Untargeted Metabolomics Approach for the Differentiation between Panax vietnamensis var. vietnamensis and Panax vietnamensis var. fuscidiscus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Material
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. UPLC-QTOF-MS Analysis
2.4. UPLC-QTOF-MS Data Processing and Normalization
2.5. Multivariate and Machine Learning Analyses
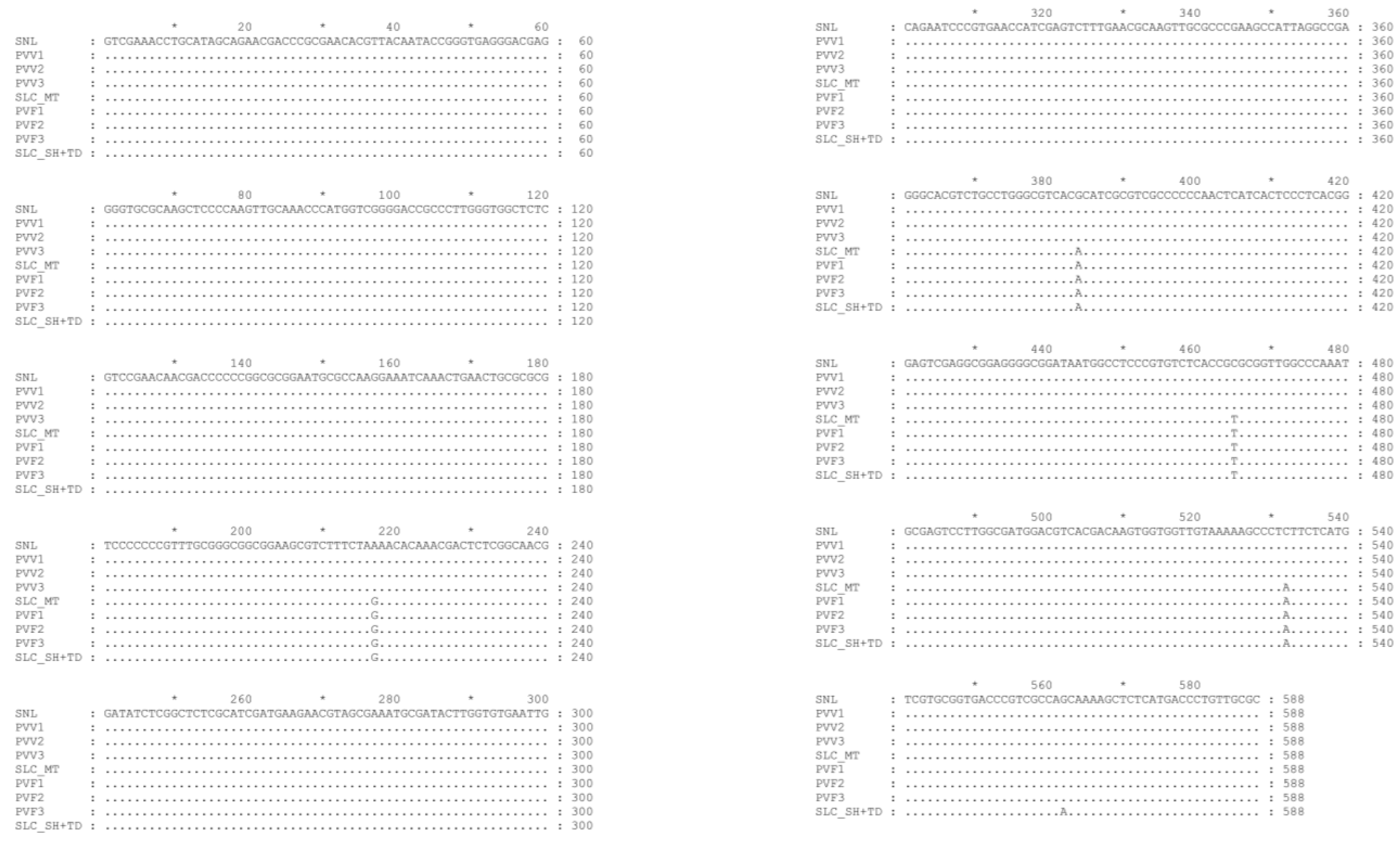
2.6. Assessment of Sample Using ITS-rDNA Sequence Method
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Authenticating the Origins of Vietnamse Ginseng by ITSr-DNA Sequence Data
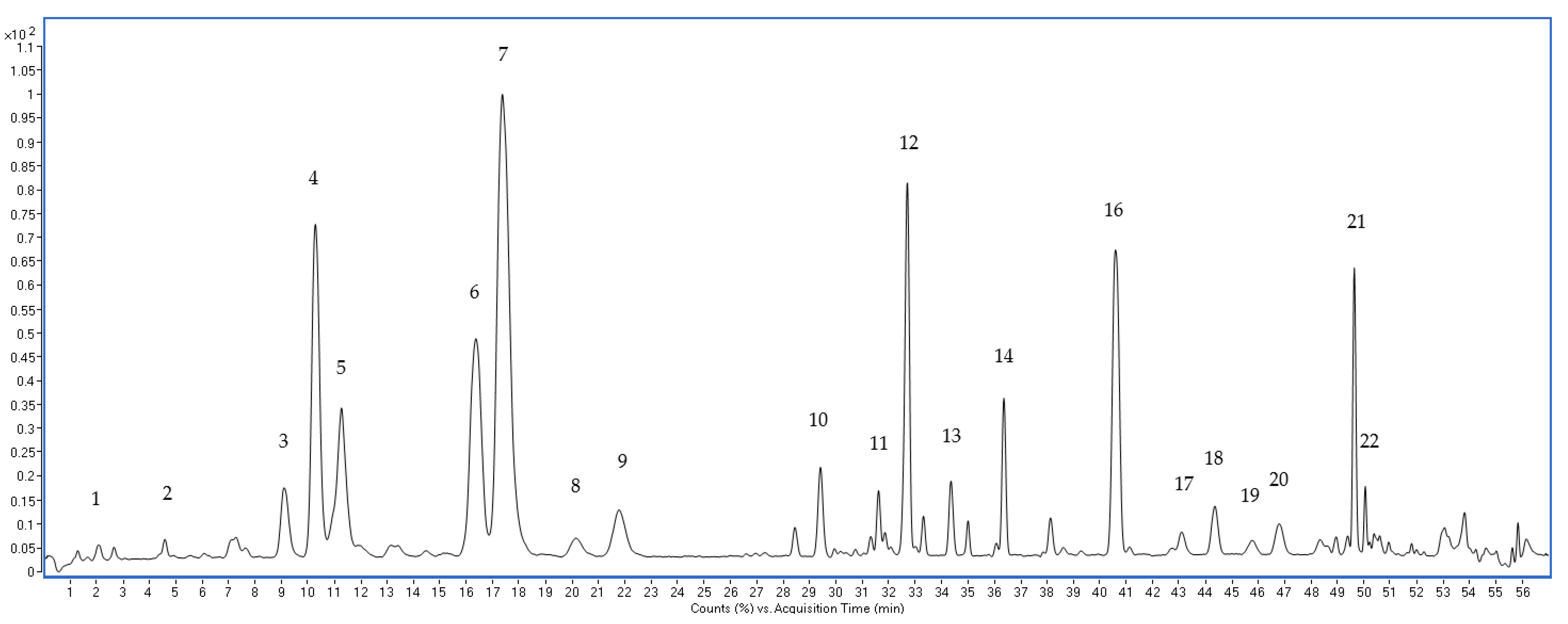
3.2. Optimization of UPLC-QTOF-MS Approach for the Ginsenosides Profiling
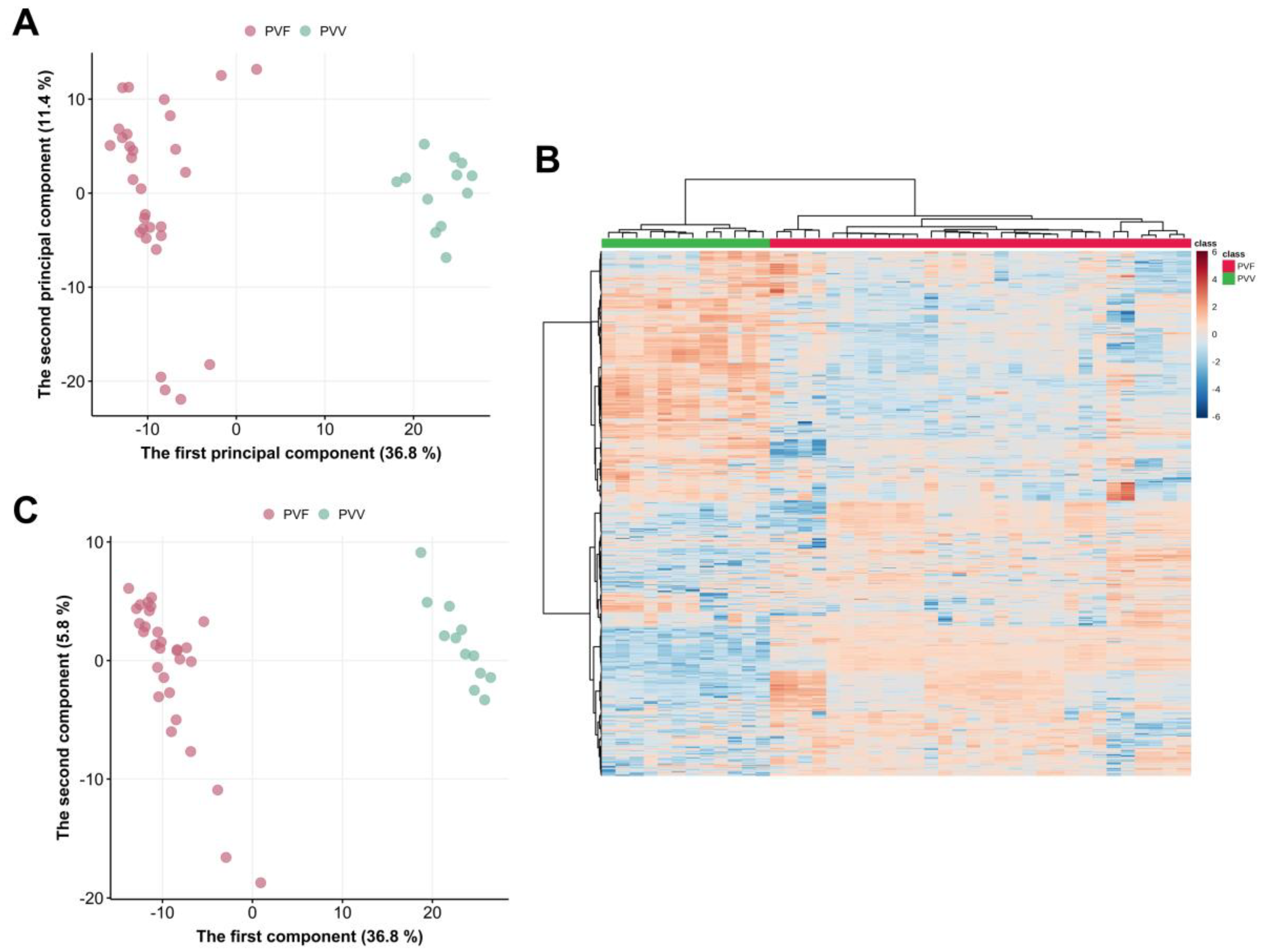
3.3. Multivariate Analysis of the Metabolome Differences between PVV and PVF
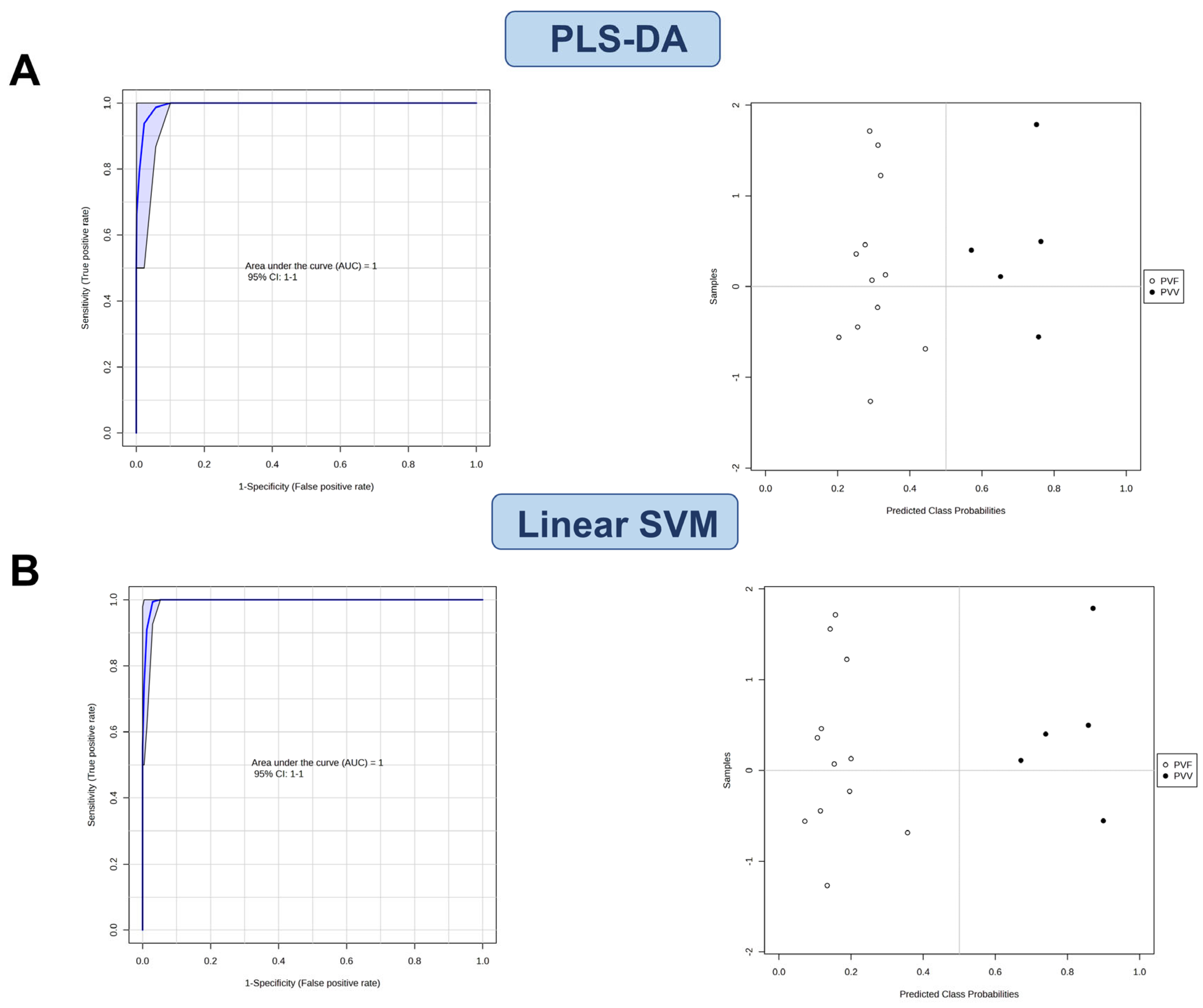
3.4. Characterization of the Potential Differential Markers Using ROC Curve-Based Modeling
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Dung, H.T.; Grushvitski, I.V. A new species of the genus Panax (Araliaceae) from Vietnam. Bot. Zhurnal 1985, 70, 519–522. [Google Scholar]
- Duc, N.M.; Nham, N.T.; Kasai, R.; Ito, A.; Yamasaki, K.; Tanaka, O. Saponins from Vietnamese ginseng, Panax vietnamensis Ha et Grushv. Collected in central Vietnam. I. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1993, 41, 2010–2014. [Google Scholar]
- Duc, N.M.; Nham, N.T.; Kasai, R.; Ito, A.; Yamasaki, K.; Tanaka, O. Saponins from Vietnamese Ginseng, Panax vietnamensis Ha et Grushv. Collected in central Vietnam. II. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1994, 42, 115–122. [Google Scholar]
- Duc, N.M.; Nham, N.T.; Kasai, R.; Ito, A.; Yamasaki, K.; Tanaka, O. Saponins from Vietnamese ginseng, Panax vietnamensis Ha et Grushv. collected in central Vietnam. III. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1994, 42, 634–640. [Google Scholar]
- Huong, N.T.T.; Matsumoto, K.; Watanabe, H. The antistress effect of majonoside-R2, a major saponin component of Vietnamese ginseng: Neuronal mechanisms of action. Methods Find. Exp. Clin. Pharmacol. 1998, 20, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huong, N.T.T.; Matsumoto, K.; Yamasaki, K.; Duc, N.M.; Nham, N.T.; Watanabe, H. Crude sponin extracted from Vietnamese ginseng and its major constituent majonoside-R2 attenuate the psychological stress- and foot-shock stress-induced antinociception in mice. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1995, 52, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huong, N.T.T.; Matsumoto, K.; Yamasaki, K.; Duc, N.M.; Nham, N.T.; Watanabe, H. Effects of majonoside-R2 on pentobarbital sleep and gastric lesion in psychologically stressed mice. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1996, 53, 957–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huong, N.T.T.; Murakami, Y.; Tohda, M.; Watanabe, H.; Matsumoto, K. Social Isolation Stress-Induced Oxidative Damage in Mouse Brain and Its Modulation by Majonoside-R2, a Vietnamese Ginseng Saponin. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2005, 28, 1389–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konoshima, T.; Takasaki, M.; Ichiishi, E.; Murakami, T.; Tokuda, H.; Nishino, H.; Duc, N.M.; Kasai, R.; Yamasaki, K. Cancer chemopreventive activity of majonoside-R2 from Vietnamese ginseng, Panax vietnamensis. Cancer Lett. 1999, 147, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konoshima, T.; Takasaki, M.; Tokuda, H.; Nishino, H.; Duc, N.M.; Kasai, R.; Yamasaki, K. Anti-tumor-promoting Activity of Majonoside-R2 from Veitnamese Ginseng, Panax vietnamensis HA et GRUSHV. (I). Biol. Pharm. Bull. 1998, 21, 834–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, T.L.; Adnyana, I.K.; Tezuka, Y.; Harimaya, Y.; Saiki, I.; Kurashige, Y.; Qui, T.K.; Kadota, S. Hepatoprotective effect of majonoside R2, the major saponin from Vietnamese ginseng (Panax vietnamensis). Planta Med. 2002, 68, 402–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu-Huynh, K.L.; Le, T.H.V.; Nguyen, H.T.; Kim, H.M.; Kang, K.S.; Park, J.H.; Nguyen, M.D. Increase in Protective Effect of Panax vietnamensis by Heat Processing on Cisplatin-Induced Kidney Cell Toxicity. Molecules 2019, 24, 4627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Fushimi, H.; Cai, S.; Chen, H.; Komatsu, K. A new variety of the genus Panax from southern Yunnan, China and its nucleotide sequences of 18S ribosomal RNA gene and matK gene. J. Jpn. Bot. 2003, 78, 86–94. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, S.; Zou, K.; Cai, S.; Meselhy, M.R.; Komatsu, K. Simultaneous Determination of Triterpene Saponins in Ginseng Drugs by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2004, 52, 995–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, P.K.; Son, L.T.; Loc, P.K.; Duy, V.D.; The, P.V. Lai Chau ginseng Panax vietnamensis var. fuscidiscus K. Komatsu, S. Zhu & SQ Cai, I. morphology, ecology, distribution and conservation status. In Proceedings of the 2nd VAST-KAST Workshop on Biodiversity and Bio-Active Compounds, Hanoi, Vietnam, 28 October 2013; pp. 28–29. [Google Scholar]
- Linh, N.N.; Hang, P.L.B.; Hue, H.T.T.; Ha, N.H.; Hanh, H.H.; Ton, N.D. Species discrimination of novel chloroplast DNA barcodes and their application for identification of Panax (Aralioideae, Araliaceae). PhytoKeys 2022, 188, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trang, N.T.P.; Mai, N.T.H. rbcL and rpoL gene sequences of Panax vietnamensis var. fuscidiscus and Panax vietnamensis, the background for identification and comparison. Acad. J. Biol. 2017, 39, 80–85. [Google Scholar]
- Long, P.K.; Duy, V.D.; Loc, P.K.; Son, N.G.; Trang, N.T.P.; Linh, L.T.M.; Son, L.T. Phylogenetic relationships of the Panax samples collected in Lai Chau Province based on MATK and ITS-rDNA sequences. J. Biotechnol. 2014, 12, 327–337. [Google Scholar]
- Tsugawa, H.; Cajka, T.; Kind, T.; Ma, Y.; Higgins, B.; Ikeda, K.; Kanazawa, M.; VanderGheynst, J.; Fiehn, O.; Arita, M. MS-DIAL: Data-independent MS/MS deconvolution for comprehensive metabolome analysis. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 523–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, R.; Wang, J.; Su, M.; Jia, E.; Chen, S.; Chen, T.; Ni, Y. Missing Value Imputation Approach for Mass Spectrometry-based Metabolomics Data. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, J.E.; Long, N.P.; Hong, J.Y.; Kim, S.J.; Anh, N.H.; Wang, D.; Wang, X.; Park, J.H.; Kwon, S.W.; Lee, S.J. The dehiscence process in Panax ginseng seeds and the stigmasterol biosynthesis pathway in terms of metabolomics. J. Ginseng Res. 2022, 46, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, Z.; Zhou, G.; Ewald, J.; Chang, L.; Hacariz, O.; Basu, N.; Xia, J. Using MetaboAnalyst 5.0 for LC–HRMS spectra processing, multi-omics integration and covariate adjustment of global metabolomics data. Nat. Protoc. 2022, 17, 1735–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, Y.N. Rhizome Saponins of Panax pseudo-ginseng subsp. himalaicus and its var. bipinnatifidus. Planta Med. 1989, 55, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.-J.; Van Le, T.H.; Lee, S.-Y.; Eun, S.-H.; Nguyen, M.D.; Park, J.H.; Kim, D.-H. Anti-inflammatory effects of vina-ginsenoside R2 and majonoside R2 isolated from Panax vietnamensis and their metabolites in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophages. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2015, 28, 700–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Shen, L.-h.; Zhang, J.-t. Anti-amnestic and anti-aging effects of ginsenoside Rg1 and Rb1 and its mechanism of action. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2005, 26, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, A.; Xu, X.; Lin, J.; Cui, X.; Xu, R. Neuroprotection by Saponins. Phytother. Res. 2015, 29, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Gao, Y.; Cheng, D.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, W.; Shen, Y.; Huang, Q.; An, X.; Wang, B.; Yu, Z.; et al. Notoginsenoside Fc ameliorates renal tubular injury and mitochondrial damage in acetaminophen-induced acute kidney injury partly by regulating SIRT3/SOD2 pathway. Front. Med. 2023, 9, 1055252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-y.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Shen, L.; Jiang, X.; Xie, Z.-g.; Liang, N.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Z.-h. Anti-diabetic effects of Panax notoginseng saponins and its major anti-hyperglycemic components. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 130, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Guo, R.; Zhou, G.; Zhou, X.; Kou, Z.; Sui, F.; Li, C.; Tang, L.; Wang, Z. Traditional uses, botany, phytochemistry, pharmacology and toxicology of Panax notoginseng (Burk.) F.H. Chen: A review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 188, 234–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
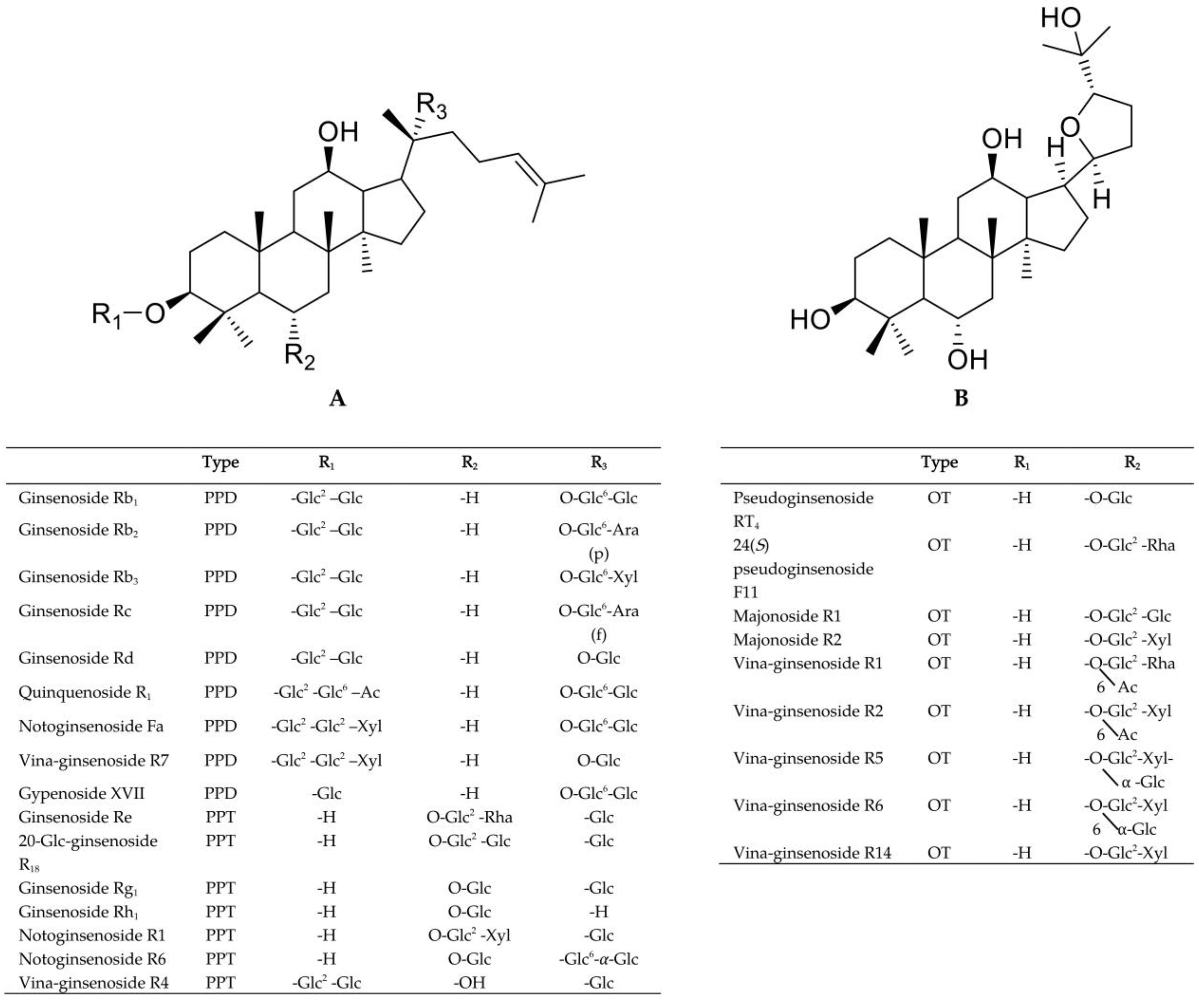


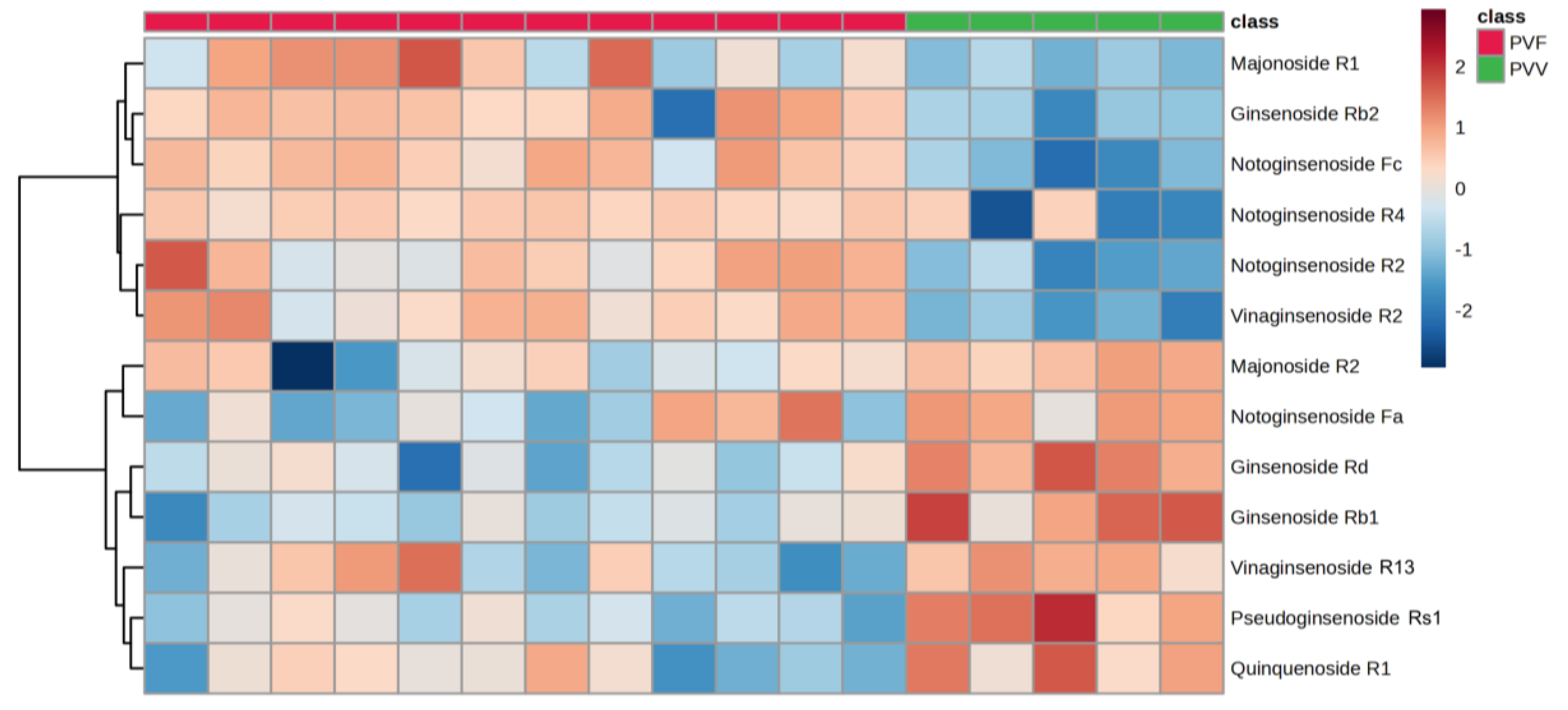
| Ginsenoside | Fold Change (PVV/PVF) | p-Value | False-Discovery Rate | VIP Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ginsenoside Rb1 | 2.00 | 1.20E-05 | 3.15E-05 | 0.71 |
| Ginsenoside Rb2 | 0.12 | 5.03E-08 | 2.39E-07 | 1.62 |
| Ginsenoside Rd | 2.23 | 3.77E-08 | 1.85E-07 | 0.87 |
| Majonoside R1 | 0.31 | 3.47E-05 | 8.18E-05 | 0.84 |
| Majonoside R2 | 1.39 | 5.31E-03 | 0.008724 | 0.41 |
| Notoginsenoside Fa | 6.62 | 5.83E-09 | 3.47E-08 | 1.37 |
| Notoginsenoside Fc | 0.03 | 9.39E-21 | 8.35E-19 | 2.07 |
| Notoginsenoside R2 | 0.08 | 5.57E-13 | 1.03E-11 | 1.65 |
| Notoginsenoside R4 | 0.20 | 8.89E-09 | 5.08E-08 | 2.09 |
| Pseudoginsenoside Rs1 | 8.54 | 3.43E-10 | 2.70E-09 | 1.49 |
| Quinquenoside R1 | 4.99 | 1.54E-11 | 1.81E-10 | 1.30 |
| Vinaginsenoside R13 | 1.56 | 1.08E-05 | 2.87E-05 | 0.62 |
| Vinaginsenoside R2 | 0.13 | 2.27E-24 | 1.45E-21 | 1.58 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, H.T.; Phan, L.K.; Huynh, K.-L.V.; Duong, T.-H.; Le, H.T.; Hai-Yen, N.T.; Yen, N.T.H.; Long, N.P.; Nguyen, M.D. Untargeted Metabolomics Approach for the Differentiation between Panax vietnamensis var. vietnamensis and Panax vietnamensis var. fuscidiscus. Metabolites 2023, 13, 763. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13060763
Nguyen HT, Phan LK, Huynh K-LV, Duong T-H, Le HT, Hai-Yen NT, Yen NTH, Long NP, Nguyen MD. Untargeted Metabolomics Approach for the Differentiation between Panax vietnamensis var. vietnamensis and Panax vietnamensis var. fuscidiscus. Metabolites. 2023; 13(6):763. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13060763
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Huy Truong, Long Ke Phan, Kim-Long Vu Huynh, Thuc-Huy Duong, Huong Thuy Le, Nguyen Trang Hai-Yen, Nguyen Thi Hai Yen, Nguyen Phuoc Long, and Minh Duc Nguyen. 2023. "Untargeted Metabolomics Approach for the Differentiation between Panax vietnamensis var. vietnamensis and Panax vietnamensis var. fuscidiscus" Metabolites 13, no. 6: 763. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13060763
APA StyleNguyen, H. T., Phan, L. K., Huynh, K.-L. V., Duong, T.-H., Le, H. T., Hai-Yen, N. T., Yen, N. T. H., Long, N. P., & Nguyen, M. D. (2023). Untargeted Metabolomics Approach for the Differentiation between Panax vietnamensis var. vietnamensis and Panax vietnamensis var. fuscidiscus. Metabolites, 13(6), 763. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13060763









