Synthesis and Structure–Activity Relationships of Novel Non-Steroidal CYP17A1 Inhibitors as Potential Prostate Cancer Agents
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis
2.2. Assays
2.3. Molecular Modeling
3. Results and Discussion
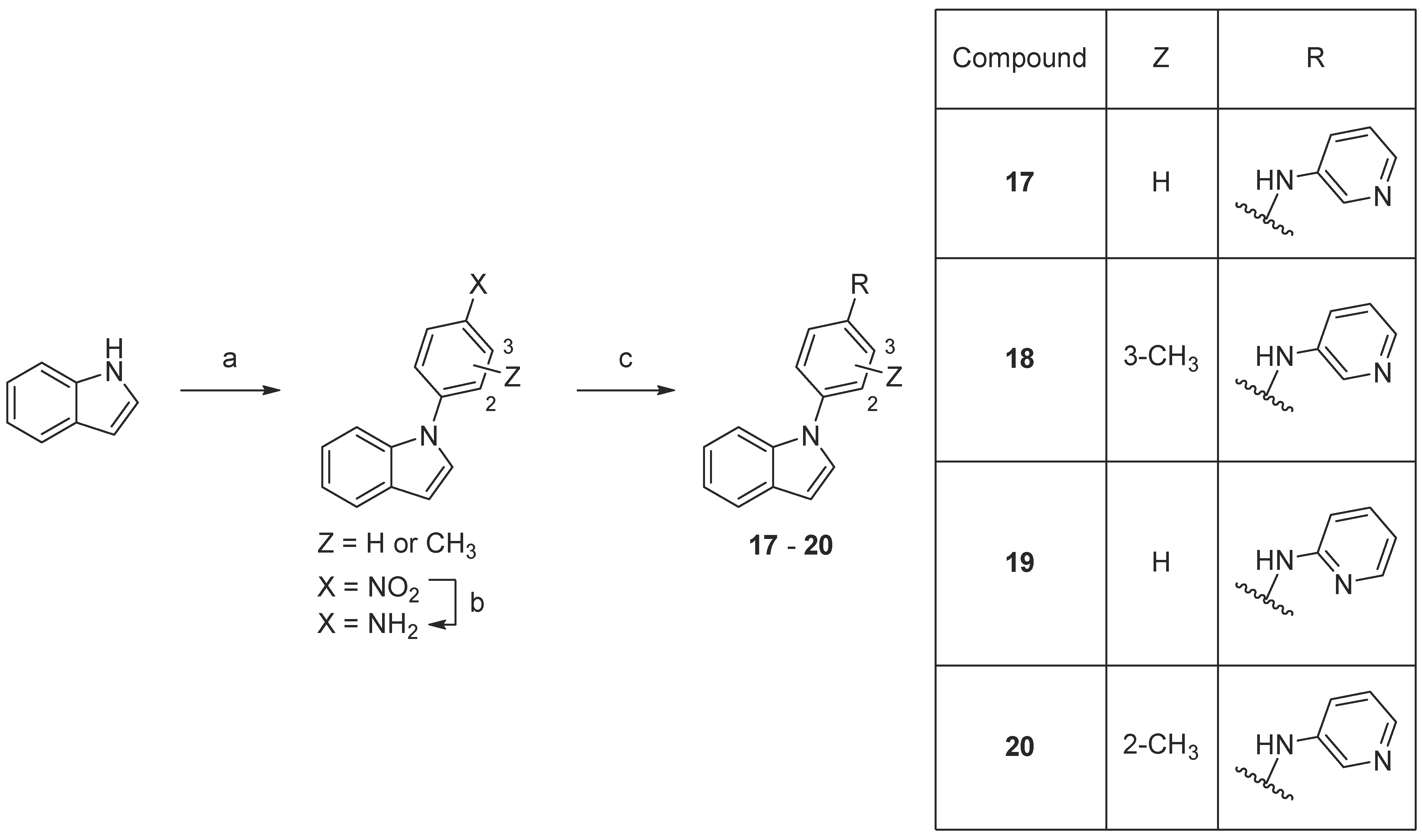
3.1. Synthesis
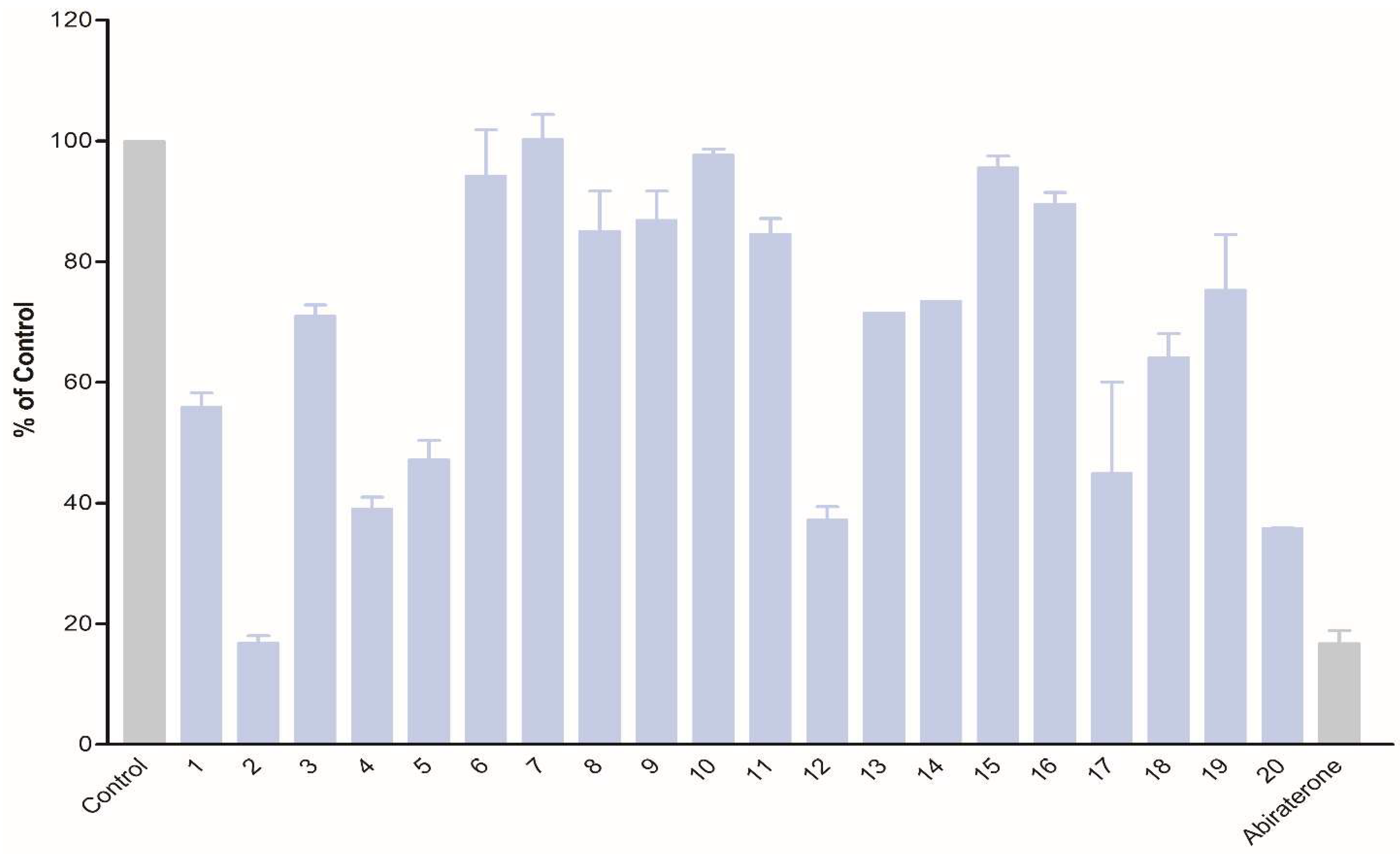
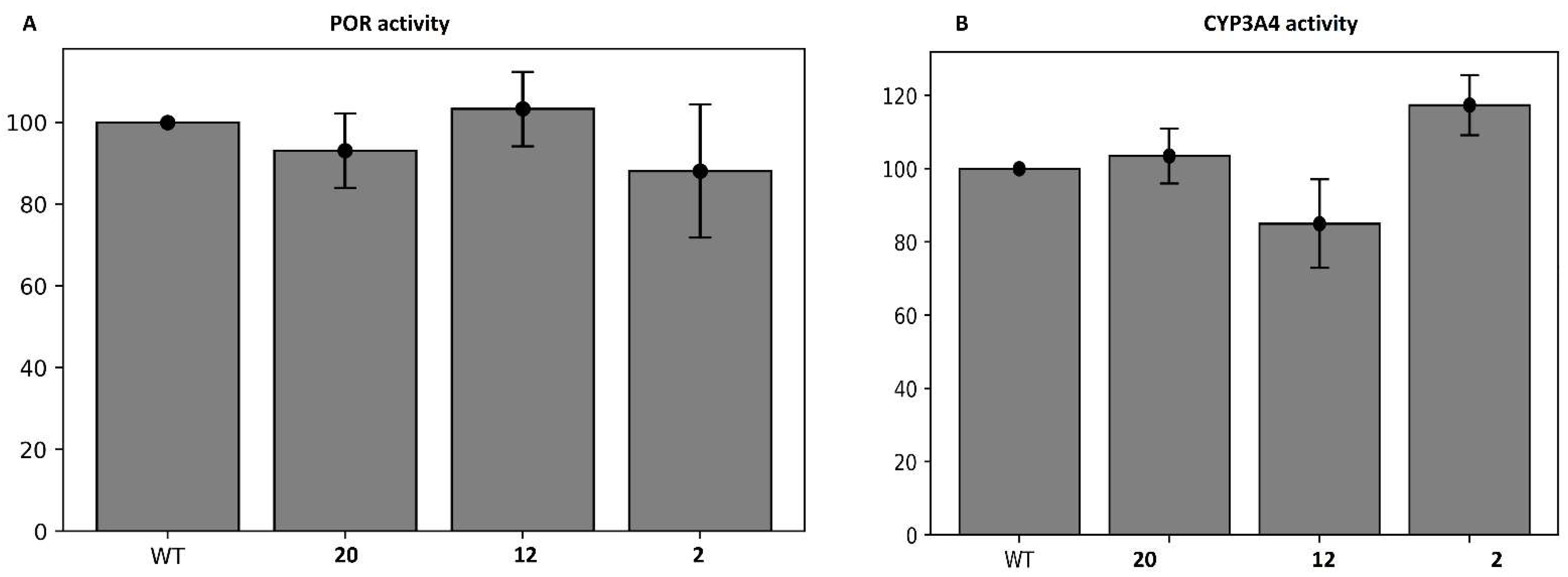
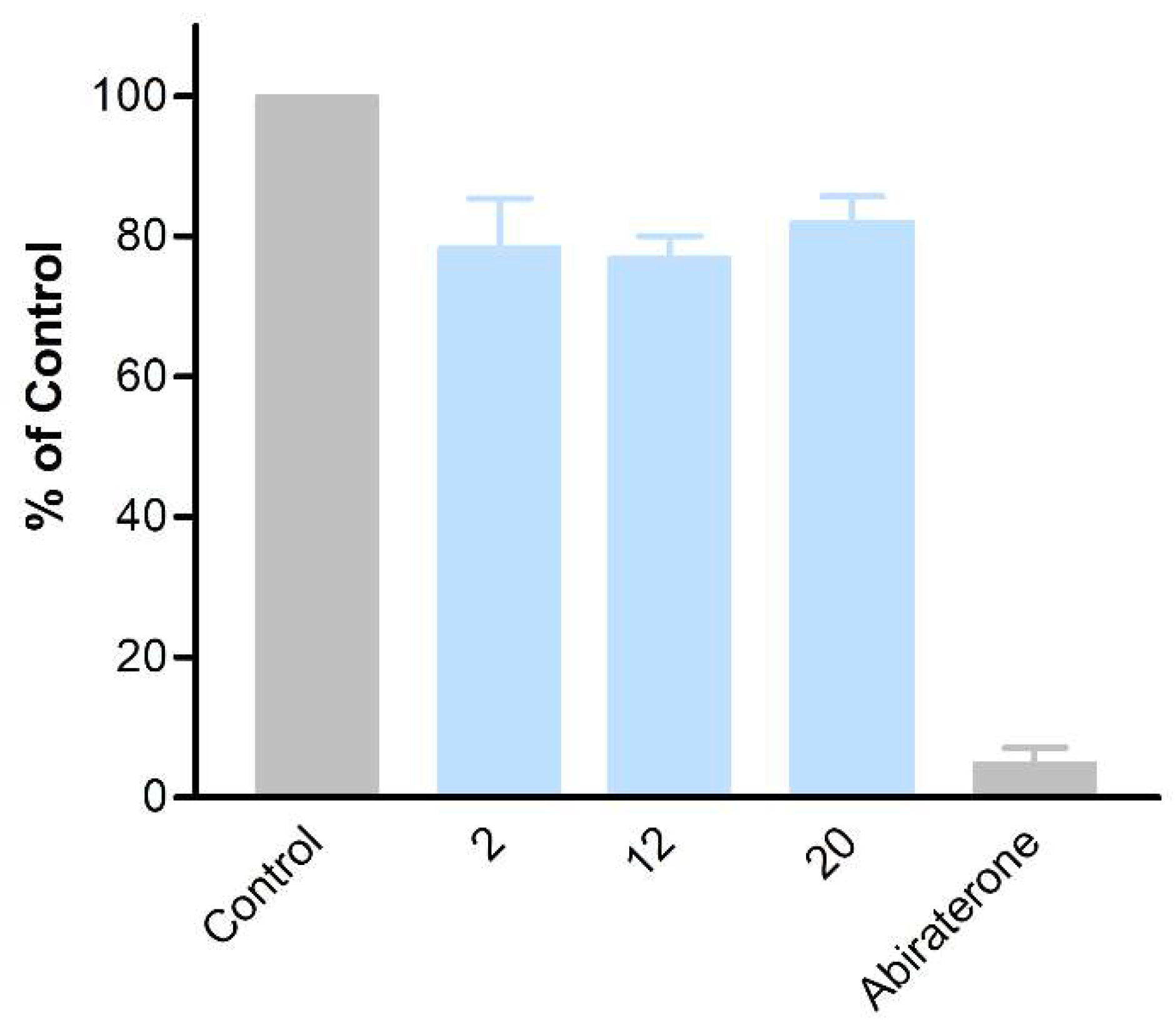
3.2. Biological Evaluation
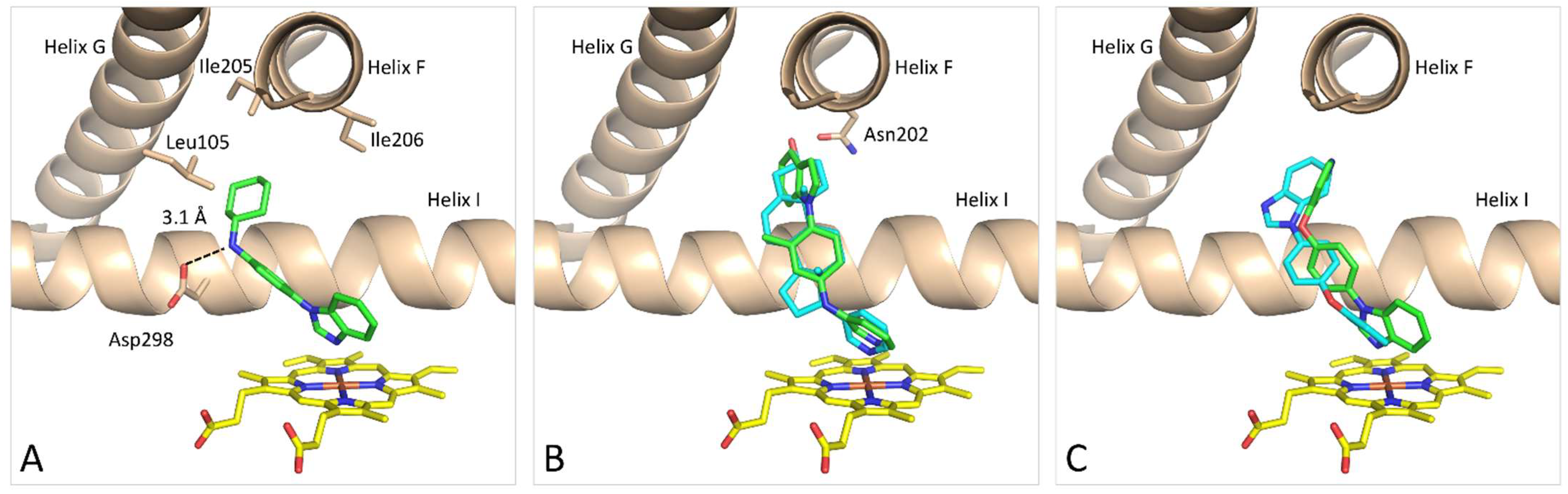
3.3. Molecular Modeling
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velho, P.I.; Anna, P.T.S.; da Silva, R.F.P.; Ferreira, R.D.P.; Venero, F.C. The development of apalutamide for the treatment of prostate cancer. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2021, 16, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risdon, E.N.; Chau, C.H.; Price, D.K.; Sartor, O.; Figg, W.D. PARP Inhibitors and Prostate Cancer: To Infinity and Beyond BRCA. Oncologist 2021, 26, e115–e129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rana, Z.; Diermeier, S.; Hanif, M.; Rosengren, R.J. Understanding Failure and Improving Treatment Using HDAC Inhibitors for Prostate Cancer. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rathi, N.; McFarland, T.R.; Nussenzveig, R.; Agarwal, N.; Swami, U. Evolving Role of Immunotherapy in Metastatic Castration Refractory Prostate Cancer. Drugs 2021, 81, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Sullivan, S.E.; Kaczocha, M. FABP5 as a novel molecular target in prostate cancer. Drug Discov. Today 2020, 25, 2056–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeVore, N.M.; Scott, E.E. Structures of cytochrome P450 17A1 with prostate cancer drugs abiraterone and TOK-001. Nature 2012, 482, 116–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nakajin, S.; Hall, P.F.; Onoda, M. Testicular microsomal cytochrome P-450 for C21 steroid side chain cleavage. Spectral and binding studies. J. Biol. Chem. 1981, 256, 6134–6139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, B.C.; Picado-Leonard, J.; Haniu, M.; Bienkowski, M.; Hall, P.F.; Shively, J.E.; Miller, W.L. Cytochrome P450c17 (steroid 17 alpha-hydroxylase/17,20 lyase): Cloning of human adrenal and testis cDNAs indicates the same gene is expressed in both tissues. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakajin, S.; Shively, J.E.; Yuan, P.M.; Hall, P.F. Microsomal cytochrome P-450 from neonatal pig testis: Two enzymatic activities (17 alpha-hydroxylase and c17,20-lyase) associated with one protein. Biochemistry 1981, 20, 4037–4042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Hu, Q. CYP17 inhibitors—abiraterone, C17,20-lyase inhibitors and multi-targeting agents. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2013, 11, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, I.M.; Abbott, D.H. The hunt for a selective 17,20 lyase inhibitor; learning lessons from nature. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 163, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flück, C.E.; Meyer-Boni, M.; Pandey, A.V.; Kempna, P.; Miller, W.L.; Schoenle, E.J.; Biason-Lauber, A. Why boys will be boys: Two pathways of fetal testicular androgen biosynthesis are needed for male sexual differentiation. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2011, 89, 201–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wróbel, T.M.; Rogova, O.; Andersen, K.L.; Yadav, R.; Brixius-Anderko, S.; Scott, E.E.; Olsen, L.; Jørgensen, F.S.; Björkling, F. Discovery of Novel Non-Steroidal Cytochrome P450 17A1 Inhibitors as Potential Prostate Cancer Agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parween, S.; Fernandez-Cancio, M.; Benito-Sanz, S.; Camats, N.; Velazquez, M.N.R.; Lopez-Siguero, J.P.; Udhane, S.S.; Kagawa, N.; Fluck, C.E.; Audi, L.; et al. Molecular Basis of CYP19A1 Deficiency in a 46,XX Patient With R550W Mutation in POR: Expanding the PORD Phenotype. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 105, e1272–e1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Udhane, S.S.; Dick, B.; Hu, Q.; Hartmann, R.W.; Pandey, A.V. Specificity of anti-prostate cancer CYP17A1 inhibitors on androgen biosynthesis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 477, 1005–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.H.; Rodriguez, H.; Ohno, S.; Miller, W.L. Serine phosphorylation of human P450c17 increases 17,20-lyase activity: Implications for adrenarche and the polycystic ovary syndrome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 10619–10623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pandey, A.V.; Miller, W.L. Regulation of 17,20 lyase activity by cytochrome b5 and by serine phosphorylation of P450c17. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 13265–13271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lephart, E.D.; Simpson, E.R. Assay of aromatase activity. Methods Enzymol. 1991, 206, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Flück, C.E.; Mullis, P.E.; Pandey, A.V. Reduction in hepatic drug metabolizing CYP3A4 activities caused by P450 oxidoreductase mutations identified in patients with disordered steroid metabolism. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 401, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udhane, S.S.; Parween, S.; Kagawa, N.; Pandey, A.V. Altered CYP19A1 and CYP3A4 Activities Due to Mutations A115V, T142A, Q153R and P284L in the Human P450 Oxidoreductase. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jensen, S.B.; Thodberg, S.; Parween, S.; Moses, M.E.; Hansen, C.C.; Thomsen, J.; Sletfjerding, M.B.; Knudsen, C.; Del Giudice, R.; Lund, P.M.; et al. Biased cytochrome P450-mediated metabolism via small-molecule ligands binding P450 oxidoreductase. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sastry, G.M.; Adzhigirey, M.; Day, T.; Annabhimoju, R.; Sherman, W. Protein and ligand preparation: Parameters, protocols, and influence on virtual screening enrichments. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2013, 27, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berman, H.M.; Battistuz, T.; Bhat, T.N.; Bluhm, W.F.; Bourne, P.E.; Burkhardt, K.; Feng, Z.; Gilliland, G.L.; Iype, L.; Jain, S.; et al. The Protein Data Bank. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2002, 58, 899–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, G.; Willett, P.; Glen, R.C.; Leach, A.R.; Taylor, R. Development and validation of a genetic algorithm for flexible docking. J. Mol. Biol. 1997, 267, 727–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Verdonk, M.L.; Cole, J.C.; Hartshorn, M.J.; Murray, C.W.; Taylor, R.D. Improved protein-ligand docking using GOLD. Proteins 2003, 52, 609–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirton, S.B.; Murray, C.W.; Verdonk, M.L.; Taylor, R.D. Prediction of binding modes for ligands in the cytochromes P450 and other heme-containing proteins. Proteins 2005, 58, 836–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Wu, C.; Ghoreishi, D.; Chen, W.; Wang, L.; Damm, W.; Ross, G.A.; Dahlgren, M.K.; Russell, E.; Von Bargen, C.D.; et al. OPLS4: Improving Force Field Accuracy on Challenging Regimes of Chemical Space. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2021, 17, 4291–4300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, J.B. The Chemistry of the Benzimidazoles. Chem. Rev. 1951, 48, 397–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovering, F.; Bikker, J.; Humblet, C. Escape from Flatland: Increasing Saturation as an Approach to Improving Clinical Success. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 6752–6756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, C.S.; Leung, S.S.F.; Tirado-Rives, J.; Jorgensen, W.L. Methyl Effects on Protein–Ligand Binding. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 4489–4500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barreiro, E.J.; Kümmerle, A.E.; Fraga, C.A.M. The Methylation Effect in Medicinal Chemistry. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 5215–5246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, K.; Zanger, U.M. Pharmacogenomics of Cytochrome P450 3A4: Recent Progress Toward the “Missing Heritability” Problem. Front. Genet. 2013, 4, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Velazquez, M.N.R.; Parween, S.; Udhane, S.S.; Pandey, A.V. Variability in human drug metabolizing cytochrome P450 CYP2C9, CYP2C19 and CYP3A5 activities caused by genetic variations in cytochrome P450 oxidoreductase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 515, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, A.V.; Flück, C.E. NADPH P450 oxidoreductase: Structure, function, and pathology of diseases. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 138, 229–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, D.; You, Z. In vitro and in vivo model systems used in prostate cancer research. J. Biol. Methods 2015, 2, e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hafner, M.; Niepel, M.; Chung, M.; Sorger, P.K. Growth rate inhibition metrics correct for confounders in measuring sensitivity to cancer drugs. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petrunak, E.M.; DeVore, N.M.; Porubsky, P.R.; Scott, E.E. Structures of Human Steroidogenic Cytochrome P450 17A1 with Substrates. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 32952–32964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamaoka, M.; Hara, T.; Hitaka, T.; Kaku, T.; Takeuchi, T.; Takahashi, J.; Asahi, S.; Miki, H.; Tasaka, A.; Kusaka, M. Orteronel (TAK-700), a novel non-steroidal 17,20-lyase inhibitor: Effects on steroid synthesis in human and monkey adrenal cells and serum steroid levels in cynomolgus monkeys. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2012, 129, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrunak, E.M.; Rogers, S.A.; Aubé, J.; Scott, E.E. Structural and Functional Evaluation of Clinically Relevant Inhibitors of Steroidogenic Cytochrome P450 17A1. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2017, 45, 635–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fehl, C.; Vogt, C.D.; Yadav, R.; Li, K.; Scott, E.E.; Aubé, J. Structure-Based Design of Inhibitors with Improved Selectivity for Steroidogenic Cytochrome P450 17A1 over Cytochrome P450 21A2. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 4946–4960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonomo, S.; Hansen, C.H.; Petrunak, E.M.; Scott, E.E.; Styrishave, B.; Jørgensen, F.S.; Olsen, L. Promising Tools in Prostate Cancer Research: Selective Non-Steroidal Cytochrome P450 17A1 Inhibitors. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]









Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wróbel, T.M.; Rogova, O.; Sharma, K.; Rojas Velazquez, M.N.; Pandey, A.V.; Jørgensen, F.S.; Arendrup, F.S.; Andersen, K.L.; Björkling, F. Synthesis and Structure–Activity Relationships of Novel Non-Steroidal CYP17A1 Inhibitors as Potential Prostate Cancer Agents. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12020165
Wróbel TM, Rogova O, Sharma K, Rojas Velazquez MN, Pandey AV, Jørgensen FS, Arendrup FS, Andersen KL, Björkling F. Synthesis and Structure–Activity Relationships of Novel Non-Steroidal CYP17A1 Inhibitors as Potential Prostate Cancer Agents. Biomolecules. 2022; 12(2):165. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12020165
Chicago/Turabian StyleWróbel, Tomasz M., Oksana Rogova, Katyayani Sharma, Maria Natalia Rojas Velazquez, Amit V. Pandey, Flemming Steen Jørgensen, Frederic S. Arendrup, Kasper L. Andersen, and Fredrik Björkling. 2022. "Synthesis and Structure–Activity Relationships of Novel Non-Steroidal CYP17A1 Inhibitors as Potential Prostate Cancer Agents" Biomolecules 12, no. 2: 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12020165
APA StyleWróbel, T. M., Rogova, O., Sharma, K., Rojas Velazquez, M. N., Pandey, A. V., Jørgensen, F. S., Arendrup, F. S., Andersen, K. L., & Björkling, F. (2022). Synthesis and Structure–Activity Relationships of Novel Non-Steroidal CYP17A1 Inhibitors as Potential Prostate Cancer Agents. Biomolecules, 12(2), 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12020165







