C-KIT Expression in Orbital Cavernous Venous Hemangiomas
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
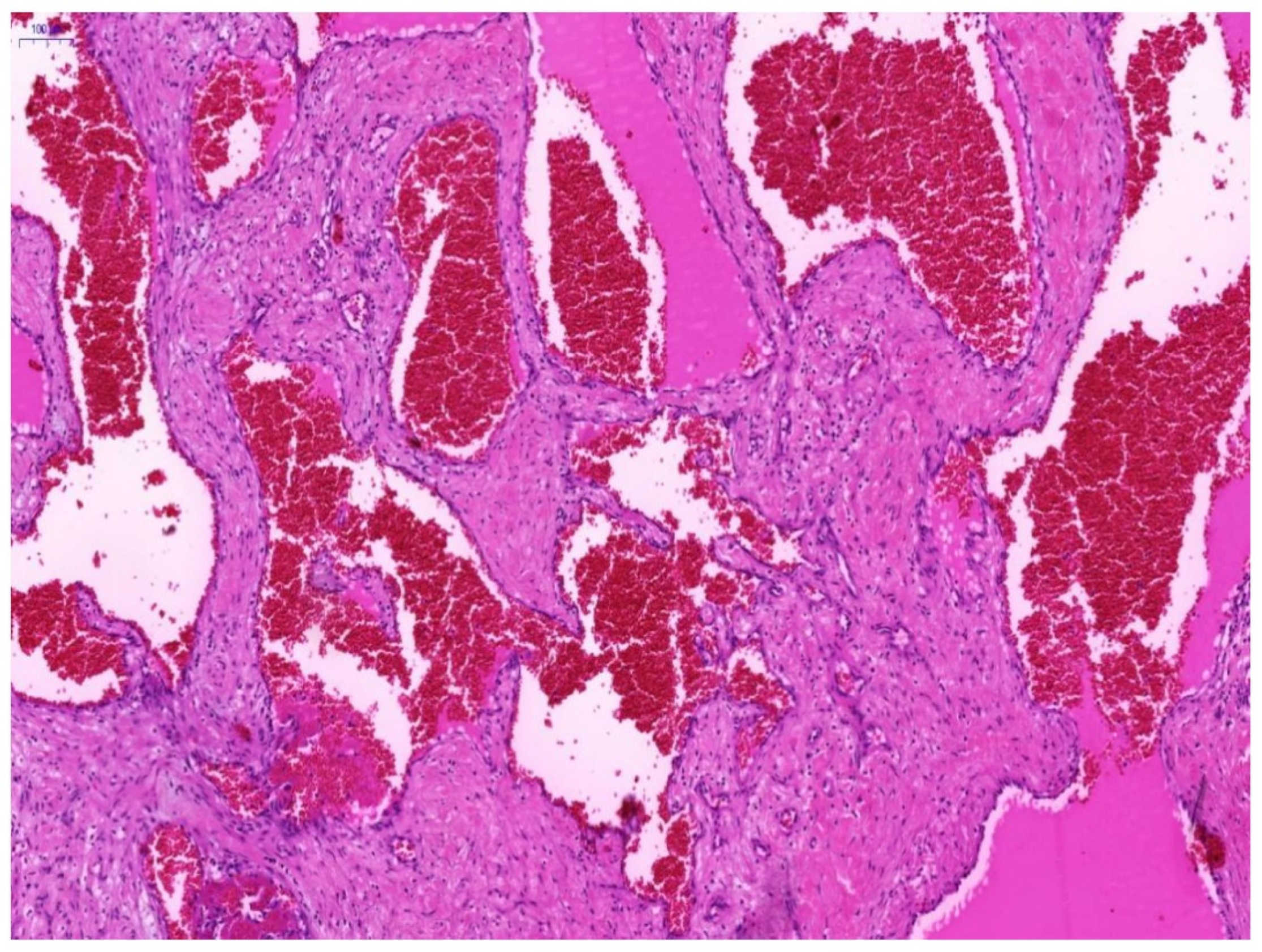
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kennedy, R.E. An evaluation of 820 orbital cases. Trans. Am. Ophthalmol. Soc. 1984, 82, 134–157. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bonavolontà, G.; Strianese, D.; Grassi, P.; Comune, C.; Tranfa, F.; Uccello, G.; Iuliano, A. An Analysis of 2480 Space-Occupying Lesions of the Orbit From 1976 to 2011. Ophthal. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2013, 29, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, G.J.; Jakobiec, F.A. Cavernous hemangioma of the orbit. J. Neurosurg. 1979, 51, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Tommaso, L.; Scarpellini, F.; Salvi, F.; Ragazzini, T.; Foschini, M.P. Progesterone receptor expression in orbital cavernous hemangiomas. Virchows Arch. 2000, 436, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagasaka, M.; Naganuma, H.; Satoh, E. Growth potential of orbital cavernous hemangioma suggested by vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptor flk-1. Neurol. Med. Chir. 2007, 47, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gupta, A.; Prabhakaran, V.C.; Dodd, T.; Davis, G.; Selva, D. Orbital Cavernous Haemangiomas: Immunohistochemical Study of Proliferative Capacity, Vascular Differentiation and Hormonal Receptor Status. Orbit 2012, 31, 386–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osaki, T.H.; Jakobiec, F.A.; Mendoza, P.R.; Lee, Y.; Fay, A.M. Immunohistochemical Investigations of Orbital Infantile Hemangiomas and Adult Encapsulated Cavernous Venous Lesions (Malformation Versus Hemangioma). Ophthal. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2013, 29, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okayama, Y.; Hunt, T.C.; Kassel, O.; Ashman, L.K.; Church, M.K. Assessment of the anti-c-kit monoclonal antibody YB5.B8 in affinity magnetic enrichment of human lung mast cells. J. Immunol. Methods 1994, 169, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Austen, K.F.; Friend, D.S.; Heidtman, M.; Boyce, J.A. Human peripheral blood eosinophils express a functional c-kit receptor for stem cell factor that stimulates very late antigen 4 (VLA-4)-mediated cell adhesion to fibronectin and vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM-1). J. Exp. Med. 1997, 186, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Columbo, M.; Horowitz, E.M.; Botana, L.M.; MacGlashan, D.W.; Bochner, B.S., Jr.; Gillis, S.; Zsebo, K.M.; Galli, S.J.; Lichtenstein, L.M. The human recombinant c-kit receptor ligand, rhSCF, induces mediator release from human cutaneous mast cells and enhances IgE-dependent media torrelease from both skin mast cells and peripheral blood basophils. J. Immunol. 1992, 149, 599–608. [Google Scholar]
- Hollenbeck, S.T.; Sakakibara, K.; Faries, P.L.; Workhu, B.; Liu, B.; Kent, K.C. Stem cell factor and c-kit are expressed by and may affect vascular SMCs through an autocrine pathway. J. Surg. Res. 2004, 120, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, E.M.; Maurer, M.; Botchkarev, V.A.; Jensen, K.D.; Welker, P.; Scott, G.A.; Paus, R.K. it is expressed by epithelial cells in vivo. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2003, 121, 976–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aye, M.T.; Hashemi, S.; Leclair, B.; Zeibdawi, A.; Trudel, E.; Halpenny, M.; Fuller, V.; Cheng, G. Expression of stem cell factor and c-kit mRNAin cultured endothelial cells, monocytes and cloned human bone marrowstromal cells (CFU-RF). Exp. Hematol. 1992, 20, 523–527. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Broudy, V.C.; Kovach, N.L.; Bennett, L.G.; Lin, N.; Jacobsen, F.W.; Kidd, P.G. Human umbilical vein endothelial cells display high-affinity c-kitreceptors and produce a soluble form of the c-kit receptor. Blood 1994, 83, 2145–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Furitsu, T.; Tsujimura, T.; Tono, T.; Ikeda, H.; Kitayama, H.; Koshimizu, U.; Sugahara, H.; Butterfield, J.H.; Ashman, L.K.; Kanayama, Y.; et al. Identification of mutations in the coding sequence of the proto-oncogene c-kit in a human mast cell eukemia cell line causing ligand-independent activation ofc-kit product. J. Clin. Investig. 1993, 92, 1736–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirota, S.; Isozaki, K.; Moriyama, Y.; Hashimoto, K.; Nishida, T.; Ishiguro, S.; Kawano, K.; Hanada, M.; Kurata, A.; Takeda, M.; et al. Gain-of-function mutations of c-kit inhuman gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Science 1998, 279, 577–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, H.; Worobec, A.S.; Oh, C.K.; Chowdhury, B.A.; Tannenbaum, S.; Suzuki, Y.; Metcalfe, D.D. Identification of a point mutation in the catalytic domain of the proto-oncogene c-kit in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients who have mastocytosis with an associated hematologic disorder. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 10560–10564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Longley, B.J.; Tyrrell, L.; Lu, S.Z.; Ma, Y.S.; Langley, K.; Ding, T.G.; Duffy, T.; Jacobs, P.; Tang, L.H.; Modlin, I. Somaticc-kit activating mutation in urticarial pigmentosa and aggressive mastocytosis: Establishment of clonality in a human mast cell neoplasm. Nat. Genet. 1996, 12, 312–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Q.; Frierson, H.F.; Krystal, G.W., Jr.; Moskaluk, C.A. Activating c-kit gene mutations in human germ cell tumors. Am. J. Pathol. 1999, 154, 1643–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grisanti, S.; Tura, A. Uveal Melanoma. In Noncutaneous Melanoma; Internet; Codon Publications: Brisbane, QLD, Australia, 2018; Chapter 1; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lammie, A.; Drobnjak, M.; Gerald, W.; Saad, A.; Cote, R.; Cordon-Cardo, C. Expression of c-kit and kit ligand proteins in normal human tissues. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1994, 42, 1417–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miettinen, M.; Sarlomo-Rikala, M.; Lasota, J. KIT expression in angiosarcomas and fetal endothelial cells: Lack of mutations of exon 11 and exon 17 of C-kit. Mod. Pathol. 2000, 13, 536–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, L.; Kakiuchi-Kiyota, S.; Arnold, L.L.; Johansson, S.L.; Wert, D.; Cohen, S.M. Pathogenesis of human hemangiosarcomas and hemangiomas. Hum. Pathol. 2013, 44, 2302–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernatchez, P.N.; Soker, S.H.; Sirois, M.G. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Effect on Endothelial Cell Proliferation, Migration, and Platelet-activating Factor Synthesis Is Flk-1-dependent. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 31047–31054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kearney, J.B.; Ambler, C.A.; Monaco, K.A.; Johnson, N.; Rapoport, R.G.; Bautch, V.L. Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor Flt-1 negatively regulates developmental blood vessel formation by modulating endothelial cell division. Blood 2002, 99, 2397–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Notelet, L.; Houtteville, J.P.; Khoury, S.; Lechevalier, B.; Chapon, F. Proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) in cerebral cavernomas: An immunocytochemical study of 42 cases. Surg. Neurol. 1997, 47, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholzen, T.; Gerdes, J. The Ki-67 protein: From the known and the unknown. J. Cell Physiol. 2000, 182, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, H.J.; Bailey, D.; Marks, A. Monoclonal antibody D2-40, a new marker of lymphatic endothelium, reacts with Kaposi’s and a subset of angiosarcomas. Mod. Pathol. 2002, 15, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hood, I. Cavernous hemangioma of the orbit. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1970, 83, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarden, Y.; Kuang, W.J.; Yang-Feng, T.; Coussens, L.; Munemitsu, S.; Dull, T.J.; Chen, E.; Schlessinger, J.; Francke, U.; Ullrich, A. Human proto-oncogenec-kit: A new cell surface receptor tyrosine kinase for an unidentified ligand. EMBO J. 1987, 6, 3341–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, E.; Nocka, K.; Beier, D.R.; Chu, T.Y.; Buck, J.; Lahm, H.W.; Wellner, D.; Leder, P.; Besmer, P. The hematopoietic growth factor KL is encoded by the Sl locus and is the ligand of the c-kit receptor, the gene product of the W locus. Cell 1990, 63, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakuma, Y.; Sakurai, S.; Oguni, S.; Satoh, M.; Hironaka, M.; Saito, K. c-kit gene mutations in intracranial germinomas. Cancer Sci. 2004, 95, 716–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oensuu, H.; Roberts, P.J.; Sarlomo-Rikala, M.; Andersson, L.C.; Tervahartiala, P.; Tuveson, D.; Silberman, S.; Capdeville, R.; Dimitrijevic, S.; Druker, B.; et al. Effect of the tyrosine kinase inhibitor STI571 in a patient with a metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumor. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 1052–1056. [Google Scholar]
- Mauro, M.J.; Druker, B.J. STI571: Targeting BCRABL as therapy for CML. Oncologist 2001, 6, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Druker, B.J.; Tamura, S.; Buchdunger, E.; Ohno, S.; Segal, G.M.; Fanning, S.; Zimmermann, J.; Lydon, N.B. Effects of a selective inhibitor of the Abl tyrosine kinase on the growth of Bcr-Abl positive cells. Nat. Med. 1996, 2, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchdunger, E.; Cioffi, C.L.; Law, N.; Stover, D.; Ohno-Jones, S.; Druker, B.J.; Lydon, N.B. Abl protein-tyrosine kinase inhibitor STI571 inhibits in vitro signal transduction mediated by c-kit and platelet-derived growth factor receptors. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2000, 295, 139–145. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Isozaki, K.; Kinoshita, K.; Ohashi, A.; Shinomura, Y.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Kitamura, Y.; Hirota, S. Imatinib inhibits various types of activating mutant KIT found in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Int. J. Cancer 2003, 105, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuveson, D.A.; Willis, N.A.; Jacks, T.; Griffin, J.D.; Singer, S.; Fletcher, C.D.; Fletcher, J.A.; Demetri, G.D. STI571 inactivation of the gastrointestinal stromal tumor c-KIT oncoprotein: Biological andclinical implications. Oncogene 2001, 20, 5054–5058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Demetri, G.D.; von Mehren, M.; Blanke, C.D.; Van den Abbeele, A.D.; Eisenberg, B.; Roberts, P.J.; Heinrich, M.C.; Tuveson, D.A.; Singer, S.; Janicek, M.; et al. Efficacy and safety of imatinibmesylate in advanced gastrointestinalstromaltumors. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 472–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Enjolras, O. Classification and management of the various superficial vascular anomalies: Hemangiomas and vascular malformations. J. Dermatol. 1997, 24, 701–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzon, M.C.; Huang, J.T.; Enjolras, O.; Frieden, I.J. Vascular malformations: Part, I. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2007, 56, 353–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulliken, J.B.; Glowacki, J. Hemangiomas and vascular malformations in infants and children: A classification based on endothelial characteristics. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1982, 69, 412–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legiehn, G.M.; Heran, M.K. Venous malformations: Classification, development, diagnosis, and interventional radiologic management. Radiol. Clin. N. Am. 2008, 46, 545–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, I.T.; Carreño, R.; Potparic, Z.; Hussain, K. Hemangiomas, vascular malformations, and lymphovenous malformations: Classification and methods of treatment. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1993, 91, 1216–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rootman, D.B.; Heran, M.K.; Rootman, J.; White, V.A.; Luemsamran, P.; Yucel, Y.H. Cavernous venous malformations of the orbit (so-called cavernous haemangioma): A comprehensive evaluation of their clinical, imaging and histologic nature. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2014, 98, 880–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vliagoftis, H. Thrombin induces mast cell adhesion to fibronectin: Evidence for involvement of protease-activated receptor-1. J. Immunol. 2002, 169, 4551–4558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leslie, M.C.; Bar-Eli, M. Regulation of Gene Expression in Melanoma: New Approaches for Treatment. J. Cell Biochem. 2005, 94, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Case | Staining Score |
|---|---|
| 1 | 2 |
| 2 | 2 |
| 3 | 3 |
| 4 | 1 |
| 5 | 2 |
| 6 | 1 |
| 7 | 2 |
| 8 | 1 |
| 9 | 1 |
| 10 | 1 |
| 11 | 3 |
| 12 | 1 |
| 13 | 1 |
| 14 | 1 |
| 15 | 2 |
| 16 | 2 |
| Case | Age Range | Sex | Tumor Side | Duration of Symptoms (yrs) | Symptom of Onset | Proptosis | Location | Tumor Size (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 70′s | M | RT | 1 | proptosis + ptosis | V | Extraconal | 12 × 10 × 7 |
| 2 | 50′s | F | LT | 2 | proptosis | V | Intraconal | 15 × 25×10 |
| 3 | 30′s | M | LT | 10 | proptosis | V | Intraconal | 15 × 20 × 25 |
| 4 | 30′s | M | LT | 1.5 | Visual disturbance | NO | Extraconal | 8 × 5 × 7 |
| 5 | 50′s | F | RT | 1 | Visual disturbance | V | Intraconal | 20 × 20 |
| 6 | Under10 | F | RT | 4 | Visual disturbance | V | Extraconal | 18 × 10 |
| 7 | 40′s | F | LE | 1 | Visual disturbance | V | Extraconal | 15 × 10 × 8 |
| 8 | 20′s | F | LE | 22 | proptosis | V | Intraconal | 15 × 15 × 10 |
| 9 | 30′s | M | RT | 1 | proptosis | V | Intraconal | 25 × 15 × 10 |
| 10 | 40′s | F | LE | 4 | proptosis | V | Extraconal | 25 × 15 × 15 |
| 11 | 60′s | M | LE | 0.5 | proptosis | V | Intraconal | 20 × 15 × 10 |
| 12 | 40′s | M | RE | 11 | Visual disturbance | V | Extraconal | 28 × 8 |
| 13 | 20′s | F | RE | 1 | Visual disturbance | NO | Extraconal | 8 × 5 × 3 |
| 14 | 60′s | M | RE | 2 | proptosis | V | Extraconal | 20 × 15 × 10 |
| 15 | 50′s | F | LE | 1 | Visual disturbance | NO | Extraconal | 10 × 10 × 8 |
| 16 | 30′s | M | RE | 2 | Visual disturbance | V | Intraconal | 18 × 15 × 15 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Atallah, M.; Edison, N.; Levi, E.; Elmalah, I.; Briscoe, D. C-KIT Expression in Orbital Cavernous Venous Hemangiomas. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1199. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11081199
Atallah M, Edison N, Levi E, Elmalah I, Briscoe D. C-KIT Expression in Orbital Cavernous Venous Hemangiomas. Biomolecules. 2021; 11(8):1199. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11081199
Chicago/Turabian StyleAtallah, Mizhir, Natalia Edison, Esther Levi, Irit Elmalah, and Daniel Briscoe. 2021. "C-KIT Expression in Orbital Cavernous Venous Hemangiomas" Biomolecules 11, no. 8: 1199. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11081199
APA StyleAtallah, M., Edison, N., Levi, E., Elmalah, I., & Briscoe, D. (2021). C-KIT Expression in Orbital Cavernous Venous Hemangiomas. Biomolecules, 11(8), 1199. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11081199





