Inter-Laboratory Comparison of Metabolite Measurements for Metabolomics Data Integration
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Data Acquisition and Integration
2.3. Comparison of Analytical Methods for Relative Quantification
2.4. Community-Based Correction of Targeted Metabolome Analysis Methods
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Cell Cultures
3.2. Preparation of Cell Extract for Metabolite Quantification
3.3. Analytical Procedure
3.4. Data Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mapelli, V.; Olsson, L.; Nielsen, J. Metabolic footprinting in microbiology: Methods and applications in functional genomics and biotechnology. Trends Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, K.; Matsuda, F. Metabolomics for functional genomics, systems biology, and biotechnology. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2010, 61, 463–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrimpe-Rutledge, A.C.; Codreanu, S.G.; Sherrod, S.D.; McLean, J.A. Untargeted metabolomics strategies–challenges and emerging directions. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2016, 27, 1897–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Wang, C.; Han, R.H.; Han, X. Novel advances in shotgun lipidomics for biology and medicine. Prog. Lipid Res. 2016, 61, 83–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilcoxen, K.M.; Uehara, T.; Myint, K.T.; Sato, Y.; Oda, Y. Practical metabolomics in drug discovery. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2010, 5, 249–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamski, J. Genome-wide association studies with metabolomics. Genome Med. 2012, 4, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, W.B.; Lin, W.; Broadhurst, D.; Begley, P.; Brown, M.; Zelena, E.; Vaughan, A.A.; Halsall, A.; Harding, N.; Knowles, J.D.; et al. Molecular phenotyping of a UK population: Defining the human serum metabolome. Metabolomics 2015, 11, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Kremling, K.A.; Bandillo, N.; Richter, A.; Zhang, Y.K.; Ahern, K.R.; Artyukhin, A.B.; Hui, J.X.; Younkin, G.C.; Schroeder, F.C.; et al. Metabolome-scale genome-wide association studies reveal chemical diversity and genetic control of maize specialized metabolites. Plant Cell 2019, 31, 937–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, M.E. Perspectives on the draft ICH-M10 guidance: An interview with Mark Arnold. Bioanalysis 2019, 11, 1379–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindon, J.C.; Nicholson, J.K.; Holmes, E.; Keun, H.C.; Craig, A.; Pearce, J.T.; Bruce, S.J.; Hardy, N.; Sansone, S.-A.; Antti, H.; et al. Summary recommendations for standardization and reporting of metabolic analyses. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 833–838. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, L.; Lu, H.; Lee, Y.H. Challenges and emergent solutions for LC-MS/MS based untargeted metabolomics in diseases. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2018, 37, 772–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaleckis, R.; Meister, I.; Zhang, P.; Wheelock, C.E. Challenges, progress and promises of metabolite annotation for LC-MS-based metabolomics. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2019, 55, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liebisch, G.; Ekroos, K.; Hermansson, M.; Ejsing, C.S. Reporting of lipidomics data should be standardized. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2017, 1862, 747–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, B.C.; Hunter, C.L.; Liu, Y.; Schilling, B.; Rosenberger, G.; Bader, S.L.; Chan, D.W.; Gibson, B.W.; Gingras, A.-C.; Held, J.M.; et al. Multi-laboratory assessment of reproducibility, qualitative and quantitative performance of SWATH-mass spectrometry. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siskos, A.P.; Jain, P.; Römisch-Margl, W.; Bennett, M.; Achaintre, D.; Asad, Y.; Marney, L.; Richardson, L.; Koulman, A.; Griffin, J.L.; et al. Interlaboratory reproducibility of a targeted metabolomics platform for analysis of human serum and plasma. Anal. Chem. 2016, 89, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulmer, C.Z.; Ragland, J.M.; Koelmel, J.P.; Heckert, A.; Jones, C.M.; Garrett, T.J.; Yost, R.A.; Bowden, J.A. LipidQC: Method validation tool for visual comparison to SRM 1950 using NIST interlaboratory comparison exercise lipid consensus mean estimate values. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 13069–13073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowden, J.A.; Heckert, A.; Ulmer, C.Z.; Jones, C.M.; Koelmel, J.P.; Abdullah, L.; Ahonen, L.; Alnouti, Y.; Armando, A.M.; Asara, J.M.; et al. Harmonizing lipidomics: NIST interlaboratory comparison exercise for lipidomics using SRM 1950–Metabolites in Frozen Human Plasma. J. Lipid Res. 2017, 58, 2275–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burla, B.; Arita, M.; Arita, M.; Bendt, A.K.; Cazenave-Gassiot, A.; Dennis, E.A.; Ekroos, K.; Han, X.; Ikeda, K.; Liebisch, G.; et al. MS-based lipidomics of human blood plasma: A community-initiated position paper to develop accepted guidelines. J. Lipid Res. 2018, 59, 2001–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anton, G.; Wilson, R.; Yu, Z.H.; Prehn, C.; Zukunft, S.; Adamski, J.; Heier, M.; Meisinger, C.; Römisch-Margl, W.; Wang-Sattler, R.; et al. Pre-analytical sample quality: metabolite ratios as an intrinsic marker for prolonged room temperature exposure of serum samples. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haid, M.; Muschet, C.; Wahl, S.; Römisch-Margl, W.; Prehn, C.; Möller, G.; Adamski, J. Long-term stability of human plasma metabolites during storage at–80 °C. J. Proteome Res. 2017, 17, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Checa, A.; Bedia, C.; Jaumot, J. Lipidomic data analysis: Tutorial, practical guidelines and applications. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 885, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonelli, J.; Claggett, B.L.; Henglin, M.; Kim, A.; Ovsak, G.; Kim, N.; Deng, K.; Rao, K.; Tyagi, O.; Watrous, J.D.; et al. Statistical workflow for feature selection in human metabolomics data. Metabolites 2019, 9, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, V.L.; Hoover, E.; Wang, Y.; Zanetti, K.A. Pre-analytical factors that affect metabolite stability in human urine, plasma, and serum: A review. Metabolites 2019, 9, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, B.; Zanetti, K.A.; Temprosa, M.; Albanes, D.; Appel, N.; Barrera, C.B.; Ben-Shlomo, Y.; Boerwinkle, E.; Casas, J.P.; Clish, C.; et al. The consortium of metabolomics studies (COMETS): Metabolomics in 47 prospective cohort studies. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2019, 188, 991–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soga, T.; Ohashi, Y.; Ueno, Y.; Naraoka, H.; Tomita, M.; Nishioka, T. Quantitative metabolome analysis using capillary electrophoresis mass spectrometry. J. Proteome Res. 2003, 2, 488–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soga, T.; Igarashi, K.; Ito, C.; Mizobuchi, K.; Zimmermann, H.P.; Tomita, M. Metabolomic profiling of anionic metabolites by capillary electrophoresis mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 6165–6174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogami, C.; Sawada, H. Positional and geometrical anionic isomer separations by capillary electrophoresis-electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry. Electrophoresis 2005, 26, 1406–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klampfl, C.W.; Buchberger, W. Determination of carbohydrates by capillary electrophoresis with electrospray-mass spectrometric detection. Electrophoresis 2001, 22, 2737–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wikoff, W.R.; Gangoiti, J.A.; Barshop, B.A.; Siuzdak, G. Metabolomics identifies perturbations in human disorders of propionate metabolism. Clin. Chem. 2007, 53, 2169–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawada, Y.; Akiyama, K.; Sakata, A.; Kuwahara, A.; Otsuki, H.; Sakurai, T.; Saito, K.; Hirai, M.Y. Widely targeted metabolomics based on large-scale MS/MS data for elucidating metabolite accumulation patterns in plants. Plant Cell Physiol. 2008, 50, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, R.; Todoroki, K.; Maruoka, H.; Yoshida, H.; Fujioka, T.; Nakashima, M.; Yamaguchi, M.; Nohta, H. Amino acid metabolomics using LC-MS/MS: Assessment of cancer-cell resistance in a simulated tumor microenvironment. Anal. Sci. 2016, 32, 893–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimbo, K.; Oonuki, T.; Yahashi, A.; Hirayama, K.; Miyano, H. Precolumn derivatization reagents for high-speed analysis of amines and amino acids in biological fluid using liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2009, 23, 1483–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, H.; Mizukoshi, T.; Hirayama, K.; Miyano, H. Comprehensive analytical method for the determination of hydrophilic metabolites by high-performance liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; Wang, J.; Ji, E.H.; Christison, T.; Lopez, L.; Huang, Y. Targeted metabolomic analysis of head and neck cancer cells using high performance Ion chromatography coupled with a Q exactive HF mass spectrometer. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 6371–6379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okahashi, N.; Kawana, S.; Iida, J.; Shimizu, H.; Matsuda, F. Fragmentation of dicarboxylic and tricarboxylic acids in the krebs cycle using GC-EI-MS and GC-EI-MS/MS. Mass Spectrom. (Tokyo) 2019, 8, A0073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiehn, O.; Kopka, J.; Trethewey, R.N.; Willmitzer, L. Identification of uncommon plant metabolites based on calculation of elemental compositions using gas chromatography and quadrupole mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2000, 72, 3573–3580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiumi, S.; Kobayashi, T.; Kawana, S.; Unno, Y.; Sakai, T.; Okamoto, K.; Yamada, Y.; Sudo, K.; Yamaji, T.; Saito, Y.; et al. Investigations in the possibility of early detection of colorectal cancer by gas chromatography/triple-quadrupole mass spectrometry. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 17115–17126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsugawa, H.; Ikeda, K.; Tanaka, W.; Senoo, Y.; Arita, M.; Arita, M. Comprehensive identification of sphingolipid species by in silico retention time and tandem mass spectral library. J. Cheminform. 2017, 9, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamada, T.; Uchikata, T.; Sakamoto, S.; Yokoi, Y.; Fukusaki, E.; Bamba, T. Development of a lipid profiling system using reverse-phase liquid chromatography coupled to high-resolution mass spectrometry with rapid polarity switching and an automated lipid identification software. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1292, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, K.; Ikeda, M.; Kojima, Y.; Hosoi, H.; Saito, Y.; Kondo, S. Lipid profiling of pre-treatment plasma reveals biomarker candidates associated with response rates and hand-foot skin reactions in sorafenib-treated patients. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacolo 2018, 82, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shindou, H.; Koso, H.; Sasaki, J.; Nakanishi, H.; Sagara, H.; Nakagawa, K.M.; Takahashi, Y.; Hishikawa, D.; Iizuka-Hishikawa, Y.; Tokumasu, F.; et al. Docosahexaenoic acid preserves visual function by maintaining correct disc morphology in retinal photoreceptor cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 12054–12064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Okudaira, M.; Inoue, A.; Shuto, A.; Nakanaga, K.; Kano, K.; Makide, K.; Saigusa, D.; Tomioka, Y.; Aoki, J. Separation and quantification of 2-acyl-1-lysophospholipids and 1-acyl-2-lysophospholipids in biological samples by LC-MS/MS. J. Lipid Res. 2014, 55, 2178–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Takeda, H.; Izumi, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Paxton, T.; Tamura, S.; Koike, T.; Yu, Y.; Kato, N.; Nagase, K.; Shiomi, M.; et al. Widely-targeted quantitative lipidomics method by supercritical fluid chromatography triple quadrupole mass spectrometry. J. Lipid Res. 2018, 59, 1283–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ogawa, T.; Izumi, Y.; Kusumoto, K.; Fukusaki, E.; Bamba, T. Wide target analysis of acylglycerols in miso (Japanese fermented soybean paste) by supercritical fluid chromatography coupled with triple quadrupole mass spectrometry and the analysis of the correlation between taste and both acylglycerols and free fatty acids. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2017, 31, 928–936. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]

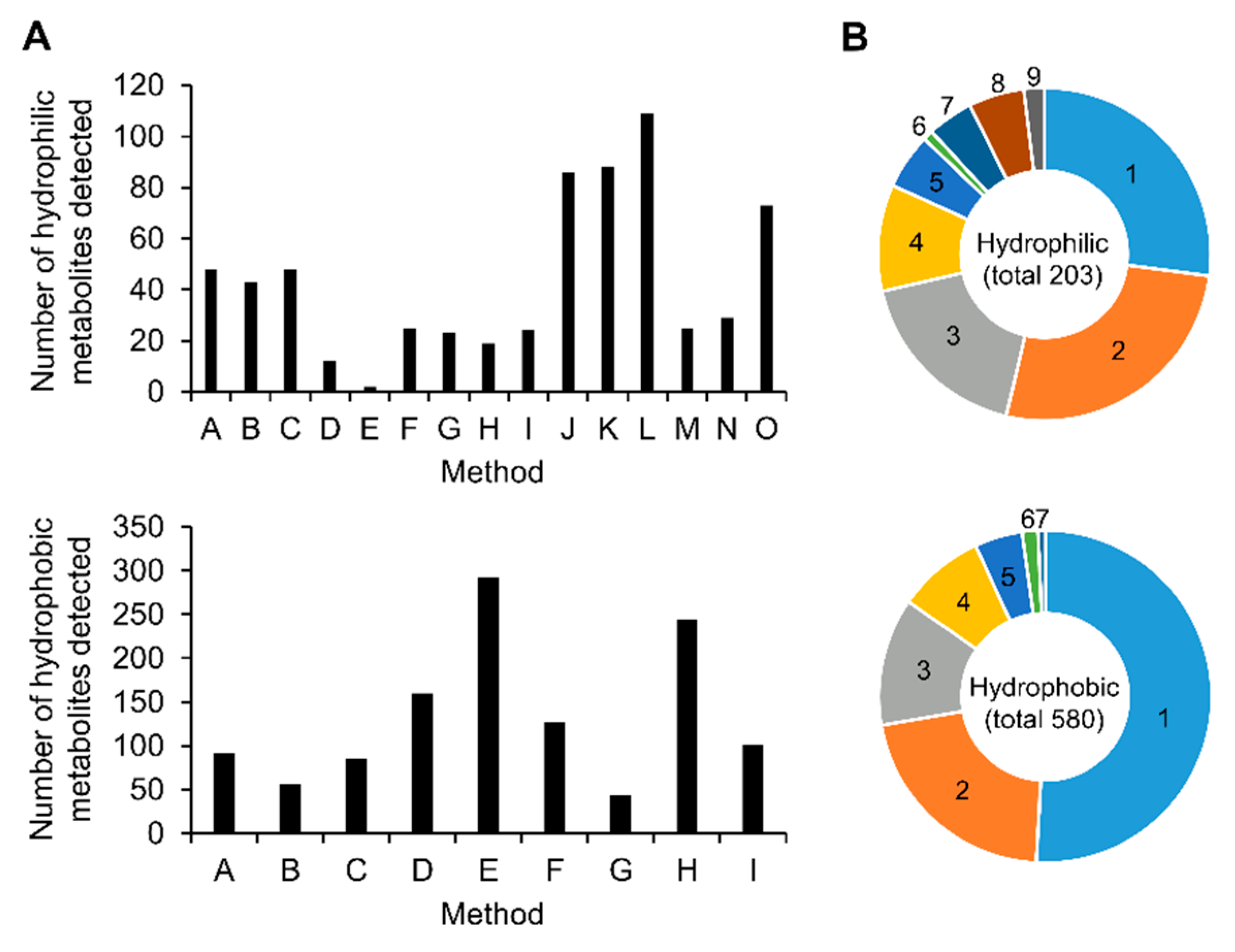


| Method ID | Lab ID | Analytical Method | Analytical Mode | Targeted Hydrophilic Metabolites | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 1 | CE-TOFMS (cation mode) | Scan (positive) | Amino acids, Bases, Nucleosides, Amines, etc. | [25] |
| B | 2 | CE-TOFMS (cation mode) | Scan (positive) | Amino acids, Bases, Nucleosides, Amines, etc. | [25] |
| C | 1 | CE-TOFMS (anion mode) | Scan (negative) | Organic acids, Sugar phosphates, Nucleotides, etc. | [26] |
| D | 2 | CE-TOFMS (anion mode) | Scan (negative) | Organic acids, Sugar phosphates, Nucleotides, etc. | [27] |
| E | 1 | CE-TQMS (anion mode) | MRM (negative) | Monosaccharides | [28] |
| F | 2 | C18-LC/QTOFMS | Scan (positive/negative) | Amino acids, Organic acids, Nucleotides, etc. | [29] |
| G | 3 | C18-LC/TQMS | MRM (positive/negative) | Amino acids, Organic acids, Nucleotides, etc. | [30] |
| H | 4 | C18-LC/TQMS | MRM (positive) | Amino acids | [31] |
| I | 5 | Derivatization and C18-LC/TQMS | MRM (positive) | Amino acids, etc. | [32] |
| J | 6 | PFPP-LC/Q Exactive | Scan (positive/negative) | Amino acids, Bases, Nucleosides, Amines, Organic acids, etc. | [33] |
| K | 1 | Capillary-IC/Q Exactive | Scan (negative) | Organic acids, Sugar phosphates, Nucleotides, etc. | [34] |
| L | 6 | IC/Q Exactive | Scan (positive/negative) | Organic acids, Sugar phosphates, Nucleotides, etc. | [34] |
| M | 7 | Derivatization and GC/QMS | SIM | Amino acids, Organic acid, etc. | [35] |
| N | 6 | Derivatization and GC/QMS | Scan | Amino acids, Organic acid, etc. | [36] |
| O | 8 | Derivatization and GC/TQMS | MRM | Amino acids, Organic acid, Base, Nucleosides, etc. | [37] |
| Method ID | Lab ID | Analytical Method | Analytical Mode | Targeted Lipids | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 9 | C18-LC/QTOFMS | Scan (positive/negative) | ChE, Cer(NS), DG, FA, HexCer(NS), LPC, LPE, LPI, LPS, PC, PE, PG, PI, PS, SM | [38] |
| B | 5 | C8-LC/Q Exactive | Scan (positive) | AC, HexCer(NS), LPC, LPE, LPS, PC, PE, SM | [39] |
| C | 5 | C8-LC/Q Exactive | Scan (negative) | LPE, LPG, LPI, PC, PE, PG, PI, PS | [39] |
| D | 10 | C18-LC/Orbitrap Fusion | Scan (positive/negative) | AC, ChE, Cer(NS), DG, HexCer(NS), LPC, LPE, LPI, LPS, PC, PE, PG, PI, PS, SM, TG | [40] |
| E | 11 | C8-LC/TQMS | MRM (positive/negative) | LPC, LPE, LPI, LPS, PC, PE, PI, PS, SM | ‒ |
| F | 12 | C18-LC/TQMS | MRM (positive) | ChE, Cer(NS), LPA, LPC, LPE, LPG, LPI, LPS, MG | [41] |
| G | 8 | C18-LC/TQMS | MRM (positive/negative) | LPA, LPC, LPE, LPG, LPI, LPS | [42] |
| H | 6 | Diethylamine-SFC/TQMS | MRM (positive/negative) | Cer(NS), DG, HexCer(NS), LPC, LPE, MG, PA, PC, PE, PG, PI, PS, SM | [43] |
| I | 6 | C18-SFC/TQMS | MRM (positive/negative) | ChE, FA, TG | [44] |
| Hydrophilic Metabolite | Hydrophobic Metabolite | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Number of identified metabolites from HT-29 and/or AsPc-1 samples by at least one analytical method | 206 | 584 | 790 |
| 2. Number of identified metabolites from both samples by two or more methods | 148 | 285 | 433 |
| 3. Number of metabolites that were statistically significant between samples HT-29 and AsPc-1 among multiple methods based on a two-sided Student’s t-test (α = 0.05) | 104 | 199 | 303 |
| 4. Number of metabolites that showed HT-29/AsPc-1 levels in different directions among methods based on a two-sided Student’s t-test (α = 0.05) and a relative quantitative value of 1 | 5 | 7 | 12 |
| 5. Number of metabolites that were statistically similar HT-29/AsPc-1 levels among multiple methods using a one-way ANOVA (α = 0.05) | 57 | 113 | 170 |
| 6. Number of metabolites that were statistically similar HT-29/AsPc-1 levels among multiple methods ignoring one outlier method using a one-way ANOVA (α = 0.05) | 98 | 162 | 260 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Izumi, Y.; Matsuda, F.; Hirayama, A.; Ikeda, K.; Kita, Y.; Horie, K.; Saigusa, D.; Saito, K.; Sawada, Y.; Nakanishi, H.; et al. Inter-Laboratory Comparison of Metabolite Measurements for Metabolomics Data Integration. Metabolites 2019, 9, 257. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9110257
Izumi Y, Matsuda F, Hirayama A, Ikeda K, Kita Y, Horie K, Saigusa D, Saito K, Sawada Y, Nakanishi H, et al. Inter-Laboratory Comparison of Metabolite Measurements for Metabolomics Data Integration. Metabolites. 2019; 9(11):257. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9110257
Chicago/Turabian StyleIzumi, Yoshihiro, Fumio Matsuda, Akiyoshi Hirayama, Kazutaka Ikeda, Yoshihiro Kita, Kanta Horie, Daisuke Saigusa, Kosuke Saito, Yuji Sawada, Hiroki Nakanishi, and et al. 2019. "Inter-Laboratory Comparison of Metabolite Measurements for Metabolomics Data Integration" Metabolites 9, no. 11: 257. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9110257
APA StyleIzumi, Y., Matsuda, F., Hirayama, A., Ikeda, K., Kita, Y., Horie, K., Saigusa, D., Saito, K., Sawada, Y., Nakanishi, H., Okahashi, N., Takahashi, M., Nakao, M., Hata, K., Hoshi, Y., Morihara, M., Tanabe, K., Bamba, T., & Oda, Y. (2019). Inter-Laboratory Comparison of Metabolite Measurements for Metabolomics Data Integration. Metabolites, 9(11), 257. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9110257







