Profiling of Metabolome in the Plasma Following a circH19 Knockdown Intervention in Diet-Induced Obese Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Animal Treatments
2.2. Adenovirus Knockdown
2.3. Biochemical Indicator Test
2.4. RNA Extraction and qRT-PCR Assay
2.5. Metabolite Extraction
2.6. Non-Targeted Metabolomics Analysis
2.7. Data Processing and Metabolite Identification
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. CircH19 Knockdown Can Alleviate Lipid Metabolism Disorder in Obese Mice
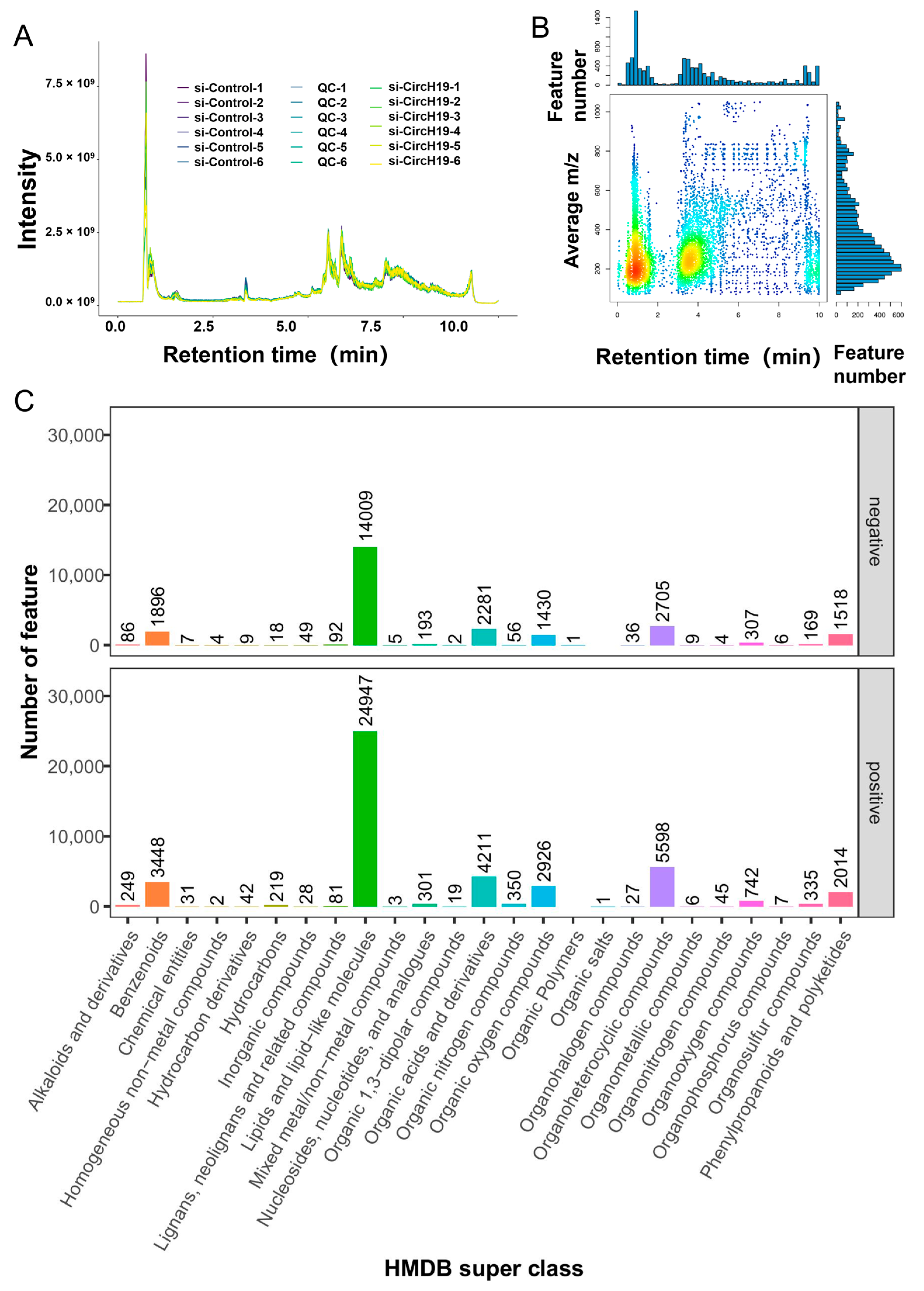
3.2. Metabolite Detection Quality Control and Metabolite Identification and Quantification
3.3. Effect of circH19 Knockdown on Metabolic Profiles in Obese Mice
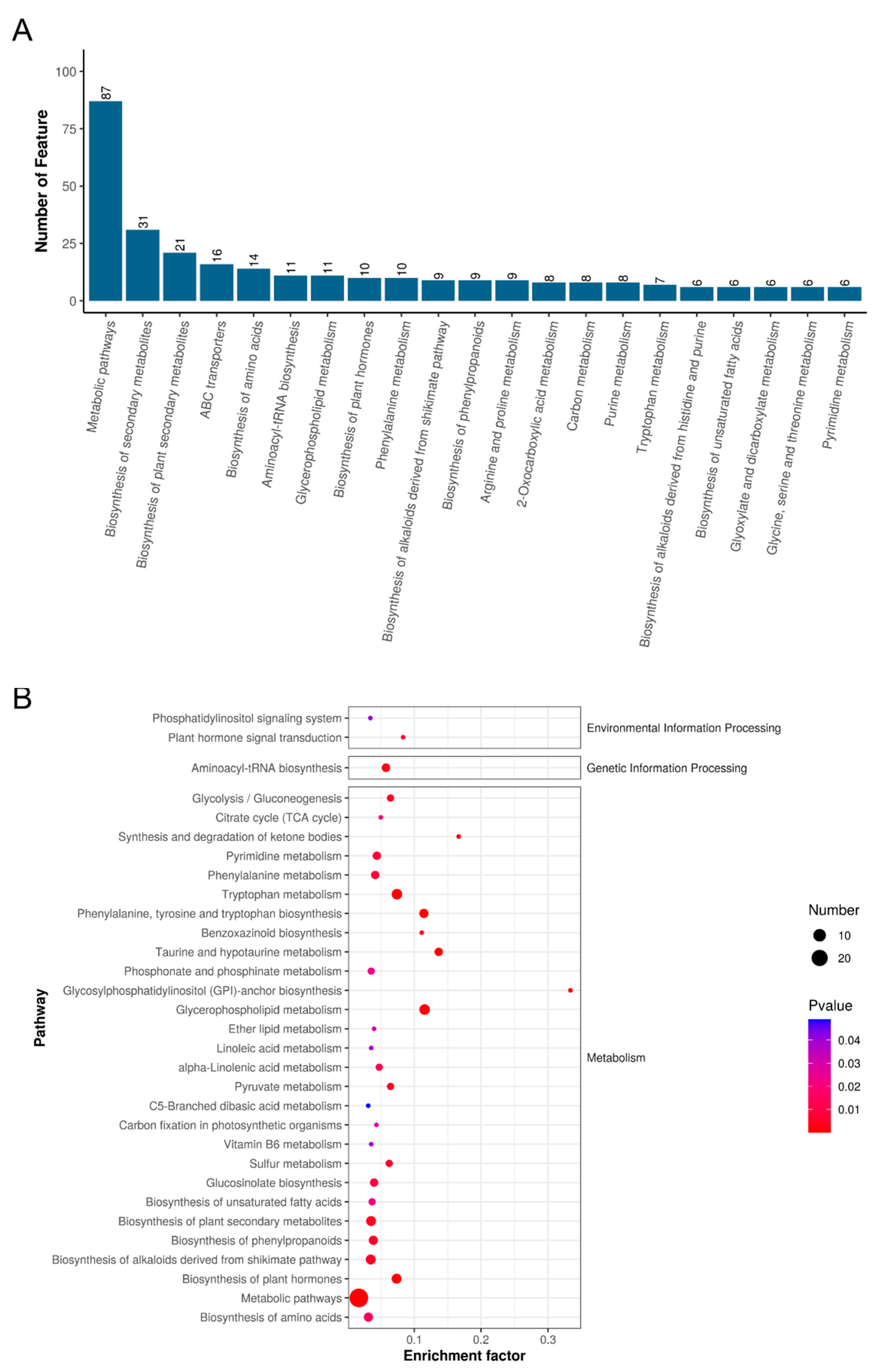
3.4. Impact of circH19 Knockdown on Metabolic Function and Pathway Analysis in Obese Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, X.; Li, H. Obesity: Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, and Therapeutics. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 706978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payab, M.; Tayanloo-Beik, A.; Falahzadeh, K.; Mousavi, M.; Salehi, S.; Djalalinia, S.; Ebrahimpur, M.; Rezaei, N.; Rezaei-Tavirani, M.; Larijani, B.; et al. Metabolomics prospect of obesity and metabolic syndrome; a systematic review. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2022, 21, 889–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafiee, A.; Nakhaee, Z.; Bahri, R.A.; Amini, M.J.; Salehi, A.; Jafarabady, K.; Seighali, N.; Rashidian, P.; Fathi, H.; Abianeh, F.E.; et al. Global prevalence of obesity and overweight among medical students: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Public Health 2024, 24, 1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tang, B.; Long, L.; Luo, P.; Xiang, W.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; Jiang, Q.; Tan, X.; Luo, S.; et al. Improvement of obesity-associated disorders by a small-molecule drug targeting mitochondria of adipose tissue macrophages. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avelino, T.M.; Provencio, M.G.-A.; Peroni, L.A.; Domingues, R.R.; Torres, F.R.; de Oliveira, P.S.L.; Leme, A.F.P.; Figueira, A.C.M. Improving obesity research: Unveiling metabolic pathways through a 3D In vitro model of adipocytes using 3T3-L1 cells. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0303612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.X.; Chen, L.L. Circular RNAs: Characterization, cellular roles, and applications. Cell 2022, 185, 2016–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.L. The expanding regulatory mechanisms and cellular functions of circular RNAs. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 475–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glažar, P.; Papavasileiou, P.; Rajewsky, N. circBase: A database for circular RNAs. RNA 2014, 20, 1666–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gui, W.; Zhu, W.F.; Zhu, Y.; Tang, S.; Zheng, F.; Yin, X.; Lin, X.; Li, H. LncRNAH19 improves insulin resistance in skeletal muscle by regulating heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1. Cell Commun. Signal. 2020, 18, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Gui, W.; Lin, X.; Li, H. Knock-down of circular RNA H19 induces human adipose-derived stem cells adipogenic differentiation via a mechanism involving the polypyrimidine tract-binding protein 1. Exp. Cell Res. 2020, 387, 111753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottosson, F.; Smith, E.; Ericson, U.; Brunkwall, L.; Orho-Melander, M.; Di Somma, S.; Antonini, P.; Nilsson, P.M.; Fernandez, C.; Melander, O. Metabolome-Defined Obesity and the Risk of Future Type 2 Diabetes and Mortality. Diabetes Care 2022, 45, 1260–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teruya, T.; Sunagawa, S.; Mori, A.; Masuzaki, H.; Yanagida, M. Markers for obese and non-obese Type 2 diabetes identified using whole blood metabolomics. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cirulli, E.T.; Guo, L.; Swisher, C.L.; Shah, N.; Huang, L.; Napier, L.A.; Kirkness, E.F.; Spector, T.D.; Caskey, C.T.; Thorens, B.; et al. Profound Perturbation of the Metabolome in Obesity Is Associated with Health Risk. Cell Metab. 2019, 29, 488–500.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, P.; Parks, R.J.; Cummings, D.T.; Evelegh, C.M.; Graham, F.L. An enhanced system for construction of adenoviral vectors by the two-plasmid rescue method. Hum. Gene Ther. 2000, 11, 693–699. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Zhang, X.; Deng, Y.; Cui, Q.; Zhu, J.; Ren, H.; Liu, Y.; Hu, X.; Zuo, J.; Peng, Y. Regulatory roles of circRNAs in adipogenesis and lipid metabolism: Emerging insights into lipid-related diseases. FEBS J. 2021, 288, 3663–3682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, M.P.; Shryack, G.; Alessi, I.; Wieschhaus, N.; Meers, G.M.; Johnson, S.A.; Wheeler, A.A.; Ibdah, J.A.; Parks, E.J.; Rector, R.S. Relationship between serum β-hydroxybutyrate hepatic fatty acid oxidation in individuals with obesity, NAFLD. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 326, E493–E502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Xu, X.; Yang, L.; Cai, Y.; Sun, Y.; Guo, J.; Lin, Y.; Hu, Y.; Chen, M.; Li, H.; et al. Exploring the association between circRNA expression and pediatric obesity based on a case-control study and related bioinformatics analysis. BMC Pediatr. 2023, 23, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, X.; Miao, R.; Wei, J.; Wu, H.; Tian, J. Advances in multi-omics study of biomarkers of glycolipid metabolism disorder. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2022, 20, 5935–5951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Yerena, A.; Domínguez-López, I.; Vallverdú-Queralt, A.; Pérez, M.; Jáuregui, O.; Escribano-Ferrer, E.; Lamuela-Raventós, R.M. Metabolomics Technologies for the Identification and Quantification of Dietary Phenolic Compound Metabolites: An Overview. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heaney, L.M.; Deighton, K.; Suzuki, T. Non-targeted metabolomics in sport and exercise science. J. Sports Sci. 2019, 37, 959–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guasch-Ferré, M.; Santos, J.L.; Martínez-González, M.A.; Clish, C.B.; Razquin, C.; Wang, D.; Liang, L.; Li, J.; Dennis, C.; Corella, D.; et al. Glycolysis/gluconeogenesis- and tricarboxylic acid cycle-related metabolites, Mediterranean diet, and type 2 diabetes. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 111, 835–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Veen, J.N.; Kennelly, J.P.; Wan, S.; Vance, J.E.; Vance, D.E.; Jacobs, R.L. The critical role of phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylethanolamine metabolism in health and disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2017, 1859, 1558–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravaut, G.; Légiot, A.; Bergeron, K.F.; Mounier, C. Monounsaturated Fatty Acids in Obesity-Related Inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 22, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Choi, J.; Alpergin, E.S.S.; Zhao, L.; Hartung, T.; Scafidi, S.; Riddle, R.C.; Wolfgang, M.J. Loss of Hepatic Mitochondrial Long-Chain Fatty Acid Oxidation Confers Resistance to Diet-Induced Obesity and Glucose Intolerance. Cell Rep. 2017, 20, 655–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huan, C.; Wang, M.; Song, Y.; Jia, Z.; Wei, D.; Wang, L.; Xu, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhao, M.; Geng, J.; et al. Inflammatory markers and androstenedione modify the effect of serum testosterone on obesity among men: Findings from a Chinese population. Andrology 2024, 12, 850–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, H.; Shi, D.; Gui, W.; Lin, X.; Chen, J.; Yu, W. Profiling of Metabolome in the Plasma Following a circH19 Knockdown Intervention in Diet-Induced Obese Mice. Metabolites 2024, 14, 603. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14110603
Zhao H, Shi D, Gui W, Lin X, Chen J, Yu W. Profiling of Metabolome in the Plasma Following a circH19 Knockdown Intervention in Diet-Induced Obese Mice. Metabolites. 2024; 14(11):603. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14110603
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Hanxin, Dike Shi, Weiwei Gui, Xihua Lin, Jionghuang Chen, and Weihua Yu. 2024. "Profiling of Metabolome in the Plasma Following a circH19 Knockdown Intervention in Diet-Induced Obese Mice" Metabolites 14, no. 11: 603. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14110603
APA StyleZhao, H., Shi, D., Gui, W., Lin, X., Chen, J., & Yu, W. (2024). Profiling of Metabolome in the Plasma Following a circH19 Knockdown Intervention in Diet-Induced Obese Mice. Metabolites, 14(11), 603. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14110603




