Pyroptosis: A Newly Discovered Therapeutic Target for Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury
Abstract
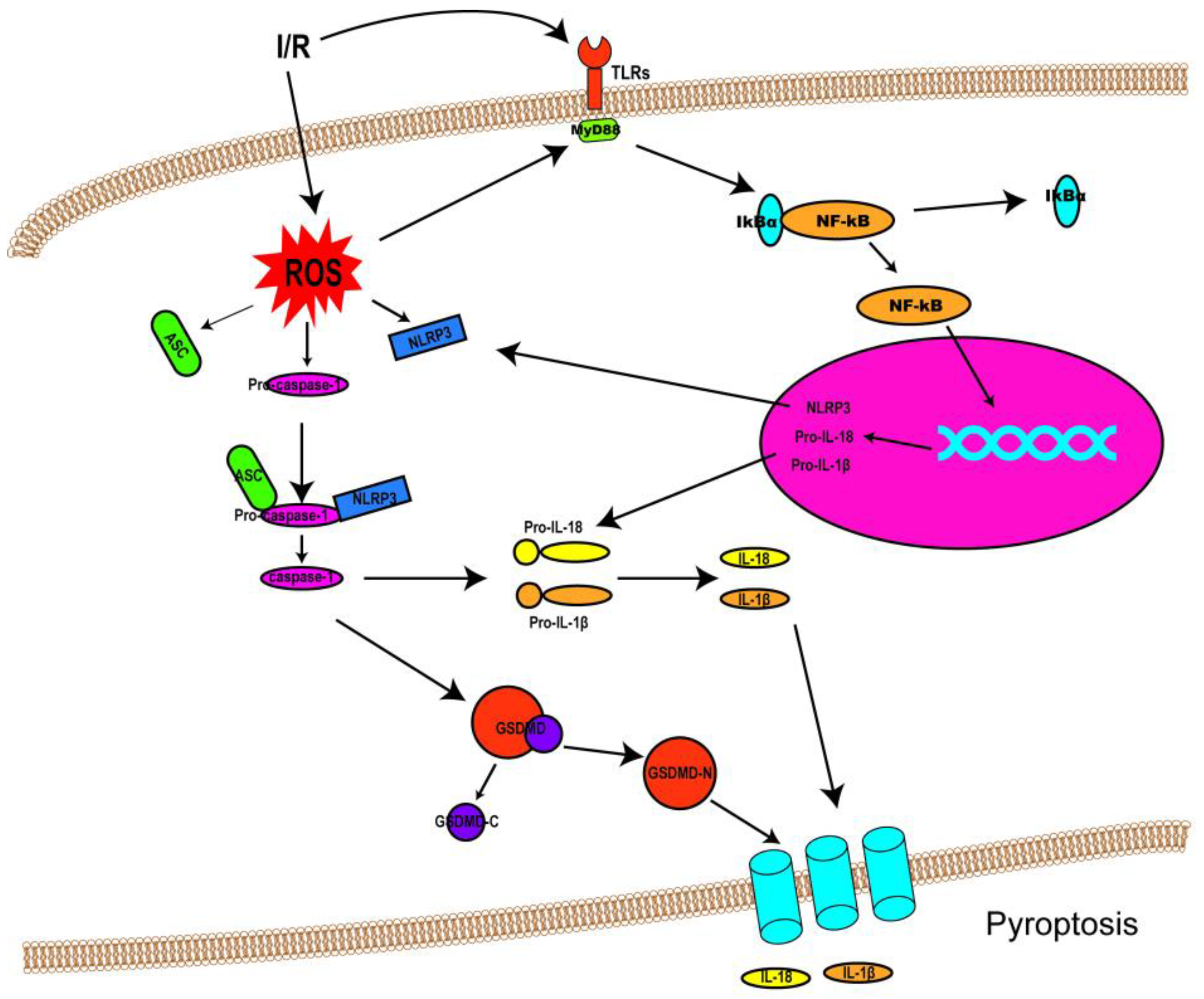
:1. Introduction
2. Overview of Pyroptosis
3. Mechanisms of Pyroptosis
3.1. Canonical Pathway
3.2. Non-Canonical Pathway
3.3. Caspase-3/8-Mediated Pathway
3.4. Granzyme-Mediated Pathway
4. Pyroptosis and I/R Injury
4.1. Pyroptosis and Cerebral I/R Injury
4.2. Pyroptosis and Myocardial I/R Injury
4.3. Pyroptosis and Renal I/R Injury
4.4. Pyroptosis and Hepatic I/R Injury
4.5. Pyroptosis and Other I/R Injuries
5. Conclusions and Perspective
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eltzschig, H.K.; Eckle, T. Ischemia and reperfusion—From mechanism to translation. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 1391–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lamkanfi, M.; Dixit, V.M. Mechanisms and functions of inflammasomes. Cell 2014, 157, 1013–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, P.; Zhang, X.; Liu, N.; Tang, L.; Peng, C.; Chen, X. Pyroptosis: Mechanisms and diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantazi, E.; Bejaoui, M.; Folch-Puy, E.; Adam, R.; Rosello-Catafau, J. Advances in treatment strategies for ischemia reperfusion injury. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2016, 17, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zychlinsky, A.; Prevost, M.C.; Sansonetti, P.J. Shigella flexneri induces apoptosis in infected macrophages. Nature 1992, 358, 167–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Smith, M.R.; Thirumalai, K.; Zychlinsky, A. A bacterial invasin induces macrophage apoptosis by binding directly to ICE. EMBO J. 1996, 15, 3853–3860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersh, D.; Monack, D.M.; Smith, M.R.; Ghori, N.; Falkow, S.; Zychlinsky, A. The Salmonella invasin SipB induces macrophage apoptosis by binding to caspase-1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 2396–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brennan, M.A.; Cookson, B.T. Salmonella induces macrophage death by caspase-1-dependent necrosis. Mol. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fink, S.L.; Bergsbaken, T.; Cookson, B.T. Anthrax lethal toxin and Salmonella elicit the common cell death pathway of caspase-1-dependent pyroptosis via distinct mechanisms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 4312–4317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kayagaki, N.; Warming, S.; Lamkanfi, M.; Vande, W.L.; Louie, S.; Dong, J.; Newton, K.; Qu, Y.; Liu, J.; Heldens, S.; et al. Non-canonical inflammasome activation targets caspase-11. Nature 2011, 479, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, K.; Shi, X.; Wang, Y.; Huang, H.; Zhuang, Y.; Cai, T.; Wang, F.; Shao, F. Cleavage of GSDMD by inflammatory caspases determines pyroptotic cell death. Nature 2015, 526, 660–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, J.; Wang, K.; Liu, W.; She, Y.; Sun, Q.; Shi, J.; Sun, H.; Wang, D.C.; Shao, F. Pore-forming activity and structural autoinhibition of the gasdermin family. Nature 2016, 535, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, W.T.; Wan, H.; Hu, L.; Chen, P.; Wang, X.; Huang, Z.; Yang, Z.H.; Zhong, C.Q.; Han, J. Gasdermin D is an executor of pyroptosis and required for interleukin-1beta secretion. Cell Res. 2015, 25, 1285–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Nagasu, H.; Murakami, T.; Hoang, H.; Broderick, L.; Hoffman, H.M.; Horng, T. Inflammasome activation leads to Caspase-1-dependent mitochondrial damage and block of mitophagy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 15514–15519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bergsbaken, T.; Fink, S.L.; den Hartigh, A.B.; Loomis, W.P.; Cookson, B.T. Coordinated host responses during pyroptosis: Caspase-1-dependent lysosome exocytosis and inflammatory cytokine maturation. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 2748–2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rogers, C.; Erkes, D.A.; Nardone, A.; Aplin, A.E.; Fernandes-Alnemri, T.; Alnemri, E.S. Gasdermin pores permeabilize mitochondria to augment caspase-3 activation during apoptosis and inflammasome activation. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, C.; Yang, J.; Zhou, B.; Yang, R.; Ramachandran, R.; Abbott, D.W.; Xiao, T.S. Crystal Structures of the Full-Length Murine and Human Gasdermin D Reveal Mechanisms of Autoinhibition, Lipid Binding, and Oligomerization. Immunity 2019, 51, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, S.; Zheng, J.; Yang, H.; Li, S.; Duan, S.; Shen, Y.; Ji, C.; Gan, J.; Xu, X.W.; Li, J. Structure insight of GSDMD reveals the basis of GSDMD autoinhibition in cell pyroptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci USA 2017, 114, 10642–10647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rogers, C.; Fernandes-Alnemri, T.; Mayes, L.; Alnemri, D.; Cingolani, G.; Alnemri, E.S. Cleavage of DFNA5 by caspase-3 during apoptosis mediates progression to secondary necrotic/pyroptotic cell death. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kayagaki, N.; Stowe, I.B.; Lee, B.L.; O’Rourke, K.; Anderson, K.; Warming, S.; Cuellar, T.; Haley, B.; Roose-Girma, M.; Phung, Q.T.; et al. Caspase-11 cleaves gasdermin D for non-canonical inflammasome signalling. Nature 2015, 526, 666–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aglietti, R.A.; Dueber, E.C. Recent Insights into the Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Pyroptosis and Gasdermin Family Functions. Trends Immunol. 2017, 38, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Ruan, J.; Pan, Y.; Magupalli, V.G.; Wu, H.; Lieberman, J. Inflammasome-activated gasdermin D causes pyroptosis by forming membrane pores. Nature 2016, 535, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liston, A.; Masters, S.L. Homeostasis-altering molecular processes as mechanisms of inflammasome activation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strowig, T.; Henao-Mejia, J.; Elinav, E.; Flavell, R. Inflammasomes in health and disease. Nature 2012, 481, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorgensen, I.; Zhang, Y.; Krantz, B.A.; Miao, E.A. Pyroptosis triggers pore-induced intracellular traps (PITs) that capture bacteria and lead to their clearance by efferocytosis. J. Exp. Med. 2016, 213, 2113–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Levy, M.; Thaiss, C.A.; Zeevi, D.; Dohnalova, L.; Zilberman-Schapira, G.; Mahdi, J.A.; David, E.; Savidor, A.; Korem, T.; Herzig, Y.; et al. Microbiota-Modulated Metabolites Shape the Intestinal Microenvironment by Regulating NLRP6 Inflammasome Signaling. Cell 2015, 163, 1428–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martinon, F.; Burns, K.; Tschopp, J. The inflammasome: A molecular platform triggering activation of inflammatory caspases and processing of proIL-beta. Mol. Cell 2002, 10, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broz, P.; Dixit, V.M. Inflammasomes: Mechanism of assembly, regulation and signalling. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zitvogel, L.; Kepp, O.; Galluzzi, L.; Kroemer, G. Inflammasomes in carcinogenesis and anticancer immune responses. Nat. Immunol. 2012, 13, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamkanfi, M. Emerging inflammasome effector mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, T.; Akira, S. Toll-like receptors and their crosstalk with other innate receptors in infection and immunity. Immunity 2011, 34, 637–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barton, G.M.; Medzhitov, R. Toll-like receptor signaling pathways. Science 2003, 300, 1524–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sollberger, G.; Strittmatter, G.E.; Garstkiewicz, M.; Sand, J.; Beer, H.D. Caspase-1: The inflammasome and beyond. Innate Immun. 2014, 20, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sborgi, L.; Ruhl, S.; Mulvihill, E.; Pipercevic, J.; Heilig, R.; Stahlberg, H.; Farady, C.J.; Muller, D.J.; Broz, P.; Hiller, S. GSDMD membrane pore formation constitutes the mechanism of pyroptotic cell death. EMBO J. 2016, 35, 1766–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergsbaken, T.; Fink, S.L.; Cookson, B.T. Pyroptosis: Host cell death and inflammation. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 7, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xia, S.; Zhang, Z.; Magupalli, V.G.; Pablo, J.L.; Dong, Y.; Vora, S.M.; Wang, L.; Fu, T.M.; Jacobson, M.P.; Greka, A.; et al. Gasdermin D pore structure reveals preferential release of mature interleukin-1. Nature 2021, 593, 607–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Gao, W.; Ding, J.; Li, P.; Hu, L.; Shao, F. Inflammatory caspases are innate immune receptors for intracellular LPS. Nature 2014, 514, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aglietti, R.A.; Estevez, A.; Gupta, A.; Ramirez, M.G.; Liu, P.S.; Kayagaki, N.; Ciferri, C.; Dixit, V.M.; Dueber, E.C. GsdmD p30 elicited by caspase-11 during pyroptosis forms pores in membranes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 7858–7863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baker, P.J.; Boucher, D.; Bierschenk, D.; Tebartz, C.; Whitney, P.G.; D’Silva, D.B.; Tanzer, M.C.; Monteleone, M.; Robertson, A.A.; Cooper, M.A.; et al. NLRP3 inflammasome activation downstream of cytoplasmic LPS recognition by both caspase-4 and caspase-5. Eur. J. Immunol. 2015, 45, 2918–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruhl, S.; Broz, P. Caspase-11 activates a canonical NLRP3 inflammasome by promoting K(+) efflux. Eur. J. Immunol. 2015, 45, 2927–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid-Burgk, J.L.; Gaidt, M.M.; Schmidt, T.; Ebert, T.S.; Bartok, E.; Hornung, V. Caspase-4 mediates non-canonical activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome in human myeloid cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2015, 45, 2911–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; He, Y.; Munoz-Planillo, R.; Liu, Q.; Nunez, G. Caspase-11 Requires the Pannexin-1 Channel and the Purinergic P2X7 Pore to Mediate Pyroptosis and Endotoxic Shock. Immunity 2015, 43, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, W.; Shi, X.; Ding, J.; Liu, W.; He, H.; Wang, K.; Shao, F. Chemotherapy drugs induce pyroptosis through caspase-3 cleavage of a gasdermin. Nature 2017, 547, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orning, P.; Weng, D.; Starheim, K.; Ratner, D.; Best, Z.; Lee, B.; Brooks, A.; Xia, S.; Wu, H.; Kelliher, M.A.; et al. Pathogen blockade of TAK1 triggers caspase-8-dependent cleavage of gasdermin D and cell death. Science 2018, 362, 1064–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sarhan, J.; Liu, B.C.; Muendlein, H.I.; Li, P.; Nilson, R.; Tang, A.Y.; Rongvaux, A.; Bunnell, S.C.; Shao, F.; Green, D.R.; et al. Caspase-8 induces cleavage of gasdermin D to elicit pyroptosis during Yersinia infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E10888–E10897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Fang, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, Z.; Liang, X.; Zhang, T.; Liu, M.; Zhou, N.; Lv, J.; Tang, K.; et al. Gasdermin E-mediated target cell pyroptosis by CAR T cells triggers cytokine release syndrome. Sci. Immunol. 2020, 5, eaax7969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, S.; Kong, Q.; Li, S.; Liu, X.; Junqueira, C.; Meza-Sosa, K.F.; Mok, T.; Ansara, J.; et al. Gasdermin E suppresses tumour growth by activating anti-tumour immunity. Nature 2020, 579, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; He, H.; Wang, K.; Shi, X.; Wang, Y.; Su, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, D.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Granzyme A from cytotoxic lymphocytes cleaves GSDMB to trigger pyroptosis in target cells. Science 2020, 368, 6494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Qian, J.; Zhang, P.; Li, H.; Shen, H.; Li, X.; Chen, G. Gasdermin D serves as a key executioner of pyroptosis in experimental cerebral ischemia and reperfusion model both in vivo and in vitro. J. Neurosci. Res. 2019, 97, 645–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Peng, M.; Xu, P.; Huang, F.; Xie, Y.; Li, J.; Hong, Y.; Guo, H.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, W. Low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR) regulates NLRP3-mediated neuronal pyroptosis following cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. J. Neuroinflammation 2020, 17, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Dong, Z.; Xiang, F.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Rao, J. Dendrobium Alkaloids Promote Neural Function After Cerebral Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury Through Inhibiting Pyroptosis Induced Neuronal Death in both In Vivo and In Vitro Models. Neurochem. Res. 2020, 45, 437–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, P.; Xie, J.; Qiu, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Xiu, X.; Li, L.; Tang, M. Hispidulin exhibits neuroprotective activities against cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury through suppressing NLRP3-mediated pyroptosis. Life Sci. 2019, 232, 116599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- She, Y.; Shao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Hao, Y.; Cai, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Deng, C.; Liu, X. Neuroprotective effect of glycosides in Buyang Huanwu Decoction on pyroptosis following cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 242, 112051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, M.; Chen, J.; Liu, T.; Dai, W.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, L.; Xie, Y. Protective Effects of Remimazolam on Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Rats by Inhibiting of NLRP3 Inflammasome-Dependent Pyroptosis. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2022, 16, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Wang, Y.; Gao, L. CHRFAM7A Overexpression Attenuates Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury via Inhibiting Microglia Pyroptosis Mediated by the NLRP3/Caspase-1 pathway. Inflammation 2021, 44, 1023–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Jia, L.; Zhan, K.; Wang, L.; Song, N.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Yang, Y.; Guan, L.; et al. Valproic acid attenuates global cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in gerbils via anti-pyroptosis pathways. Neurochem. Int. 2019, 124, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yao, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J. Downregulated XBP-1 Rescues Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury-Induced Pyroptosis via the NLRP3/Caspase-1/GSDMD Axis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2022, 2022, 8007078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Li, J.J.; Feng, Z.R.; Liu, H.Y.; Meng, A.G. MicroRNA-124 regulates cell pyroptosis during cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by regulating STAT3. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 20, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Hu, S.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, H.; Yang, Y.; Liu, C.; Ding, H. Ginsenoside Rd attenuates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by exerting an anti-pyroptotic effect via the miR-139-5p/FoxO1/Keap1/Nrf2 axis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 105, 108582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, M.; Liu, H.; Zhu, R.; He, H.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Liang, D.; Zeng, Q.; et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes attenuate cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury-induced neuroinflammation and pyroptosis by modulating microglia M1/M2 phenotypes. Exp. Neurol. 2021, 341, 113700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, H. Salvianolic Acids for Injection alleviates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by switching M1/M2 phenotypes and inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome/pyroptosis axis in microglia in vivo and in vitro. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 270, 113776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Lv, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, M.; Leng, Y. MircoRNA-29a in Astrocyte-derived Extracellular Vesicles Suppresses Brain Ischemia Reperfusion Injury via TP53INP1 and the NF-κB/NLRP3 Axis. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2021, 42, 1487–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, Z.; Lu, E.; Sheng, Q.; Zhao, Y. Berberine exerts neuroprotective activities against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury through up-regulating PPAR-γ to suppress NF-κB-mediated pyroptosis. Brain Res. Bull. 2021, 177, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Luo, L.; Fu, J.; He, J.; Chen, M.; He, Z.; Jia, J. Exercise-induced neuroprotection against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury is mediated via alleviating inflammasome-induced pyroptosis. Exp. Neurol. 2022, 349, 113952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Yao, Z.; Yang, L.; Xu, X.; Luo, M.; Dong, M.; Zhou, G. Mechanism of Electroacupuncture Against Cerebral Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury: Reducing Inflammatory Response and Cell Pyroptosis by Inhibiting NLRP3 and Caspase-1. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 822088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Wang, Q.; Li, J.; Guo, T.; Yu, D. Long non-coding RNA MEG3 promotes cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury through increasing pyroptosis by targeting miR-485/AIM2 axis. Exp. Neurol. 2020, 325, 113139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, S.; Gadi, I.; Al-Dabet, M.M.; Elwakiel, A.; Kohli, S.; Ghosh, S.; Manoharan, J.; Ranjan, S.; Bock, F.; Braun-Dullaeus, R.C.; et al. Cytoprotective activated protein C averts Nlrp3 inflammasome-induced ischemia-reperfusion injury via mTORC1 inhibition. Blood 2017, 130, 2664–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiu, Z.; Lei, S.; Zhao, B.; Wu, Y.; Su, W.; Liu, M.; Meng, Q.; Zhou, B.; Leng, Y.; Xia, Z. NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation-Mediated Pyroptosis Aggravates Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Diabetic Rats. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 9743280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, R.; Lu, S.; Luo, Y.; Wang, T.; Liang, H.; Zeng, J.; Liu, J.; Hu, H. Calpain silencing alleviates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury through the NLRP3/ASC/Caspase-1 axis in mice. Life Sci. 2019, 233, 116631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, B.; Chen, X.; Dai, S.; Han, J.; Liang, X.; Lin, S.; Cai, X.; Huang, Z.; Huang, W. Emodin alleviates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting gasdermin D-mediated pyroptosis in cardiomyocytes. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2019, 13, 975–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Liu, D.; Wang, L.; Wang, G.; Zhu, Y. Inhibiting MicroRNA-29a Protects Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Targeting SIRT1 and Suppressing Oxidative Stress and NLRP3-Mediated Pyroptosis Pathway. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2019, 372, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Y.; Li, Y.P.; Yin, Y.Q.; Hu, B.L.; Gao, H. Dexmedetomidine inhibits pyroptosis by down-regulating miR-29b in myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury in rats. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 86, 106768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Y.; Wang, S.; Chang, S.; Ren, D.; Shali, S.; Li, C.; Yang, H.; Huang, Z.; Ge, J. M2 macrophage-derived exosomes carry microRNA-148a to alleviate myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury via inhibiting TXNIP and the TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3 inflammasome signaling pathway. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2020, 142, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Xie, L.; Xiao, P.; Chen, X.; Kong, W.; Lou, Q.; Chen, F.; Lu, X. Cardiac fibroblasts secrete exosome microRNA to suppress cardiomyocyte pyroptosis in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2022, 477, 1249–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Sun, C.; Liu, Y.; Bai, F.; Tu, T.; Liu, Q. Exosomal miR-27b-3p Derived from Hypoxic Cardiac Microvascular Endothelial Cells Alleviates Rat Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury through Inhibiting Oxidative Stress-Induced Pyroptosis via Foxo1/GSDMD Signaling. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 8215842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Jin, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, L.; Ma, Y.; Lu, L.; Ma, J.; Ding, P.; Yang, X.; Liu, J.; et al. Exosomes Derived from Mesenchymal Stem Cells Protect the Myocardium Against Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury Through Inhibiting Pyroptosis. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2020, 14, 3765–3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, R.; Lu, S.; Luo, Y.; Zeng, J.; Liang, H.; Qin, D.; Wang, X.; Wang, T.; Pu, J.; Hu, H. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal microRNA-182-5p alleviates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by targeting GSDMD in mice. Cell Death Discov. 2022, 8, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Jiang, Y.; Yan, L.; Yin, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Fang, L.; Du, G. Aesculin suppresses the NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis via the Akt/GSK3β/NF-κB pathway to mitigate myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Phytomedicine 2021, 92, 153687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Lei, Z.; Rao, Z.; Yang, R.; Zheng, L.; Fan, Y.; Luan, F.; Zeng, N. Cardioprotective activity of ethyl acetate extract of Cinnamomi Ramulus against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats via inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation and pyroptosis. Phytomedicine 2021, 93, 153798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Lei, Y.S.; Meng, X.W.; Liu, H.Y.; Li, L.G.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.X.; Tao, W.H.; Peng, K.; Lin, J.; et al. Iguratimod Alleviates Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury Through Inhibiting Inflammatory Response Induced by Cardiac Fibroblast Pyroptosis via COX2/NLRP3 Signaling Pathway. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 746317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Guo, X.; Zhang, J.; Han, X.; Wang, H.; Du, F.; Zeng, X.; Guo, C. Protective Effects of the Soluble Receptor for Advanced Glycation End-Products on Pyroptosis during Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 9570971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Cai, W.; Du, R.; Li, H.; Wang, B.; Zhou, Y.; Shen, D.; Shen, H.; Lan, Y.; Chen, L.; et al. Sevoflurane Alleviates Myocardial Ischemia Reperfusion Injury by Inhibiting P2X7-NLRP3 Mediated Pyroptosis. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 768594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, G.; Liu, X.; Zhong, Y.; Mo, J.; Li, Z.; Li, D.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y. IP3R1 regulates Ca2+ transport and pyroptosis through the NLRP3/Caspase-1 pathway in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Cell Death Discov. 2021, 7, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luan, F.; Rao, Z.; Peng, L.; Lei, Z.; Zeng, J.; Peng, X.; Yang, R.; Liu, R.; Zeng, N. Cinnamic acid preserves against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury via suppression of NLRP3/Caspase-1/GSDMD signaling pathway. Phytomedicine 2022, 100, 154047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.; Luan, F.; Zhang, X.; Peng, L.; Li, B.; Peng, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, R.; Zeng, N. Piperazine ferulate protects against cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury in rat via the suppression of NLRP3 inflammasome activation and pyroptosis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 920, 174856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Lin, S.; Dai, S.; Han, J.; Shan, P.; Wang, W.; Huang, Z.; Ye, B.; Huang, W. Trimetazidine affects pyroptosis by targeting GSDMD in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Inflamm. Res. 2022, 71, 227–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhao, X.; Jiang, X.; He, L.; Wu, X.; Wang, J.; Chen, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhang, M. Tubastatin A Improves Post-Resuscitation Myocardial Dysfunction by Inhibiting NLRP3-Mediated Pyroptosis Through Enhancing Transcription Factor EB Signaling. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2022, 11, e024205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yang, D.H.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, F.; Gao, F.; Sun, J.; Shi, G. Geniposide suppresses NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis via the AMPK signaling pathway to mitigate myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Chin. Med. 2022, 17, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhao, C.; Zhu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, G.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Wu, N.; Ma, C. Sweroside Protects Against Myocardial Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and Pyroptosis Partially via Modulation of the Keap1/Nrf2 Axis. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 650368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; He, F.; Cheng, C.; Xu, B.; Sheng, J. Uric acid aggravates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury via ROS/NLRP3 pyroptosis pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 133, 110990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Dong, X.; Hu, D.; Chen, L.; Luo, Y. Aquaporin 4 inhibition alleviates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury by restraining cardiomyocyte pyroptosis. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 9021–9030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, X.; Hang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Li, D.; Shen, F.; Guan, P.; Dong, J.; Shi, L.; Hu, W. CircRNA circ-NNT mediates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury through activating pyroptosis by sponging miR-33a-5p and regulating USP46 expression. Cell Death Discov. 2021, 7, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Li, S.; Wang, F. Mechanism of METTL3-Mediated m6A Modification in Cardiomyocyte Pyroptosis and Myocardial Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2022, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yao, F.; Zhang, J.; Ji, Z.; Li, K.; Zhan, J.; Tong, Y.; Lin, L.; He, Y. Ischemia-reperfusion induces renal tubule pyroptosis via the CHOP-caspase-11 pathway. Am. J. Physiol.-Ren. Physiol. 2014, 306, F75–F84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Chen, Z.; Weng, X.; Chen, H.; Du, Y.; Diao, C.; Liu, X.; Wang, L. Enhancer of zeste homolog 2 modulates oxidative stress—mediated pyroptosis in vitro and in a mouse kidney ischemia—reperfusion injury model. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 835–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tajima, T.; Yoshifuji, A.; Matsui, A.; Itoh, T.; Uchiyama, K.; Kanda, T.; Tokuyama, H.; Wakino, S.; Itoh, H. beta-hydroxybutyrate attenuates renal ischemia-reperfusion injury through its anti-pyroptotic effects. Kidney Int. 2019, 95, 1120–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Diao, C.; Chen, Z.; Qiu, T.; Liu, H.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; Wu, J.; Wang, L. Inhibition of PRMT5 Attenuates Oxidative Stress-Induced Pyroptosis via Activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 Signal Pathway in a Mouse Model of Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 2345658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Lu, R.; Li, H.; Li, J.; Fu, H.; Cao, Y.; Fang, G.; Liu, B.; Wu, J.; et al. Andrade-Oliveira Salvianolic Acid B Modulates Caspase-1—Mediated Pyroptosis in Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury via Nrf2 Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 541426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.; Zhao, H.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Su, Q.; Zhao, F.; Wang, R. Tisp40 Induces Tubular Epithelial Cell GSDMD-Mediated Pyroptosis in Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury via NF-κB Signaling. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Liu, D.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, T.; Ma, J.; Wang, D.; Li, J.; Qian, W.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, D.; et al. Cholecalciferol pretreatment ameliorates ischemia/reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury through inhibiting ROS production, NF-κB pathway and pyroptosis. Acta Histochem. 2022, 124, 151875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, H.; Su, Q.; Qi, H.; Deng, J.; Xiao, C. Identification of MicroRNA-92a-3p as an Essential Regulator of Tubular Epithelial Cell Pyroptosis by Targeting Nrf1 via HO-1. Front. Genet. 2021, 11, 616947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Ma, M.; Feng, X.; Song, T.; Wei, Q.; Lin, T. Overexpression of aquaporin 2 in renal tubular epithelial cells alleviates pyroptosis. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2021, 10, 2340–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonnus, W.; Maremonti, F.; Belavgeni, A.; Latk, M.; Kusunoki, Y.; Brucker, A.; von Massenhausen, A.; Meyer, C.; Locke, S.; Gembardt, F.; et al. Gasdermin D-deficient mice are hypersensitive to acute kidney injury. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Zhao, F.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Shi, P.; Sun, X.; Zhang, F.; Tong, L. DHA attenuates hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury by inhibiting pyroptosis and activating PI3K/Akt pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 835, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Yu, S.; Wang, J.; Li, W.; Li, H.; Bai, C.; Sheng, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, C.; Liu, J.; et al. N-acetyl-L-tryptophan attenuates hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury via regulating TLR4/NLRP3 signaling pathway in rats. PeerJ 2021, 9, e11909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagenson, A.M.; Xu, K.; Saaoud, F.; Nanayakkara, G.; Jhala, N.C.; Liu, L.; Drummer, C.; Sun, Y.; Lau, K.N.; Di Carlo, A.; et al. Liver Ischemia Reperfusion Injury, Enhanced by Trained Immunity, Is Attenuated in Caspase 1/Caspase 11 Double Gene Knockout Mice. Pathogens 2020, 9, 879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, S.; Ma, M.; Fei, X.; Zhang, Y.; Gong, F.; Fang, M. Glycyrrhizin attenuates hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury by suppressing HMGB1-dependent GSDMD-mediated kupffer cells pyroptosis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 68, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zheng, W.; Bai, Y.; Li, Y.; Xin, Y.; Wang, J.; Chang, Y.; Zhang, L. Carbon Monoxide–Releasing Molecule-3 Alleviates Kupffer Cell Pyroptosis Induced by Hemorrhagic Shock and Resuscitation via sGC-cGMP Signal Pathway. Inflammation 2021, 44, 1330–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolachala, V.L.; Lopez, C.; Shen, M.; Shayakhmetov, D.; Gupta, N.A. Ischemia reperfusion injury induces pyroptosis and mediates injury in steatotic liver thorough Caspase 1 activation. Apoptosis 2021, 26, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, C.; Gong, J.; Xu, X. STING Induces Liver Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Promoting Calcium-Dependent Caspase 1-GSDMD Processing in Macrophages. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 8123157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sisi, A.E.E.; Sokar, S.S.; Shebl, A.M.; Mohamed, D.Z.; Abu-Risha, S.E. Octreotide and melatonin alleviate inflammasome-induced pyroptosis through inhibition of TLR4-NF-κB-NLRP3 pathway in hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2021, 410, 115340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Y.; Cui, R.; Wang, C.; Feng, Y.; Li, Z.; Tong, Y.; Qu, K.; Liu, C.; Zhang, J. Metformin protects against intestinal ischemia-reperfusion injury and cell pyroptosis via TXNIP-NLRP3-GSDMD pathway. Redox Biol. 2020, 32, 101534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, P.; Su, W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Deng, C.; Li, J.; Jiang, N.; Huang, S.; Long, E.; Zhuo, Y. LncRNA H19 initiates microglial pyroptosis and neuronal death in retinal ischemia/reperfusion injury. Cell Death Differ. 2020, 27, 176–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, P.; Guo, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, Q.; Qiao, X.; Lu, Y.; Mei, P.; Zheng, Z.; Li, J. Monocytes promote pyroptosis of endothelial cells during lung ischemia-reperfusion via IL-1R/NF-κB/NLRP3 signaling. Life Sci. 2021, 276, 119402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, P.; Song, N.C.; Zheng, Z.K.; Li, Y.Q.; Li, J.S. MMP2 and MMP9 contribute to lung ischemia-reperfusion injury via promoting pyroptosis in mice. BMC Pulm. Med. 2022, 22, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, X. Ferroptosis as a novel therapeutic target for cardiovascular disease. Theranostics 2021, 11, 3052–3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, T.; Dewitz, C.; Schmitz, J.; Schroder, A.S.; Brasen, J.H.; Stockwell, B.R.; Murphy, J.M.; Kunzendorf, U.; Krautwald, S. Necroptosis and ferroptosis are alternative cell death pathways that operate in acute kidney failure. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2017, 74, 3631–3645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, K.; Wu, B.; Lin, Z.; Zhu, C.; Xue, Y.; Ji, K. Shexiang Baoxin Pill attenuates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by activating autophagy via modulating the ceRNA-Map3k8 pathway. Phytomedicine 2022, 104, 154336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malireddi, R.; Gurung, P.; Kesavardhana, S.; Samir, P.; Burton, A.; Mummareddy, H.; Vogel, P.; Pelletier, S.; Burgula, S.; Kanneganti, T.D. Innate immune priming in the absence of TAK1 drives RIPK1 kinase activity-independent pyroptosis, apoptosis, necroptosis, and inflammatory disease. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217, e20191644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malireddi, R.; Kesavardhana, S.; Kanneganti, T.D. ZBP1 and TAK1: Master Regulators of NLRP3 Inflammasome/Pyroptosis, Apoptosis, and Necroptosis (PAN-optosis). Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.T.; Zhao, W.J.; Hu, X.M.; Ban, X.X.; Ning, W.Y.; Wan, H.; Zhang, Q.; Xiong, K. PANoptosis-like cell death in ischemia/reperfusion injury of retinal neurons. Neural Regen. Res. 2023, 18, 357–363. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, W.T.; Yang, Y.D.; Hu, X.M.; Ning, W.Y.; Liao, L.S.; Lu, S.; Zhao, W.J.; Zhang, Q.; Xiong, K. Do pyroptosis, apoptosis, and necroptosis (PANoptosis) exist in cerebral ischemia? Evidence from cell and rodent studies. Neural Regen. Res. 2022, 17, 1761–1768. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, M.; Yang, Y.; Li, R.; Xu, J.; Yang, C.; Li, Y.; Chen, H.; Liu, S.; et al. Inhibition of GSDMD Activates Poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation and Promotes Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 1115749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, Y.; Xu, X.; Chi, F.; Cong, N. Pyroptosis: A Newly Discovered Therapeutic Target for Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1625. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12111625
Zheng Y, Xu X, Chi F, Cong N. Pyroptosis: A Newly Discovered Therapeutic Target for Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Biomolecules. 2022; 12(11):1625. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12111625
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Yu, Xinda Xu, Fanglu Chi, and Ning Cong. 2022. "Pyroptosis: A Newly Discovered Therapeutic Target for Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury" Biomolecules 12, no. 11: 1625. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12111625
APA StyleZheng, Y., Xu, X., Chi, F., & Cong, N. (2022). Pyroptosis: A Newly Discovered Therapeutic Target for Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Biomolecules, 12(11), 1625. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12111625





