Update on CSF Biomarkers in Parkinson’s Disease
Abstract
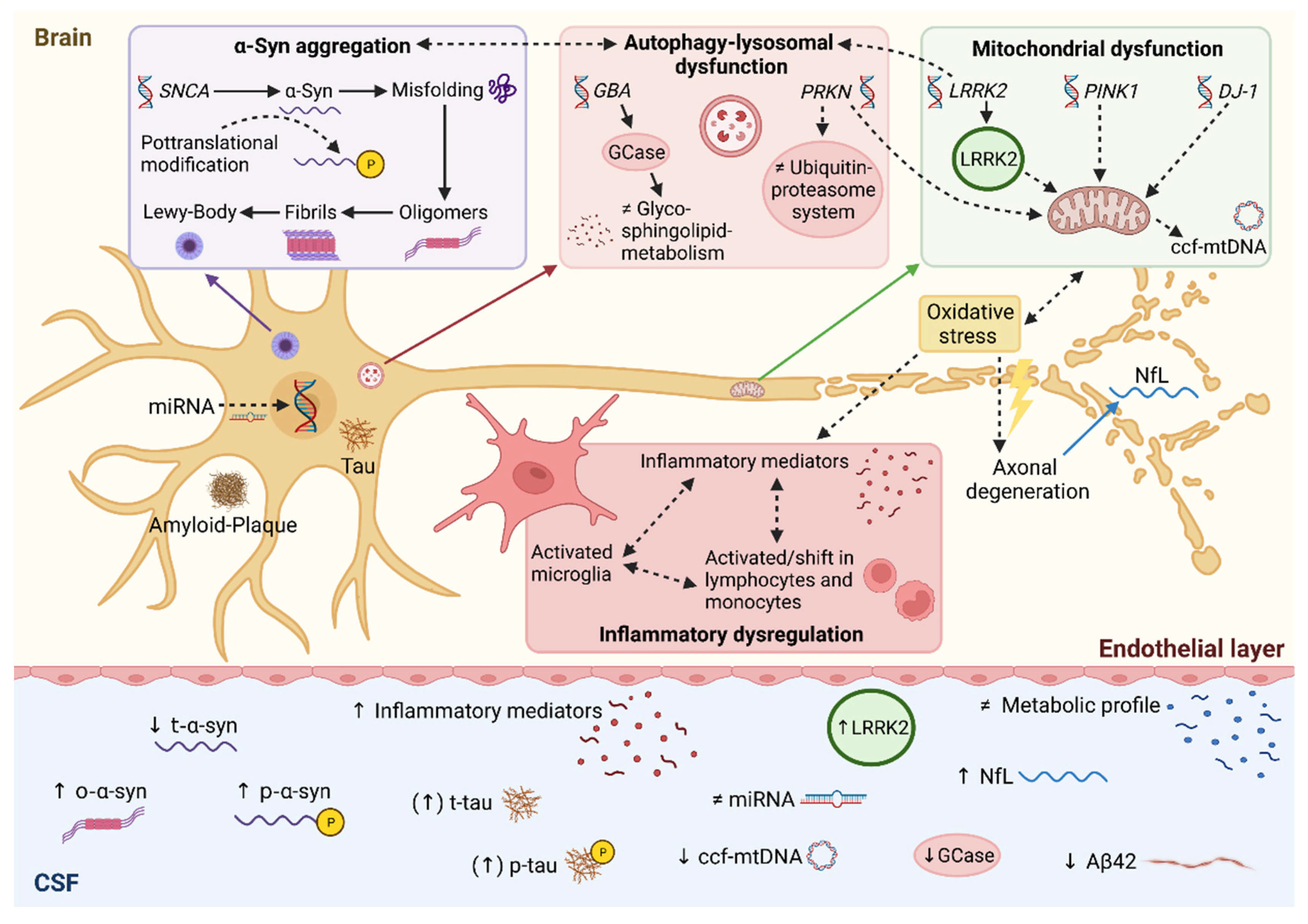
:1. Introduction
2. Alpha-Synuclein
3. Amyloid-Beta and Tau Protein
4. Neurofilament Light Chain
5. Lysosomal Biomarkers
6. Inflammatory Biomarkers
7. Metabolomics
8. Genetic Perspective
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feigin, V.L.; Abajobir, A.A.; Abate, K.H.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdulle, A.M.; Abera, S.F.; Abyu, G.Y.; Ahmed, M.B.; Aichour, A.N.; Aichour, I.; et al. GBD 2015 Neurological Disorders Collaborator Group. Global, regional, and national burden of neurological disorders during 1990–2015: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet Neurol. 2017, 16, 877–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rizzo, G.; Copetti, M.; Arcuti, S.; Martino, D.; Fontana, A.; Logroscino, G. Accuracy of clinical diagnosis of Parkinson disease. Neurology 2016, 86, 566–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.-C.; Ulane, C.M.; Burke, R. Clinical progression in Parkinson disease and the neurobiology of axons. Ann. Neurol. 2010, 67, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahlknecht, P.; Seppi, K.; Poewe, W. The Concept of Prodromal Parkinson’s Disease. J. Park. Dis. 2015, 5, 681–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reiber, H. Dynamics of brain-derived proteins in cerebrospinal fluid. Clin. Chim. Acta 2001, 310, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prakash, N.; Caspell-Garcia, C.; Coffey, C.; Siderowf, A.; Tanner, C.M.; Kieburtz, K.; Mollenhauer, B.; Galasko, D.; Merchant, K.; Foroud, T.; et al. Feasibility and safety of lumbar puncture in the Parkinson’s disease research participants: Parkinson’s Progression Marker Initiative (PPMI). Park. Relat. Disord. 2019, 62, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meade, R.M.; Fairlie, D.P.; Mason, J.M. Alpha-synuclein structure and Parkinson’s disease—Lessons and emerging principles. Mol. Neurodegener. 2019, 14, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Førland, M.G.; Tysnes, O.; Aarsland, D.; Maple-Grødem, J.; Pedersen, K.F.; Alves, G.; Lange, J. The value of cerebrospinal fluid α-synuclein and the tau/α-synuclein ratio for diagnosis of neurodegenerative disorders with Lewy pathology. Eur. J. Neurol. 2019, 27, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shim, K.H.; Kang, M.J.; Suh, J.W.; Pyun, J.-M.; Ryoo, N.; Park, Y.H.; Youn, Y.C.; Jang, J.-W.; Jeong, J.H.; Park, K.W.; et al. CSF total tau/α-synuclein ratio improved the diagnostic performance for Alzheimer’s disease as an indicator of tau phosphorylation. Alzheimer Res. Ther. 2020, 12, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahine, L.M.; Beach, T.G.; Brumm, M.C.; Adler, C.H.; Coffey, C.S.; Mosovsky, S.; Caspell-Garcia, C.; Serrano, G.E.; Munoz, D.G.; White, C.L.; et al. In vivo distribution of α-synuclein in multiple tissues and biofluids in Parkinson disease. Neurology 2020, 95, e1267–e1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, S.; Yuan, Y.; Li, J.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, K. Relationship between the plasma levels of neurodegenerative proteins and motor subtypes of Parkinson’s disease. J. Neural Transm. 2016, 124, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-W.; Yang, S.-Y.; Yang, C.-C.; Chang, C.-W.; Wu, Y.-R. Plasma and Serum Alpha-Synuclein as a Biomarker of Diagnosis in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Neurol. 2020, 10, 1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fayyad, M.; Salim, S.; Majbour, N.; Erskine, D.; Stoops, E.; Mollenhauer, B.; El-Agnaf, O.M.A. Parkinson’s disease biomarkers based on α-synuclein. J. Neurochem. 2019, 150, 626–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parnetti, L.; Gaetani, L.; Eusebi, P.; Paciotti, S.; Hansson, O.; El-Agnaf, O.; Mollenhauer, B.; Blennow, K.; Calabresi, P. CSF and blood biomarkers for Parkinson’s disease. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 573–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, I.; Kruse, N.; Gera, R.G.; Kremer, T.; Cedarbaum, J.; Barbour, R.; Zago, W.; Schade, S.; Otte, B.; Bartl, M.; et al. Systematic Assessment of 10 Biomarker Candidates Focusing on α-Synuclein-Related Disorders. Mov. Disord. 2021, 36, 2874–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foulds, P.G.; Yokota, O.; Thurston, A.; Davidson, Y.; Ahmed, Z.; Holton, J.; Thompson, J.C.; Akiyama, H.; Arai, T.; Hasegawa, M.; et al. Post mortem cerebrospinal fluid α-synuclein levels are raised in multiple system atrophy and distinguish this from the other α-synucleinopathies, Parkinson’s disease and Dementia with Lewy bodies. Neurobiol. Dis. 2012, 45, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twohig, D.; Rodriguez-Vieitez, E.; Sando, S.B.; Berge, G.; Lauridsen, C.; Møller, I.; Grøntvedt, G.R.; Bråthen, G.; Patra, K.; Bu, G.; et al. The relevance of cerebrospinal fluid α-synuclein levels to sporadic and familial Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2018, 6, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vergallo, A.; Bun, R.; Toschi, N.; Baldacci, F.; Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K.; Cavedo, E.; Lamari, F.; Habert, M.O.; Dubois, B.; et al. Association of cerebrospinal fluid α-synuclein with total and phospho-tau 181 protein concentrations and brain amyloid load in cognitively normal subjective memory complainers stratified by Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2018, 14, 1623–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parkkinen, L.; Pirttilä, T.; Tervahauta, M.; Alafuzoff, I. Widespread and abundant alpha-synuclein pathology in a neurologically unimpaired subject. Neuropathology 2005, 25, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majbour, N.; Msc, N.N.V.; Eusebi, P.; Chiasserini, D.; Ardah, M.; Varghese, S.; Haque, M.E.; Tokuda, T.; Auinger, P.; Calabresi, P.; et al. Longitudinal changes in CSF alpha-synuclein species reflect Parkinson’s disease progression. Mov. Disord. 2016, 31, 1535–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, S.; Surova, Y.; Öhrfelt, A.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H.; Hansson, O.; the Swedish BioFINDER Study. Longitudinal Measurements of Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers in Parkinson’s Disease. Mov. Disord. 2016, 31, 898–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollenhauer, B.; Ms, C.J.C.; Coffey, C.S.; Taylor, P.; Singleton, A.; Shaw, L.M.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Frasier, M.; Simuni, T.; Iranzo, A.; et al. Longitudinal analyses of cerebrospinal fluid α-Synuclein in prodromal and early Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2019, 34, 1354–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paoletti, F.P.; Gaetani, L.; Parnetti, L. The Challenge of Disease-Modifying Therapies in Parkinson’s Disease: Role of CSF Biomarkers. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eusebi, P.; Giannandrea, D.; Biscetti, L.; Abraha, I.; Chiasserini, D.; Orso, M.; Calabresi, P.; Parnetti, L. Diagnostic utility of cerebrospinal fluid α-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Mov. Disord. 2017, 32, 1389–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cariulo, C.; Martufi, P.; Verani, M.; Azzollini, L.; Bruni, G.; Weiss, A.; Deguire, S.M.; Lashuel, H.A.; Scaricamazza, E.; Sancesario, G.M.; et al. Phospho-S129 Alpha-Synuclein Is Present in Human Plasma but Not in Cerebrospinal Fluid as Determined by an Ultrasensitive Immunoassay. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tokuda, T.; Qureshi, M.M.; Ardah, M.T.; Varghese, S.; Shehab, S.A.S.; Kasai, T.; Ishigami, N.; Tamaoka, A.; Nakagawa, M.; El-Agnaf, O.M.A. Detection of elevated levels of -synuclein oligomers in CSF from patients with Parkinson disease. Neurology 2010, 75, 1766–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eparnetti, L.; Efarotti, L.; Eeusebi, P.; Echiasserini, D.; Carlo, C.E.; Egiannandrea, D.; Esalvadori, N.; Elisetti, V.; Etambasco, N.; Erossi, A.; et al. Differential role of CSF alpha-synuclein species, tau, and Aβ42 in Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2014, 6, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, U.J.; Boehme, A.K.; Bs, G.F.; Shahnawaz, M.; Ma, T.; Hutten, S.J.; Green, A.; Soto, C. Comparative study of cerebrospinal fluid α-synuclein seeding aggregation assays for diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2019, 34, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, M.; Candelise, N.; Baiardi, S.; Capellari, S.; Giannini, G.; Orrù, C.D.; Antelmi, E.; Mammana, A.; Hughson, A.G.; Calandra-Buonaura, G.; et al. Ultrasensitive RT-QuIC assay with high sensitivity and specificity for Lewy body-associated synucleinopathies. Acta Neuropathol. 2020, 140, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, W.; Schmeichel, A.M.; Shahnawaz, M.; Schmelzer, J.D.; Boeve, B.F.; Sletten, D.M.; Gehrking, T.L.; Gehrking, J.A.; Olson, A.D.; Savica, R.; et al. Alpha-Synuclein Oligomers and Neurofilament Light Chain in Spinal Fluid Differentiate Multiple System Atrophy from Lewy Body Synucleinopathies. Ann. Neurol. 2020, 88, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahnawaz, M.; Mukherjee, A.; Pritzkow, S.; Mendez, N.; Rabadia, P.; Liu, X.; Hu, B.; Schmeichel, A.; Singer, W.; Wu, G.; et al. Discriminating α-synuclein strains in Parkinson’s disease and multiple system atrophy. Nature 2020, 578, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkovits, K.; Kruse, N.; Linden, A.; Tönges, L.; Pfeiffer, K.; Mollenhauer, B.; Marcus, K. Blood Contamination in CSF and Its Impact on Quantitative Analysis of Alpha-Synuclein. Cells 2020, 9, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Compta, Y.; Parkkinen, L.; O’Sullivan, S.S.; Vandrovcova, J.; Holton, J.L.; Collins, C.; Lashley, T.; Kallis, C.; Williams, D.R.; de Silva, R.; et al. Lewy- and Alzheimer-type pathologies in Parkinson’s disease dementia: Which is more important? Brain 2011, 134, 1493–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Irwin, D.J.; Lee, V.M.-Y.; Trojanowski, J.Q. Parkinson’s disease dementia: Convergence of α-synuclein, tau and amyloid-β pathologies. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2013, 14, 626–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jellinger, K.A.; Seppi, K.; Wenning, G.K.; Poewe, W. Impact of coexistent Alzheimer pathology on the natural history of Parkinson’s disease. J. Neural Transm. 2002, 109, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinton, L.K.; Blurton-Jones, M.; Myczek, K.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; LaFerla, F.M. Synergistic Interactions between Aβ, Tau, and -Synuclein: Acceleration of Neuropathology and Cognitive Decline. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 7281–7289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alves, G.; Lange, J.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H.; Andreasson, U.; Førland, M.G.; Tysnes, O.-B.; Larsen, J.P.; Pedersen, K.F. CSF A 42 predicts early-onset dementia in Parkinson disease. Neurology 2014, 82, 1784–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stav, A.L.; Aarsland, D.; Johansen, K.K.; Hessen, E.; Auning, E.; Fladby, T. Amyloid-β and α-synuclein cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers and cognition in early Parkinson’s disease. Park. Relat. Disord. 2015, 21, 758–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, S.; Surova, Y.; Öhrfelt, A.; Zetterberg, H.; Lindqvist, D.; Hansson, O. CSF biomarkers and clinical progression of Parkinson disease. Neurology 2014, 84, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vranová, H.P.; Hényková, E.; Kaiserová, M.; Menšíková, K.; Vaštík, M.; Mareš, J.; Hluštík, P.; Zapletalová, J.; Strnad, M.; Stejskal, D.; et al. Tau protein, beta-amyloid1–42 and clusterin CSF levels in the differential diagnosis of Parkinsonian syndrome with dementia. J. Neurol. Sci. 2014, 343, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaerst, L.; Kuhlmann, A.; Wedekind, D.; Stoeck, K.; Lange, P.; Zerr, I. Using Cerebrospinal Fluid Marker Profiles in Clinical Diagnosis of Dementia with Lewy Bodies, Parkinson’s Disease, and Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimer Dis. 2013, 38, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Irwin, D.J.; Fedler, J.; Coffey, C.S.; Ms, C.C.; Kang, J.H.; Simuni, T.; Foroud, T.; Toga, A.W.; Tanner, C.M.; Kieburtz, K.; et al. Evolution of Alzheimer’s Disease Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers in Early Parkinson’s Disease. Ann. Neurol. 2020, 88, 574–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochester, L.; Galna, B.; Lord, S.; Yarnall, A.; Morris, R.; Duncan, G.; Khoo, T.K.; Mollenhauer, B.; Burn, D. Decrease in Aβ42 predicts dopa-resistant gait progression in early Parkinson disease. Neurology 2017, 88, 1501–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hall, S.; Öhrfelt, A.; Constantinescu, R.; Andreasson, U.; Surova, Y.; Bostrom, F.; Nilsson, C.; Widner, H.; Decraemer, H.; Nägga, K.; et al. Accuracy of a Panel of 5 Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers in the Differential Diagnosis of Patients with Dementia and/or Parkinsonian Disorders. Arch. Neurol. 2012, 69, 1445–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, G.; Brønnick, K.; Aarsland, D.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H.; Ballard, C.; Kurz, M.W.; Andreasson, U.; Tysnes, O.-B.; Larsen, J.P.; et al. CSF amyloid- and tau proteins, and cognitive performance, in early and untreated Parkinson’s Disease: The Norwegian ParkWest study. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2010, 81, 1080–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Yang, Y.; Gong, D. Changes of cerebrospinal fluid Aβ42, t-tau, and p-tau in Parkinson’s disease patients with cognitive impairment relative to those with normal cognition: A meta-analysis. Neurol. Sci. 2017, 38, 1953–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbert, M.K.; Eeftens, J.M.; Aerts, M.B.; Esselink, R.A.J.; Bloem, B.R.; Kuiperij, H.B.; Verbeek, M.M. CSF levels of DJ-1 and tau distinguish MSA patients from PD patients and controls. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2014, 20, 112–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdo, W.F.; Bloem, B.R.; Van Geel, W.J.; Esselink, R.A.J.; Verbeek, M.M. CSF neurofilament light chain and tau differentiate multiple system atrophy from Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2007, 28, 742–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmio, J.; Suhonen, J.; Keränen, T.; Hulkkonen, J.; Peltola, J.; Pirttilä, T. Cerebrospinal fluid tau as a marker of neuronal damage after epileptic seizure. Seizure 2009, 18, 474–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brinkmalm, A.; Portelius, E.; Brinkmalm, G.; Pannee, J.; Dahlén, R.; Gobom, J.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H. Fluid-based proteomics targeted on pathophysiological processes and pathologies in neurodegenerative diseases. J. Neurochem. 2018, 151, 417–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Cholerton, B.; Shi, M.; Ginghina, C.; Cain, K.C.; Auinger, P.; Zhang, J. CSF tau and tau/Aβ42 predict cognitive decline in Parkinson’s disease. Park. Relat. Disord. 2015, 21, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zetterberg, H. Neurofilament Light: A Dynamic Cross-Disease Fluid Biomarker for Neurodegeneration. Neuron 2016, 91, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bäckström, D.C.; Domellöf, M.E.; Linder, J.; Olsson, B.; Öhrfelt, A.; Trupp, M.; Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K.; Forsgren, L. Cerebrospinal Fluid Patterns and the Risk of Future Dementia in Early, Incident Parkinson Disease. JAMA Neurol. 2015, 72, 1175–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, X.; Yang, Y.; Gong, D. Cerebrospinal fluid levels of neurofilament light chain in multiple system atrophy relative to Parkinson’s disease: A meta-analysis. Neurol. Sci. 2016, 38, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridel, C.; van Wieringen, W.N.; Zetterberg, H.; Tijms, B.M.; Teunissen, C.E.; Alvarez-Cermeño, J.C.; Andreasson, U.; Axelsson, M.; Bäckström, D.C.; Bartos, A.; et al. Diagnostic Value of Cerebrospinal Fluid Neurofilament Light Protein in Neurology. JAMA Neurol. 2019, 76, 1035–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollenhauer, B.; Dakna, M.; Kruse, N.; Galasko, D.; Foroud, T.; Zetterberg, H.; Schade, S.; Gera, R.G.; Wang, W.; Gao, F.; et al. Validation of Serum Neurofilament Light Chain as a Biomarker of Parkinson’s Disease Progression. Mov. Disord. 2020, 35, 1999–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerche, S.; Wurster, I.; Röben, B.; Zimmermann, M.; Machetanz, G.; Wiethoff, S.; Dehnert, M.; Rietschel, L.; Riebenbauer, B.; Deuschle, C.; et al. CSF NFL in a Longitudinally Assessed PD Cohort: Age Effects and Cognitive Trajectories. Mov. Disord. 2020, 35, 1138–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oosterveld, L.P.; Verberk, I.M.V.; Majbour, N.K.; El-Agnaf, O.M.; Weinstein, H.C.; Berendse, H.W.; Teunissen, C.E.; van de Berg, W.D. CSF or Serum Neurofilament Light Added to α-Synuclein Panel Discriminates Parkinson’s from Controls. Mov. Disord. 2019, 35, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moors, T.; Paciotti, S.; Chiasserini, D.; Calabresi, P.; Parnetti, L.; Beccari, T.; van de Berg, W. Lysosomal Dysfunction and α-Synuclein Aggregation in Parkinson’s Disease: Diagnostic Links. Mov. Disord. 2016, 31, 791–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalls, M.A.; Duran, R.; Lopez, G.; Kurzawa-Akanbi, M.; McKeith, I.; Chinnery, P.F.; Morris, C.; Theuns, J.; Crosiers, D.; Cras, P.; et al. A Multicenter Study of Glucocerebrosidase Mutations in Dementia with Lewy Bodies. JAMA Neurol. 2013, 70, 727–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidransky, E.; Nalls, M.A.; Aasly, J.O.; Aharon-Peretz, J.; Annesi, G.; Barbosa, E.R.; Bar-Shira, A.; Berg, D.; Bras, J.; Brice, A.; et al. Multicenter Analysis of Glucocerebrosidase Mutations in Parkinson’s Disease. New Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 1651–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mazzulli, J.R.; Xu, Y.-H.; Sun, Y.; Knight, A.L.; McLean, P.J.; Caldwell, G.A.; Sidransky, E.; Grabowski, G.A.; Krainc, D. Gaucher Disease Glucocerebrosidase and α-Synuclein Form a Bidirectional Pathogenic Loop in Synucleinopathies. Cell 2011, 146, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robak, L.A.; Jansen, I.E.; Van Rooij, J.; Uitterlinden, A.G.; Kraaij, R.; Jankovic, J.; Heutink, P.; Shulman, J.M.; Nalls, M.; Plagnol, V.; et al. Excessive burden of lysosomal storage disorder gene variants in Parkinson’s disease. Brain 2017, 140, 3191–3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurzawa-Akanbi, M.; Tammireddy, S.; Fabrik, I.; Gliaudelytė, L.; Doherty, M.K.; Heap, R.; Matečko-Burmann, I.; Burmann, B.M.; Trost, M.; Lucocq, J.M.; et al. Altered ceramide metabolism is a feature in the extracellular vesicle-mediated spread of alpha-synuclein in Lewy body disorders. Acta Neuropathol. 2021, 142, 961–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paciotti, S.; Gatticchi, L.; Beccari, T.; Parnetti, L. Lysosomal enzyme activities as possible CSF biomarkers of synucleinopathies. Clin. Chim. Acta 2019, 495, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parnetti, L.; Paciotti, S.; Farotti, L.; Bellomo, G.; Sepe, F.N.; Eusebi, P. Parkinson’s and Lewy body dementia CSF biomarkers. Clin. Chim. Acta 2019, 495, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parnetti, L.; Paciotti, S.; Eusebi, P.; Dardis, A.; Zampieri, S.; Chiasserini, D.; Tasegian, A.; Tambasco, N.; Bembi, B.; Calabresi, P.; et al. Cerebrospinal fluid β-glucocerebrosidase activity is reduced in parkinson’s disease patients. Mov. Disord. 2017, 32, 1423–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parnetti, L.; Chiasserini, D.; Persichetti, E.; Eusebi, P.; Varghese, S.; Msc, M.M.Q.; Dardis, A.; Deganuto, M.; De Carlo, C.; Castrioto, A.; et al. Cerebrospinal fluid lysosomal enzymes and alpha-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2014, 29, 1019–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parnetti, L.; Balducci, C.; Pierguidi, L.; De Carlo, C.; Peducci, M.; D’Amore, C.; Padiglioni, C.; Mastrocola, S.; Persichetti, E.; Paciotti, S.; et al. Cerebrospinal fluid β-glucocerebrosidase activity is reduced in Dementia with Lewy Bodies. Neurobiol. Dis. 2009, 34, 484–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balducci, C.; Pierguidi, L.; Persichetti, E.; Parnetti, L.; Sbaragli, M.; Tassi, C.; Orlacchio, A.; Calabresi, P.; Beccari, T.; Rossi, A. Lysosomal hydrolases in cerebrospinal fluid from subjects with Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2007, 22, 1481–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerche, S.; Schulte, C.; Wurster, I.; Machetanz, G.; Roeben, B.; Zimmermann, M.; Deuschle, C.; Hauser, A.; Böhringer, J.; Krägeloh-Mann, I.; et al. The Mutation Matters: CSF Profiles of GCase, Sphingolipids, α-Synuclein in PD GBA. Mov. Disord. 2021, 36, 1216–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, E.M.; Smith, G.A.; Park, E.; Cao, H.; Brown, E.; Hallett, P.; Isacson, O. Progressive decline of glucocerebrosidase in aging and P arkinson’s disease. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2015, 2, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, Y.E.; Park, H.; Chiang, M.S.R.; Tuncali, I.; Liu, G.; Locascio, J.J.; Shirvan, J.; Hutten, S.J.; Rotunno, M.S.; Viel, C.; et al. Glucosylceramide in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with GBA-associated and idiopathic Parkinson’s disease enrolled in PPMI. NPJ Park. Dis. 2021, 7, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosley, R.L.; Hutter-Saunders, J.A.; Stone, D.K.; Gendelman, H.E. Inflammation and Adaptive Immunity in Parkinson’s Disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2, a009381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schröder, J.B.; Pawlowski, M.; zu Horste, G.M.; Gross, C.; Wiendl, H.; Meuth, S.G.; Ruck, T.; Warnecke, T. Immune Cell Activation in the Cerebrospinal Fluid of Patients with Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Magdalinou, N.K.; Paterson, R.W.; Schott, J.; Fox, N.; Mummery, C.; Blennow, K.; Bhatia, K.; Morris, H.; Giunti, P.; Warner, T.; et al. A panel of nine cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers may identify patients with atypical parkinsonian syndromes. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2015, 86, 1240–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santaella, A.; Kuiperij, H.B.; Van Rumund, A.; Esselink, R.A.J.; Van Gool, A.J.; Bloem, B.R.; Verbeek, M.M. Cerebrospinal fluid monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 correlates with progression of Parkinson’s disease. NPJ Park. Dis. 2020, 6, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santaella, A.; Kuiperij, H.B.; van Rumund, A.; Esselink, R.A.J.; van Gool, A.J.; Bloem, B.R.; Verbeek, M.M. Inflammation biomarker discovery in Parkinson’s disease and atypical parkinsonisms. BMC Neurol. 2020, 20, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jabbari, E.; Woodside, J.; Guo, T.; Magdalinou, N.K.; Chelban, V.; Athauda, D.; Lees, A.J.; Foltynie, T.; Houlden, H.; Church, A.; et al. Proximity extension assay testing reveals novel diagnostic biomarkers of atypical parkinsonian syndromes. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2019, 90, 768–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rydbirk, R.; Elfving, B.; Andersen, M.D.; Langbøl, M.A.; Folke, J.; Winge, K.; Pakkenberg, B.; Brudek, T.; Aznar, S. Cytokine profiling in the prefrontal cortex of Parkinson’s Disease and Multiple System Atrophy patients. Neurobiol. Dis. 2017, 106, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wennstrom, M.; Surova, Y.; Hall, S.; Nilsson, C.; Minthon, L.; Hansson, O.; Nielsen, H.M. The Inflammatory Marker YKL-40 Is Elevated in Cerebrospinal Fluid from Patients with Alzheimer’s but Not Parkinson’s Disease or Dementia with Lewy Bodies. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindqvist, D.; Hall, S.; Surova, Y.; Nielsen, H.M.; Janelidze, S.; Brundin, L.; Hansson, O. Cerebrospinal fluid inflammatory markers in Parkinson’s disease—Associations with depression, fatigue, and cognitive impairment. Brain Behav. Immun. 2013, 33, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bartl, M.; Dakna, M.; Galasko, D.; Hutten, S.J.; Foroud, T.; Quan, M.; Marek, K.; Siderowf, A.; Franz, J.; Trenkwalder, C.; et al. Biomarkers of neurodegeneration and glial activation validated in Alzheimer’s disease assessed in longitudinal cerebrospinal fluid samples of Parkinson’s disease. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0257372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, S.; Janelidze, S.; Surova, Y.; Widner, H.; Zetterberg, H.; Hansson, O. Cerebrospinal fluid concentrations of inflammatory markers in Parkinson’s disease and atypical parkinsonian disorders. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magdalinou, N.; Noyce, A.; Pinto, R.; Lindstrom, E.; Holmén-Larsson, J.; Holtta, M.; Blennow, K.; Morris, H.; Skillbäck, T.; Warner, T.; et al. Identification of candidate cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers in parkinsonism using quantitative proteomics. Park. Relat. Disord. 2017, 37, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olsson, B.; Constantinescu, R.; Holmberg, B.; Andreasen, N.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H. The glial marker YKL-40 is decreased in synucleinopathies. Mov. Disord. 2013, 28, 1882–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollenhauer, B.; Zimmermann, J.; Sixel-Döring, F.; Focke, N.K.; Wicke, T.; Ebentheuer, J.; Ms, M.S.; Bs, E.L.; Friede, T.; Trenkwalder, C.; et al. Baseline predictors for progression 4 years after Parkinson’s disease diagnosis in the De Novo Parkinson Cohort (DeNoPa). Mov. Disord. 2018, 34, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majbour, N.K.; Aasly, J.O.; Hustad, E.; Thomas, M.A.; Vaikath, N.N.; Elkum, N.; van de Berg, W.; Tokuda, T.; Mollenhauer, B.; Berendse, H.W.; et al. CSF total and oligomeric α-Synuclein along with TNF-α as risk biomarkers for Parkinson’s disease: A study in LRRK2 mutation carriers. Transl. Neurodegener. 2020, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starhof, C.; Winge, K.; Heegaard, N.H.H.; Skogstrand, K.; Friis, S.; Hejl, A. Cerebrospinal fluid pro-inflammatory cytokines differentiate parkinsonian syndromes. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 15, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delgado-Alvarado, M.; Gago, B.; Gorostidi, A.; Jiménez-Urbieta, H.; Aguayo, R.D.; Navalpotro, I.; Ruiz-Martínez, J.; Bergareche, A.; Martí-Massó, J.F.; Martínez-Lage, P.; et al. Tau/α-synuclein ratio and inflammatory proteins in Parkinson’s disease: An exploratory study. Mov. Disord. 2017, 32, 1066–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatcher-Martin, J.M.; McKay, J.L.; Pybus, A.F.; Sommerfeld, B.; Howell, J.C.; Goldstein, F.C.; Wood, L.; Hu, W.T.; Factor, S.A. Cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers in Parkinson’s disease with freezing of gait: An exploratory analysis. NPJ Park. Dis. 2021, 7, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compta, Y.; Dias, S.P.; Giraldo, D.M.; Pérez-Soriano, A.; Muñoz, E.; Saura, J.; Fernández, M.; Bravo, P.; Cámara, A.; Pulido-Salgado, M.; et al. Cerebrospinal fluid cytokines in multiple system atrophy: A cross-sectional Catalan MSA registry study. Park. Relat. Disord. 2019, 65, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eidson, L.N.; Kannarkat, G.T.; Barnum, C.J.; Chang, J.; Chung, J.; Caspell-Garcia, C.; Taylor, P.; Mollenhauer, B.; Schlossmacher, M.G.; Ereshefsky, L.; et al. Candidate inflammatory biomarkers display unique relationships with alpha-synuclein and correlate with measures of disease severity in subjects with Parkinson’s disease. J. Neuroinflamm. 2017, 14, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harms, A.S.; Ferreira, S.A.; Romero-Ramos, M. Periphery and brain, innate and adaptive immunity in Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2021, 141, 527–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, E.; Thomas, A. Systemic Inflammation in Lewy Body Diseases. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 2017, 31, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botas, A.; Campbell, H.M.; Han, X.; Maletic-Savatic, M. Chapter Two—Metabolomics of Neurodegenerative Diseases. In International Review of Neurobiology: Omic Studies of Neurodegenerative Disease: Part B; Hurley, M.J., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015; pp. 53–80. ISBN 0074-7742. [Google Scholar]
- Plewa, S.; Poplawska-Domaszewicz, K.; Florczak-Wyspianska, J.; Klupczynska-Gabryszak, A.; Sokol, B.; Miltyk, W.; Jankowski, R.; Kozubski, W.; Kokot, Z.J.; Matysiak, J. The Metabolomic Approach Reveals the Alteration in Human Serum and Cerebrospinal Fluid Composition in Parkinson’s Disease Patients. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos-Lobato, B.L.; Gardinassi, L.G.; Bortolanza, M.; Peti, A.P.F.; Pimentel, V.; Faccioli, L.H.; Del-Bel, E.A.; Tumas, V. Metabolic Profile in Plasma AND CSF of LEVODOPA-induced Dyskinesia in Parkinson’s Disease: Focus on Neuroinflammation. Mol. Neurobiol. 2021. epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwaoka, K.; Otsuka, C.; Maeda, T.; Yamahara, K.; Kato, K.; Takahashi, K.; Takahashi, K.; Terayama, Y. Impaired metabolism of kynurenine and its metabolites in CSF of parkinson’s disease. Neurosci. Lett. 2019, 714, 134576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havelund, J.F.; Heegaard, N.H.H.; Færgeman, N.J.K.; Gramsbergen, J.B. Biomarker Research in Parkinson’s Disease Using Metabolite Profiling. Metabolites 2017, 7, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wuolikainen, A.; Jonsson, P.; Ahnlund, M.; Antti, H.; Marklund, S.L.; Moritz, T.; Forsgren, L.; Andersen, P.M.; Trupp, M. Multi-platform mass spectrometry analysis of the CSF and plasma metabolomes of rigorously matched amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease and control subjects. Mol. BioSyst. 2016, 12, 1287–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öhman, A.; Forsgren, L. NMR metabonomics of cerebrospinal fluid distinguishes between Parkinson’s disease and controls. Neurosci. Lett. 2015, 594, 36–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trupp, M.; Jonsson, P.; Öhrfelt, A.; Zetterberg, H.; Obudulu, O.; Malm, L.; Wuolikainen, A.; Linder, J.; Moritz, T.; Blennow, K.; et al. Metabolite and Peptide Levels in Plasma and CSF Differentiating Healthy Controls from Patients with Newly Diagnosed Parkinson’s Disease. J. Park. Dis. 2014, 4, 549–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoessel, D.; Schulte, C.; Dos Santos, M.C.T.; Scheller, D.; Rebollo-Mesa, I.; Deuschle, C.; Walther, D.; Schauer, N.; Berg, D.; Da Costa, A.N.; et al. Promising Metabolite Profiles in the Plasma and CSF of Early Clinical Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2018, 10, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trezzi, J.-P.; Galozzi, S.; Jaeger, C.; Barkovits, K.; Brockmann, K.; Maetzler, W.; Berg, D.; Marcus, K.; Betsou, F.; Hiller, K.; et al. Distinct metabolomic signature in cerebrospinal fluid in early parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2017, 32, 1401–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willkommen, D.; Lucio, M.; Moritz, F.; Forcisi, S.; Kanawati, B.; Smirnov, K.S.; Schroeter, M.; Sigaroudi, A.; Schmitt-Kopplin, P.; Michalke, B. Metabolomic investigations in cerebrospinal fluid of Parkinson’s disease. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0208752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- LeWitt, P.A.; Li, J.; Lu, M.; Guo, L.; Auinger, P. Metabolomic biomarkers as strong correlates of Parkinson disease progression. Neurology 2017, 88, 862–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lill, C.M. Genetics of Parkinson’s disease. Mol. Cell. Probes 2016, 30, 386–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polissidis, A.; Petropoulou-Vathi, L.; Nakos-Bimpos, M.; Rideout, H.J. The Future of Targeted Gene-Based Treatment Strategies and Biomarkers in Parkinson’s Disease. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-D.; Chan, P. Clinicogenetics of Parkinson′s disease: A drawing but not completed picture. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2014, 1, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reed, X.; Bandrés-Ciga, S.; Blauwendraat, C.; Cookson, M.R. The role of monogenic genes in idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2018, 124, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riboldi, G.M.; Di Fonzo, A.B. GBA, Gaucher Disease, and Parkinson’s Disease: From Genetic to Clinic to New Therapeutic Approaches. Cells 2019, 8, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mullin, S.; Smith, L.; Lee, K.; D’Souza, G.; Woodgate, P.; Elflein, J.; Hällqvist, J.; Toffoli, M.; Streeter, A.; Hosking, J.; et al. Ambroxol for the Treatment of Patients with Parkinson Disease With and Without Glucocerebrosidase Gene Mutations: A Nonrandomized, Noncontrolled Trial. JAMA Neurol. 2020, 77, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Healy, D.G.; Falchi, M.; O’Sullivan, S.S.; Bonifati, V.; Durr, A.; Bressman, S.; Brice, A.; Aasly, J.; Zabetian, C.P.; Goldwurm, S.; et al. Phenotype, genotype, and worldwide genetic penetrance of LRRK2-associated Parkinson’s disease: A case-control study. Lancet Neurol. 2008, 7, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, A.J.; Wang, Y.; Alcalay, R.N.; Mejia-Santana, H.; Saunders-Pullman, R.; Bressman, S.; Corvol, J.-C.; Brice, A.; Lesage, S.; Mangone, G.; et al. Penetrance estimate of LRRK2 p.G2019S mutation in individuals of non-Ashkenazi Jewish ancestry. Mov. Disord. 2017, 32, 1432–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, A.; Mazzocchetti, P.; Sciaccaluga, M.; Megaro, A.; Bellingacci, L.; Beccano-Kelly, D.A.; Di Filippo, M.; Tozzi, A.; Calabresi, P. From Synaptic Dysfunction to Neuroprotective Strategies in Genetic Parkinson’s Disease: Lessons from LRRK2. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, K.B.; Moehle, M.S.; Daher, J.P.; Webber, P.J.; Williams, J.Y.; Stewart, C.A.; Yacoubian, T.A.; Cowell, R.M.; Dokland, T.; Ye, T.; et al. LRRK2 secretion in exosomes is regulated by 14-3-3. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2013, 22, 4988–5000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Liu, Z.; Ye, T.; Mabrouk, O.S.; Maltbie, T.; Aasly, J.; West, A.B. Elevated LRRK2 autophosphorylation in brain-derived and peripheral exosomes in LRRK2 mutation carriers. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2017, 5, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabrouk, O.S.; Chen, S.; Edwards, A.L.; Yang, M.; Hirst, W.D.; Graham, D.L. Quantitative Measurements of LRRK2 in Human Cerebrospinal Fluid Demonstrates Increased Levels in G2019S Patients. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trempe, J.-F.; Fon, E.A. Structure and Function of Parkin, PINK1, and DJ-1, the Three Musketeers of Neuroprotection. Front. Neurol. 2013, 4, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiong, H.; Wang, D.; Chen, L.; Choo, Y.S.; Ma, H.; Tang, C.; Xia, K.; Jiang, W.; Ronai, Z.; Zhuang, X.; et al. Parkin, PINK1, and DJ-1 form a ubiquitin E3 ligase complex promoting unfolded protein degradation. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 650–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pyle, A.; Brennan, R.; Kurzawa-Akanbi, M.; Yarnall, A.; Thouin, A.; Mollenhauer, B.; Burn, D.; Chinnery, P.F.; Hudson, G. Reduced cerebrospinal fluid mitochondrial DNA is a biomarker for early-stage Parkinson’s disease. Ann. Neurol. 2015, 78, 1000–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowes, H.; Pyle, A.; Santibanez-Koref, M.; Hudson, G. Circulating cell-free mitochondrial DNA levels in Parkinson’s disease are influenced by treatment. Mol. Neurodegener. 2020, 15, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farotti, L.; Paoletti, F.P.; Simoni, S.; Parnetti, L. Unraveling Pathophysiological Mechanisms of Parkinson’s Disease: Contribution of CSF Biomarkers. Biomark. Insights 2020, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvesen, L.; Bech, S.; Lokkegaard, A.; Hjermind, L.E.; Nielsen, J.E.; Pakkenberg, B.; Tanassi, J.T.; Heegaard, N.H.; Winge, K. The DJ-1 concentration in cerebrospinal fluid does not differentiate among parkinsonian syndromes. Park. Relat. Disord. 2012, 18, 899–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, Biogenesis, Mechanism, and Function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sohel, M.H. Extracellular/Circulating MicroRNAs: Release Mechanisms, Functions and Challenges. Achiev. Life Sci. 2016, 10, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dos Santos, M.C.T.; Barreto-Sanz, M.A.; Correia, B.R.S.; Bell, R.; Widnall, C.; Perez, L.T.; Berteau, C.; Schulte, C.; Scheller, D.; Berg, D.; et al. miRNA-based signatures in cerebrospinal fluid as potential diagnostic tools for early stage Parkinson’s disease. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 17455–17465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gui, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, L.; Lv, W.; Hu, X. Altered microRNA profiles in cerebrospinal fluid exosome in Parkinson disease and Alzheimer disease. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 37043–37053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marques, T.M.; Kuiperij, B.; Bruinsma, I.B.; Van Rumund, A.; Aerts, M.B.; Esselink, R.A.J.; Bloem, B.R.; Verbeek, M.M. MicroRNAs in Cerebrospinal Fluid as Potential Biomarkers for Parkinson’s Disease and Multiple System Atrophy. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 54, 7736–7745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gomes, L.C.; Roser, A.; Jain, G.; Centeno, T.P.; Maass, F.; Schilde, L.; May, C.; Schneider, A.; Bähr, M.; Marcus, K.; et al. MicroRNAs from extracellular vesicles as a signature for Parkinson’s disease. Clin. Transl. Med. 2021, 11, e357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starhof, C.; Hejl, A.-M.; Heegaard, N.H.; Carlsen, A.L.; Burton, M.; Lilje, B.; Winge, K. The biomarker potential of cell-free microRNA from cerebrospinal fluid in Parkinsonian Syndromes. Mov. Disord. 2018, 34, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Berg, M.M.J.; Krauskopf, J.; Ramaekers, J.G.; Kleinjans, J.C.S.; Prickaerts, J.; Briedé, J.J. Circulating microRNAs as potential biomarkers for psychiatric and neurodegenerative disorders. Prog. Neurobiol. 2020, 185, 101732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Pathomechanism | CSF Biomarker | Differential-/Diagnosis | Biomarker Changes in Advanced Disease |
|---|---|---|---|
| α-syn misfolding and aggregation | t-α-syn | ↓ PD/APS vs. HC | No certain correlation with disease progression |
| p-α-syn | ↑ PD vs. HC | ↓ over disease course | |
| o-α-syn | ↑ PD vs. HC | ↑ over disease course ↑ o-/t-α-syn ratio correlates with motor progression | |
| α-syn aggregates | ↑ PD/MSA/DLB vs. HC | ||
| Amyloidosis | Aβ42 | ↓ DLB/AD/PDD vs. PD/HC | ↓ predicts earlier cognitive decline |
| Tauopathy | t-tau | ↑ MSA vs. PD | ↑ t-/p-tau plus Aβ42 predicts cognitive decline |
| p-tau | Inconclusive | ||
| Axonal damage | NfL | ↑ APS > PD | ↑ correlates with motor and cognitive impairment |
| Autophagy–lysosomal pathway dysfunction | GCase | ↓ sPD/GBA-PD/DLB vs. HC | ↓ in more advanced motor stages |
| cathepsin D, β-hexosaminidase | ↓ PD vs. HC | ↓ correlates with worse cognitive performance | |
| GlcCer, SM | ↓ GBA-PD vs. HC | ↑ GlcCer/SM ratio correlates with accelerated cognitive decline in sPD | |
| Neuroinflammation | immune cell composition | Shift in PD vs. HC | |
| MCP-1 | ↑ PD/MSA vs. HC | ↑ correlates with motor progression and depression | |
| YKL-40 | Inconclusive | ↑ correlates with faster cognitive decline | |
| CRP | ↑ PDD/MSA vs. PD/HC | ↑ correlates with motor and non-motor symptoms | |
| Altered metabolic pathways | threonic acid, mannose, fructose | ↑ PD vs. HC | |
| proline metabolites | ↑ PD/APS vs. HC | ||
| glycosphingolipid metabolism | PD with LID vs. PD without LID | Correlation with severity of dyskinesia | |
| ↑ LRRK2 kinase activity | pS1292-LRRK2 | LRRK2-PD = sPD/HC | |
| LRRK2 | ↑ LRRK2-PD vs. sPD | ||
| Mitochondrial dysfunction (PINK1/Parkin/DJ1) | Ccf-mtDNA | ↓ PD vs. HC | ↓ correlates with ↑PD medication |
| DJ-1 | Inconclusive | ||
| Regulation of gene expression | miRNA | Altered profile in PD vs. HC |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kwon, E.H.; Tennagels, S.; Gold, R.; Gerwert, K.; Beyer, L.; Tönges, L. Update on CSF Biomarkers in Parkinson’s Disease. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 329. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12020329
Kwon EH, Tennagels S, Gold R, Gerwert K, Beyer L, Tönges L. Update on CSF Biomarkers in Parkinson’s Disease. Biomolecules. 2022; 12(2):329. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12020329
Chicago/Turabian StyleKwon, Eun Hae, Sabrina Tennagels, Ralf Gold, Klaus Gerwert, Léon Beyer, and Lars Tönges. 2022. "Update on CSF Biomarkers in Parkinson’s Disease" Biomolecules 12, no. 2: 329. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12020329
APA StyleKwon, E. H., Tennagels, S., Gold, R., Gerwert, K., Beyer, L., & Tönges, L. (2022). Update on CSF Biomarkers in Parkinson’s Disease. Biomolecules, 12(2), 329. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12020329







