Dietary Soy Prevents Alcohol-Mediated Neurocognitive Dysfunction and Associated Impairments in Brain Insulin Pathway Signaling in an Adolescent Rat Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. General
2.2. Experimental Model
2.3. Morris Water Maze
2.4. Sacrifice
2.5. Preparation of Protein Homogenates
2.6. Multiplex Akt and Phospho-Akt Pathway ELISAs
2.7. Duplex Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assays (ELISAs)
2.8. Statistics
2.9. Materials
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Ethanol, Sex, and Dietary Soy on Body Weight and Brain Weight
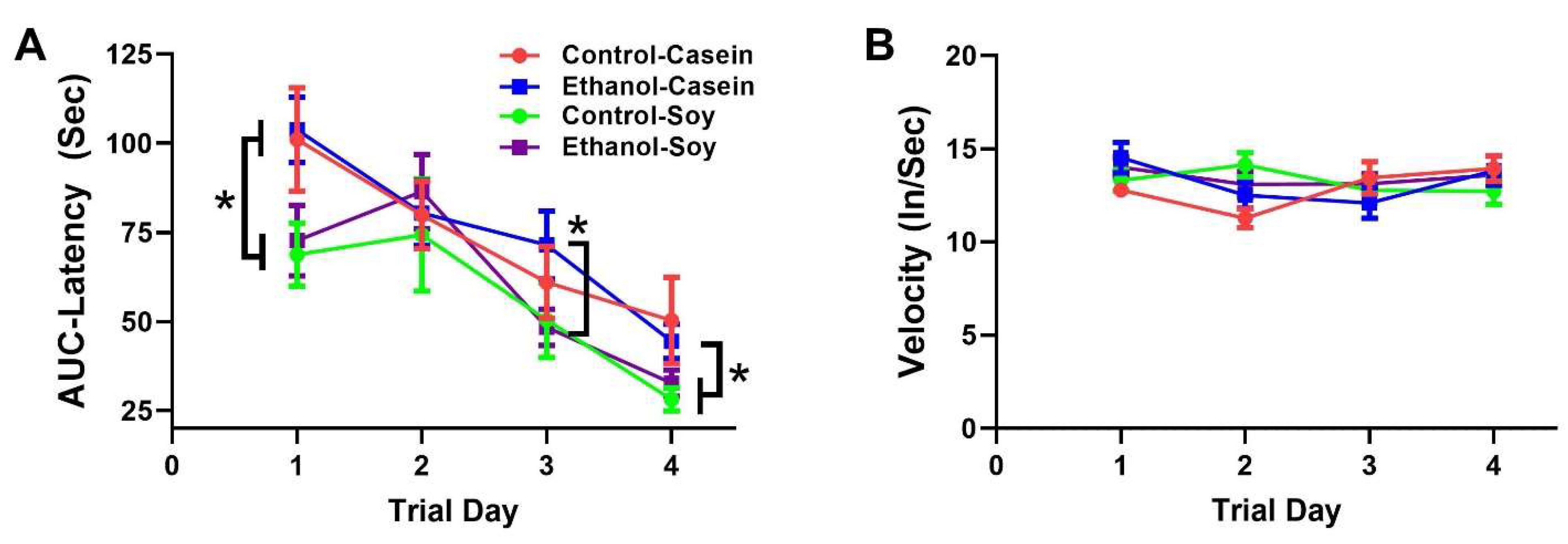
3.2. Ethanol and Soy Effects on Morris Water Maze (MWM) Performance
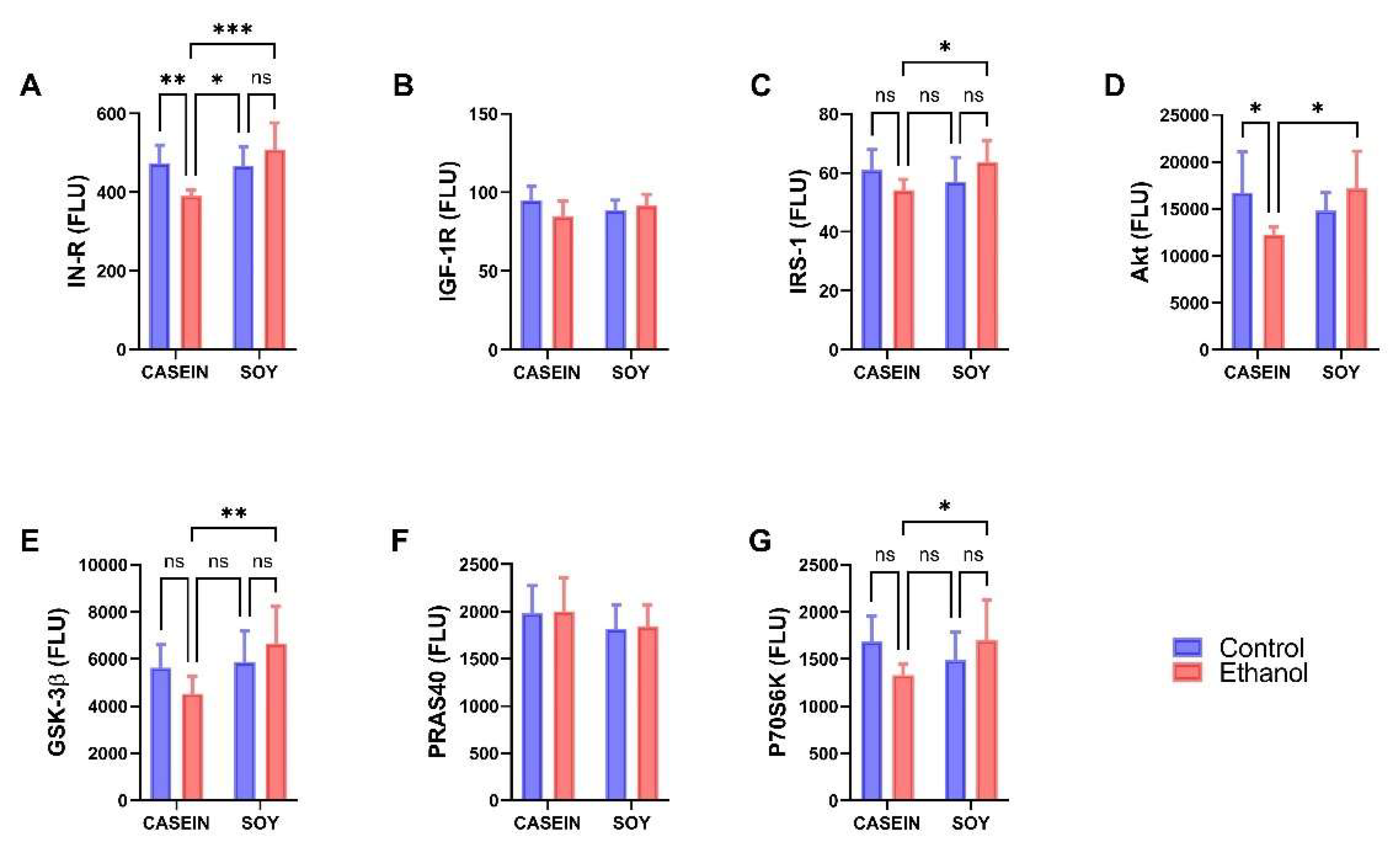
3.3. Ethanol and Dietary Soy Effects on Akt-Pathway Proteins
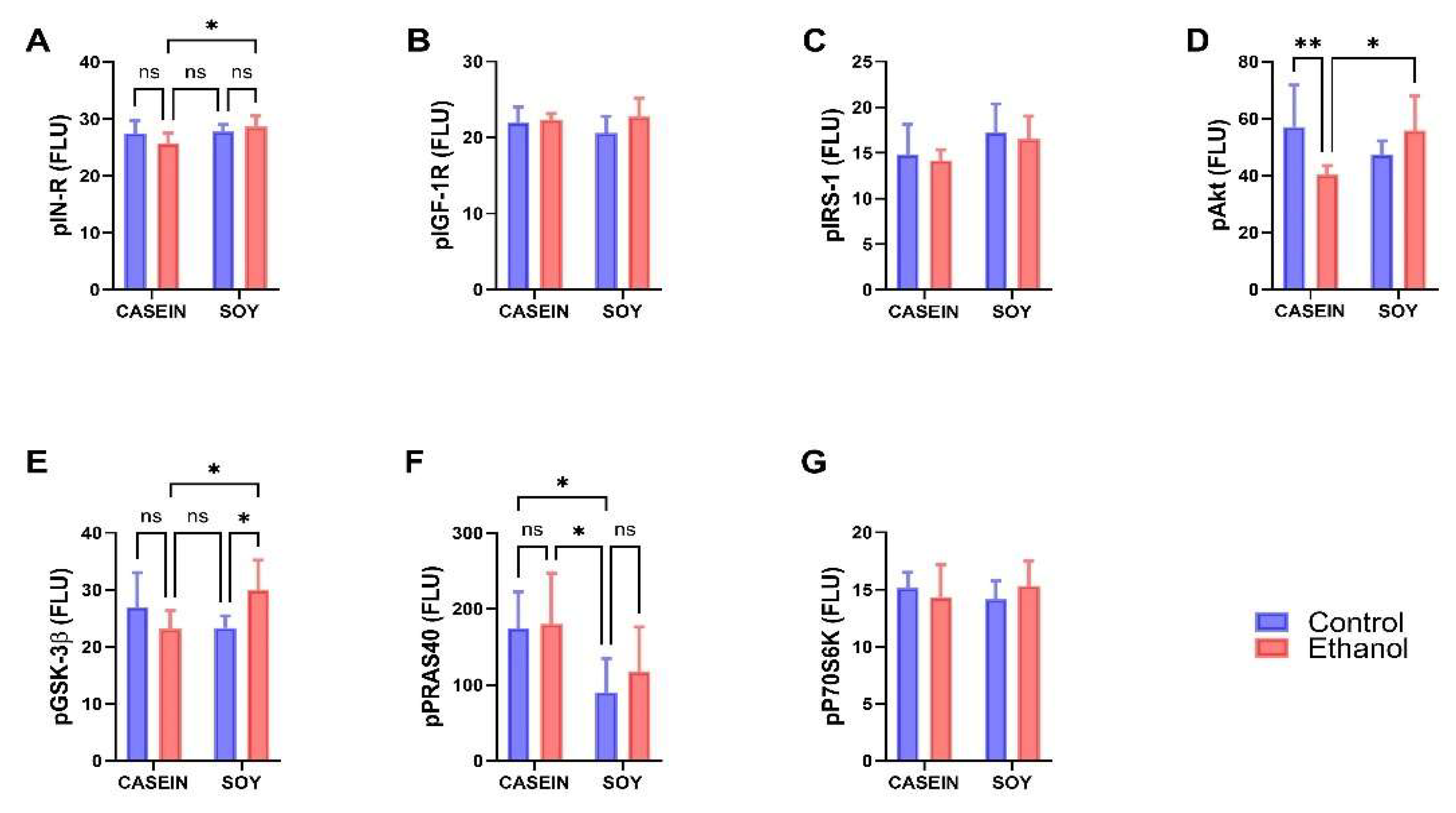
3.4. Ethanol and Dietary Soy Effects on Phospho-Akt-Pathway Proteins
3.5. Ethanol and Soy Effects on ASPH Proteins
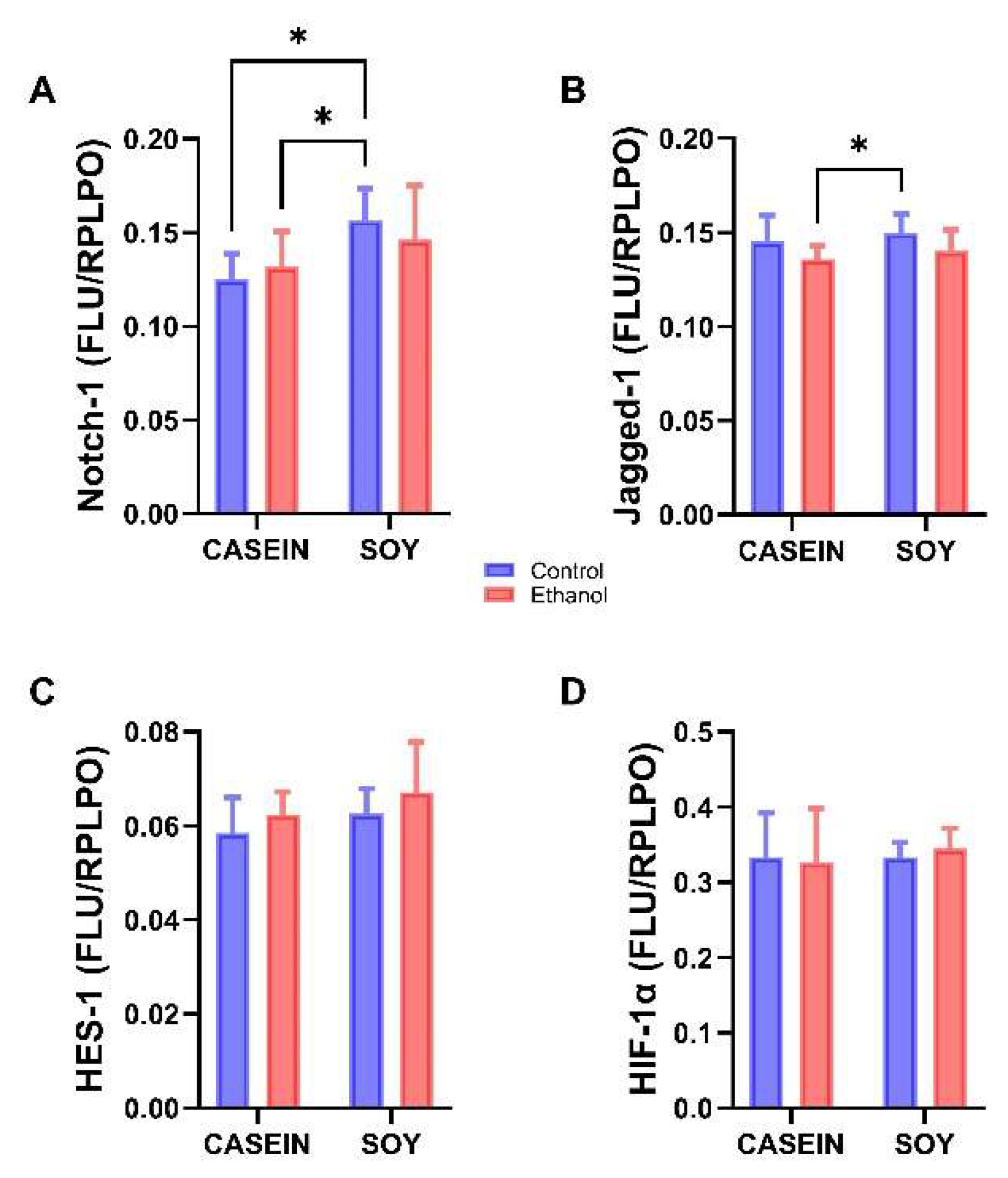
3.6. Ethanol and Soy Effects on NOTCH Pathway Proteins
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chanraud, S.; Martelli, C.; Delain, F.; Kostogianni, N.; Douaud, G.; Aubin, H.J.; Reynaud, M.; Martinot, J.L. Brain morphometry and cognitive performance in detoxified alcohol-dependents with preserved psychosocial functioning. Neuropsychopharmacology 2007, 32, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, T.K. Quantifying the risk for alcohol-use and alcohol-attributable health disorders: Present findings and future research needs. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 23 (Suppl. 1), S2–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, K.S.; Gallo, J.L.; Ferri, C.; Giovannetti, T.; Sestito, N.; Libon, D.J.; Schmidt, P.S. The neuropsychological profile of alcohol-related dementia suggests cortical and subcortical pathology. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2005, 20, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harper, C. Neuropathology of brain damage caused by alcohol. Med. J. Aust. 1982, 2, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Monte, S.M.; Kril, J.J. Human alcohol-related neuropathology. Acta Neuropathol. 2014, 127, 71–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elofson, J.; Gongvatana, W.; Carey, K.B. Alcohol use and cerebral white matter compromise in adolescence. Addict. Behav. 2013, 38, 2295–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jacobus, J.; Squeglia, L.M.; Bava, S.; Tapert, S.F. White matter characterization of adolescent binge drinking with and without co-occurring marijuana use: A 3-year investigation. Psychiatry Res. 2013, 214, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de la Monte, S.M. Disproportionate atrophy of cerebral white matter in chronic alcoholics. Arch. Neurol. 1988, 45, 990–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, C.G.; Smith, N.A.; Kril, J.J. The effects of alcohol on the female brain: A neuropathological study. Alcohol Alcohol. 1990, 25, 445–448. [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland, G.T.; Sheedy, D.; Kril, J.J. Neuropathology of alcoholism. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2014, 125, 603–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCorkindale, A.N.; Sheedy, D.; Kril, J.J.; Sutherland, G.T. The effects of chronic smoking on the pathology of alcohol-related brain damage. Alcohol 2016, 53, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kril, J.J.; Gundlach, A.L.; Dodd, P.R.; Johnston, G.A.; Harper, C.G. Cortical dihydropyridine binding sites are unaltered in human alcoholic brain. Ann. Neurol. 1989, 26, 395–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kril, J.J.; Halliday, G.M. Brain shrinkage in alcoholics: A decade on and what have we learned? Prog. Neurobiol. 1999, 58, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, C.G.; Kril, J.J.; Holloway, R.L. Brain shrinkage in chronic alcoholics: A pathological study. Br. Med. J. 1985, 290, 501–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phillips, S.C.; Harper, C.G.; Kril, J. A quantitative histological study of the cerebellar vermis in alcoholic patients. Brain J. Neurol. 1987, 110 Pt 2, 301–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, C.; Dixon, G.; Sheedy, D.; Garrick, T. Neuropathological alterations in alcoholic brains. Studies arising from the New South Wales Tissue Resource Centre. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2003, 27, 951–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapert, S.F.; Caldwell, L.; Burke, C. Alcohol and the adolescent brain: Human studies. Alcohol Res. Health 2004, 28, 205–212. [Google Scholar]
- de Goede, J.; van der Mark-Reeuwijk, K.G.; Braun, K.P.; le Cessie, S.; Durston, S.; Engels, R.; Goudriaan, A.E.; Moons, K.G.M.; Vollebergh, W.A.M.; de Vries, T.J.; et al. Alcohol and Brain Development in Adolescents and Young Adults: A Systematic Review of the Literature and Advisory Report of the Health Council of the Netherlands. Adv. Nutr. 2021, 12, 1379–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, E.M.; Xia, Y. Neurodevelopmental Trajectories Following Prenatal Alcohol Exposure. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 695855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreani, T.; Tong, M.; Gundogan, F.; Silbermann, E.; de la Monte, S.M. Differential Effects of 3rd Trimester-Equivalent Binge Ethanol and Tobacco-Specific Nitrosamine Ketone Exposures on Brain Insulin Signaling in Adolescence. J. Diabetes Relat. Disord. 2016, 1, 105–114. [Google Scholar]
- Carter, J.J.; Tong, M.; Silbermann, E.; Lahousse, S.A.; Ding, F.F.; Longato, L.; Roper, N.; Wands, J.R.; de la Monte, S.M. Ethanol impaired neuronal migration is associated with reduced aspartyl-asparaginyl-beta-hydroxylase expression. Acta Neuropathol. 2008, 116, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, A.C.; Tong, M.; Wands, J.R.; de la Monte, S.M. Insulin and insulin-like growth factor resistance with neurodegeneration in an adult chronic ethanol exposure model. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 2007, 31, 1558–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Monte, S.M. Alcohol-Related Liver Disease: Roles of Insulin Resistance, Lipotoxic Ceramide Accumulation, and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. In Alcohol, Nutrition, and Health Consequences; Watson, R.S., Preedy, V.R., Zibadi, S., Eds.; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 507–522. [Google Scholar]
- de la Monte, S.M.; Longato, L.; Tong, M.; DeNucci, S.; Wands, J.R. The liver-brain axis of alcohol-mediated neurodegeneration: Role of toxic lipids. Int. J. Environ. 2009, 6, 2055–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewenczyk, A.; Ziplow, J.; Tong, M.; Le, T.; de la Monte, S.M. Sustained Impairments in Brain Insulin/IGF Signaling in Adolescent Rats Subjected to Binge Alcohol Exposures during Development. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2012, 2, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lindtner, C.; Scherer, T.; Zielinski, E.; Filatova, N.; Fasshauer, M.; Tonks, N.K.; Puchowicz, M.; Buettner, C. Binge drinking induces whole-body insulin resistance by impairing hypothalamic insulin action. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 170ra114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Resnicoff, M.; Rubini, M.; Baserga, R.; Rubin, R. Ethanol inhibits insulin-like growth factor-1-mediated signalling and proliferation of C6 rat glioblastoma cells. Lab. Investig. 1994, 71, 657–662. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Soscia, S.J.; Tong, M.; Xu, X.J.; Cohen, A.C.; Chu, J.; Wands, J.R.; de la Monte, S.M. Chronic gestational exposure to ethanol causes insulin and IGF resistance and impairs acetylcholine homeostasis in the brain. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2006, 63, 2039–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, M.; Yu, R.; Deochand, C.; de la Monte, S.M. Differential Contributions of Alcohol and the Nicotine-Derived Nitrosamine Ketone (NNK) to Insulin and Insulin-Like Growth Factor Resistance in the Adolescent Rat Brain. Alcohol Alcohol. 2015, 50, 670–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, J.; Yeon, J.E.; Chang, H.; Tison, G.; Chen, G.J.; Wands, J.; de la Monte, S. Ethanol impairs insulin-stimulated neuronal survival in the developing brain: Role of PTEN phosphatase. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 26929–26937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lavaissiere, L.; Jia, S.; Nishiyama, M.; de la Monte, S.; Stern, A.M.; Wands, J.R.; Friedman, P.A. Overexpression of human aspartyl(asparaginyl)beta-hydroxylase in hepatocellular carcinoma and cholangiocarcinoma. J. Clin. Investig. 1996, 98, 1313–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dinchuk, J.E.; Henderson, N.L.; Burn, T.C.; Huber, R.; Ho, S.P.; Link, J.; O’Neil, K.T.; Focht, R.J.; Scully, M.S.; Hollis, J.M.; et al. Aspartyl beta-hydroxylase (Asph) and an evolutionarily conserved isoform of Asph missing the catalytic domain share exons with junctin. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 39543–39554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ince, N.; de la Monte, S.M.; Wands, J.R. Overexpression of human aspartyl (asparaginyl) beta-hydroxylase is associated with malignant transformation. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 1261–1266. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- de la Monte, S.M.; Tong, M.; Carlson, R.I.; Carter, J.J.; Longato, L.; Silbermann, E.; Wands, J.R. Ethanol inhibition of aspartyl-asparaginyl-beta-hydroxylase in fetal alcohol spectrum disorder: Potential link to the impairments in central nervous system neuronal migration. Alcohol 2009, 43, 225–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- de la Monte, S.M.; Yeon, J.E.; Tong, M.; Longato, L.; Chaudhry, R.; Pang, M.Y.; Duan, K.; Wands, J.R. Insulin resistance in experimental alcohol-induced liver disease. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 23, e477–e486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gundogan, F.; Elwood, G.; Longato, L.; Tong, M.; Feijoo, A.; Carlson, R.I.; Wands, J.R.; de la Monte, S.M. Impaired placentation in fetal alcohol syndrome. Placenta 2008, 29, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, C.K.; Iwagami, Y.; Aihara, A.; Chung, W.; de la Monte, S.; Thomas, J.M.; Olsen, M.; Carlson, R.; Yu, T.; Dong, X.; et al. Anti-Tumor Effects of Second Generation beta-Hydroxylase Inhibitors on Cholangiocarcinoma Development and Progression. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawton, M.; Tong, M.; Gundogan, F.; Wands, J.R.; de la Monte, S.M. Aspartyl-(asparaginyl) beta-hydroxylase, hypoxia-inducible factor-alpha and Notch cross-talk in regulating neuronal motility. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2010, 3, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silbermann, E.; Moskal, P.; Bowling, N.; Tong, M.; de la Monte, S.M. Role of aspartyl-(asparaginyl)-beta-hydroxylase mediated notch signaling in cerebellar development and function. Behav. Brain Funct. 2010, 6, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Finotti, A.; Treves, S.; Zorzato, F.; Gambari, R.; Feriotto, G. Upstream stimulatory factors are involved in the P1 promoter directed transcription of the A beta H-J-J locus. BMC Mol. Biol. 2008, 9, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cantarini, M.C.; de la Monte, S.M.; Pang, M.; Tong, M.; D’Errico, A.; Trevisani, F.; Wands, J.R. Aspartyl-asparagyl beta hydroxylase over-expression in human hepatoma is linked to activation of insulin-like growth factor and notch signaling mechanisms. Hepatology 2006, 44, 446–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, C.B.; Peng, Y.; Nguyen, H.; Gaiano, N.; Fishell, G.; Nye, J.S. Spatiotemporal selectivity of response to Notch1 signals in mammalian forebrain precursors. Development 2001, 128, 689–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irvin, D.K.; Zurcher, S.D.; Nguyen, T.; Weinmaster, G.; Kornblum, H.I. Expression patterns of Notch1, Notch2, and Notch3 suggest multiple functional roles for the Notch-DSL signaling system during brain development. J. Comp. Neurol. 2001, 436, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Ren, K.Y.; Wang, Y.H.; Kou, Y.H.; Zhang, P.X.; Peng, J.P.; Deng, L.; Zhang, H.B.; Jiang, B.G. Effect of active Notch signaling system on the early repair of rat sciatic nerve injury. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2015, 43, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatakeyama, J.; Bessho, Y.; Katoh, K.; Ookawara, S.; Fujioka, M.; Guillemot, F.; Kageyama, R. Hes genes regulate size, shape and histogenesis of the nervous system by control of the timing of neural stem cell differentiation. Development 2004, 131, 5539–5550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sturla, L.M.; Tong, M.; Hebda, N.; Gao, J.; Thomas, J.M.; Olsen, M.; de la Monte, S.M. Aspartate-beta-hydroxylase (ASPH): A potential therapeutic target in human malignant gliomas. Heliyon 2016, 2, e00203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Chan, S.L.; Miele, L.; Yao, P.J.; Mackes, J.; Ingram, D.K.; Mattson, M.P.; Furukawa, K. Involvement of Notch signaling in hippocampal synaptic plasticity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 9458–9462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Le, T.; Tong, M.; Nguyen, V.; de la Monte, S.M. PPAR Agonist Rescue of Ethanol-Impaired Brain Insulin Signaling: Cerebellar Slice Culture Model. J. Drug Alcohol Res. 2013, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de la Monte, S.M.; Pang, M.; Chaudhry, R.; Duan, K.; Longato, L.; Carter, J.; Ouh, J.; Wands, J.R. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor agonist treatment of alcohol-induced hepatic insulin resistance. Hepatol. Res. 2011, 41, 386–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pang, M.; de la Monte, S.M.; Longato, L.; Tong, M.; He, J.; Chaudhry, R.; Duan, K.; Ouh, J.; Wands, J.R. PPARdelta agonist attenuates alcohol-induced hepatic insulin resistance and improves liver injury and repair. J. Hepatol. 2009, 50, 1192–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramirez, T.; Tong, M.; Ayala, C.A.; Monfils, P.R.; McMillan, P.N.; Zabala, V.; Wands, J.R.; de la Monte, S.M. Structural Correlates of PPAR Agonist Rescue of Experimental Chronic Alcohol-Induced Steatohepatitis. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2012, 2, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tong, M.; Dominguez, C.; Didsbury, J.; de la Monte, S.M. Targeting Alzheimer’s Disease Neuro-Metabolic Dysfunction with a Small Molecule Nuclear Receptor Agonist (T3D-959) Reverses Disease Pathologies. J. Alzheimers Dis. Parkinsonism 2016, 6, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Monte, S.M.; Tong, M.; Lester-Coll, N.; Plater, M., Jr.; Wands, J.R. Therapeutic rescue of neurodegeneration in experimental type 3 diabetes: Relevance to Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2006, 10, 89–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Monte, S.M.; Tong, M.; Schiano, I.; Didsbury, J. Improved Brain Insulin/IGF Signaling and Reduced Neuroinflammation with T3D-959 in an Experimental Model of Sporadic Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2017, 55, 849–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wagner, J.D.; Zhang, L.; Shadoan, M.K.; Kavanagh, K.; Chen, H.; Tresnasari, K.; Kaplan, J.R.; Adams, M.R. Effects of soy protein and isoflavones on insulin resistance and adiponectin in male monkeys. Metabolism 2008, 57, S24–S31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clark, J.L.; Taylor, C.G.; Zahradka, P. Rebelling against the (Insulin) Resistance: A Review of the Proposed Insulin-Sensitizing Actions of Soybeans, Chickpeas, and Their Bioactive Compounds. Nutrients 2018, 10, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gundogan, F.; QI, W.; Gilligan, J.; de la Monte, S.M. Effects of dietary soy on ethanol-impaired placentation and fetal growth. Placenta 2013, 34, A37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, M.; Yu, R.; Silbermann, E.; Zabala, V.; Deochand, C.; de la Monte, S.M. Differential Contributions of Alcohol and Nicotine-Derived Nitrosamine Ketone (NNK) to White Matter Pathology in the Adolescent Rat Brain. Alcohol Alcohol. 2015, 50, 680–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tong, M.; Deochand, C.; Didsbury, J.; de la Monte, S.M. T3D-959: A Multi-Faceted Disease Remedial Drug Candidate for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2016, 51, 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tong, M.; Gonzalez-Navarrete, H.; Kirchberg, T.; Gotama, B.; Yalcin, E.B.; Kay, J.; de la Monte, S.M. Ethanol-Induced White Matter Atrophy Is Associated with Impaired Expression of Aspartyl-Asparaginyl-beta-Hydroxylase (ASPH) and Notch Signaling in an Experimental Rat Model. J. Drug Alcohol Res. 2017, 6, 236033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stern-Straeter, J.; Bonaterra, G.A.; Hormann, K.; Kinscherf, R.; Goessler, U.R. Identification of valid reference genes during the differentiation of human myoblasts. BMC Mol. Biol. 2009, 10, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feriotto, G.; Finotti, A.; Breveglieri, G.; Treves, S.; Zorzato, F.; Gambari, R. Transcriptional activity and Sp 1/3 transcription factor binding to the P1 promoter sequences of the human AbetaH-J-J locus. FEBS J. 2007, 274, 4476–4490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, B.; Xing, A.; Li, S. The forgotten type 2 diabetes mellitus medicine: Rosiglitazone. Diabetol. Int. 2022, 13, 49–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Xie, X.B.; Cheng, X.C.; Wang, R.L. Multitargeted bioactive ligands for PPARs discovered in the last decade. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2016, 88, 635–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tovar, A.R.; Torre-Villalvazo, I.; Ochoa, M.; Elias, A.L.; Ortiz, V.; Aguilar-Salinas, C.A.; Torres, N. Soy protein reduces hepatic lipotoxicity in hyperinsulinemic obese Zucker fa/fa rats. J. Lipid Res. 2005, 46, 1823–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Homans, C.; Yalcin, E.B.; Tong, M.; Gallucci, G.; Bautista, D.; Moriel, N.; Monte, S.d.l. Therapeutic Effects of Myriocin in Experimental Alcohol-Related Neurobehavioral Dysfunction and Frontal Lobe White Matter Biochemical Pathology. Behav. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 23–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalcin, E.B.; Tong, M.; Homans, C.; de la Monte, S.M. Myriocin Treatment Reverses Alcohol-Induced Alterations in Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid-Containing Phospholipid Expression in the Liver. Nutr. Metab. Insights 2022, 15, 11786388221082012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dees, W.L.; Hiney, J.K.; Srivastava, V.K. Alcohol and Puberty: Mechanisms of Delayed Development. Alcohol. Res. 2017, 38, 277. [Google Scholar]
- Maskal, J.M.; Brito, L.F.; Duttlinger, A.W.; Kpodo, K.R.; McConn, B.R.; Byrd, C.J.; Richert, B.T.; Marchant, J.N.; Lay, D.C., Jr.; Perry, S.D.; et al. Characterizing the postnatal hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis response of in utero heat stressed pigs at 10 and 15 weeks of age. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 22527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, S.J.; Cox, S.R.; Shen, X.; Lombardo, M.V.; Reus, L.M.; Alloza, C.; Harris, M.A.; Alderson, H.L.; Hunter, S.; Neilson, E.; et al. Sex Differences in the Adult Human Brain: Evidence from 5216 UK Biobank Participants. Cereb. Cortex 2018, 28, 2959–2975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, C.G.; Blumbergs, P.C. Brain weights in alcoholics. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1982, 45, 838–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Estruch, R.; Nicolas, J.M.; Salamero, M.; Aragon, C.; Sacanella, E.; Fernandez-Sola, J.; Urbano-Marquez, A. Atrophy of the corpus callosum in chronic alcoholism. J. Neurol. Sci. 1997, 146, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rintala, J.; Jaatinen, P.; Lu, W.; Sarviharju, M.; Eriksson, C.J.; Laippala, P.; Kiianmaa, K.; Hervonen, A. Effects of lifelong ethanol consumption on cerebellar layer volumes in AA and ANA rats. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 1997, 21, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Monte, S.M.; Wands, J.R. Chronic gestational exposure to ethanol impairs insulin-stimulated survival and mitochondrial function in cerebellar neurons. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2002, 59, 882–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, M.; Ziplow, J.; Chen, W.C.; Nguyen, Q.G.; Kim, C.; de la Monte, S.M. Motor Function Deficits Following Chronic Prenatal Ethanol Exposure are Linked to Impairments in Insulin/IGF, Notch and Wnt Signaling in the Cerebellum. Diabetes. Metab. J. 2013, 4, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alessi, D.R.; Downes, C.P. The role of PI 3-kinase in insulin action. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1998, 1436, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Chiang, S.H.; Saltiel, A.R. Insulin signaling and the regulation of glucose transport. Mol. Med. 2004, 10, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hers, I.; Vincent, E.E.; Tavare, J.M. Akt signalling in health and disease. Cell Signal. 2011, 23, 1515–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, A.; Sabio, G.; Risco, A.M.; Cuenda, A.; Alonso, J.C.; Soler, G.; Centeno, F. Lithium blocks the PKB and GSK3 dephosphorylation induced by ceramide through protein phosphatase-2A. Cell Signal. 2002, 14, 557–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pap, M.; Cooper, G.M. Role of glycogen synthase kinase-3 in the phosphatidylinositol 3- Kinase/Akt cell survival pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 19929–19932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, J.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wang, X.; Li, L.; He, M.; Xue, A.; Zhu, K.; Shen, Y.; Li, B. Phosphorylation of PRAS40 contributes to the activation of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway and the inhibition of autophagy following status epilepticus in rats. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 20, 3625–3632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Xie, R.; Zhang, H.; Gu, L.; Xie, W.; Cheng, M.; Jian, Z.; Kovacina, K.; Zhao, H. PRAS40 plays a pivotal role in protecting against stroke by linking the Akt and mTOR pathways. Neurobiol. Dis. 2014, 66, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lahousse, S.A.; Carter, J.J.; Xu, X.J.; Wands, J.R.; de la Monte, S.M. Differential growth factor regulation of aspartyl-(asparaginyl)-beta-hydroxylase family genes in SH-Sy5y human neuroblastoma cells. BMC Cell Biol. 2006, 7, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aihara, A.; Huang, C.K.; Olsen, M.J.; Lin, Q.; Chung, W.; Tang, Q.; Dong, X.; Wands, J.R. A cell-surface beta-hydroxylase is a biomarker and therapeutic target for hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2014, 60, 1302–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luu, M.; Sabo, E.; de la Monte, S.M.; Greaves, W.; Wang, J.; Tavares, R.; Simao, L.; Wands, J.R.; Resnick, M.B.; Wang, L. Prognostic value of aspartyl (asparaginyl)-beta-hydroxylase/humbug expression in non-small cell lung carcinoma. Hum. Pathol. 2009, 40, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maeda, T.; Sepe, P.; Lahousse, S.; Tamaki, S.; Enjoji, M.; Wands, J.R.; de la Monte, S.M. Antisense oligodeoxynucleotides directed against aspartyl (asparaginyl) beta-hydroxylase suppress migration of cholangiocarcinoma cells. J. Hepatol. 2003, 38, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepe, P.S.; Lahousse, S.A.; Gemelli, B.; Chang, H.; Maeda, T.; Wands, J.R.; de la Monte, S.M. Role of the aspartyl-asparaginyl-beta-hydroxylase gene in neuroblastoma cell motility. Lab. Investig. J. Tech. Methods Pathol. 2002, 82, 881–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.H. Overexpression of humbug promotes malignant progression in human gastric cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2008, 19, 795–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; de la Monte, S.M.; Sabo, E.; Kethu, S.; Tavares, R.; Branda, M.; Simao, L.; Wands, J.R.; Resnick, M.B. Prognostic value of humbug gene overexpression in stage II colon cancer. Hum. Pathol. 2007, 38, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizarazo, D.; Zabala, V.; Tong, M.; Longato, L.; de la Monte, S.M. Ceramide inhibitor myriocin restores insulin/insulin growth factor signaling for liver remodeling in experimental alcohol-related steatohepatitis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 28, 1660–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, M.H.; Kang, K.S. Isoflavones as a smart curer for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and pathological adiposity via ChREBP and Wnt signaling. Prev. Med. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, G.; Ko, K.S. Long-Term Feeding of Soy Protein Attenuates Choline Deficient-Induced Adverse Effects in Wild Type Mice and Prohibitin 1 Deficient Mice Response More Sensitively. Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 2019, 24, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, S.M. Soybean, Nutrition and Health. In Soybean Bio-Active Compounds; El-Shemy, H.A., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ryan, S.H.; Williams, J.K.; Thomas, J.D. Choline supplementation attenuates learning deficits associated with neonatal alcohol exposure in the rat: Effects of varying the timing of choline administration. Brain Res. 2008, 1237, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thomas, J.D.; Biane, J.S.; O’Bryan, K.A.; O’Neill, T.M.; Dominguez, H.D. Choline supplementation following third-trimester-equivalent alcohol exposure attenuates behavioral alterations in rats. Behav. Neurosci. 2007, 121, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.D.; Idrus, N.M.; Monk, B.R.; Dominguez, H.D. Prenatal choline supplementation mitigates behavioral alterations associated with prenatal alcohol exposure in rats. Birth Defects Res. A. Clin. Mol. Teratol. 2010, 88, 827–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wozniak, J.R.; Fuglestad, A.J.; Eckerle, J.K.; Kroupina, M.G.; Miller, N.C.; Boys, C.J.; Brearley, A.M.; Fink, B.A.; Hoecker, H.L.; Zeisel, S.H.; et al. Choline supplementation in children with fetal alcohol spectrum disorders has high feasibility and tolerability. Nutr. Res. 2013, 33, 897–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wozniak, J.R.; Fink, B.A.; Fuglestad, A.J.; Eckerle, J.K.; Boys, C.J.; Sandness, K.E.; Radke, J.P.; Miller, N.C.; Lindgren, C.; Brearley, A.M.; et al. Four-year follow-up of a randomized controlled trial of choline for neurodevelopment in fetal alcohol spectrum disorder. J. Neurodev. Disord. 2020, 12, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Sex Effect | Exposure Effect | Sex x Exposure | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight | f-Ratio | p-Value | f-Ratio | p-Value | f-Ratio | p-Value |
| Body | f = 649.0 | p < 0.0001 | f = 214.2 | p < 0.0001 | f = 4.189 | p = 0.011 |
| Brain | f = 27.88 | p < 0.0001 | f = 19.34 | p < 0.0001 | f = 0.144 | NS |
| Trial Day Effect | Dietary Protein Effect | Trial Day x Diet | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MWM | f-Ratio | p-Value | f-Ratio | p-Value | f-Ratio | p-Value |
| Latency | f = 19.48 | p < 0.0001 | f = 4.259 | p = 0.009 | f = 0.723 | NS |
| Velocity | f = 01.94 | NS | f = 0.551 | NS | f = 1.822 | NS |
| Ethanol Effect | Diet Effect | Ethanol x Diet | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Protein | f-Ratio | p-Value | f-Ratio | p-Value | f-Ratio | p-Value |
| IN-R | 1.128 | NS | 8.284 | 0.0093 | 10.13 | 0.0047 |
| IGF-1R | 1.194 | NS | 0.013 | NS | 3.887 | 0.063 |
| IRS-1 | 0.002 | NS | 0.967 | NS | 6.08 | 0.0228 |
| Akt | 0.664 | NS | 1.356 | NS | 7.228 | 0.014 |
| GSK-3β | 0.100 | NS | 5.96 | 0.024 | 3.713 | 0.068 |
| PRAS40 | 0.035 | NS | 1.961 | NS | 0.001 | NS |
| P70S6K | 0.379 | NS | 0.509 | NS | 5.402 | 0.031 |
| Ethanol Effect | Diet Effect | Ethanol x Diet | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Protein | f-Ratio | p-Value | f-Ratio | p-Value | f-Ratio | p-Value |
| pIN-R | 0.448 | NS | 4.975 | 0.037 | 3.184 | 0.089 |
| pIGF-1R | 2.422 | NS | 0.388 | NS | 1.302 | NS |
| pIRS-1 | 0.427 | NS | 4.800 | 0.041 | 0.001 | NS |
| pAkt | 1.049 | NS | 0.485 | NS | 9.570 | 0.006 |
| pGSK-3b | 0.620 | NS | 0.775 | NS | 8.521 | 0.008 |
| pPRAS40 | 0.521 | NS | 10.68 | 0.004 | 0.225 | NS |
| pP70S6K | 0.038 | NS | 0.000 | NS | 1.390 | NS |
| Ethanol Effect | Diet Effect | Ethanol x Diet | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Protein | f-Ratio | p-Value | f-Ratio | p-Value | f-Ratio | p-Value |
| ASPH-A86G6 | f = 11.88 | p = 0.003 | f = 4.63 | p = 0.044 | f = 0.573 | NS |
| ASPH-A85E6 | f = 25.75 | p < 0.0001 | f = 15.02 | p = 0.0009 | f = 2.952 | NS |
| Notch-1 | f = 0.052 | NS | f = 7.67 | p = 0.012 | f = 1.104 | NS |
| Jagged-1 | f = 4.573 | p = 0.04 | f = 1.12 | NS | f < 0.001 | NS |
| HES-1 | f = 2.017 | NS | f = 2.16 | NS | f = 0.011 | NS |
| HIF-1α | f = 0.016 | NS | f = 0.20 | NS | f = 0.209 | NS |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tong, M.; Ziplow, J.L.; Mark, P.; de la Monte, S.M. Dietary Soy Prevents Alcohol-Mediated Neurocognitive Dysfunction and Associated Impairments in Brain Insulin Pathway Signaling in an Adolescent Rat Model. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 676. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12050676
Tong M, Ziplow JL, Mark P, de la Monte SM. Dietary Soy Prevents Alcohol-Mediated Neurocognitive Dysfunction and Associated Impairments in Brain Insulin Pathway Signaling in an Adolescent Rat Model. Biomolecules. 2022; 12(5):676. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12050676
Chicago/Turabian StyleTong, Ming, Jason L. Ziplow, Princess Mark, and Suzanne M. de la Monte. 2022. "Dietary Soy Prevents Alcohol-Mediated Neurocognitive Dysfunction and Associated Impairments in Brain Insulin Pathway Signaling in an Adolescent Rat Model" Biomolecules 12, no. 5: 676. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12050676
APA StyleTong, M., Ziplow, J. L., Mark, P., & de la Monte, S. M. (2022). Dietary Soy Prevents Alcohol-Mediated Neurocognitive Dysfunction and Associated Impairments in Brain Insulin Pathway Signaling in an Adolescent Rat Model. Biomolecules, 12(5), 676. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12050676





