Current Views on the Roles of O-Glycosylation in Controlling Notch-Ligand Interactions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Glycosylation on Notch/Recognition of EGF Repeats by Glycosyltransferases
2.1. Structural Classification of O-Glycans Is Critical to Elucidate Notch Receptor Functions
2.2. Advances in the Understanding of the Recognition and Modification of Notch EGF Repeats by Enzymes
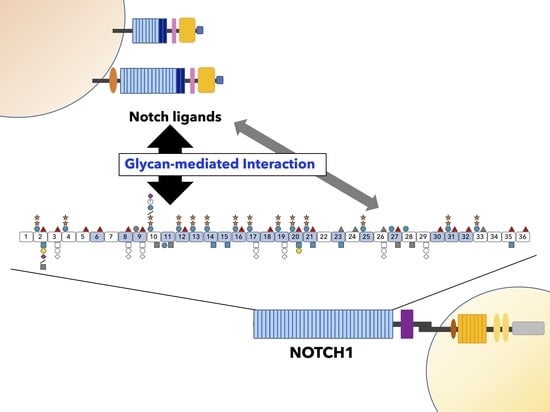
3. Notch-Ligand Interactions
3.1. Identification of Ligand-Binding Domain (LBD) in the Notch ECD
3.2. Amino Acids and Sugars Directly Involved in Notch-Ligand Binding
3.3. Roles of O-Glycans Located on LBD in Ligand Interactions in Drosophila Notch and Mammalian NOTCH1
3.3.1. O-Fucose Glycans on Drosophila Notch LBD
3.3.2. Critical Roles of O-Fucosylation in the LBD of Mammalian Notch
3.3.3. O-Glucose Glycans in the LBD of Notch
3.3.4. O-GlcNAc Glycans in the LBD of Notch
3.4. Calcium-Binding of EGF Repeats
3.5. Structure and Function of O-Glycosylation Outside of the LBD
3.5.1. Importance of EGF Repeats Outside of the LBD in Ligand Interaction
3.5.2. Roles of O-glycosylation Observed on EGF1-7
3.5.3. Roles of O-glycosylation Observed on EGF13-36
3.6. Role of O-Glycans in Cis- and Trans-Interactions
3.7. O-Glycosylation on Notch Ligands
4. Perspective
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dexter, J.S. The analysis of a case of continuous variation in Drosophila by a study of its linkage relations. Am. Nat. 1914, 48, 712–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, T.H. The Theory of the Gene. Am. Nat. 1917, 51, 513–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kid, S.; Locke, T.J.; Young’, M.W. The Notch Locus of Drosophila melanogaster. Cell 1983, 34, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artavanis-Tsakonas, S.; Muskavitch, M.A.; Yedvobnick, B. Molecular cloning of Notch, a locus affecting neurogenesis in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1983, 80, 1977–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siebel, C.; Lendahl, U. Notch signaling in development, tissue homeostasis, and disease. Physiol. Rev. 2017, 97, 1235–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aster, J.C.; Pear, W.S.; Blacklow, S.C. The Varied Roles of Notch in Cancer. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2017, 12, 245–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- D’Souza, B.; Meloty-Kapella, L.; Weinmaster, G. Canonical and non-canonical Notch ligands. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2010, 92, 73–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chillakuri, C.R.; Sheppard, D.; Lea, S.M.; Handford, P.A. Notch receptor-ligand binding and activation: Insights from molecular studies. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2012, 23, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gordon, W.R.; Zimmerman, B.; He, L.; Perrimon, N.; Loparo, J.J.; Blacklow, S.C.; Gordon, W.R.; Zimmerman, B.; He, L.; Miles, L.J.; et al. Mechanical Allostery: Evidence for a Force Requirement in the Proteolytic Activation of Notch Short Article Mechanical Allostery: Evidence for a Force Requirement in the Proteolytic Activation of Notch. Dev. Cell 2015, 33, 729–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Tetering, G.; van Diest, P.; Verlaan, I.; van der Wall, E.; Kopan, R.; Vooijs, M. Metalloprotease ADAM10 is required for Notch1 site 2 cleavage. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 31018–31027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kopan, R.; Ilagan, M.X.G. The Canonical Notch Signaling Pathway: Unfolding the Activation Mechanism. Cell 2009, 137, 216–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kovall, R.A.; Gebelein, B.; Sprinzak, D.; Kopan, R. Review The Canonical Notch Signaling Pathway: Structural and Biochemical Insights into Shape, Sugar, and Force. Dev. Cell 2017, 41, 228–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fehon, R.G.; Kooh, P.J.; Rebay, I.; Regan, C.L.; Xu, T.; Muskavitch, M.A.T.; Artavanis-Tsakonas, S. Molecular Interactions between the Protein Products of the Neurogenic Loci Notch and Delta, Two EGF Homologous Genes in Drosophila. Cell 1990, 61, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panin, V.M.; Papayannopoulos, V.; Wilson, R.; Irvine, K.D. Fringe modulates Notch-ligand interactions. Nature 1997, 387, 908–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irvine, K.D.; Wieschaus, E. fringe, a Boundary-Specific Signaling Molecule, Mediates Interactions between Dorsal and Ventral Cells during brosophila Wing Development. Cell 1994, 79, 595–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, R.J.; Gu, Y.; Hukriede, N.A. Serrate-mediated activation of Notch is specifically blocked by the product ofthe gene fringe in the dorsal compartment of the Drosophila wing imaginaldisc. Development 1997, 124, 2973–2981. [Google Scholar]
- Moloney, D.J.; Panin, V.M.; Johnston, S.H.; Chen, J.; Shao, L.; Wilson, R.; Wang, Y.; Stanley, P.; Irvine, K.D.; Haltiwanger, R.S.; et al. Fringe is a glycosyltransferase that modifies Notch. Nature 2000, 406, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brückner, K.; Perez, L.; Clausen, H.; Cohen, S. Glycosyltransferase activity of Fringe modulates Notch-Delta interactions. Nature 2000, 406, 411–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moloney, D.J.; Shair, L.H.; Lu, F.M.; Xia, J.; Locke, R.; Matta, K.L.; Haltiwanger, R.S. Mammalian Notch1 Is Modified with Two Unusual Forms of O-Linked Glycosylation Found on Epidermal Growth Factor-like Modules. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 9604–9611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Okajima, T.; Xu, A.; Irvine, K.D. Modulation of Notch-Ligand Binding by Protein O-Fucosyltransferase 1 and Fringe. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 42340–42345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, A.; Haines, N.; Dlugosz, M.; Rana, N.A.; Takeuchi, H.; Haltiwanger, R.S.; Irvine, K.D. In vitro reconstitution of the modulation of Drosophila Notch-ligand binding by fringe. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 35153–35162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Acar, M.; Jafar-Nejad, H.; Takeuchi, H.; Rajan, A.; Ibrani, D.; Rana, N.A.; Pan, H.; Haltiwanger, R.S.; Bellen, H.J. Rumi Is a CAP10 Domain Glycosyltransferase that Modifies Notch and Is Required for Notch Signaling. Cell 2008, 132, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lebon, L.; Lee, T.V.; Sprinzak, D.; Jafar-nejad, H.; Elowitz, M.B. Fringe proteins modulate Notch-ligand cis and trans interactions to specify signaling states. Elife 2014, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawaguchi, S.; Varshney, S.; Ogawa, M.; Sakaidani, Y.; Yagi, H.; Takeshita, K.; Murohara, T.; Kato, K.; Sundaram, S.; Stanley, P.; et al. O-GlcNAc on NOTCH1 EGF repeats regulates ligand-induced Notch signaling and vascular development in mammals. Elife 2017, 6, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, H.; Schneider, M.; Williamson, D.B.; Ito, A.; Takeuchi, M.; Handford, P.A.; Haltiwanger, R.S. Two novel protein O -glucosyltransferases that modify sites distinct from POGLUT1 and affect Notch trafficking and signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E8395–E8402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luca, V.C.; Jude, K.M.; Pierce, N.W.; Nachury, M.V.; Fischer, S.; Garcia, K.C. Structural basis for Notch1 engagement of Delta-like4. Science 2015, 347, 847–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luca, V.C.; Kim, B.C.; Ge, C.; Kakuda, S.; Wu, D.; Roein-peikar, M.; Haltiwanger, R.S.; Zhu, C.; Ha, T.; Garcia, C.; et al. Notch-Jagged complex structure implicates a catch bond in tuning ligand sensitivity. Science 2017, 355, 1320–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kakuda, S.; Haltiwanger, R.S. Deciphering the Fringe-Mediated Notch Code: Identification of Activating and Inhibiting Sites Allowing Discrimination between Ligands. Dev. Cell 2017, 40, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Moloney, D.J.; Stanley, P. Fringe modulation of Jagged1-induced Notch signaling requires the action of β4galactosyltransferase-1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 13716–13721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wharton, K.A.; Johansen, K.M.; Xu, T.; Artavanis-Tsakonas, S. Nucleotide Sequence from the Neumgenic Locus Notch Implies a Gene Product That Shares Homology with Proteins Containing EGF-like Repeats. Cell 1985, 43, 567–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebay, L.; Fleming, R.J.; Fehon, R.G.; Cherbas, L.; Cherbas, P.; Artavanis-Tsakonas’, S. Specific EGF Repeats of Notch Mediate Interactions with Delta and Serrate: Implications for Notch as a Multifunctional Receptor. Cell 1991, 67, 687–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, H.; Fernandez-Valdivia, R.C.; Caswell, D.S.; Nita-Lazar, A.; Rana, N.A.; Garner, T.P.; Weldeghiorghis, T.K.; Macnaughtan, M.A.; Jafar-Nejad, H.; Haltiwanger, R.S. Rumi functions as both a protein O-glucosyltransferase and a protein O-xylosyltransferase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 16600–16605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luo, Y.; Haltiwanger, R.S. O-fucosylation of notch occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 11289–11294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okajima, T.; Xu, A.; Lei, L.; Irvine, K.D. Chaperone Activity of Protein O-Fucosyltransferase 1 Promotes Notch Receptor Folding. Science 2005, 307, 1599–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Takeuchi, H.; Kantharia, J.; Sethi, M.K.; Bakker, H.; Haltiwanger, R.S. Site-specific O-glucosylation of the epidermal growth factor-like (EGF) repeats of notch: Efficiency of glycosylation is affected by proper folding and amino acid sequence of individual EGF repeats. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 33934–33944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ogawa, M.; Sawaguchi, S.; Kawai, T.; Nadano, D.; Matsuda, T.; Yagi, H.; Kato, K.; Furukawa, K.; Okajima, T. Impaired O-linked N-acetylglucosaminylation in the endoplasmic reticulum by mutated epidermal growth factor (EGF) domain-specific O-linked N-acetylglucosamine transferase found in adams-oliver syndrome. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 2137–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vasudevan, D.; Haltiwanger, R.S. Novel roles for O-linked glycans in protein folding. Glycoconj J. 2014, 31, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Urata, Y.; Saiki, W.; Tsukamoto, Y.; Sago, H.; Hibi, H.; Okajima, T.; Takeuchi, H. Xylosyl Extension of O-Glucose Glycans on the Extracellular Domain of NOTCH1 and NOTCH2 Regulates Notch Cell Surface Trafficking. Cells 2020, 9, 1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, M.; Senoo, Y.; Ikeda, K.; Takeuchi, H.; Okajima, T. Structural Divergence in O-GlcNAc Glycans Displayed on Epidermal Growth Factor-like Repeats of Mammalian Notch1. Molecules 2018, 23, 1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Servián-morilla, E.; Takeuchi, H.; Lee, T.V.; Clarimon, J.; Mavillard, F.; Area-gómez, E.; Rivas, E.; Nieto-gonzález, J.L.; Rivero, M.C.; Cabrera-, M.; et al. A POGLUT 1 mutation causes a muscular dystrophy with reduced Notch signaling and satellite cell loss. EMBO Mol. Med. 2016, 8, 1289–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Servián-Morilla, E.; Cabrera-Serrano, M.; Johnson, K.; Pandey, A.; Ito, A.; Rivas, E.; Chamova, T.; Muelas, N.; Mongini, T.; Nafissi, S.; et al. POGLUT1 biallelic mutations cause myopathy with reduced satellite cells, α-dystroglycan hypoglycosylation and a distinctive radiological pattern. Acta Neuropathol. 2020, 139, 565–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, H.; Haltiwanger, R.S. Significance of glycosylation in Notch signaling. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 453, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Varshney, S.; Stanley, P. Multiple Roles for O-Glycans in Notch Signalling. FEBS Lett. 2018, 592, 3819–3834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Urata, Y.; Takeuchi, H. Effects of Notch glycosylation on health and diseases. Dev. Growth Differ. 2020, 62, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pandey, A.; Niknejad, N.; Jafar-Nejad, H. Multifaceted regulation of Notch signaling by glycosylation. Glycobiology 2020, 31, 8–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombard, V.; Golaconda Ramulu, H.; Drula, E.; Coutinho, P.M.; Henrissat, B. The carbohydrate-active enzymes database (CAZy) in 2013. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vrielink, A.; Rüger, W.; Driessen, H.P.C.; Freemont, P.S. Crystal structure of the DNA modifying enzyme β-glucosyltransferase in the presence and absence of the substrate uridine diphosphoglucose. EMBO J. 1994, 13, 3413–3422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moremen, K.W.; Haltiwanger, R.S. Emerging structural insights into glycosyltransferase-mediated synthesis of glycans. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2019, 15, 853–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lairson, L.L.; Henrissat, B.; Davies, G.J.; Withers, S.G. Glycosyl transferases: Structures, functions, and mechanisms. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2008, 77, 521–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, H.; Takeuchi, M.; LeBarron, J.; Kantharia, J.; London, E.; Bakker, H.; Haltiwanger, R.S.; Li, H.; Takeuchi, H. Notch-modifying xylosyltransferase structures support an SNi-like retaining mechanism. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2015, 11, 847–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Fischer, M.; Satkunarajah, M.; Zhou, D.; Withers, S.G.; Rini, J.M. Structural basis of Notch O-glucosylation and O-xylosylation by mammalian protein-O-glucosyltransferase 1 (POGLUT1). Nat. Commun. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Han, K.; Pak, J.E.; Satkunarajah, M.; Zhou, D.; Rini, J.M. Recognition of EGF-like domains by the Notch-modifying O-fucosyltransferase POFUT1. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2017, 13, 757–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Takeuchi, H. Protein O-glucosylation: Another essential role of glucose in biology. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2019, 56, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Takeuchi, H.; Takeuchi, M.; Liu, Q.; Kantharia, J.; Haltiwanger, R.S.; Li, H. Structural analysis of Notch-regulating Rumi reveals basis for pathogenic mutations. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2016, 12, 735–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamamoto, S.; Charng, W.L.; Rana, N.A.; Kakuda, S.; Jaiswal, M.; Bayat, V.; Xiong, B.; Zhang, K.; Sandoval, H.; David, G.; et al. A mutation in EGF repeat-8 of notch discriminates between serrate/jagged and delta family ligands. Science 2012, 338, 1229–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Andrawes, M.B.; Xu, X.; Liu, H.; Ficarro, S.B.; Marto, J.A.; Aster, J.C.; Blacklow, S.C. Intrinsic Selectivity of Notch 1 for Delta-like 4 Over Delta-like 1. J. Biol. Chem. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pandey, A.; Harvey, B.M.; Lopez, M.F.; Ito, A.; Haltiwanger, R.S.; Jafar-Nejad, H. Glycosylation of Specific Notch EGF Repeats by O-Fut1 and Fringe Regulates Notch Signaling in Drosophila. Cell Rep. 2019, 29, 2054–2066.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ge, C.; Liu, T.; Hou, X.; Stanley, P. In vivo consequences of deleting EGF repeats 8–12 including the ligand binding domain of mouse Notch1. BMC Dev. Biol. 2008, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cordle, J.; Redfield, C.; Stacey, M.; Van Der Merwe, P.A.; Willis, A.C.; Champion, B.R.; Hambleton, S.; Handford, P.A. Localization of the delta-like-1-binding site in human Notch-1 and its modulation by calcium affinity. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 11785–11793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Whiteman, P.; De Madrid, B.H.; Taylor, P.; Li, D.; Heslop, R.; Viticheep, N.; Tan, J.Z.; Shimizu, H.; Callaghan, J.; Masiero, M.; et al. Molecular basis for jagged-1/serrate ligand recognition by the notch receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 7305–7312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cordle, J.; Johnson, S.; Zi Yan Tay, J.; Roversi, P.; Wilkin, M.B.; De Madrid, B.H.; Shimizu, H.; Jensen, S.; Whiteman, P.; Jin, B.; et al. A conserved face of the Jagged/Serrate DSL domain is involved in Notch trans-activation and cis-inhibition. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2008, 15, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weisshuhn, P.C.; Sheppard, D.; Taylor, P.; Whiteman, P.; Lea, S.M.; Handford, P.A.; Weisshuhn, P.C.; Sheppard, D.; Taylor, P.; Whiteman, P.; et al. Non-Linear and Flexible Regions of the Human Notch1 Extracellular Domain Revealed by High- Article Non-Linear and Flexible Regions of the Human Notch1 Extracellular Domain Revealed by High-Resolution Structural Studies. Struct. Des. 2016, 24, 555–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harvey, B.M.; Rana, N.A.; Moss, H.; Leonardi, J.; Jafar-Nejad, H.; Haltiwanger, R.S. Mapping sites of O-glycosylation and fringe elongation on Drosophila Notch. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 16348–16360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Okajima, T.; Irvine, K.D. Regulation of Notch Signaling by O-Linked Fucose. Cell 2002, 111, 893–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sasamura, T.; Sasaki, N.; Miyashita, F.; Nakao, S.; Ishikawa, H.O.; Ito, M.; Kitagawa, M.; Harigaya, K.; Spana, E.; Bilder, D.; et al. Neurotic, a novel maternal neurogenic gene, encodes an O-fucosyltransferase that is essential for Notch-Delta interactions. Development 2003, 130, 4785–4795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lei, L.; Xu, A.; Panin, V.M.; Irvine, K.D. An O-fucose site in the ligand binding domain inhibits Notch activation. Development 2003, 130, 6411–6421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, A.; Lei, L.; Irvine, K.D. Regions of Drosophila notch that contribute to ligand binding and the modulatory influence of Fringe. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 30158–30165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, S.; Stanley, P. Protein O-fucosyltransferase 1 is an essential component of Notch signaling pathways. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 5234–5239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ge, C.; Stanley, P. The O-fucose glycan in the ligand-binding domain of Notch1 regulates embryogenesis and T cell development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 1539–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Varshney, S.; Wei, H.X.; Batista, F.; Nauman, M.; Sundaram, S.; Siminovitch, K.; Tanwar, A.; Stanley, P. A modifier in the 129S2/SvPasCrl genome is responsible for the viability of Notch1[12f/12f] mice. BMC Dev. Biol. 2019, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taylor, P.; Takeuchi, H.; Sheppard, D.; Chillakuri, C.; Lea, S.M.; Haltiwanger, R.S.; Handford, P.A. Fringe-mediated extension of O -linked fucose in the ligand-binding region of Notch1 increases binding to mammalian Notch ligands. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 7290–7295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tveriakhina, L.; Schuster-Gossler, K.; Jarrett, S.M.; Andrawes, M.B.; Rohrbach, M.; Blacklow, S.C.; Gossler, A. The ectodomains determine ligand function in vivo and selectivity of DLL1 and DLL4 toward NOTCH1 and NOTCH2 in vitro. Elife 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, K.I.; Suganami, A.; Tamura, Y.; Yagita, H.; Habu, S.; Kitagawa, M.; Sato, T.; Hozumi, K. Delta-like 1 and delta-like 4 differently require their extracellular domains for triggering notch signaling in mice. Elife 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, L.; Moloney, D.J.; Haltiwanger, R. Fringe modifies O-fucose on mouse Notch1 at epidermal growth factor-like repeats within the ligand-binding site and the Abruptex region. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 7775–7782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hou, X.; Tashima, Y.; Stanley, P. Galactose differentially modulates lunatic and manic fringe effects on Delta1-induced NOTCH signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 474–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schneider, M.; Kumar, V.; Nordstrøm, L.U.; Feng, L.; Takeuchi, H.; Hao, H.; Luca, V.C.; Garcia, K.C.; Stanley, P.; Wu, P.; et al. Inhibition of Delta-induced Notch signaling using fucose analogs. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2018, 14, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, S.; Yokoi, Y.; Hinou, H.; Nishimura, S.I. Chemical Synthesis Demonstrates That Dynamic O-Glycosylation Regulates the Folding and Functional Conformation of a Pivotal EGF12 Domain of the Human NOTCH1 Receptor. Biochemistry 2017, 56, 4379–4391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonardi, J.; Fernandez-Valdivia, R.; Li, Y.D.; Simcox, A.A.; Jafar-Nejad, H. Multiple O-glucosylation sites on Notch function as a buffer against temperature-dependent loss of signaling. Development 2011, 138, 3569–3578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernandez-Valdivia, R.; Takeuchi, H.; Samarghandi, A.; Lopez, M.; Leonardi, J.; Haltiwanger, R.S.; Jafar-Nejad, H. Regulation of mammalian Notch signaling and embryonic development by the protein O-glucosyltransferase Rumi. Development 2011, 138, 1925–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ogawa, M.; Okajima, T. Structure and function of extracellular O-GlcNAc. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2019, 56, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, S.-I.; Yokoi, Y. Effect of Site-specific O-Glycosylation on the Structural Behavior of NOTCH1 Receptor Extracellular EGF-like Domains 11 and 10. Chem. Eur. J. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, H.; Yu, H.; Hao, H.; Takeuchi, M.; Ito, A.; Li, H.; Haltiwanger, R.S. O-Glycosylation modulates the stability of epidermal growth factor-like repeats and thereby regulates Notch trafficking. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 15964–15973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ogawa, M.; Tashima, Y.; Sakaguchi, Y.; Takeuchi, H.; Okajima, T. Contribution of extracellular O-GlcNAc to the stability of folded epidermal growth factor-like domains and Notch1 trafficking. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 526, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hambleton, S.; Valeyev, N.V.; Muranyi, A.; Knott, V.; Werner, J.M.; McMichael, A.J.; Handford, P.A.; Downing, A.K. Structural and functional properties of the human Notch-1 ligand binding region. Structure 2004, 12, 2173–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Handford, P.A.; Baron, M.; Mayhew, M.; Willis, A.; Beesley, T.; Brownlee, G.G.; Campbell, I.D. The first EGF-like domain from human factor IX contains a high-affinity calcium binding site. EMBO J. 1990, 9, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunnerhagens, M.S.; Persaonq, E.; Dahlqvistq, I.; Drakenbergs, T.; Stenfloq, J.; Mayhewllii, M.; Robin, M.; Handfordllssoq, P.; Tilleyll Llll, J.W.; Campbell, I.D.; et al. The Effect of Aspartate Hydroxylation on Calcium Binding to Epidermal Growth Factor-like Modules in Coagulation Factors IX and X*. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 23339–23344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeffer, I.; Brewitz, L.; Krojer, T.; Jensen, S.A.; Kochan, G.T.; Kershaw, N.J.; Hewitson, K.S.; McNeill, L.A.; Kramer, H.; Münzel, M.; et al. Aspartate/asparagine-β-hydroxylase crystal structures reveal an unexpected epidermal growth factor-like domain substrate disulfide pattern. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Celis, J.F.; Barrio, R.; Del Arco, A.; Garcfa-Bellidot, A. Genetic and molecular characterization of a Notch mutation in its Delta-and Serrate-binding domain in Drosophila. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 4037–4041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Handford, P.A.; Mayhew, M.; Baront, M.; Winship, P.; CampbeiiU, I.D.; Brownlee, G.G. Key residues involved in calcium-binding motifs in EGF -like domains. Nature 1991, 345, 164–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.J.; Sanborn, Z.; Arnett, K.L.; Bayston, L.J.; Liao, W.; Proby, C.M.; Leigh, I.M.; Collisson, E.A.; Gordon, P.B.; Jakkula, L.; et al. Loss-of-function mutations in Notch receptors in cutaneous and lung squamous cell carcinoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 17761–17766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lawrence, N.; Klein, T.; Brennan, K.; Martinez Arias, A. Structural requirements for Notch signalling with Delta and Serrate during thedevelopment and patterning of the wing disc of Drosophila. Development 2000, 127, 3185–3195. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kangsamaksin, T.; Murtomaki, A.; Kofler, N.M.; Cuervo, H.; Chaudhri, R.A.; Tattersall, I.W.; Rosenstiel, P.E.; Shawber, C.J.; Kitajewski, J. NOTCH decoys that selectively block DLL/NOTCH or JAG/NOTCH disrupt angiogenesis by unique mechanisms to inhibit tumor growth. Cancer Discov. 2015, 5, 182–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Celis’, J.F.; Garcia-Bellido, A. Modifications of the Notch Function by Abruptex Mutations in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 1994, 136, 183–194. [Google Scholar]
- Kidd, S.; Baylies, M.K.; Gasic, G.P.; Young, M.W. Structure and distribution of the Notch protein in developing Drosophila. Genes Dev. 1989, 3, 1113–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pei, Z.; Baker, N.E. Competition between Delta and the Abruptex domain of Notch. BMC Dev. Biol. 2008, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vooijs, M.; Schroeter, E.H.; Pan, Y.; Blandford, M.; Kopan, R. Ectodomain shedding and intramembrane cleavage of mammalian Notch proteins is not regulated through oligomerization. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 50864–50873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nandagopal, N.; Santat, L.A.; LeBon, L.; Sprinzak, D.; Bronner, M.E.; Elowitz, M.B. Dynamic Ligand Discrimination in the Notch Signaling Pathway. Cell 2018, 172, 869–880.e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, I.K.; Gacquer, D.; Van Heurck, R.; Kumar, D.; Wojno, M.; Bilheu, A.; Herpoel, A.; Lambert, N.; Cheron, J.; Polleux, F.; et al. Human-Specific NOTCH2NL Genes Expand Cortical Neurogenesis through Delta/Notch Regulation. Cell 2018, 173, 1370–1384.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fiddes, I.T.; Lodewijk, G.A.; Mooring, M.; Bosworth, C.M.; Ewing, A.D.; Mantalas, G.L.; Novak, A.M.; van den Bout, A.; Bishara, A.; Rosenkrantz, J.L.; et al. Human-Specific NOTCH2NL Genes Affect Notch Signaling and Cortical Neurogenesis. Cell 2018, 173, 1356–1369.e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, I.K.; Vanderhaeghen, P. Evolving brains with new genes. Opera Med. Physiol. 2018, 4, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampal, R.; Arboleda-Velasquez, J.F.; Nita-Lazar, A.; Kosik, K.S.; Haltiwanger, R.S. Highly conserved O-fucose sites have distinct effects on Notch1 function. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 32133–32140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rana, N.A.; Nita-Lazar, A.; Takeuchi, H.; Kakuda, S.; Luther, K.B.; Haltiwanger, R.S. O-glucose trisaccharide is present at high but variable stoichiometry at multiple sites on mouse Notch1. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 31623–31637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Li, L.; Irvine, K.D.; Baker, N.E. Notch activity in neural cells triggered by a mutant allele with altered glycosylation. Development 2003, 130, 2829–2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, T.V.; Sethi, M.K.; Leonardi, J.; Rana, N.A.; Buettner, F.F.R.; Haltiwanger, R.S.; Bakker, H.; Jafar-Nejad, H. Negative Regulation of Notch Signaling by Xylose. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, T.V.; Pandey, A.; Jafar-Nejad, H. Xylosylation of the Notch receptor preserves the balance between its activation by trans-Delta and inhibition by cis-ligands in Drosophila. PLoS Genet. 2017, 13, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pandey, A.; Li-Kroeger, D.; Sethi, M.K.; Lee, T.V.; Fr Buettner, F.; Bakker, H.; Jafar-Nejad, H. Sensitized genetic backgrounds reveal differential roles for EGF repeat xylosyltransferases in Drosophila Notch signaling. Glycobiology 2018, 28, 849–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandagopal, N.; Santat, L.A.; Elowitz, M.B. Cis-activation in the Notch signaling pathway. Elife 2019, 8, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprinzak, D.; Lakhanpal, A.; Lebon, L.; Santat, L.A.; Fontes, M.E.; Anderson, G.A.; Garcia-Ojalvo, J.; Elowitz, M.B. Cis-interactions between Notch and Delta generate mutually exclusive signalling states. Nature 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kakuda, S.; Lopilato, R.K.; Ito, A.; Haltiwanger, R.S. Canonical Notch ligands and Fringes have distinct effects on NOTCH1 and NOTCH2. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 14710–14722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panin, V.M.; Shao, L.; Lei, L.; Moloney, D.J.; Irvine, K.D.; Haltiwanger, R.S. Notch ligands are substrates for protein O-fucosyltransferase-1 and Fringe. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 29945–29952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Müller, J.; Rana, N.A.; Serth, K.; Kakuda, S.; Haltiwanger, R.S.; Gossler, A. O-fucosylation of the NOTCH ligand mDll1 by POFUT1 is dispensable for ligand function. PLoS ONE 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Serth, K.; Schuster-Gossler, K.; Kremmer, E.; Hansen, B.; Marohn-Köhn, B.; Gossler, A. O-fucosylation of DLL3 Is required for its function during somitogenesis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thakurdas, S.M.; Lopez, M.F.; Kakuda, S.; Fernandez-Valdivia, R.; Zarrin-Khameh, N.; Haltiwanger, R.S.; Jafar-Nejad, H. Jagged1 Heterozygosity in Mice Results in a Congetital Cholangiuopathy Which Is Reversed by Concomitant Deletiuon of One Copy of Poglut1 (Rumi). Hepatology 2016, 63, 550–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hozumi, K. Distinctive properties of the interactions between Notch and Notch ligands. Dev. Growth Differ. 2020, 62, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, D.; Huang, Y.; Huang, X.; Wang, W.; Yan, Q.; Wei, L.; Xin, W.; Gerson, S.; Stanley, P.; Lowe, J.B.; et al. Protein O-fucosyltransferase 1 (Pofut1) regulates lymphoid and myeloid homeostasis through modulation of Notch receptor ligand interactions. Blood 2011, 117, 5652–5662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hicks, C.; Johnston, S.H.; diSibio, G.; Collazo, A.; Vogt, T.F.; Weinmaster, G. Fringe differentially modulates Jagged1 and Delta1 signalling through Notch1 and Notch2. Nat. Cell Biol. 2000, 2, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, K.; Chiba, S.; Saito, T.; Kumano, K.; Takahashi, T.; Hirai, H. Manic Fringe and Lunatic Fringe Modify Different Sites of the Notch2 Extracellular Region, Resulting in Different Signaling Modulation. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 25753–25758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geisler, F.; Nagl, F.; Mazur, P.K.; Lee, M.; Zimber-Strobl, U.; Strobl, L.J.; Radtke, F.; Schmid, R.M.; Siveke, J.T. Liver-specific inactivation of Notch2, but not Notch1, compromises intrahepatic bile duct development in mice. Hepatology 2008, 48, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, J.L.; Berechid, B.E.; Cutting, F.B.; Presente, A.; Chambers, C.B.; Foltz, D.R.; Ferreira, A.; Nye, J.S. Autonomous and non-autonomous regulation of mammalian neurite development by Notch1 and Delta1. Curr. Biol. 1999, 9, 1448–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.; Brunskill, E.; Varnum-finney, B.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, A.; Jay, P.Y.; Bernstein, I.; Morimoto, M.; Kopan, R. The intracellular domains of Notch1 and Notch2 are functionally equivalent during development and carcinogenesis. Development 2015, 142, 2452–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.; Chen, S.; Boyle, S.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, A.; Piwnica-worms, D.R.; Ilagan, M.X.G. The Extracellular Domain of Notch2 Increases Its Cell-Surface Abundance and Ligand Responsiveness during Kidney Development. Dev. Cell 2013, 25, 585–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fiorini, E.; Merck, E.; Wilson, A.; Ferrero, I.; Jiang, W.; Koch, U.; Auderset, F.; Laurenti, E.; Tacchini-Cottier, F.; Pierres, M.; et al. Dynamic Regulation of Notch 1 and Notch 2 Surface Expression during T Cell Development and Activation Revealed by Novel Monoclonal Antibodies. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 7212–7222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van de Walle, I.; Waegemans, E.; De Medts, J.; De Smet, G.; De Smedt, M.; Snauwaert, S.; Vandekerckhove, B.; Kerre, T.; Leclercq, G.; Plum, J.; et al. Specific notch receptor-ligand interactions control human TCR-αβ/γδ development by inducing differential notch signal strength. J. Exp. Med. 2013, 210, 683–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suckling, R.J.; Korona, B.; Whiteman, P.; Chillakuri, C.; Holt, L.; Handford, P.A.; Lea, S.M. Structural and functional dissection of the interplay between lipid and Notch binding by human Notch ligands. EMBO J. 2017, 36, 2204–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, J.M.; Jafar-Nejad, H. The Roles of Notch Signaling in Liver Development and Disease. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tanaka, E.; Asanuma, K.; Kim, E.; Sasaki, Y.; Trejo, J.A.O.; Seki, T.; Nonaka, K.; Asao, R.; Nagai-Hosoe, Y.; Akiba-Takagi, M.; et al. Notch2 activation ameliorates nephrosis. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Sandy, A.R.; Wang, J.; Radojcic, V.; Shan, G.T.; Tran, I.T.; Friedman, A.; Kato, K.; He, S.; Cui, S.; et al. Notch signaling is a critical regulator of allogeneic CD4 T-cell responses mediating graft-versus-host disease. Blood 2011, 117, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poe, J.C.; Jia, W.; Su, H.; Anand, S.; Rose, J.J.; Tata, P.V.; Suthers, A.N.; Jones, C.D.; Kuan, P.F.; Vincent, B.G.; et al. An aberrant NOTCH2-BCR signaling axis in B cells from patients with chronic GVHD. Blood 2017, 130, 2131–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mochizuki, K.; Meng, L.; Mochizuki, I.; Tong, Q.; He, S.; Liu, Y.; Purushe, J.; Fung, H.; Zaidi, M.R.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Programming of donor T cells using allogeneic δ-like ligand 4-positive dendritic cells to reduce GVHD in mice. Blood 2016, 127, 3270–3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luo, X.; Xu, L.; Liu, L.; Li, Y.; Tan, H. Notch inhibition enhances graft-versus-leukemia while reducing graft-versus-host disease. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 843, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yu, S.; Myers, J.; Wang, Y.; Xin, W.W.; Albakri, M.; Xin, A.W.; Li, M.; Huang, A.Y.; Xin, W.; et al. Notch2 blockade enhances hematopoietic stem cell mobilization and homing. Haematologica 2017, 102, 1785–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Albakri, M.; Tashkandi, H.; Zhou, L. A Review of Advances in Hematopoietic Stem Cell Mobilization and the Potential Role of Notch2 Blockade. Cell Transplant. 2020, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radojcic, V.; Paz, K.; Chung, J.; Du, J.; Perkey, E.T.; Flynn, R.; Ivcevic, S.; Zaiken, M.; Friedman, A.; Yan, M.; et al. Notch signaling mediated by Delta-like ligands 1 and 4 controls the pathogenesis of chronic GVHD in mice. Blood 2018, 132, 2188–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]




| NOTCH1/DLL1 | Ligand Binding | Activation |
|---|---|---|
| +Fringe | Increased | Increased |
| Thr466Val (O-Fucose site on EGF12) | Decreased | Decreased |
| Thr466Val + Ser435Ala (O-Glucose site on EGF11) | Nearly equal to Thr466Val | Further Decreased |
| NOTCH1/JAG1 | Ligand Binding | Activation |
| +Fringe | Increased | Decreased |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saiki, W.; Ma, C.; Okajima, T.; Takeuchi, H. Current Views on the Roles of O-Glycosylation in Controlling Notch-Ligand Interactions. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 309. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11020309
Saiki W, Ma C, Okajima T, Takeuchi H. Current Views on the Roles of O-Glycosylation in Controlling Notch-Ligand Interactions. Biomolecules. 2021; 11(2):309. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11020309
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaiki, Wataru, Chenyu Ma, Tetsuya Okajima, and Hideyuki Takeuchi. 2021. "Current Views on the Roles of O-Glycosylation in Controlling Notch-Ligand Interactions" Biomolecules 11, no. 2: 309. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11020309