Effects of a High Trans Fatty Acid Diet on Kidney-, Liver-, and Heart-Associated Diseases in a Rabbit Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. FT-IR Analysis of Samples
2.3. Animal Maintenance and Treatment Groups
2.4. Measuring Physical Parameters
2.5. Dissection, Blood Collection, and Tissue Preparation
2.6. Biochemical Assays for Liver, Heart, and Kidney
2.7. Antioxidant Markers for Liver and Kidney
2.8. HPLC Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Elaidic Acid in Food Samples
3.2. Physical Parameters
3.3. Elaidic Acid in Blood Samples
3.4. Determination of Biomarkers in Serum
3.5. Determination of Antioxidant Enzymes
3.6. HPLC Analysis of Serum
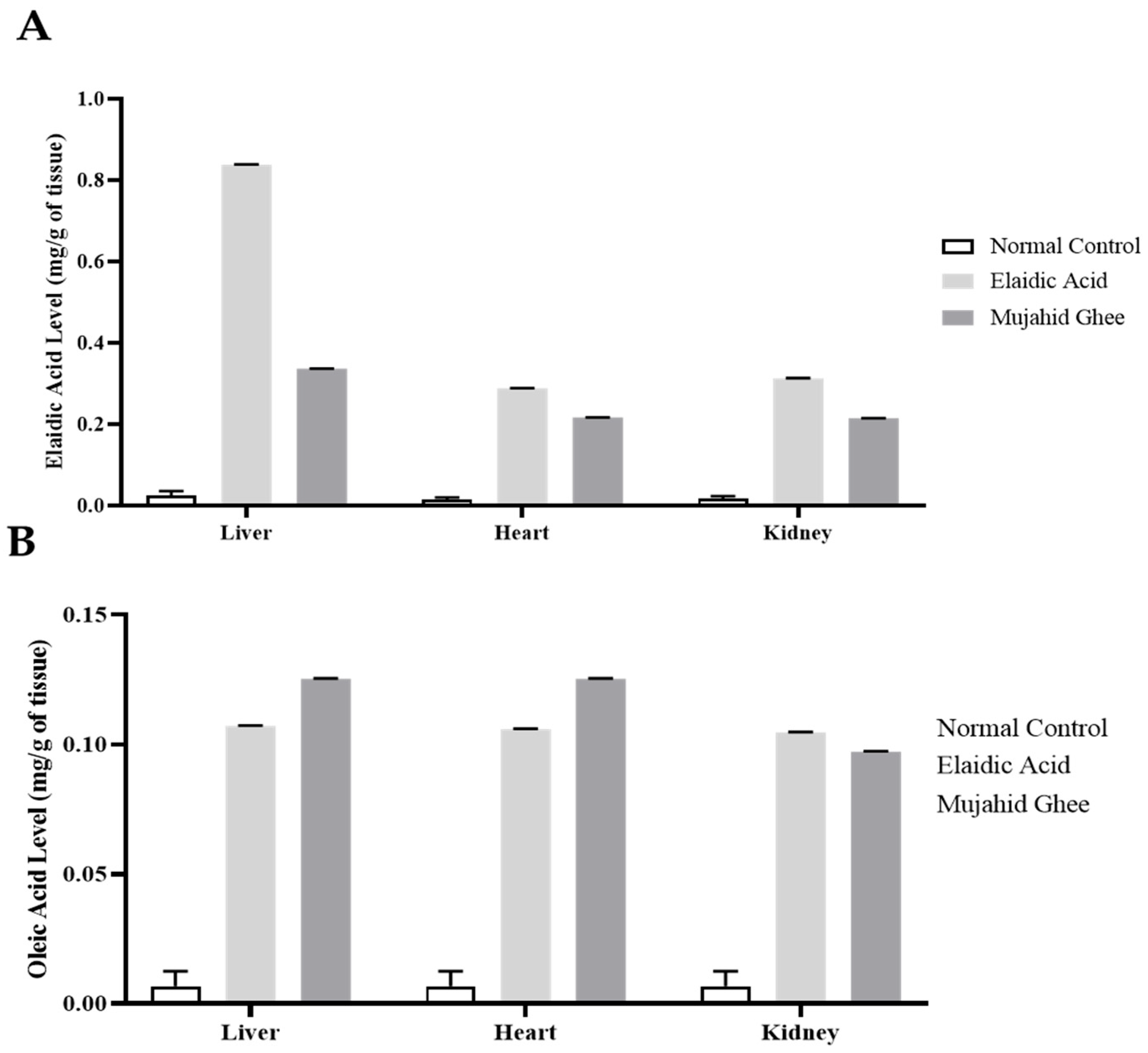
3.7. HPLC Analysis of Organ Tissue
3.8. Histopathology of Organ Tissues
3.9. Comparison of Oleic Acid and Elaidic Acid
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ohmori, H.; Fujii, K.; Kadochi, Y.; Mori, S.; Nishiguchi, Y.; Fujiwara, R.; Kishi, S.; Sasaki, T.; Kuniyasu, H. Elaidic acid, a trans-fatty acid, enhances the metastasis of colorectal cancer cells. Pathobiology 2017, 84, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, Y. Effect of trans–fatty acids on lipid metabolism: Mechanisms for their adverse health effects. Food Rev. Int. 2016, 32, 323–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, R.R.; Collier, R.J.; Preedy, V.R. Nutrients in Dairy and Their Implications for Health and Disease; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kiralan, M.; Ketenoglu, O.; Kiralan, S.S. Chapter 10—Trans fatty acids—Occurrence, technical aspects, and worldwide regulations. In Studies in Natural Products Chemistry; Atta ur, R., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; Volume 70, pp. 313–343. [Google Scholar]
- Khanal, R.C.; Dhiman, T.R. Biosynthesis of conjugated linoleic acid (CLA): A review. Pak. J. Nutr. 2004, 3, 72–81. [Google Scholar]
- Wallace, S.K.; Mozaffarian, D. Trans-fatty acids and nonlipid risk factors. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2009, 11, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Targher, G.; Byrne, C.D. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: An emerging driving force in chronic kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2017, 13, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amarapurkar, D.; Kamani, P.; Patel, N.; Gupte, P.; Kumar, P.; Agal, S.; Baijal, R.; Lala, S.; Chaudhary, D.; Deshpande, A. Prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Population based study. Ann. Hepatol. 2007, 6, 161–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchisello, S.; Di Pino, A.; Scicali, R.; Urbano, F.; Piro, S.; Purrello, F.; Rabuazzo, A.M. Pathophysiological, molecular and therapeutic issues of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: An overview. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauter, A.M. Metabolic Significance of Systemic DHA Deficiency. Doctoral Thesis, Department of Molecular Biosciences, The Wenner-Gren Institute, Stockholm, Sweden, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Donnelly, K.L.; Smith, C.I.; Schwarzenberg, S.J.; Jessurun, J.; Boldt, M.D.; Parks, E.J. Sources of fatty acids stored in liver and secreted via lipoproteins in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 1343–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsoddini, A.; Sobhani, V.; Chehreh, M.E.G.; Alavian, S.M.; Zaree, A. Effect of aerobic and resistance exercise training on liver enzymes and hepatic fat in Iranian men with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepat. Mon. 2015, 15, e31434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merrell, M.D.; Cherrington, N.J. Drug metabolism alterations in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Drug Metab. Rev. 2011, 43, 317–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estadella, D.; Oyama, L.M.; Ribeiro, E.B.; Damaso, A.R.; de Piano, A. Lipotoxicity: Effects of dietary saturated and transfatty acids. Mediat. Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 137579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhibi, M.; Brahmi, F.; Mnari, A.; Houas, Z.; Chargui, I.; Bchir, L.; Gazzah, N.; Alsaif, M.A.; Hammami, M. The intake of high fat diet with different trans fatty acid levels differentially induces oxidative stress and non alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in rats. Nutr. Metab. 2011, 8, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canbay, A.; Sowa, J.-P.; Syn, W.-K.; Treckmann, J. NASH cirrhosis-the new burden in liver transplantation: How should it be managed? Visc. Med. 2016, 32, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikolasevic, I.; Milic, S.; Wensveen, T.T.; Grgic, I.; Jakopcic, I.; Stimac, D.; Wensveen, F.; Orlic, L. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-A multisystem disease? World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 9488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dongiovanni, P.; Paolini, E.; Corsini, A.; Sirtori, C.R.; Ruscica, M. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease or metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease diagnoses and cardiovascular diseases: From epidemiology to drug approaches. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 51, e13519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musso, G.; Cassader, M.; Cohney, S.; Pinach, S.; Saba, F.; Gambino, R. Emerging liver–kidney interactions in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Trends Mol. Med. 2015, 21, 645–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcuccilli, M.; Chonchol, M. NAFLD and chronic kidney disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, W.; Wu, W.; Wen, W.; Xu, F.; Han, D.; Lyu, J.; Huang, Y. Association of NAFLD with cardiovascular disease and all-cause mortality: A large-scale prospective cohort study based on UK Biobank. Ther. Adv. Chronic Dis. 2022, 13, 20406223221122478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, L.A.; Anstee, Q.M.; Tilg, H.; Targher, G. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and its relationship with cardiovascular disease and other extrahepatic diseases. Gut 2017, 66, 1138–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanova, M.; Younossi, Z.M. Independent association between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and cardiovascular disease in the US population. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 10, 646–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.Y.; Fan, J.G. Incidence of chronic kidney disease in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 214–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pipoyan, D.; Stepanyan, S.; Stepanyan, S.; Beglaryan, M.; Costantini, L.; Molinari, R.; Merendino, N. The effect of trans fatty acids on human health: Regulation and consumption patterns. Foods 2021, 10, 2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suleman, R.; Wang, Z.; Aadil, R.M.; Hui, T.; Hopkins, D.L.; Zhang, D. Effect of cooking on the nutritive quality, sensory properties and safety of lamb meat: Current challenges and future prospects. Meat Sci. 2020, 167, 108172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherazi, S.T.H.; Kandhro, A.; Mahesar, S.A.; Bhanger, M.I.; Talpur, M.Y.; Arain, S. Application of transmission FT-IR spectroscopy for the trans fat determination in the industrially processed edible oils. Food Chem. 2009, 114, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parasuraman, S.; Raveendran, R.; Kesavan, R. Blood sample collection in small laboratory animals. J. Pharmacol. Pharmacother. 2010, 1, 87. [Google Scholar]
- Bradley, M.P.; Doerning, C.M.; Nowland, M.H.; Lester, P.A. Intramuscular administration of alfaxalone alone and in combination for sedation and anesthesia of rabbits (Oryctolagus cuniculus). J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2019, 58, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahreen, S.; Khan, M.R.; Khan, R.A. Hepatoprotective effects of methanol extract of Carissa opaca leaves on CCl 4-induced damage in rat. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2011, 11, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashmi, W.J.; Ismail, H.; Mehmood, F.; Mirza, B. Neuroprotective, antidiabetic and antioxidant effect of Hedera nepalensis and lupeol against STZ+ AlCl3 induced rats model. DARU J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 26, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannister, J.V.; Calabrese, L. Assays for superoxide dismutase. Methods Biochem. Anal. 1987, 32, 279–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beier, R.C.; Feldman, S.F.; Dutko, T.J.; Petersen, H.D.; Stanker, L.H. Immunoassay and HPLC detection of halofuginone in chicken liver samples obtained from commercial slaughterhouses: A combined study. Food Agric. Immunol. 2002, 14, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pena-Serna, C.; Gomez-Rami, B.; Zapata-Lop, N. Nutritional Aspects of Ghee Based on Lipid Composition. Pak. J. Nutr. 2019, 18, 1107–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitale, S.; Palumbo, E.; Polesel, J.; Hebert, J.R.; Shivappa, N.; Montagnese, C.; Porciello, G.; Calabrese, I.; Luongo, A.; Prete, M. One-year nutrition counselling in the context of a Mediterranean diet reduced the dietary inflammatory index in women with breast cancer: A role for the dietary glycemic index. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 1560–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavanagh, K.; Sajadian, S.; Jenkins, K.A.; Wilson, M.D.; Carr, J.J.; Wagner, J.D.; Rudel, L.L. Neonatal and fetal exposure to trans-fatty acids retards early growth and adiposity while adversely affecting glucose in mice. Nutr. Res. 2010, 30, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wei, J.; Ren, G.; Zhang, C.; Zheng, Z.; Fan, C. BiOBr-photocatalyzed cis–trans isomerization of 9-octadecenoic acids in different atmospheres. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2019, 9, 3380–3387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozaffarian, D.; Katan Martijn, B.; Ascherio, A.; Stampfer Meir, J.; Willett Walter, C. Trans Fatty Acids and Cardiovascular Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 1601–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baer, D.J.; Judd, J.T.; Clevidence, B.A.; Tracy, R.P. Dietary fatty acids affect plasma markers of inflammation in healthy men fed controlled diets: A randomized crossover study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 79, 969–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Li, D.; Song, X.; Liu, F.; Wang, X.; Ma, Q.; Zhang, X.; Li, X. Joint associations of serum uric acid and ALT with NAFLD in elderly men and women: A Chinese cross-sectional study. J. Transl. Med. 2018, 16, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhary, A.; Chauhan, V. Lactate dehydrogenase as an indicator of liver diseases. J. Adv. Med. Dent. Sci. Res. 2015, 3, S20. [Google Scholar]
- Prabha, S.; Ansil, P.; Nitha, A.; Wills, P.; Latha, M. Anti-atherogenic activity of methanolic extract of Gardenia gummifera Linn. f. on high fat diet induced atherosclerosis in rats. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 5, 388–393. [Google Scholar]
- Willett, W.C.; Stampfer, M.J.; Manson, J.E.; Colditz, G.A.; Speizer, F.E.; Rosner, B.A.; Hennekens, C.H.; Sampson, L.A. Intake of trans fatty acids and risk of coronary heart disease among women. Lancet 1993, 341, 581–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidya, V.S.; Ferguson, M.A.; Bonventre, J.V. Biomarkers of acute kidney injury. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2008, 48, 463–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, R.J.; Nakagawa, T.; Jalal, D.; Sánchez-Lozada, L.G.; Kang, D.H.; Ritz, E. Uric acid and chronic kidney disease: Which is chasing which? Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2013, 28, 2221–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lichtenstein, A.H. Dietary Trans Fatty Acids and Cardiovascular Disease Risk: Past and Present. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2014, 16, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Judd, S.; Le, A.; Ard, J.; Newsome, B.B.; Howard, G.; Warnock, D.G.; McClellan, W. Associations of dietary fat with albuminuria and kidney dysfunction1234. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 92, 897–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noeman, S.A.; Hamooda, H.E.; Baalash, A.A. Biochemical study of oxidative stress markers in the liver, kidney and heart of high fat diet induced obesity in rats. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2011, 3, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Einollahi, B.; Naghii, M.R.; Sepandi, M. Association of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) with urolithiasis. Endocr. Regul. 2013, 47, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasgupta, A.; Klein, K. Antioxidants in Food, Vitamins and Supplements: Prevention and Treatment of Disease; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, S.K.; Cho, H.W.; Song, S.E.; Song, D.K. Catalase and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Pflüg. Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2018, 470, 1721–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutosławska, G.; Tkaczyk, J.; Panczenko-Kresowska, B.; Hübner-Woźniak, E.; Skierska, E.; Gajewski, A.K. Plasma TBARS, blood GSH concentrations, and erythrocyte antioxidant enzyme activities in regularly menstruating women with ovulatory and anovulatory menstrual cycles. Clin. Chim. Acta 2003, 331, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazidi, M.; Katsiki, N.; Mikhailidis, D.P.; Banach, M. Link between plasma trans-fatty acid and fatty liver is moderated by adiposity. Int. J. Cardiol. 2018, 272, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebauer, S.K.; Psota, T.L.; Kris-Etherton, P.M. The diversity of health effects of individual trans fatty acid isomers. Lipids 2007, 42, 787–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aro, A.; Salminen, I.; Huttunen, J.K.; Kardinaal, A.F.M.; van’t Veer, P.; Kark, J.D.; Riemersma, R.A.; Delgado-Rodriguez, M.; Gomez-Aracena, J.; Kohlmeier, L. Adipose tissue isomeric trans fatty acids and risk of myocardial infarction in nine countries: The EURAMIC study. Lancet 1995, 345, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Tan, H.-Y.; Wang, N.; Zhang, Z.-J.; Lao, L.; Wong, C.-W.; Feng, Y. The Role of Oxidative Stress and Antioxidants in Liver Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 26087–26124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buettner, R.; Parhofer, K.G.; Woenckhaus, M.; Wrede, C.E.; Kunz-Schughart, L.A.; Scholmerich, J.; Bollheimer, L.C. Defining high-fat-diet rat models: Metabolic and molecular effects of different fat types. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2006, 36, 485–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocquelin, G.; Guenot, L.; Astorg, P.O.; David, M. Phospholipid content and fatty acid composition of human heart. Lipids 1989, 24, 775–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrne, C.D.; Targher, G. NAFLD as a driver of chronic kidney disease. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 785–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Shen, C.; Zhu, H.; Wang, C.; Liu, X.; Sun, X.; Han, S.; Wang, P.; Dong, Z.; Ma, X.; et al. Trans-Fatty Acids Aggravate Obesity, Insulin Resistance and Hepatic Steatosis in C57BL/6 Mice, Possibly by Suppressing the IRS1 Dependent Pathway. Molecules 2016, 21, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slaoui, M.; Fiette, L. Histopathology procedures: From tissue sampling to histopathological evaluation. In Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 69–82. [Google Scholar]
- Handayani, D.; Febrianingsih, E.; Desi Kurniawati, A.; Kusumastuty, I.; Nurmalitasari, S.; Widyanto, R.M.; Oktaviani, D.N.; Maghfirotun Innayah, A.; Sulistyowati, E. High-fructose diet initially promotes increased aortic wall thickness, liver steatosis, and cardiac histopathology deterioration, but does not increase body fat index. J. Public Health Res. 2021, 10, jphr-2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henegar, J.R.; Bigler, S.A.; Henegar, L.K.; Tyagi, S.C.; Hall, J.E. Functional and structural changes in the kidney in the early stages of obesity. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2001, 12, 1211–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, J.; de La Fuente, V.G.; García, M.F.; Sánchez, J.G.; Redondo, B.I.; Villar, C.; Lombó, F. A diet based on cured acorn-fed ham with oleic acid content promotes anti-inflammatory gut microbiota and prevents ulcerative colitis in an animal model. Lipids Health Dis. 2020, 19, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutunchi, H.; Ostadrahimi, A.; Saghafi-Asl, M. The effects of diets enriched in monounsaturated oleic acid on the management and prevention of obesity: A systematic review of human intervention studies. Adv. Nutr. 2020, 11, 864–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Liver | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biomarker | Normal Control | Kausar Ghee | Oleic Acid | Elaidic Acid | Mujahid Ghee |
| ALT (IU/L) | 47.71 ± 0.87 | 51.51 ± 0.76 *** | 49.4 ± 0.77 ** | 74.68 ± 0.92 *** | 64.67 ± 0.82 *** |
| AST (IU/L) | 44.51 ± 1.42 | 55.62 ± 0.98 *** | 46.77 ± 0.98 ** | 111.31 ± 1.08 *** | 86.72 ± 1.13 *** |
| ALP (IU/L) | 32.84 ± 1.16 | 47.95 ± 1.08 *** | 34.4 ± 1.30 * | 79.31 ± 0.76 *** | 58.74 ± 1.02 *** |
| LDH (IU/L) | 309.88 ± 1.30 | 313.74 ± 1.26 *** | 311.78 ± 1.09 * | 351.81 ± 0.98 *** | 332.14 ± 1.40 *** |
| Heart | |||||
| CPK (IU/L) | 152.34 ± 0.69 | 160.31 ± 0.67 *** | 155.01 ± 0.97 *** | 253.87 ± 0.9 *** | 210.57 ± 0.87 *** |
| TC (mg/dL) | 48.1 ± 0.77 | 58.01 ± 0.99 *** | 51.31 ± 0.79 *** | 78.45 ± 0.74 *** | 65.64 ± 0.56 *** |
| HDL (mg/dL) | 24.27 ± 0.55 | 21.1 ± 0.64 *** | 26.31 ± 0.79 *** | 16 ± 0.7 *** | 18.3 ± 7.2 *** |
| LDL (mg/dL) | 26.81 ± 0.60 | 34.64 ± 0.82 *** | 30.35 ± 0.75 *** | 48.35 ± 0.51 *** | 45.68 ± 0.78 *** |
| TAG (mg/dL) | 63.28 ± 0.84 | 70.11 ± 0.72 *** | 66.27 ± 0.76 *** | 90.47 ± 0.84 *** | 82.58 ± 0.46 *** |
| Kidney | |||||
| Serum Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.728 ± 0.33 | 0.82 ± 0.34 NS | 1.5 ± 0.40 * | 2.97 ± 0.73 *** | 2.44 ± 0.67 ** |
| Blood Urea Nitrogen (mg/dL) | 17.28 ± 0.89 | 18.64 ± 1.90 * | 19.72 ± 0.94 ** | 24.12 ± 0.89 *** | 20.84 ± 1.05 *** |
| Serum Uric Acid (mg/dL) | 4.77 ± 0.59 | 5.7 ± 0.8 NS | 6.08 ± 0.37 *** | 8.22 ± 0.69 *** | 8.04 ± 0.74 *** |
| Liver | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enzyme | Normal Control | Kausar Ghee | Oleic Acid | Elaidic Acid | Mujahid Ghee |
| Total protein (μg/mg tissue) | 13.83 ± 0.73 | 13.65 ± 0.32 | 14.21 ± 0.58 | 13.12 ± 0.61 | 14.30 ± 0.51 |
| POD (U/min) | 0.18 ± 0.01 | 0.16 ± 0.004 NS | 0.14 ± 0.02 * | 0.12 ± 0.01 ** | 0.06 ± 0.04 *** |
| GSH (mM/g tissue) | 0.96 ± 0.04 | 0.89 ± 0.06 NS | 0.62 ± 0.24 *** | 0.33 ± 0.01 *** | 0.36 ± 0.13 *** |
| TBARS (nM/min/mg tissue) | 4.15 ± 0.01 | 2.34 ± 0.15 *** | 3.45 ± 0.18 *** | 1.05 ± 0.02 *** | 1.56 ± 0.25 *** |
| CAT (U/min) | 2.28 ± 0.92 | 1.07 ± 1.09 * | 0.69 ± 0.56 ** | 0.52 ± 0.18 *** | 0.89 ± 0.87 *** |
| SOD (U/mg protein) | 4.58 ± 0.57 | 4.05 ± 0.04 NS | 3.31 ± 1.07 * | 2.08 ± 0.59 *** | 3.21 ± 1.33 * |
| Kidney | |||||
| Total protein (μg/mg tissue) | 13.27 ± 0.64 | 13.38 ± 0.46 | 13.49 ± 0.99 | 12.38 ± 0.0.75 | 13.48 ± 0.65 |
| POD (U/min) | 0.17 ± 0.01 | 0.13 ± 0.018 * | 0.129 ± 0.02 ** | 0.123 ± 0.02 *** | 0.10 ± 0.01 *** |
| GSH (mM/g tissue) | 0.85 ± 0.04 | 0.59 ± 0.17 * | 0.61 ± 0.24 * | 0.14 ± 0.08 *** | 0.31 ± 0.15 *** |
| TBARS (nM/min/mg tissue) | 3.40 ± 0.31 | 2.16 ± 0.74 *** | 2.63 ± 0.57 * | 0.16 ± 0.07 *** | 0.93 ± 0.24 *** |
| CAT (U/min) | 2.59 ± 1.39 | 1.30 ± 0.73 * | 0.70 ± 0.42 *** | 0.65 ± 0.42 *** | 0.79 ± 0.57 *** |
| SOD (U/mg protein) | 4.11 ± 0.50 | 3.23 ± 0.41 * | 2.99 ± 0.45 ** | 0.73 ± 0.0.47 *** | 1.48 ± 0.80 *** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ismail, H.; Mubashar, Z.; Khan, H.; Naveed, Z.; Dilshad, E.; Bhatti, M.Z.; Anwaar, S.; Saleem, S.; Mehmood, S.; Rahman, A.; et al. Effects of a High Trans Fatty Acid Diet on Kidney-, Liver-, and Heart-Associated Diseases in a Rabbit Model. Metabolites 2024, 14, 442. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14080442
Ismail H, Mubashar Z, Khan H, Naveed Z, Dilshad E, Bhatti MZ, Anwaar S, Saleem S, Mehmood S, Rahman A, et al. Effects of a High Trans Fatty Acid Diet on Kidney-, Liver-, and Heart-Associated Diseases in a Rabbit Model. Metabolites. 2024; 14(8):442. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14080442
Chicago/Turabian StyleIsmail, Hammad, Zaryab Mubashar, Hajra Khan, Zeenat Naveed, Erum Dilshad, Muhammad Zeeshan Bhatti, Sadaf Anwaar, Samreen Saleem, Sabba Mehmood, Abdur Rahman, and et al. 2024. "Effects of a High Trans Fatty Acid Diet on Kidney-, Liver-, and Heart-Associated Diseases in a Rabbit Model" Metabolites 14, no. 8: 442. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14080442
APA StyleIsmail, H., Mubashar, Z., Khan, H., Naveed, Z., Dilshad, E., Bhatti, M. Z., Anwaar, S., Saleem, S., Mehmood, S., Rahman, A., Rashid, U., Fouad, D., De Waard, M., & Batiha, G. E.-S. (2024). Effects of a High Trans Fatty Acid Diet on Kidney-, Liver-, and Heart-Associated Diseases in a Rabbit Model. Metabolites, 14(8), 442. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14080442








