Antioxidant-Based Medicinal Properties of Stingless Bee Products: Recent Progress and Future Directions
Abstract
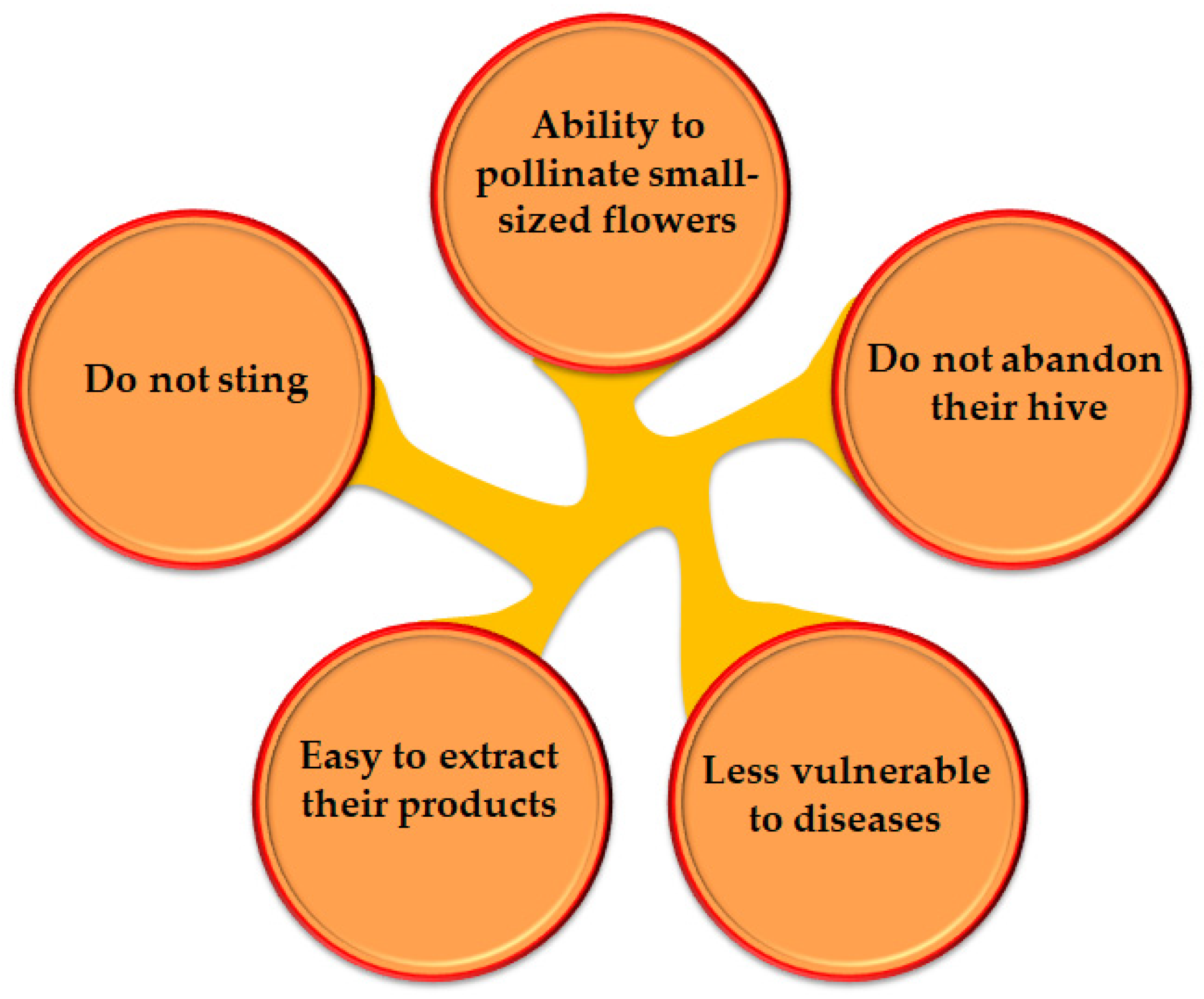
:1. Introduction
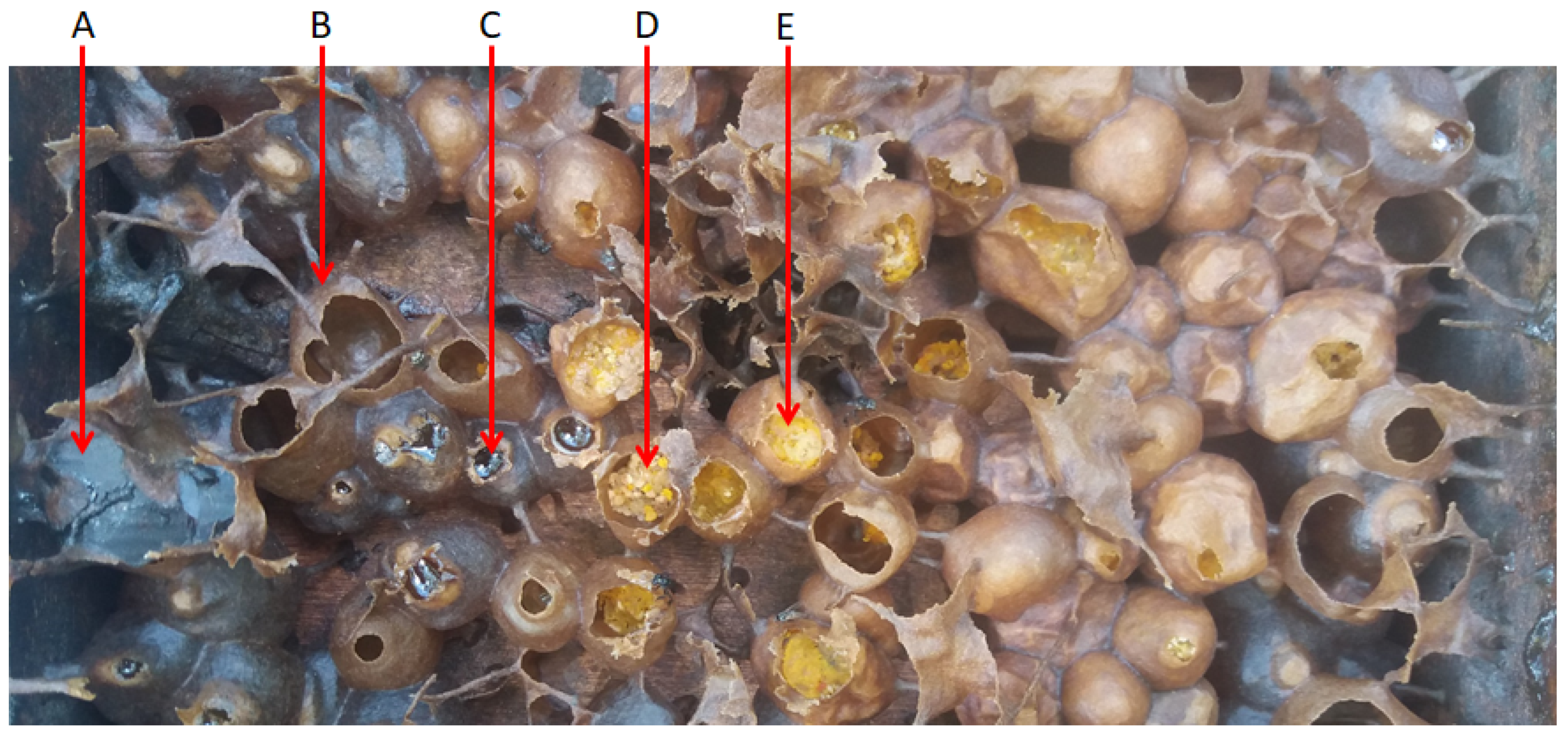
2. Harvesting and Characterization of Stingless Bee Products
3. Stingless Bee Honey
3.1. Antioxidant Activity of SBH
3.2. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of SBH
3.3. Anti-Obesity Activity of SBH
3.4. Anticancer Activity of SBH
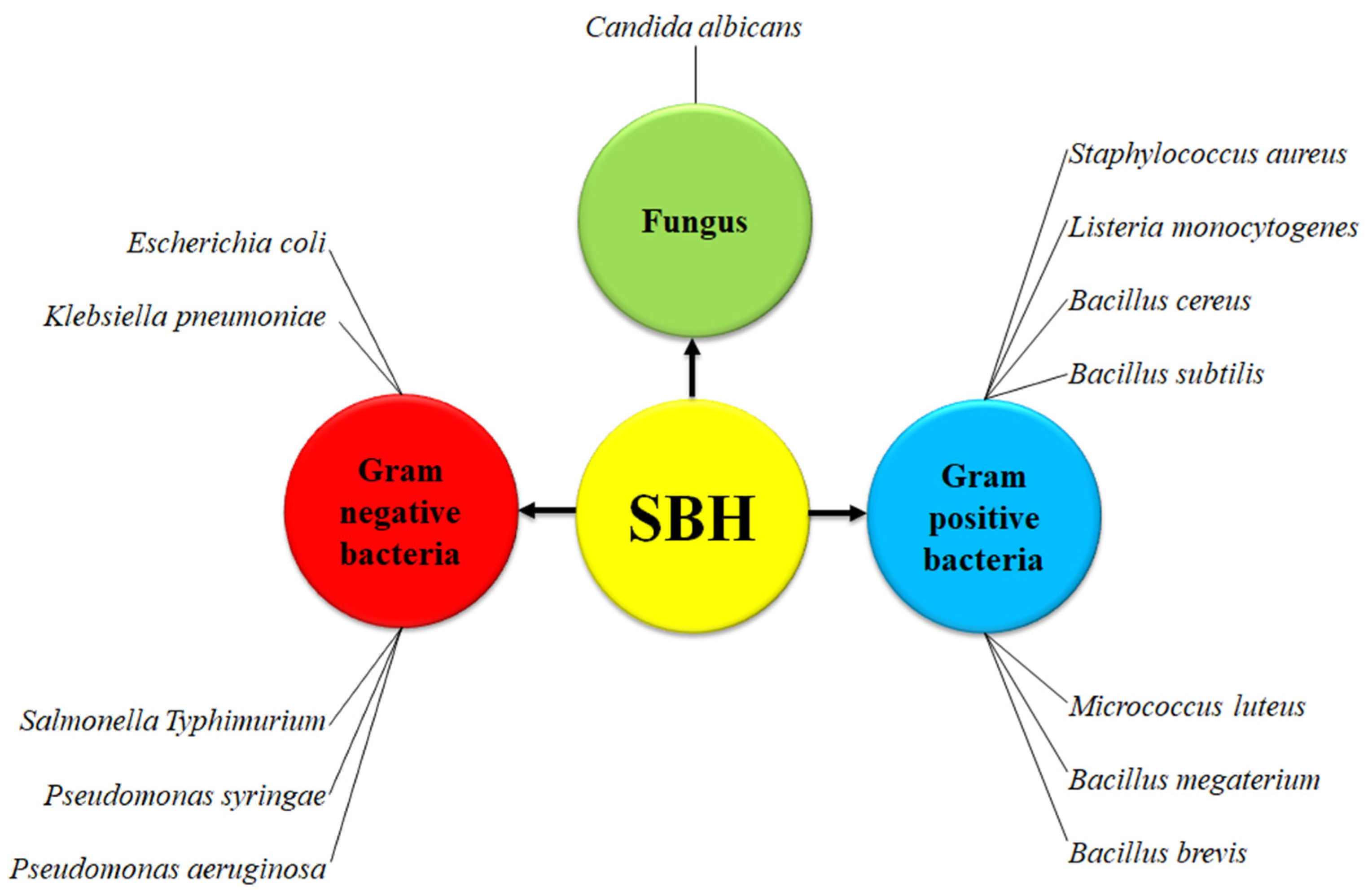
3.5. Antimicrobial Activity of SBH
3.6. Other Promising Properties of SBH
3.7. SBH Production in Malaysia
4. Stingless Bee Propolis (SBP)
4.1. Antioxidant Activity of SBP
4.2. Anticancer Activity of SBP
4.3. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of SBP
4.4. Antimicrobial Activity of SBP
5. Stingless Bee Cerumen
6. Stingless Bee Pollen
7. Comparison of Stingless Bee Products and Their Health Benefits
8. Bacterial Isolates from Stingless Bee Products
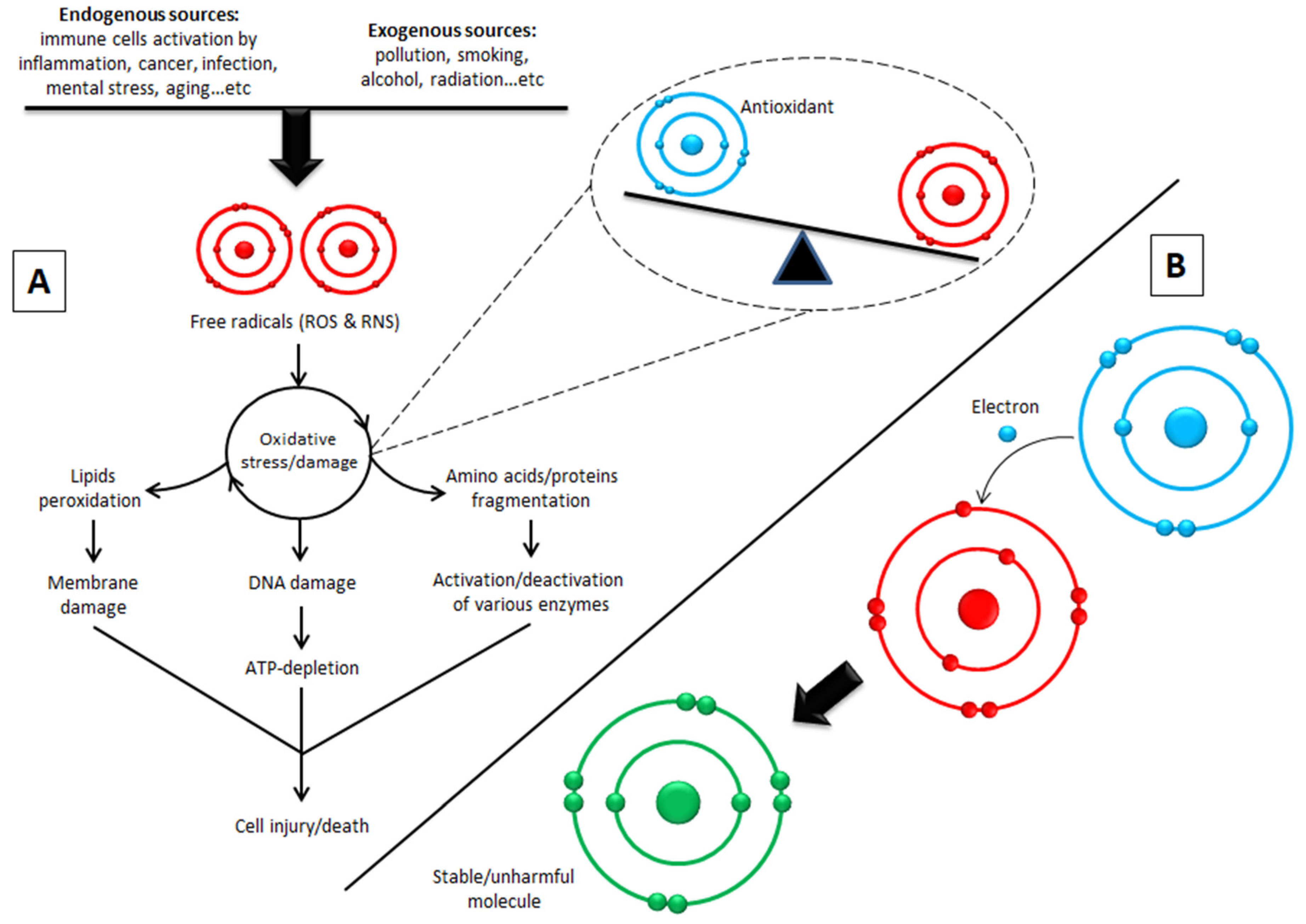
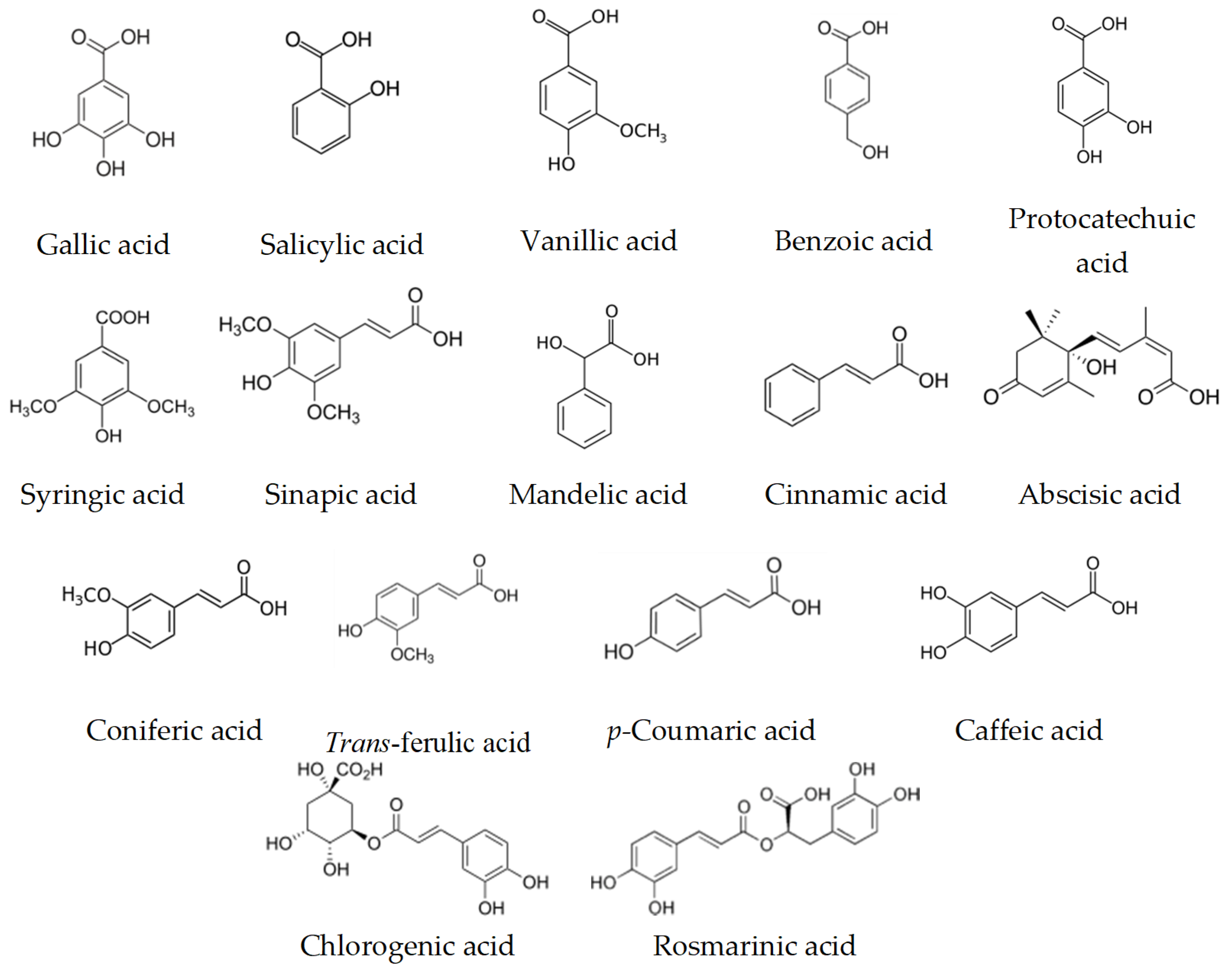
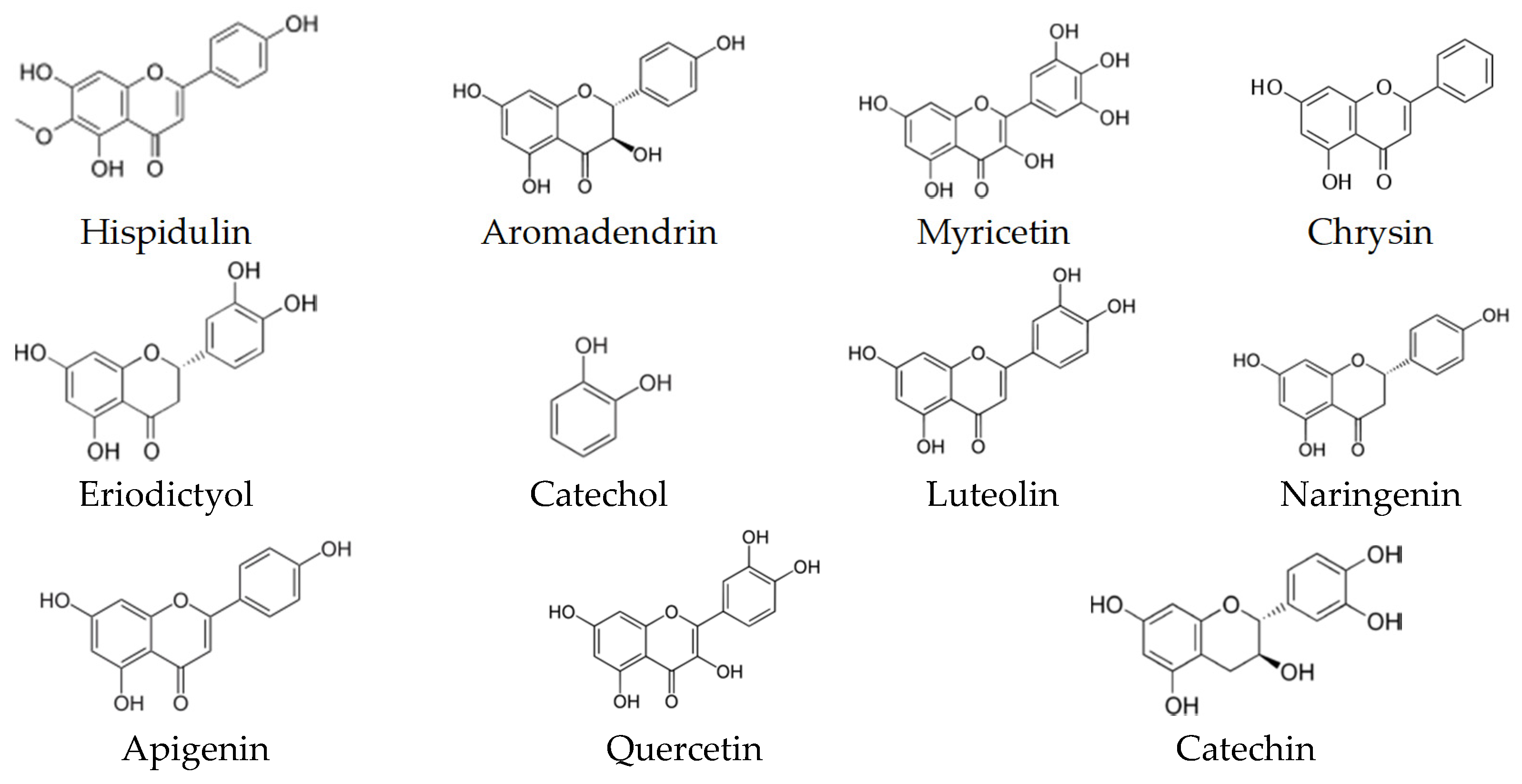
9. Biological Activity and Targets of Phenolic Compounds
10. Future Directions
11. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bradbear, N. Bees and Their Role in Forest Livelihoods: A Guide to the Services Provided by Bees and the Sustainable Harvesting, Processing and Marketing of Their Products; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Samarghandian, S.; Farkhondeh, T.; Samini, F. Honey and Health: A Review of Recent Clinical Research. Pharmacogn. Res. 2017, 9, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michener, C.D. The meliponini. In Pot-Honey; Vit, P., Pedro, S.R., Roubik, D., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 3–17. [Google Scholar]
- Crane, E. The Past and Present Status of Beekeeping with Stingless Bees. Bee World 1992, 73, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rattanawannee, A.; Duangphakdee, O. Southeast Asian Meliponiculture for Sustainable Livelihood. In Modern Beekeeping—Bases for Sustainable Production; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Michener, C. The Bees of the World; John Hopkins University Press: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Abd Jalil, M.A.; Kasmuri, A.R.; Hadi, H. Stingless Bee Honey, the Natural Wound Healer: A Review. Skin Pharmacol. Physiol. 2017, 30, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuttong, B.; Chanbang, Y.; Sringarm, K.; Burgett, M. Physicochemical profiles of stingless bee (Apidae: Meliponini) honey from South East Asia (Thailand). Food Chem. 2016, 192, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewnetu, Y.; Lemma, W.; Birhane, N. Antibacterial effects of Apis mellifera and stingless bees honeys on susceptible and resistant strains of Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus and Klebsiella pneumoniae in Gondar, Northwest Ethiopia. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 13, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fuenmayor, C.A.; Díaz-Moreno, A.C.; Zuluaga-Domínguez, C.M.; Quicazán, M.C. Honey of Colombian stingless bees: Nutritional characteristics and physicochemical quality indicators. In Pot-Honey; Vit, P., Pedro, S.R., Roubik, D., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 383–394. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, E.; O’Brien, M.; Georges, K.; Suepaul, S. Physical characteristics and antimicrobial properties of Apis mellifera, Frieseomelitta nigra and Melipona favosa bee honeys from apiaries in Trinidad and Tobago. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2020, 20, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nweze, J.A.; Okafor, J.I.; Nweze, E.I.; Nweze, J.E. Evaluation of physicochemical and antioxidant properties of two stingless bee honeys: A comparison with Apis mellifera honey from Nsukka, Nigeria. BMC Res. Notes 2017, 10, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zulkhairi Amin, F.A.; Sabri, S.; Mohammad, S.M.; Ismail, M.; Chan, K.W.; Ismail, N.; Norhaizan, M.E.; Zawawi, N. Therapeutic Properties of Stingless Bee Honey in Comparison with European Bee Honey. Adv. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 2018, 6179596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kustiawan, P.M.; Puthong, S.; Arung, E.T.; Chanchao, C. In vitro cytotoxicity of Indonesian stingless bee products against human cancer cell lines. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2014, 4, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nugitrangson, P.; Puthong, S.; Iempridee, T.; Pimtong, W.; Pornpakakul, S.; Chanchao, C. In vitro and in vivo characterization of the anticancer activity of Thai stingless bee (Tetragonula laeviceps) cerumen. Exp. Biol. Med. 2016, 241, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ismail, W.I.W.; Hussin, N.N.; Mazlan, S.N.F.; Hussin, N.H.; Radzi, M.N.F.M. Physicochemical Analysis, Antioxidant and Anti Proliferation Activities of Honey, Propolis and Beebread Harvested from Stingless Bee. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, Vanderbijlpark, South Africa, 23–26 October 2018; p. 012048. [Google Scholar]
- Lavinas, F.C.; Macedo, E.H.B.; Sá, G.B.; Amaral, A.C.F.; Silva, J.R.; Azevedo, M.; Vieira, B.A.; Domingos, T.F.S.; Vermelho, A.B.; Carneiro, C.S. Brazilian stingless bee propolis and geopropolis: Promising sources of biologically active compounds. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2019, 29, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syafrizal, A.A.; Sila, M.; Marji, D. Diversity of kelulut bee (Trigona spp.) in Lempake education forest. Mulawarman Sci. 2012, 11, 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- Sommeijer, M.J. Beekeeping with stingless bees: A new type of hive. Bee World 1999, 80, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, G. Honey from Stingless Bees. Available online: https://www.meliponinibeehoney.com/blog/honey-from-stingless-bees (accessed on 27 May 2020).
- Souza, B.A.; Roubik, D.W.; Barth, O.M.; Heard, T.A.; Enríquez, E.; Carvalho, C.; Villas-Bôas, J.; Marchini, L.; Locatelli, J.; Persano-Oddo, L. Composition of stingless bee honey: Setting quality standards. Interciencia 2006, 31, 867–875. [Google Scholar]
- Menezes, C.; Vollet Neto, A.; Fonseca, V.L.I. A method for harvesting unfermented pollen from stingless bees (Hymenoptera, Apidae, Meliponini). J. Apic. Res. 2012, 51, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Department of Standards Malaysia. Kelulut (Stingless bee) honey-Specification, MS 2683. 2017. Available online: https://www.scribd.com/document/398215369/Kelulut-Stingless-bee-honey-Specification (accessed on 27 May 2020).
- Arshad, N.; Lin, T.S.; Yahaya, M.F. Stingless bee honey reduces anxiety and improves memory of the metabolic disease-induced rats. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biluca, F.C.; da Silva, B.; Caon, T.; Mohr, E.T.B.; Vieira, G.N.; Gonzaga, L.V.; Vitali, L.; Micke, G.; Fett, R.; Dalmarco, E.M.; et al. Investigation of phenolic compounds, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities in stingless bee honey (Meliponinae). Food Res. Int. 2020, 129, 108756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, M.Z.; Zulkifli, F.N.; Fernandez, I.; Mariatulqabtiah, A.R.; Sangu, M.; Nor Azfa, J.; Mohamed, M.; Roslan, N. Stingless Bee Honey Improves Spatial Memory in Mice, Probably Associated with Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) and Inositol 1,4,5-Triphosphate Receptor Type 1 (Itpr1) Genes. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2019, 2019, 8258307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdul Malik, N.; Mohamed, M.; Mustafa, M.Z.; Zainuddin, A. In vitro modulation of extracellular matrix genes by stingless bee honey in cellular aging of human dermal fibroblast cells. J. Food Biochem. 2019, 44, e13098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazirah, H.; Yasmin, A.M.; Norwahidah, A. Antioxidant Properties of Stingless Bee Honey and Its Effect on the Viability of Lymphoblastoid Cell Line. Med. Health 2019, 14, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Kafaween, M.A.; Hilmi, A.B.M.; Khan, R.S.; Bouacha, M.; Amonov, M. Effect of Trigona honey on Escherichia coli cell culture growth: In vitro study. J. Apither. 2019, 5, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila, S.; Hornung, P.S.; Teixeira, G.L.; Malunga, L.N.; Apea-Bah, F.B.; Beux, M.R.; Beta, T.; Ribani, R.H. Bioactive compounds and biological properties of Brazilian stingless bee honey have a strong relationship with the pollen floral origin. Food Res. Int. 2019, 123, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvaraju, K.; Vikram, P.; Soon, J.M.; Krishnan, K.T.; Mohammed, A. Melissopalynological, physicochemical and antioxidant properties of honey from West Coast of Malaysia. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 2508–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ranneh, Y.; Akim, A.M.; Hamid, H.A.; Khazaai, H.; Fadel, A.; Mahmoud, A.M. Stingless bee honey protects against lipopolysaccharide induced-chronic subclinical systemic inflammation and oxidative stress by modulating Nrf2, NF-kappaB and p38 MAPK. Nutr. Metab. 2019, 16, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, F.; Seerangan, P.; Mustafa, M.Z.; Osman, Z.F.; Abdullah, J.M.; Idris, Z. Anti-Cancer Properties of Heterotrigona itama sp. Honey Via Induction of Apoptosis in Malignant Glioma Cells. Malays. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 26, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Rafie, A.Z.; Syahir, A.; Wan Ahmad, W.A.N.; Mustafa, M.Z.; Mariatulqabtiah, A.R. Supplementation of Stingless Bee Honey from Heterotrigona itama Improves Antiobesity Parameters in High-Fat Diet Induced Obese Rat Model. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 2018, 6371582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohamad, M.A.M.; Mazlan, M.A.; Ibrahim, M.; Yusof, A.M.; Shamsuddin, S.A.A.; Hassan, N.F.N.; Muhammad, H.; Isa, M.L.M. The effect of Malaysian stingless bee, Trigona spp. honey in promoting proliferation of the undifferentiated stem cell. Asia Pac. J. Mol. Biol. Biotechnol. 2018, 27, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordin, A.; Omar, N.; Sainik, N.Q.A.V.; Chowdhury, S.R.; Omar, E.; Saim, A.B.; Idrus, R.B.H. Low dose stingless bee honey increases viability of human dermal fibroblasts that could potentially promote wound healing. Wound Med. 2018, 23, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, W.-J.; Lye, P.-Y.; Chan, Y.-J.; Lau, Z.-K.; Ee, K.-Y. Synergistic effect of trigona honey and ampicillin on Staphylococcus aureus isolated from infected wound. Int. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 13, 403–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aziz, M.S.A.; Giribabu, N.; Rao, P.V.; Salleh, N. Pancreatoprotective effects of Geniotrigona thoracica stingless bee honey in streptozotocin-nicotinamide-induced male diabetic rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 89, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budin, S.B.; Jubaidi, F.F.; Azam, S.N.F.M.N.; Yusof, N.L.M.; Taib, I.S.; Mohamed, J. Kelulut honey supplementation prevents sperm and testicular oxidative damage in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J. Teknol. 2017, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zamora, L.G.; Beukelman, C.J.; van den Berg, A.J.; Aerts, P.C.; Quarles van Ufford, H.C.; Nijland, R.; Arias, M.L. An insight into the antibiofilm properties of Costa Rican stingless bee honeys. J. Wound Care 2017, 26, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saiful Yazan, L.; Muhamad Zali, M.F.; Mohd Ali, R.; Zainal, N.A.; Esa, N.; Sapuan, S.; Ong, Y.S.; Tor, Y.S.; Gopalsamy, B.; Voon, F.L.; et al. Chemopreventive Properties and Toxicity of Kelulut Honey in Sprague Dawley Rats Induced with Azoxymethane. Biomed. Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 4036926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Syam, Y.; Natsir, R.; Rahardjo, S.P.; Usman, A.N.; Dwiyanti, R.; Hatta, M. Effect of Trigona honey to mRNA expression of interleukin-6 on Salmonella Typhi induced of BALB/c mice. Am. J. Microbiol. Res. 2016, 4, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaro, C.F.; Shelley, D.; Heard, T.A.; Brooks, P. In vitro antibacterial phenolic extracts from “sugarbag” pot-honeys of Australian stingless bees (Tetragonula carbonaria). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 12209–12217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsato, D.M.; Prudente, A.S.; Doll-Boscardin, P.M.; Borsato, A.V.; Luz, C.F.; Maia, B.H.; Cabrini, D.A.; Otuki, M.F.; Miguel, M.D.; Farago, P.V.; et al. Topical anti-inflammatory activity of a monofloral honey of Mimosa scabrella provided by Melipona marginata during winter in southern Brazil. J. Med. Food 2014, 17, 817–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilechie, A.A.; Kwapong, P.K.; Mate-Kole, E.; Kyei, S.; Darko-Takyi, C. The efficacy of stingless bee honey for the treatment of bacteria-induced conjunctivitis in guinea pigs. J. Exp. Pharmacol. 2012, 4, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boorn, K.L.; Khor, Y.Y.; Sweetman, E.; Tan, F.; Heard, T.A.; Hammer, K.A. Antimicrobial activity of honey from the stingless bee Trigona carbonaria determined by agar diffusion, agar dilution, broth microdilution and time-kill methodology. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 108, 1534–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garedew, A.; Schmolz, E.; Lamprecht, I. Microcalorimetric investigation on the antimicrobial activity of honey of the stingless bee Trigona spp. and comparison of some parameters with those obtained with standard methods. Thermochim. Acta 2004, 415, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, A.; Garedew, A.; Schmolz, E.; Lamprecht, I. Calorimetric investigation of the antimicrobial action and insight into the chemical properties of “angelita” honey—A product of the stingless bee Tetragonisca angustula from Colombia. Thermochim. Acta 2004, 415, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patricia, V. Effect of stingless bee honey in selenite induced cataracts. Apiacta 2002, 3, 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Comert, E.D.; Gokmen, V. Evolution of food antioxidants as a core topic of food science for a century. Food Res. Int. 2018, 105, 76–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonamigo, T.; Campos, J.F.; Alfredo, T.M.; Balestieri, J.B.; Cardoso, C.A.; Paredes-Gamero, E.J.; de Picoli Souza, K.; Dos Santos, E.L. Antioxidant, Cytotoxic, and Toxic Activities of Propolis from Two Native Bees in Brazil: Scaptotrigona depilis and Melipona quadrifasciata anthidioides. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 1038153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dzialo, M.; Mierziak, J.; Korzun, U.; Preisner, M.; Szopa, J.; Kulma, A. The Potential of Plant Phenolics in Prevention and Therapy of Skin Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dharmaraja, A.T. Role of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) in Therapeutics and Drug Resistance in Cancer and Bacteria. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 3221–3240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinisalo, M.; Karlund, A.; Koskela, A.; Kaarniranta, K.; Karjalainen, R.O. Polyphenol Stilbenes: Molecular Mechanisms of Defence against Oxidative Stress and Aging-Related Diseases. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2015, 2015, 340520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Hatamleh, M.A.I.; Baig, A.A.; Simbak, N.B.; Nadeem, M.I.; Khan, S.U.; Ariff, T.M. Molecular Modulation of Stress Induced to Abnormal Haematological Indices in Medical Students, Malaysian Perspective. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2017, 20, 478–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham-Huy, L.A.; He, H.; Pham-Huy, C. Free radicals, antioxidants in disease and health. Int. J. Biomed. Sci. 2008, 4, 89–96. [Google Scholar]
- White, P.A.; Oliveira, R.C.; Oliveira, A.P.; Serafini, M.R.; Araujo, A.A.; Gelain, D.P.; Moreira, J.C.; Almeida, J.R.; Quintans, J.S.; Quintans-Junior, L.J.; et al. Antioxidant activity and mechanisms of action of natural compounds isolated from lichens: A systematic review. Molecules 2014, 19, 14496–14527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kek, S.P.; Chin, N.L.; Yusof, Y.A.; Tan, S.W.; Chua, L.S. Total phenolic contents and colour intensity of Malaysian honeys from the Apis spp. and Trigona spp. bees. Agric. Agric. Sci. Procedia 2014, 2, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- da Silva, I.A.; da Silva, T.M.; Camara, C.A.; Queiroz, N.; Magnani, M.; de Novais, J.S.; Soledade, L.E.; Lima Ede, O.; de Souza, A.L.; de Souza, A.G. Phenolic profile, antioxidant activity and palynological analysis of stingless bee honey from Amazonas, Northern Brazil. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 3552–3558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Biluca, F.C.; de Gois, J.S.; Schulz, M.; Braghini, F.; Gonzaga, L.V.; Maltez, H.F.; Rodrigues, E.; Vitali, L.; Micke, G.A.; Borges, D.L. Phenolic compounds, antioxidant capacity and bioaccessibility of minerals of stingless bee honey (Meliponinae). J. Food Compos. Anal. 2017, 63, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, M.M.; Nunes, G.S.; Ribeiro, D.B.; Silva, F.E.P.S.; Catanante, G.; Marty, J.-L. Determination of the Antioxidant Capacity of Red Fruits by Miniaturized Spectrophotometry Assays. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2019, 30, 1108–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajurkar, N.S.; Hande, S.M. Estimation of phytochemical content and antioxidant activity of some selected traditional Indian medicinal plants. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 73, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oliveira, R.G.; Jain, S.; Luna, A.C.; Freitas, L.D.; Araujo, E.D. Screening for quality indicators and phenolic compounds of biotechnological interest in honey samples from six species of stingless bees (Hymenoptera: Apidae). Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 37, 552–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.; Deng, H.; Cui, H.; Fang, J.; Zuo, Z.; Deng, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, L. Inflammatory responses and inflammation-associated diseases in organs. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 7204–7218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hussain, T.; Tan, B.; Yin, Y.; Blachier, F.; Tossou, M.C.; Rahu, N. Oxidative stress and inflammation: What polyphenols can do for us? Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 7432797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yahfoufi, N.; Alsadi, N.; Jambi, M.; Matar, C. The Immunomodulatory and Anti-Inflammatory Role of Polyphenols. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arulselvan, P.; Fard, M.T.; Tan, W.S.; Gothai, S.; Fakurazi, S.; Norhaizan, M.E.; Kumar, S.S. Role of Antioxidants and Natural Products in Inflammation. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 5276130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roy, J.; Galano, J.M.; Durand, T.; Le Guennec, J.Y.; Lee, J.C. Physiological role of reactive oxygen species as promoters of natural defenses. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 3729–3745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Costa, J.D.S.; Ramos, R.D.S.; Costa, K.; Brasil, D.; Silva, C.; Ferreira, E.F.B.; Borges, R.D.S.; Campos, J.M.; Macedo, W.; Santos, C. An In Silico Study of the Antioxidant Ability for Two Caffeine Analogs Using Molecular Docking and Quantum Chemical Methods. Molecules 2018, 23, 2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Al-Hatamleh, M.A.I.; Ear, E.N.; Boer, J.C.; Ferji, K.; Six, J.L.; Chen, X.; Elkord, E.; Plebanski, M.; Mohamud, R. Synergistic Effects of Nanomedicine Targeting TNFR2 and DNA Demethylation Inhibitor-An Opportunity for Cancer Treatment. Cells 2019, 9, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Al-Hatamleh, M.; Tengku, M.; Alshajrawi, O.; Ilyas, M.; Rao, S.; Majid, L.; Zubaidi, A.; Nordin, S.; Atif, A. Obesity Leads to Elevated Level of Circulating Cell-Free DNA. Curr. Trends Biomed. Eng. Biosci. 2018, 16, 102–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi-Sunyer, X. The medical risks of obesity. Postgrad. Med. 2009, 121, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Rahman, H.; Saari, N.; Abas, F.; Ismail, A.; Mumtaz, M.W.; Abdul Hamid, A. Anti-obesity and antioxidant activities of selected medicinal plants and phytochemical profiling of bioactive compounds. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20, 2616–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hatamleh, M.A.; Ahmad, S.; Boer, J.C.; Lim, J.; Chen, X.; Plebanski, M.; Mohamud, R. A Perspective Review on the Role of Nanomedicine in the Modulation of TNF-TNFR2 Axis in Breast Cancer Immunotherapy. J. Oncol. 2019, 2019, 6313242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grivennikov, S.I.; Greten, F.R.; Karin, M. Immunity, inflammation, and cancer. Cell 2010, 140, 883–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waheed, M.; Hussain, M.B.; Javed, A.; Mushtaq, Z.; Hassan, S.; Shariati, M.A.; Khan, M.U.; Majeed, M.; Nigam, M.; Mishra, A.P.; et al. Honey and cancer: A mechanistic review. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 2499–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hatamleh, M.A.I.; Hussin, T.; Taib, W.R.W.; Ismail, I. The Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) gene Val66Met (rs6265) polymorphism and stress among preclinical medical students in Malaysia. J. Taibah Univ. Med. Sci. 2019, 14, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schorge, S.; van de Leemput, J.; Singleton, A.; Houlden, H.; Hardy, J. Human ataxias: A genetic dissection of inositol triphosphate receptor (ITPR1)-dependent signaling. Trends Neurosci. 2010, 33, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ismail, M.M.; Ismail, W.I.W. Development of stingless beekeeping projects in Malaysia. Proceedings of E3S Web of Conferences, Polanica-Zdrój, Poland, 16–18 April 2018; p. 00028. [Google Scholar]
- Mustafa, M.Z.; Yaacob, N.S.; Sulaiman, S.A. Reinventing the Honey Industry: Opportunities of the Stingless Bee. Malays. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 25, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismail, M.M. Honey Marketing in Malaysia. In Agricultural Marketing Issues of Selected Commodities; Universiti Putra Malaysia Press: Serdang, Selangor, Malaysia, 2012; pp. 136–152. [Google Scholar]
- Omar, S.; Enchang, F.K.; Nazri, M.U.I.A.; Ismail, M.M.; Ismail, W.I.W. Physicochemical profiles of honey harvested from four major species of stingless bee (Kelulut) in North East Peninsular of Malaysia. Malays. Appl. Biol. 2019, 48, 111–116. [Google Scholar]
- Martinotti, S.; Ranzato, E. Propolis: A new frontier for wound healing? Burns Trauma 2015, 3, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fernandes, J.R.A.; Leomil, L.; Fernandes, A.A.H.; Sforcin, J.M. The antibacterial activity of propolis produced by Apis mellifera L. and Brazilian stingless bees. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins 2001, 7, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Cunha, M.G.; de Cassia Orlandi Sardi, J.; Freires, I.A.; Franchin, M.; Rosalen, P.L. Antimicrobial, anti-adherence and antibiofilm activity against Staphylococcus aureus of a 4-phenyl coumarin derivative isolated from Brazilian geopropolis. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 139, 103855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinho, M.P.; de Carvalho, P.L.N.; Reis, A.; Reis, E.; de Alencar, S.M.; Ruiz, A.; de Carvalho, J.E.; Ikegaki, M. A comprehensive characterization of polyphenols by LC-ESI-QTOF-MS from Melipona quadrifasciata anthidioides geopropolis and their antibacterial, antioxidant and antiproliferative effects. Nat. Prod. Res. 2019, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pujirahayu, N.; Bhattacharjya, D.K.; Suzuki, T.; Katayama, T. alpha-Glucosidase Inhibitory Activity of Cycloartane-Type Triterpenes Isolated from Indonesian Stingless Bee Propolis and Their Structure-Activity Relationship. Pharmaceuticals 2019, 12, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdullah, N.A.; Ja’afar, F.; Yasin, H.M.; Taha, H.; Petalcorin, M.I.R.; Mamit, M.H.; Kusrini, E.; Usman, A. Physicochemical analyses, antioxidant, antibacterial, and toxicity of propolis particles produced by stingless bee Heterotrigona itama found in Brunei Darussalam. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iqbal, M.; Fan, T.P.; Watson, D.; Alenezi, S.; Saleh, K.; Sahlan, M. Preliminary studies: The potential anti-angiogenic activities of two Sulawesi Island (Indonesia) propolis and their chemical characterization. Heliyon 2019, 5, e01978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cisilotto, J.; Sandjo, L.P.; Faqueti, L.G.; Fernandes, H.; Joppi, D.; Biavatti, M.W.; Creczynski-Pasa, T.B. Cytotoxicity mechanisms in melanoma cells and UPLC-QTOF/MS(2) chemical characterization of two Brazilian stingless bee propolis: Uncommon presence of piperidinic alkaloids. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 149, 502–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodkiewicz, Y.; Marcinkevicius, K.; Reynoso, M.; Salomon, V.; Maldonado, L.; Vera, N. Studies of the biological and therapeutic effects of Argentine stingless bee propolis. J. Drug Deliv. Ther. 2018, 8, 382–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kustiawan, P.M.; Lirdprapamongkol, K.; Palaga, T.; Puthong, S.; Phuwapraisirisan, P.; Svasti, J.; Chanchao, C. Molecular mechanism of cardol, isolated from Trigona incisa stingless bee propolis, induced apoptosis in the SW620 human colorectal cancer cell line. BMC Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2017, 18, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sabir, A.; Sumidarti, A. Interleukin-6 expression on inflamed rat dental pulp tissue after capped with Trigona sp. propolis from south Sulawesi, Indonesia. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2017, 24, 1034–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utispan, K.; Chitkul, B.; Koontongkaew, S. Cytotoxic Activity of Propolis Extracts from the Stingless Bee Trigona Sirindhornae Against Primary and Metastatic Head and Neck Cancer Cell Lines. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2017, 18, 1051–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.X.; Nguyen, M.T.T.; Nguyen, N.T.; Awale, S. Chemical Constituents of Propolis from Vietnamese Trigona minor and Their Antiausterity Activity against the PANC-1 Human Pancreatic Cancer Cell Line. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 2345–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, H.F.D.; Campos, J.F.; Santos, C.M.D.; Balestieri, J.B.P.; Silva, D.B.; Carollo, C.A.; de Picoli Souza, K.; Estevinho, L.M.; Dos Santos, E.L. Chemical Profile and Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory, Antimutagenic and Antimicrobial Activities of Geopropolis from the Stingless Bee Melipona orbignyi. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utispan, K.; Chitkul, B.; Monthanapisut, P.; Meesuk, L.; Pugdee, K.; Koontongkaew, S. Propolis Extracted from the Stingless Bee Trigona sirindhornae Inhibited S. mutans Activity In Vitro. Oral Health Prev. Dent. 2017, 15, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massaro, C.F.; Smyth, T.J.; Smyth, W.F.; Heard, T.; Leonhardt, S.D.; Katouli, M.; Wallace, H.M.; Brooks, P. Phloroglucinols from anti-microbial deposit-resins of Australian stingless bees (Tetragonula carbonaria). Phytother. Res. 2015, 29, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, J.F.; Dos Santos, U.P.; da Rocha Pdos, S.; Damiao, M.J.; Balestieri, J.B.; Cardoso, C.A.; Paredes-Gamero, E.J.; Estevinho, L.M.; de Picoli Souza, K.; Dos Santos, E.L. Antimicrobial, Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory, and Cytotoxic Activities of Propolis from the Stingless Bee Tetragonisca fiebrigi (Jatai). Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2015, 2015, 296186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanpa, S.; Popova, M.; Bankova, V.; Tunkasiri, T.; Eitssayeam, S.; Chantawannakul, P. Antibacterial Compounds from Propolis of Tetragonula laeviceps and Tetrigona melanoleuca (Hymenoptera: Apidae) from Thailand. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kothai, S.; Jayanthi, B. Anti cancer activity of silver nano particles bio-synthesized using stingless bee propolis (Tetragonula iridipennis) of Tamilnadu. Asian J. Biomed. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 5, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kustiawan, P.M.; Phuwapraisirisan, P.; Puthong, S.; Palaga, T.; Arung, E.T.; Chanchao, C. Propolis from the Stingless Bee Trigona incisa from East Kalimantan, Indonesia, Induces In Vitro Cytotoxicity and Apoptosis in Cancer Cell lines. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2015, 16, 6581–6589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dutra, R.P.; Abreu, B.V.; Cunha, M.S.; Batista, M.C.; Torres, L.M.; Nascimento, F.R.; Ribeiro, M.N.; Guerra, R.N. Phenolic acids, hydrolyzable tannins, and antioxidant activity of geopropolis from the stingless bee Melipona fasciculata Smith. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 2549–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaro, C.F.; Katouli, M.; Grkovic, T.; Vu, H.; Quinn, R.J.; Heard, T.A.; Carvalho, C.; Manley-Harris, M.; Wallace, H.M.; Brooks, P. Anti-staphylococcal activity of C-methyl flavanones from propolis of Australian stingless bees (Tetragonula carbonaria) and fruit resins of Corymbia torelliana (Myrtaceae). Fitoterapia 2014, 95, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, J.F.; dos Santos, U.P.; Macorini, L.F.; de Melo, A.M.; Balestieri, J.B.; Paredes-Gamero, E.J.; Cardoso, C.A.; de Picoli Souza, K.; dos Santos, E.L. Antimicrobial, antioxidant and cytotoxic activities of propolis from Melipona orbignyi (Hymenoptera, Apidae). Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 65, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Farias, J.H.; Reis, A.S.; Araujo, M.A.; Araujo, M.J.; Assuncao, A.K.; de Farias, J.C.; Fialho, E.M.; Silva, L.A.; Costa, G.C.; Guerra, R.N.; et al. Effects of stingless bee propolis on experimental asthma. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 2014, 951478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- da Cunha, M.G.; Franchin, M.; de Carvalho Galvao, L.C.; de Ruiz, A.L.; de Carvalho, J.E.; Ikegaki, M.; de Alencar, S.M.; Koo, H.; Rosalen, P.L. Antimicrobial and antiproliferative activities of stingless bee Melipona scutellaris geopropolis. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 13, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choudhari, M.K.; Haghniaz, R.; Rajwade, J.M.; Paknikar, K.M. Anticancer activity of Indian stingless bee propolis: An in vitro study. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 928280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cinegaglia, N.C.; Bersano, P.R.; Araujo, M.J.; Bufalo, M.C.; Sforcin, J.M. Anticancer effects of geopropolis produced by stingless bees on canine osteosarcoma cells in vitro. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 737386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Massaro, F.C.; Brooks, P.R.; Wallace, H.M.; Nsengiyumva, V.; Narokai, L.; Russell, F.D. Effect of Australian propolis from stingless bees (Tetragonula carbonaria) on pre-contracted human and porcine isolated arteries. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Franchin, M.; da Cunha, M.G.; Denny, C.; Napimoga, M.H.; Cunha, T.M.; Koo, H.; de Alencar, S.M.; Ikegaki, M.; Rosalen, P.L. Geopropolis from Melipona scutellaris decreases the mechanical inflammatory hypernociception by inhibiting the production of IL-1beta and TNF-alpha. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 143, 709–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhari, M.K.; Punekar, S.A.; Ranade, R.V.; Paknikar, K.M. Antimicrobial activity of stingless bee (Trigona sp.) propolis used in the folk medicine of Western Maharashtra, India. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 141, 363–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umthong, S.; Phuwapraisirisan, P.; Puthong, S.; Chanchao, C. In vitro antiproliferative activity of partially purified Trigona laeviceps propolis from Thailand on human cancer cell lines. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2011, 11, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liberio, S.A.; Pereira, A.L.; Dutra, R.P.; Reis, A.S.; Araujo, M.J.; Mattar, N.S.; Silva, L.A.; Ribeiro, M.N.; Nascimento, F.R.; Guerra, R.N.; et al. Antimicrobial activity against oral pathogens and immunomodulatory effects and toxicity of geopropolis produced by the stingless bee Melipona fasciculata Smith. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2011, 11, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Umthong, S.; Puthong, S.; Chanchao, C. Trigona laeviceps propolis from Thailand: Antimicrobial, antiproliferative and cytotoxic activities. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2009, 37, 855–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farnesi, A.P.; Aquino-Ferreira, R.; De Jong, D.; Bastos, J.K.; Soares, A.E. Effects of stingless bee and honey bee propolis on four species of bacteria. Genet. Mol. Res. 2009, 8, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manrique, A.J.; Santana, W.C. Flavonoids, antibacterial and antioxidant activities of propolis of stingless bees, Melipona quadrifasciata, Melipona compressipes, Tetragonisca angustula, and Nannotrigona sp. from Brazil and Venezuela. Zootec. Trop. 2008, 26, 157–166. [Google Scholar]
- Velikova, M.; Bankova, V.; Marcucci, M.C.; Tsvetkova, I.; Kujumgiev, A. Chemical composition and biological activity of propolis from Brazilian meliponinae. Z. Nat. C J. Biosci. 2000, 55, 785–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, S.A.; da Silva, T.M.G.; da Silva, E.M.S.; Camara, C.A.; Silva, T.M.S. Characterisation of phenolic compounds by UPLC-QTOF-MS/MS of geopropolis from the stingless bee Melipona subnitida (jandaira). Phytochem. Anal. 2018, 29, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pino, J.A.; Marbot, R.; Delgado, A.; Zumárraga, C.; Sauri, E. Volatile Constituents of Propolis from Honey Bees and Stingless Bees from Yucatán. J. Essent. Oil Res. 2006, 18, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utegenova, G.A.; Pallister, K.B.; Kushnarenko, S.V.; Ozek, G.; Ozek, T.; Abidkulova, K.T.; Kirpotina, L.N.; Schepetkin, I.A.; Quinn, M.T.; Voyich, J.M. Chemical Composition and Antibacterial Activity of Essential Oils from Ferula L. Species against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Molecules 2018, 23, 1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dahham, S.S.; Tabana, Y.M.; Iqbal, M.A.; Ahamed, M.B.; Ezzat, M.O.; Majid, A.S.; Majid, A.M. The Anticancer, Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Properties of the Sesquiterpene beta-Caryophyllene from the Essential Oil of Aquilaria crassna. Molecules 2015, 20, 11808–11829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crane, E. Bee Products. In Encyclopedia of Insects; Resh, V., Cardé, R., Eds.; Elsevier: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2009; pp. 71–75. [Google Scholar]
- Massaro, F.C.; Brooks, P.R.; Wallace, H.M.; Russell, F.D. Cerumen of Australian stingless bees (Tetragonula carbonaria): Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry fingerprints and potential anti-inflammatory properties. Naturwissenschaften 2011, 98, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paludo, C.R.; Pishchany, G.; Andrade-Dominguez, A.; Silva-Junior, E.A.; Menezes, C.; Nascimento, F.S.; Currie, C.R.; Kolter, R.; Clardy, J.; Pupo, M.T. Microbial community modulates growth of symbiotic fungus required for stingless bee metamorphosis. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, A.J.O.; Vasconcelos, C.C.; Garcia, J.B.S.; Doria Pinheiro, M.S.; Pereira, F.A.N.; Camelo, D.S.; Morais, S.V.; Freitas, J.R.B.; Rocha, C.Q.D.; de Sousa Ribeiro, M.N.; et al. Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Activity of Pollen Extract Collected by Scaptotrigona affinis postica: In silico, in vitro, and in vivo Studies. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Belina-Aldemita, M.D.; Schreiner, M.; D’Amico, S. Characterization of phenolic compounds and antioxidative potential of pot-pollen produced by stingless bees (Tetragonula biroi Friese) from the Philippines. J. Food Biochem. 2020, 44, e13102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, A.J.O.; Vasconcelos, C.C.; Pereira, F.A.N.; Silva, R.H.M.; Queiroz, P.; Fernandes, C.V.; Garcia, J.B.S.; Ramos, R.M.; Rocha, C.Q.D.; Lima, S.; et al. Anti-Inflammatory and Antinociceptive Activity of Pollen Extract Collected by Stingless Bee Melipona fasciculata. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Omar, W.A.W.; Azhar, N.A.; Fadzilah, N.H.; Kamal, N.N.S.N.M. Bee pollen extract of Malaysian stingless bee enhances the effect of cisplatin on breast cancer cell lines. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2016, 6, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barbara, M.S.; Machado, C.S.; Sodre Gda, S.; Dias, L.G.; Estevinho, L.M.; de Carvalho, C.A. Microbiological Assessment, Nutritional Characterization and Phenolic Compounds of Bee Pollen from Mellipona mandacaia Smith, 1983. Molecules 2015, 20, 12525–12544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tomás, A.; Falcão, S.I.; Russo-Almeida, P.; Vilas-Boas, M. Potentialities of beebread as a food supplement and source of nutraceuticals: Botanical origin, nutritional composition and antioxidant activity. J. Apic. Res. 2017, 56, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, A.N.; Syam, Y.; Natzir, R.; Rahardjo, S.P.; Hatta, M.; Dwiyanti, R.; Widaningsih, Y. The effect of giving trigona honey and honey propolis trigona to the mRNA Foxp3 expression in mice Balb/c strain induced by Salmonella typhi. Am. J. Biomed. Res. 2016, 4, 42–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngalimat, M.S.; Raja Abd Rahman, R.N.Z.; Yusof, M.T.; Syahir, A.; Sabri, S. Characterisation of bacteria isolated from the stingless bee, Heterotrigona itama, honey, bee bread and propolis. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cambronero-Heinrichs, J.C.; Matarrita-Carranza, B.; Murillo-Cruz, C.; Araya-Valverde, E.; Chavarria, M.; Pinto-Tomas, A.A. Phylogenetic analyses of antibiotic-producing Streptomyces sp. isolates obtained from the stingless-bee Tetragonisca angustula (Apidae: Meliponini). Microbiology 2019, 165, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, F.M.; Couto, J.A.; Figueiredo, A.R.; Toth, I.V.; Rangel, A.O.; Hogg, T.A. Cell membrane damage induced by phenolic acids on wine lactic acid bacteria. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2009, 135, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lechner, D.; Gibbons, S.; Bucar, F. Plant phenolic compounds as ethidium bromide efflux inhibitors in Mycobacterium smegmatis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2008, 62, 345–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodrigues, L.; Ainsa, J.; Amaral, L.; Viveiros, M. Inhibition of drug efflux in mycobacteria with phenothiazines and other putative efflux inhibitors. Recent Pat. Anti-Infect. Drug Discov. 2011, 6, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, K.W.; Lee, J.Y.; Kang, D.I.; Lee, J.U.; Shin, S.Y.; Kim, Y. Screening of flavonoids as candidate antibiotics against Enterococcus faecalis. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 719–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.R.; Ettefagh, K.A.; Todd, D.; Cole, P.S.; Egan, J.M.; Foil, D.H.; Graf, T.N.; Schindler, B.D.; Kaatz, G.W.; Cech, N.B. A mass spectrometry-based assay for improved quantitative measurements of efflux pump inhibition. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, D.; Kong, Y.; Han, C.; Chen, J.; Hu, L.; Jiang, H.; Shen, X. D-Alanine:D-alanine ligase as a new target for the flavonoids quercetin and apigenin. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2008, 32, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Zhang, M.; Wang, T.; Li, Y.; Wang, C. The roles of CDR1, CDR2, and MDR1 in kaempferol-induced suppression with fluconazole-resistant Candida albicans. Pharm. Biol. 2016, 54, 984–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Randhawa, H.K.; Hundal, K.K.; Ahirrao, P.N.; Jachak, S.M.; Nandanwar, H.S. Efflux pump inhibitory activity of flavonoids isolated from Alpinia calcarata against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Biologia 2016, 71, 484–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimse, S.B.; Pal, D. Free radicals, natural antioxidants, and their reaction mechanisms. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 27986–28006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teles Fujishima, M.A.; Silva, N.; Ramos, R.D.S.; Batista Ferreira, E.F.; Santos, K.; Silva, C.; Silva, J.O.D.; Campos Rosa, J.M.; Santos, C. An Antioxidant Potential, Quantum-Chemical and Molecular Docking Study of the Major Chemical Constituents Present in the Leaves of Curatella americana Linn. Pharmaceuticals 2018, 11, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kek, S.P.; Chin, N.L.; Tan, S.W.; Yusof, Y.A.; Chua, L.S. Classification of honey from its bee origin via chemical profiles and mineral content. Food Anal. Methods 2017, 10, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razali, M.; Zainal, Z.; Maulidiani, M.; Shaari, K.; Zamri, Z.; Mohd Idrus, M.; Khatib, A.; Abas, F.; Ling, Y.; Rui, L. Classification of Raw Stingless Bee Honeys by Bee Species Origins Using the NMR-and LC-MS-Based Metabolomics Approach. Molecules 2018, 23, 2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, H.; Steele, M.I.; Leonard, S.P.; Motta, E.V.S.; Moran, N.A. Honey bees as models for gut microbiota research. Lab. Anim. 2018, 47, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamud, R.; Xiang, S.D.; Selomulya, C.; Rolland, J.M.; O’Hehir, R.E.; Hardy, C.L.; Plebanski, M. The effects of engineered nanoparticles on pulmonary immune homeostasis. Drug Metab. Rev. 2014, 46, 176–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, M.; Fawcett, D.; Sharma, S.; Tripathy, S.K.; Poinern, G.E.J. Green Synthesis of Metallic Nanoparticles via Biological Entities. Materials 2015, 8, 7278–7308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalpana, V.N.; Devi Rajeswari, V. A Review on Green Synthesis, Biomedical Applications, and Toxicity Studies of ZnO NPs. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2018, 2018, 3569758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasooriya, E.R.; Jayasinghe, C.D.; Jayawardena, U.A.; Ruwanthika, R.W.D.; Mendis de Silva, R.; Udagama, P.V. Honey mediated green synthesis of nanoparticles: New era of safe nanotechnology. J. Nanomater. 2017, 2017, 5919836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyewumi, M.O.; Kumar, A.; Cui, Z. Nano-microparticles as immune adjuvants: Correlating particle sizes and the resultant immune responses. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2010, 9, 1095–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmad, S.; Azid, N.A.; Boer, J.C.; Lim, J.; Chen, X.; Plebanski, M.; Mohamud, R. The Key Role of TNF-TNFR2 Interactions in the Modulation of Allergic Inflammation: A Review. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, P.; Martinson, V.G.; Moran, N.A. Functional diversity within the simple gut microbiota of the honey bee. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 11002–11007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, F.J.; Rusch, D.B.; Stewart, F.J.; Mattila, H.R.; Newton, I.L. Saccharide breakdown and fermentation by the honey bee gut microbiome. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 796–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinson, V.G.; Danforth, B.N.; Minckley, R.L.; Rueppell, O.; Tingek, S.; Moran, N.A. A simple and distinctive microbiota associated with honey bees and bumble bees. Mol. Ecol. 2011, 20, 619–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwong, W.K.; Moran, N.A. Cultivation and characterization of the gut symbionts of honey bees and bumble bees: Description of Snodgrassella alvi gen. nov., sp. nov., a member of the family Neisseriaceae of the Betaproteobacteria, and Gilliamella apicola gen. nov., sp. nov., a member of Orbaceae fam. nov., Orbales ord. nov., a sister taxon to the order ‘Enterobacteriales’ of the Gammaproteobacteria. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2013, 63, 2008–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, P.; Kwong, W.K.; Moran, N.A. Frischella perrara gen. nov., sp. nov., a gammaproteobacterium isolated from the gut of the honeybee, Apis mellifera. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2013, 63, 3646–3651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





| Study ID | Country of Origin | Species | Reported Properties |
|---|---|---|---|
| Arshad 2020 [24] | Malaysia | Trigona | Improve memory Reduces anxiety |
| Biluca 2020 [25] | Brazil | Melipona marginata Tetragona clavipes Scaptotrigona bicunctata Melipona quadriasciata Tetragonisca angustula Trigona hypogea | Antioxidant Anti-inflammatory |
| Mustafa 2019 [26] | Malaysia | Heterotrigona itama | Improves memory and learning |
| Abdul Malik 2019 [27] | Malaysia | Heterotrigona itama | Antiaging |
| Hazirah 2019 [28] | Malaysia | Trigona | Antioxidant |
| Al Kafaween 2019 [29] | Malaysia | Trigona | Antimicrobial |
| Avila 2019 [30] | Brazil | Melipona bicolor Melipona quadrifasciata Melipona marginata Scaptotrigona bipuncata | Antimicrobial Antioxidant |
| Selvaraju 2019 [31] | Malaysia | Heterotrigona itama Geniotrigona thoracica | Antioxidant |
| Ranneh 2019 [32] | Malaysia | Trigona | Anti-inflammatory Antioxidant |
| Ahmad 2019 [33] | Malaysia | Heterotrigona itama | Anticancer |
| Mohd Rafie 2018 [34] | Malaysia | Heterotrigona itama | Anti-obesity |
| Mohamad 2018 [35] | Malaysia | Trigona itama | Antiproliferative |
| Nordin 2018 [36] | Malaysia | Trigona itama Trigona thorasica | Improve wound healing |
| Ng 2017 [37] | Malaysia | Trigona | Antibacterial |
| Aziz 2017 [38] | Malaysia | Geniotrigona thoracica | Anti-obesity Antidiabetic Antioxidant |
| Budin 2017 [39] | Malaysia | Trigona | Antioxidant Improves fertility |
| Zamora 2017 [40] | Costa Rica | Tetragonisca angustula Melipona beecheii | Antimicrobial |
| Saiful Yazan 2016 [41] | Malaysia | Trigona | Anticancer |
| Syam 2016 [42] | Indonesia | Trigona | Anti-inflammatory |
| Massora 2014 [43] | Australia | Tetragonula carbonaria | Antimicrobial |
| Borsato 2014 [44] | Brazil | Melipona marginata | Anti-inflammatory Antioxidant |
| Ilechie 2012 [45] | Ghana | Meliponula | Antimicrobial Anti-inflammatory |
| Boorn 2010 [46] | Australia | Trigona carbonaria | Antimicrobial |
| Garedew 2004 [47] | Ethiopia | Trigona | Antimicrobial |
| Torres 2004 [48] | Colombia | Tetragonisca angustula | Antimicrobial |
| Patricia 2002 [49] | Venezuela | Melipona favosa | Anti-inflammatory |
| Study ID | Country of Origin | Species | Reported Properties |
|---|---|---|---|
| da Cunha 2020 [85] | Brazil | Melipona scutellaris | Antimicrobial Anti-adherence and Anti-biofilm |
| Rubinho 2019 [86] | Brazil | Melipona quadrifasciata | Antioxidant Antimicrobial |
| Pujirahayu 2019 [87] | Indonesia | Tetragonula sapiens | Antioxidant |
| Abdullah 2019 [88] | Brunei Darussalam | Heterotrigona itama | Antioxidant Antimicrobial |
| Iqbal 2019 [89] | Indonesia | Trigona | Anticancer |
| Cisilotto 2018 [90] | Brazil | Scaptotrigona bipunctata Melipona quadrifasciata | Antioxidant |
| Brodkiewicz 2018 [91] | Argentina | Tetragonisca fiebrigi Scaptotrigona jujuyensis | Antioxidant Antimicrobial Anti-inflammatory Anticancer |
| Kustiawan 2017 [92] | Thailand | Trigona incisa | Anticancer |
| Sabir 2017 [93] | Indonesia | Trigona | Anti-inflammatory |
| Bonamigo 2017 [51] | Brazil | Scaptotrigona depilis Melipona quadrifasciata anthidioides | Antioxidant Anticancer |
| Utispan 2017 [94] | Thailand | Trigona sirindhornae | Anticancer |
| Nguyen 2017 [95] | Vietnam | Trigona minor | Anticancer |
| Santos 2017 [96] | Brazil | Melipona orbignyi | Antioxidant Antimicrobial |
| Utispan 2017 [97] | Thailand | Trigona sirindhornae | Antibacterial |
| Massaro 2015 [98] | Australia | Tetragonula carbonaria | Antibacterial |
| Campos 2015 [99] | Brazil | Tetragonisca fiebrigi | Antioxidant Anti-inflammatory Antimicrobial Anticancer |
| Sanpa 2015 [100] | Thailand | Tetragonula laeviceps Tetrigona melanoleuca | Antibacterial |
| Kothai 2015 [101] | India | Tetragonula iridipennis | Anticancer |
| Kustiawan 2015 [102] | Thailand | Trigona incisa | Anticancer |
| Dutra 2014 [103] | Brazil | Melipona fasciculata | Antioxidant |
| Massaro 2014 [104] | Australia | Tetragonula carbonaria | Antibacterial |
| Campos 2014 [105] | Brazil | Melipona orbignyi | Antioxidant Anticancer |
| de Farias 2014 [106] | Brazil | Scaptotrigona postica | Anti-inflammatory |
| da Cunha 2013 [107] | Brazil | Melipona scutellaris | Antibacterial Anticancer |
| Choudhari 2013 [108] | India | Trigona | Anticancer Antioxidant |
| Cinegaglia 2013 [109] | Brazil | Melipona fasciculata | Anticancer |
| Massaro 2013 [110] | Australia | Tetragonula carbonaria | Management of cardiovascular disorders |
| Franchin 2012 [111] | Brazil | Melipona scutellaris | Anti-inflammatory |
| Choudhari 2012 [112] | India | Trigona | Antimicrobial |
| Umthong 2011 [113] | Thailand | Trigona laeviceps | Anticancer |
| Liberio 2011 [114] | Brazil | Melipona fasciculata | Antimicrobial |
| Umthong 2009 [115] | Thailand | Trigona laeviceps | Antimicrobial Anticancer |
| Farnesi 2009 [116] | Brazil | Melipona quadrifasciata Scaptotrigona | Antimicrobial |
| Manrique 2008 [117] | Brazil and Venezuela | Melipona quadrifasciata Tetragonisca angustula Melipona compressipes Nannotrigona | Antioxidant Antimicrobial |
| Velikova 2000 [118] | Brazil | Meliponinae | Antimicrobial |
| Study ID | Country of Origin | Species | Reported Properties |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cerumen | |||
| Paludo 2019 [125] | Brazil | Scaptotrigona depilis | Antimicrobial |
| Nugitrangson 2015 [15] | Thailand | Tetragonula laeviceps | Anticancer |
| Massaro 2011 [124] | Australia | Tetragonula carbonaria | Anti-inflammatory |
| Bee Pollen | |||
| Lopes 2020 [126] | Brazil | Scaptotrigona affinis postica | Antioxidant Anti-inflammatory |
| Belina-Aldemita 2020 [127] | Philippine | Tetragonula biroi Friese | Antioxidant |
| Lopes 2019 [128] | Brazil | Melipona fasciculata | Antioxidant Anti-inflammatory |
| Omar 2016 [129] | Malaysia | Lepidotrigona terminata | Antioxidant Anticancer |
| Barbara 2015 [130] | Brazil | Melipona mandacaia | Antimicrobial |
| Study ID | Country of Origin | Species | Products | Reported Properties |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ngalimat 2019 [133] | Malaysia | Heterotrigona itama | Honey Propolis Beebread | Antimicrobial |
| Cambronero-Heinrichs 2019 [134] | Costa Rica | Tetragonisca angustula | Adult bees and different substrates of the hive (pollen and honey storage, garbage pellets and cerumen) | Antimicrobial |
| Ismail 2018 [16] | Malaysia | Trigona | Honey Propolis Beebread | Antioxidant Anticancer |
| Kustiawan 2014 [14] | Thailand | Trigona incise Timia apicalis Trigona fuscobalteata Trigona fuscibasis | Propolis Bee pollen Honey | Anticancer |
| Usman 2016 [132] | Indonesia | Trigona | Honey Propolis | Anti-inflammatory |
| Compound | Mechanisms of Action | Target | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| p-Coumaric Caffeic acid Ferulic acid | Damaging the cytoplasmic membrane by inducing ion leakages and proton influx | Oenococcus oeni and Lactobacillus hilgardii | [135] |
| Myricetin | Inhibition of the intrinsic efflux pump system | Mycobacterium smegmatis | [136] |
| Luteolin | Inhibition of the intrinsic efflux pump system | Mycobacteria spp. | [136,137] |
| Naringenin Eriodictyol Taxifolin | Inhibition of β-Ketoacyl–Acyl Carrier Protein Synthase III (PfKASIII) | Enterococcus faecalis | [138] |
| Quercetin | Inhibition of the intrinsic efflux pump system | S. aureus | [139] |
| Targeting d-Alanine:d-alanine Ligase | Helicobacter pylori and E. coli | [140] | |
| Apigenin | Targeting d-Alanine:d-alanine Ligase | Helicobacter pylori and E. coli | [140] |
| Kaempferol | Inhibition of the intrinsic efflux pump system | C. albicans and S. aureus | [141,142] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Hatamleh, M.A.I.; Boer, J.C.; Wilson, K.L.; Plebanski, M.; Mohamud, R.; Mustafa, M.Z. Antioxidant-Based Medicinal Properties of Stingless Bee Products: Recent Progress and Future Directions. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 923. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10060923
Al-Hatamleh MAI, Boer JC, Wilson KL, Plebanski M, Mohamud R, Mustafa MZ. Antioxidant-Based Medicinal Properties of Stingless Bee Products: Recent Progress and Future Directions. Biomolecules. 2020; 10(6):923. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10060923
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Hatamleh, Mohammad A. I., Jennifer C. Boer, Kirsty L. Wilson, Magdalena Plebanski, Rohimah Mohamud, and Mohd Zulkifli Mustafa. 2020. "Antioxidant-Based Medicinal Properties of Stingless Bee Products: Recent Progress and Future Directions" Biomolecules 10, no. 6: 923. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10060923
APA StyleAl-Hatamleh, M. A. I., Boer, J. C., Wilson, K. L., Plebanski, M., Mohamud, R., & Mustafa, M. Z. (2020). Antioxidant-Based Medicinal Properties of Stingless Bee Products: Recent Progress and Future Directions. Biomolecules, 10(6), 923. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10060923








