Optimization Strategies for Mass Spectrometry-Based Untargeted Metabolomics Analysis of Small Polar Molecules in Human Plasma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Materials
2.2. Plasma Sample Preparation
2.3. HILIC Chromatography
2.4. Detection and Electrospray Ionization
2.5. Orbitrap-Based Mass Spectrometry Experiment
2.6. Computational Analysis of MS Data
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Reconstitution Solvent
- Total number of features found in MS OT.
- Distribution of elution features over the retention time.
- Number of matches with mzCloud Best Match score >80%.
- Visual evaluation of the peak shapes associated with the compounds expected to be identified in human plasma.
- Summed ion intensities.
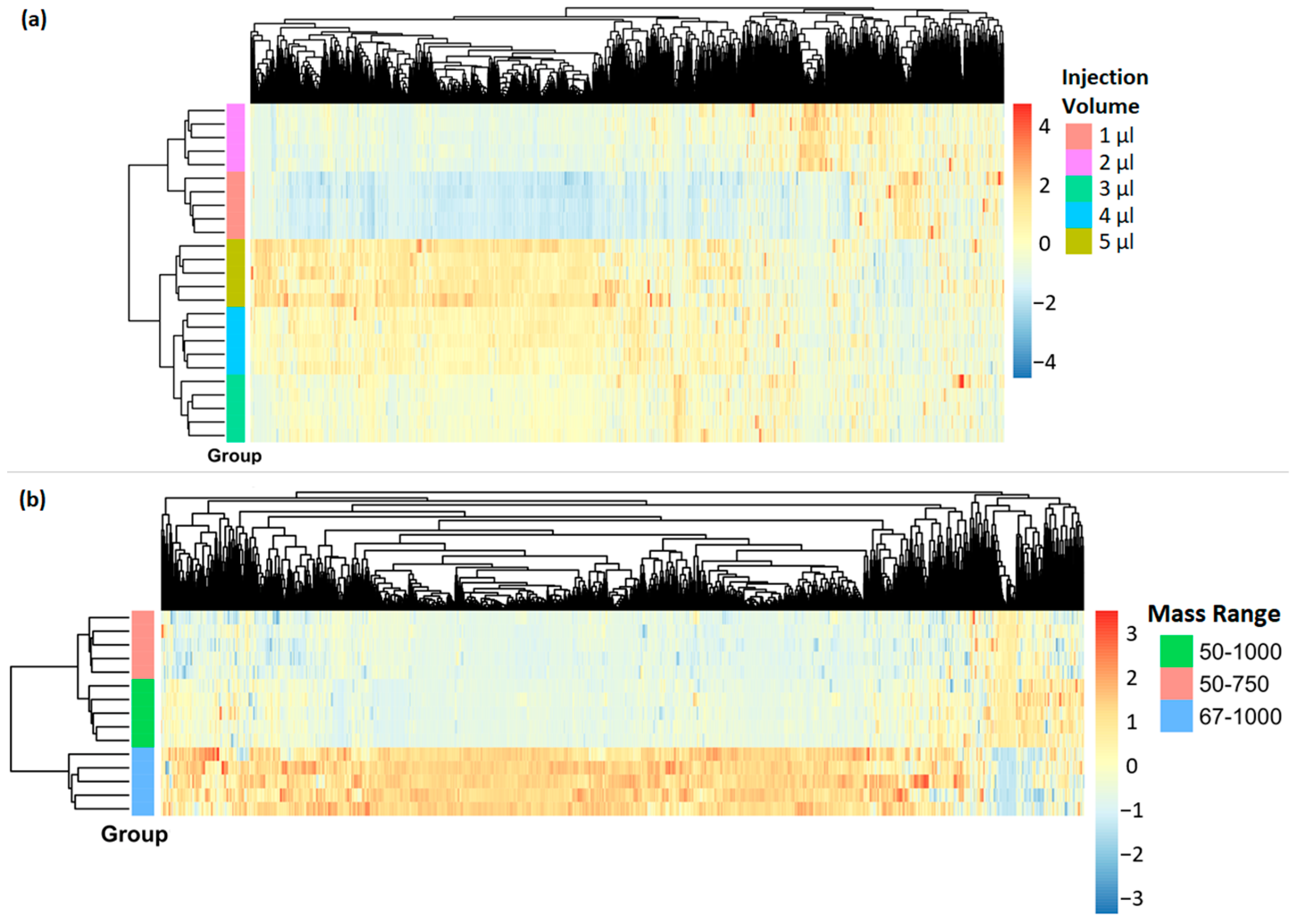
3.2. Injection Volume
- Total number of features found in MS OT.
- The number of common features in MS OT per group having the highest response (area under the peak) among all five injection volume groups.
3.3. Mass Range
3.4. Number of ddMS2 OT HCD Scans
- Total number of features found in MS OT.
- Number of matches with mzCloud Best Match score > 80%.
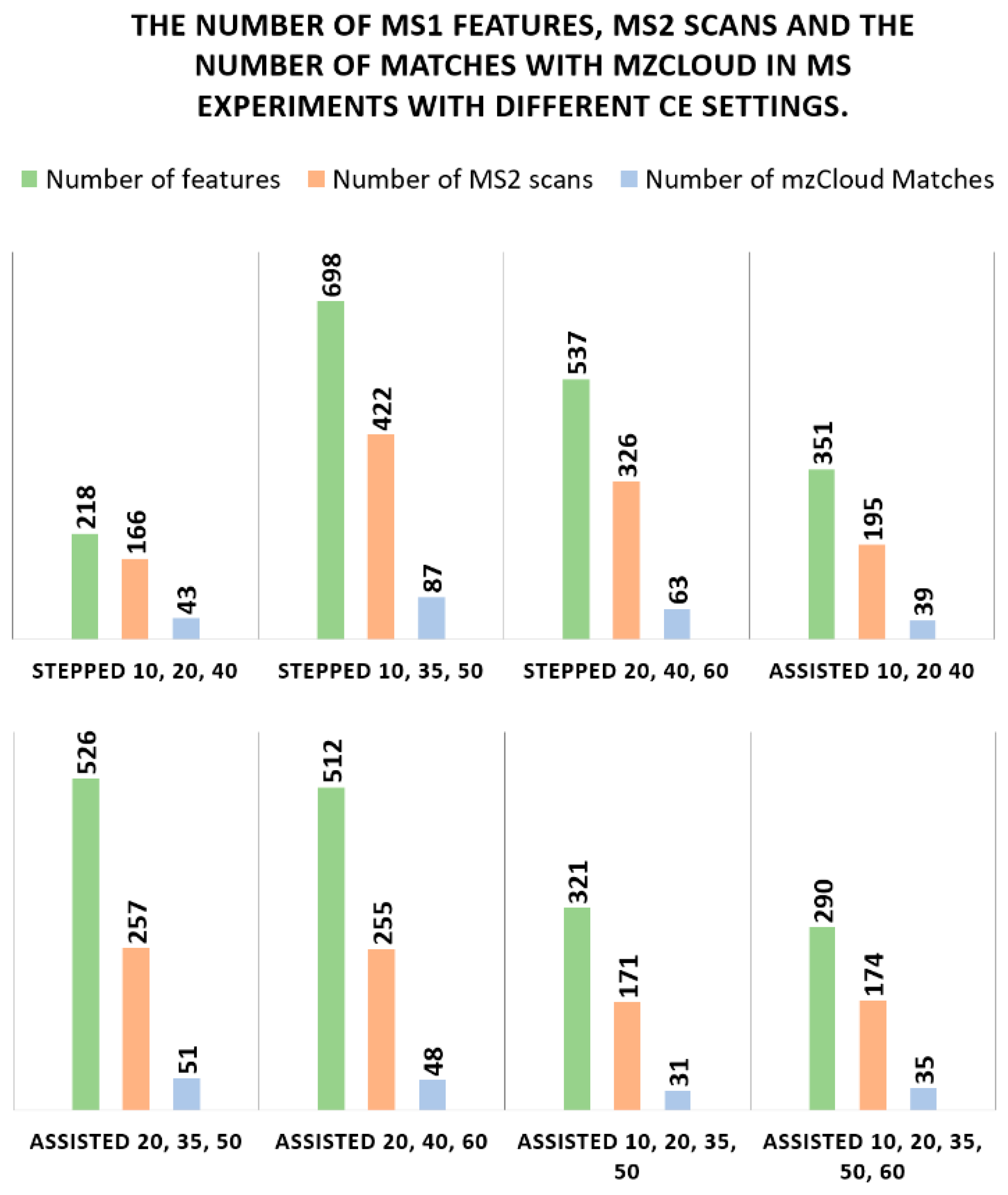
3.5. Collision Energy (CE) Mode
- Stepped CE 10, 20, 40
- Stepped CE 10, 35, 50
- Stepped CE 20, 40, 60
- Assisted CE 10, 20 40
- Assisted CE 20, 35, 50
- Assisted CE 20, 40, 60
- Assisted CE 10, 20, 35, 50
- Assisted CE 10, 20, 35, 50, 60
- The number of features found in MS OT.
- The number of unique MS2 scans.
- The number of matches with mzCloud Best Match score > 80%.
3.6. Dynamic Exclusion Time
3.7. Mass Resolution of Scan Event
- Number of features found in MS OT.
- Number of unique MS2 scans.
- Number of matches with mzCloud Best Match score > 80%.
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Patti, G.J.; Yanes, O.; Siuzdak, G. Metabolomics: The apogee of the omics trilogy. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 13, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roca, M.; Alcoriza, M.I.; Garcia-Cañaveras, J.C.; Lahoz, A. Reviewing the metabolome coverage provided by LC-MS: Focus on sample preparation and chromatography-A tutorial. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1147, 38–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, L.D.; Souza, A.L.; Gerszten, R.E.; Clish, C.B. Targeted Metabolomics. Curr. Protoc. Mol. Biol. 2012, 98, 30.2.1–30.2.23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinayavekhin, N.; Saghatelian, A. Untargeted Metabolomics. In Current Protocols in Molecular Biology; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelli, V.; Belardo, A.; Timperio, A.M. From Targeted Quantification to Untargeted Metabolomics. In Metabolomics—Methodology and Applications in Medical Sciences and Life Sciences; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhu, X.; Wang, C.; Zhang, H.; Cai, Z. Non-targeted and targeted metabolomics approaches to diagnosing lung cancer and predicting patient prognosis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 63437–63448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vaniya, A.; Fiehn, O. Using fragmentation trees and mass spectral trees for identifying unknown compounds in metabolomics. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2015, 69, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, J.C.; Edwards, A.V.G.; Verano-Braga, T.; Schwämmle, V.; Kjeldsen, F.; Jensen, O.N.; Larsen, M.R. High-performance hybrid Orbitrap mass spectrometers for quantitative proteome analysis: Observations and implications. Proteomics 2016, 16, 907–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.H.; Kraus, W.E.; Newgard, C.B. Metabolomic Profiling for the Identification of Novel Biomarkers and Mechanisms Related to Common Cardiovascular Diseases. Circulation 2012, 126, 1110–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cubbon, S.; Antonio, C.; Wilson, J.; Thomas-Oates, J. Metabolomic applications of HILIC-LC-MS. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2010, 29, 671–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.-Q.; Zou, L.; Yin, X.-X.; Ong, C.N. HILIC-MS for metabolomics: An attractive and complementary approach to RPLC-MS. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2016, 35, 574–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morán-Garrido, M.; Muñoz-Escudero, P.; García-Álvarez, A.; García-Lunar, I.; Barbas, C.; Sáiz, J. Optimization of sample extraction and injection-related parameters in HILIC performance for polar metabolite analysis. Application to the study of a model of pulmonary hypertension. J. Chromatogr. A 2022, 1685, 463626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spagou, K.; Tsoukali, H.; Raikos, N.; Gika, H.; Wilson, I.D.; Theodoridis, G. Hydrophilic interaction chromatography coupled to MS for metabonomic/metabolomic studies. J. Sep. Sci. 2010, 33, 716–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, J.; Van Der Velpen, V.; Teav, T.; Guitton, Y.; Gallart-Ayala, H.; Ivanisevic, J. Single-Step Extraction Coupled with Targeted HILIC-MS/MS Approach for Comprehensive Analysis of Human Plasma Lipidome and Polar Metabolome. Metabolites 2020, 10, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, D.K.; Iles, R.K. HILIC-MS-based shotgun metabolomic profiling of maternal urine at 9–23 weeks of gestation—Establishing the baseline changes in the maternal metabolome. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2015, 29, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Røst, L.M.; Shafaei, A.; Fuchino, K.; Bruheim, P. Zwitterionic HILIC tandem mass spectrometry with isotope dilution for rapid, sensitive and robust quantification of pyridine nucleotides in biological extracts. J. Chromatogr. B 2020, 1144, 122078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virgiliou, C.; Sampsonidis, I.; Gika, H.G.; Raikos, N.; Theodoridis, G.A. Development and validation of a HILIC-MS/MS multitargeted method for metabolomics applications. Electrophoresis 2015, 36, 2215–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanisevic, J.; Zhu, Z.-J.; Plate, L.; Tautenhahn, R.; Chen, S.; O’brien, P.J.; Johnson, C.H.; Marletta, M.A.; Patti, G.J.; Siuzdak, G. Toward ‘Omic Scale Metabolite Profiling: A Dual Separation–Mass Spectrometry Approach for Coverage of Lipid and Central Carbon Metabolism. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 6876–6884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Periat, A.; Boccard, J.; Veuthey, J.-L.; Rudaz, S.; Guillarme, D. Systematic comparison of sensitivity between hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography and reversed phase liquid chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1312, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Southam, A.D.; Haglington, L.D.; Najdekr, L.; Jankevics, A.; Weber, R.J.M.; Dunn, W.B. Assessment of human plasma and urine sample preparation for reproducible and high-throughput UHPLC-MS clinical metabolic phenotyping. Analyst 2020, 145, 6511–6523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, G.F.; Lynn, F.; Meade, B.D. Use of Coefficient of Variation in Assessing Variability of Quantitative Assays. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2002, 9, 1235–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Liu, C.; Zhao, L.; Xu, D.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Q.; Cabooter, D.; Jiang, Z. A systematic investigation of the effect of sample solvent on peak shape in nano- and microflow hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography columns. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1655, 462498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fall, F.; Lenuzza, N.; Lamy, E.; Brollo, M.; Naline, E.; Devillier, P.; Thévenot, E.; Grassin-Delyle, S. A split-range acquisition method for the non-targeted metabolomic profiling of human plasma with hydrophilic interaction chromatography—High-resolution mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2019, 1128, 121780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madala, N.E.; Steenkamp, P.A.; Piater, L.A.; Dubery, I.A. Collision energy alteration during mass spectrometric acquisition is essential to ensure unbiased metabolomic analysis. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 404, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohli, B.M.; Eng, J.K.; Nitsch, R.M.; Konietzko, U. An alternative sampling algorithm for use in liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry experiments. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2005, 19, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodge, K.; Have, S.T.; Hutton, L.; Lamond, A.I. Cleaning up the masses: Exclusion lists to reduce contamination with HPLC-MS/MS. J. Proteom. 2013, 88, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murray, K.K.; Boyd, R.K.; Eberlin, M.N.; Langley, G.J.; Li, L.; Naito, Y. Definitions of terms relating to mass spectrometry (IUPAC Recommendations 2013). Pure Appl. Chem. 2013, 85, 1515–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Makarov, A.; Denisov, E.; Kholomeev, A.; Balschun, W.; Lange, O.; Strupat, K.; Horning, S. Performance Evaluation of a Hybrid Linear Ion Trap/Orbitrap Mass Spectrometer. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 2113–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardman, M.; Makarov, A.A. Interfacing the Orbitrap Mass Analyzer to an Electrospray Ion Source. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 1699–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Time (min) | Mobile Phase Composition (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| A | B | |
| Initial | 99 | 1 |
| 1 | 99 | 1 |
| 3 | 85 | 15 |
| 6 | 50 | 50 |
| 9 | 5 | 95 |
| 10 | 5 | 95 |
| 10.5 | 99 | 1 |
| 15 | 99 | 1 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Reconstitution Solvent, Acetonitrile/Water Mass Range | 80:20 (v/v) |
| 67–1000 m/z | |
| RF Lens Amplitude | 35% |
| Injection Volume | 5 µL |
| Number of ddMS2 OT HCD Scans per Cycle | 8 |
| HCD Collision Energy Mode (normalized) | Stepped 20, 40, 60% |
| Dynamic Exclusion Time | 2.5 s |
| MS OT Resolution | 60 k |
| Intensity Threshold | 2.0 e4 |
| ddMS2 Resolution | 30 k |
| MS OT Normalized Automatic Gain Control (AGC) Target | 100% |
| MS OT Maximum Injection Time (custom) | 50 ms |
| ddMS2 OT Normalized AGC Target | 50% |
| Maximum Injection Time (custom) | 54 ms |
| Reconstitution Solvent Composition (Acetonitrile:Water) | Number of Features (MS OT) | Number of mzCloud Matches | Summed Ion Intensities |
|---|---|---|---|
| 60:40 | 781 | 97 | 1.13 E + 10 |
| 70:30 | 736 | 105 | 1.37 E + 10 |
| 80:20 | 795 | 103 | 1.14 E + 10 |
| 90:10 | 872 | 86 | 9.97 E + 10 |
| Number of ddMS2 OT HCD Per Cycle | Number of Features (MS OT) | Number of mzCloud Matches |
|---|---|---|
| 7 | 732 | 90 |
| 8 | 755 | 101 |
| 9 | 713 | 100 |
| 10 | 735 | 104 |
| 12 | 621 | 93 |
| Resolution | Number of Features | Number of Unique MS2 | Number of mzCloud Matches | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full MS | MS2 | |||
| 120 k | 30 k | 840 | 466 | 105 |
| 120 k | 15 k | 896 | 509 | 103 |
| 60 k | 30 k | 775 | 445 | 99 |
| 60 k | 15 k | 808 | 506 | 107 |
| 50 k | 30 k | 723 | 445 | 93 |
| 50 k | 15 k | 744 | 504 | 101 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Reconstitution solvent composition, Acetonitrile/Water | 70:30 (v/v) |
| Injection Volume | 5 µL |
| Mass range | 67–1000 m/z |
| Number of ddMS2 OT HCD scans per cycle | 8 |
| HCD Collision Energy Mode (normalized) | Stepped 10, 35, 50% |
| Dynamic Exclusion Time | 2.5 |
| MS OT Resolution | 120 k |
| ddMS2 Resolution | 15 k |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kaczmarek, M.; Zhang, N.; Buzhansky, L.; Gilead, S.; Gazit, E. Optimization Strategies for Mass Spectrometry-Based Untargeted Metabolomics Analysis of Small Polar Molecules in Human Plasma. Metabolites 2023, 13, 923. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13080923
Kaczmarek M, Zhang N, Buzhansky L, Gilead S, Gazit E. Optimization Strategies for Mass Spectrometry-Based Untargeted Metabolomics Analysis of Small Polar Molecules in Human Plasma. Metabolites. 2023; 13(8):923. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13080923
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaczmarek, Michał, Nanyun Zhang, Ludmila Buzhansky, Sharon Gilead, and Ehud Gazit. 2023. "Optimization Strategies for Mass Spectrometry-Based Untargeted Metabolomics Analysis of Small Polar Molecules in Human Plasma" Metabolites 13, no. 8: 923. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13080923
APA StyleKaczmarek, M., Zhang, N., Buzhansky, L., Gilead, S., & Gazit, E. (2023). Optimization Strategies for Mass Spectrometry-Based Untargeted Metabolomics Analysis of Small Polar Molecules in Human Plasma. Metabolites, 13(8), 923. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13080923






