Elongated Gravity Sources as an Analytical Limit for Flat Galaxy Rotation Curves
Abstract
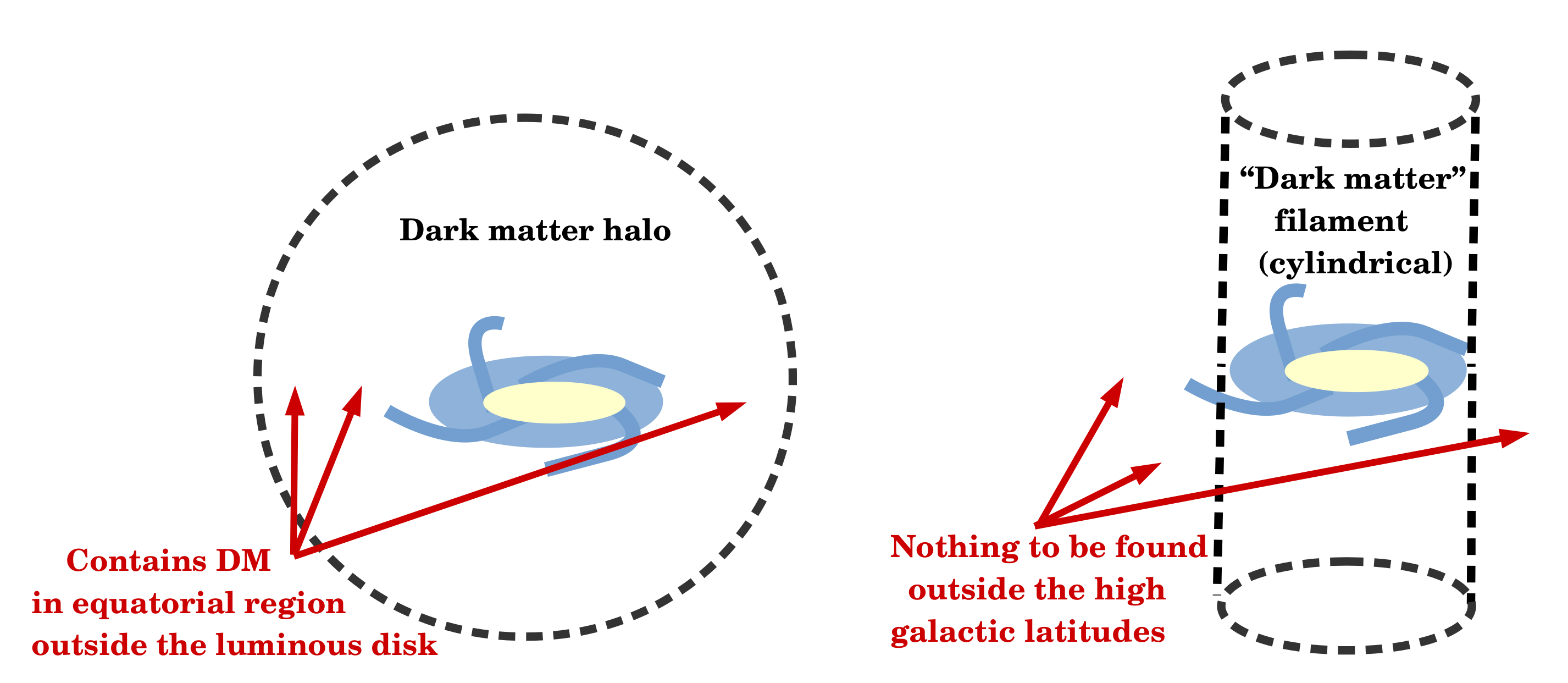
:1. Introduction
2. Most Common Explanations for Flat Rotation Curves
2.1. Kepler’s Problem
2.2. Standard Isothermal, Spherical Dark Matter Halo
2.3. Modified Newtonian Dynamics
3. Cylindrical Symmetry of the Gravitational Source
3.1. Corrections to a Basic Filamentary Geometry
3.1.1. Finite-Length Cylinder
3.1.2. Finite-Width Cylinder
3.1.3. Rotation Curve Outside a Sphere + Filament Distribution Arrangement
4. Classical Equations of Motion Outside the Filament
4.1. Helicoidal Motion along the Filament
4.1.1. Cyclotron/Synchrotron Radiation
4.1.2. Galactic Aurora
4.2. Radial Motion towards the Filament
4.3. Precession of Orbits Outside but near the Galactic Plane
5. The Tully–Fisher Relation
5.1. Luminous Matter Accretion on a Filamentary Overdensity
5.2. Scaling down to the Solar System
5.3. Inference by Stellar Scattering
5.4. Direct Imaging
6. Further Consequences
6.1. Galaxy Plane—Galaxy Plane Correlations
6.2. Virial Theorem for Small Galaxy Clusters
6.3. Gravitational Lensing
7. Discussion
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rubin, V.C.; Ford, W.K., Jr. Rotation of the Andromeda Nebula from a Spectroscopic Survey of Emission Regions. Astrophys. J. 1970, 159, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelli, F.; McGaugh, S.S.; Schombert, J.M. SPARC: Mass Models for 175 Disk Galaxies with Spitzer Photometry and Accurate Rotation Curves. Astron. J. 2016, 152, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Epps, S.D.; Hudson, M.J. The Weak Lensing Masses of Filaments between Luminous Red Galaxies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 468, 2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weinberg, S. Cosmology; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2008; ISBN 10 0198526822. [Google Scholar]
- Boveia, A.; Doglioni, C. Dark Matter Searches at Colliders. Ann. Rev. Nucl. Part Sci. 2018, 68, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cebrián, S. Small scale direct dark matter search experiments. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1910.13947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, M. Dark Matter searches via direct detection. PoS Proc. Sci. 2019, 2018, 037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hooper, D. TASI Lectures on Indirect Searches For Dark Matter. PoS Proc. Sci. 2019, 2018, 010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monroy-Rodríguez, M.A.; Allen, C. The end of the MACHO era- revisited: New limits on MACHO masses from halo wide binaries. Astrophys. J. 2014, 790, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garcia-Bellido, J.; Clesse, S.; Fleury, P. Primordial black holes survive SN lensing constraints. Phys. Dark Univ. 2018, 20, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Natarajan, P.; Zhao, H. MOND plus classical neutrinos not enough for cluster lensing. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 2008, 389, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Milgrom, M. Gravitational waves in bimetric MOND. Phys. Rev. D 2014, 89, 024027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Varieschi, G.U. Newtonian Fractional-Dimension Gravity and MOND. Found. Phys. 2020, 50, 1608–1644, Erratum in 2021, 51, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varieschi, G.U. Newtonian Fractional-Dimension Gravity and Disk Galaxies. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2021, 136, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varieschi, G.U. Newtonian Fractional-Dimension Gravity and Rotationally Supported Galaxies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2021, 503, 1915–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giusti, A. MOND-like Fractional Laplacian Theory. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 101, 124029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giusti, A.; Garrappa, R.; Vachon, G. On the Kuzmin model in fractional Newtonian gravity. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2020, 135, 798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodelson, S. The Real Problem with MOND. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2011, 20, 2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pina, P.E.; Fraternali, F.; Adams, E.A.; Marasco, A.; Oosterloo, T.; Oman, K.A.; Leisman, L.; Di Teodoro, E.M.; Posti, L.; Battipaglia, M.; et al. Off the Baryonic Tully–Fisher Relation: A Population of Baryon-dominated Ultra-diffuse Galaxies. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2019, 883, L33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clowe, D.; Gonzalez, A.; Markevitch, M. Weak lensing mass reconstruction of the interacting cluster 1E0657-558: Direct evidence for the existence of dark matter. Astrophys. J. 2004, 604, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sofue, Y. Dark halos of M 31 and the Milky Way. Publ. Astron. Soc. Jpn. 2015, 67, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bariego-Quintana, A.; Manzanilla, O.; Llanes-Estrada, F.J. Contribution to the EPS-HEP 2021 European Conference on High Energy Physics. Extended Work in Preparation. Available online: https://indico.desy.de/event/28202/contributions/105991/ (accessed on 10 September 2021).
- Su, M.; Slatyer, T.R.; Finkbeiner, D.P. Giant Gamma-ray Bubbles from Fermi-LAT: AGN Activity or Bipolar Galactic Wind? Astrophys. J. 2010, 724, 1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pawlowski, M.S. The Planes of Satellite Galaxies Problem, Suggested Solutions, and Open Questions. Mod. Phys. Lett. A 2018, 33, 1830004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gialluca, M.T.; Naidu, R.P.; Bonaca, A. Velocity Dispersion of the GD-1 Stellar Stream. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2021, 911, L32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tully, R.B.; Fisher, J.R. A New method of determining distances to galaxies. Astron. Astrophys. 1977, 54, 661. [Google Scholar]
- McGaugh, S. The Baryonic Tully-Fisher Relation of Gas Rich Galaxies as a Test of LCDM and MOND. Astron. J. 2012, 143, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prusti, T.; De Bruijne, J.H.; Brown, A.G.; Vallenari, A.; Babusiaux, C.; Bailer-Jones, C.A.; Bastian, U.; Biermann, M.; Evans, D.W.; Eyer, L.; et al. The Gaia Mission. Astron. Astrophys. 2016, 595, A1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.G.; Vallenari, A.; Prusti, T.; De Bruijne, J.H.; Babusiaux, C.; Bailer-Jones, C.A.; Biermann, M.; Evans, D.W.; Eyer, L.; Jansen, F.; et al. Gaia Data Release 2: Summary of the contents and survey properties. Astron. Astrophys. 2018, 616, A1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alves, J.; Zucker, C.; Goodman, A.A.; Speagle, J.S.; Meingast, S.; Robitaille, T.; Finkbeiner, D.P.; Schlafly, E.F.; Green, G.M. A Galactic-scale gas wave in the solar neighbourhood. Nature 2020, 578, 237–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Draine, B.T. Physics of the Interstellar and Intergalactic Medium; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, S.; Albareti Franco, D.; Allende Prieto, C.; Anders, F.; Anderson Scott, F.; Anderton, T.; Andrews Brett, H.; Armengaud, E.; Aubourg, É.; Bailey, S.; et al. The Eleventh and Twelfth Data Releases of the Sloan Digital Sky Survey: Final Data from SDSS-III. Astrophys. J. 2015, 219, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eckert, D.; Jauzac, M.; Shan, H.; Kneib, J.; Erben, T.; Israel, H.; Jullo, E.; Klein, M.; Massey, R.; Richard, J.; et al. Warm-hot baryons comprise 5–10 per cent of filaments in the cosmic web. Nature 2015, 528, 105–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Umehata, H.; Fumagalli, M.; Smail, I.; Matsuda, Y.; Swinbank, A.M.; Cantalupo, S.; Sykes, C.; Ivison, R.J.; Steidel, C.C.; Shapley, A.E.; et al. Gas filaments of the cosmic web located around active galaxies in a protocluster. Science 2019, 366, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, P.; Guo, Q.; Kang, X.; Libeskind, N.I. Illustris-1 simulation. Astrophys. J. 2018, 866, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okabe, T.; Nishimichi, T.; Oguri, M.; Peirani, S.; Kitayama, T.; Sasaki, S.; Suto, Y. Projected alignment of non-sphericities of stellar, gas, and dark matter distributions in galaxy clusters: Analysis of the Horizon-AGN simulation. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 478, 1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pen, U.; Lee, J.; Seljak, U. Tentative Detection of Galaxy Spin Correlations in the Tully Catalog. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2000, 543, L107–L110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turyshev, S.G.; Toth, V.T. Multipole decomposition of gravitational lensing. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.13126. [Google Scholar]
- Trendafilova, C.S.; Fulling, S.A. Static solutions of Einstein’s equations with cylindrical symmetry. Eur. J. Phys. 2011, 32, 1663–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jauzac, M.; Harvey, D.; Massey, R. The shape of galaxy dark matter haloes in massive galaxy clusters: Insights from strong gravitational lensing. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 477, 4046–4051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mocz, P.; Fialkov, A.; Vogelsberger, M.; Becerra, F.; Shen, X.; Robles, V.H.; Amin, M.A.; Zavala, J.; Boylan-Kolchin, M.; Bose, S.; et al. Galaxy formation with BECDM—II. Cosmic filaments and first galaxies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 494, 2027–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaer, V.B.; Moore, G.D. Global cosmic string networks as a function of tension. arXiv 2020, arXiv:1912.08058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, M.D.; Frenk, C.S.; Cole, S. The Shapes and Alignments of Dark Matter Halos. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2012, 1205, 030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]










Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Llanes-Estrada, F.J. Elongated Gravity Sources as an Analytical Limit for Flat Galaxy Rotation Curves. Universe 2021, 7, 346. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe7090346
Llanes-Estrada FJ. Elongated Gravity Sources as an Analytical Limit for Flat Galaxy Rotation Curves. Universe. 2021; 7(9):346. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe7090346
Chicago/Turabian StyleLlanes-Estrada, Felipe J. 2021. "Elongated Gravity Sources as an Analytical Limit for Flat Galaxy Rotation Curves" Universe 7, no. 9: 346. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe7090346
APA StyleLlanes-Estrada, F. J. (2021). Elongated Gravity Sources as an Analytical Limit for Flat Galaxy Rotation Curves. Universe, 7(9), 346. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe7090346





