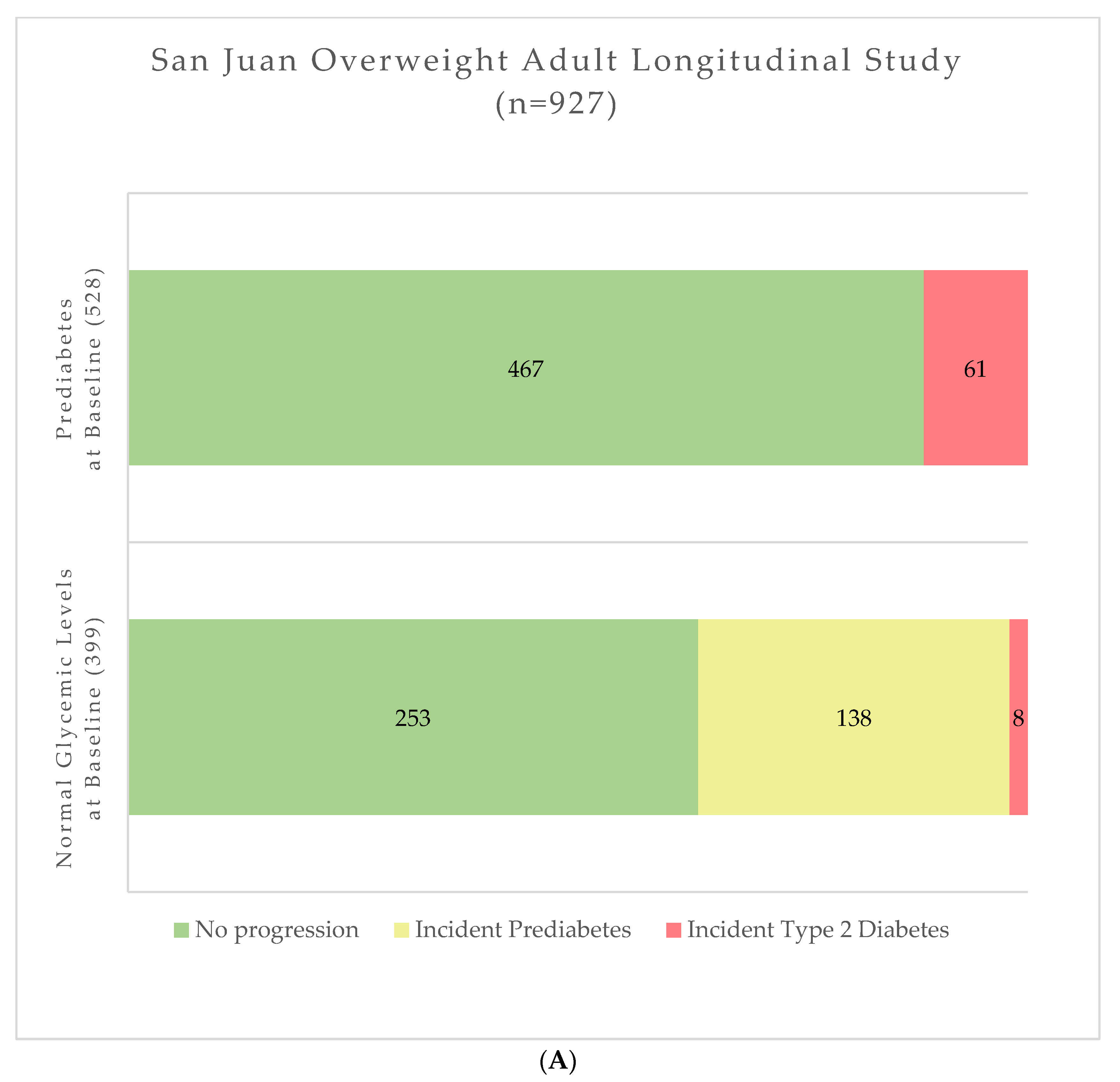
2.1. Progression to Type 2 Diabetes
2.2. Progression from Prediabetes to Type 2 Diabetes
2.3. Progression of Normoglycemic Participants to Prediabetes
2.4. Progression to Prediabetes or Type 2 Diabetes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Cohorts
4.2. Assessment of Plasma Metabolite Levels
4.3. Assessment of Study Outcomes
4.4. Assessment of Potential Confounders
4.5. Data Analysis Methods
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Global Health Estimates 2020: Deaths by Cause, Age, Sex, by Country and by Region, 2000–2019; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National Diabetes Statistics Report Website. Available online: Https://Www.Cdc.Gov/Diabetes/Data/Statistics-Report/Index.Html (accessed on 8 April 2022).
- Global Diabetes Compact. Available online: Https://Www.Who.Int/Initiatives/the-Who-Global-Diabetes-Compact (accessed on 5 May 2022).
- Wang, D.D.; Hu, F.B. Precision Nutrition for Prevention and Management of Type 2 Diabetes. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018, 6, 416–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morze, J.; Wittenbecher, C.; Schwingshackl, L.; Danielewicz, A.; Rynkiewicz, A.; Hu, F.B.; Guasch-Ferré, M. Metabolomics and Type 2 Diabetes Risk: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies. Diabetes Care 2022, 45, 1013–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guasch-Ferré, M.; Hruby, A.; Toledo, E.; Clish, C.B.; Martínez-González, M.A.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Hu, F.B. Metabolomics in Prediabetes and Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 833–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haslam, D.E.; Liang, L.; Wang, D.D.; Kelly, R.S.; Wittenbecher, C.; Pérez, C.M.; Martínez, M.; Lee, C.-H.; Clish, C.B.; Wong, D.T.W.; et al. Associations of Network-Derived Metabolite Clusters with Prevalent Type 2 Diabetes among Adults of Puerto Rican Descent. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2021, 9, e002298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Q.; Ma, R.C.W. Metabolomics in Diabetes and Diabetic Complications: Insights from Epidemiological Studies. Cells 2021, 10, 2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Brunius, C.; Lehtonen, M.; Auriola, S.; Bergdahl, I.A.; Rolandsson, O.; Hanhineva, K.; Landberg, R. Plasma Metabolites Associated with Type 2 Diabetes in a Swedish Population: A Case–Control Study Nested in a Prospective Cohort. Diabetologia 2018, 61, 849–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Menni, C.; Fauman, E.; Erte, I.; Perry, J.R.B.; Kastenmüller, G.; Shin, S.-Y.; Petersen, A.-K.; Hyde, C.; Psatha, M.; Ward, K.J.; et al. Biomarkers for Type 2 Diabetes and Impaired Fasting Glucose Using a Nontargeted Metabolomics Approach. Diabetes 2013, 62, 4270–4276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gall, W.E.; Beebe, K.; Lawton, K.A.; Adam, K.-P.; Mitchell, M.W.; Nakhle, P.J.; Ryals, J.A.; Milburn, M.v.; Nannipieri, M.; Camastra, S.; et al. α-Hydroxybutyrate Is an Early Biomarker of Insulin Resistance and Glucose Intolerance in a Nondiabetic Population. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fiehn, O.; Garvey, W.T.; Newman, J.W.; Lok, K.H.; Hoppel, C.L.; Adams, S.H. Plasma Metabolomic Profiles Reflective of Glucose Homeostasis in Non-Diabetic and Type 2 Diabetic Obese African-American Women. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e15234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lynch, C.J.; Adams, S.H. Branched-Chain Amino Acids in Metabolic Signalling and Insulin Resistance. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2014, 10, 723–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagao, K.; Yamakado, M. The Role of Amino Acid Profiles in Diabetes Risk Assessment. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2016, 19, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Zong, G.; Wu, Q.; Yun, H.; Niu, Z.; Zheng, H.; Zeng, R.; Sun, L.; Lin, X. Associations of Plasma Glycerophospholipid Profile with Modifiable Lifestyles and Incident Diabetes in Middle-Aged and Older Chinese. Diabetologia 2022, 65, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chew, W.S.; Torta, F.; Ji, S.; Choi, H.; Begum, H.; Sim, X.; Khoo, C.M.; Khoo, E.Y.H.; Ong, W.-Y.; van Dam, R.M.; et al. Large-Scale Lipidomics Identifies Associations between Plasma Sphingolipids and T2DM Incidence. JCI Insight 2019, 4, 126925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Floegel, A.; Stefan, N.; Yu, Z.; Mühlenbruch, K.; Drogan, D.; Joost, H.-G.; Fritsche, A.; Häring, H.-U.; Hrabě de Angelis, M.; Peters, A.; et al. Identification of Serum Metabolites Associated With Risk of Type 2 Diabetes Using a Targeted Metabolomic Approach. Diabetes 2013, 62, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hilvo, M.; Salonurmi, T.; Havulinna, A.S.; Kauhanen, D.; Pedersen, E.R.; Tell, G.S.; Meyer, K.; Teeriniemi, A.-M.; Laatikainen, T.; Jousilahti, P.; et al. Ceramide Stearic to Palmitic Acid Ratio Predicts Incident Diabetes. Diabetologia 2018, 61, 1424–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neeland, I.J.; Singh, S.; McGuire, D.K.; Vega, G.L.; Roddy, T.; Reilly, D.F.; Castro-Perez, J.; Kozlitina, J.; Scherer, P.E. Relation of Plasma Ceramides to Visceral Adiposity, Insulin Resistance and the Development of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: The Dallas Heart Study. Diabetologia 2018, 61, 2570–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Razquin, C.; Toledo, E.; Clish, C.B.; Ruiz-Canela, M.; Dennis, C.; Corella, D.; Papandreou, C.; Ros, E.; Estruch, R.; Guasch-Ferré, M.; et al. Plasma Lipidomic Profiling and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes in the PREDIMED Trial. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 2617–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rhee, E.P.; Cheng, S.; Larson, M.G.; Walford, G.A.; Lewis, G.D.; McCabe, E.; Yang, E.; Farrell, L.; Fox, C.S.; O’Donnell, C.J.; et al. Lipid Profiling Identifies a Triacylglycerol Signature of Insulin Resistance and Improves Diabetes Prediction in Humans. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 1402–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, G.-C.; Chai, J.C.; Yu, B.; Michelotti, G.A.; Grove, M.L.; Fretts, A.M.; Daviglus, M.L.; Garcia-Bedoya, O.L.; Thyagarajan, B.; Schneiderman, N.; et al. Serum Sphingolipids and Incident Diabetes in a US Population with High Diabetes Burden: The Hispanic Community Health Study/Study of Latinos (HCHS/SOL). Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 112, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousri, N.A.; Suhre, K.; Yassin, E.; Al-Shakaki, A.; Robay, A.; Elshafei, M.; Chidiac, O.; Hunt, S.C.; Crystal, R.G.; Fakhro, K.A. Metabolic and Metabo-Clinical Signatures of Type 2 Diabetes, Obesity, Retinopathy, and Dyslipidemia. Diabetes 2022, 71, 184–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Crécy-Lagard, V.; Haas, D.; Hanson, A.D. Newly-Discovered Enzymes That Function in Metabolite Damage-Control. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2018, 47, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunther, S.H.; Khoo, C.M.; Tai, E.-S.; Sim, X.; Kovalik, J.-P.; Ching, J.; Lee, J.J.; van Dam, R.M. Serum Acylcarnitines and Amino Acids and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes in a Multiethnic Asian Population. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2020, 8, e001315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, J.; Kim, O.; Jo, G.; Shin, M.-J. Alterations in Circulating Amino Acid Metabolite Ratio Associated with Arginase Activity Are Potential Indicators of Metabolic Syndrome: The Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study. Nutrients 2017, 9, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, Y.-F.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, J.; Sun, X.-Y.; Feng, X.-F.; Luo, H.-H.; Yang, W.; Li, S.-N.; Yang, X.; et al. Plasma Levels of Amino Acids Related to Urea Cycle and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Chinese Adults. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Joshipura, K.J.; Muñoz-Torres, F.J.; Dye, B.A.; Leroux, B.G.; Ramírez-Vick, M.; Pérez, C.M. Longitudinal Association between Periodontitis and Development of Diabetes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2018, 141, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, K.L.; Mattei, J.; Noel, S.E.; Collado, B.M.; Mendez, J.; Nelson, J.; Griffith, J.; Ordovas, J.M.; Falcon, L.M. The Boston Puerto Rican Health Study, a Longitudinal Cohort Study on Health Disparities in Puerto Rican Adults: Challenges and Opportunities. BMC Public Health 2010, 10, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Evans, A.M.; DeHaven, C.D.; Barrett, T.; Mitchell, M.; Milgram, E. Integrated, Nontargeted Ultrahigh Performance Liquid Chromatography/Electrospray Ionization Tandem Mass Spectrometry Platform for the Identification and Relative Quantification of the Small-Molecule Complement of Biological Systems. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 6656–6667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clauset, A.; Newman, M.E.J.; Moore, C. Finding Community Structure in Very Large Networks. Phys. Rev. E 2004, 70, 066111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, Y.; Gao, H.-Y.; Fan, Z.-Y.; He, Y.; Yan, Y.-X. Metabolomics Signatures in Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Integrative Analysis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 105, 1000–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Han, Q.; Liu, Y.; Sun, C.; Gang, X.; Wang, G. The Relationship between Branched-Chain Amino Acid Related Metabolomic Signature and Insulin Resistance: A Systematic Review. J. Diabetes Res. 2016, 2016, 2794591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Yang, Z.; Wang, L.; Han, Y.; Peng, C.; Yan, C.; Yan, D. Metabolite Biomarkers of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Pre-Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2020, 20, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, L.; Li, Q.; Yi, H.; Kuang, T.; Tang, Y.; Fan, G. Gut Microbiota-Derived Metabolites as Key Actors in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 149, 112839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remchak, M.-M.E.; Heiston, E.M.; Ballantyne, A.; Dotson, B.L.; Stewart, N.R.; Spaeth, A.M.; Malin, S.K. Insulin Sensitivity and Metabolic Flexibility Parallel Plasma TCA Levels in Early Chronotype with Metabolic Syndrome. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, dgac233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, N.; Dong, X.; Zhu, J.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Fu, C. Associations between Serum Amino Acids and Incident Type 2 Diabetes in Chinese Rural Adults. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2021, 31, 2416–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palau-Rodriguez, M.; Tulipani, S.; Isabel Queipo-Ortuño, M.; Urpi-Sarda, M.; Tinahones, F.J.; Andres-Lacueva, C. Metabolomic Insights into the Intricate Gut Microbial–Host Interaction in the Development of Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roberts, L.D.; Boström, P.; O’Sullivan, J.F.; Schinzel, R.T.; Lewis, G.D.; Dejam, A.; Lee, Y.-K.; Palma, M.J.; Calhoun, S.; Georgiadi, A.; et al. β-Aminoisobutyric Acid Induces Browning of White Fat and Hepatic β-Oxidation and Is Inversely Correlated with Cardiometabolic Risk Factors. Cell Metab. 2014, 19, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paffenbarger, R.S.; Wing, A.L.; Hyde, R.T. Physical activity as an index of heart attack risk in college alumni. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1995, 142, 889–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paffenbarger, R.S.; Hyde, R.T.; Wing, A.L.; Lee, I.-M.; Jung, D.L.; Kampert, J.B. The Association of Changes in Physical-Activity Level and Other Lifestyle Characteristics with Mortality among Men. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 328, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzer, G. Meta: An R Package for Meta-Analysis. R News 2007, 7, 40–45. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/doc/Rnews/Rnews_2007-3.pdf (accessed on 5 May 2022).
- Balduzzi, S.; Rücker, G.; Schwarzer, G. How to perform a meta-analysis with R: A practical tutorial. Evid.-Based Ment. Health 2019, 22, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2008; Available online: https://www.R-Project.Org/ (accessed on 5 May 2022).
- Benjamini, Y.; Yekutieli, D. The Control of the False Discovery Rate in Multiple Testing under Dependency. Ann. Stat. 2001, 29, 1165–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Characteristic | SOALS | BPRHS | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All (n = 927) | Participants Who Progressed to Type 2 Diabetes (n = 69) | Participants Who Did Not Progress to Type 2 Diabetes (n = 858) | All (n = 294) | Participants Who Progressed to Type 2 Diabetes (n = 48) | Participants Who Did Not Progress to Type 2 Diabetes (n = 246) | |
| Age, years | ||||||
| Mean ± SD | 50.6 ± 6.8 | 50.5 ± 6.6 | 50.6 ± 6.8 | 55.4 ± 7.1 | 56.1 ± 7.1 | 55.3 ± 7.2 |
| Median (IQR) | 50.0 (45.0–56.0) | 50.0 (46.0–55.0) | 50.0 (45.0–56.0) | 54.0 (50.0–61.0) | 54.5 (50.5–61.0) | 54.0 (50.0–60.0) |
| Biological sex, male, n (%) | 239 (25.8) | 25 (36.2) | 214 (24.9) | 73 (24.8) | 13 (27.1) | 60 (24.4) |
| Smoking history | ||||||
| Current | 168 (18.1) | 17 (24.6) | 151 (17.6) | 77 (26.2) | 10 (20.8) | 67 (27.2) |
| Former | 165 (17.8) | 14 (20.3) | 151 (17.6) | 82 (27.9) | 19 (39.6) | 63 (25.6) |
| Never | 594 (64.1) | 38 (55.1) | 556 (64.8) | 135 (45.9) | 19 (39.6) | 116 (47.2) |
| Family history of diabetes, yes, n (%) | 572 (61.7) | 43 (62.3) | 529 (61.7) | - | - | - |
| Educational level a, n (%) | ||||||
| Less than high school | 101 (10.9) | 6 (8.7) | 95 (11.1) | 139 (47.3) | 27 (56.3) | 112 (45.5) |
| High school | 399 (43.0) | 29 (42.0) | 370 (43.1) | 112 (38.1) | 14 (29.2) | 98 (39.8) |
| Some college | 130 (14.0) | 15 (21.7) | 115 (13.4) | 43 (14.6) | 7 (14.6) | 36 (14.6) |
| College degree | 297 (32.0) | 19 (27.5) | 370 (43.1) | |||
| Physical activity b, METs | ||||||
| Mean ± SD | 22.1 ± 40.3 | 14.1 ± 23.4 | 22.7 ± 41.3 | 32.1 ± 4.9 | 31.5 ± 5.1 | 32.2 ± 4.8 |
| Median (IQR) | 7.9 (0–26.9) | 7.9 (0–16.8) | 7.9 (0–26.9) | 31 (28.9–34.2) | 30.8 (28.1–33.2) | 31.0 (29.0–34.5) |
| Waist circumference, cm | ||||||
| Mean ± SD | 106 ± 14.2 | 108 ± 13.3 | 103 ± 14.3 | 98.0 ± 14.1 | 105 ± 16.1 | 96.6 ± 13.2 |
| Median (IQR) | 104 (96.2–113) | 107 (98.3–114) | 104 (96.1–113) | 97.0 (89.5–106) | 103 (93.3–113) | 96.5 (89.0–105) |
| Alcohol intake, g | ||||||
| Mean ± SD | 2.2 ± 5.7 | 3.5 ± 9.6 | 2.2 ± 5.3 | 6.3 ± 21.5 | 1.1 ± 3.6 | 7.3 ± 23.3 |
| Median (IQR) | 0 (0.0–1.0) | 0 (0.0–1.0) | 0 (0.0–0.7) | 0.1 (0.0–2.9) | 0 (0.0–0.4) | 0.2 (0.01–4.0) |
| BMI, kg/m2 | ||||||
| Mean ± SD | 33.3 ± 6.2 | 33.9 ± 5.9 | 33.2 ± 6.3 | 30.9 ± 6.4 | 33.8 ± 7.7 | 30.3 ± 6.0 |
| Median (IQR) | 31.7 (28.8–36.3) | 32.9 (29.3–37.2) | 31.5 (28.8–36.3) | 30.0 (26.7–33.9) | 33.0 (28.3–36.8) | 29.8 (26.4–33.6) |
| Use of antihypertensive medications, yes, n (%) | 268 (28.9) | 25 (36.2) | 243 (28.3) | 119 (40.5) | 27 (56.3) | 92 (37.4) |
| Use of statins or other lipid-lowering medications, yes, n (%) | 82 (8.9) | 7 (10.1) | 75 (8.7) | 75 (25.5) | 18 (37.5) | 57 (23.2) |
| Cluster Name | Number of Included Metabolites | Among All Participants (n = 1221) | Among Participants with Prediabetes at Baseline (n = 751) | Among Participants with Normal Blood Glucose Concentration at Baseline (n = 459) | Among All Participants (n = 1221) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Progression to Type 2 Diabetes | Progression to Diabetes | Progression to Prediabetes | Progression to Prediabetes or Type 2 Diabetes | ||||||
| Multivariable-Adjusted IRR (95% CI) | p-Value | Multivariable-Adjusted IRR (95% CI) | p-Value | Multivariable-Adjusted IRR (95% CI) | p-Value | Multivariable-Adjusted IRR (95% CI) | p-Value | ||
| Sphingolipids 1 | 18 | 0.94 (0.67; 1.31) | 0.72 | 0.86 (0.60; 1.23) | 0.41 | 0.82 (0.63; 1.08) | 0.16 | 0.85 (0.69; 1.04) | 0.12 |
| BCAA metabolism 2 | 15 | 1.39 (0.92; 2.09) | 0.11 | 1.19 (0.76; 1.86) | 0.44 | 1.22 (0.88; 1.70) | 0.23 | 1.15 (0.89; 1.48) | 0.28 |
| BCAA and aromatic amino acid metabolism 3 | 13 | 1.87 (1.28; 2.73) | 0.001 | 1.62 (1.09; 2.41) | 0.02 | 1.13 (0.84; 1.54) | 0.42 | 1.20 (0.95; 1.51) | 0.13 |
| Acyl cholines 4 | 9 | 0.77 (0.55; 1.07) | 0.12 | 0.79 (0.55; 1.13) | 0.19 | 0.81 (0.62; 1.07) | 0.14 | 0.88 (0.71; 1.08) | 0.23 |
| Aromatic amino acid metabolism 5 | 11 | 0.96 (0.68; 1.33) | 0.79 | 0.88 (0.62; 1.26) | 0.50 | 1.01 (0.77; 1.34) | 0.92 | 0.99 (0.81; 1.23) | 0.96 |
| Cell membrane components 6 | 8 | 1.54 (1.04; 2.27) | 0.03 | 1.31 (0.87; 1.98) | 0.20 | 1.09 (0.78; 1.52) | 0.62 | 1.24 (0.97; 1.58) | 0.08 |
| Glucose transport 7 | 6 | 1.27 (0.88; 1.83) | 0.20 | 1.13 (0.77; 1.66) | 0.53 | 0.79 (0.57; 1.07) | 0.13 | 0.96 (0.76; 1.21) | 0.72 |
| Fatty acid biosynthesis 8 | 6 | 1.16 (0.91; 1.48) | 0.22 | 1.11 (0.86; 1.44) | 0.43 | 1.06 (0.87; 1.29) | 0.54 | 1.02 (0.88; 1.19) | 0.77 |
| Sugar metabolism 9 | 5 | 1.32 (0.90; 1.94) | 0.15 | 1.19 (0.80; 1.77) | 0.38 | 0.93 (0.66; 1.30) | 0.67 | 1.01 (0.79; 1.29) | 0.91 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rivas-Tumanyan, S.; Pacheco, L.S.; Haslam, D.E.; Liang, L.; Tucker, K.L.; Joshipura, K.J.; Bhupathiraju, S.N. Novel Plasma Metabolomic Markers Associated with Diabetes Progression in Older Puerto Ricans. Metabolites 2022, 12, 513. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12060513
Rivas-Tumanyan S, Pacheco LS, Haslam DE, Liang L, Tucker KL, Joshipura KJ, Bhupathiraju SN. Novel Plasma Metabolomic Markers Associated with Diabetes Progression in Older Puerto Ricans. Metabolites. 2022; 12(6):513. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12060513
Chicago/Turabian StyleRivas-Tumanyan, Sona, Lorena S. Pacheco, Danielle E. Haslam, Liming Liang, Katherine L. Tucker, Kaumudi J. Joshipura, and Shilpa N. Bhupathiraju. 2022. "Novel Plasma Metabolomic Markers Associated with Diabetes Progression in Older Puerto Ricans" Metabolites 12, no. 6: 513. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12060513
APA StyleRivas-Tumanyan, S., Pacheco, L. S., Haslam, D. E., Liang, L., Tucker, K. L., Joshipura, K. J., & Bhupathiraju, S. N. (2022). Novel Plasma Metabolomic Markers Associated with Diabetes Progression in Older Puerto Ricans. Metabolites, 12(6), 513. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12060513






