Abstract
A3 adenosine receptor (A3AR) agonists have emerged as potent relievers of neuropathic pain by a T cell-mediated production of IL-10. The H4 histamine receptor (H4R), also implicated in pain modulation, is expressed on T cells playing a preeminent role in its activation and release of IL-10. To improve the therapeutic opportunities, this study aimed to verify the hypothesis of a possible cross-talk between A3AR and H4R in the resolution of neuropathic pain. In the mouse model of Chronic Constriction Injury (CCI), the acute intraperitoneal co-administration of the A3AR agonist IB-MECA (0.5 mg/kg) and the H4R agonist VUF 8430 (10 mg/kg), were additive in counteracting mechano-allodynia increasing IL-10 plasma levels. In H4R−/− mice, IB-MECA activity was reduced, lower pain relief and lower modulation of plasma IL-1β, TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-10 were shown. The complete anti-allodynia effect of IB-MECA in H4R−/− mice was restored after intravenous administration of CD4+ T cells obtained from naïve wild type mice. In conclusion, a role of the histaminergic system in the mechanism of A3AR-mediated neuropathic pain relief was suggested highlighting the driving force evoked by CD4+ T cells throughout IL-10 up-regulation.
Keywords:
neuropathic pain; A3AR; H4R; allodynia; interleukin-10; CD4+ T cells; H4R−/− mice; chronic constriction injury 1. Introduction
The prevalence of neuropathic pain in the general population is estimated to lie between 6.9% and 10% [1]. Neuropathic pain refers to a broad range of clinical conditions that can be categorized anatomically (e.g., peripheral vs. central) and etiologically (e.g., degenerative, traumatic, infectious, metabolic, and toxic) [2]. Signs and symptoms associated with neuropathic pain include paresthesia, hyperalgesia, hypoalgesia, allodynia, ongoing pain (burning pain), paroxysmal pain (electrical shock-like pain), and abnormal temporal summation [3].
Current systemic and topical pharmacological treatments have substantial limitations in terms of the level of efficacy provided and/or the side effect profile. This means the management of neuropathic pain is unsatisfactory in preventing its development and progression [4]. This is why new pharmacological approaches are required.
Recently, the adenosine A3 receptor (A3AR) emerged as a novel target for neuropathic pain management. Preclinical studies demonstrated that A3AR agonists are effective in the prevention and treatment of neuropathies originated by different chemotherapeutic drugs like taxanes, platinum-complex and proteasome inhibitors [5,6] or by nerve trauma (e.g., the loose ligation of the sciatic nerve; Chronic Constriction Injury, CCI) [5,7]. A3ARs are expressed in both the peripheral [8] and central nervous systems [9], including glial cells, as well as in inflammatory and immune cells (i.e., macrophages and T cells). It is known that A3ARs are also located on the membrane of CD4+ T cells, a prominent source of IL-10 [10], and CD8+ T cells; their expression is increased under pathological settings correlated with the progression of the inflammatory response [11]. Moreover, the pivotal pharmacodynamic role of the CD4+ T-dependent IL-10 release in the pain-relieving effect of A3AR agonists was recently demonstrated [7].
The histamine H4 receptor (H4R), the last discovered histamine receptor subtype, also emerged as a promising target for pharmacological intervention in the development of new analgesics. Sanna and colleagues demonstrated that molecules acting on H4R are able to counteract neuropathic pain evoked by the spared nerve injury in mice, reducing both oxidative stress and pro-neuroinflammatory pathways [12,13]. Recent data showed the presence of H4Rs on neurons, highlighting its participation in nervous functions [12,14]. H4Rs are expressed in structures related to nociceptive transmission, such as dorsal root ganglia and spinal cord [12,14,15,16]. They have been also documented in several cell types of the immune system including T cells [17] where also A3ARs are expressed. H4Rs are implicated in the activation of CD4+ T cells [18] evoking the secretion release of different regulatory cytokines like IL-10 and IFN-γ [19]. On this basis, CD4+ T cells emerged as a possible crossroad between A3AR and H4R signaling suggesting synergistic or additive mechanisms in counteracting persistent pain.
The present work analyzed the relationship between the A3AR and H4R in modulating neuropathic pain induced by nerve trauma in the mouse model of loose ligation of the sciatic nerve. Wild type (WT) and H4R knockout mice were used to investigate the anti-hyperalgesic effects of the acute administration of the selective A3AR and H4R agonists, IB-MECA and VUF 8430, respectively, in comparison to their combination. The transplant of WT CD4+ T cells in H4R−/− was used to highlight the role of the immune system in the H4R-dependent component of A3AR agonist pain relieving effect.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
Male BALB/C WT and H4R−/− mice (7 weeks old, 22–25 g starting weight) were used for the experiments. Histamine H4 receptor knockout mice were generated by Lexicon Genetics (Woodlands Park, TX, USA) and provided by Janssen Research and Development (LLC La Jolla, CA, USA) and back crossed to BALB/C background. Corresponding homozygous BALB/C WT controls were obtained from Envigo RMS S.r.l (Udine, Italy). Animals were housed in the Centro Stabulazione Animali da Laboratorio (University of Florence, Italy) and used at least 1 week after their arrival. Ten mice were housed per cage (size 26 × 41 cm); animals were fed a standard laboratory diet and tap water ad libitum and kept at 23 ± 1 °C with a 12 h light/dark cycle (light at 7 a.m.). The experimental protocol was carried out after approval by the Animal Care and Research Ethics Committee of the University of Florence, Italy, under license from the Italian Department of Health (No. 142/2017) and in compliance with international laws and policies (Directive, 2010/63/EU of the European parliament and of the council of 22 September 2010 on the protection of animals used for scientific purposes; Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, US National Research Council, 2011).
Experiments involving animals have been reported according to ARRIVE guidelines [20]. All efforts were made to minimize animal suffering and to reduce the number of animals used.
2.2. Chronic Constriction Injury (CCI)-Induced Neuropathic Pain
CCI to the sciatic nerve of the left hind leg was performed under general anesthesia using the well-characterized Bennett and Xie model [21]. Briefly, animals (weighing 25–30 g at the time of surgery) were anesthetized with 2% isoflurane/O2 inhalation and maintained on 2% isoflurane/O2 for the duration of surgery. The left thigh was shaved and a small incision (1–1.5 cm in length) was made in the middle of the lateral aspect of the left thigh to expose the sciatic nerve. The nerve was loosely ligated around the entire diameter of the nerve at 3 distinct sites (spaced 1 mm apart) using silk sutures (6.0). The surgical site was closed with a single muscle suture and a skin clip. Pilot studies established that under our experimental conditions, the peak of mechano-allodynia develops by day 5–7 (D5–D7) following CCI. Test substances or their vehicles were given at peak of mechanical allodynia (D8–D9). A total of 70 animals underwent surgery for CCI.
2.3. Administration of Compounds
The selective A3AR agonist, IB-MECA (0.5–1 mg/kg; Tocris Bioscience, Milan, Italy), and the selective H4R agonist, VUF 8430 (10–30 mg/kg; Tocris Bioscience, Milan, Italy) were dissolved in sterile saline solution and intraperitoneally (i.p.) administered on day 8 after CCI surgery. Control animals received an equal volume of vehicle. Behavioral measurements were performed before and 30 min, 1 h, 2 h, 3 h and 5 h after compounds injection.
2.4. T Cells Isolation and Adoptive Transfer
Single-cell suspensions were obtained from spleens and lymph nodes of BALB/C WT mice by passing organs through 70 μm strainers, after which cells were washed with PBS plus 0.1% bovine serum albumin. T-cell population was purified by negative selection. Briefly, T cells were incubated with biotinylated antibodies against CD11b, CD11c, CD49b, B220, TER-119, CD4 and CD8a, all purchased from BioLegend (San Diego, CA, USA), and they were negatively selected by autoMACS sorting. After MACS purification, T cells were washed, counted and resuspended in PBS for intravenous (i.v.) injections (2 × 106/200 μL/mouse). On day 7 after surgery, T cells or PBS were injected i.v. into the tail vein in a volume of 200 μL. An aliquot of the sorted population was assessed for the purity check analysis: cells were labelled with anti-CD3-FITC and the purity was determined by Flow Cytometry. The efficiency of transfer was confirmed by the restored presence of H4R in the spinal cord of H4R−/− mice after the CD4+ T cells implantation (RT-PCR analysis; Supplementary Figure S1).
2.5. Von Frey Test
The animals were placed in 20 × 20 cm plexiglass boxes equipped with a metallic mesh floor, 20 cm above the bench. A habituation of 15 min was allowed before the test. An electronic von Frey hair unit (Ugo Basile, Varese, Italy) was used: the withdrawal threshold was evaluated by applying force ranging from 0 to 5 g with a 0.2 g accuracy. Punctate stimulus was delivered to the mid-plantar area of each ipsilateral (injured side) hindpaw from below the mesh floor through a plastic tip and the withdrawal threshold was automatically displayed on the screen. Paw sensitivity threshold was defined as the minimum pressure required to elicit a robust and immediate withdrawal reflex of the ipsilateral hindpaw. Voluntary movements associated with locomotion were not taken as a withdrawal response. Stimuli were applied on each anterior paw with an interval of 5 s. The measure was repeated 5 times and the final value was obtained by averaging the 5 measures [22,23].
2.6. Cytokine Measurements
On day 8 after CCI surgery, WT and H4R−/− mice were treated with IB-MECA, VUF 8430 or IB-MECA + VUF 8430 and 1 h post-dosing plasma samples were harvested to evaluate the levels of different cytokines. The quantitative determination of the interleukin-10 (IL-10), interleukin-6 (IL-6), interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, was performed by a bead-based multiplex immunoassay, following the protocol provided by the manufacturer (EDM Millipore Corporation, Billerica, MA, USA). Briefly, neat plasma samples were added to antibody-conjugated beads directed against the cytokines listed above in a 96-well filter plate. After a 30 min incubation, the plate was washed, and biotinylated anti-cytokine antibody solution was added before overnight incubation. The plate was then washed, and streptavidin-conjugated PE was added.
After a final wash, each well was suspended with assay buffer and analyzed with the Bio-plex 200 system (Bio-Rad, Milan, Italy). Standard curves were derived from various concentrations of the different cytokine standards following the same protocol as the plasma samples.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
Data are expressed as mean ± SD for n animals. Behavioral data were analyzed by two-way repeated measures ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s test and Turkey comparisons. Calculation were made with Prism 6.1 statistical software (GraphPad Software Inc., San Diego, CA, USA). Electrophysiology averaged data are reported as mean ± SEM for n cells tested. Student’s paired t-test was used for statistical comparisons between data obtained from the same cell before and after treatment. Significant differences were defined as a value of p < 0.05.
3. Results and Discussion
In this study we showed a cross-talk between the molecular mechanisms underlying the effect of A3AR and H4R agonists in reducing neuropathic pain induced in mice by the loose ligation of the sciatic nerve. In particular, we demonstrated that submaximal doses of the selective A3AR agonist IB-MECA and the H4R agonist VUF 8430 showed additive effects in decreasing hypersensitivity. Further, IB-MECA efficacy partly depended from H4Rs with a mechanism involving the presence of CD4+ T cells and their ability to release the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10.
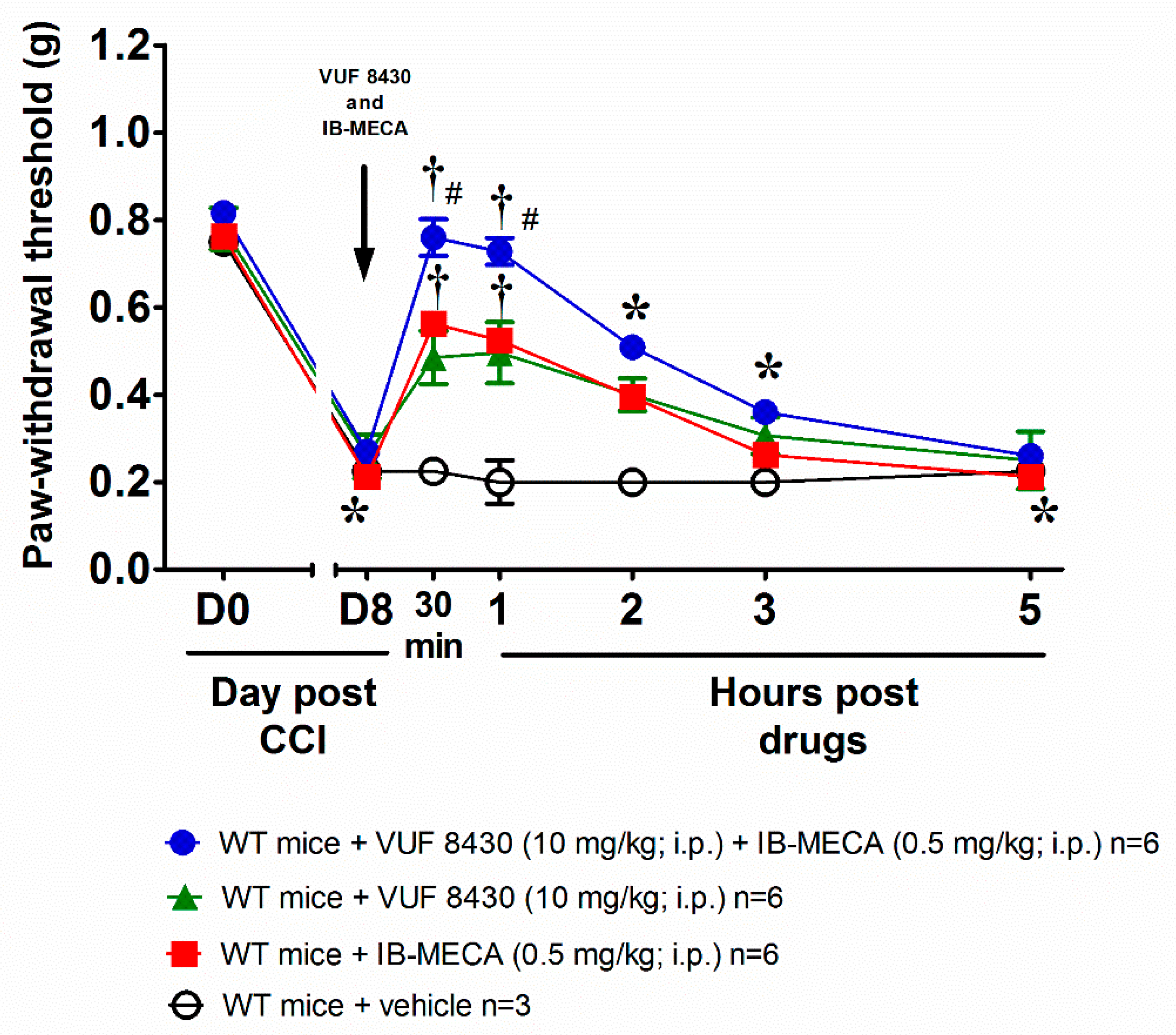
We reproduced the murine model of neuropathic pain induced by CCI, on day 8 after surgery the paw withdrawal threshold to non-noxious mechanical stimuli (von Frey test) was significantly decreased with respect to the same measure performed before the nerve damage (day 0). Intraperitoneal co-treatment with the selective A3AR (IB-MECA 0.5 mg/kg) and H4R (VUF 8430 10 mg/kg) agonists reversed mechanical allodynia in WT male mice with an effect that last up to 3 h after treatment (Figure 1). To note, the injections of the single agonists at the same dose used in the co-treatment were still active but did not reach the efficacy of the combination (Figure 1). The additive effect allowed to hypothesize a link between the mechanism of action triggered by the stimulation of both A3AR and H4R receptors. The dose of the A3AR agonist was chosen from previous studies to cause a near-to-maximal reversal of mechano-allodynia in this model [24], while the dose of the H4R agonist was selected on the basis of the results obtained after the acute administration of VUF 8430 and reported in the Supplementary Figure S2.
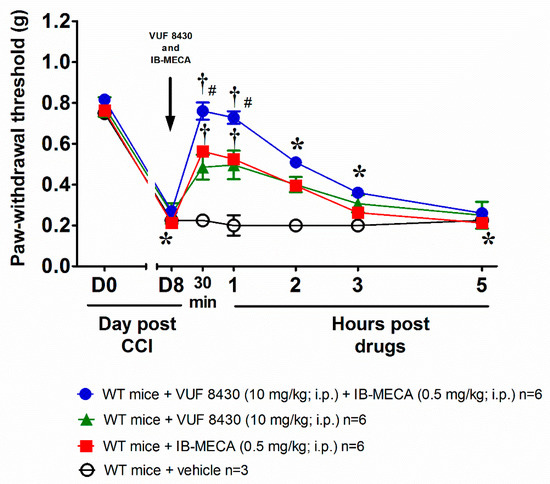
Figure 1.
Anti-allodynic effect of A3 adenosine receptor (A3AR) and H4 histamine receptor (H4R) agonists on Chronic Constriction Injury (CCI)-induced neuropathic pain in wild type (WT) mice. Sciatic nerve ligation was performed 8 days before the acute injection of IB-MECA (0.5 mg/kg, i.p.), VUF 8430 (10 mg/kg, i.p.) or the combination of both (VUF 8430 10 mg/kg + IB-MECA 0.5 mg/kg). The response to a non-noxious mechanical stimulus was assessed by the von Frey test. Measurements were performed before and 30 min, 1 h, 2 h, 3 h and 5 h after compounds administration. Values reported in the graph are referred to the tests conducted on the ipsilateral paw. Data are mean ± SD for n mice per group; * p < 0.05 vs. Day 0 by two-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s test; † p < 0.001 vs. Day 8 by two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s comparisons; # p < 0.001 vs. WT + VUF 8430 (10 mg/kg) and WT + IB-MECA (0.5 mg/kg) by two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s comparisons.
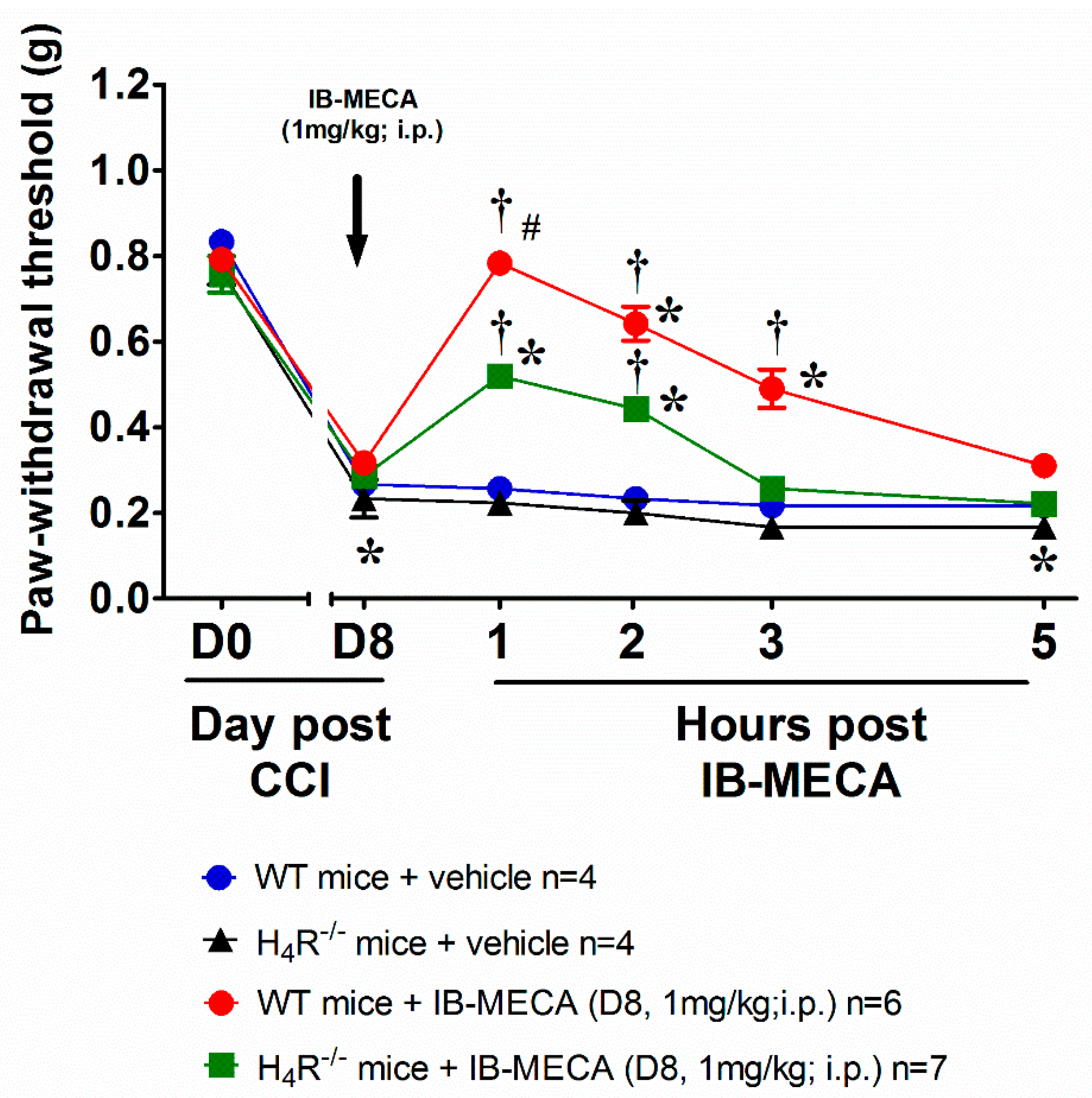
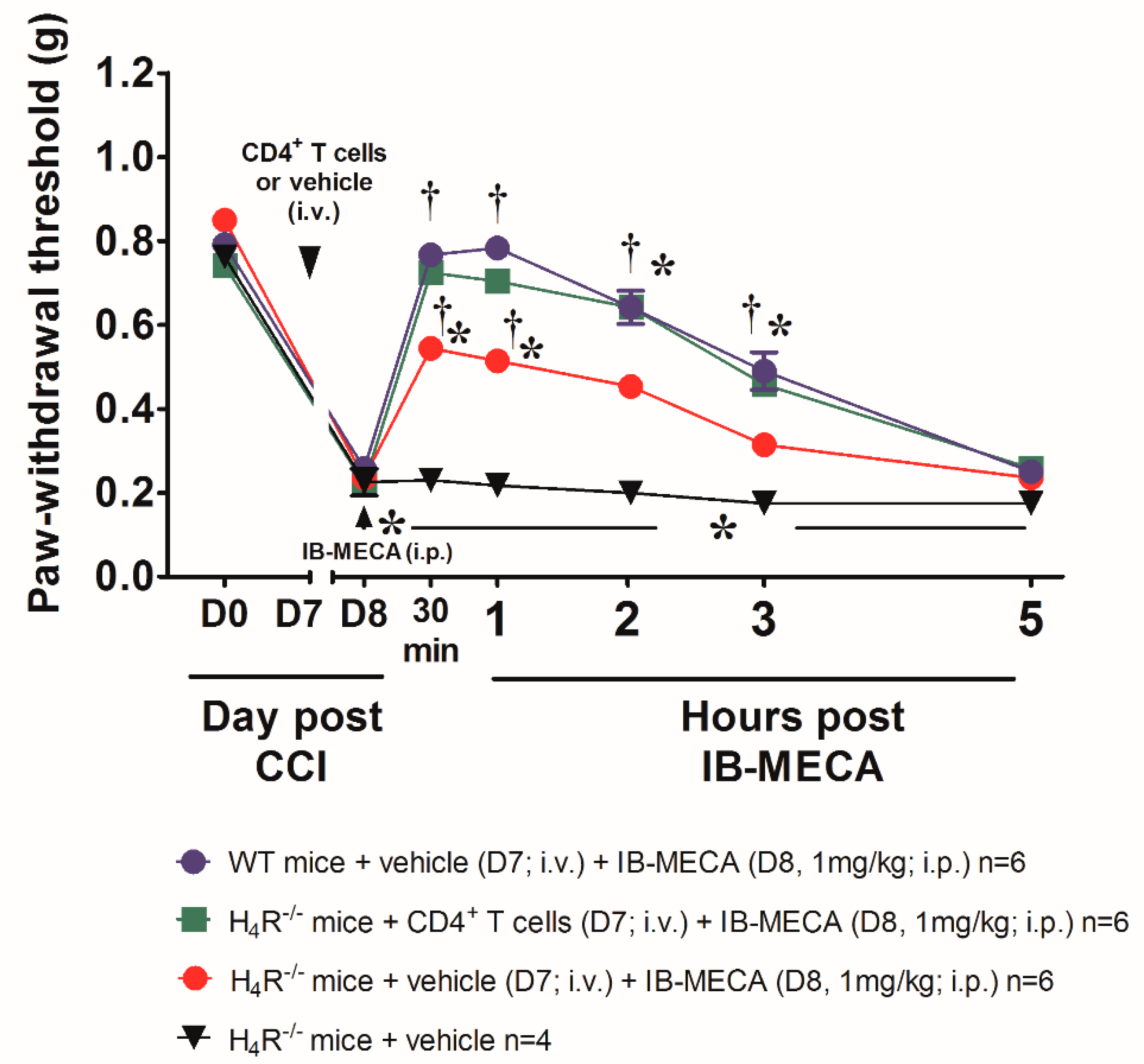
To confirm the crosstalk between the histaminergic and adenosine system in the mechanism of action of IB-MECA, neuropathic WT and H4R−/− mice were acutely treated with the A3AR agonist IB-MECA 1 mg/kg (the dose that exerts the full anti-hyperalgesic effect). In WT mice, IB-MECA fully counteracted CCI-induced mechanical allodynia 1 h after administration, the relief was significant up to 3 h (Figure 2). On the contrary, in H4R−/− mice the compound was only partially effective (Figure 2) confirming a pivotal role of H4R in the anti-hypersensitivity action evoked by the A3AR agonist.
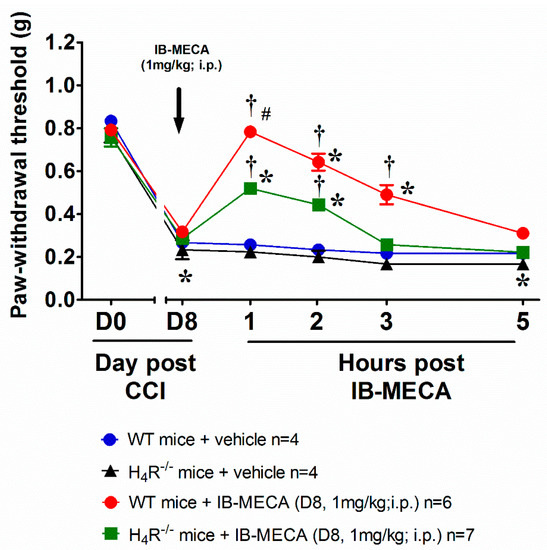
Figure 2.
Anti-allodynic effect of A3AR agonist IB-MECA on CCI-induced neuropathic pain in WT and H4R−/− mice. Sciatic nerve ligation was performed in WT and H4R−/− mice 8 days before the acute injection of IB-MECA (1 mg/kg, i.p.). The response to a non-noxious mechanical stimulus was assessed by the Von Frey test. Measurements were performed before and 1 h, 2 h, 3 h and 5 h after IB-MECA administration. Values reported in the graph are referred to the tests conducted on the ipsilateral paw. Data are mean ± SD for n mice per group; * p < 0.05 vs. Day 0 by two-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s test; † p < 0.001 vs. Day 8 by two-way ANOVA with Turkey comparisons; # p < 0.001 vs. H4R−/− mice + IB-MECA (1 mg/kg) by two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s comparisons.
To investigate the possible interactions, we started to analyse one of the A3AR-mediated mechanisms: the attenuation of inflammatory cytokines, like TNF-α and IL-1β, and the increased formation of the anti-inflammatory IL-10 [25].
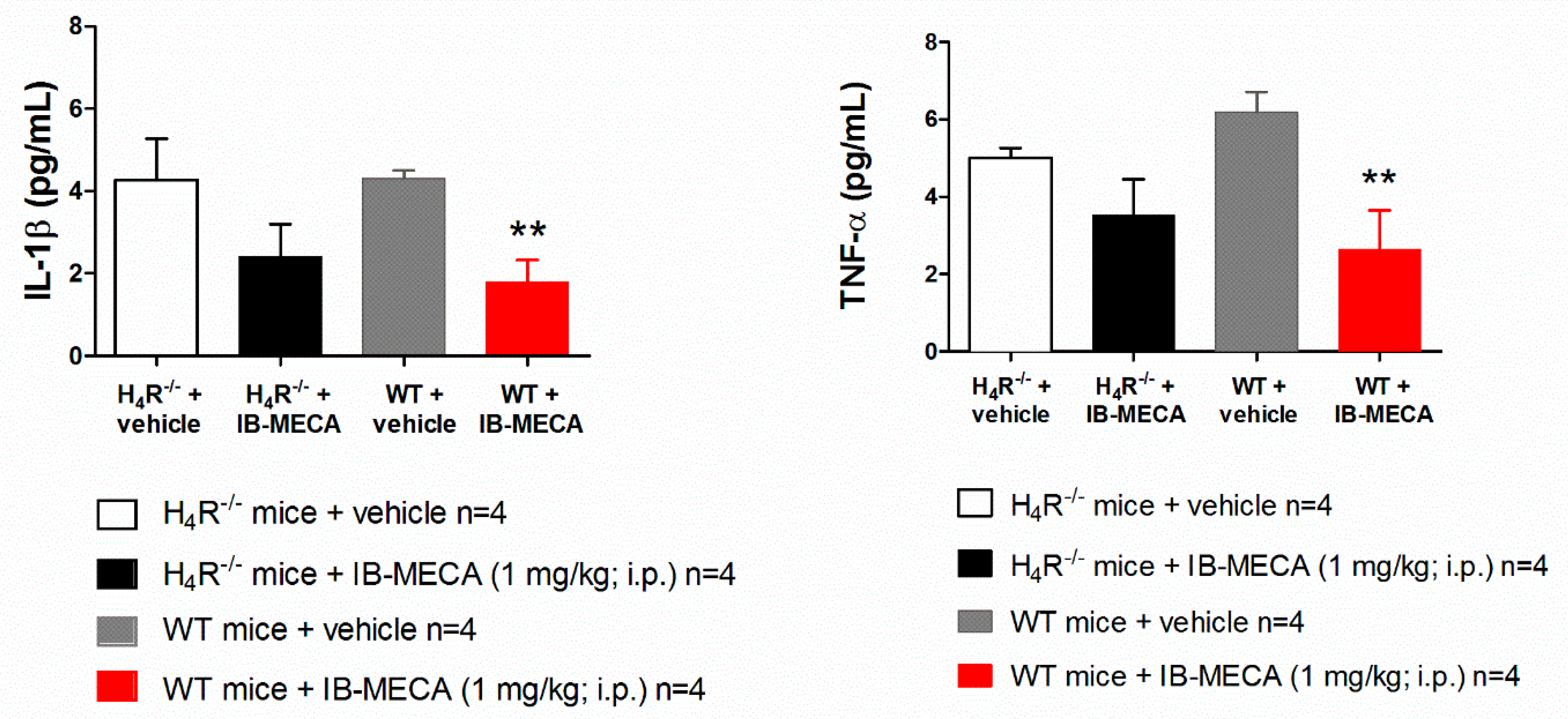
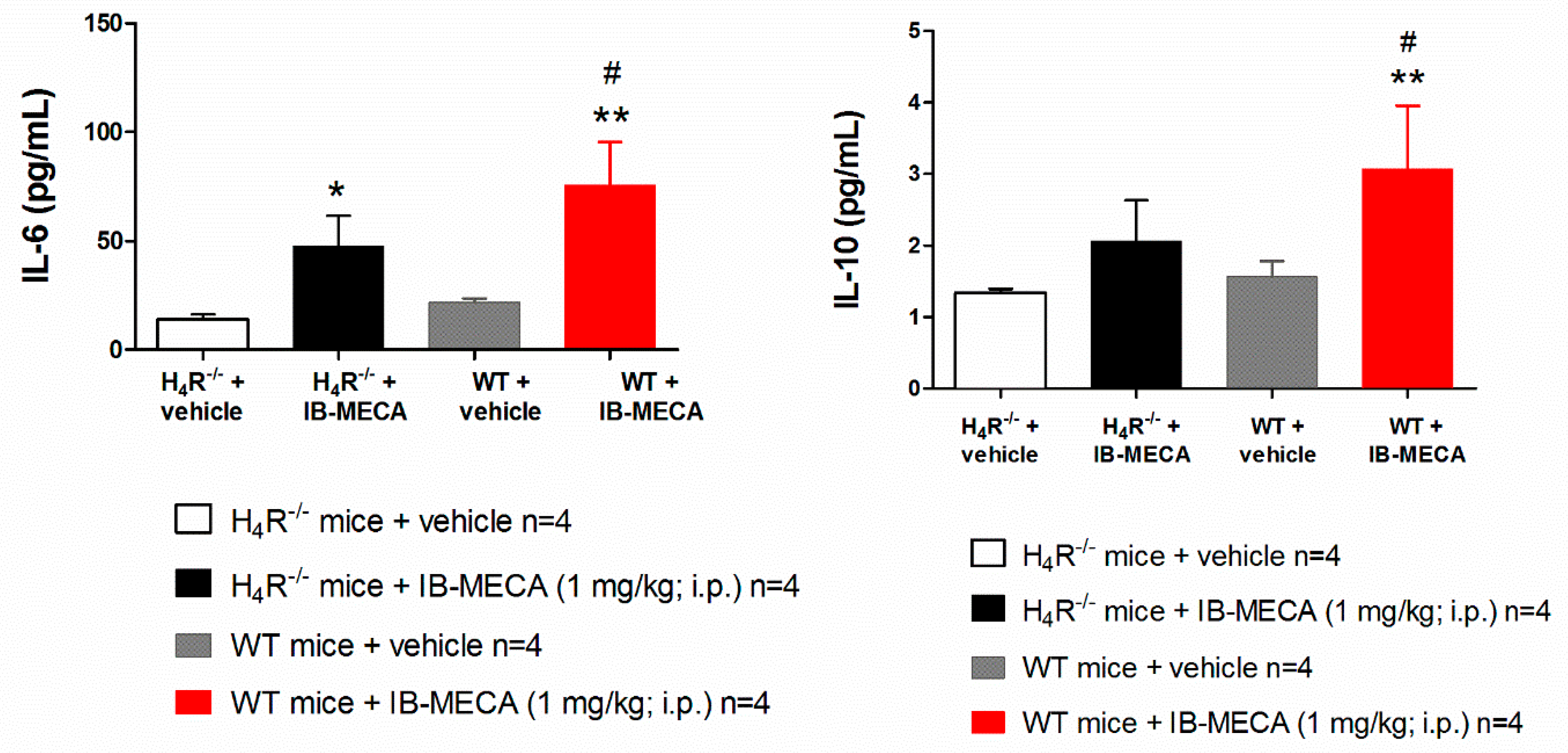
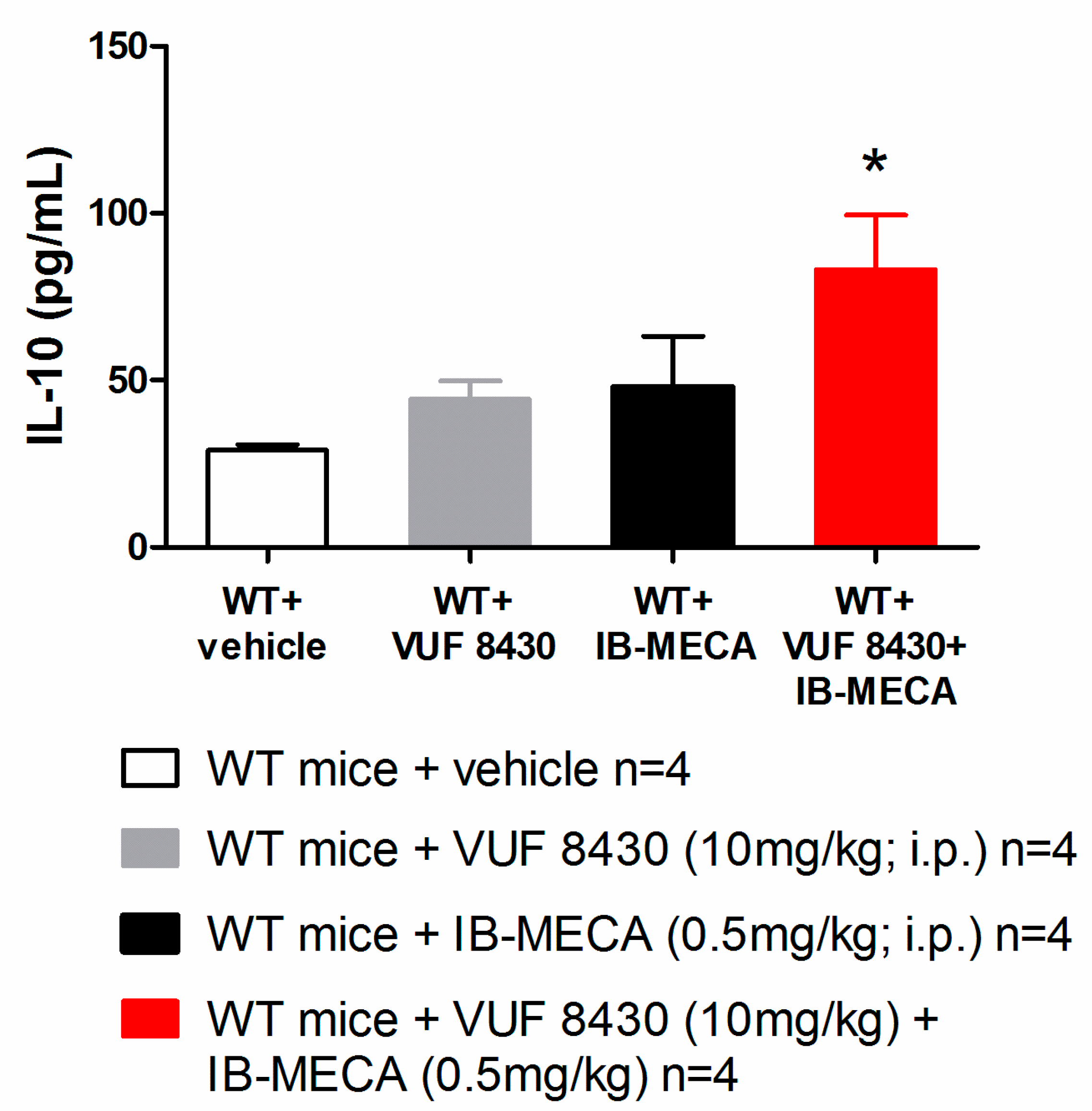
In our study, IB-MECA (1 mg/kg, 1 h after administration in CCI mice) significantly reduced IL-1β and TNF-α plasma levels in WT animals with respect to the vehicle-treated group (WT + vehicle), on the contrary in H4R−/−, IB-MECA did not modify the secretion of cytokines (Figure 3). Regarding IL-6 and IL-10, IB-MECA evoked a significantly higher increase in WT in comparison to H4R−/− (Figure 4) reiterating the relevance of H4Rs in A3AR-mediated effects. Accordingly, IB-MECA and VUF 8430 were additive in increasing the plasma IL-10 concentration when administered at lower (per se ineffective) dose in WT (Figure 5).
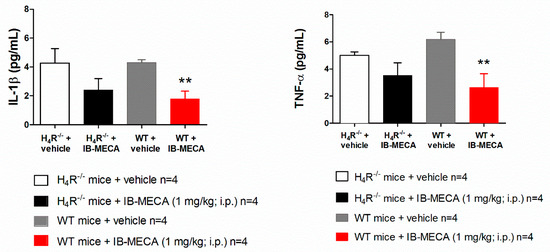
Figure 3.
Effect of A3AR agonist IB-MECA on IL-1β and TNF-α plasma levels on CCI-induced neuropathic pain in WT and H4R−/− mice. Sciatic nerve ligation was performed in WT and H4R−/− mice 8 days before the acute injection of IB-MECA (1 mg/kg, i.p.). One hour after administration, blood was collected for dosing IL-1β and TNF-α plasma levels. Data are mean ± SD for 4 mice per group; ** p < 0.01 vs. WT mice + vehicle by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s test.
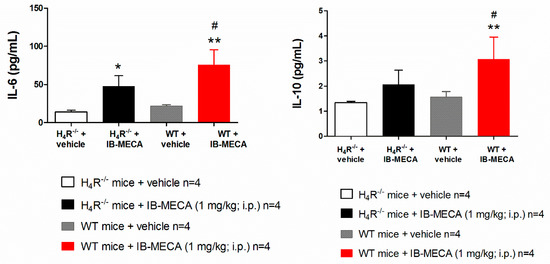
Figure 4.
Effect of A3AR agonist IB-MECA on IL-6 and IL-10 plasma levels on CCI-induced neuropathic pain in WT and H4R−/− mice. Sciatic nerve ligation was performed in WT and H4R−/− mice 8 days before the acute injection of IB-MECA (1 mg/kg, i.p.). One hour after administration, blood was collected for measuring IL-6 and IL-10 plasma levels. Data are mean ± SD for 4 mice per group; * p < 0.05 and ** p < 0.01 vs. vehicle; # p < 0.05 vs. H4R−/− mice + IB-MECA by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s test.
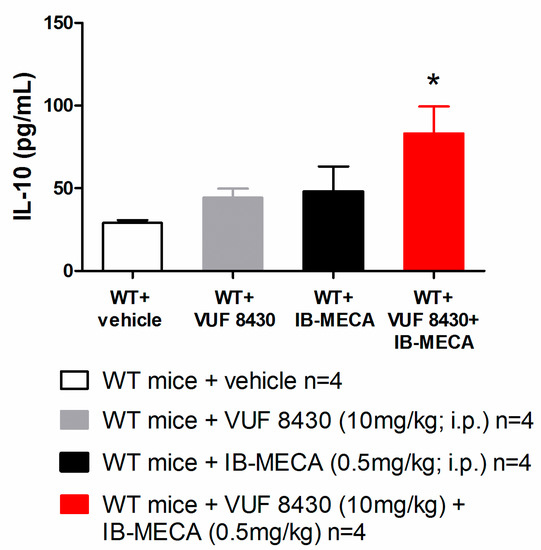
Figure 5.
Effect of A3AR and H4R agonists on IL-10 plasma levels in WT mice underwent to CCI-induced neuropathic pain. Sciatic nerve ligation was performed 8 days before the acute injection of IB-MECA (0.5 mg/kg, i.p.), VUF 8430 (10 mg/kg, i.p.) or the combination of both (VUF 8430 0.5 mg/kg + IB-MECA 10 mg/kg). One hour after compounds administration, blood was collected for measuring the IL-10 plasma levels. Data are mean ± SD for 4 mice per group; * p < 0.05 vs. WT mice + VUF 8430 and WT + IB-MECA by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s comparisons.
On the other hand, the role of IL-10 in the A3AR-mediated pain relief overwhelmingly emerged since it was established that release of IL-10 from CD4+ T cells is required and sufficient for the A3AR agonists efficacy [7]. As a negative regulator, IL-10 is primarily produced by Th2 cells, activated B cells, monocytes, macrophages, and glial cells and regulates pleiotropic effects in inflammation and immunoregulation [26,27]. IL-10 is able to attenuate nociception in many animal models through the inhibition of pro-inflammatory cytokines and spinal glial cell activation [28]. Intrathecal IL-10 gene therapy has been shown to have a therapeutic effect in a rat model of neuropathic pain [29]. Moreover, IL-10 attenuates thermal hyperalgesia induced by chronic sciatic nerve constriction [30] and enhances morphine analgesia [31]. IL-10 is also a powerful neuroinhibitory cytokine; therapeutic manipulations aimed at increasing its presence in spinal cord (i.e., with plasmid DNA encoding IL-10) [32] or by indirectly increasing its production through the removal of peroxynitrite have been shown to block paclitaxel-induced neuropathic pain [33]. Andres-Hernando and colleagues demonstrated that IL-6 directly increases IL-10 production predominantly in the spleen and in CD4+ T cells participating to counteract the inflammatory response [34].
Focusing on CD4+ T cells, pivotal in the activity of A3ARs, it is interesting to note that also H4R is functionally expressed on these cells and implied in their activation [18] and the consequent production of different regulatory cytokines [17]. H4R activation was able to mitigate chronic inflammation increasing IL-10 and IFN-γ and inducing the recruitment of CD4+FoxP3+T cells [19]. So, hypothesizing CD4+ T cells as a potential site where the interaction between the two receptors takes place, WT mice were used to isolate CD4+ T cells that were intravenously administered in CCI H4R−/− mice one day before the acute treatment with IB-MECA (1 mg/kg). The acute i.p. administration of IB-MECA reversed mechano-allodynia in H4R−/− mice receiving CD4+ T cells in a comparable manner to that evoked by the same compound in WT mice (Figure 6) The baseline values showed that CD4+ T cells transfer did not influence the pain threshold of H4R−/− mice.
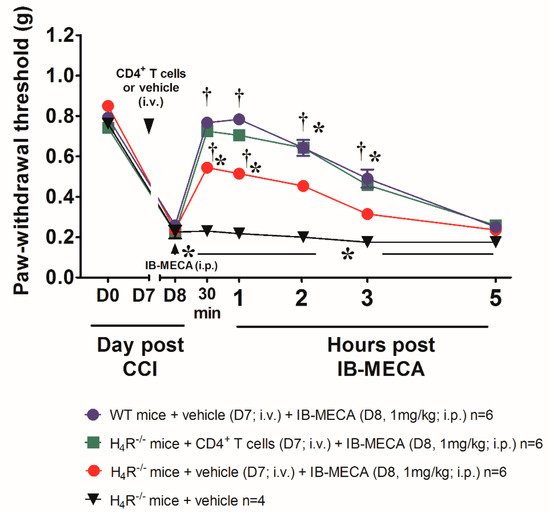
Figure 6.
Effect of A3AR agonist IB-MECA after CD4+ T cells transfer in H4R−/− mice underwent to CCI. Sciatic nerve ligation was performed in H4R−/− mice 7 days before the intravenously administration of CD4+ T cells (2 × 106/200 μL/mouse) obtained from naïve WT mice, 24 h the acute injection of IB-MECA (1 mg/kg, i.p.) was performed. The response to a non-noxious mechanical stimulus was assessed by the Von Frey test. Measurements were performed before and 30 min, 1 h, 2 h, 3 h and 5 h after compounds administration. Data are mean ± SD for n mice per group; * p < 0.05 vs. Day 0 by two-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s test; † p < 0.001 vs. Day 8 by two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s comparisons.
4. Conclusions
In conclusion, we confirmed the crucial role of H4Rs on CD4+ T cells in modulating the antinociceptive responses of A3AR agonists. This effect seems to be regulated by the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 enhancement. The selective stimulation of H4Rs together with low doses of A3AR agonists could have a clinical relevance for the treatment of neuropathic pain.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/biom11101447/s1, Figure S1: H4R expression in spinal cord of H4R−/− mice after CD4+ T cells transfer, Figure S2: Anti-allodynic effect of H4R agonist VUF 8430 on CCI-induced neuropathic pain in WT mice.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.M. and C.G.; methodology, L.M. and M.D.; software, L.L. and E.L.; validation, S.S.; formal analysis, M.D. and L.M.; investigation, L.D.C.M.; resources, E.M.; data curation, L.L.; writing—original draft preparation, L.M. and L.D.C.M.; writing—review and editing, E.M. and C.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Italian Ministry of Instruction, University and Research (MIUR), the University of Florence and Cassa di Risparmio Foundation Florence.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The ethical policy of the University of Florence complies with the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals of the US National Institutes of Health (NIH Publication No. 85-23, revised 1996; University of Florence assurance number: A5278-01). Formal approval to conduct the experiments described was obtained from the Italian Ministry of Health (No. 142/2017) and from the Animal Subjects Review Board of the University of Florence.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- van Hecke, O.; Austin, S.K.; Khan, R.A.; Smith, B.H.; Torrance, N. Neuropathic pain in the general population: A systematic review of epidemiological studies. Pain 2014, 155, 654–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilron, I.; Jensen, T.S.; Dickenson, A.H. Combination pharmacotherapy for management of chronic pain: From bench to bedside. Lancet Neurol. 2013, 12, 1084–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gierthmühlen, J.; Baron, R. Neuropathic Pain. Semin. Neurol. 2016, 36, 462–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Finnerup, N.B.; Attal, N.; Haroutounian, S.; McNicol, E.; Baron, R.; Dworkin, R.H.; Gilron, I.; Haanpää, M.; Hansson, P.; Jensen, T.S.; et al. Pharmacotherapy for neuropathic pain in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Z.; Janes, K.; Chen, C.; Doyle, T.; Bryant, L.; Tosh, D.K.; Jacobson, K.A.; Salvemini, D. Controlling murine and rat chronic pain through A3 adenosine receptor activation. FASEB J. 2012, 26, 1855–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Janes, K.; Little, J.W.; Li, C.; Bryant, L.; Chen, C.; Chen, Z.; Kamocki, K.; Doyle, T.; Snider, A.; Esposito, E.; et al. The Development and Maintenance of Paclitaxel-induced Neuropathic Pain Require Activation of the Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Receptor Subtype 1. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 21082–21097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Durante, M.; Squillace, S.; Lauro, F.; Giancotti, L.A.; Coppi, E.; Cherchi, F.; Di Cesare Mannelli, L.; Ghelardini, C.; Kolar, G.; Wahlman, C.; et al. Adenosine A3 agonists reverse neuropathic pain via T cell—Mediated production of IL-10. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e139299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ru, F.; Surdenikova, L.; Brozmanova, M.; Kollarik, M. Adenosine-induced activation of esophageal nociceptors. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 2011, 300, G485–G493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lopes, L.V.; Rebola, N.; Pinheiro, P.C.; Richardson, P.J.; Oliveira, C.R.; Cunha, R.A. Adenosine A3 receptors are located in neurons of the rat hippocampus. Neuroreport 2003, 14, 1645–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, J.T.; Hendrix, S.; Boato, F.; Smirnov, I.; Zheng, J.; Lukens, J.R.; Gadani, S.; Hechler, D.; Gölz, G.; Rosenberger, K.; et al. MHCII-independent CD4+ T cells protect injured CNS neurons via IL-4. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 699–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoskin, D.W.; Butler, J.J.; Drapeau, D.; Haeryfar, S.M.M.; Blay, J. Adenosine acts through an A3 receptor to prevent the induction of murine anti-CD3-activated killer T cells. Int. J. Cancer 2002, 99, 386–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanna, M.D.; Stark, H.; Lucarini, L.; Ghelardini, C.; Masini, E.; Galeotti, N. Histamine H4 receptor activation alleviates neuropathic pain through differential regulation of ERK, JNK, and P38 MAPK phosphorylation. Pain 2015, 156, 2492–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanna, M.D.; Lucarini, L.; Durante, M.; Ghelardini, C.; Masini, E.; Galeotti, N. Histamine H4 receptor agonist-induced relief from painful peripheral neuropathy is mediated by inhibition of spinal neuroinflammation and oxidative stress: Neuronal H4 receptors in neuropathic pain. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Connelly, W.; Shenton, F.; Lethbridge, N.; Leurs, R.; Waldvogel, H.; Faull, R.; Lees, G.; Chazot, P. The histamine H4 receptor is functionally expressed on neurons in the mammalian CNS: Histamine H4 receptor functionally expressed on neurons in the mammalian CNS. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 157, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kajihara, Y.; Murakami, M.; Imagawa, T.; Otsuguro, K.; Ito, S.; Ohta, T. Histamine potentiates acid-induced responses mediating transient receptor potential V1 in mouse primary sensory neurons. Neuroscience 2010, 166, 292–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanna, M.D.; Ghelardini, C.; Thurmond, R.L.; Masini, E.; Galeotti, N. Behavioural phenotype of histamine H4 receptor knockout mice: Focus on central neuronal functions. Neuropharmacology 2017, 114, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutzmer, R.; Mommert, S.; Gschwandtner, M.; Zwingmann, K.; Stark, H.; Werfel, T. The histamine H4 receptor is functionally expressed on TH2 cells. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 123, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunford, P.J.; O’Donnell, N.; Riley, J.P.; Williams, K.N.; Karlsson, L.; Thurmond, R.L. The Histamine H4 Receptor Mediates Allergic Airway Inflammation by Regulating the Activation of CD4+ TCells. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 7062–7070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morgan, R.K.; McAllister, B.; Cross, L.; Green, D.S.; Kornfeld, H.; Center, D.M.; Cruikshank, W.W. Histamine 4 Receptor Activation Induces Recruitment of FoxP3 T Cells and Inhibits Allergic Asthma in a Murine Model. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 8081–8089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McGrath, J.C.; Lilley, E. Implementing guidelines on reporting research using animals (ARRIVE etc.): New requirements for publication in BJP. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 3189–3193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bennett, G.J.; Xie, Y.-K. A peripheral mononeuropathy in rat that produces disorders of pain sensation like those seen in man. Pain 1988, 33, 87–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, M.; Egashira, N.; Kawashiri, T.; Yano, T.; Ikesue, H.; Oishi, R. Oxaliplatin-induced neuropathy in the rat: Involvement of oxalate in cold hyperalgesia but not mechanical allodynia. Pain 2009, 147, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannelli, L.D.C.; Micheli, L.; Maresca, M.; Cravotto, G.; Bellumori, M.; Innocenti, M.; Mulinacci, N.; Ghelardini, C. Anti-neuropathic effects of Rosmarinus officinalis L. terpenoid fraction: Relevance of nicotinic receptors. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ford, A.; Castonguay, A.; Cottet, M.; Little, J.W.; Chen, Z.; Symons-Liguori, A.M.; Doyle, T.; Egan, T.M.; Vanderah, T.W.; De Koninck, Y.; et al. Engagement of the GABA to KCC2 Signaling Pathway Contributes to the Analgesic Effects of A3AR Agonists in Neuropathic Pain. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 6057–6067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haskó, G.; Szabó, C.; Németh, Z.H.; Kvetan, V.; Pastores, S.M.; Vizi, E.S. Adenosine receptor agonists differentially regulate IL-10, TNF-alpha, and nitric oxide production in RAW 264.7 macrophages and in endotoxemic mice. J. Immunol. 1996, 157, 4634–4640. [Google Scholar]
- Asadullah, K.; Sterry, W.; Volk, H.D. Interleukin-10 Therapy—Review of a New Approach. Pharmacol. Rev. 2003, 55, 241–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankovic, D.; Kugler, D.G.; Sher, A. IL-10 production by CD4+ effector T cells: A mechanism for self-regulation. Mucosal Immunol. 2010, 3, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, L.R.; Hutchinson, M.R.; Ledeboer, A.; Wieseler-Frank, J.; Milligan, E.D.; Maier, S.F. Glia as the “bad guys”: Implications for improving clinical pain control and the clinical utility of opioids. Brain. Behav. Immun. 2007, 21, 131–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fiorentino, D.F.; Bond, M.W.; Mosmann, T.R. Two types of mouse T helper cell. IV. Th2 clones secrete a factor that inhibits cytokine production by Th1 clones. J. Exp. Med. 1989, 170, 2081–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, R.; Janjigian, M.; Myers, R.R. Anti-inflammatory interleukin-10 therapy in CCI neuropathy decreases thermal hyperalgesia, macrophage recruitment, and endoneurial TNF-α expression. Pain 1998, 74, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, I.N.; Milligan, E.D.; Wieseler-Frank, J.; Frank, M.G.; Zapata, V.; Campisi, J.; Langer, S.; Martin, D.; Green, P.; Fleshner, M.; et al. A role for proinflammatory cytokines and fractalkine in analgesia, tolerance, and subsequent pain facilitation induced by chronic intrathecal morphine. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 7353–7365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parimi, M.; Buelter, J.; Thanugundla, V.; Condoor, S.; Parkar, N.; Danon, S.; King, W. Feasibility and Validity of Printing 3D Heart Models from Rotational Angiography. Pediatr. Cardiol. 2018, 39, 653–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, S.C.; Sedler, J.; Jones, T.W.; Seckeler, M. Utility of three-dimensional models in resident education on simple and complex intracardiac congenital heart defects: 3D Printing in Pediatric Resident Education. Congenit. Heart Dis. 2018, 13, 1045–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andres-Hernando, A.; Okamura, K.; Bhargava, R.; Kiekhaefer, C.M.; Soranno, D.; Kirkbride-Romeo, L.A.; Gil, H.; Altmann, C.; Faubel, S. Circulating IL-6 upregulates IL-10 production in splenic CD4+ T cells and limits acute kidney injury–induced lung inflammation. Kidney Int. 2017, 91, 1057–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).