Sulfation and Its Effect on the Bioactivity of Magnolol, the Main Active Ingredient of Magnolia Officinalis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Animals
2.3. Cell Culture
2.4. Magnolol Metabolism by the Liver S9 Fractions of Different Species and Seven Recombinant Human SULTs
2.5. Identification and Quantification of Magnolol and Its Sulfated Metabolite
2.6. Enzyme Kinetic Studies
2.7. Assessment of the Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Magnolol and Its Sulfated Metabolite
2.8. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Identification of Magnolol Sulfated Metabolite by UPLC-Q-TOF-MS and 1H-NMR
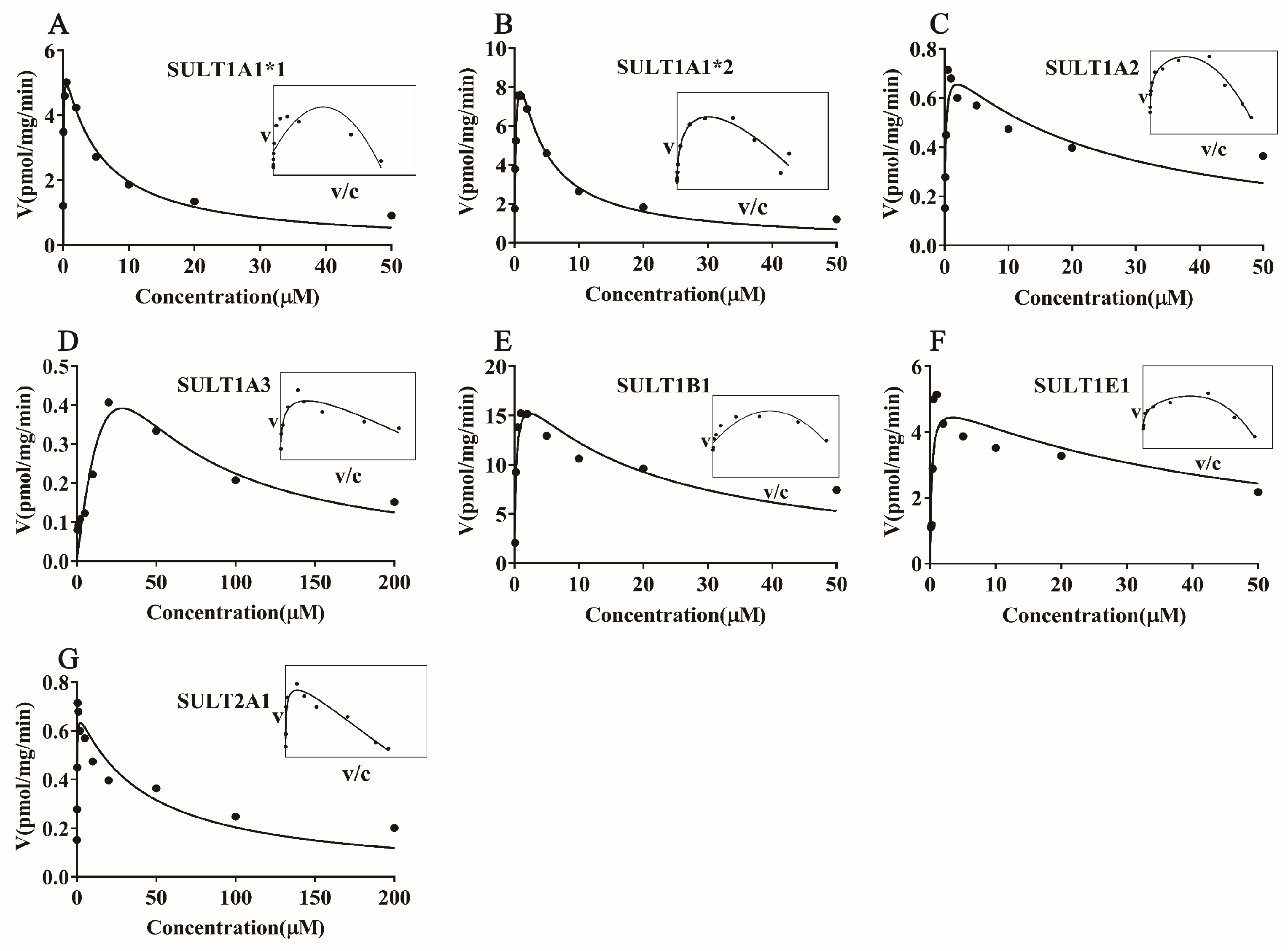
3.2. Kinetic Analysis of Magnolol Sulfation in Liver S9 Fractions from Different Species
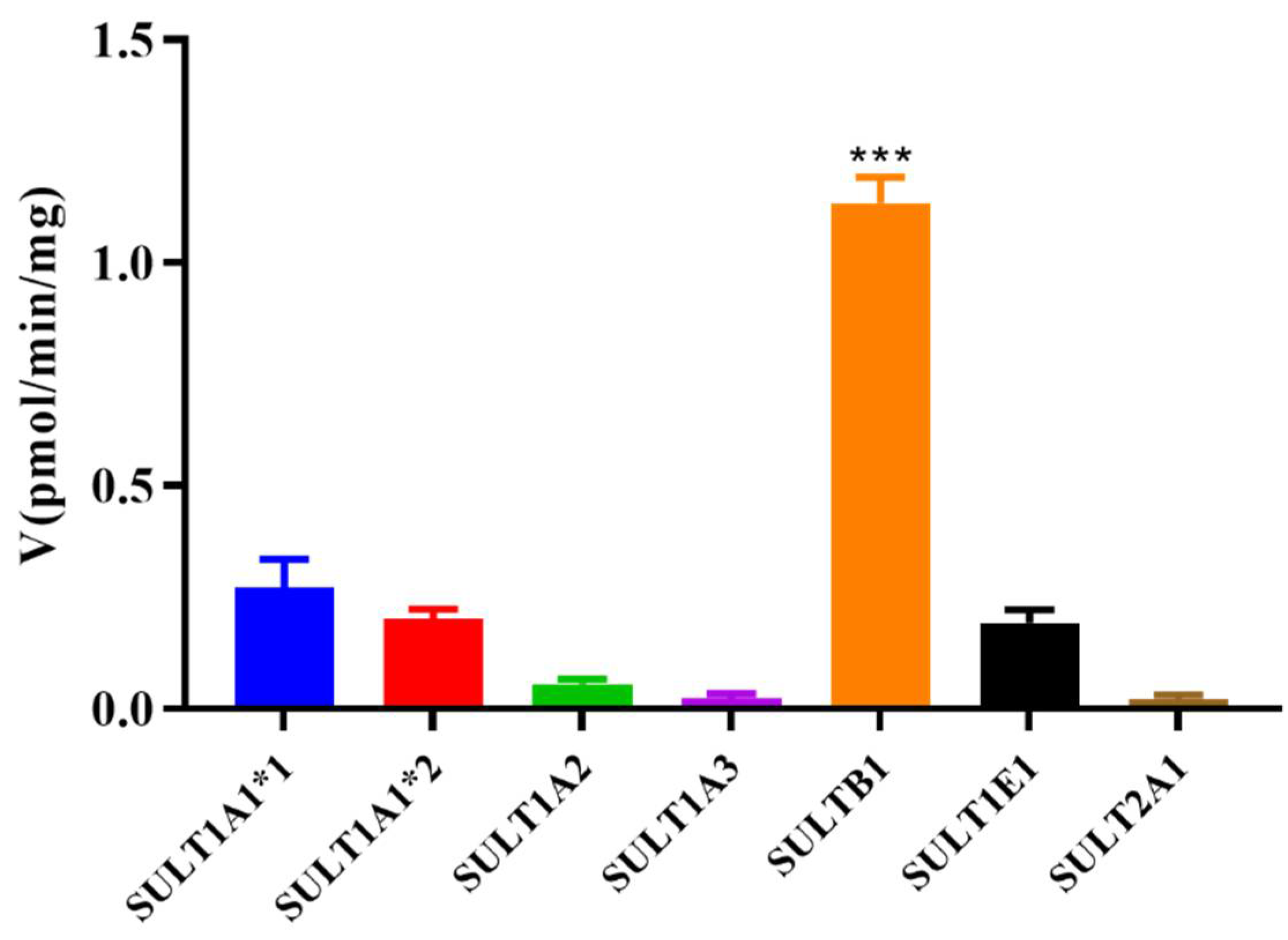
3.3. Magnolol Sulfation by Seven Recombinant Human SULT Isoforms
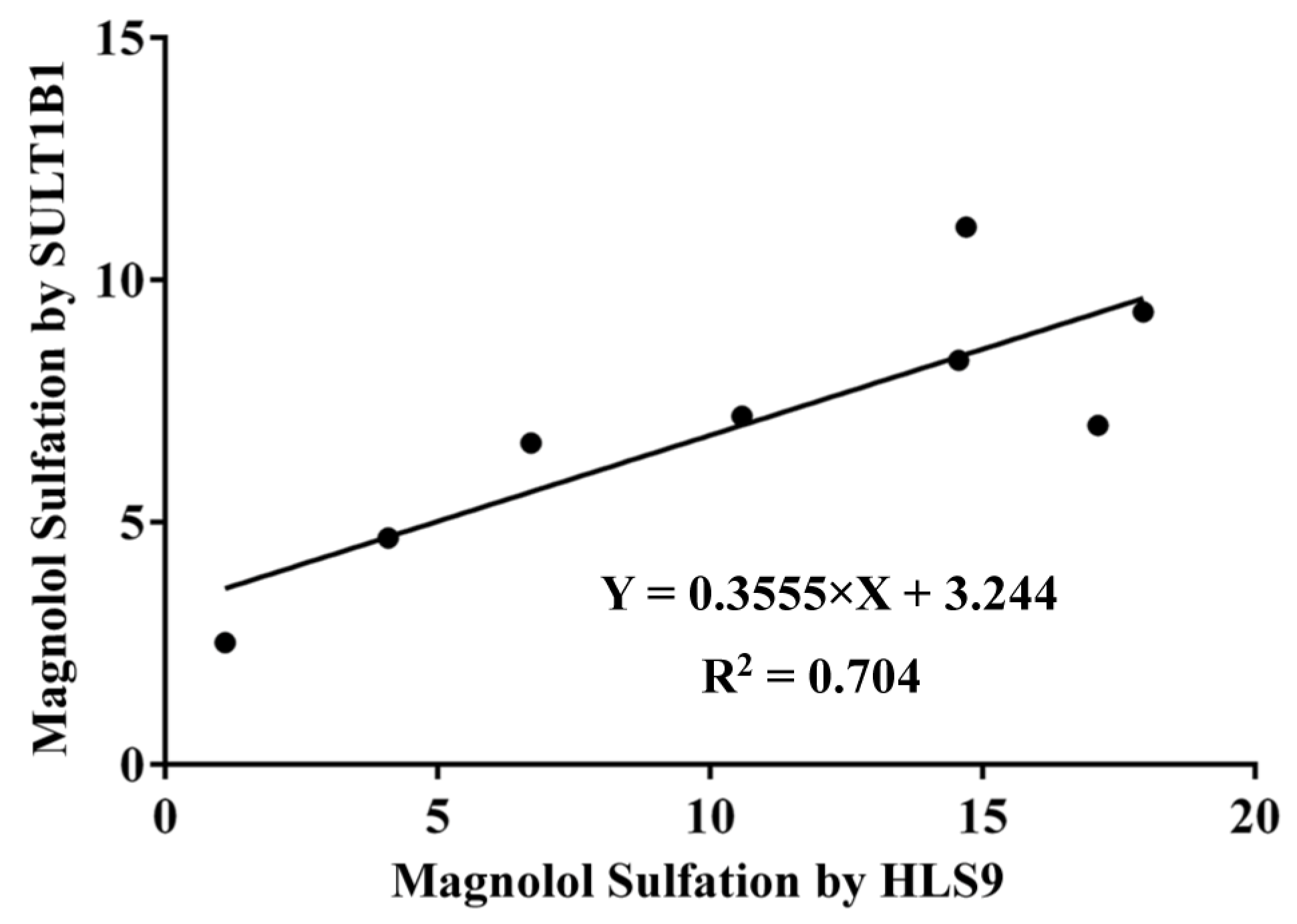
3.4. Correlation Study
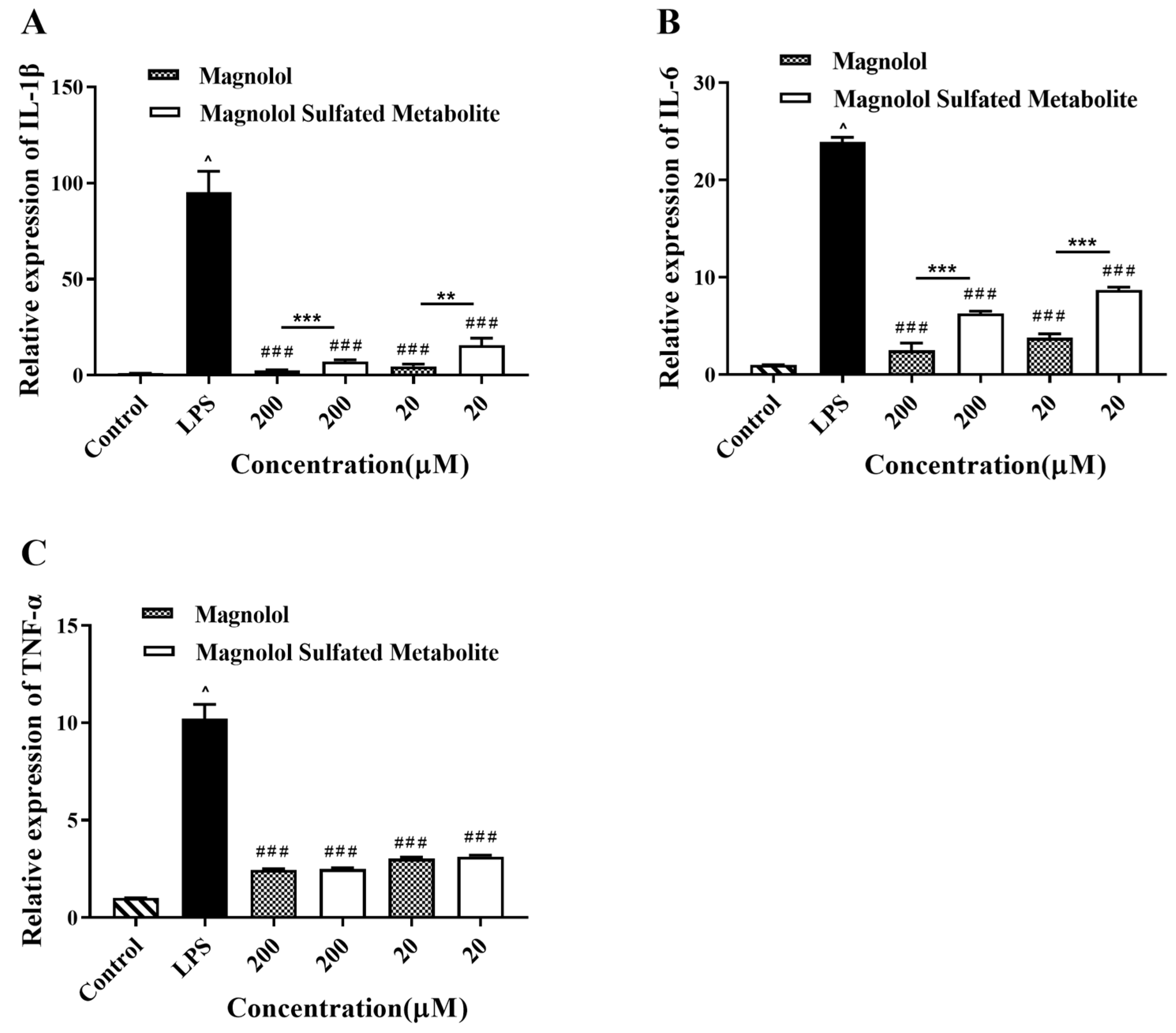
3.5. Effect of Magnolol and Magnolol Sulfated Metabolite on the Expression of IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α in LPS-Stimulated RAW264.7 Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Cui, W.; Zhang, X.; Li, N.; Chen, J.; Wong, A.W.; Roberts, A. Evaluation of short-term and subchronic toxicity of magnolia bark extract in rats. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2007, 49, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Liu, C.; Liu, S.; Liu, Z.; Li, S.; Wang, Y. In vitro metabolism of magnolol and honokiol in rat liver microsomes and their interactions with seven cytochrome P substrates. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2019, 33, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poivre, M.; Duez, P. Biological activity and toxicity of the Chinese herb Magnolia officinalis Rehder & E. Wilson (Houpo) and its constituents. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2017, 18, 194–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, Z.; Huang, X.; Shi, W.; Zhang, R.; Chen, M.; Huang, H.; Wu, L. Insights on the Multifunctional Activities of Magnolol. Biomed. Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 1847130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, P.; Zhang, Z.; He, Y.; Gu, C.; Zhu, K.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Lu, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, N.; et al. Magnolol treatment attenuates dextran sulphate sodium-induced murine experimental colitis by regulating inflammation and mucosal damage. Life Sci. 2018, 196, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, M.H.; Chen, M.C.; Chen, T.H.; Chang, H.Y.; Chou, T.C. Magnolol ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in rats through PPAR-γ-dependent inhibition of NF-kB activation. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2015, 28, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.P.; Tsai, S.Y.; Lee Chao, P.D.; Chen, Y.C.; Hou, Y.C. Pharmacokinetics, bioavailability, and tissue distribution of magnolol following single and repeated dosing of magnolol to rats. Planta Med. 2011, 77, 1800–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarrica, A.; Kirika, N.; Romeo, M.; Salmona, M.; Diomede, L. Safety and Toxicology of Magnolol and Honokiol. Planta Med. 2018, 84, 1151–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, L.; Zhu, L.; Li, W.; Li, C.; Cao, Y.; Ge, G.; Sun, X. New Insights into SN-38 Glucuronidation: Evidence for the Important Role of UDP Glucuronosyltransferase 1A9. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2018, 122, 424–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Daibani, A.A.; Xi, Y.; Luo, L.; Mei, X.; Zhou, C.; Yasuda, S.; Liu, M.C. Sulfation of hesperetin, naringenin and apigenin by the human cytosolic sulfotransferases: A comprehensive analysis. Nat. Prod. Res. 2020, 34, 797–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aires, V.; Limagne, E.; Cotte, A.K.; Latruffe, N.; Ghiringhelli, F.; Delmas, D. Resveratrol metabolites inhibit human metastatic colon cancer cells progression and synergize with chemotherapeutic drugs to induce cell death. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2013, 57, 1170–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.; Schueller, K.; Schaefer, L.M.; Pignitter, M.; Esefelder, L.; Somoza, V. Resveratrol and its metabolites inhibit pro-inflammatory effects of lipopolysaccharides in U-937 macrophages in plasma-representative concentrations. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.L.; Yin, X.J.; Yan, Y.L.; Wu, Q.F. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Huanglian-Houpo Decoction Based on Berberine Hydrochloride and Magnolol against H1N1 Influenza Virus. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2022, 47, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Du, D.; Wen, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, R.; Jin, T.; Yang, J.; Shi, N.; Jiang, K.; Deng, L.; et al. Chaiqin chengqi decoction ameliorates acute pancreatitis in mice via inhibition of neuron activation-mediated acinar cell SP/NK1R signaling pathways. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 274, 114029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Zhu, L.; Li, X.; Zheng, H.; Yan, T.; Xie, C.; Zeng, S.; Yu, J.; Jiang, H.; Lu, L.; et al. High-Throughput and Reliable Isotope Label-free Approach for Profiling 24 Metabolic Enzymes in FVB Mice and Sex Differences. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2017, 45, 624–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cagiola, M.; Giulio, S.; Miriam, M.; Katia, F.; Paola, P.; Macrì, A.; Pasquali, P. In vitro down regulation of proinflammatory cytokines induced by LPS tolerance in pig CD14+ cells. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2006, 112, 316–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartley, J.W.; Evans, L.H.; Green, K.Y.; Naghashfar, Z.; Macias, A.R.; Zerfas, P.M.; Ward, J.M. Expression of infectious murine leukemia viruses by RAW264.7 cells, a potential complication for studies with a widely used mouse macrophage cell line. Retrovirology 2008, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi-Matsui, M.; Yano, S.; Matsumoto, N.; Futai, M. Lipopolysaccharide induces multinuclear cell from RAW264.7 line with increased phagocytosis activity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 425, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.H.; Tang, L.; Lv, C.; Ye, L.; Xia, B.J.; Hu, M.; Liu, Z.Q. Sulfation of selected mono-hydroxyflavones by sulfotransferases in vitro: A species and gender comparison. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2011, 63, 967–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seibert, E.; Trancy, T.S. Fundamentals of Enzyme Kinetics: Michaelis-Menten and Non-Michaelis-Type (Aypitcal) Enzyme Kinetics. In Enzyme Kinetics in Drug Metabolism; Nagar, S., Argikar, U.A., Tweedie, D., Eds.; Humana: New York, NY, USA, 2021; Volume 2342, Methods in Molecular Biology. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, F.; Maren, N.A.; Kosentka, P.Z.; Liao, Y.Y.; Lu, H.; Duduit, J.R.; Huang, D.; Ashrafi, H.; Zhao, T.; Huerta, A.I.; et al. An optimized protocol for stepwise optimization of real-time RT-PCR analysis. Hortic. Res. 2021, 8, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukaka, M.M. Statistics corner: A guide to appropriate use of correlation coefficient in medical research. Malawi Med. J. 2012, 24, 69–71. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schober, P.; Boer, C.; Schwarte, L.A. Correlation Coefficients: Appropriate Use and Interpretation. Anesth. Analg. 2018, 126, 1763–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, X.; Xie, L.; Liu, K.; Liang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Lu, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, X. The neuropharmacological effects of magnolol and honokiol: A review of signal pathways and molecular mechanisms. Curr. Mol. Pharmacol. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.J.; Lee, Y.M.; Lee, C.K.; Jung, J.K.; Han, S.B.; Hong, J.T. Therapeutic applications of compounds in the Magnolia family. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 130, 157–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Ge, G.; Zhang, H.; Liu, H.; He, G.; Liang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Fang, Z.; Dong, P.; Finel, M.; et al. Characterization of hepatic and intestinal glucuronidation of magnolol: Application of the relative activity factor approach to decipher the contributions of multiple UDP-glucuronosyltransferase isoforms. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2012, 40, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y.L.; Xu, J.H.; Shi, C.H.; Li, W.; Xu, H.Y.; Li, N.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Zhang, X.R. UPLC-MS/MS-ESI assay for simultaneous determination of magnolol and honokiol in rat plasma: Application to pharmacokinetic study after administration emulsion of the isomer. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 155, 1568–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, T.; Guan, J.; Wang, J.; Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Qian, J.; Xu, X.; Qu, W.; Huang, Z.; et al. Oral Delivery of Honokiol Microparticles for Nonrapid Eye Movement Sleep. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 16, 737–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z. Comparative studies on the interactions of honokiol and magnolol with human serum albumin. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2012, 66, 240–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Tang, L.; Ye, L.; Cai, Z.; Xia, B.; Zhang, J.; Hu, M.; Liu, Z. Species and gender differences affect the metabolism of emodin via glucuronidation. AAPS J. 2010, 12, 424–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.J.; Zuo, M.T.; Qi, X.J.; Ma, X.; Wang, Z.Y.; Liu, Z.Y. In vitro Metabolism of Humantenine in Liver Microsomes from Human, Pig, Goat and Rat. Curr. Drug Metab. 2021, 22, 795–7801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riches, Z.; Stanley, E.L.; Bloomer, J.C.; Coughtrie, M.W. Quantitative evaluation of the expression and activity of five major sulfotransferases (SULTs) in human tissues: The SULT “pie”. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2009, 37, 2255–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, I.; Wang, T.; Leyh, T.S. Sulfotransferase 1A1 Substrate Selectivity: A Molecular Clamp Mechanism. Biochemistry 2015, 54, 6114–6122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coughtrie, M.W.H. Function and organization of the human cytosolic sulfotransferase (SULT) family. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2016, 259, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, M.O.; Ambadapadi, S. Interactions of cytosolic sulfotransferases with xenobiotics. Drug Metab. Rev. 2013, 45, 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutzler, J.M.; Tracy, T.S. Atypical kinetic profiles in drug metabolism reactions. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2002, 30, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karakhim, S.O.; Shlykov, S.G.; Babich, L.G.; Sinko, D.V. Analysis of decay kinetics of the cytosolic calcium transient induced by oxytocin in rat myometrium smooth muscle cells. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 2021, 42, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uno, Y.; Murayama, N.; Yamazaki, H. Molecular and functional characterization of cytosolic sulfotransferases in cynomolgus macaque. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2019, 166, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Harps, L.C.; Bureik, M.; Parr, M.K. Human Sulfotransferase Assays with PAPS Production in situ. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 827638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.; Huo, X.; Dong, P.; Wu, B.; Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Liu, K.; Ma, X. Sulfation of melatonin: Enzymatic characterization, differences of organs, species and genders, and bioactivity variation. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2015, 94, 282–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.S.; Lee, Y.J.; Park, S.N. Synergistic Antimicrobial Effect of Lonicera japonica and Magnolia obovata Extracts and Potential as a Plant-Derived Natural Preservative. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 28, 1814–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Lee, J.; Jung, E.; Park, Y.; Kim, K.; Park, B.; Jung, K.; Park, E.; Kim, J.; Park, D. In vitro antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects of honokiol and magnolol against Propionibacterium sp. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 496, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bocheva, G.; Slominski, R.M.; Slominski, A.T. The Impact of Vitamin D on Skin Aging. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
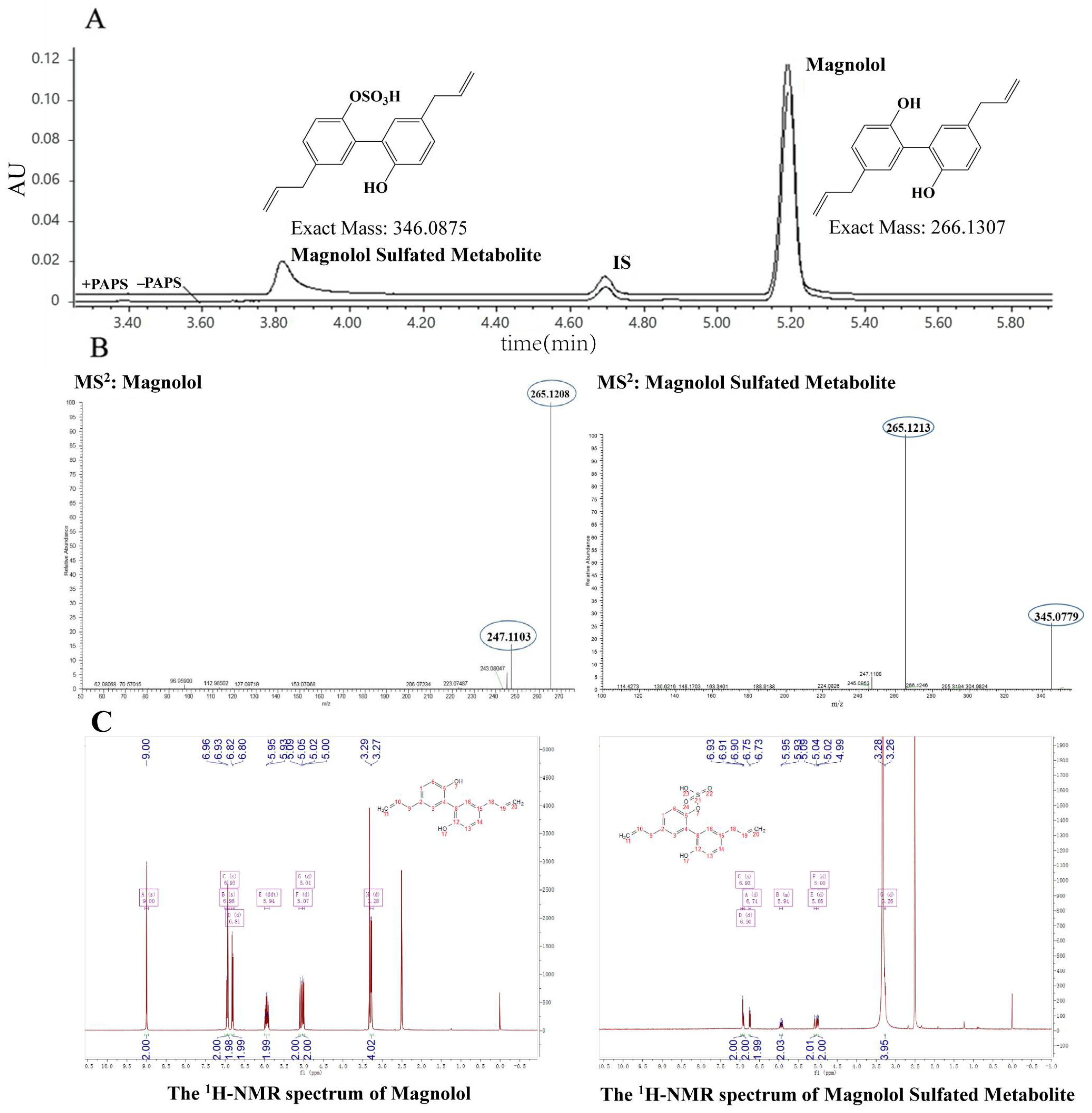



| Proton | Magnolol (ppm) | Magnolol Sulfated Metabolite (ppm) |
|---|---|---|
| 7 | 9.0 | - |
| 11 | 5.00 | 4.99 |
| 10 | 5.91 | 5.90 |
| 9 | 3.27 | 3.27 |
| 1 | 6.90 | 6.93 |
| 6 | 6.74 | 6.81 |
| Species | Km (μM) | Vmax (pmol/mg/min) | CLint (Vmax/Km μL/min/mg) | Kinetic Mechanism Model |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RLS9 | 32.25 ± 8.166 | 31.15 ± 2.967 | 0.96 | SI |
| MLS9 | 36.82 ± 3.365 | 11.12 ± 0.365 | 0.30 | MM |
| HLS9 | 26.85 ± 6.797 | 26.82 ± 3.214 | 0.99 | SI |
| Isoform | Km (μM) | Vmax (pmol/mg/min) | CLint (Vmax/Km μL/min/mg) | Kinetic Mechanism Model |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SULT1A1*1 | 0.49 ± 0.01 | 5.94 ± 0.32 | 12.12 | SI |
| SULT1A1*2 | 0.32 ± 0.06 | 13.04 ± 1.24 | 40.75 | SI |
| SULT1A2 | 0.16 ± 0.07 | 0.76 ± 0.09 | 4.75 | SI |
| SULT1A3 | 69.34 ± 149.80 | 2.29 ± 4.31 | 0.03 | SI |
| SULT1B1 | 0.29 ± 0.15 | 18.93 ± 3.16 | 65.27 | SI |
| SULT1E1 | 0.26 ± 0.16 | 5.11 ± 0.90 | 19.65 | SI |
| SULT2A1 | 0.14 ± 0.06 | 0.71 ± 0.07 | 5.07 | SI |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, C.; Hu, W.; Gan, L.; Fu, B.; Zhao, X.; Tang, D.; Liao, R.; Ye, L. Sulfation and Its Effect on the Bioactivity of Magnolol, the Main Active Ingredient of Magnolia Officinalis. Metabolites 2022, 12, 870. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12090870
Xie C, Hu W, Gan L, Fu B, Zhao X, Tang D, Liao R, Ye L. Sulfation and Its Effect on the Bioactivity of Magnolol, the Main Active Ingredient of Magnolia Officinalis. Metabolites. 2022; 12(9):870. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12090870
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Cong, Wanyu Hu, Lili Gan, Bingxuan Fu, Xiaojie Zhao, Dafu Tang, Rongxin Liao, and Ling Ye. 2022. "Sulfation and Its Effect on the Bioactivity of Magnolol, the Main Active Ingredient of Magnolia Officinalis" Metabolites 12, no. 9: 870. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12090870
APA StyleXie, C., Hu, W., Gan, L., Fu, B., Zhao, X., Tang, D., Liao, R., & Ye, L. (2022). Sulfation and Its Effect on the Bioactivity of Magnolol, the Main Active Ingredient of Magnolia Officinalis. Metabolites, 12(9), 870. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12090870





