Abstract
The application of graphene-based materials in medicine has led to significant technological breakthroughs. The remarkable properties of these carbon materials and their potential for functionalization with various molecules and compounds make them highly attractive for numerous medical applications. To enhance their functionality and applicability, extensive research has been conducted on surface modification of graphene (GN) and its derivatives, including modifications with antimicrobials, metals, polymers, and natural compounds. This review aims to discuss recent and relevant studies related to advancements in the formulation of graphene composites, addressing their antimicrobial and/or antibiofilm properties and evaluating their biocompatibility, with a primary focus on their biomedical applications. It was concluded that GN surface modification, particularly with compounds intrinsically active against bacteria (e.g., antimicrobial peptides, silver and copper nanomaterials, and chitosan), has resulted in biomaterials with improved antimicrobial performance. Furthermore, the association of GN materials with non-natural polymers provides composites with increased biocompatibility when interfaced with human tissues, although with slightly lower antimicrobial efficacy. However, it is crucial to highlight that while modified GN materials hold huge potential, their widespread use in the medical field is still undergoing research and development. Comprehensive studies on safety, long-term effects, and stability are essential before their adoption in real-world medical scenarios.
1. Introduction
In recent years, graphene materials have attracted significant interest due to their remarkable properties and various applications. Graphene (GN) is a two-dimensional carbon allotrope composed of a single layer of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice [1]. This structure, which has a high surface area and large aspect ratio, confers high electronic and thermal conductivities to GN, as well as superior mechanical strength [2,3,4]. In addition, GN exhibits a high ability to interact with other molecules through various processes, including physical and chemical interactions [5].
Graphene derivatives can be generated by introducing oxygen-containing functional groups to the GN structure or reducing its oxide form, obtaining graphene oxide (GO) or reduced graphene oxide (rGO) [6], respectively. Additionally, GN monolayers can be modified with metals, antimicrobial drugs, polymers, and natural compounds [7,8,9,10]. While these derivatives preserve their original properties, they also offer enhanced advantages, such as improving the GN dispersion factor in solvents or polymeric matrices and reducing GN toxicity [11,12,13]. As a result, GN has been applied in numerous industries, including construction [14], energy [15], food [16], environmental [17], and biomedical [18].
Within the medical field, there have been notable technological advances in the application of GN and its derivatives in drug/gene delivery, biosensing, bioimaging [19], wound healing [20], and tissue engineering [18]. Furthermore, due to the antimicrobial activity and biocompatibility of GN-based materials, they are deemed suitable for manufacturing implantable medical devices such as cardiovascular stents, orthopaedic scaffolds, and urinary implants [21,22].
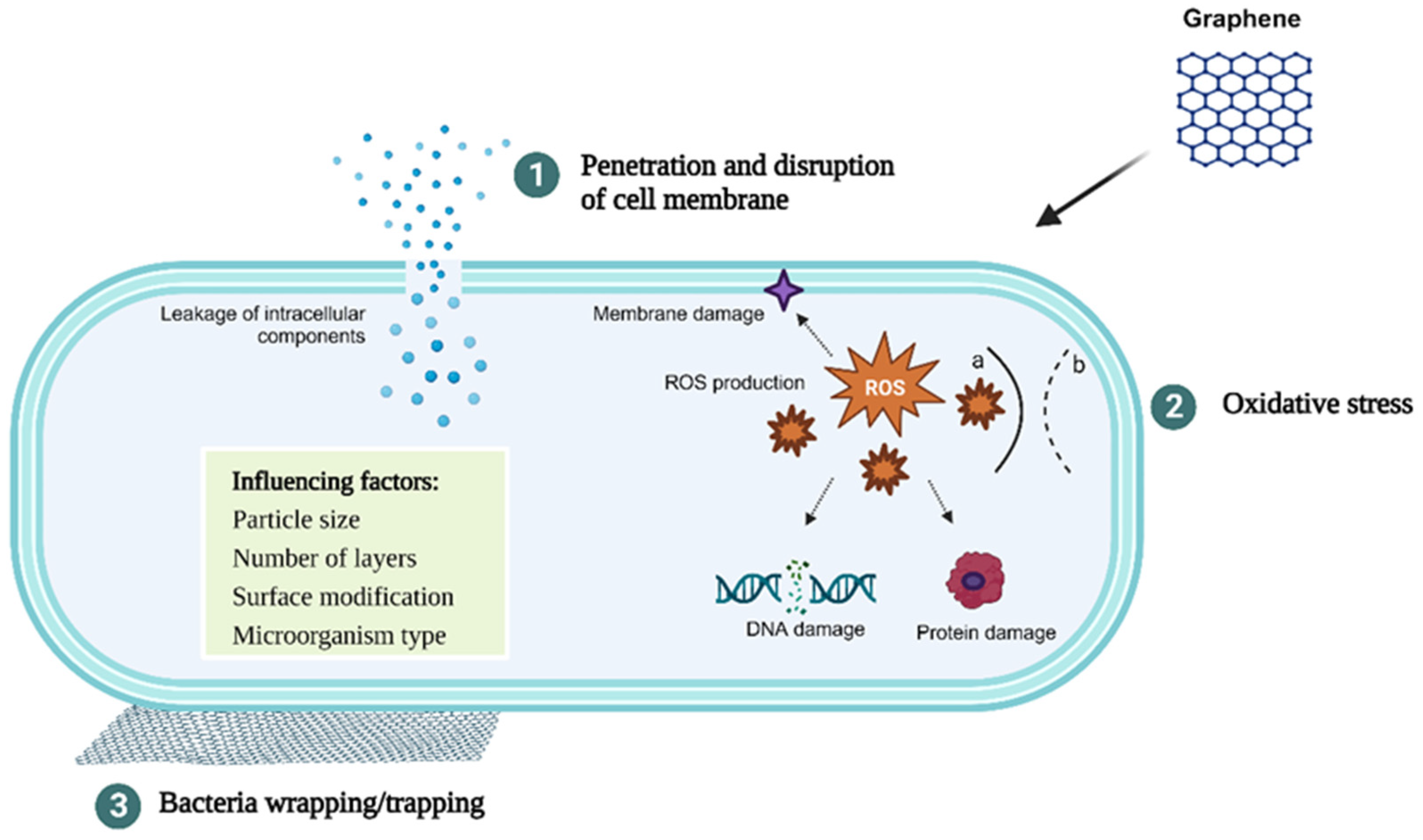
To date, different mechanisms have been proposed to explain the antimicrobial activity of GN and its derivatives (Figure 1). GN’s sharp edges can physically damage bacterial cell membranes, leading to loss of their integrity, leakage of intracellular content, and, ultimately, cell death [23,24,25]. GN can also generate oxidative stress, which may come from different paths—reactive oxygen species (ROS)-dependent or ROS-independent pathways—which, in either case, disrupt cellular functions, resulting in cell inactivation [25,26]. Lastly, GN-based materials can also wrap and trap bacterial cells [26,27,28]. GN can act as a barrier that traps and isolates bacteria from the environment, further inhibiting their proliferation. Furthermore, this wrapping/trapping effect induces cell membrane damage in combination with the other mechanisms mentioned previously [28]. The interaction between GN and bacterial cell membranes is believed to be the driving factor behind the toxicity exerted by these carbon materials.
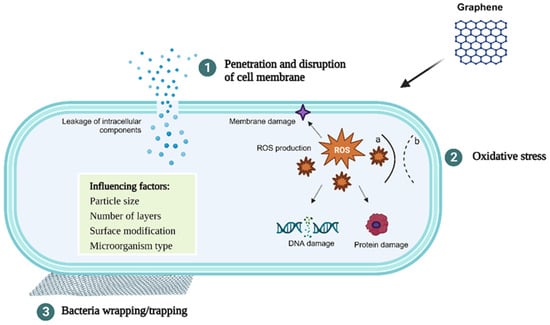
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the antibacterial mechanisms of GN and factors influencing its antimicrobial activity. (1) Penetration and disruption of the bacterial cell membrane with consequent leakage of the intracellular content; (2) oxidative stress with (a) and without (b) generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS); (3) bacteria wrapping/trapping.
The antimicrobial potential of GN is related not only to its structural properties (e.g., particle size and number of layers) but also to the surface modification, the nature of the targeted microorganism (Gram-positive or Gram-negative bacteria), and the environment where GN and microbial cells interact (Figure 1).
Smaller GN particles with a higher surface-to-volume ratio can interact more effectively with microbial cells and affect their membrane integrity [29,30]. In addition, smaller particles may diffuse more easily within microbial biofilms, allowing better disruption of their structure and function [31]. Likewise, few-layer GN sheets have shown a strong antimicrobial effect, leading to significant damage to microbial cell membranes [32]. Contrarily, more layers decrease the GN dispersibility and its contact with microorganisms [26]. Previous studies have also reported that GN modified with cationic functional groups is more toxic to microbial cells than GN containing neutral or negatively charged groups [33,34]. This may be attributed to favorable electrostatic interactions between the positively charged GN surfaces and negatively charged microbial cell membranes [34]. Functionalization can also change the GN surface hydrophobicity [33], thereby enhancing its dispersibility [35]. Furthermore, GN surface modification allows the attachment of bioactive molecules, such as antimicrobial agents or peptides, which specifically target and disrupt microbial cells [8,36].
Studies have revealed that GN and its derivatives, such as GO and rGO, can inactivate both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria in either planktonic or sessile states [37]. However, it has been evidenced that these graphene-based materials are more effective towards Gram-positive than Gram-negative bacteria [38,39]. While Gram-positive bacteria contain a plasmatic membrane and a thick peptidoglycan layer, Gram-negative bacteria have an outer membrane mainly composed of lipopolysaccharides, which may offer additional protection against chemical and physical stress [40]. Additionally, GN materials have shown promising antimicrobial activity against drug-resistant bacteria; therefore, they can be considered for therapeutic purposes [41].
When using GN materials for medical applications, it is crucial to comprehensively evaluate their biocompatibility to ensure that they are safe for use in real scenarios, such as medical devices or wound dressings. Numerous studies have been conducted and the results are mostly promising [27,42,43,44]. In vitro studies have shown that GN-based materials can interact with human cells, and their effects on cell viability and proliferation can vary depending on factors like GN size, concentration, and surface functionalization [45,46]. In general, lower concentrations and well-dispersed GN tend to be more biocompatible. Likewise, surface functionalization plays a significant role in increasing GN biocompatibility [45].
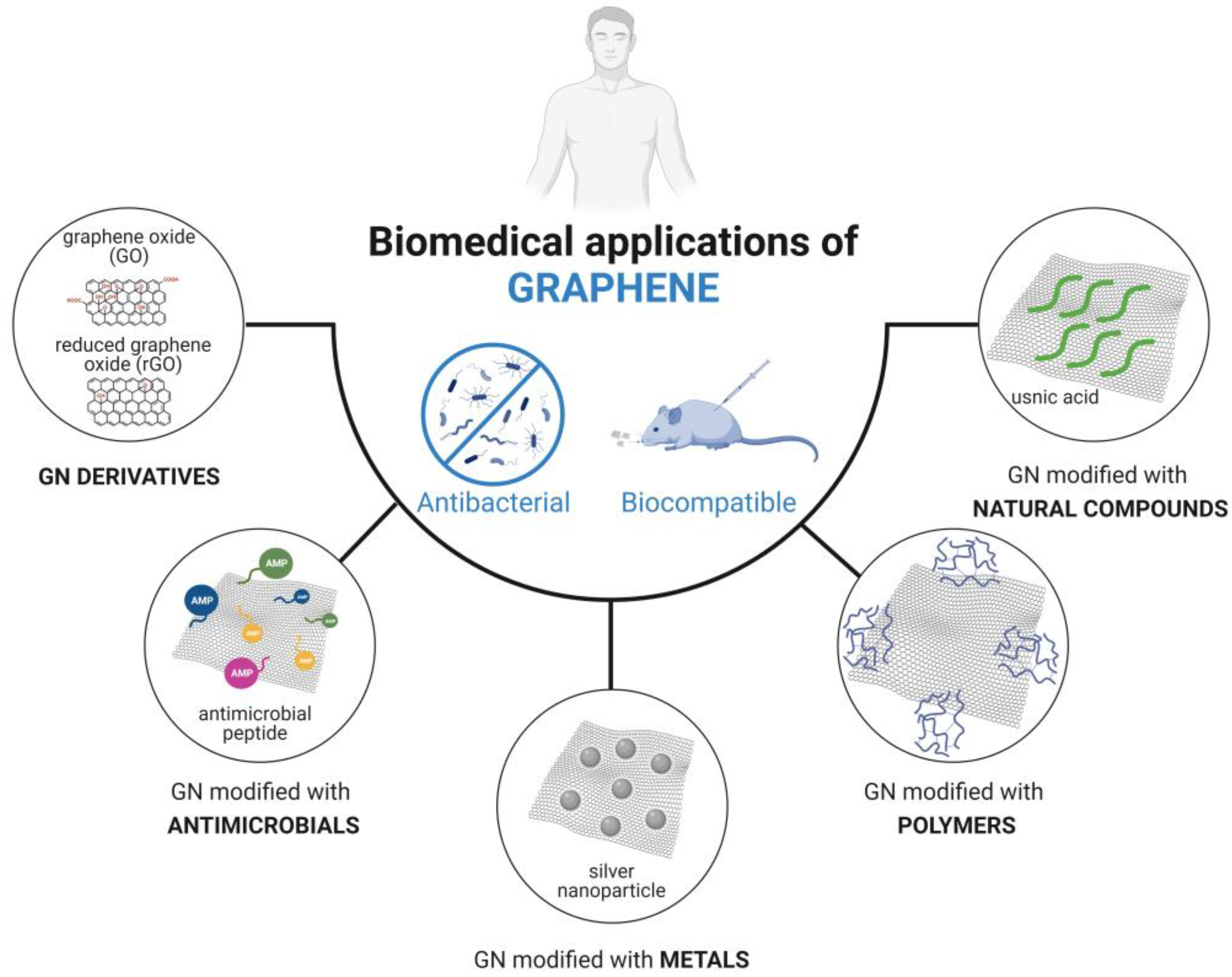
Despite the plentiful range of GN-based materials developed in recent years, most are still far from practical biomedical applications. As a result, further investigation is necessary to understand the functionality, applicability, and safety of these carbon materials. Hence, this review aims to critically discuss recent progress in the formulation of graphene composites, assessing their antimicrobial and/or antibiofilm activities while also evaluating their biocompatibility, with a focus on biomedical applications. Research involving GN and its derivatives modified with antimicrobials, metals, polymers, or natural compounds is addressed (Figure 2). By summarizing and categorizing recently developed GN-based composites based on their surface modification type, this review provides a comprehensive perspective on the applicability and effectiveness of GN materials in the medical field, including insights into GN–bacteria interactions. Additionally, it serves as a valuable resource to aid researchers in the development and optimization of GN materials tailored for specific medical applications.
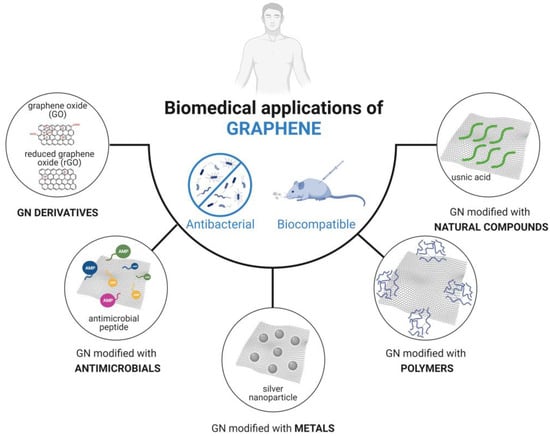
Figure 2.
Types of graphene (GN) modifications discussed in this review for potential use in the biomedical field.
2. Graphene Modified with Antimicrobials
One desirable feature of graphene is its capacity to bind to a variety of molecules, including antimicrobial agents, peptides, and biocides. This capability not only broadens the range of potential applications of GN materials but also has the potential to enhance their antimicrobial activity and biocompatibility [47]. Table 1 summarizes recent studies that assessed the biocompatibility and antimicrobial performance of GN materials modified with antimicrobial compounds, including antibiotics [48], antimicrobial peptides [8,49,50], and disinfectants [36].

Table 1.
Studies focusing on the biocompatibility and antimicrobial activity of graphene modified with antimicrobials.
Tran et al. [48] modified the GO surface with doxycycline (Dox), a bacteriostatic antibiotic, and coated titanium (TiO2) surfaces for potential application in medical devices. The results demonstrated that Dox-modified GO/TiO2 surfaces reduced the viability of adhered bacteria by 90% compared to the 40% reduction observed with GO/TiO2 surfaces. This suggests that Dox exhibited a synergistic effect with the GO material, efficiently inhibiting bacterial adhesion. This antibiotic acts by inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis [51] and likely makes cells more susceptible to the action of GO. Concerning biocompatibility, these materials did not adversely affect the viability of human fibroblasts, making them suitable for potential medical applications [48].
Other authors have modified GO surfaces with antimicrobial peptides (AMP), including the N-terminal fragment of Cathelicidin-2 (CATH-2) [49], ponericin G1 [8], or OH-CATH30 (OH30) [50]. In vitro results demonstrated that this association significantly impaired the growth of Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus (up to 95% reduction). Furthermore, data from an in vivo study revealed that wounds containing AMP-GO materials exhibited six times fewer S. aureus cells than those containing AMP or the GN material alone [50]. The antimicrobial activity of AMP is well known, as they act by interacting with bacterial cell membranes, increasing their permeability and leading to cell death [49]. Thus, both AMP and GO target bacterial membranes, strengthening the antimicrobial action of the synthesized material. Additionally, these AMP-GO materials displayed low cytotoxicity towards mammalian cells (over 80% cell viability) [8,49,50].
Lastly, Lan et al. [36] developed an N-halamine-GO fibrous membrane, which was capable of inactivating E. coli cells by over 90%. N-halamines can transfer active halogen ions (e.g., Cl+) to bacteria through direct contact or release, thereby exerting antibacterial effects in combination with GO.
Although the materials mentioned above have been tested against a limited number of bacterial species (only E. coli and S. aureus), results suggest that they have promising antibacterial activity (over 90% biocidal activity) and excellent biocompatibility with human tissues.
3. Graphene Modified with Metals
Various metals and metal oxides have been utilized to modify the surface of GN and its derivatives in order to enhance their antimicrobial activity. Metals are known for their strong antimicrobial properties against a wide range of pathogens [52,53,54]. However, their biocompatibility can vary depending on factors such as the type of metal chosen and the method of conjugation.
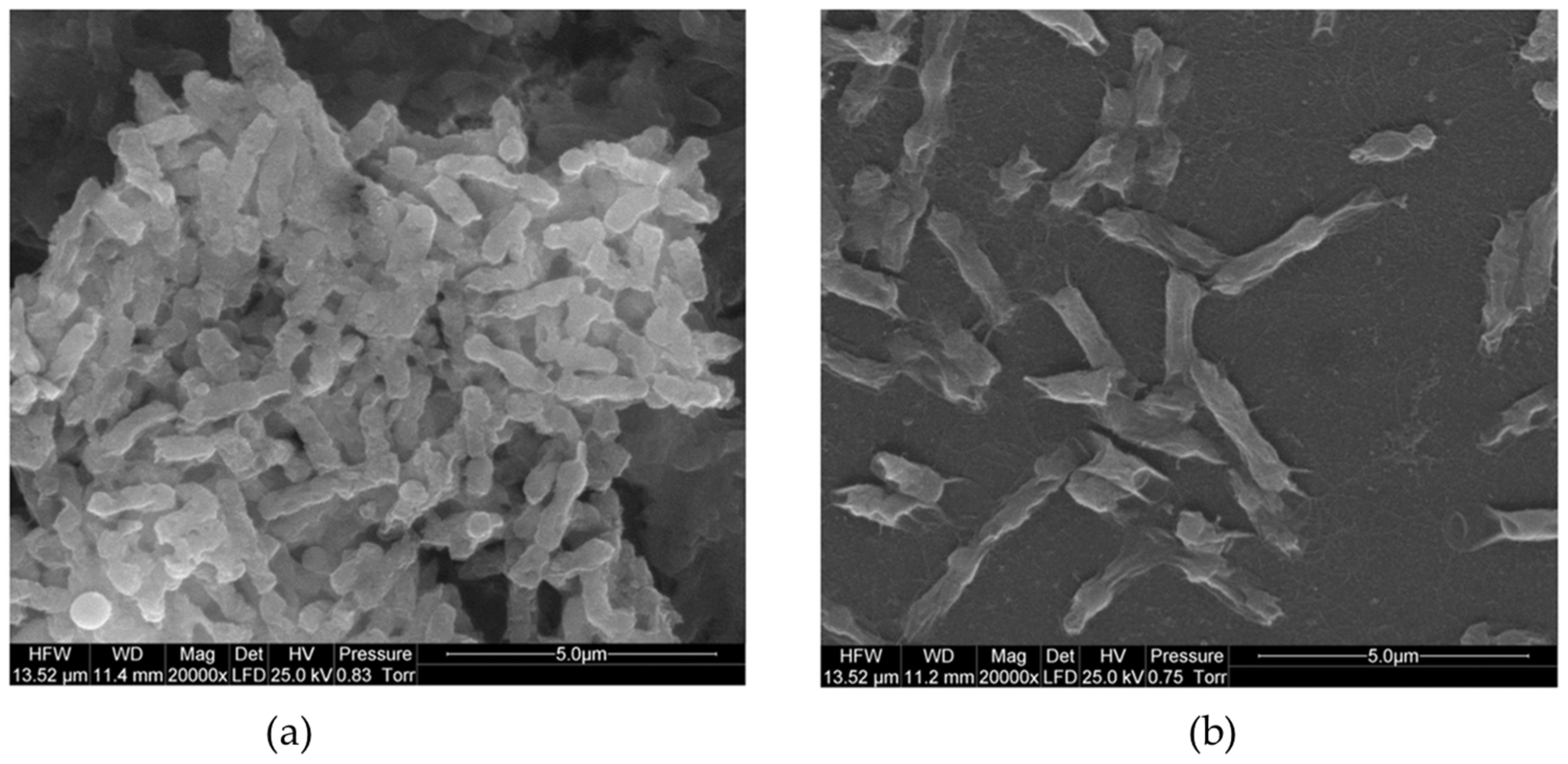
Table 2 presents studies that have evaluated the antimicrobial activity and biocompatibility of GN materials modified with metals or metal oxides. Several authors have focused on surface-modifying GO [55,56] or rGO [57,58] with silver nanoparticles (AgNPs). The resulting composites exhibited higher inactivation rates against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, with the exception of the composite synthesized and tested by Wierzbicki et al. [55] against Salmonella enteritidis (approximately 50% reduction; Figure 3). The modification of GN-based materials with AgNPs results in a synergistic effect, as they inactivate bacteria by interacting with proteins and enzymatic thiol groups [57]. Furthermore, composites containing AgNPs appear safe for medical use.

Table 2.
Studies addressing the biocompatibility and antimicrobial activity of graphene modified with metals.
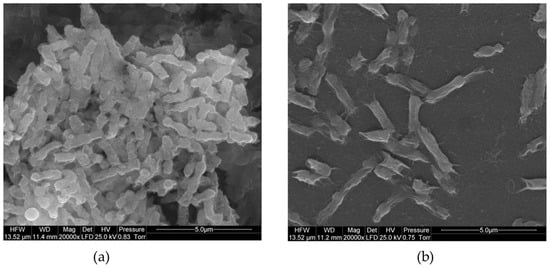
Figure 3.
Scanning electron microscope (SEM) images of (a) Salmonella enteritidis bacteria and (b) S. enteritidis growing on silver nanoparticles (AgNPs)-graphene oxide (GO)-coated nanoplatform. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [55]. Copyright 2019 The Authors.
The second most common metal used for GN surface modification is copper (Cu), either in the nanoparticle [54] or oxide form [52,53]. In general, Cu-GN materials demonstrated superior antimicrobial activity against Gram-positive bacteria (100% inactivation) compared to Gram-negative ones (20–90% inactivation), which can be attributed to the more intricate cell membrane structure of Gram-negative bacteria. The synthesized materials carry a positive charge that attracts bacterial membranes through physical adsorption and electrostatic interactions [52]. Additionally, they induced the generation of ROS, which ultimately kill bacteria. Furthermore, the developed materials exhibit excellent compatibility with human tissues [52,53].
The surface modification of GO with gold (Au) also exhibited promising activity against pathogenic bacteria (five-fold reduction) and did not affect the viability of human cells [59].
Although palladium (Pd)-reduced GO exhibited low biocompatibility, it is considered a promising material for tissue engineering, with bacterial inactivation ratios ranging from 72 to 90%, depending on the type of bacteria [60]. This composite wraps the bacterial cells and inhibits their metabolism. Lastly, cerium oxide (CeO2)-GO materials demonstrated moderate antimicrobial activity (30–40% bacterial inactivation) against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria by inducing ROS production [61].
Although they may be associated with lower biocompatibility, composites resulting from the combination of carbon materials and metals, particularly silver and copper, exhibit strong antimicrobial activity, mainly against Gram-positive bacteria. In addition, approximately 80% of the antimicrobial activity of developed GN–metal composites is attributed to GN action.
4. Graphene Modified with Polymers
Graphene surface modification with polymers is an interesting approach that can offer several advantages, including enhanced GN dispersion and improved mechanical properties and biocompatibility [62,63]. In addition, the association with polymers can potentially increase the antimicrobial activity of GN-based materials, as the polymers serve as a matrix that helps GN dispersion [35], thus promoting contact with microorganisms. Furthermore, some polymers have inherent antimicrobial properties because they contain cationic groups that can facilitate interactions with bacteria [64,65].
Table 3 summarizes studies addressing the biocompatibility and antimicrobial activity of GN materials modified with natural and non-natural polymers. Both pristine GN and GO have been modified with various polymers for potential medical applications (e.g., tissue engineering, wound dressing, or implantable medical devices).
Hajduga et al. [64] produced polycaprolactone (PCL)-GN composites and evaluated their antimicrobial activity against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. While these composites were able to inactivate S. aureus by 90%, no effect was observed against E. coli, although both materials (GN and PCL) have known antimicrobial activity. These discrepant results may be related to the morphology of the tested bacteria, as previously described. In turn, poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA)-GN composites were developed and tested against E. coli under electric stimulation [9]. Results indicated that, at lower frequencies, synthesized films decreased bacterial viability by up to 60%. Lastly, Oliveira et al. [66] demonstrated that polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS)-GN composites significantly reduced the number of total (57%), viable (69%), culturable (55%), and viable but non-culturable (VBNC) cells (85%) of S. aureus biofilms, while a decrease of 25% in total cells and approximately 52% in viable, culturable, and VBNC cells was observed for Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms.
Concerning GO, its association with polyoxyalkyleneamine (POAA) [67] or poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL) [68] resulted in composites that significantly decreased the viability of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria (approximately 80%). Furthermore, a recently developed epoxy resin rich in GO demonstrated promising in vitro inactivation percentages against E. coli and S. aureus (57 and 97%, respectively) [69]. However, when evaluated in vivo, the antibacterial efficacy of this composite decreased to 47% for E. coli and 68% for S. aureus.
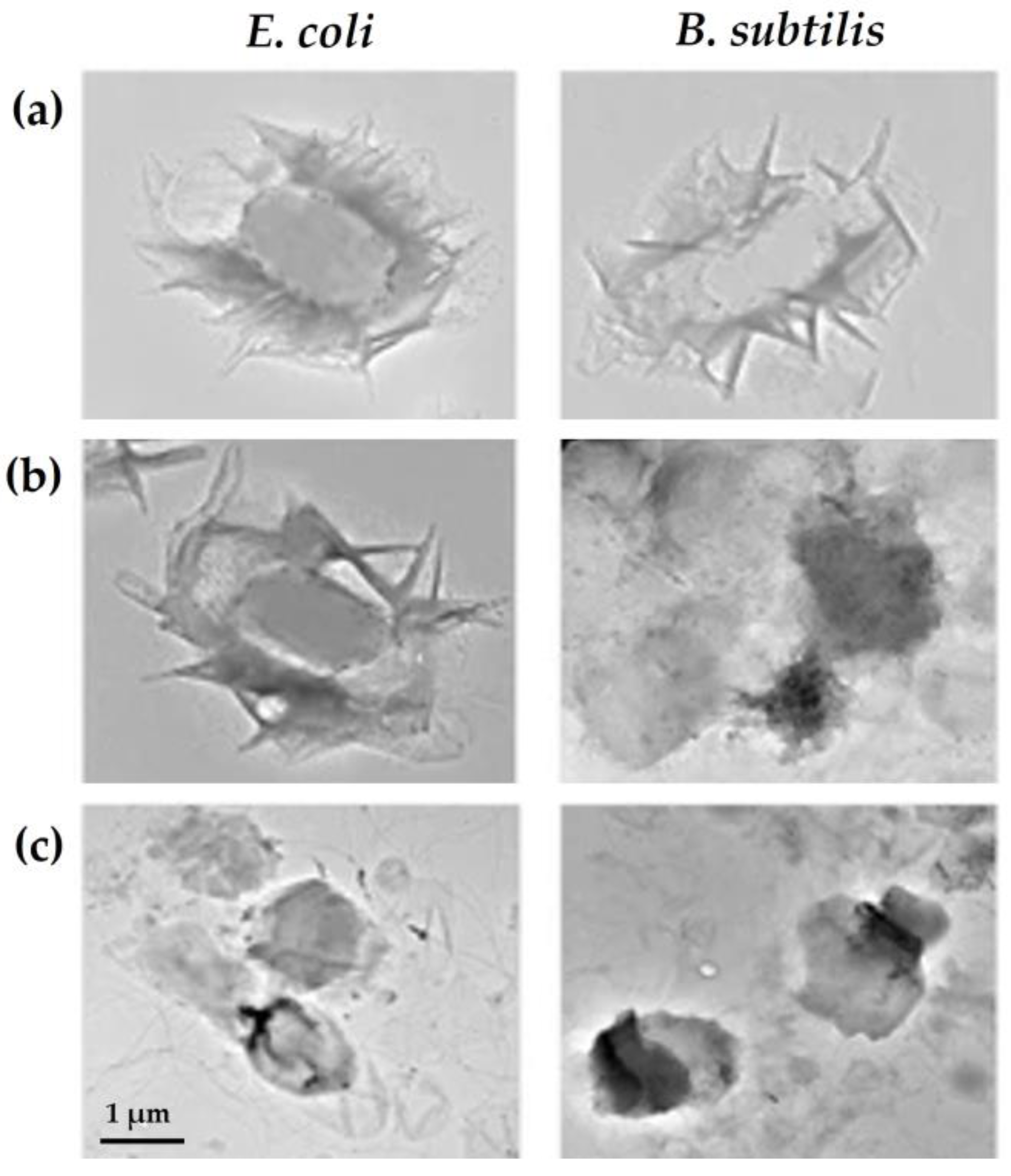
In vitro and in vivo studies have shown that GO surface modification with natural polymers, such as chitosan (CS) or carboxymethyl CS, increased its antimicrobial activity, resulting in over 90% inactivation of Bacillus subtilis, E. coli, and S. aureus cells [43,67], with no toxic effects observed in mammalian cells [43]. The combination of CS/poly(vinyl alcohol) with GO resulted in nanocomposites that could completely inhibit the growth of a wide range of pathogens, even at low concentrations (0.75 and 1 wt.%) [10,70]. Furthermore, biocompatibility assays demonstrated that these composites exhibited no toxicity towards pre-osteoblast cells, with over 70% cell viability [10]. Also, CS/polyethylene glycol-GO composites were promising for reducing E. coli and S. aureus viability (over 95% cell inactivation) while maintaining mammalian cell viability at 95% [42]. In fact, CS is known to be a powerful antibacterial compound that inactivates bacterial cells by interacting with their negatively charged membranes, leading to a decrease in their permeability and leakage of intracellular content. Additionally, CS can bind to bacterial DNA, thereby inhibiting the replication process. Lastly, CS is able to chelate metal ions which are essential for bacterial growth and proliferation [71]. Therefore, the surface modification of GN materials with CS enhances their interactions with bacteria, leading to more significant cell damage (Figure 4a,c).
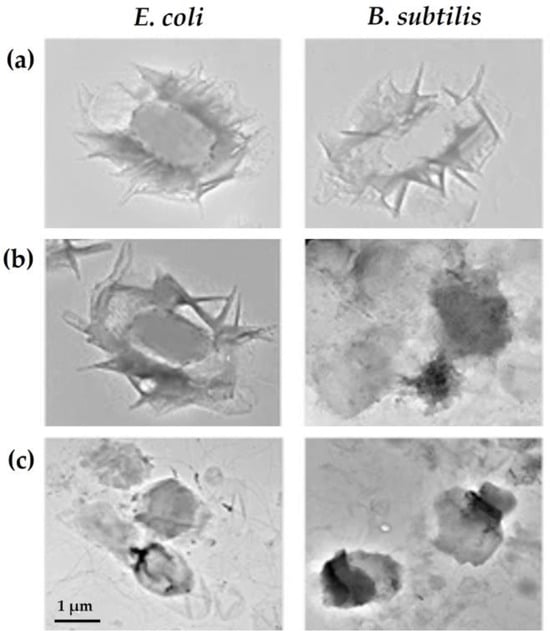
Figure 4.
Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis exposed to (a) graphene oxide (GO), (b) polyoxyalkyleneamine (POAA)-GO, and (c) chitosan (CS)-GO for 3 h and characterized by transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Reprinted with permission from Ref. [67]. Copyright 2018 The Authors.
Furthermore, the GO surface modification with folic acid and silk fibroin resulted in composites with high antibiofilm activity (80% inhibition of biofilm formation by P. aeruginosa) and biocompatibility (97% fibroblast viability) [71].
In general, these results indicate that the addition of GN materials to natural and non-natural polymers increased their antimicrobial activity by up to 70%, demonstrating a synergistic effect. Several authors have suggested that the main mechanism of action of polymer–GN composites is the wrapping of bacterial cells. When an external barrier made of GN-based materials is formed around the bacteria (Figure 4c) [67], it facilitates contact with cells, reduces access to essential nutrients for microbial growth, and induces oxidative stress, ultimately leading to cell death. Other authors have demonstrated that the effectiveness of polymer-containing composites results from a combined bactericidal and bacterial-repelling effect [72].
Regarding biocompatibility, human cells exposed to GN-based composites maintained their viability and proliferation capability [68,69]. In general, the combination of GN materials and polymers yielded composites with improved biocompatibility and substantial in vitro antimicrobial activity against medical pathogens.

Table 3.
Studies reporting the biocompatibility and antimicrobial activity of graphene modified with polymers.
Table 3.
Studies reporting the biocompatibility and antimicrobial activity of graphene modified with polymers.
| Graphene Material | Biomedical Application | Biocompatibility | Microorganism | Main Conclusions | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-natural polymers | |||||
| Polyoxyalkyleneamine (POAA)-graphene oxide (GO) | Surface coatings | NP | Bacillus subtilis Escherichia coli | After 3 h, bacteria exposed to POAA-GO decreased their viability to at least 75%. | [67] |
| Poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL)-GO | Tissue engineering | Human fibroblasts kept their culturability and proliferation for up to 14 days. | E. coli Staphylococcus epidermidis | PCL-GO composites inactivated S. epidermidis and E. coli adhered cells by 80% after 24 h. | [68] |
| PCL-graphene (GN) | Nasal implants | NP | E. coli Staphylococcus aureus | The efficacy of PCL-GN against S. aureus was about 90%. In contrast, this composite did not exhibit activity against E. coli. | [64] |
| Epoxy-rich-GO (er-GO) | Wound dressing | Human cells exposed to er-GO exhibited viability ratios greater than 100%. | E. coli S. aureus | er-GO composite decreased in vitro E. coli and S. aureus viability by up to 57 and 97%, respectively. In vivo data indicated that E. coli and S. aureus viability was reduced by 47 and 68%, respectively, in presence of er-GO. | [69] * |
| Poly(Lactic-co-Glycolic Acid) (PLGA)-graphene nanoplatelets (GNP) | NE | NP | E. coli | At 15 MHz, PLGA-GNP composites reduced E. coli viability by 33%, while at lower frequencies (10 and 5 MHz), these films decreased bacteria viability by up to 60%. | [9] |
| Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS)-GNP | Implantable medical devices | NP | Pseudomonas aeruginosa S. aureus | The PDMS-GNP reduced the number of total (57%), viable (69%), culturable (55%), and VBNC cells (85%) of S. aureus biofilms. A decrease of 25% in total cells and about 52% in viable, culturable, and VBNC cells was observed for P. aeruginosa biofilms. | [66] |
| Natural polymers | |||||
| Chitosan (CS)-graphene oxide (GO) | Surface coatings | NP | B. subtilis E. coli | After 3 h, bacteria exposed to CS-GO composite decreased their viability to less than 10%. | [67] |
| CS/poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA)-GO nanocomposites | Tissue engineering | After 30 days of film implantation, the absence of injuries in the intervened areas with normal healing was observed. | Bacillus cereus S. aureus E. coli Salmonella spp. | Biocomposites containing 0.75 and 1 wt.% GO completely inhibited pathogen growth. | [70] * |
| CS/PVA-GO | Wound healing | CS/PVA-GO hydrogels showed nontoxicity towards pre-osteoblast cells (>70% cell viability). | E. coli S. aureus | Hydrogels exhibited high antimicrobial activity against E. coli and S. aureus (up to 35 and 32 mm inhibition halo, respectively). | [10] |
| CS/polyethylene glycol (PEG)-decorated GO biocomposite | Wound healing | Cell survival on CS/PEG-GO was 95.4%. | E. coli S. aureus | CS, 1 wt% CS/GO and 1 wt% CS/PEG-GO were able to inactivate S. aureus by 80, 85, and 100% and E. coli by 65, 85, and 95%, respectively. | [42] |
| Carboxymethyl Chitosan (CC)-GO-based Sponge | Wound healing | CC/L-cysteine-GO sponge showed a high cell viability rate, as demonstrated by Live/Dead staining. | E. coli S. aureus | In vivo data indicated that the CC/L-cysteine-GO sponge had a faster wound-healing rate than CC/GO. In vitro tests revealed that the addition of L-cysteine-GO and GO to CC increased sponges’ antimicrobial activity. | [43] * |
| Folic acid (FA)/silk fibroin (SF)-GO | Wound healing Tissue engineering | The viability of fibroblast cells exposed to FA/SF-GO for 24 h was 97%. | P. aeruginosa | After 24 h, FA/SF-GO film reduced biofilm formation by 80% compared to control (polystyrene). | [73] |
NP, Not Performed; NS, Not Specified; VBNC, viable but non-culturable; *, in vivo study.
5. Graphene Modified with Natural Compounds
Owing to their biodegradability, renewability, and biocompatibility, there has been growing interest in composites that incorporate natural compounds. In recent years, several natural compounds, including vivianite [74], usnic acid (UA) [75], quercetin [76], and juglone [76], have been studied in conjugation with GN composites. Table 4 presents the biocompatibility and antimicrobial activity of these modified GN materials against several Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacterial species.

Table 4.
Studies demonstrating the biocompatibility and antimicrobial activity of graphene modified with natural compounds.
Among the studies presented, natural compounds were mainly associated with graphene oxide.
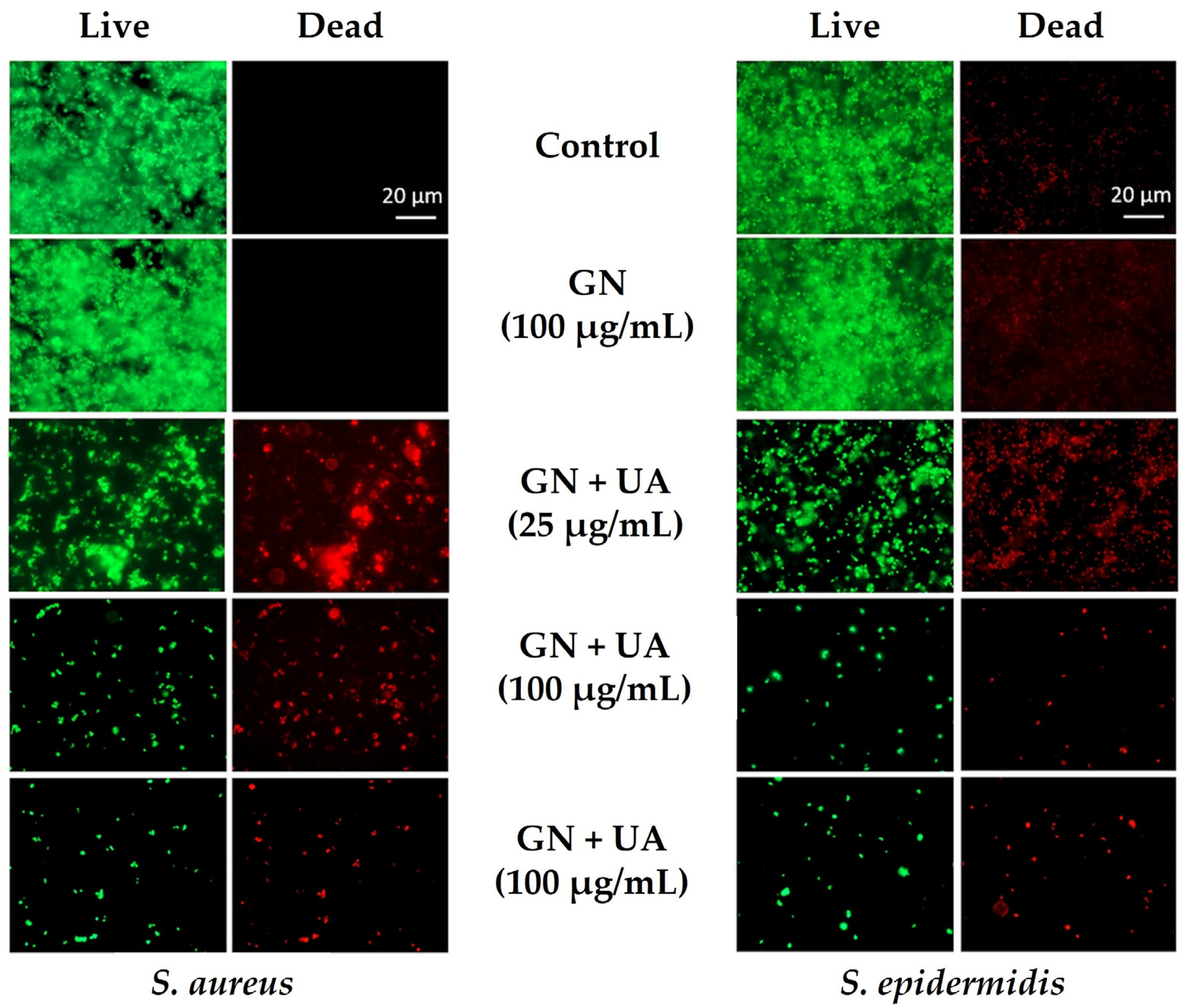
Pandit et al. [75] conjugated GN with usnic acid and observed that, after 24 h of contact, the synthesized composites reduced the growth of S. aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis by up to 3 Log in a dose-dependent manner (Figure 5). Furthermore, after 96 h, staphylococcal biofilms were reduced by 5 Log. The potent antimicrobial activity of UA is mainly based on the inhibition of RNA synthesis [75], which, in combination with GN antibacterial mechanisms, impairs bacterial growth. The hydroxyapatite/vivianite-GO composite also displayed promising antimicrobial activity against E. coli and S. aureus while preserving the viability of osteoblast cells [74]. The ferrous (Fe2+) and calcium (Ca2+) ions released from the composite may have contributed to potentiating its antimicrobial performance. Moreover, hydroxyapatite is well known for its exceptional biocompatibility. Croitoru et al. [76] modified GO surfaces with two natural antimicrobial agents, quercetin and juglone. Quercetin and juglone/GO composites reduced S. aureus culturability by 1 and 3 Log, respectively, and E. coli culturability by 5 Log. These GO-based materials showed biocompatible behavior at lower concentrations.
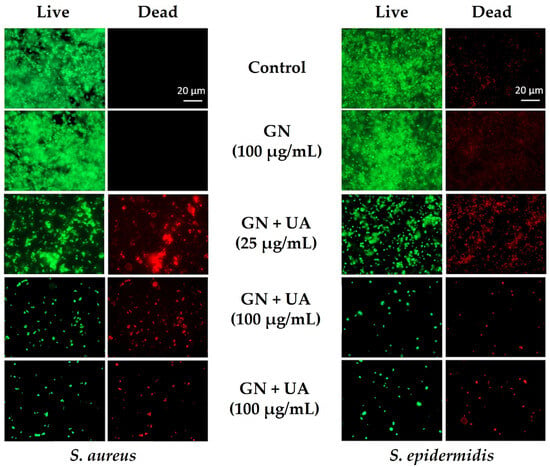
Figure 5.
Antibiofilm capability of graphene (GN) and usnic acid (UA)-loaded graphene films against Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis. Representative fluorescence microscopic images from Live/Dead staining of staphylococcal biofilms. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [75]. Copyright 2021 The Authors.
Overall, natural compounds, particularly quercetin and juglone, enhanced the antimicrobial activity and biocompatibility of GN-based materials intended for medical purposes.
6. Conclusions
This review comprehensively summarizes and discusses recently developed graphene-based materials, with a focus on their antimicrobial properties and biocompatibility, while exploring potential medical applications such as tissue engineering, medical devices, and wound healing.
Biocompatible and antibacterial nanomaterials are in high demand for a variety of medical applications. The surface modification of GN and its derivatives (e.g., graphene oxide or reduced graphene oxide) with antimicrobials (e.g., antimicrobial peptides or biocides), metals or metal oxides, polymers, and natural compounds has enhanced the functionality and applicability of these materials, resulting in improved antimicrobial performance and increased biocompatibility towards human tissues.
The combination of graphene materials with agents that possess intrinsic antimicrobial properties, such as antimicrobial peptides, metals (silver or copper), or chitosan, enhances the effectiveness of GN materials in inactivating bacteria, especially Gram-positive bacteria, because of their less complex membrane structure. Conversely, although promising for a wide range of applications, the use of non-natural polymers for GN surface modification results in composites with lower antimicrobial activity than those obtained through the modifications mentioned above. However, GN–polymer composites exhibit superior biocompatibility compared to antimicrobial or metal-based GN composites. In the latter case, adverse effects on human cells are highly dependent on the type of metal used and the methodology employed for their production.
Despite the significant progress made in these biomaterials, few in vivo studies have validated their effectiveness and applicability, which may hinder their translation into real medical scenarios. Additionally, studies addressing the long-term effectiveness, biocompatibility, and stability of these composites are lacking. Therefore, further research is needed to introduce these promising biomaterials in the medical field.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.T.-S. and L.C.G.; literature searches and data extraction, R.T.-S., S.B. and R.V.; analysis and interpretation of data, R.T.-S.; writing—original draft preparation, R.T.-S. and S.B.; writing— review and editing, L.C.G. and F.J.M.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was financially supported by LA/P/0045/2020 (ALiCE), UIDB/00511/2020 and UIDP/00511/2020 (LEPABE), funded by national funds through FCT/MCTES (PIDDAC); project PTDC/CTM-COM/4844/2020 (NanoCAT), funded by national funds through FCT/MCTES (PIDDAC); and project 2SMART (NORTE-01-0145-FEDER-000054), supported by Norte Portugal Regional Operational Programme (NORTE 2020) under the PORTUGAL 2020 Partnership Agreement through the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF). R.T.-S. acknowledges the receipt of a junior researcher fellowship from project PTDC/CTM-COM/4844/2020 (NanoCAT).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Wang, J.; Ma, F.; Sun, M. Graphene, hexagonal boron nitride, and their heterostructures: Properties and applications. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 16801–16822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novoselov, K.S.; Fal’ko, V.I.; Colombo, L.; Gellert, P.R.; Schwab, M.G.; Kim, K. A roadmap for graphene. Nature 2012, 490, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novoselov, K.S. Nobel Lecture: Graphene: Materials in the Flatland. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2011, 83, 837–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Feng, X.; Wang, L.; Tang, K.; Maier, J.; Müllen, K. Graphene-Based Nanosheets with a Sandwich Structure. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 4795–4799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magne, T.M.; de Oliveira Vieira, T.; Alencar, L.M.R.; Junior, F.F.M.; Gemini-Piperni, S.; Carneiro, S.V.; Fechine, L.M.U.D.; Freire, R.M.; Golokhvast, K.; Metrangolo, P.; et al. Graphene and its derivatives: Understanding the main chemical and medicinal chemistry roles for biomedical applications. J. Nanostructure Chem. 2022, 12, 693–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dideikin, A.T.; Vul’, A.Y. Graphene Oxide and Derivatives: The Place in Graphene Family. Front. Phys. 2019, 6, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kichukova, D.; Spassova, I.; Kostadinova, A.; Staneva, A.; Kovacheva, D. Facile Synthesized Cu-RGO and Ag-RGO Nanocomposites with Potential Biomedical Applications. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, D.; Yang, X. The dual delivery of growth factors and antimicrobial peptide by PLGA/GO composite biofilms to promote skin-wound healing. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 1463–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora-Ledezma, C.; Chicaiza-Zambrano, A.; Santiago Vispo, N.; Debut, A.; Vizuete, K.; Guerrero, V.H.; Almeida, C.E.; Alexis, F. Frequency Based Control of Antifouling Properties Using Graphene Nanoplatelet/Poly(Lactic-co-Glycolic Acid) Composite Films. Compos. Interfaces 2021, 28, 1137–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.U.A.; Yaqoob, Z.; Ansari, M.N.M.; Razak, S.I.A.; Raza, M.A.; Sajjad, A.; Haider, S.; Busra, F.M. Chitosan/Poly Vinyl Alcohol/Graphene Oxide Based pH-Responsive Composite Hydrogel Films: Drug Release, Anti-Microbial and Cell Viability Studies. Polymers 2021, 13, 3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Cui, L.; Liu, J. Review of functionalization, structure and properties of graphene/polymer composite fibers. Compos. A Appl. Sci. 2016, 87, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perumal, S.; Atchudan, R.; Cheong, I.W. Recent Studies on Dispersion of Graphene–Polymer Composites. Polymers 2021, 13, 2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanda, S.S.; Papaefthymiou, G.C.; Yi, D.K. Functionalization of Graphene Oxide and its Biomedical Applications. Crit. Rev. Solid. State Mater. Sci. 2015, 40, 291–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asim, N.; Badiei, M.; Samsudin, N.A.; Mohammad, M.; Razali, H.; Soltani, S.; Amin, N. Application of graphene-based materials in developing sustainable infrastructure: An overview. Compos. B Eng. 2022, 245, 110188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabot, V.; Higgins, D.; Yu, A.; Xiao, X.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, J. A review of graphene and graphene oxide sponge: Material synthesis and applications to energy and the environment. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 1564–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundramoorthy, A.K.; Gunasekaran, S. Applications of graphene in quality assurance and safety of food. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2014, 60, 36–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa-Cardoso, F.; Teixeira-Santos, R.; Campos, A.F.; Lima, M.; Gomes, L.C.; Soares, O.S.G.P.; Mergulhão, F.J. Graphene-Based Coating to Mitigate Biofilm Development in Marine Environments. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, R.G.; Tuvikene, R. Chapter 12—Biomedical Applications of Graphene. In Handbook of Carbon-Based Nanomaterials; Thomas, S., Sarathchandran, C., Ilangovan, S.A., Moreno-Pirajan, J.C., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 551–571. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Asiri, A.M.; Tang, Z.; Du, D.; Lin, Y. Graphene based materials for biomedical applications. Mater. Today 2013, 16, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariati, A.; Hosseini, S.M.; Chegini, Z.; Seifalian, A.; Arabestani, M.R. Graphene-Based Materials for Inhibition of Wound Infection and Accelerating Wound Healing. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 158, 114184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arkowski, J.; Obremska, M.; Kędzierski, K.; Sławuta, A.; Wawrzyńska, M. Applications for graphene and its derivatives in medical devices: Current knowledge and future applications. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2020, 29, 1497–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaragalla, S.; Bhavitha, K.B.; Athanassiou, A. A Review on Graphene Based Materials and Their Antimicrobial Properties. Coatings 2021, 11, 1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhavan, O.; Ghaderi, E. Toxicity of Graphene and Graphene Oxide Nanowalls Against Bacteria. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 5731–5736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, I.M.J.; Shamsi, S. Graphene Oxide (GO): A Promising Nanomaterial against Infectious Diseases Caused by Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zeng, T.H.; Hofmann, M.; Burcombe, E.; Wei, J.; Jiang, R.; Kong, J.; Chen, Y. Antibacterial Activity of Graphite, Graphite Oxide, Graphene Oxide, and Reduced Graphene Oxide: Membrane and Oxidative Stress. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 6971–6980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammed, H.; Kumar, A.; Bekyarova, E.; Al-Hadeethi, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, M.; Ansari, M.S.; Cochis, A.; Rimondini, L. Antimicrobial Mechanisms and Effectiveness of Graphene and Graphene-Functionalized Biomaterials. A Scope Review. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mejías Carpio, I.E.; Santos, C.M.; Wei, X.; Rodrigues, D.F. Toxicity of a polymer–graphene oxide composite against bacterial planktonic cells, biofilms, and mammalian cells. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 4746–4756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Peng, H.; Wang, X.; Shao, F.; Yuan, Z.; Han, H. Graphene oxide exhibits broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity against bacterial phytopathogens and fungal conidia by intertwining and membrane perturbation. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 1879–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staneva, A.D.; Dimitrov, D.K.; Gospodinova, D.N.; Vladkova, T.G. Antibiofouling Activity of Graphene Materials and Graphene-Based Antimicrobial Coatings. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deokar Archana, R.; Sinha, M.; Gollavelli, G.; Ling, Y.-C. Antimicrobial Perspectives for Graphene-Based Nanomaterials. In Graphene Science Handbook; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Shree, P.; Singh, C.K.; Sodhi, K.K.; Surya, J.N.; Singh, D.K. Biofilms: Understanding the structure and contribution towards bacterial resistance in antibiotics. Med. Microecol. 2023, 16, 100084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.; Luo, Y. Mechanisms of the Antimicrobial Activities of Graphene Materials. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 2064–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Chakraborty, S.; Monikh, F.A.; Varsou, D.-D.; Chetwynd, A.J.; Afantitis, A.; Lynch, I.; Zhang, P. Surface Functionalization of Graphene-Based Materials: Biological Behavior, Toxicology, and Safe-By-Design Aspects. Adv. Biol. 2021, 5, 2100637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hudson-Smith, N.V.; Frand, S.D.; Cahill, M.S.; Davis, L.S.; Feng, Z.V.; Haynes, C.L.; Hamers, R.J. Influence of the Spatial Distribution of Cationic Functional Groups at Nanoparticle Surfaces on Bacterial Viability and Membrane Interactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 10814–10823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, C.; Zhang, X. Chemical Functionalization of Graphene Nanoplatelets with Hydroxyl, Amino, and Carboxylic Terminal Groups. Chemistry 2021, 3, 873–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, S.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Guo, Y.; Sheng, X.; Dong, A. An N-Halamine/Graphene Oxide-Functionalized Electrospun Polymer Membrane That Inactivates Bacteria on Contact and by Releasing Active Chlorine. Polymers 2021, 13, 2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sengupta, I.; Bhattacharya, P.; Talukdar, M.; Neogi, S.; Pal, S.K.; Chakraborty, S. Bactericidal effect of graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide: Influence of shape of bacteria. Colloids Interface Sci. Commun. 2019, 28, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belo, S.; Sousa-Cardoso, F.; Teixeira-Santos, R.; Gomes, L.C.; Vieira, R.; Sjollema, J.; Soares, O.S.G.P.; Mergulhão, F.J. Production and Characterization of Graphene Oxide Surfaces against Uropathogens. Coatings 2023, 13, 1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Giulio, M.; Zappacosta, R.; Di Lodovico, S.; Di Campli, E.; Siani, G.; Fontana, A.; Cellini, L. Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Efficacy of Graphene Oxide against Chronic Wound Microorganisms. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e00547-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai-Prochnow, A.; Clauson, M.; Hong, J.; Murphy, A.B. Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria differ in their sensitivity to cold plasma. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aunkor, M.T.H.; Raihan, T.; Prodhan, S.H.; Metselaar, H.S.C.; Malik, S.U.F.; Azad, A.K. Antibacterial activity of graphene oxide nanosheet against multidrug resistant superbugs isolated from infected patients. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2020, 7, 200640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, S.; Babaei, A.; Arab-Bafrani, Z. Polyethylene Glycol-decorated GO Nanosheets as a Well-Organized Nanohybrid to Enhance the Performance of Chitosan Biopolymer. J. Polym. Environ. 2022, 30, 5130–5147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Zou, L.; Xie, F.; Zhang, X.; Ou, X.; Gao, G. Biocompatible Carboxymethyl Chitosan/GO-Based Sponge to Improve the Efficiency of Hemostasis and Wound Healing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 44799–44808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patarroyo, J.L.; Cifuentes, J.; Muñoz, L.N.; Cruz, J.C.; Reyes, L.H. Novel antibacterial hydrogels based on gelatin/polyvinyl-alcohol and graphene oxide/silver nanoconjugates: Formulation, characterization, and preliminary biocompatibility evaluation. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Pang, Y.X.; Yan, Y.; Qian, P.; Zhao, H.; Manickam, S.; Wu, T.; Pang, C.H. Synthesis and Functionalization of Graphene Materials for Biomedical Applications: Recent Advances, Challenges, and Perspectives. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2205292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, C.; Li, Y.; Tjong, S.C. Graphene Nanomaterials: Synthesis, Biocompatibility, and Cytotoxicity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Kong, H.; Yang, G.; Zhu, D.; Luan, X.; He, P.; Wei, G. Graphene-Based Functional Hybrid Membranes for Antimicrobial Applications: A Review. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 4834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, D.L.; Le Thi, P.; Hoang Thi, T.T.; Park, K.D. Graphene oxide immobilized surfaces facilitate the sustained release of doxycycline for the prevention of implant related infection. Colloids Surf. B 2019, 181, 576–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, S.; Siddiqui, R.; Sharma, P.; Kumar, R.; Verma, G.; Saini, A. Green synthesis of peptide functionalized reduced graphene oxide (rGO) nano bioconjugate with enhanced antibacterial activity. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, D.; Guo, X.; Wang, Y.; Huang, X.; Guo, L.; Zou, P.; Ge, D.; Wang, X.; Lee, W.; Sun, T.; et al. PEGylated Graphene Oxide Carried OH-CATH30 to Accelerate the Healing of Infected Skin Wounds. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 4769–4780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyriere, H.; Makinson, A.; Marchandin, H.; Reynes, J. Doxycycline in the management of sexually transmitted infections. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.-Y.; Hu, X.-H.; Zhang, Y.-W.; Wahid, F.; Chu, L.-Q.; Jia, S.-R.; Zhong, C. Development and antibacterial activities of bacterial cellulose/graphene oxide-CuO nanocomposite films. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 229, 115456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alayande, A.B.; Obaid, M.; Kim, I.S. Antimicrobial mechanism of reduced graphene oxide-copper oxide (rGO-CuO) nanocomposite films: The case of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 109, 110596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasilopoulos, V.; Pitou, M.; Fekas, I.; Papi, R.; Ouranidis, A.; Pavlidou, E.; Patsalas, P.; Choli-Papadopoulou, Τ. Graphene-Wrapped Copper Nanoparticles: An Antimicrobial and Biocompatible Nanomaterial with Valuable Properties for Medical Uses. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 26329–26334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wierzbicki, M.; Jaworski, S.; Sawosz, E.; Jung, A.; Gielerak, G.; Jaremek, H.; Łojkowski, W.; Woźniak, B.; Stobiński, L.; Małolepszy, A.; et al. Graphene Oxide in a Composite with Silver Nanoparticles Reduces the Fibroblast and Endothelial Cell Cytotoxicity of an Antibacterial Nanoplatform. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pipattanachat, S.; Qin, J.; Rokaya, D.; Thanyasrisung, P.; Srimaneepong, V. Biofilm inhibition and bactericidal activity of NiTi alloy coated with graphene oxide/silver nanoparticles via electrophoretic deposition. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, N.; Mutalik, S.; Younas, M.W.; Chan, C.Y.; Thakur, S.; Wang, F.; Yao, M.Z.; Mou, Q.; Leung, P.H.-M. Durable Antimicrobial Behaviour from Silver-Graphene Coated Medical Textile Composites. Polymers 2019, 11, 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeili, E.; Eslami-Arshaghi, T.; Hosseinzadeh, S.; Elahirad, E.; Jamalpoor, Z.; Hatamie, S.; Soleimani, M. The biomedical potential of cellulose acetate/polyurethane nanofibrous mats containing reduced graphene oxide/silver nanocomposites and curcumin: Antimicrobial performance and cutaneous wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 152, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, S.; Bai, Q.; Sui, N.; Zhu, Z. Gold nanoclusters decorated amine-functionalized graphene oxide nanosheets for capture, oxidative stress, and photothermal destruction of bacteria. Colloids Surf. B 2020, 196, 111313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugesan, B.; Pandiyan, N.; Arumugam, M.; Sonamuthu, J.; Samayanan, S.; Yurong, C.; Juming, Y.; Mahalingam, S. Fabrication of palladium nanoparticles anchored polypyrrole functionalized reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite for antibiofilm associated orthopedic tissue engineering. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 510, 145403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.; Prema, D.; Venkataprasanna, K.S.; Prakash, J.; Sahabuddin, S.; Devanand Venkatasubbu, G. Photo induced antibacterial activity of CeO2/GO against wound pathogens. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 7680–7694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Yoon, S.J.; Jeon, I.-Y. Graphene/Polymer Nanocomposites: Preparation, Mechanical Properties, and Application. Polymers 2022, 14, 4733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, A.M.; Moreira, J.A.; Magalhães, F.D.; Gonçalves, I.C. Polymer surface adsorption as a strategy to improve the biocompatibility of graphene nanoplatelets. Colloids Surf. B 2016, 146, 818–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajduga, M.B.; Bobiński, R.; Dutka, M.; Ulman-Włodarz, I.; Bujok, J.; Pająk, C.; Ćwiertnia, M.; Kurowska, A.; Dziadek, M.; Rajzer, I. Analysis of the antibacterial properties of polycaprolactone modified with graphene, bioglass and zinc-doped bioglass. Acta Bioeng. Biomech. 2021, 23, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, W.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, D.-G.; Tran, C.H.; Wang, M.; Varyambath, A.; Kim, J.; Kim, I. Efficient Synthesis of Folate-Conjugated Hollow Polymeric Capsules for Accurate Drug Delivery to Cancer Cells. Biomacromolecules 2021, 22, 732–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, I.M.; Gomes, M.; Gomes, L.C.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Soares, O.S.G.P.; Mergulhão, F.J. Performance of Graphene/Polydimethylsiloxane Surfaces against S. aureus and P. aeruginosa Single- and Dual-Species Biofilms. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.-C.; Chen, H.-H.; Chen, S.-Y.; Wang, W.-L.; Yang, K.-L.; Huang, C.-H.; Kao, H.-F.; Chang, J.-C.; Hsu, C.-L.L.; Wang, J.-Y.; et al. Graphene oxide conjugated with polymers: A study of culture condition to determine whether a bacterial growth stimulant or an antimicrobial agent? J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, S.F.; Neves, S.C.; Pereira, A.T.; Borges, I.; Granja, P.L.; Magalhães, F.D.; Gonçalves, I.C. Incorporation of graphene oxide into poly(ɛ-caprolactone) 3D printed fibrous scaffolds improves their antimicrobial properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 109, 110537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Li, S.; Han, D.; Kong, L.; Wang, J.; Zhao, M.; Cheng, W.; Ju, H.; Yang, Z.; Ding, S. Eco-Friendly Preparation of Epoxy-Rich Graphene Oxide for Wound Healing. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 7, 752–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, S.; Tamayo, J.A.; Delgado Ospina, J.; Navia Porras, D.P.; Valencia Zapata, M.E.; Mina Hernandez, J.H.; Valencia, C.H.; Zuluaga, F.; Grande Tovar, C.D. Antimicrobial Films Based on Nanocomposites of Chitosan/Poly(vinyl alcohol)/Graphene Oxide for Biomedical Applications. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz Atay, H. Antibacterial Activity of Chitosan-Based Systems. In Functional Chitosan: Drug Delivery and Biomedical Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 457–489. [Google Scholar]
- Song, W.; Zhang, M.; Huang, X.; Chen, B.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, D.G.; Kim, I. Smart l-borneol-loaded hierarchical hollow polymer nanospheres with antipollution and antibacterial capabilities. Mater. Today Chem. 2022, 26, 101252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eivazzadeh-Keihan, R.; Alimirzaloo, F.; Aghamirza Moghim Aliabadi, H.; Bahojb Noruzi, E.; Akbarzadeh, A.R.; Maleki, A.; Madanchi, H.; Mahdavi, M. Functionalized graphene oxide nanosheets with folic acid and silk fibroin as a novel nanobiocomposite for biomedical applications. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 6205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Naggar, M.E.; Abu Ali, O.A.; Saleh, D.I.; Abu-Saied, M.A.; Ahmed, M.K.; Abdel-Fattah, E.; Mansour, S.F. Microstructure, morphology and physicochemical properties of nanocomposites containing hydroxyapatite/vivianite/graphene oxide for biomedical applications. Luminescence 2022, 37, 290–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandit, S.; Rahimi, S.; Derouiche, A.; Boulaoued, A.; Mijakovic, I. Sustained release of usnic acid from graphene coatings ensures long term antibiofilm protection. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croitoru, A.-M.; Moroșan, A.; Tihăuan, B.; Oprea, O.; Motelică, L.; Trușcă, R.; Nicoară, A.I.; Popescu, R.-C.; Savu, D.; Mihăiescu, D.E.; et al. Novel Graphene Oxide/Quercetin and Graphene Oxide/Juglone Nanostructured Platforms as Effective Drug Delivery Systems with Biomedical Applications. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).