The Impact of Coronal Mass Ejections on the Seasonal Variation of the Ionospheric Critical Frequency f0F2
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data Sources
3. Methodology
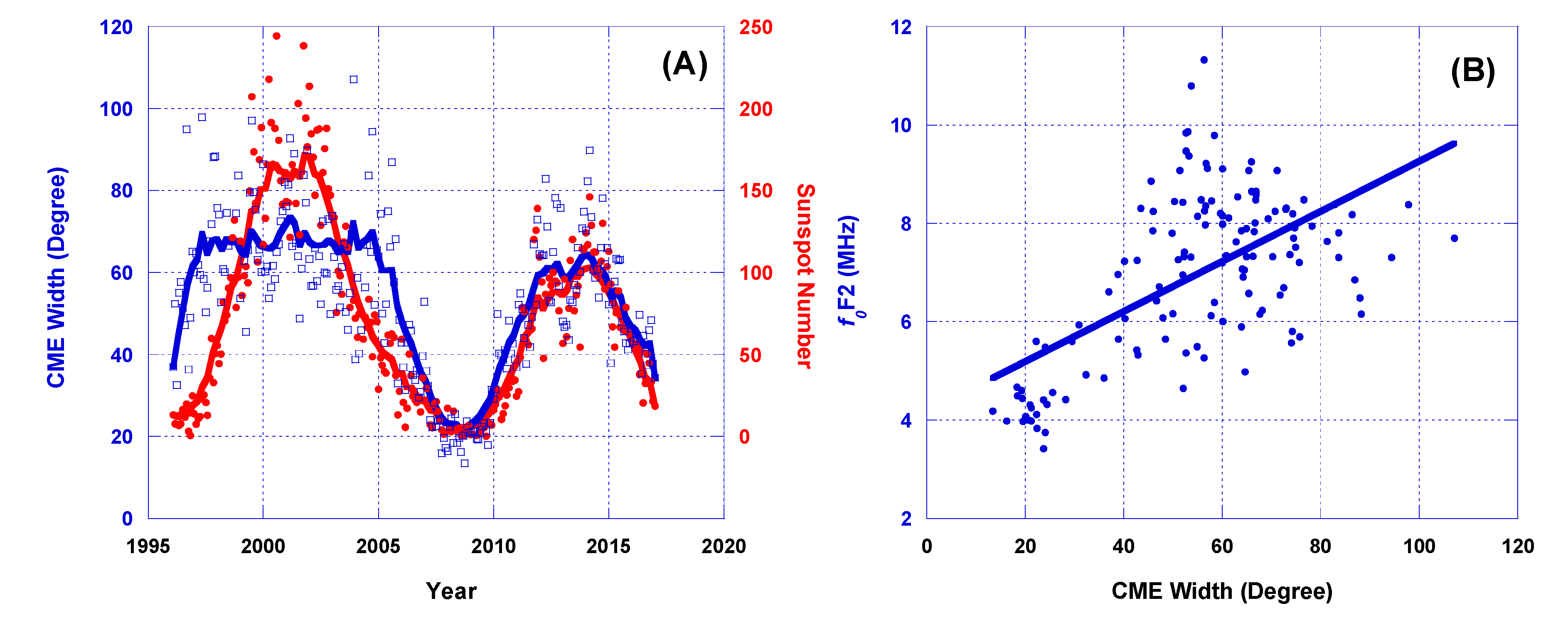
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Monthly Variation
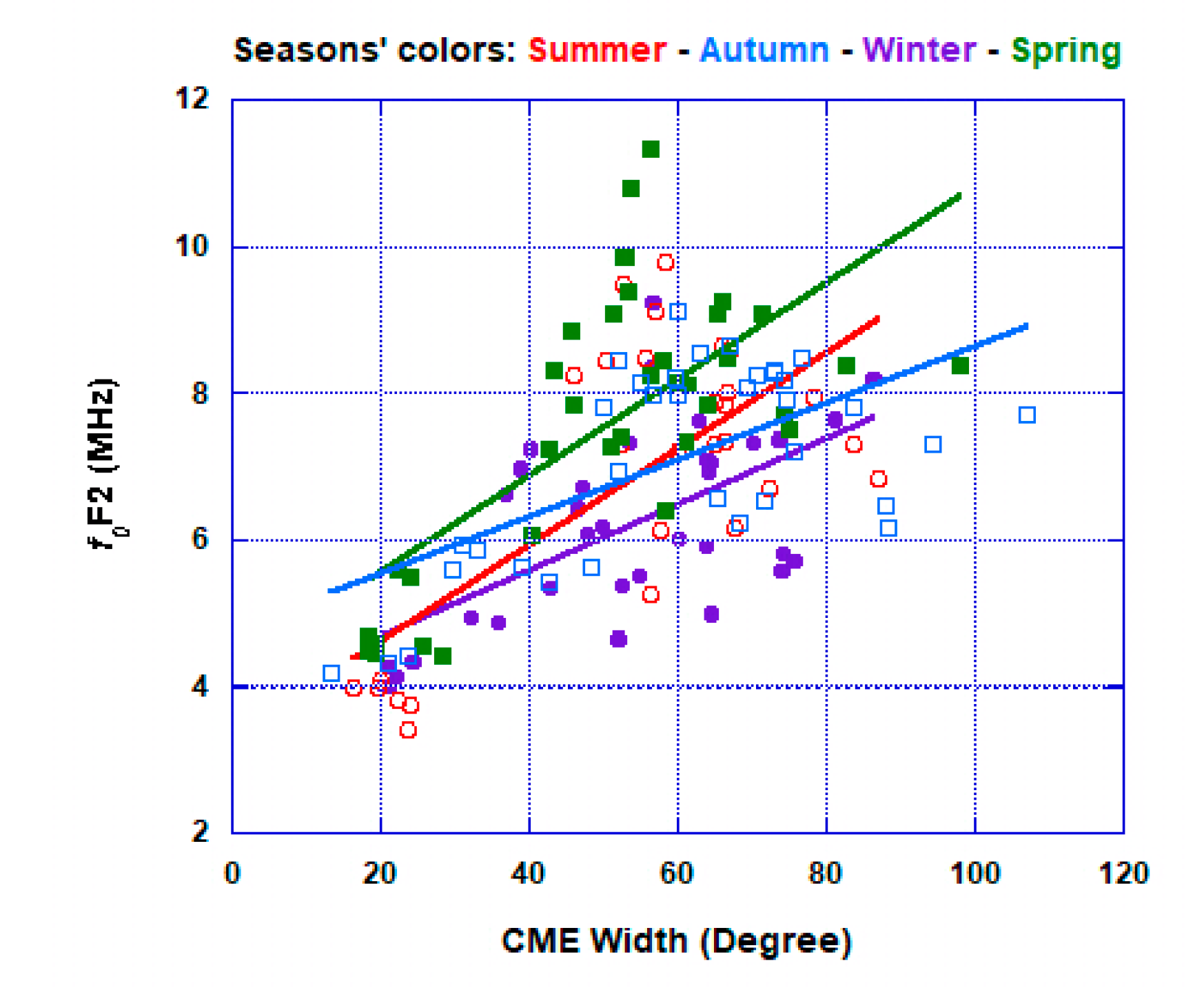
4.2. Seasonal Variation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, L.; Wan, W.; Ning, B.; Pirog, O.M.; Kurkin, V.I. Solar activity variations of the ionospheric peak electron density. J. Geophys. Res. Sp. Phys. 2006, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, K.N.; Jadav, R.M.; Jadeja, A.K.; Manoharan, P.K. Space Weather Effects of Coronal Mass Ejection. J. Astrophys. Astr. 2006, 27, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutiev, I.; Tsagouri, I.; Perrone, L.; Pancheva, D.; Mukhtarov, P.; Mikhailov, A.; Lastovicka, J.; Jakowski, N.; Buresova, D.; Blanch, E.; et al. Solar activity impact on the Earth’s upper atmosphere. J. Sp. Weather Sp. Clim. 2013, 3, A06. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buresova, D.; Lastovicka, J.; Hejda, P.; Bochnicek, J. Ionospheric disturbances under low solar activity conditions. Adv. Sp. Res. 2014, 54, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikubanni, S.O.; Adebesin, B.O.; Adebiyi, S.J.; Adeniyi, J.O. Relationship between F2 layer critical frequency and solar activity indices during several solar epochs. Indian J. Radio Sp. Phys. 2013, 42, 73–81. [Google Scholar]
- Farid, H.M.; Mawad, R.; Yousef, M.; Yousef, S. The Impacts of CMEs on the Ionospheric Critical Frequency foF2. Elixir Sp. Sci. 2015, 80, 31067–31070. [Google Scholar]
- Seyoum, A.; Gopalswamy, N.; Nigussie, M.; Mezgebe, N. The impact of CMEs on the critical frequency of F2-layer ionosphere (foF2). arXiv 2019, arXiv:2004.08278. [Google Scholar]
- Yiǧit, E.; Immel, T.; Ridley, A.; Frey, H.U.; Moldwin, M. General Circulation Modeling of the Thermosphere-Ionosphere during a Geomagnetic Storm. 41st COSPAR Scientific Assembly, Abstracts from the the Meeting that was to be Held 30 July–7 August at the Istanbul Congress Center (ICC), Turkey, but was Cancelled. Abstract id. C1.1-1-16. Available online: http://cospar2016.tubitak.gov.tr/en/ (accessed on 27 October 2020).
- Moldwin, M. An Introduction to Space Weather; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Seba, E.B.; Nigussie, M. Investigating the effect of geomagnetic storm and equatorial electrojet on equatorial ionospheric irregularity over East African sector. Adv. Sp. Res. 2016, 58, 1708–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvath, I.; Essex, E.A. The southern-hemisphere mid-latitude day-time and night-time trough at low-sunspot numbers. J. Atmos. Solar Terr. Phys. 2003, 65, 917–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalswamy, N. Coronal mass ejections and space weather. In Climate and Weather of the Sun-Earth System (CAWSES): Selected Papers from the 2007 Kyoto Symposium; Tsuda, T., Fujii, R., Shibata, K., Geller, M.A., Eds.; Terrapub: Tokyo, Japan, 2009; pp. 77–120. [Google Scholar]
- Karim, G.; Jean, L.Z.; Kaboré, S.; Frédéric, O. Solar events and seasonal variation of foF2 at Korhogo station from 1992 to 2002. Int. J. Phys. Sci. 2020, 15, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, P.A.; Legrand, J.P. Solar cycle and geomagnetic activity: A review for geophysicists. Part. I. The contributions to geomagnetic activity of shock waves and of the solar wind. J. Ann. Geophys. Atmos. Hydrospheres Space Sci. 1989, 7, 565–578. [Google Scholar]
- Richardson, I.G.; Cane, H.V. Sources of Geomagnetic Activity during Nearly Three Solar Cycles (1972–2000). J. Geophys. Res. 2000, 107, 1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, I.G.; Cliver, E.W.; Cane, H.V. Sources of Geomagnetic Activity over the Solar Cycle: Relative Importance of Coronal Mass Ejections, High-Speed Streams, and Slow Solar Wind. J. Geophys. Res. 2002, 105, 18203–18213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalswamy, N.; Lara, A.; Yashiro, S.; Kaiser, M.L.; Howard, R.A. Predicting the 1-AU arrival times of coronal mass ejections. J. Geophys. Res. Sp. Phys. 2001, 106, 29207–29217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, M.J.; Cargill, P. Predictions of the arrival time of Coronal Mass Ejections at 1AU, an analysis of the causes of errors. In Annales Geophysicae; Copernicus GmbH: Göttingen, Germany, 2004; Volume 22, pp. 661–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, M.; Mawad, R.; Shaltout, M. Empirical Model of the Travel Time of Interplanetary Coronal Mass Ejection Shocks. NRIAG J. Astron. Geophys. 2011, 47–61. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/269518496_Empirical_Model_of_the_Travel_Time_of_Interplanetary_Coronal_Mass_Ejection_Shocks (accessed on 27 October 2020).
- Mawad, R.; Youssef, M.; Yousef, S.; Abdel-Sattar, W. Quantized variability of Earth’s magnetopause distance, Quantized variability of Earth’s magnetopause distance. J. Mod. Trends Phys. Res. 2014, 14, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mawad, R.; Farid, H.M.; Yousef, M.; Yousef, S. Empirical CME-SSC listing model. J. Mod. Trends Phys. Res. 2014, 14, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mawad, R.; Radi, A.; Saber, R.; Mahrous, A.; Youssef, M.; Abdel-Sattar, W.; Hussein, M.; Yousef, S. Detection of interplanetary coronal mass ejections’ signature using artificial neural networks. J. Mod. Trends Phys. Res. 2016, 16, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, S.A.; Abdu, M.A.; Batista, I.S.; Sobra, J.H.; Kallio, E.; Maguire, W.C.; Verigin, M.I. On the responses to solar X-ray flare and coronal mass ejection in the ionospheres of Mars and Earth. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebesin, B.O.; Ikupanni, S.O.; Ojediran, J.O.; Kayode, J.S. An investigation into the geomagnetic and ionospheric response during a magnetic activity at high and mid-latitude. Adv. Appl. Sci. Res. 2012, 3, 146–155. [Google Scholar]
- Chaitanya, P.P.; Patra, A.K.; Balan, N.; Rao, S.V.B. Ionospheric variations over Indian low latitudes close to the equator and comparison with IRI-2012. Ann. Geophys. 2015, 33, 997–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schunk, R.; Nagy, A. Ionospheres: Physics, Plasma Physics, and Chemistry, 2nd ed.; Cambridge Atmospheric and Space Science Series; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Parwani, M.; Atulkar, R.; Mukherjee, S.; Purohit, P.K. Latitudinal variation of ionospheric TEC at Northern Hemispheric region. Russ. J. Earth Sci. 2019, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Code | Name | Latitude | Longitude |
|---|---|---|---|
| PRJ18 | Puerto Rico | 18.5° | −67.2° |
| The Seasons | The Period | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Northern Hemisphere | Southern Hemisphere | Start | End |
| Winter | Summer | 1 December | 28 February |
| Spring | Autumn | 1 March | 31 May |
| Summer | Winter | 1 June | 31 August |
| Autumn | Spring | 1 September | 30 November |
| Seasons | Max CME Energy | Average CME Energy | CME Width | CME Speed | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | χ2 | R | χ2 | R | χ2 | R | χ2 | |
| Winter | 0.67 | 33.244 | 0.64 | 36.431 | 0.61 | 38.765 | 0.65 | 35.593 |
| Spring | 0.75 | 52.89 | 0.59 | 79.476 | 0.68 | 64.845 | 0.72 | 58.644 |
| Summer | 0.82 | 31.656 | 0.76 | 41.242 | 0.69 | 51.213 | 0.64 | 57.484 |
| Autumn | 0.80 | 21.987 | 0.35 | 55.283 | 0.62 | 38.906 | 0.46 | 49.43 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Farid, H.M.; Mawad, R.; Ghamry, E.; Yoshikawa, A. The Impact of Coronal Mass Ejections on the Seasonal Variation of the Ionospheric Critical Frequency f0F2. Universe 2020, 6, 200. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe6110200
Farid HM, Mawad R, Ghamry E, Yoshikawa A. The Impact of Coronal Mass Ejections on the Seasonal Variation of the Ionospheric Critical Frequency f0F2. Universe. 2020; 6(11):200. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe6110200
Chicago/Turabian StyleFarid, Hussein M., Ramy Mawad, Essam Ghamry, and Akimasa Yoshikawa. 2020. "The Impact of Coronal Mass Ejections on the Seasonal Variation of the Ionospheric Critical Frequency f0F2" Universe 6, no. 11: 200. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe6110200
APA StyleFarid, H. M., Mawad, R., Ghamry, E., & Yoshikawa, A. (2020). The Impact of Coronal Mass Ejections on the Seasonal Variation of the Ionospheric Critical Frequency f0F2. Universe, 6(11), 200. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe6110200








