A Metabolomic Signature of Obesity and Risk of Colorectal Cancer: Two Nested Case–Control Studies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Metabolomic Profiling
2.3. Exposure and Covariate Measurement
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Population Characteristics
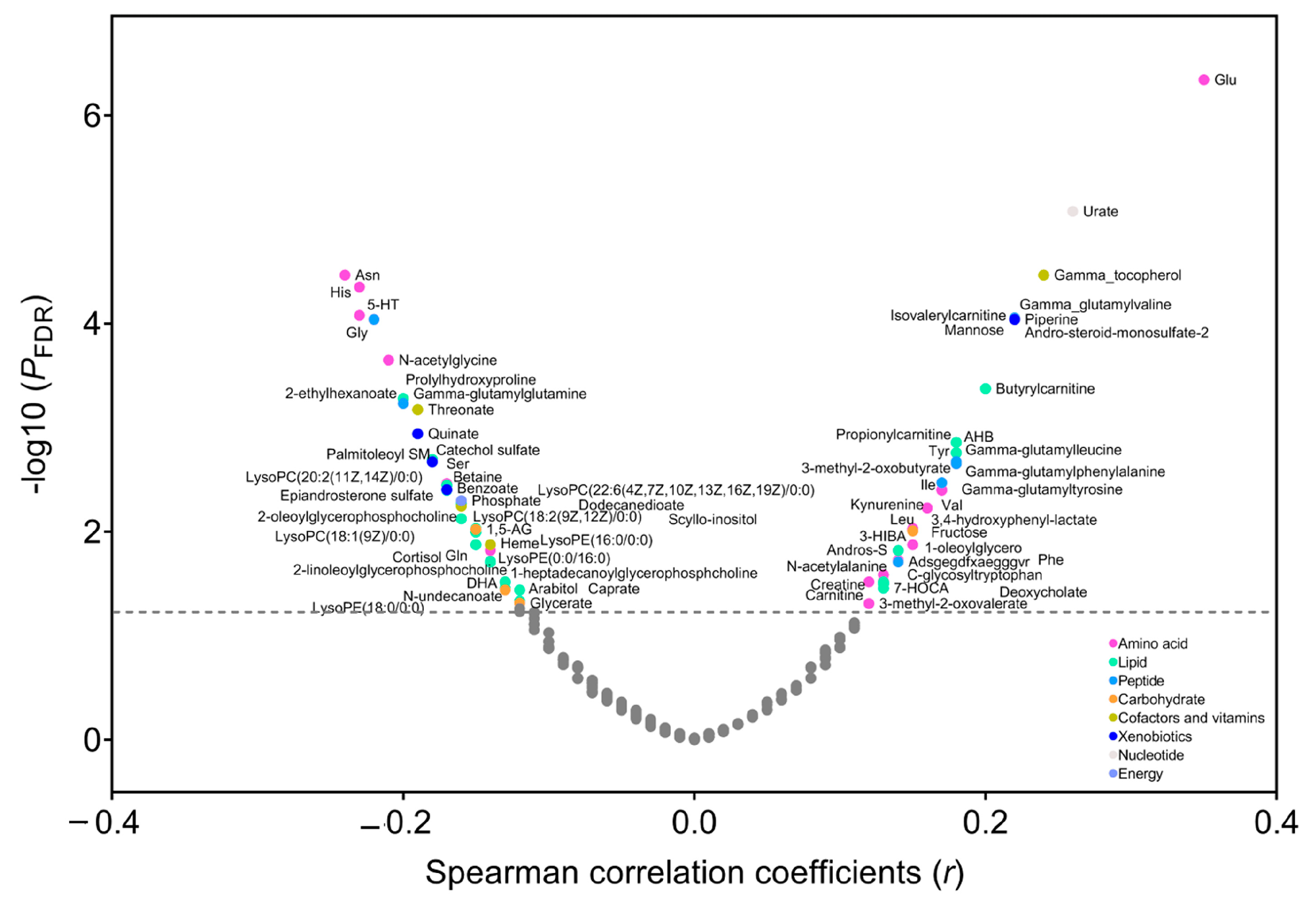
3.2. Metabolites Correlated with BMI
3.3. Metabolomic Signature and CRC Risk
3.4. Mediation Effect
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, E.; Arnold, M.; Gini, A.; Lorenzoni, V.; Cabasag, C.J.; Laversanne, M.; Vignat, J.; Ferlay, J.; Murphy, N.; Bray, F. Global burden of colorectal cancer in 2020 and 2040: Incidence and mortality estimates from GLOBOCAN. Gut 2023, 72, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauby-Secretan, B.; Scoccianti, C.; Loomis, D.; Grosse, Y.; Bianchini, F.; Straif, K. Body Fatness and Cancer—Viewpoint of the IARC Working Group. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 794–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, N.; Jenab, M.; Gunter, M.J. Adiposity and gastrointestinal cancers: Epidemiology, mechanisms and future directions. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 659–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, G.I.; Mittendorfer, B.; Klein, S. Metabolically healthy obesity: Facts and fantasies. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 3978–3989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, B.; Li, H.; Peng, X.X. Functional metabolomics: From biomarker discovery to metabolome reprogramming. Protein Cell 2015, 6, 628–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, J.E.; Larson, M.G.; Ghorbani, A.; Cheng, S.; Chen, M.-H.; Keyes, M.; Rhee, E.P.; Clish, C.B.; Vasan, R.S.; Gerszten, R.E.; et al. Metabolomic Profiles of Body Mass Index in the Framingham Heart Study Reveal Distinct Cardiometabolic Phenotypes. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0148361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Rhee, E.P.; Larson, M.G.; Lewis, G.D.; McCabe, E.L.; Shen, D.; Palma, M.J.; Roberts, L.D.; Dejam, A.; Souza, A.L.; et al. Metabolite profiling identifies pathways associated with metabolic risk in humans. Circulation 2012, 125, 2222–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, S.C.; Matthews, C.E.; Sampson, J.N.; Stolzenberg-Solomon, R.Z.; Zheng, W.; Cai, Q.; Tan, Y.T.; Chow, W.-H.; Ji, B.-T.; Liu, D.K.; et al. Human metabolic correlates of body mass index. Metabolomics 2014, 10, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottosson, F.; Brunkwall, L.; Ericson, U.; Nilsson, P.M.; Almgren, P.; Fernandez, C.; Melander, O.; Orho-Melander, M. Connection Between BMI-Related Plasma Metabolite Profile and Gut Microbiota. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 103, 1491–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moore, S.C.; Playdon, M.C.; Sampson, J.N.; Hoover, R.N.; Trabert, B.; E Matthews, C.; Ziegler, R.G. A Metabolomics Analysis of Body Mass Index and Postmenopausal Breast Cancer Risk. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2018, 110, 588–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickerman, B.A.; Ebot, E.M.; Healy, B.C.; Wilson, K.M.; Eliassen, A.H.; Ascherio, A.; Pernar, C.H.; Zeleznik, O.A.; Heiden, M.G.V.; Clish, C.B.; et al. A Metabolomics Analysis of Adiposity and Advanced Prostate Cancer Risk in the Health Professionals Follow-Up Study. Metabolites 2020, 10, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cirulli, E.T.; Guo, L.; Swisher, C.L.; Shah, N.; Huang, L.; Napier, L.A.; Kirkness, E.F.; Spector, T.D.; Caskey, C.T.; Thorens, B.; et al. Profound Perturbation of the Metabolome in Obesity Is Associated with Health Risk. Cell Metab. 2019, 29, 488–500.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kliemann, N.; Viallon, V.; Murphy, N.; Beeken, R.J.; Rothwell, J.A.; Rinaldi, S.; Assi, N.; van Roekel, E.H.; Schmidt, J.A.; Borch, K.B.; et al. Metabolic signatures of greater body size and their associations with risk of colorectal and endometrial cancers in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition. BMC Med. 2021, 19, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prorok, P.C.; Andriole, G.L.; Bresalier, R.S.; Buys, S.S.; Chia, D.; Crawford, E.D.; Fogel, R.; Gelmann, E.P.; Gilbert, F.; Hasson, M.A.; et al. Design of the prostate, lung, colorectal and ovarian (PLCO) cancer screening trial. Control. Clin. Trials 2000, 21, 273S–309S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hang, D.; Yang, X.; Lu, J.; Shen, C.; Dai, J.; Lu, X.; Jin, G.; Hu, Z.; Gu, D.; Ma, H.; et al. Untargeted plasma metabolomics for risk prediction of hepatocellular carcinoma: A prospective study in two Chinese cohorts. Int. J. Cancer 2022, 151, 2144–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, A.M.; DeHaven, C.D.; Barrett, T.; Mitchell, M.; Milgram, E. Integrated, nontargeted ultrahigh performance liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry platform for the identification and relative quantification of the small-molecule complement of biological systems. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 6656–6667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.; Yi, X.; Sun, Y.; Bi, X.; Du, J.; Zhang, C.; Quan, S.; Zhang, F.; Sun, R.; Qian, L.; et al. Proteomic and Metabolomic Characterization of COVID-19 Patient Sera. Cell 2020, 182, 59–72.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi-Sunyer, F.X. Obesity: Criteria and classification. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2000, 59, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.F.; Cooperative Meta-Analysis Group of the Working Group on Obesity in China. Predictive values of body mass index and waist circumference for risk factors of certain related diseases in Chinese adults—Study on optimal cut-off points of body mass index and waist circumference in Chinese adults. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2002, 15, 83–96. [Google Scholar]
- Troy, J.D.; Hartge, P.; Weissfeld, J.L.; Oken, M.M.; Colditz, G.A.; Mechanic, L.E.; Morton, L.M. Associations between anthropometry, cigarette smoking, alcohol consumption, and non-Hodgkin lymphoma in the Prostate, Lung, Colorectal, and Ovarian Cancer Screening Trial. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2010, 171, 1270–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibshirani, R. Regression Shrinkage and Selection Via the Lasso. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 1996, 58, 267–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Guasch-Ferré, M.; Chung, W.; Ruiz-Canela, M.; Toledo, E.; Corella, D.; Bhupathiraju, S.; Tobias, D.; Tabung, F.; Hu, J.; et al. The Mediterranean diet, plasma metabolome, and cardiovascular disease risk. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 2645–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksandrova, K.; Reichmann, R.; Kaaks, R.; Jenab, M.; Bueno-De-Mesquita, H.B.; Dahm, C.C.; Eriksen, A.K.; Tjønneland, A.; Artaud, F.; Boutron-Ruault, M.-C.; et al. Development and validation of a lifestyle-based model for colorectal cancer risk prediction: The LiFeCRC score. BMC Med. 2021, 19, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, V.L.; Reis, J.P.; Pico, A.R.; Kitchen, R.; Lima, J.A.; Lloyd-Jones, D.; Allen, N.B.; Carnethon, M.; Lewis, G.D.; Nayor, M.; et al. Comprehensive Metabolic Phenotyping Refines Cardiovascular Risk in Young Adults. Circulation 2020, 142, 2110–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arthur, E.; Hoerl Robert, W.; Technometrics, K.J. Ridge Regression: Biased Estimation for Nonorthogonal Problems. Technometrics 2000, 42, 80–86. [Google Scholar]
- Vanderweele, T.J.; Vansteelandt, S. Odds ratios for mediation analysis for a dichotomous outcome. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2010, 172, 1339–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payab, M.; Tayanloo-Beik, A.; Falahzadeh, K.; Mousavi, M.; Salehi, S.; Djalalinia, S.; Ebrahimpur, M.; Rezaei, N.; Rezaei-Tavirani, M.; Larijani, B.; et al. Metabolomics prospect of obesity and metabolic syndrome; a systematic review. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2022, 21, 889–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butte, N.F.; Liu, Y.; Zakeri, I.F.; Mohney, R.P.; Mehta, N.R.; Voruganti, V.S.; Goring, H.H.H.; Cole, S.A.; Comuzzie, A.G. Global metabolomic profiling targeting childhood obesity in the Hispanic population. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 102, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.J.; Yang, H.J.; Kim, J.H.; Ahn, C.W.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, K.S.; Kwon, D.Y. Obesity-related metabolomic analysis of human subjects in black soybean peptide intervention study by ultraperformance liquid chromatography and quadrupole-time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J. Obes. 2013, 2013, 874981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, N.; Andiran, N. The relationship between serum phosphate levels with childhood obesity and insulin resistance. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. JPEM 2011, 24, 81–83. [Google Scholar]
- Bull, C.J.; Bell, J.A.; Murphy, N.; Sanderson, E.; Smith, G.D.; Timpson, N.J.; Banbury, B.L.; Albanes, D.; Berndt, S.I.; Bézieau, S.; et al. Adiposity, metabolites, and colorectal cancer risk: Mendelian randomization study. BMC Med. 2020, 18, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, A.; Bassot, A.; Bulteau, A.L.; Pirola, L.; Morio, B. Glycine Metabolism and Its Alterations in Obesity and Metabolic Diseases. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Daly, E.; Campioli, E.; Wabitsch, M.; Papadopoulos, V. De novo synthesis of steroids and oxysterols in adipocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 747–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Flanagan, C.H.; Bowers, L.W.; Hursting, S.D. A weighty problem: Metabolic perturbations and the obesity-cancer link. Horm. Mol. Biol. Clin. Investig. 2015, 23, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breeur, M.; Ferrari, P.; Dossus, L.; Jenab, M.; Johansson, M.; Rinaldi, S.; Travis, R.C.; His, M.; Key, T.J.; Schmidt, J.A.; et al. Pan-cancer analysis of pre-diagnostic blood metabolite concentrations in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition. BMC Med. 2022, 20, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.; Qiu, Y.; Zou, X.; Chen, T.; Xie, G.; Cheng, Y.; Dong, T.; Zhao, L.; Feng, B.; Hu, X.; et al. Metabonomics identifies serum metabolite markers of colorectal cancer. J. Proteome Res. 2013, 12, 3000–3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Djukovic, D.; Deng, L.; Gu, H.; Himmati, F.; Chiorean, E.G.; Raftery, D. Colorectal cancer detection using targeted serum metabolic profiling. J. Proteome Res. 2014, 13, 4120–4130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.W.; Qiao, S.Y.; Li, D.F. Amino acids and gut function. Amino Acids 2009, 37, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Wu, Z.; Dai, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wang, W.; Liu, C.; Wang, B.; Wang, J. Dietary requirements of “nutritionally non-essential amino acids” by animals and humans. Amino Acids 2013, 44, 1107–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, D.O.; Satsu, H.; Shimizu, M. Histidine inhibits oxidative stress- and TNF-alpha-induced interleukin-8 secretion in intestinal epithelial cells. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 4671–4677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andou, A.; Hisamatsu, T.; Okamoto, S.; Chinen, H.; Kamada, N.; Kobayashi, T.; Hashimoto, M.; Okutsu, T.; Shimbo, K.; Takeda, T.; et al. Dietary histidine ameliorates murine colitis by inhibition of proinflammatory cytokine production from macrophages. Gastroenterology 2009, 136, 564–574.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, N.; Sawada, N.; Iwasaki, M.; Yamaji, T.; Goto, A.; Shimazu, T.; Inoue, M.; Murphy, N.; Gunter, M.J.; Tsugane, S. Circulating sex hormone levels and colorectal cancer risk in Japanese postmenopausal women: The JPHC nested case-control study. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 145, 1238–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tutton, P.J.; Barkla, D.H. The influence of androgens, anti-androgens, and castration on cell proliferation in the jejunal and colonic crypt epithelia, and in dimethylhydrazine-induced adenocarcinoma of rat colon. Virchows Arch. B Cell Pathol. Incl. Mol. Pathol. 1982, 38, 351–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guha, S.; Majumder, K. Comprehensive Review of γ-Glutamyl Peptides (γ-GPs) and Their Effect on Inflammation Concerning Cardiovascular Health. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 7851–7870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, M.K.; Clish, C.B.; Kraft, P.; Wu, C.; Souza, A.L.; ADeik, A.; Tworoger, S.S.; Wolpin, B.M. Reproducibility of metabolomic profiles among men and women in 2 large cohort studies. Clin. Chem. 2013, 59, 1657–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, D.; Garmaeva, S.; Kurilshikov, A.; Vila, A.V.; Gacesa, R.; Sinha, T.; Segal, E.; Weersma, R.K.; Wijmenga, C.; et al. The long-term genetic stability and individual specificity of the human gut microbiome. Cell 2021, 184, 2302–2315.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Characteristic a | PLCO | Jiangsu | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case (n = 223) | Control (n = 223) | p b | Case (n = 190) | Control (n = 190) | p b | |
| Age, years | 64.3 (5.2) | 64.4 (5.1) | 0.95 | 59.7 (10.6) | 59.7 (10.6) | 0.98 |
| Female, % | 43.1 | 43.1 | – | 44.2 | 44.2 | – |
| Smoking status, % | 0.61 | 0.07 | ||||
| Never | 41.3 | 43.5 | 60.0 | 65.3 | ||
| Former | 47.9 | 48.4 | 6.8 | 2.1 | ||
| Current | 10.8 | 8.1 | 33.2 | 32.6 | ||
| Pack-years of smoking | 18.8 (25.2) | 18.0 (27.1) | 0.44 | 12.3 (20.3) | 10.8 (19.7) | 0.31 |
| Height, cm | 171.7 (10.2) | 171.5 (9.4) | 0.85 | 160.9 (8.7) | 160.5 (8.4) | 0.74 |
| Body weight, kg | 81.8 (17.3) | 78.4 (16.7) | 0.04 | 60.8 (10.5) | 60.8 (10.3) | 0.83 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 27.9 (4.7) | 26.7 (4.6) | 0.01 | 23.8 (3.7) | 23.6 (3.1) | 0.69 |
| Adiposity, % c | 29.7 | 20.0 | 0.02 | 14.2 | 6.3 | 0.02 |
| Alcohol, g/day | 12.2 (22.9) | 12.8 (22.3) | 0.38 | 17.4 (43.6) | 13.0 (30.8) | 0.69 |
| Prevalence of diabetes, % | 8.5 | 6.8 | 0.48 | 4.2 | 5.8 | 0.36 |
| Family history of colorectal cancer, % | 13.1 | 10.0 | 0.58 | – | – | – |
| Cohort | Quartiles of Metabolomic Signature, OR (95% CI) | p for Trend | OR per 1-SD Increase | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | ||||
| PLCO | No. of cases | 47 | 53 | 59 | 64 | ||
| Age-adjusted model | 1 (referent) | 1.31 (0.75–2.28) | 1.60 (0.93–2.77) | 2.01 (1.13–3.57) | 0.01 | 1.34 (1.09–1.65) | |
| Multivariable model a | 1 (referent) | 1.46 (0.81–2.65) | 1.82 (1.00–3.30) | 2.21 (1.15–4.25) | 0.01 | 1.38 (1.09–1.75) | |
| Jiangsu | No. of cases | 41 | 45 | 50 | 54 | ||
| Age-adjusted model | 1 (referent) | 1.27 (0.72–2.24) | 1.52 (0.86–2.69) | 1.87 (1.02–3.45) | 0.01 | 1.34 (1.07–1.67) | |
| Multivariable model a | 1 (referent) | 1.17 (0.65–2.12) | 1.35 (0.74–2.46) | 1.70 (0.90–3.19) | 0.04 | 1.28 (1.02–1.62) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, M.; Zhu, C.; Du, L.; Huang, J.; Lu, J.; Yang, J.; Tong, Y.; Zhu, M.; Song, C.; Shen, C.; et al. A Metabolomic Signature of Obesity and Risk of Colorectal Cancer: Two Nested Case–Control Studies. Metabolites 2023, 13, 234. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13020234
Yang M, Zhu C, Du L, Huang J, Lu J, Yang J, Tong Y, Zhu M, Song C, Shen C, et al. A Metabolomic Signature of Obesity and Risk of Colorectal Cancer: Two Nested Case–Control Studies. Metabolites. 2023; 13(2):234. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13020234
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Mingjia, Chen Zhu, Lingbin Du, Jianv Huang, Jiayi Lu, Jing Yang, Ye Tong, Meng Zhu, Ci Song, Chong Shen, and et al. 2023. "A Metabolomic Signature of Obesity and Risk of Colorectal Cancer: Two Nested Case–Control Studies" Metabolites 13, no. 2: 234. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13020234







