35 Years of Ground-Based Gamma-ray Astronomy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The 1980s—Hunting the Snark
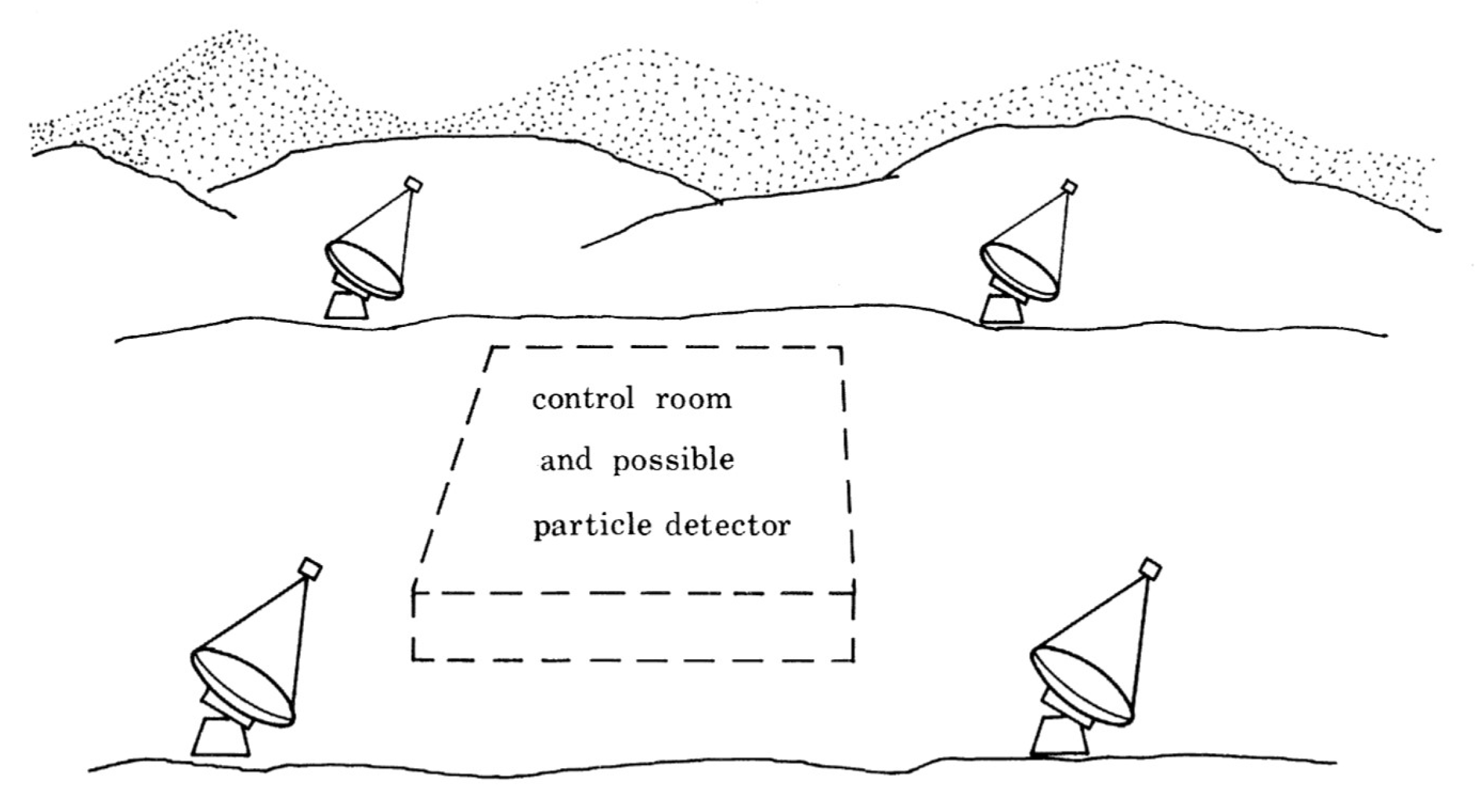
Two large reflectors of size and optical quality similar to the 10 m detector1 would be operated in parallel with a lateral spacing of about 100 m. Each reflector would have a matrix of 5 cm phototubes (19 or 37 in each), each tube having a field of view of 0.25° half-angle. The system would be triggered by a coincidence between one or more detectors in each reflector; the pulse heights of all the tube outputs would then be recorded digitally (6 bit accuracy), so that two “images” would be obtained of the angular distribution of the shower light with 0.5° resolution. By analysis of the “images” in the two systems, it will be possible to determine the energy and the angle of incidence of the shower to high precision.
2.1. Telescopes Everywhere
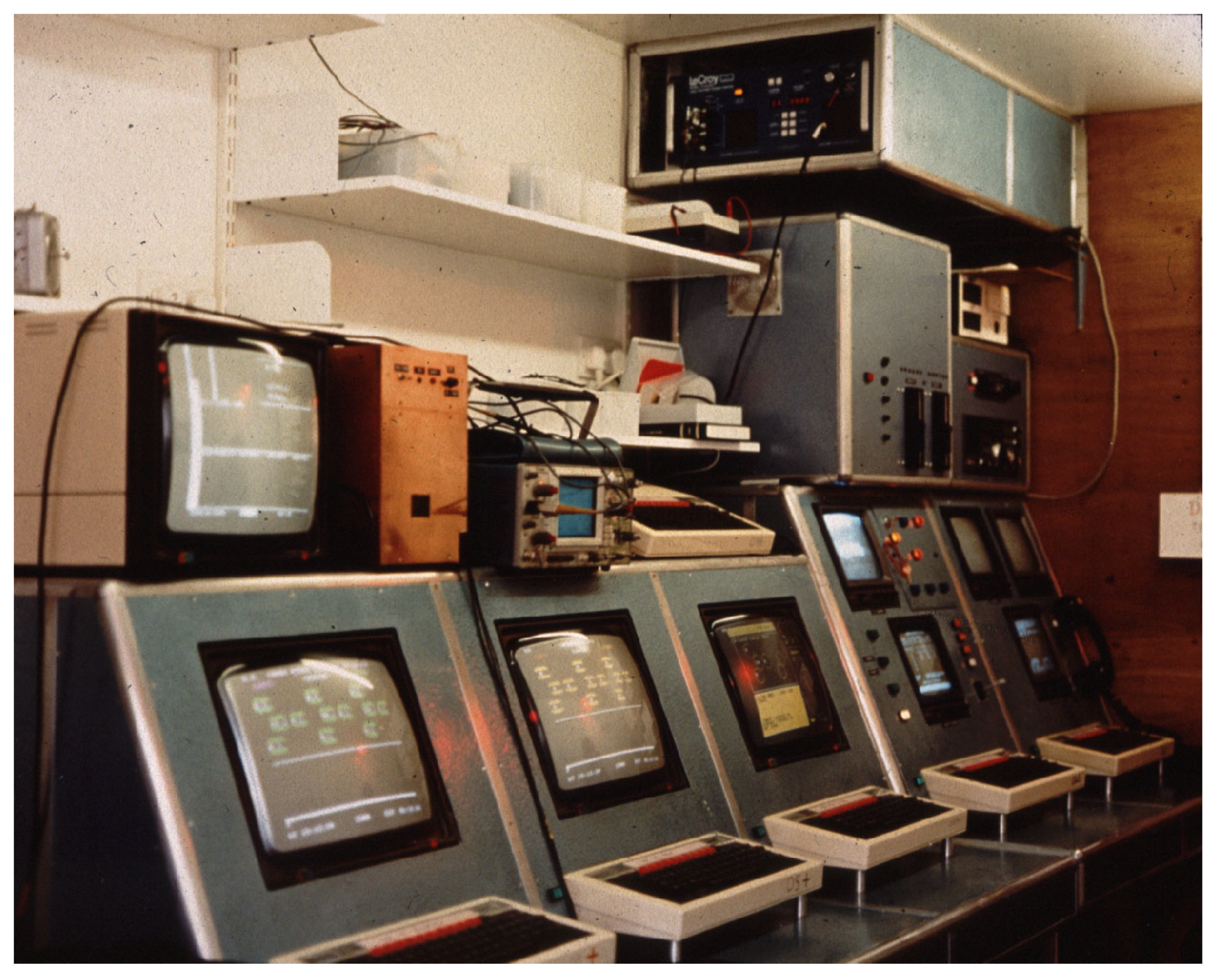
2.2. The Durham Mark III Telescope
2.2.1. Automatic Gain Control
2.2.2. Aluminium Surface, Honeycomb Mirrors
2.2.3. Signal Enhancement
2.3. Gamma-ray Sources (or Not)
Despite its obvious advantages, these ground-based techniques have not been developed to their full potential; the total investment in all such experiments on five continents since the early sixties amounts to only a few million dollars, a small percentage of the cost of GRO5, which included EGRET.), DUMAND6 or a major experiment in high energy physics.
3. The 1990s: Towards a Major Atmospheric Cherenkov Detector
…is it really obvious that the next major advances in ground-based gamma-ray astronomy will have to come with a single large “world” telescope? From my reading of the discussion at the workshop the answer was “no!”; one is bigger but more is better!
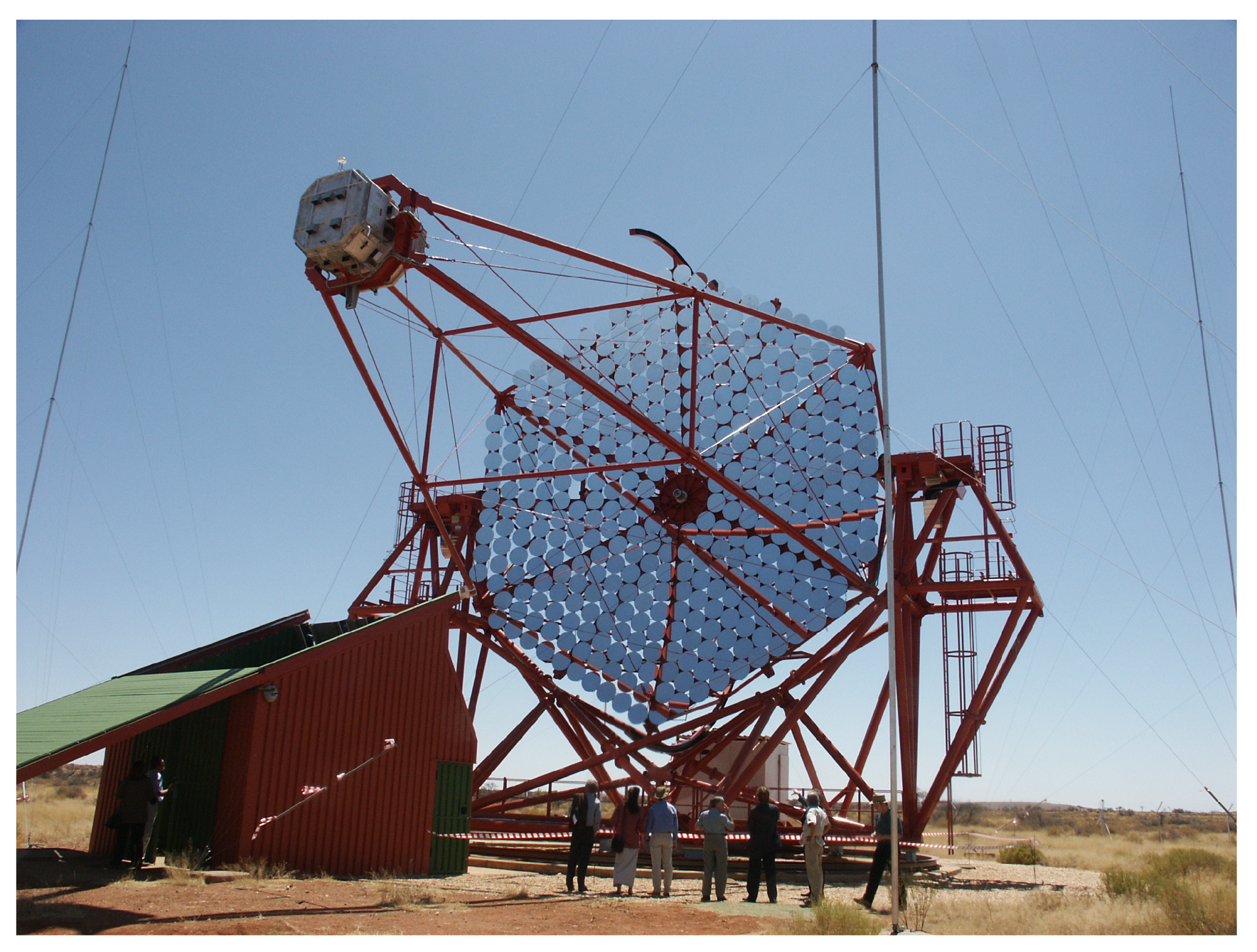
The Durham Mark 6 Telescope
4. The 2000s: Opening the Window
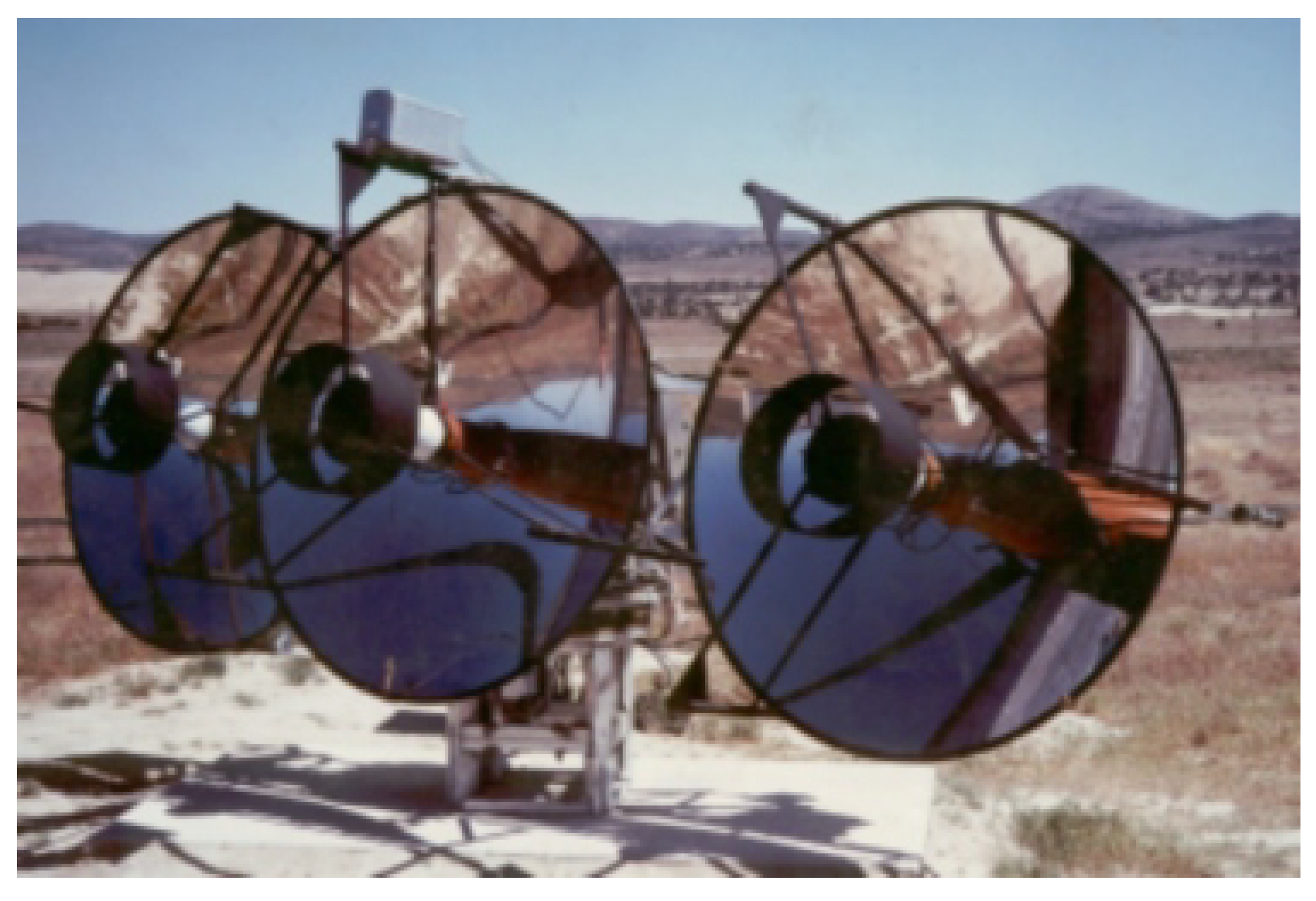
4.1. Solar Farm Telescopes
4.2. IACT Arrays
5. 2010 to the Present: May the Fourth Be with You
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
| 1 | The Whipple Telescope, operated at Mount Hopkins in Arizona. |
| 2 | High Energy Radiation Cameras Using Light Emitting Showers—this field has never been short of acronyms. |
| 3 | Available online: https://alanod.com, accessed on 30 August 2021. |
| 4 | As of 2 September 2021. |
| 5 | The Compton Gamma-Ray Observatory. |
| 6 | Deep Underwater Muon and Neutrino Detector array. Rather similar to KM3NeT in concept, it was cancelled in 1995, just before full deployment. |
| 7 | High-Energy Gamma-Ray Astronomy. |
| 8 | Gamma-ray Astronomy at the South Pole. |
| 9 | A rather wonderful acronym—Tracking High Energy Muons In Showers Triggered On Cerenkov Light Emission. |
| 10 | Pachmarhi array of Cherenkov telescopes. |
| 11 | High-Altitude GAmma Ray. |
| 12 | Durham also ran a telescope (the Mark IV) briefly on La Palma and I remember visiting the HEGRA Cherenkov telescopes. We were impressed that all the cables were cut neatly to length and no longer. This gave the impression that a need for fault-checking with an oscilloscope was not expected. |
| 13 | With the advent of imaging, the Durham telescope numbers changed from Roman to Arabic. I do not think that this was intentional! |
| 14 | the Solar Tower Atmospheric Cherenkov Effect Experiment. |
| 15 | Converted Atmospheric Cherenkov Telescope Using Solar-2. |
| 16 | an acronym that seems to be shrouded in mystery. |
| 17 | Gamma Ray Astronomy at ALmeria. |
| 18 | Another magnificent acronym—Collaboration between Australia and Nippon (Japan) for a GAmma Ray Observatory in the Outback. |
| 19 | Available online: http://tevcat.uchicago.edu/, accessed on 3 September 2021. |
| 20 | Sadly, the University of Leeds group, which had done so much for ground-based gamma-ray astronomy and astroparticle physics in general, disbanded in around 2013. |
References
- Fegan, D. Cherenkov Reflections: Gamma-ray Imaging and the Evolution Of TeV Astronomy; World Scientific: Singapore, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hillas, A.M. Evolution of ground-based gamma-ray astronomy from the early days to the Cherenkov Telescope Arrays. Astropart. Phys. 2013, 43, 19–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turver, K.E.; Weekes, T.C. Gamma Ray Astronomy from 10 to 100 GeV. Il Nuovo Cimento 1978, 45B, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelley, J.V.; Porter, N.A. Cerenkov Radiation from the Night Sky. Q. J. R. Astron. Soc. 1963, 4, 275–293. [Google Scholar]
- Turver, K.E.; Weekes, T.C. Gamma Rays above 100 GeV. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. 1981, 301, 615–628. [Google Scholar]
- Galbraith, W.; Jelley, J.V. Gamma Rays above 100 GeV. Nature 1954, 171, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weekes, T.C.; Lamb, R.C.; Hillas, A.M. Hercules—A New Instrument for TeV Astronomy. In Very High Energy Gamma Ray Astronomy; Turver, K.E., Ed.; NATO ASI Series C: Mathematical and Physical Sciences; D. Reidel: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1987; pp. 235–242. [Google Scholar]
- Brazier, K.T.; Carramiñana, A.; Chadwick, P.M.; Currell, T.R.; Dipper, N.A.; Lincoln, E.W.; Mannings, V.G.; McComb, T.J.L.; Orford, K.J.; Rayner, S.M.; et al. The Durham University Southern Hemisphere VHE Gamma Ray Telescope. Exp. Astron. 1989, 1, 77–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadwick, P.M.; Cleaver, S.A.; Dyrda, M.; Forster, A.; Michalowski, J.; Niemiec, J.; Schultz, C.; Stodulski, M. The Formation of Condensation on Cherenkov Telescope Mirrors. In Proceedings of the 33rd International Cosmic Ray Conference, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2–9 July 2013; p. 3072. [Google Scholar]
- Dowthwaite, J.C.; Harrison, A.B.; Kirkman, I.W.; Macrae, H.J.; Orford, K.J.; Turver, K.E.; Walmsley, M. Hercules X-1—A 1000 GeV Gamma-ray Pulsar. Nature 1984, 309, 691–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadwick, P.M.; Dipper, N.A.; Kirkman, I.W.; McComb, T.J.L.; Orford, K.J.; Turver, K.E. Simultaneous Measurements of VHE Gamma Rays from Hercules X-1. In Very High Energy Gamma Ray Astronomy; Turver, K.E., Ed.; NATO ASI Series C: Mathematical and Physical Sciences; D. Reidel: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1987; pp. 121–123. [Google Scholar]
- Gorham, P.W.; Cawley, M.F.; Fegan, D.J.; Gibbs, K.G.; Lamb, R.C.; Porter, N.A.; Stenger, V.J.; Weekes, T.C. TeV Observations of Her X-1 at the Whipple Observatory. In Very High Energy Gamma Ray Astronomy; Turver, K.E., Ed.; NATO ASI Series C: Mathematical and Physical Sciences; D. Reidel: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1987; pp. 125–130. [Google Scholar]
- Resvanis, L.; Learned, J.; Stenger, V.; Gaidos, D.; Weeks, J.; Loeffler, F.; Olson, J.; Palfrey, T.; Sembroski, G.; Wilson, C.; et al. VHE Gamma Rays from Her X-1 in June–July 1985. In Very High Energy Gamma Ray Astronomy; Turver, K.E., Ed.; NATO ASI Series C: Mathematical and Physical Sciences; D. Reidel: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1987; pp. 131–134. [Google Scholar]
- Gorham, P.W.; Cawley, M.F.; Fegan, D.J.; Gibbs, K.G.; Lamb, R.C.; Liebing, D.F.; Porter, N.A.; Stenger, V.J.; Weekes, T.C. Pulsed TeV Gamma Rays Detected from Hercules X-1 during X-Ray Source Eclipse. Astrophys. J. 1986, 308, L11–L15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gorham, P.W.; Cawley, M.F.; Fegan, D.J.; Gibbs, K.G.; Kenny, S.; Lamb, R.C.; Liebing, D.F.; Porter, N.A.; Stenger, V.J.; Weekes, T.C. Hercules X-1: Pulsed Gamma Rays Detected above 250 GeV. Astrophys. J. 1986, 309, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lamb, R.C.; Cawley, M.F.; Fegan, D.J.; Gibbs, K.G.; Gorham, P.W.; Hillas, A.M.; Lewis, D.A.; Porter, N.A.; Reynolds, P.T.; Weekes, T.C. TeV Gamma Rays from Hercules X-1 Pulsed at an Anomalous Frequency. Astrophys. J. 1988, 328, L13–L16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resvanis, L.K.; Szentgyorgyi, A.; Hudson, J.; Kelley, L.; Learned, J.G.; Sinnis, C.; Stenger, V.; Weeks, D.D.; Gaidos, J.; Kertzman, M.; et al. VHE Gamma Rays from Hercules X-1. Astrophys. J. 1988, 328, L9–L12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishwanath, P.R.; Bhat, P.N.; Ramanamurthy, P.V.; Sreekantan, B.V. A Possible Very High Energy Gamma-Ray Burst from Hercules X-1. Astrophys. J. 1989, 342, 489–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadwick, P.M.; McComb, T.J.L.; Turver, K.E. Very high energy gamma rays from X-ray binary pulsars. J. Phy. G Nucl. Part. Phys. 1990, 16, 1773–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanian, A.A.; Vladimirskii, B.M.; Neshpor, I.I.; Fomin, V.P. Gamma-Ray Emission Spectrum of the CYG X-3 Source and Its Possible Origin. In Proceedings of the 15th International Cosmic Ray Conference, Plovdiv, Bulgaria, 13–26 August 1977; Volume 1, pp. 135–139. [Google Scholar]
- Fomin, V.P.; Neshpor, I.I.; Stepanian, A.A.; Zyskin, I.L.; Vladimirskii, B.M. Observations of Gamma-Radiation with the Energy 1012 eV from CYG X-3 in 1979-80. In Proceedings of the 17th International Cosmic Ray Conference, Paris, France, 13–25 July 1981; Volume 1, pp. 28–32. [Google Scholar]
- Danaher, S.; Fegan, D.J.; Porter, N.A.; Weekes, T.C. Gamma-ray observations of CYG X-3 at energies of 1012 eV. Nature 1981, 289, 568–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danaher, S.; Fegan, D.J.; Porter, N.A.; Weekes, T.C. Cygnus X-3 observed at photon energies above 500 GeV. Nature 1982, 296, 543–544. [Google Scholar]
- Dowthwaite, J.C.; Gibson, A.I.; Harrison, A.B.; Kirkman, I.W.; Lotts, A.P.; Macrae, J.H.; Orford, K.J.; Turver, K.E.; Walmsley, M. Ultra high energy gamma rays from CYG X-3. Astron. Astrophys. 1983, 126, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Chadwick, P.M.; Dipper, N.A.; Dowthwaite, J.C.; Gibson, A.I.; Harrison, A.B. A 12.6-ms pulsar in Cygnus X-3. Nature 1985, 318, 642–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadwick, P.M.; Dipper, N.A.; Dowthwaite, J.C.; McComb, T.J.L.; Orford, K.J.; Turver, K.E. Further Evidence for the Emission of 1000 GeV Gamma Rays with 12 ms Periodicity in Cygnus X-3. In Very High Energy Gamma Ray Astronomy; Turver, K.E., Ed.; NATO ASI Series C: Mathematical and Physical Sciences; D. Reidel: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1987; pp. 115–121. [Google Scholar]
- Brazier, K.T.S.; Carraminana, A.; Chadwick, P.M.; Dipper, N.A.; Lincoln, E.W.; Mackie, P.C.; Mannings, V.G.; McComb, T.J.L.; Orford, K.J.; Rayner, S.M.; et al. New Measurements of the 12.6 Millisecond Pulsar in Cygnus X-3. Astrophys. J. 1990, 350, 745–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, D.A. Detection of weak signals in TeV gamma-ray astronomy: DC excess periodic amplitude. Astron. Astrophys. 1989, 219, 352–357. [Google Scholar]
- Resvanis, L.; Learned, J.; Stenger, V.; Gaidos, D.; Weeks, J.; Loeffler, F.; Olson, J.; Palfrey, T.; Sembroski, G.; Wilson, C.; et al. VHE Gamma Rays from Cygnus X-3. In Very High Energy Gamma Ray Astronomy; Turver, K.E., Ed.; NATO ASI Series C: Mathematical and Physical Sciences; D. Reidel: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1987; pp. 105–110. [Google Scholar]
- Bhat, P.N.; Ramana Murthy, P.V.; Vishwanath, P.R. Search for 12.6 millisecond periodicity in TeV gamma rays from Cygnus X-3. J. Astrophys. Astron. 1988, 9, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marshak, L.M. Periodicity Analyses of Radiation from VHE and UHE Sources. In Proceedings of the 21st International Cosmic Ray Conference, Adelaide, Australia, 6–19 January 1990; Volume 2, pp. 6–10. [Google Scholar]
- Chardin, G.; Gerbier, G. Cygnus X-3 at high energies: A critical analysis of observational results. Astron. Astrophys. 1989, 210, 52–65. [Google Scholar]
- The Fermi LAT Collaboration. Modulated High-Energy Gamma-Ray Emission from the Microquasar Cygnus X-3. Science 2009, 326, 1512–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillas, A.M. Cerenkov Light Images of EAS Produced by Primary Gamma Rays and by Nuclei. In Proceedings of the 19th International Cosmic Ray Conference, La Jolla, CA, USA, 11–23 August 1985; Volume 3, pp. 445–449. [Google Scholar]
- Weekes, T.C.; Cawley, M.F.; Fegan, D.J.; Gibbs, K.G.; Hillas, A.M.; Kowk, P.W.; Lamb, R.C.; Lewis, D.A.; Macomb, D.; Porter, N.A.; et al. Observation of TeV Gamma Rays from the Crab Nebula Using the Atmospheric Cerenkov Imaging Technique. Astrophys. J. 1989, 342, 379–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punch, M.; Akerlof, C.W.; Cawley, M.F.; Chantell, M.; Fegan, D.J.; Fennell, S.; Gaidos, J.A.; Hagan, J.; Hillas, A.M.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Detection of TeV photons from the active galaxy Markarian 421. Nature 1992, 358, 477–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quinn, J.; Akerlof, C.W.; Biller, S.; Buckley, J.; Carter-Lewis, D.A.; Cawley, M.F.; Catanese, M.; Connaughton, V.; Fegan, D.J.; Finley, J.P.; et al. Detection of Gamma Rays with E 300 GeV from Markarian 501. Astrophys. J. (Lett.) 1996, 456, L83–L86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weekes, T.C.; Akerlof, C.W.; Chantell, M.; Colombo, E.; Connaughton, V.; Fegan, D.J.; Fennell, S.; Gaidos, J.; Harris, K.; Hillas, A.M.; et al. Whipple Observatory Status Report. In Towards a Major Atmospheric Cherenkov Detector—II; Lamb, R.C., Ed.; Iowa State University: Ames, IA, USA, 1993; pp. 131–134. [Google Scholar]
- Bowden, C.C.G.; Bradbury, S.M.; Chadwick, P.M.; Dickinson, J.E.; Dipper, N.A.; Lincoln, E.W.; McComb, T.J.L.; Orford, K.J.; Osborne, J.L.; Rayner, S.M.; et al. Stereo Imaging of 350 GeV Atmospheric Cherenkov Light Signals. In Towards a Major Atmospheric Cherenkov Detector—II; Lamb, R.C., Ed.; Iowa State University: Ames, IA, USA, 1993; pp. 131–134. [Google Scholar]
- Raubenheimer, B.C.; Brink, C.; Visser, B.; van Wyk, J.P.; North, A.R.; Nel, H.I.; De Jager, O.C.; Meintjes, P.J. Nooitgedacht Mk II Telescope: An Update. In Towards a Major Atmospheric Cherenkov Detector—II; Lamb, R.C., Ed.; Iowa State University: Ames, IA, USA, 1993; pp. 87–90. [Google Scholar]
- Aharonian, F.A. [HEGRA Collaboration]. The Project of the HEGRA Imaging Cherenkov Telescope System: Status and Motivations. In Towards a Major Atmospheric Cherenkov Detector—II; Lamb, R.C., Ed.; Iowa State University: Ames, IA, USA, 1993; pp. 81–86. [Google Scholar]
- Tilav, S. [GASP Collaboration]. GASP—Gamma Ray Astronomy At The South Pole. In Towards a Major Atmospheric Cherenkov Detector—II; Lamb, R.C., Ed.; Iowa State University: Ames, IA, USA, 1993; pp. 72–74. [Google Scholar]
- Lorenz, E. A Concept for an Imaging Detector based on a fast Image Intensifier and a Matrix of Avalanche Photodiodes In Towards a Major Atmospheric Cherenkov Detector—II; Lamb, R.C., Ed.; Iowa State University: Ames, IA, USA, 1993; pp. 182–187. [Google Scholar]
- THEMISTOCLE Collaboration. Gamma ray spectrum of the Crab nebula in the multi TeV region. Astropart. Phys. 1998, 1, 341–355. [Google Scholar]
- Vishwanath, P.R.; Acharya, B.S.; Bhat, P.N.; Chitnis, V.R.; Majumdar, P.; Rahman, M.A.; Singh, B.B. Very High Energy Gamma Ray Emission from Crab Nebula with the PACT Array. In Proceedings of the 27th International Cosmic Ray Conference, Hamburg, Germany, 7–15 August 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Shukla, A.; Chitnis, V.R.; Vishwanath, P.R.; Acharya, B.S.; Anupama, G.C.; Bhattacharjee, P.; Britto, R.J.; Prabhu, T.P.; Saha, L.; Singh, B.B. Multiwavelength study of the TeV blazar Mrk 421 during a giant flare. Astron. Astrophys. 2012, 541, A140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, A.; Shukla, A.; Saha, L.; Acharya, B.S.; Anupama, G.C.; Bhattacharjee, P.; Britto, R.J.; Chitnis, V.R.; Prabhu, T.P.; Singh, B.B.; et al. Long-term study of Mkn 421 with the HAGAR Array of Telescopes. Astron. Astrophys. 2016, 591, A83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Daum, A.; Hermann, G.; Heß, M.; Hofmann, W.; Lampeitl, H.; Pühlhofer, G.; Aharonian, F.; Akhperjanian, A.G.; Barrio, J.A.; Beglarian, A.S.; et al. First results on the performance of the HEGRA IACT array. Astropart. Phys. 1997, 1–2, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aharonian, F.; Akhperjanian, A.; Barrio, J.; Bernlöhr, K.; Börst, H.; Bojahr, H.; Bolz, O.; Contreras, J.; Cortina, J.; Denninghoff, S.; et al. Evidence for TeV gamma ray emission from Cassiopeia A. Astron. Astrophys. 2001, 370, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aharonian, F.; Akhperjanian, A.; Beilicke, M.; Bernlöhr, K.; Börst, H.-G.; Bojahr, H.; Bolz, O.; Coarasa, T.; Contreras, J.L.; Cortina, J.; et al. Is the giant radio galaxy M 87 a TeV gamma-ray emitter? Astron. Astrophys. 2003, 403, L1–L5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barrau, A.; Bazer-Bachi, R.; Beyer, E.; Cabot, H.; Cerutti, M.; Chounet, L.M.; Debiais, G.; Degrange, B.; Delchini, H.; Denance, J.P.; et al. The CAT imaging telescope for very-high-energy gamma-ray astronomy. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 1998, 416, 278–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chadwick, P.M.; Dickinson, M.R.; Dipper, N.A.; Holder, J.; Kendall, T.R.; McComb, T.J.L.; Orford, K.J.; Rayner, S.M.; Roberts, I.D.; Shaw, S.E.; et al. The University of Durham Mark 6 low energy threshold ground-based gamma-ray telescope. Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 1996, 120, 657–660. [Google Scholar]
- Chadwick, P.M.; Lyons, K.; McComb, T.J.L.; Orford, K.J.; Osborne, J.L.; Rayner, S.M.; Shaw, S.E.; Turver, K.E.; Wieczorek, G.J. Very High Energy Gamma Rays from PKS 2155-304. Astrophys. J. 1999, 513, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chadwick, P.M.; Lyons, K.; McComb, T.J.L.; Orford, K.J.; Osborne, J.L.; Rayner, S.M.; Roberts, I.D.; Shaw, S.E.; Turver, K.E. Geomagnetic effects on atmospheric Cerenkov images. J. Phys. Nucl. Part. Phys. 1999, 25, 1223–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danaher, S.; Fegan, D.J.; Porter, N.A.; Weekes, T.C.; Cole, T. Possible applications of large solar arrays in astronomy and astrophysics. Sol. Energy 1982, 28, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tümer, O.T.; Kerrick, A.D.; O’Neill, T.J.; White, R.S.; Zych, A.D. Solar One Gamma Ray Observatory for Intermediate High Energies of 10 to 500 GeV. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Cosmic Ray Conference, Dublin, Ireland, 11–23 August 1991; Volume 2, pp. 634–638. [Google Scholar]
- Hanna, D.S.; Bhattacharya, D.; Boone, L.M.; Chantell, M.C.; Conner, Z.; Covault, C.E.; Dragovan, M.; Fortin, P.; Gregorich, D.T.; Hinton, J.A. The STACEE-32 ground based gamma-ray detector. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 2002, 491, 126–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zweerink, J. The Solar Two Gamma-Ray Observatory: Astronomy between 20–300 GeV. In Proceedings of the 26th International Cosmic Ray Conference, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 17–25 August 1999; pp. 223–227. [Google Scholar]
- Paré, E.; Balauge, B.; Bazer-Bachi, R.; Bergeret, H.; Berny, F.; Briand, N.; Bruel, P.; Cerutti, M.; Collon, J.; Cordier, A.; et al. CELESTE: An atmospheric Cherenkov telescope for high energy gamma astrophysics. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 2002, 490, 71–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arqueros, F. The GRAAL experiment. Nucl. Phys. Proc. Suppl. 2003, 114, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oser, S.; Bhattacharya, D.; Boone, L.M.; Chantell, M.C.; Conner, Z.; Covault, C.E.; Dragovan, M.; Fortin, P.; Gregorich, D.T.; Hanna, D.S.; et al. High-Energy Gamma-Ray Observations of the Crab Nebula and Pulsar with the Solar Tower Atmospheric Cerenkov Effect Experiment. Astrophys. J. 2001, 547, 949–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, D.A.; Bazer-Bachi, R.; Bergeret, H.; Bruel, P.; Cordier, A.; Debiais, G.; de Naurois, M.; Dezalay, J.-P.; Dumora, D.; Eschstruth, P.; et al. First Detection of Gamma Rays from the Crab Nebula with the CELESTE “Solar Farm” Cherenkov Detector. Nucl. Phys. Proc. Suppl. 2000, 80, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.A.; Brion, E.; Britto, R.; Bruel, P.; Bussons Gordo, J.; Dumora, D.; Durand, E.; Eschstruth, P.; Espigat, P.; Holder, J. Mrk 421, Mrk 501, and 1ES 1426 + 428 at 100 GeV with the CELESTE Cherenkov telescope. Astron. Astrophys. 2006, 459, 453–464. [Google Scholar]
- Boone, L.M.; Hinton, J.A.; Bramel, D.; Chae, E.; Covault, C.E.; Fortin, P.; Gingrich, D.M.; Hanna, D.S.; Mukherjee, R.; Mueller, C.; et al. STACEE Observations of Markarian 421 during an Extended Gamma-Ray Outburst. Astrophys. J. 2006, 579, L5–L8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jarvis, A.; Ong, R.A.; Williams, D.A.; Aune, T.; Ball, J.; Carson, J.E.; Covault, C.E.; Driscoll, D.D.; Fortin, P.; Gingrich, D.M.; et al. Very High Energy Observations of Gamma-ray Bursts with STACEE. Astrophys. J. 2010, 722, 862–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Naurois, M.; Holder, J.; Bazer-Bachi, R.; Bergeret, H.; Bruel, P.; Cordier, A.; Debiais, G.; Dezalay, J.-P.; Dumora, D.; Durand, E.; et al. Measurement of the Crab Flux above 60 GeV with the CELESTE Cerenkov Telescope. Astrophys. J. 2002, 566, 343–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, D.A. Review of the Solar Array Telescopes. In Towards a Network of Atmospheric Cherenkov Detectors VII; Ecole Polytechnique: Paliaseau, France, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Bernlöhr, K.; Carrol, O.; Cornils, R.; Elfahem, S.; Espigat, P.; Gillessen, S.; Heinzelmann, G.; Hermann, G.; Hofmann, W.; Horns, D.; et al. The optical system of the H.E.S.S. imaging atmospheric Cherenkov telescopes. Part I: Layout and components of the system. Astropart. Phys. 2003, 20, 111–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funk, S.; Hermann, G.; Hinton, J.; Berge, D.; Bernlöhr, K.; Hofmann, W.; Nayman, P.; Toussenel, F.; Vincent, P. The trigger system of the H.E.S.S. telescope array. Astropart. Phys. 2004, 22, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bolmont, J.; Corona, P.; Gauron, P.; Ghislain, P.; Goffin, C.; Guevara Riveros, L.; Huppert, J.-F.; Martineau-Huynh, O.; Nayman, P.; Parraud, J.-M.; et al. The camera of the fifth H.E.S.S. telescope. Part I: System description. Nucl. Inst. Methods Phys. Res. A 2014, 761, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baixeras, C. [MAGIC Collaboration]. The MAGIC Telescope. Nucl. Phys. B Proc. Suppl. 2003, 114, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferenc, D. [MAGIC Collaboration]. The MAGIC gamma-ray observatory. Nucl. Inst. Methods Phys. Res. A 2005, 553, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holder, J.; Atkins, R.W.; Badran, H.M.; Blaylock, G.; Bradbury, S.M.; Buckley, J.H.; Byrum, K.L.; Carter-Lewis, D.A.; Celik, O.; Chow, Y.C.K.; et al. The first VERITAS telescope. Astropart. Phys. 2006, 25, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gibbs, K.; Criswell, S.; Falcone, A.; Gaidos, J.; Harris, K.; Horan, D.; Schroedter, M.; Weekes, T.C.; Williams, J.T. The VERITAS Atmospheric Cerenkov Telescopes: Positioner, Optics and Associated Components. In Proceedings of the 29th International Cosmic Ray Conference, Pune, India, 31 July–7 August 2003; Volume 5, pp. 2823–2826. [Google Scholar]
- Enomoto, R.; Hara, S.; Asahara, A.; Bicknell, G.V.; Edwards, P.G.; Gunji, S.; Hara, T.; Jimbo, J.; Kajino, F.; Katagiri, H.; et al. Design study of CANGAROO-III, stereoscopic imaging atmospheric Cherenkov telescopes for sub-TeV/γ-ray detection. Astropart. Phys. 2002, 16, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mori, M. CANGAROO Project for High-Energy Gamma-Ray Astrophysics. Prog. Theor. Phys. Suppl. 2003, 151, 85–94. [Google Scholar]
- Enomoto, R.; Watanabe, S.; Tanimori, T.; Asahara, A.; Bicknell, G.V.; Clay, R.W.; Edwards, P.G.; Gunji, S.; Hara, S.; Hattori, T.; et al. CANGAROO III Observations of the Supernova Remnant RX J0852.0-4622. Astrophys. J. 2006, 652, 1268–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aharonian, F. et al. [H.E.S.S. Collaboration] H.E.S.S. observations of PKS 2155-304. Astron. Astrophys. 2005, 430, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aharonian, F. et al. [H.E.S.S. Collaboration] A new population of very high energy gamma-ray sources in the Milky Way. Science 2005, 307, 1938–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aharonian, F.A. et al. [H.E.S.S. Collaboration] High energy particle acceleration in the shell of a supernova remnant. Nature 2004, 432, 75–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aharonian, F.A.; Konopelko, A.K.; Völk, H.J.; Quintana, H. 5@5-A 5 GeV Energy Threshold Array of Imaging Atmospheric Cherenkov Telescopes at 5 km Altitude. Astropart. Phys. 2001, 15, 335–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hinton, J.A.; Sarkar, S.; Torres, D.; Knapp, J. Seeing the High-Energy Universe with the Cherenkov Telescope Array—The Science Explored with the CTA. Astropart. Phys. (Spec. Ed.) 2013, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- The CTA Consortium. Science with the Cherenkov Telescope Array; World Scientific: Singapore, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Albert, A. et al. [HAWC Collaboration] 3HWC: The third HAWC catalog of very-high-energy gamma-ray sources. Astrophys. J. 2020, 905, 76–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barres de Almeida, U. [SWGO Collaboration]. The Southern Wide-Field Gamma-ray Observatory (SWGO). In Proceedings of the IWARA 2020 Virtual Conference, virtual meeting, 6–12 September 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Z.; Aharonian, F.A.; An, Q.; Axikegu; Bai, L.X.; Bai, Y.X.; Bao, Y.W.; Bastieri, D.; Bi, X.J.; Bi, Y.J.; et al. Ultrahigh-energy photons up to 1.4 petaelectronvolts from 12 gamma-ray Galactic sources. Nature 2021, 594, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chadwick, P. 35 Years of Ground-Based Gamma-ray Astronomy. Universe 2021, 7, 432. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe7110432
Chadwick P. 35 Years of Ground-Based Gamma-ray Astronomy. Universe. 2021; 7(11):432. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe7110432
Chicago/Turabian StyleChadwick, Paula. 2021. "35 Years of Ground-Based Gamma-ray Astronomy" Universe 7, no. 11: 432. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe7110432
APA StyleChadwick, P. (2021). 35 Years of Ground-Based Gamma-ray Astronomy. Universe, 7(11), 432. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe7110432





