Hydrogen Bond Arrangement Is Shown to Differ in Coexisting Phases of Aqueous Two-Phase Systems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
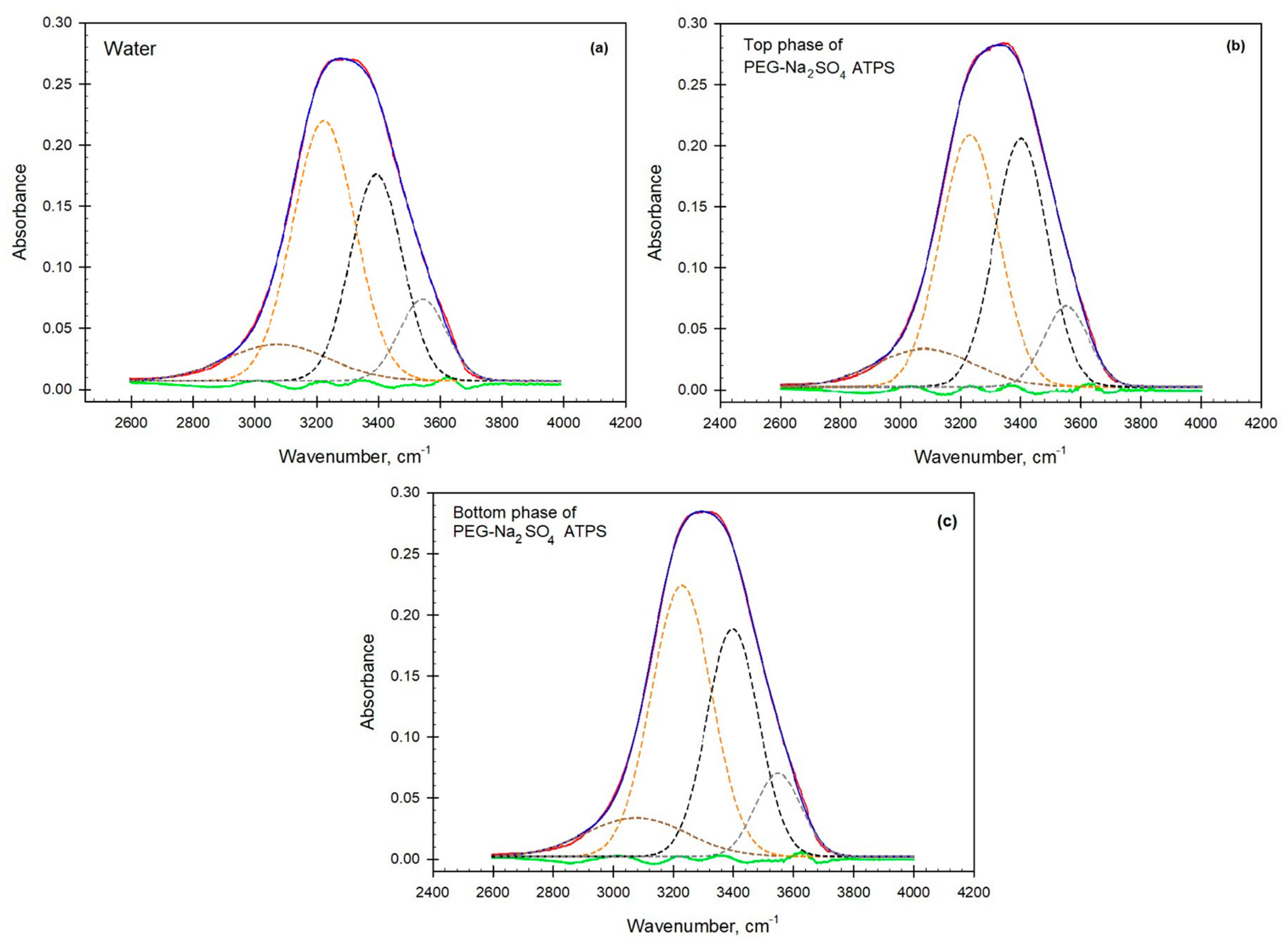
2.2.1. ATR-FTIR Measurements and Spectra Analysis
2.2.2. Analysis of Spectra
2.2.3. Preparation of Aqueous Two-Phase Systems
2.2.4. Partitioning Experiments
2.2.5. Analysis of Electrostatic and Hydrophobic Properties of the Phases
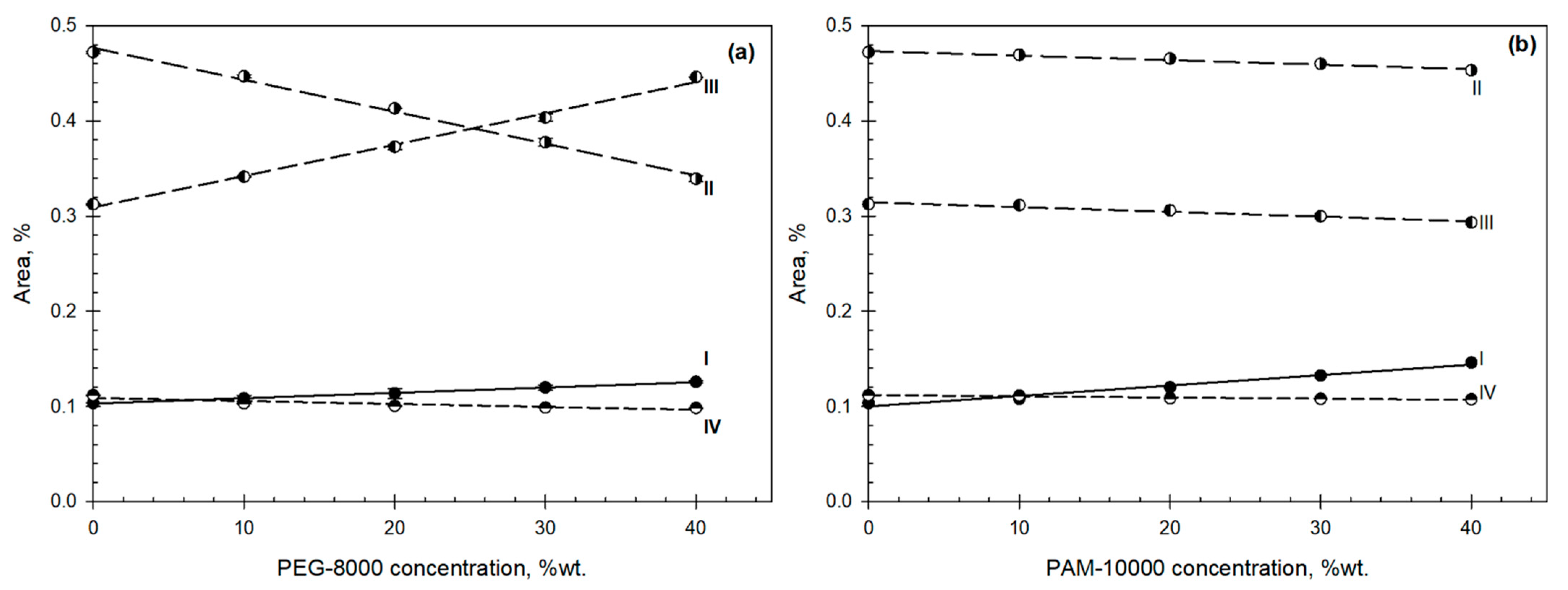
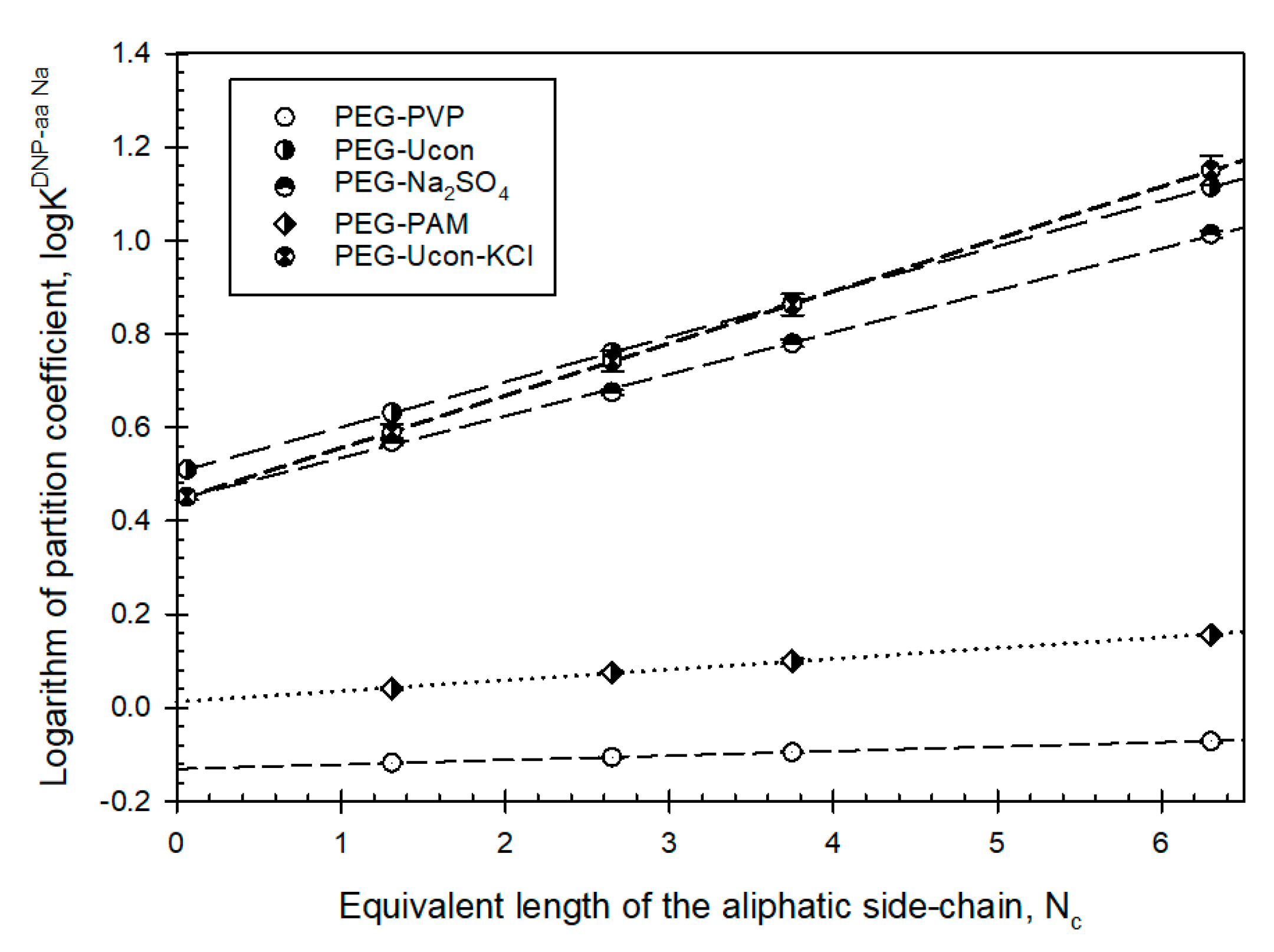
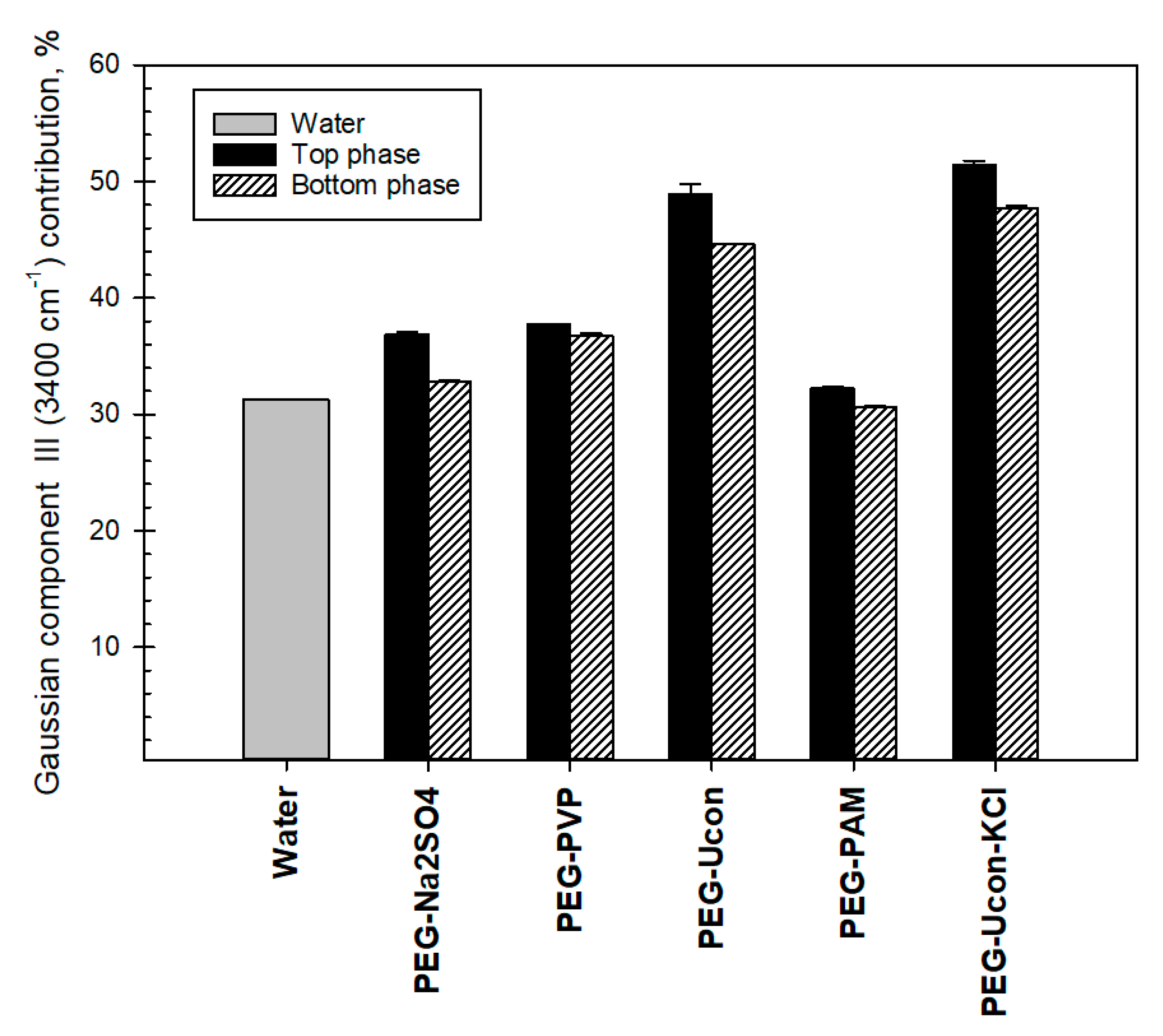
3. Results
4. Discussion
Ij3230 = k0j + k1jIj3400
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Titus, A.R.; Ferreira, L.A.; Belgovskiy, A.I.; Kooijman, E.E.; Mann, E.K.; Mann, J.A., Jr.; Meyer, W.V.; Smart, A.E.; Uversky, V.N.; Zaslavsky, B.Y. Interfacial tension and mechanism of liquid-liquid phase separation in aqueous media. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2020, 22, 4574–4580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakuta, H.; Fujimoto, T.; Yamana, Y.; Hoda, Y.; Tsumoto, K.; Yoshikawa, K. Aqueous/Aqueous Micro Phase Separation: Construction of an Artificial Model of Cellular Assembly. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aumiller, W.M., Jr.; Keating, C.D. Experimental models for dynamic compartmentalization of biomolecules in liquid organelles: Reversible formation and partitioning in aqueous biphasic systems. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 239, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nesterov, S.V.; Ilyinsky, N.S.; Uversky, V.N. Liquid-liquid phase separation as a common organizing principle of intracellular space and biomembranes providing dynamic adaptive responses. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2021, 1868, 119102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azaldegui, C.A.; Vecchiarelli, A.G.; Biteen, J.S. The emergence of phase separation as an organizing principle in bacteria. Biophys. J. 2021, 120, 1123–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalihal, A.P.; Schmidt, A.; Gao, G.; Little, S.R.; Pitchiaya, S.; Walter, N.G. Hyperosmotic phase separation: Condensates beyond inclusions, granules and organelles. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 296, 100044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hondele, M.; Heinrich, S.; De Los Rios, P.; Weis, K. Membraneless organelles: Phasing out of equilibrium. Emerg. Top. Life Sci. 2020, 4, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ji, X.; Li, P.; Liu, C.; Lou, J.; Wang, Z.; Wen, W.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhu, X. Liquid-liquid phase separation in biology: Mechanisms, physiological functions and human diseases. Sci. China Life Sci. 2020, 63, 953–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uversky, V.N.; Finkelstein, A.V. Life in Phases: Intra- and Inter- Molecular Phase Transitions in Protein Solutions. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bracha, D.; Walls, M.T.; Brangwynne, C.P. Probing and engineering liquid-phase organelles. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 1435–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, Z.; Chen, X.; Wu, X.; Zhang, M. Formation of biological condensates via phase separation: Characteristics, analytical methods, and physiological implications. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 14823–14835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Darling, A.L.; Zaslavsky, B.Y.; Uversky, V.N. Intrinsic Disorder-Based Emergence in Cellular Biology: Physiological and Pathological Liquid-Liquid Phase Transitions in Cells. Polymers 2019, 11, 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turoverov, K.K.; Kuznetsova, I.M.; Fonin, A.V.; Darling, A.L.; Zaslavsky, B.Y.; Uversky, V.N. Stochasticity of Biological Soft Matter: Emerging Concepts in Intrinsically Disordered Proteins and Biological Phase Separation. Trends BioChem. Sci. 2019, 44, 716–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentley, E.P.; Frey, B.B.; Deniz, A.A. Physical Chemistry of Cellular Liquid-Phase Separation. Chemistry 2019, 25, 5600–5610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawyer, I.A.; Sturgill, D.; Dundr, M. Membraneless nuclear organelles and the search for phases within phases. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2019, 10, e1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaslavsky, B.Y.; Ferreira, L.A.; Darling, A.L.; Uversky, V.N. The solvent side of proteinaceous membrane-less organelles in light of aqueous two-phase systems. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 117, 1224–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uversky, V.N. Intrinsically disordered proteins in overcrowded milieu: Membrane-less organelles, phase separation, and intrinsic disorder. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2017, 44, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uversky, V.N. Protein intrinsic disorder-based liquid-liquid phase transitions in biological systems: Complex coacervates and membrane-less organelles. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 239, 97–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, N. Dynamic Synthetic Cells Based on Liquid-Liquid Phase Separation. ChembioChem 2019, 20, 2553–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, H.O.; Persson, J.; Tjerneld, F. Thermoseparating water/polymer system: A novel one-polymer aqueous two-phase system for protein purification. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1999, 66, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Conley, A.J.; Brandle, J.E.; Truant, R.; Filipe, C.D. In vivo formation of protein based aqueous microcompartments. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 9094–9099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urry, D.W. Physical chemistry of biological free energy transduction as demonstrated by elastic protein-based polymers. J. Phys. Chem. B 1997, 101, 11007–110028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, L.A.; Cole, J.T.; Reichardt, C.; Holland, N.B.; Uversky, V.N.; Zaslavsky, B.Y. Solvent Properties of Water in Aqueous Solutions of Elastin-Like Polypeptide. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 13528–13547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, N.K.; Garcia Quiroz, F.; Hall, C.K.; Chilkoti, A.; Yingling, Y.G. Molecular description of the LCST behavior of an elastin-like polypeptide. Biomacromolecules 2014, 15, 3522–3530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Rumyantsev, A.M.; Srivastava, S.; Meng, S.; de Pablo, J.J.; Tirrell, M.V. Effect of solvent quality on the phase behavior of polyelectrolyte complexes. Macromolecules 2021, 54, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaslavsky, B.Y. Aqueous Two-Phase Partitioning: Physical Chemistry and Bioanalytical Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Zaslavsky, B.; Bagirov, T.; Borovskaya, A.; Gulaeva, N.; Miheeva, L.; Mahmudov, A.; Rodnikova, M. Structure of water as a key factor of phase separation in aqueous mixtures of two non-ionic polymers. Polymer 1989, 30, 2104–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edun, D.N.; Flanagan, M.R.; Serrano, A.L. Does liquid-liquid phase separation drive peptide folding? Chem. Sci. 2020, 12, 2474–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyman, A.A.; Weber, C.A.; Julicher, F. Liquid-liquid phase separation in biology. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 30, 39–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferreira, L.A.; Madeira, P.P.; Breydo, L.; Reichardt, C.; Uversky, V.N.; Zaslavsky, B.Y. Role of solvent properties of aqueous media in macromolecular crowding effects. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2016, 34, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, L.A.; Uversky, V.N.; Zaslavsky, B.Y. Role of solvent properties of water in crowding effects induced by macromolecular agents and osmolytes. Mol. Biosyst. 2017, 13, 2551–2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeira, P.P.; Reis, C.A.; Rodrigues, A.E.; Mikheeva, L.M.; Zaslavsky, B.Y. Solvent properties governing solute partitioning in polymer/polymer aqueous two-phase systems: Nonionic compounds. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madeira, P.P.; Bessa, A.; Alvares-Ribeiro, L.; Aires-Barros, M.R.; Reis, C.A.; Rodrigues, A.E.; Zaslavsky, B.Y. Salt effects on solvent features of coexisting phases in aqueous polymer/polymer two-phase systems. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1229, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, N.R.; Ferreira, L.A.; Belgovskiy, A.I.; Madeira, P.P.; Teixeira, J.A.; Mann, E.K.; Mann, J.A., Jr.; Meyer, W.V.; Smart, A.E.; Chernyak, V.Y.; et al. Effects of different solutes on the physical chemical properties of aqueous solutions via rearrangement of hydrogen bonds in water. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 335, 116288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, L.A.; Parpot, P.; Teixeira, J.A.; Mikheeva, L.M.; Zaslavsky, B.Y. Effect of NaCl additive on properties of aqueous PEG-sodium sulfate two-phase system. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1220, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kitadai, N.; Sawai, T.; Tonoue, R.; Nakashima, S.; Katsura, M.; Fukushi, K. Effects of Ions on the OH Stretching Band of Water as Revealed by ATR-IR Spectroscopy. J. Solut. Chem. 2014, 43, 1055–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brini, E.; Fennell, C.J.; Fernandez-Serra, M.; Hribar-Lee, B.; Luksic, M.; Dill, K.A. How Water’s Properties Are Encoded in Its Molecular Structure and Energies. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 12385–12414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



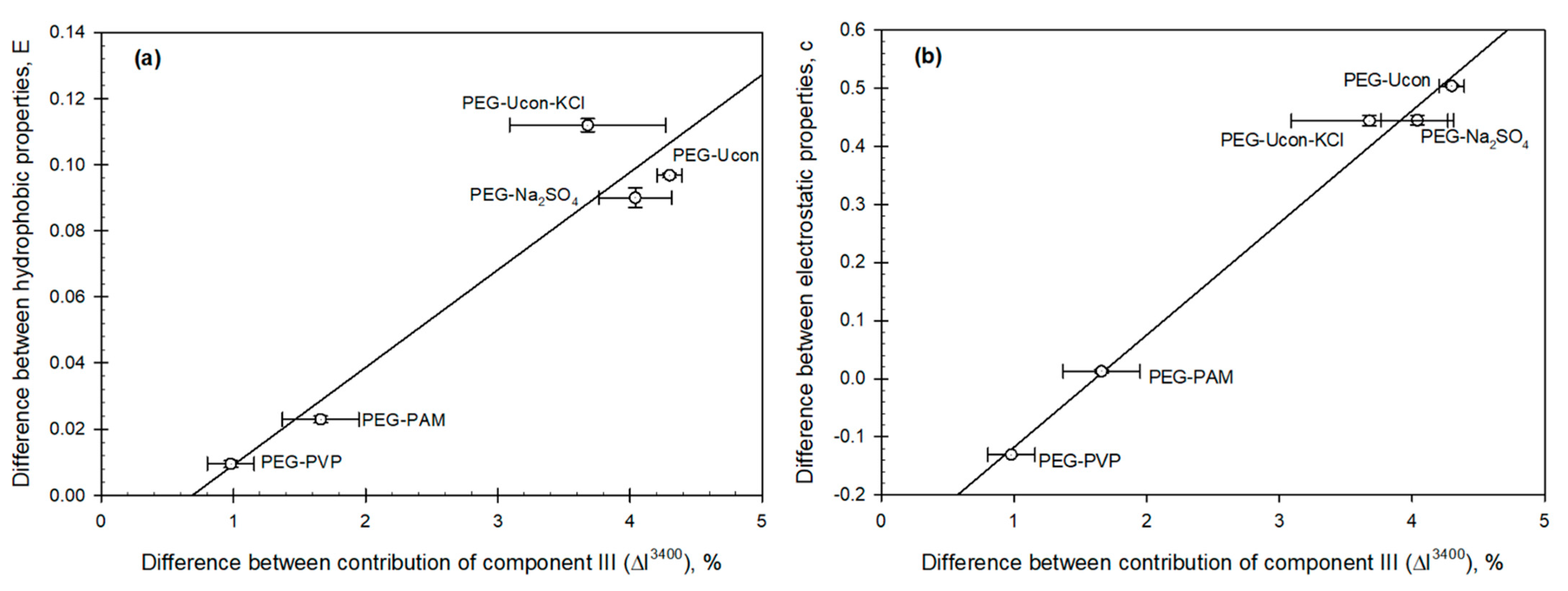
| ATPS | E | c | ΔI3400 cm−1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| PEG-Ucon a | 0.0968 ± 0.0006 | 0.504 ± 0.002 | 0.0430 ± 0.0094 |
| PEG-Ucon-KCl a | 0.112 ± 0.002 | 0.444 ± 0.009 | 0.0368 ± 0.0059 |
| PEG-PVP | 0.0095 ± 0.001 | −0.131 ± 0.001 | 0.0098 ± 0.0018 |
| PEG-PAM | 0.023 ± 0.001 | 0.013 ± 0.003 | 0.0166 ± 0.0029 |
| PEG-Na2SO4 b | 0.090 ± 0.003 | 0.445 ± 0.008 | 0.0404 ± 0.0028 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Madeira, P.P.; Titus, A.R.; Ferreira, L.A.; Belgovskiy, A.I.; Mann, E.K.; Mann, J.A., Jr.; Meyer, W.V.; Smart, A.E.; Uversky, V.N.; Zaslavsky, B.Y. Hydrogen Bond Arrangement Is Shown to Differ in Coexisting Phases of Aqueous Two-Phase Systems. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1787. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11121787
Madeira PP, Titus AR, Ferreira LA, Belgovskiy AI, Mann EK, Mann JA Jr., Meyer WV, Smart AE, Uversky VN, Zaslavsky BY. Hydrogen Bond Arrangement Is Shown to Differ in Coexisting Phases of Aqueous Two-Phase Systems. Biomolecules. 2021; 11(12):1787. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11121787
Chicago/Turabian StyleMadeira, Pedro P., Amber R. Titus, Luisa A. Ferreira, Alexander I. Belgovskiy, Elizabeth K. Mann, Jay Adin Mann, Jr., William V. Meyer, Anthony E. Smart, Vladimir N. Uversky, and Boris Y. Zaslavsky. 2021. "Hydrogen Bond Arrangement Is Shown to Differ in Coexisting Phases of Aqueous Two-Phase Systems" Biomolecules 11, no. 12: 1787. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11121787
APA StyleMadeira, P. P., Titus, A. R., Ferreira, L. A., Belgovskiy, A. I., Mann, E. K., Mann, J. A., Jr., Meyer, W. V., Smart, A. E., Uversky, V. N., & Zaslavsky, B. Y. (2021). Hydrogen Bond Arrangement Is Shown to Differ in Coexisting Phases of Aqueous Two-Phase Systems. Biomolecules, 11(12), 1787. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11121787







