Kinetics of Manganese Peroxidase Using Simple Phenolic Compounds as Substrates
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Enzyme Reaction Rate
2.3. Enzyme Kinetics
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Enzyme Reaction Rate
3.2. Enzyme Kinetics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SOM | Soil organic matter |
| MnP | Manganese peroxidase |
| PSM | Plant secondary metabolite |
References
- Chomel, M.; Guittonny-Larchevêque, M.; Fernandez, C.; Gallet, C.; DesRochers, A.; Paré, D.; Jackson, B.G.; Baldy, V. Plant secondary metabolites: A key driver of litter decomposition and soil nutrient cycling. J. Ecol. 2016, 104, 1527–1541. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Y.W.; Wang, J.; Gao, W.Y.; Wang, R.B.; Yang, W.Q.; Zhang, H.Y.; Huang, L.Q.; Guo, L.P. Dynamic metabolites: A bridge between plants and microbes. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 899, 165612. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kraus, T.E.C.; Dahlgren, R.A.; Zasoski, R.J. Tannins in nutrient dynamics of forest ecosystems—A review. Plant Soil 2003, 256, 41–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, T.; Hatano, T.; Ito, H. High Molecular Weight Plant Polyphenols (Tannins): Prospective Functions. In Chemical Ecology and Phytochemistry of Forest Ecosystems; Romeo, J.T., Ed.; Elsevier Inc.: San Diego, CA, USA, 2005; Volume 39, pp. 163–190. [Google Scholar]
- Quideau, S.; Deffieux, D.; Douat-Casassus, C.; Pouységu, L. Plant polyphenols: Chemical properties, biological activities, and synthesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 586–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanbabaee, K.; van Ree, T. Tannins: Classification and definition. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2001, 18, 641–649. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Cai, P.; Cheng, G.H.; Zhang, Y.Q. A Brief Review of Phenolic Compounds Identified from Plants: Their Extraction, Analysis, and Biological Activity. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2022, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.Y.; Yang, S.Y.; Zhou, W.; Liu, Z.W.; Tan, J.F.; Wei, M. Microbial regulation of plant secondary metabolites: Impact, mechanisms and prospects. Microbiol. Res. 2024, 283, 127688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, E.L. Allelopathy, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012; pp. 237–244. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, M.; Halvorson, J.; Gonzalez, J.; Hagerman, A. Kinetics and binding capacity of six soils for structurally defined hydrolyzable and condensed tannins and related phenols. J. Soil Sediments 2012, 12, 366–375. [Google Scholar]
- Min, K.; Freeman, C.; Kang, H.; Choi, S.U. The Regulation by Phenolic Compounds of Soil Organic Matter Dynamics under a Changing Environment. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 825098. [Google Scholar]
- Jacoby, R.P.; Koprivova, A.; Kopriva, S. Pinpointing secondary metabolites that shape the composition and function of the plant microbiome. J. Exp. Bot. 2021, 72, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiruma, K. Roles of Plant-Derived Secondary Metabolites during Interactions with Pathogenic and Beneficial Microbes under Conditions of Environmental Stress. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isah, T. Stress and defense responses in plant secondary metabolites production. Biol. Res. 2019, 52, 39. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, M.A.; Kreinberg, A.J.; Gonzalez, J.M.; Halvorson, J.J.; French, E.; Bollmann, A.; Hagerman, A.E. Soil microbial communities respond differently to three chemically defined polyphenols. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 72, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Talbot, J.M.; Finzi, A.C. Differential effects of sugar maple, red oak, and hemlock tannins on carbon and nitrogen cycling in temperate forest soils. Oecologia 2008, 155, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Guo, M.Y.; Gao, Y.H.; Bai, X.H.; Zhou, X.W. Expression and characteristics of manganese peroxidase from Ganoderma lucidum in Pichia pastoris and its application in the degradation of four dyes and phenol. BMC Biotechnol. 2017, 17, 19. [Google Scholar]
- Kuan, I.C.; Johnson, K.A.; Tien, M. Kinetic-analysis of manganese peroxidase—The reaction with manganese complexes. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 20064–20070. [Google Scholar]
- Wariishi, H.; Valli, K.; Gold, M.H. Manganese(II) oxidation by manganese peroxidase from the Basidiomycete Phanerochaete-Chrysosporium—Kinetic mechanism and role of chelators. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 23688–23695. [Google Scholar]
- Janusz, G.; Kucharzyk, K.H.; Pawlik, A.; Staszczak, M.; Paszczynski, A.J. Fungal laccase, manganese peroxidase and lignin peroxidase: Gene expression and regulation. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2013, 52, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, M. Biodiversity and geographic distribution of basidiomycetes causing esca-associated white rot in grapevine: A worldwide perspective. Phytopathol. Mediterr. 2006, 45, S30–S42. [Google Scholar]
- Merino, C.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Godoy, K.; Cornejo, P.; Matus, F. Synergy effect of peroxidase enzymes and Fenton reactions greatly increase the anaerobic oxidation of soil organic matter. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11289. [Google Scholar]
- Camarero, S.; Sarkar, S.; Ruiz-Dueñas, F.J.; Martínez, M.J.; Martínez, A.T. Description of a versatile peroxidase involved in the natural degradation of lignin that has both manganese peroxidase and lignin peroxidase substrate interaction sites. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 10324–10330. [Google Scholar]
- Nousiainen, P.; Kontro, J.; Manner, H.; Hatakka, A.; Sipilä, J. Phenolic mediators enhance the manganese peroxidase catalyzed oxidation of recalcitrant lignin model compounds and synthetic lignin. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2014, 72, 137–149. [Google Scholar]
- Urzúa, U.; Kersten, P.J.; Vicuña, R. Manganese Peroxidase-Dependent Oxidation of Glyoxylic and Oxalic Acids Synthesized by Ceriporiopsis subvermispora Produces Extracellular Hydrogen Peroxide. Appl. Env. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 68–73. [Google Scholar]
- Joanisse, G.; Bradley, R.; Preston, C.; Bending, G. Sequestration of soil nitrogen as tannin-protein complexes may improve the competitive ability of sheep laurel (Kalmia angustifolia) relative to black spruce (Picea mariana). New Phytol. 2009, 181, 187–198. [Google Scholar]
- Kraus, T.E.C.; Zasoski, R.J.; Dahlgren, R.A.; Horwath, W.R.; Preston, C.M. Carbon and nitrogen dynamics in a forest soil amended with purified tannins from different plant species. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2004, 36, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinraide, T.; Hagerman, A. Interactive intoxicating and ameliorating effects of tannic acid, aluminum (Al3+), copper (Cu2+) and selenate (SeO42-) in wheat roots. A descriptive and mathematical assessment. Physiol. Plant. 2010, 139, 68–79. [Google Scholar]
- Gruenberg, M.G.; Halvorson, J.J.; Hagerman, A.E.; Enoma, I.G.; Schmidt, M.A. Oxidation of Small Phenolic Compounds by Mn(IV). Molecules 2024, 29, 4320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halvorson, J.J.; Jin, V.L.; Liebig, M.A.; Schmidt, M.A.; Hagerman, A.E.; Luciano, R. Rapid formation of abiotic CO2 after adding phenolic gallic acid, to agricultural soils. Agrosystems Geosci. Environ. 2025, 8, e70035. [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz, J.L.; García-Molina, F.; Varón, R.; Rodriguez-Lopez, J.N.; García-Cánovas, F.; Tudela, J. Calculating molar absorptivities for quinones:: Application to the measurement of tyrosinase activity. Anal. Biochem. 2006, 351, 128–138. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Y.; Han, Y.; Xue, X.; Jiang, Y. Biodegradation of phenol-contaminated soil and plant growth promotion by Myroides xuanwuensis H13. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e00266-24. [Google Scholar]
- Valanciene, E.; Jonuskiene, I.; Syrpas, M.; Augustiniene, E.; Matulis, P.; Simonavicius, A.; Malys, N. Advances and Prospects of Phenolic Acids Production, Biorefinery and Analysis. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grgas, D.; Rukavina, M.; Beslo, D.; Stefanac, T.; Crnek, V.; Sikic, T.; Habuda-Stanic, M.; Dragicevic, T.L. The Bacterial Degradation of Lignin—A Review. Water 2023, 15, 1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofrichter, M. Review: Lignin conversion by manganese peroxidase (MnP). Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2002, 30, 454–466. [Google Scholar]
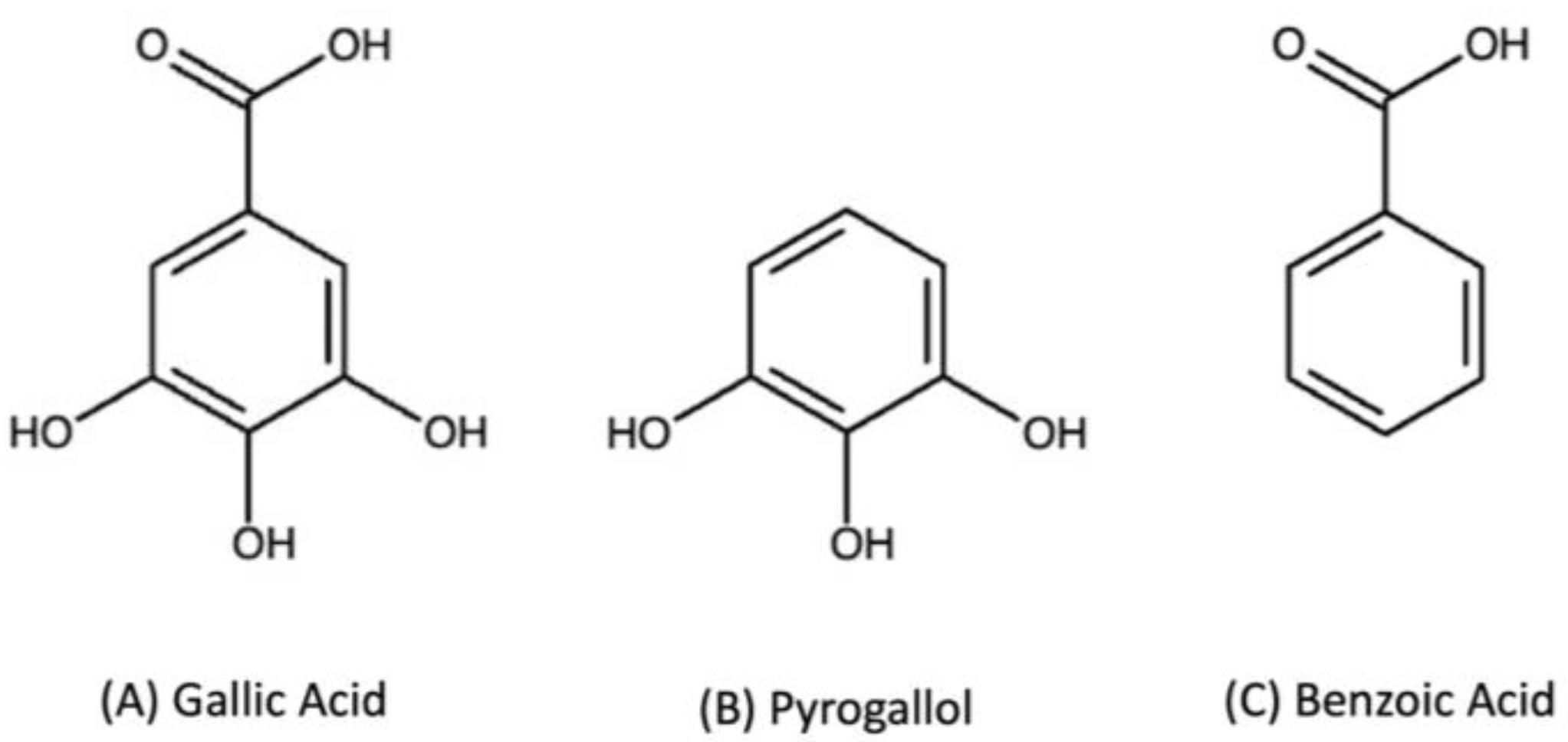
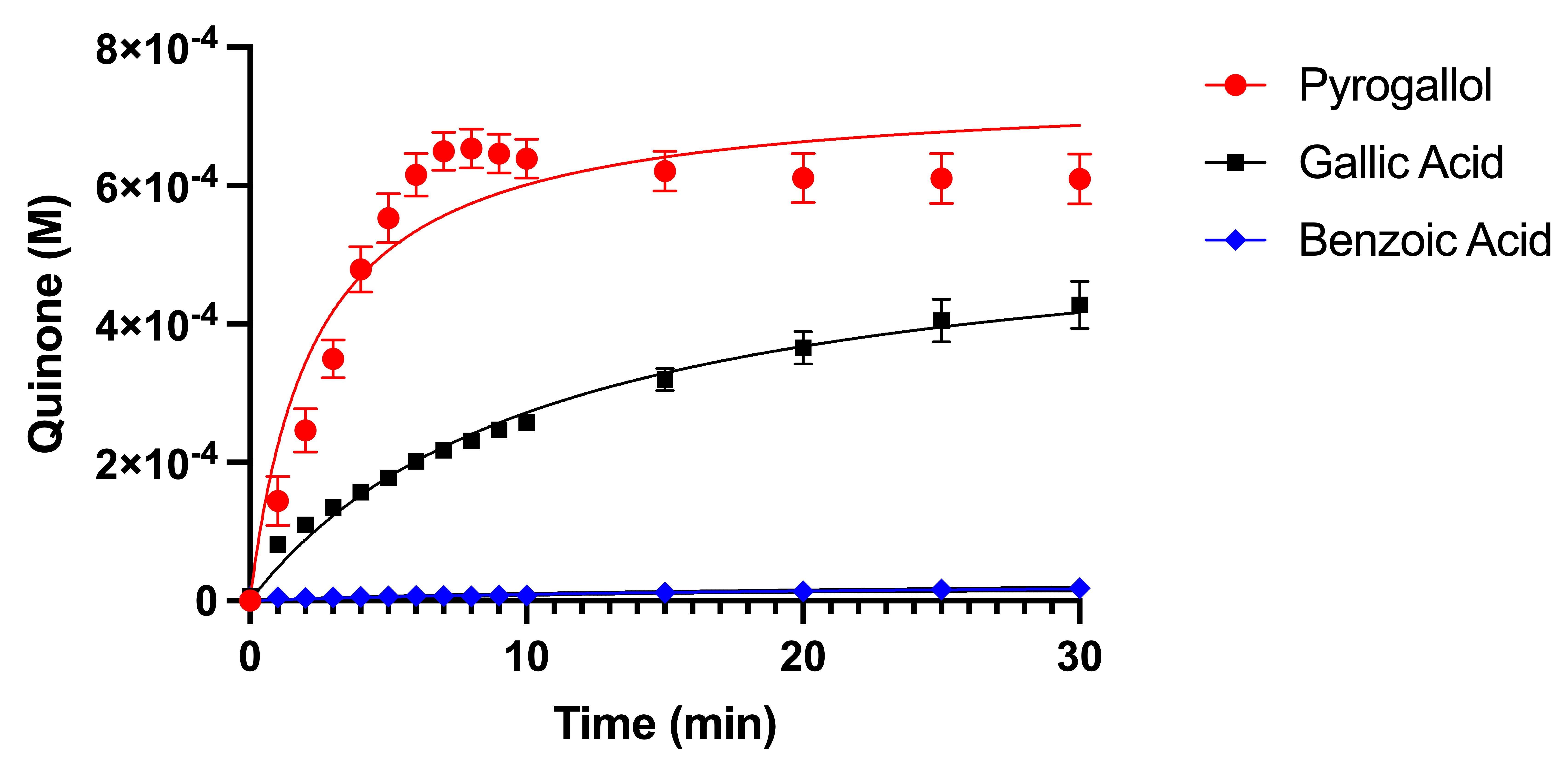
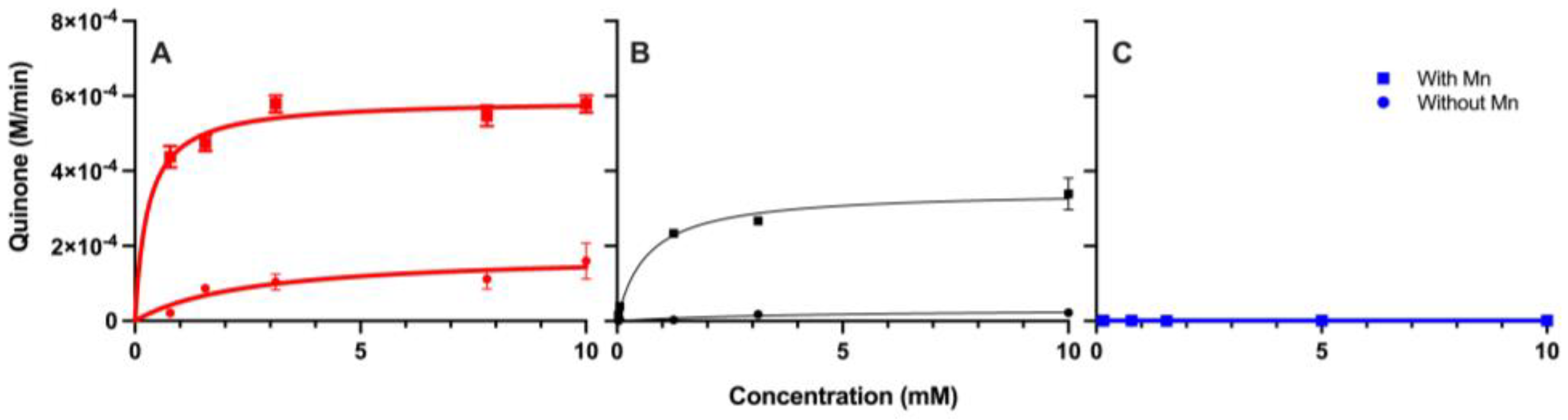
| Compound | Km with Mn (mM) | Km without Mn (mM) | Vmax with Mn (mM/Min) | Vmax without Mn (mM/Min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Benzoic Acid | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Pyrogallol | 0.28 | 2.6 | 0.59 | 0.18 |
| Gallic Acid | 0.66 | 4.3 | 0.35 | 0.03 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gruenberg, M.G.; Halvorson, J.J.; Schmidt, M.A. Kinetics of Manganese Peroxidase Using Simple Phenolic Compounds as Substrates. Metabolites 2025, 15, 254. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15040254
Gruenberg MG, Halvorson JJ, Schmidt MA. Kinetics of Manganese Peroxidase Using Simple Phenolic Compounds as Substrates. Metabolites. 2025; 15(4):254. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15040254
Chicago/Turabian StyleGruenberg, Madeline G., Jonathan J. Halvorson, and Michael A. Schmidt. 2025. "Kinetics of Manganese Peroxidase Using Simple Phenolic Compounds as Substrates" Metabolites 15, no. 4: 254. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15040254
APA StyleGruenberg, M. G., Halvorson, J. J., & Schmidt, M. A. (2025). Kinetics of Manganese Peroxidase Using Simple Phenolic Compounds as Substrates. Metabolites, 15(4), 254. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15040254






