Gut Inflammation Induced by Finasteride Withdrawal: Therapeutic Effect of Allopregnanolone in Adult Male Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Treatments
2.3. Steroid Level Evaluation by Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry Analysis
2.4. Dopamine and Serotonin Level Evaluation
2.5. Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction
2.6. Statistics
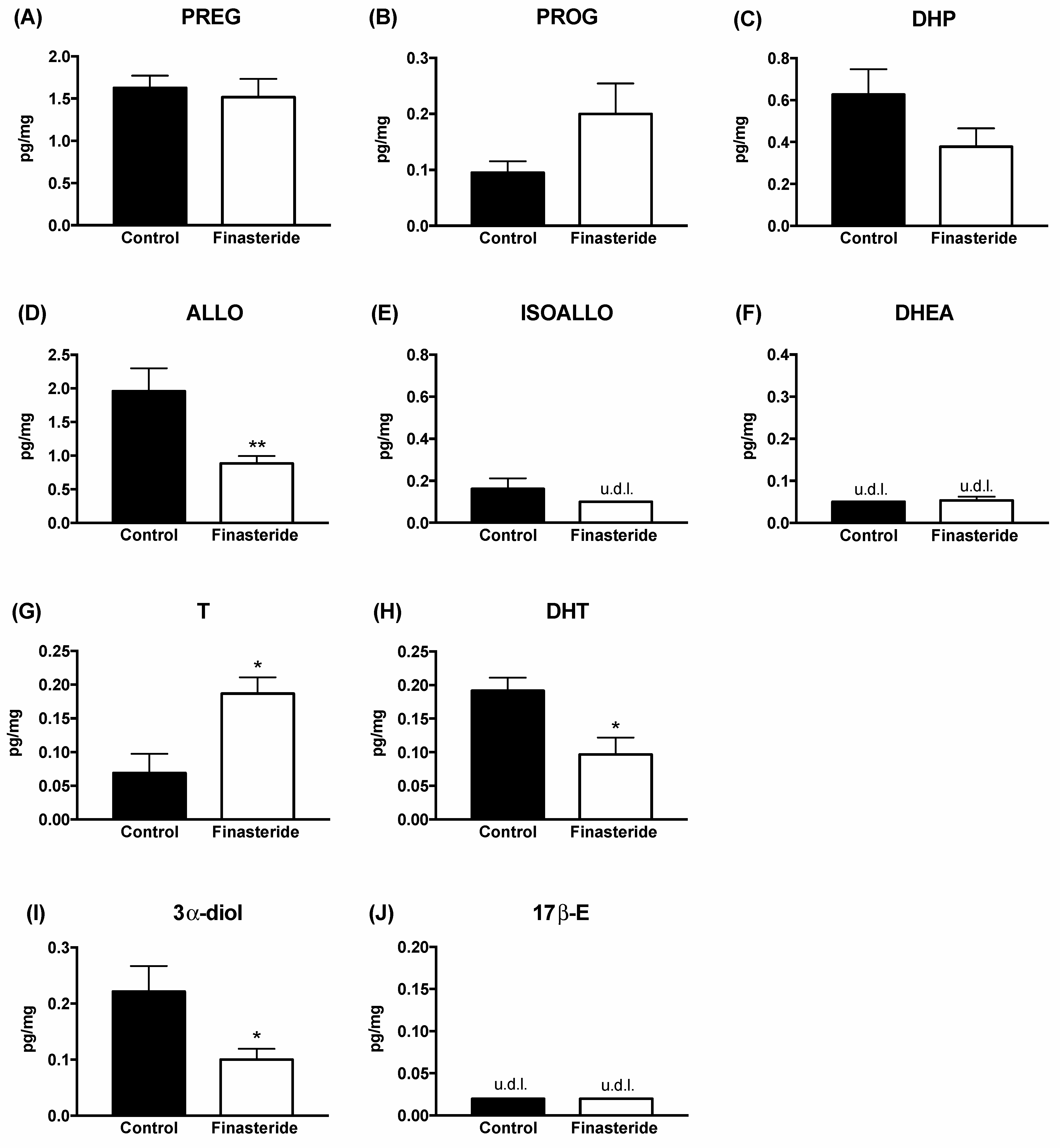
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kaufman, K.D.; Olsen, E.A.; Whiting, D.; Savin, R.; DeVillez, R.; Bergfeld, W.; Price, V.H.; Van Neste, D.; Roberts, J.L.; Hordinsky, M.; et al. Finasteride in the treatment of men with androgenetic alopecia. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1998, 39, 578–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traish, A.M.; Melcangi, R.C.; Bortolato, M.; Garcia-Segura, L.M.; Zitzmann, M. Adverse effects of 5alpha-reductase inhibitors: What do we know, don’t know, and need to know? Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2015, 16, 177–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diviccaro, S.; Melcangi, R.C.; Giatti, S. Post-finasteride syndrome: An emerging clinical problem. Neurobiol. Stress 2020, 12, 100209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giatti, S.; Diviccaro, S.; Panzica, G.; Melcangi, R.C. Post-finasteride syndrome and post-SSRI sexual dysfunction: Two sides of the same coin? Endocrine 2018, 2, 180–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traish, A.M. Post-finasteride syndrome: A surmountable challenge for clinicians. Fertil. Steril. 2020, 113, 21–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melcangi, R.C.; Santi, D.; Spezzano, R.; Grimoldi, M.; Tabacchi, T.; Fusco, M.L.; Diviccaro, S.; Giatti, S.; Carra, G.; Caruso, D.; et al. Neuroactive steroid levels and psychiatric and andrological features in post-finasteride patients. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 171, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giatti, S.; Foglio, B.; Romano, S.; Pesaresi, M.; Panzica, G.; Garcia-Segura, L.M.; Caruso, D.; Melcangi, R.C. Effects of Subchronic Finasteride Treatment and Withdrawal on Neuroactive Steroid Levels and their Receptors in the Male Rat Brain. Neuroendocrinology 2016, 103, 746–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diviccaro, S.; Giatti, S.; Borgo, F.; Barcella, M.; Borghi, E.; Trejo, J.L.; Garcia-Segura, L.M.; Melcangi, R.C. Treatment of male rats with finasteride, an inhibitor of 5alpha-reductase enzyme, induces long-lasting effects on depressive-like behavior, hippocampal neurogenesis, neuroinflammation and gut microbiota composition. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2019, 99, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cryan, J.F.; O’Riordan, K.J.; Cowan, C.S.M.; Sandhu, K.V.; Bastiaanssen, T.F.S.; Boehme, M.; Codagnone, M.G.; Cussotto, S.; Fulling, C.; Golubeva, A.V.; et al. The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 1877–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, C.R.; Osadchiy, V.; Kalani, A.; Mayer, E.A. The Brain-Gut-Microbiome Axis. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 6, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgo, F.; Macandog, A.D.; Diviccaro, S.; Falvo, E.; Giatti, S.; Cavaletti, G.; Melcangi, R.C. Alterations of gut microbiota composition in post-finasteride patients: A pilot study. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2020, 44, 1263–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetel, M.J.; de Vries, G.J.; Melcangi, R.C.; Panzica, G.; O’Mahony, S.M. Steroids, stress and the gut microbiome-brain axis. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2018, 30, e12548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fields, C.T.; Chassaing, B.; Paul, M.J.; Gewirtz, A.T.; de Vries, G.J. Vasopressin deletion is associated with sex-specific shifts in the gut microbiome. Gut Microbes 2017, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, N.; Hanaoka, R.; Hanada, K.; Izawa, T.; Inui, H.; Yamaji, R. Hypogonadism alters cecal and fecal microbiota in male mice. Gut Microbes 2016, 7, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasarevic, E.; Morrison, K.E.; Bale, T.L. Sex differences in the gut microbiome-brain axis across the lifespan. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2016, 371, 20150122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Indias, I.; Sanchez-Alcoholado, L.; Sanchez-Garrido, M.A.; Martin-Nunez, G.M.; Perez-Jimenez, F.; Tena-Sempere, M.; Tinahones, F.J.; Queipo-Ortuno, M.I. Neonatal Androgen Exposure Causes Persistent Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis Related to Metabolic Disease in Adult Female Rats. Endocrinology 2016, 157, 4888–4898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Org, E.; Mehrabian, M.; Parks, B.W.; Shipkova, P.; Liu, X.; Drake, T.A.; Lusis, A.J. Sex differences and hormonal effects on gut microbiota composition in mice. Gut Microbes 2016, 7, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurkovetskiy, L.; Burrows, M.; Khan, A.A.; Graham, L.; Volchkov, P.; Becker, L.; Antonopoulos, D.; Umesaki, Y.; Chervonsky, A.V. Gender bias in autoimmunity is influenced by microbiota. Immunity 2013, 39, 400–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diviccaro, S.; FitzGerald, J.A.; Cioffi, L.; Falvo, E.; Crispie, F.; Cotter, P.D.; O’Mahony, S.M.; Giatti, S.; Caruso, D.; Melcangi, R.C. Gut Steroids and Microbiota: Effect of Gonadectomy and Sex. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diviccaro, S.; Giatti, S.; Borgo, F.; Falvo, E.; Caruso, D.; Garcia-Segura, L.M.; Melcangi, R.C. Steroidogenic Machinery in the Adult Rat Colon. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2020, 203, 105732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Yuan, X.; Liu, J.; Shi, Z.; Cao, L.; Yang, L.; Wu, K.; Lou, Y.; Tong, H.; Jiang, L.; et al. Albuca Bracteata Polysaccharides Attenuate AOM/DSS Induced Colon Tumorigenesis via Regulating Oxidative Stress, Inflammation and Gut Microbiota in Mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 833077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.M.; Huang, H.L.; Liu, Y.D.; Zhu, J.Q.; Zhou, Y.L.; Chen, H.T.; Xu, J.; Zhao, H.L.; Guo, X.; Shi, W.; et al. Selection strategy of dextran sulfate sodium-induced acute or chronic colitis mouse models based on gut microbial profile. BMC Microbiol. 2021, 21, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzel, T.; Mirowska-Guzel, D. The Role of Serotonin Neurotransmission in Gastrointestinal Tract and Pharmacotherapy. Molecules 2022, 27, 1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, E.A. Gut feelings: The emerging biology of gut-brain communication. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2011, 12, 453–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drossman, D.A. Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders: History, Pathophysiology, Clinical Features and Rome IV. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 1262–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strandwitz, P. Neurotransmitter modulation by the gut microbiota. Brain Res. 2018, 1693, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Jahmany, A.A.; Schultheiss, G.; Diener, M. Effects of dopamine on ion transport across the rat distal colon. Pflug. Arch. 2004, 448, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, C.J.; Aherne, A.M.; Lane, E.; Power, O.; Carey, R.M.; O’Connell, D.P. Identification and regional distribution of the dopamine D(1A) receptor in the gastrointestinal tract. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2000, 279, R599–R609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirmer, M.; Smeekens, S.P.; Vlamakis, H.; Jaeger, M.; Oosting, M.; Franzosa, E.A.; ter Horst, R.; Jansen, T.; Jacobs, L.; Bonder, M.J.; et al. Linking the Human Gut Microbiome to Inflammatory Cytokine Production Capacity. Cell 2016, 167, 1125–1136.e8, Erratum in Cell 2016, 167, 1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinashi, Y.; Hase, K. Partners in Leaky Gut Syndrome: Intestinal Dysbiosis and Autoimmunity. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 673708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caruso, D.; Pesaresi, M.; Maschi, O.; Giatti, S.; Garcia-Segura, L.M.; Melcangi, R.C. Effects of Short- and Long-Term Gonadectomy on Neuroactive Steroid Levels in the Central and Peripheral Nervous System of Male and Female Rats. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2010, 22, 1137–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caruso, D.; Pesaresi, M.; Abbiati, F.; Calabrese, D.; Giatti, S.; Garcia-Segura, L.M.; Melcangi, R.C. Comparison of plasma and cerebrospinal fluid levels of neuroactive steroids with their brain, spinal cord and peripheral nerve levels in male and female rats. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2013, 38, 2278–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesaresi, M.; Maschi, O.; Giatti, S.; Garcia-Segura, L.M.; Caruso, D.; Melcangi, R.C. Sex differences in neuroactive steroid levels in the nervous system of diabetic and non-diabetic rats. Horm. Behav. 2010, 57, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, F.; Wang, F.; Zhu, R.; Li, H. Determination of 5-Hydroxytryptamine, norepinephrine, dopamine and their metabolites in rat brain tissue by LC-ESI-MS-MS. Chromatographia 2009, 69, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Evans, C.O.; Hoffman, S.W.; Oyesiku, N.M.; Stein, D.G. Progesterone and allopregnanolone reduce inflammatory cytokines after traumatic brain injury. Exp. Neurol. 2004, 189, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, C.; Zorumski, C.F.; Izumi, Y. Ethanol, neurosteroids and cellular stress responses: Impact on central nervous system toxicity, inflammation and autophagy. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2021, 124, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, C.; Karali, K.; Fodelianaki, G.; Gravanis, A.; Chavakis, T.; Charalampopoulos, I.; Alexaki, V.I. Neurosteroids as regulators of neuroinflammation. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2019, 55, 100788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diviccaro, S.; Cioffi, L.; Falvo, E.; Giatti, S.; Melcangi, R.C. Allopregnanolone: An overview on its synthesis and effects. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2021, 34, e12996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giatti, S.; Boraso, M.; Melcangi, R.; Viviani, B. Neuroactive steroids, their metabolites and neuroinflammation. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2012, 49, R125–R134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giatti, S.; Rigolio, R.; Romano, S.; Mitro, N.; Viviani, B.; Cavaletti, G.; Caruso, D.; Garcia-Segura, L.M.; Melcangi, R.C. Dihydrotestosterone as a Protective Agent in Chronic Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. Neuroendocrinology 2015, 101, 296–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cermenati, G.; Giatti, S.; Audano, M.; Pesaresi, M.; Spezzano, R.; Caruso, D.; Mitro, N.; Melcangi, R.C. Diabetes alters myelin lipid profile in rat cerebral cortex: Protective effects of dihydroprogesterone. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 168, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitro, N.; Cermenati, G.; Brioschi, E.; Abbiati, F.; Audano, M.; Giatti, S.; Crestani, M.; De Fabiani, E.; Azcoitia, I.; Garcia-Segura, L.M.; et al. Neuroactive steroid treatment modulates myelin lipid profile in diabetic peripheral neuropathy. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 143, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonelli, E.; Bianchi, R.; Cavaletti, G.; Caruso, D.; Crippa, D.; Garcia-Segura, L.M.; Lauria, G.; Magnaghi, V.; Roglio, I.; Melcangi, R.C. Progesterone and its derivatives are neuroprotective agents in experimental diabetic neuropathy: A multimodal analysis. Neuroscience 2007, 144, 1293–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belelli, D.; Lambert, J.J. Neurosteroids: Endogenous regulators of the GABA(A) receptor. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2005, 6, 565–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambert, J.J.; Cooper, M.A.; Simmons, R.D.; Weir, C.J.; Belelli, D. Neurosteroids: Endogenous allosteric modulators of GABA(A) receptors. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2009, 34 (Suppl. S1), S48–S58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Ruan, G.; Chen, L.; Ying, S.; Li, G.; Xu, F.; Xiao, Z.; Tian, Y.; Lv, L.; Ping, Y.; et al. Neurotransmitter and Intestinal Interactions: Focus on the Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis in Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 817100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.Y.; Li, X.H.; Zuo, L.; Xiong, Q.; He, W.T.; Li, D.X.; Dong, Z.F. Maternal sleep deprivation induces gut microbial dysbiosis and neuroinflammation in offspring rats. Zool. Res. 2022, 43, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mawe, G.M.; Hoffman, J.M. Serotonin signalling in the gut—Functions, dysfunctions and therapeutic targets. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 10, 473–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamamah, S.; Aghazarian, A.; Nazaryan, A.; Hajnal, A.; Covasa, M. Role of Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis in Regulating Dopaminergic Signaling. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahora, I.S.; Tsouklidis, N.; Kumar, R.; Soni, R.; Khan, S. How Serotonin Level Fluctuation Affects the Effectiveness of Treatment in Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Cureus 2020, 12, e9871, Erratum in Cureus 2020, 12, c36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikander, A.; Rana, S.V.; Prasad, K.K. Role of serotonin in gastrointestinal motility and irritable bowel syndrome. Clin. Chim. Acta 2009, 403, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojanov, S.; Berlec, A.; Strukelj, B. The Influence of Probiotics on the Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes Ratio in the Treatment of Obesity and Inflammatory Bowel disease. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, A.W.; Sanderson, J.D.; Churcher, C.; Parkes, G.C.; Hudspith, B.N.; Rayment, N.; Brostoff, J.; Parkhill, J.; Dougan, G.; Petrovska, L. High-throughput clone library analysis of the mucosa-associated microbiota reveals dysbiosis and differences between inflamed and non-inflamed regions of the intestine in inflammatory bowel disease. BMC Microbiol. 2011, 11, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruder, B.; Atreya, R.; Becker, C. Tumour Necrosis Factor Alpha in Intestinal Homeostasis and Gut Related Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magro, F.; Vieira-Coelho, M.A.; Fraga, S.; Serrao, M.P.; Veloso, F.T.; Ribeiro, T.; Soares-da-Silva, P. Impaired synthesis or cellular storage of norepinephrine, dopamine, and 5-hydroxytryptamine in human inflammatory bowel disease. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2002, 47, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolstanova, G.; Deng, X.; Ahluwalia, A.; Paunovic, B.; Prysiazhniuk, A.; Ostapchenko, L.; Tarnawski, A.; Sandor, Z.; Szabo, S. Role of Dopamine and D2 Dopamine Receptor in the Pathogenesis of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2015, 60, 2963–2975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vich Vila, A.; Imhann, F.; Collij, V.; Jankipersadsing, S.A.; Gurry, T.; Mujagic, Z.; Kurilshikov, A.; Bonder, M.J.; Jiang, X.; Tigchelaar, E.F.; et al. Gut microbiota composition and functional changes in inflammatory bowel disease and irritable bowel syndrome. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaap8914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo Presti, A.; Zorzi, F.; Del Chierico, F.; Altomare, A.; Cocca, S.; Avola, A.; De Biasio, F.; Russo, A.; Cella, E.; Reddel, S.; et al. Fecal and Mucosal Microbiota Profiling in Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, B.; Juillerat, P.; Oyas, O.; Ramon, C.; Bravo, F.D.; Franc, Y.; Fournier, N.; Michetti, P.; Mueller, C.; Geuking, M.; et al. Publisher Correction: Microbial network disturbances in relapsing refractory Crohn’s disease. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunn, B.G.; Cunningham, L.; Mitchell, S.G.; Swinny, J.D.; Lambert, J.J.; Belelli, D. GABA receptor-acting neurosteroids: A role in the development and regulation of the stress response. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2014, 36, 28–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seifi, M.; Brown, J.F.; Mills, J.; Bhandari, P.; Belelli, D.; Lambert, J.J.; Rudolph, U.; Swinny, J.D. Molecular and functional diversity of GABA-A receptors in the enteric nervous system of the mouse colon. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 10361–10378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seifi, M.; Rodaway, S.; Rudolph, U.; Swinny, J.D. GABAA Receptor Subtypes Regulate Stress-Induced Colon Inflammation in Mice. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 852–864.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auteri, M.; Zizzo, M.G.; Serio, R. GABA and GABA receptors in the gastrointestinal tract: From motility to inflammation. Pharmacol. Res. 2015, 93, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugan, S.; Jakka, P.; Namani, S.; Mujumdar, V.; Radhakrishnan, G. The neurosteroid pregnenolone promotes degradation of key proteins in the innate immune signaling to suppress inflammation. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 4596–4607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, J.H.; Chung, B.C. Nongenomic actions of neurosteroid pregnenolone and its metabolites. Steroids 2016, 111, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diviccaro, S.; Giatti, S.; Cioffi, L.; Falvo, E.; Piazza, R.; Caruso, D.; Melcangi, R.C. Paroxetine effects in adult male rat colon: Focus on gut steroidogenesis and microbiota. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2022, 143, 105828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osman, M.M.; El-Khatib, F.M.; Roberts, N.H.; Huynh, L.M.; Yafi, F.A. The Gut Microbiome and Men’s Sexual Health. Curr. Sex Health Rep. 2019, 11, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, T.; Hatakeyama, S.; Imai, A.; Yamamoto, H.; Yoneyama, T.; Mori, K.; Yoneyama, T.; Hashimoto, Y.; Nakaji, S.; Ohyama, C. The association between gut microbiome and erectile dysfunction: A community-based cross-sectional study in Japan. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2020, 52, 1421–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Li, W.; Song, B.; Wang, C.; Shen, Q.; Li, B.; Tang, D.; Xu, C.; Geng, H.; Gao, Y.; et al. Differences in the Gut Microbiome of Women with and Without Hypoactive Sexual Desire Disorder: Case Control Study. J. Med. Internet Res. 2021, 23, e25342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tirandaz, H.; Ebrahim-Habibi, M.B.; Moradveisi, B.; Raoofi, S.; Salehi-Najafabadi, A.; Mohammadi, E. Microbiota potential for the treatment of sexual dysfunction. Med. Hypotheses 2018, 115, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Diviccaro, S.; Giatti, S.; Cioffi, L.; Falvo, E.; Herian, M.; Caruso, D.; Melcangi, R.C. Gut Inflammation Induced by Finasteride Withdrawal: Therapeutic Effect of Allopregnanolone in Adult Male Rats. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1567. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12111567
Diviccaro S, Giatti S, Cioffi L, Falvo E, Herian M, Caruso D, Melcangi RC. Gut Inflammation Induced by Finasteride Withdrawal: Therapeutic Effect of Allopregnanolone in Adult Male Rats. Biomolecules. 2022; 12(11):1567. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12111567
Chicago/Turabian StyleDiviccaro, Silvia, Silvia Giatti, Lucia Cioffi, Eva Falvo, Monika Herian, Donatella Caruso, and Roberto Cosimo Melcangi. 2022. "Gut Inflammation Induced by Finasteride Withdrawal: Therapeutic Effect of Allopregnanolone in Adult Male Rats" Biomolecules 12, no. 11: 1567. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12111567
APA StyleDiviccaro, S., Giatti, S., Cioffi, L., Falvo, E., Herian, M., Caruso, D., & Melcangi, R. C. (2022). Gut Inflammation Induced by Finasteride Withdrawal: Therapeutic Effect of Allopregnanolone in Adult Male Rats. Biomolecules, 12(11), 1567. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12111567






