Characterization of a Novel Ginsenoside MT1 Produced by an Enzymatic Transrhamnosylation of Protopanaxatriol-Type Ginsenosides Re
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Biotransformation of Ginsenosides Using Recombinant MT619
2.3. Optimization of the Substrate Concentration
2.4. Scaled-Up Ginsenoside MT1 Production
2.5. Purification of MT1 from the Enzymatically Converted Products
2.6. Recycling Preparative High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (RPHPLC) Purification of MT1 from Biotransformed Products
2.7. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Analysis
2.8. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) and Mass Spectrometry (MS) Analyses
2.9. Acidic Hydrolysis of MT1 and TLC Analysis
3. Results
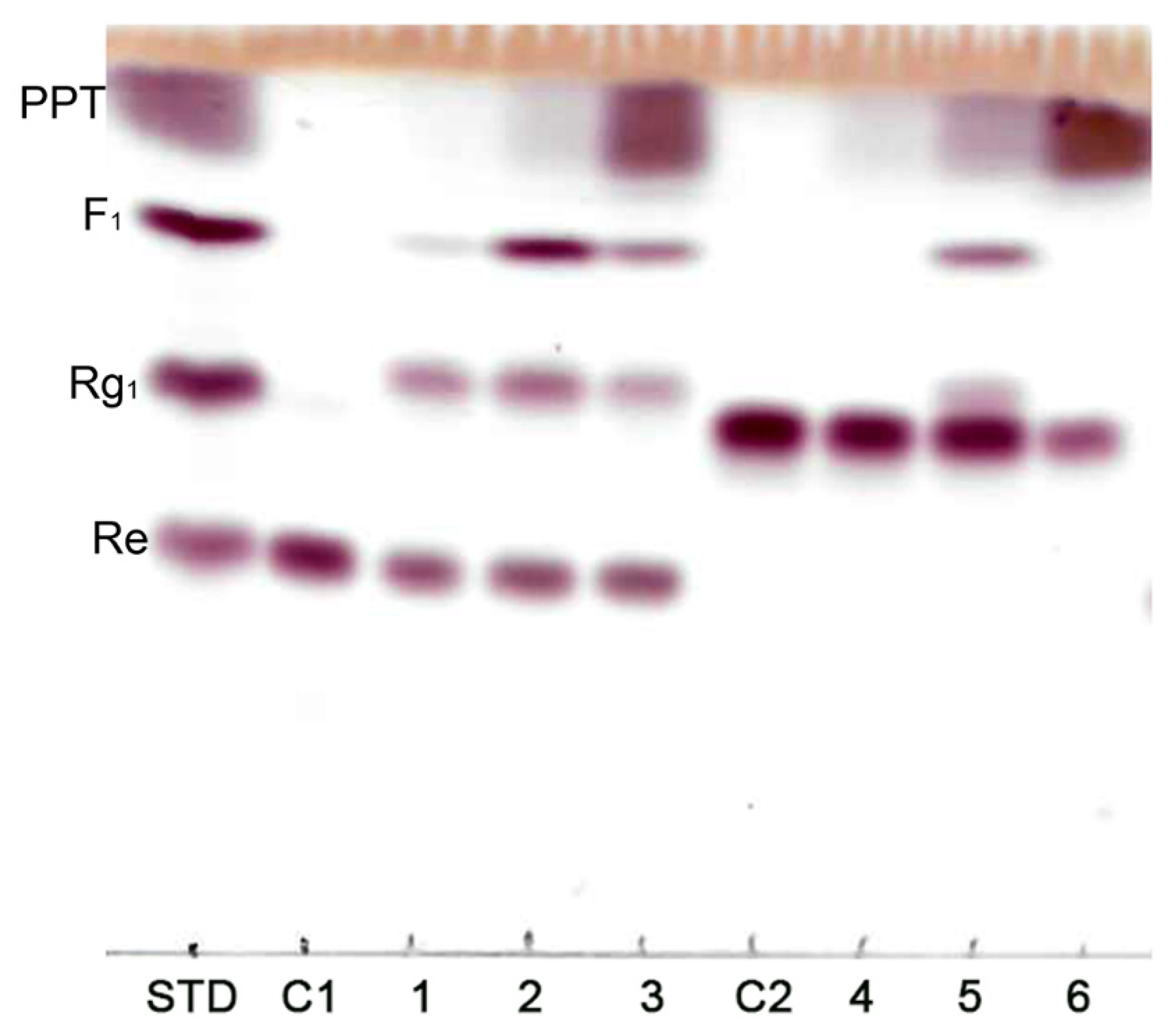
3.1. Ginsenoside Re Transformation of MT619
3.2. Optimization for Ginsenoside MT1 Production
3.3. Mass Production of MT1
3.4. Purification of MT1 using RPHPLC
3.5. Structural Characterization of Ginsenoside MT1
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chung, H.S.; Lee, Y.C.; Rhee, Y.K.; Lee, S.Y. Consumer acceptance of ginseng food products. J. Food Sci. 2011, 76, S516–S522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Sun, C.J.; Zheng, B.; Gao, B.; Sun, A.M. Simultaneous Determination of Ten Ginsenosides in American Ginseng Functional Foods and Ginseng Raw Plant Materials by Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Food Anal. Methods 2013, 6, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Zhao, Y.Q. Current Evaluation of the Millennium Phytomedicine-Ginseng (I): Etymology, Pharmacognosy, Phytochemistry, Market and Regulations. Curr. Med. Chem. 2009, 16, 2475–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leung, K.W.; Leung, F.P.; Mak, N.K.; Tombran-Tink, J.; Huang, Y.; Wong, R.N. Protopanaxadiol and protopanaxatriol bind to glucocorticoid and oestrogen receptors in endothelial cells. Brit. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 156, 626–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wong, A.S.T.; Che, C.M.; Leung, K.W. Recent advances in ginseng as cancer therapeutics: A functional and mechanistic overview. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2015, 32, 256–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, T.; Mathur, A.K.; Mathur, A. A literature update elucidating production of Panax ginsenosides with a special focus on strategies enriching the anti-neoplastic minor ginsenosides in ginseng preparations. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 2017, 101, 4009–4032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, H.P.; Zheng, X.; Wang, G.J. Insights into drug discovery from natural medicines using reverse pharmacokinetics. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2014, 35, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.S.; Xu, J.D.; Zhu, H.; Shen, H.; Xu, J.; Mao, Q.; Li, S.L.; Yan, R. Simultaneous determination of original, degraded ginsenosides and aglycones by ultra high performance liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry for quantitative evaluation of Du-Shen-Tang, the decoction of ginseng. Molecules 2014, 19, 4083–4104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, W.Y.; Kim, J.M.; Han, S.B.; Lee, S.K.; Kim, N.D.; Park, M.K.; Kim, C.K.; Park, J.H. Steaming of ginseng at high temperature enhances biological activity. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 1702–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, E.A.; Han, M.J.; Kim, E.J.; Kim, D.H. Transformation of ginseng saponins to ginsenoside Rh2 by acids and human intestinal bacteria and biological activities of their transformants. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2004, 27, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, T.K.; Lee, Y.S.; Lee, Y.H.; Kim, S.I.; Yun, H.Y. Anticarcinogenic effect of Panax ginseng CA Meyer and identification of active compounds. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2001, 16, S6–S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cui, C.H.; Kim, S.C.; Im, W.T. Characterization of the ginsenoside-transforming recombinant beta-glucosidase from Actinosynnema mirum and bioconversion of major ginsenosides into minor ginsenosides. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 2013, 97, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, K.-C.; Oh, D.-K. Classification of glycosidases that hydrolyze the specific positions and types of sugar moieties in ginsenosides. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2016, 36, 1036–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, C.S.; Yoo, M.H.; Noh, K.H.; Oh, D.K. Biotransformation of ginsenosides by hydrolyzing the sugar moieties of ginsenosides using microbial glycosidases. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 87, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, C.-h.; Jeon, B.-M.; Fu, Y.; Im, W.-T.; Kim, S.-C. High-density immobilization of a ginsenoside-transforming β-glucosidase for enhanced food-grade production of minor ginsenosides. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 7003–7015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- An, D.-S.; Cui, C.-H.; Siddiqi, M.Z.; Yu, H.S.; Jin, F.-X.; Kim, S.-G.; Im, W.-T. Gram-Scale Production of Ginsenoside F1 Using a Recombinant Bacterial β-Glucosidase. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 27, 1559–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, C.-H.; Fu, Y.; Jeon, B.-M.; Kim, S.-C.; Im, W.-T. Novel enzymatic elimination method for the chromatographic purification of ginsenoside Rb3 in an isomeric mixture. J. ginseng Res. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqi, M.Z.; Cui, C.H.; Park, S.K.; Han, N.S.; Kim, S.C.; Im, W.T. Comparative analysis of the expression level of recombinant ginsenoside-transforming beta-glucosidase in GRAS hosts and mass production of the ginsenoside Rh2-Mix. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.H.; Kim, J.K.; Kim, S.C.; Im, W.T. Characterization of a ginsenoside-transforming beta-glucosidase from Paenibacillus mucilaginosus and its application for enhanced production of minor ginsenoside F(2). PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85727. [Google Scholar]
- Park, M.K.; Cui, C.H.; Park, S.C.; Park, S.K.; Kim, J.K.; Jung, M.S.; Jung, S.C.; Kim, S.C.; Im, W.T. Characterization of recombinant beta-glucosidase from Arthrobacter chlorophenolicus and biotransformation of ginsenosides Rb1, Rb 2, Rc, and Rd. J. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Cui, C.H.; Park, S.C.; Kim, J.K.; Yu, H.S.; Jin, F.X.; Sun, C.; Kim, S.C.; Im, W.T. Identification and characterization of a ginsenoside-transforming beta-glucosidase from Pseudonocardia sp. Gsoil 1536 and its application for enhanced production of minor ginsenoside Rg2(S). PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, C.H.; Liu, Q.M.; Kim, J.K.; Sung, B.H.; Kim, S.G.; Kim, S.C.; Im, W.T. Identification and characterization of a Mucilaginibacter sp. strain QM49 beta-glucosidase and its use in the production of the pharmaceutically active minor ginsenosides (S)-Rh1 and (S)-Rg2. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 5788–5798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ren, G.; Chen, F. Simultaneous quantification of ginsenosides in American ginseng (Panax quinquefolium) root powder by visible/near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 2771–2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Pan, J.Y.; Xiao, X.Y.; Lin, R.C.; Cheng, Y.Y. Simultaneous determination of ginsenosides in Panax ginseng with different growth ages using high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Phytochem. Anal. 2006, 17, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwamoto, M.; Fujioka, T.; Okabe, H.; Mihashi, K.; Yamauchi, T. Studies on the Constituents of Actinostemma-Lobatum Maxim.1. Structures of Actinostemmoside-a, Actinostemmoside-B, Actinostemmoside-C, Actinostemmoside-D, Dammarane Triterpene Glycosides Isolated from the Herb. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1987, 35, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bissaro, B.; Monsan, P.; Faure, R.; O’Donohue, M.J. Glycosynthesis in a waterworld: New insight into the molecular basis of transglycosylation in retaining glycoside hydrolases. Biochem. J. 2015, 467, 17–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geronimo, I.; Payne, C.M.; Sandgren, M. Hydrolysis and Transglycosylation Transition States of Glycoside Hydrolase Family 3 beta-Glucosidases Differ in Charge and Puckering Conformation. J. Phys. Chem. B 2018, 122, 9452–9459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, R.; Igarashi, K.; Kitaoka, M.; Ishii, T.; Samejima, M. Kinetics of substrate transglycosylation by glycoside hydrolase family 3 glucan (1 -> 3)-beta-glucosidase from the white-rot fungus Planerochaete chrysosporium. Carbohyd. Res. 2004, 339, 2851–2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thongpoo, P.; McKee, L.S.; Araujo, A.C.; Kongsaeree, P.T.; Brumer, H. Identification of the acid/base catalyst of a glycoside hydrolase family 3 (GH3) beta-glucosidase from Aspergillus niger ASKU28. Bba-Gen. Subjects 2013, 1830, 2739–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.S.; Lee, H.J.; Mathiyalagan, R.; Kim, Y.J.; Yang, D.U.; Lee, D.Y.; Min, J.W.; Jimenez, Z.; Yang, D.C. Synthesis of a Novel alpha-Glucosyl Ginsenoside F1 by Cyclodextrin Glucanotransferase and Its In Vitro Cosmetic Applications. Biomolecules 2018, 8, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, D.D.; Jin, Y.; Wang, C.; Kim, Y.J.; Perez, Z.E.J.; Baek, N.I.; Mathiyalagan, R.; Markus, J.; Yang, D.C. Rare ginsenoside Ia synthesized from F1 by cloning and overexpression of the UDP-glycosyltransferase gene from Bacillus subtilis: Synthesis, characterization, and in vitro melanogenesis inhibition activity in BL6B16 cells. J. Ginseng. Res. 2018, 42, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.J.; Kim, Y.H.; Song, G.S.; Suzuki, Y.; Kim, M.K. Enzymatic transglycosylation of ginsenoside Rg1 by rice seed alpha-glucosidase. Biosci. Biotech. Bioch. 2016, 80, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, D.G.; Quilantang, N.G.; Lee, J.S.; Geraldino, P.J.L.; Kim, H.Y.; Lee, S.H. Quantitative Analysis of Dammarane-type Ginsenosides in Different Ginseng Products. Nat. Prod. Sci. 2018, 24, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leem, D.G.; Shin, J.S.; Kim, K.T.; Choi, S.Y.; Lee, M.H.; Lee, K.T. Dammarane-type triterpene ginsenoside-Rg18 inhibits human non-small cell lung cancer A549 cell proliferation via G1 phase arrest. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 6043–6049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Choi, S.Y.; Kim, K.T.; Rhee, Y.K.; Hur, J. Ginsenoside Rg18 suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced neuroinflammation in BV2 microglia and amyloid-beta-induced oxidative stress in SH-SY5Y neurons via nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2/heme oxygenase-1 induction. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 31, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Z.; Zhang, B.; Song, W.X.; Wang, A.; Ni, M.; Luo, X.; Aung, H.H.; Xie, J.T.; Tong, R.; He, T.C.; et al. Steamed American ginseng berry: Ginsenoside analyses and anticancer activities. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 9936–9942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.R.; Yau, L.F.; Zhang, R.; Xia, Y.; Ma, J.; Ho, H.M.; Hu, P.; Hu, M.; Liu, L.; Jiang, Z.H. Transformation of ginsenosides from notoginseng by artificial gastric juice can increase cytotoxicity toward cancer cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 2558–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Liu, H.-Y.; Guo, X.-X.; Luo, Y.; Wang, C.-X.; He, J.-H.; Xu, T.-R.; Yang, Y.; Cui, X.-M. Converting ginsenosides from stems and leaves of Panax notoginseng by microwave processing and improving their anticoagulant and anticancer activities. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 40471–40482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





| Aglycon Moiety Position | δH mult., (J Hz) | δC mult. | Sugar Moiety Position | δH mult., (J Hz) | δC mult. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.73 m, 1.06 m | 39.4 t | Glc-1′ | 5.25 d (6.3) | 96.7 d |
| 2 | 1.93 m, 1.88 m | 28.2 t | Glc-2′ | 4.29b | 76.6 d |
| 3 | 3.56 t-like (5.6) | 78.4 d | Glc-3′ | 4.29b | 79.8 d |
| 4 | 40.4 s | Glc-4′ | 4.09 t (9.1) | 71.6 d | |
| 5 | 1.27 d (10.5) | 61.8 d | Glc-5′ | 3.88 m | 78.4 d |
| 6 | 4.40c | 67.8 d | Glc-6′ | 4.40c, 4.25 m | 62.5 t |
| 7 | 2.04 m, 1.90 m | 47.5 t | Rha-1″ | 6.61 s | 101.4 d |
| 8 | 41.2 s | Rha-2″ | 4.79 brs | 72.5 d | |
| 9 | 1.67 m | 49.7 d | Rha-3″ | 4.64 t (4.9) | 72.6 d |
| 10 | 39.3 s | Rha-4″ | 4.40c | 74.2 d | |
| 11 | 2.20 m, 1.55 m | 31.1 t | Rha-5″ | 4.89 dd (9.1, 5.6) | 69.4 d |
| 12 | 4.11 m | 70.7 d | Rha-6″ | 1.83 d (5.6) | 19.0 q |
| 13 | 2.00 m | 49.0 d | 3′-OH | 7.50 brs | |
| 14 | 51.6 s | 4′-OH | 7.40 d (4.2) | ||
| 15 | 1.58 m, 1.03 m | 30.9 t | 6′-OH | 5.90 brs | |
| 16 | 1.95 m, 1.44 m | 26.7 t | 2″-OH | 6.76 d (4.2) | |
| 17 | 2.77 dd (18.2, 10.5) | 53.3 d | 3″-OH | 6.46 brs | |
| 18 | 1.12 s | 17.4 q | 4″-OH | 6.81 d (3.5) | |
| 19 | 1.05 s | 17.5 q | |||
| 20 | 84.0 s | ||||
| 21 | 1.59 s | 22.8 q | |||
| 22 | 2.45 m, 1.98 m | 35.9 t | |||
| 23 | 2.29 m | 24.0 t | |||
| 24 | 5.28d | 126.0 d | |||
| 25 | 130.8 s | ||||
| 26 | 1.62 s | 25.8 q | |||
| 27 | 1.65 s | 17.9 q | |||
| 28 | 2.02 s | 32.0 q | |||
| 29 | 1.48 s | 16.5 q | |||
| 30 | 1.17 s | 17.2 q | |||
| 3-OH | 5.76 d (5.6) | ||||
| 6-OH | 5.28d | ||||
| 12-OH | 5.58 s |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeon, B.-M.; Baek, J.-I.; Kim, M.-S.; Kim, S.-C.; Cui, C.-h. Characterization of a Novel Ginsenoside MT1 Produced by an Enzymatic Transrhamnosylation of Protopanaxatriol-Type Ginsenosides Re. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 525. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10040525
Jeon B-M, Baek J-I, Kim M-S, Kim S-C, Cui C-h. Characterization of a Novel Ginsenoside MT1 Produced by an Enzymatic Transrhamnosylation of Protopanaxatriol-Type Ginsenosides Re. Biomolecules. 2020; 10(4):525. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10040525
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeon, Byeong-Min, Jong-In Baek, Min-Sung Kim, Sun-Chang Kim, and Chang-hao Cui. 2020. "Characterization of a Novel Ginsenoside MT1 Produced by an Enzymatic Transrhamnosylation of Protopanaxatriol-Type Ginsenosides Re" Biomolecules 10, no. 4: 525. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10040525
APA StyleJeon, B.-M., Baek, J.-I., Kim, M.-S., Kim, S.-C., & Cui, C.-h. (2020). Characterization of a Novel Ginsenoside MT1 Produced by an Enzymatic Transrhamnosylation of Protopanaxatriol-Type Ginsenosides Re. Biomolecules, 10(4), 525. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10040525





