Abstract
Researchers have suggested a potential relationship between gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT) level and stroke. We investigated a potential causal relationship between GGT level as exposures and stroke and stroke subtypes (cardioembolic, small vessel, and large artery) in a European population. We performed a two-sample Mendelian randomization (MR) study using the genome-wide association study (GWAS) data from the UK Biobank as the exposure set. For the outcome set, we used stroke in the GWAS data from the GIGASTROKE Consortium. We considered alcohol consumption, atrial fibrillation, and body mass index as confounders. We used PhenoScanner searches for removal of SNPs and multivariable MR analysis for assessing confounders. We observed significant causal associations between GGT level and stroke (odds ratio [OR] = 1.23, 95% CI = [1.05–1.44], and p = 0.012 with IVW; OR = 1.19, 95% CI= [1.02–1.39], and p = 0.031 with MR-PRESSO). These results were consistent after removing SNPs related to confounding factors. Similarly, in multivariable MR, GGT was associated with stroke after adjusting for confounding factors (OR = 1.30, 95% CI 1.07–1.60), p = 0.010). Because GGT level has a causal relationship with stroke, researchers should test its significance as a potential risk factor for stroke. Additional research is required to validate these results.
1. Introduction
Stroke is a leading cause of death and accounts for the largest proportion of neurological disorders that are more often disabling than fatal; it causes both physical and mental disability [1,2,3]. With the growing burden of stroke, novel prevention strategies that target modifiable risk factors are needed. Cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk factors are well known to be independent risk factors for stroke [4,5], but other risk factors for strokes should also be considered.
Recently, researchers have shown interest in the potential role of liver function in the development of CVDs [6]. For example, the gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT) level is an indicator of hepatobiliary dysfunction and alcohol abuse. GGT is located on the cellular membrane and is responsible for regulating the entry of amino acids and peptides into the cell in the form of γ-glutamyl peptides [7]. It is also involved in maintaining the physiological concentration of glutathione in cells and reflects the oxidation–antioxidant balance in the body [8,9]. According to previous studies, GGT level is associated with a CVD diagnosis [9,10,11]. After a period of observation, researchers found that individuals with a higher GGT level were more likely than those with a lower GGT level to experience stroke [12,13]. Researchers also investigated the relationship between GGT level and adverse CVD clinical outcomes in stroke patients [14,15]. In addition, a previous study reported that an elevated GGT level is related to stroke recurrence and transient ischemic attack [13]. However, after adjusting for multiple factors, a previous study found that the association between GGT activity and stroke was no longer significant, suggesting that GGT activity might not be a good predictor of the severity of cardio-cerebrovascular diseases [16]. Therefore, whether GGT level has a causal association with stroke remains to be elucidated.
Mendelian randomization (MR) is a genetic epidemiological technique that uses genetic variants associated with potential exposures as instrumental variables (IVs) to evaluate their causal effects on disease outcomes [17,18]. Several previous studies have used MR analyses to find risk factors for stroke [19,20,21,22]. An MR study has shown an association between high level of bilirubin and decreased stroke risk in a Korean population, in agreement with observational results [23], whereas non-alcoholic fatty liver disease has a causal association with small vessel occlusion [6]. As previously described, increased circulating GGT activity is an indicator of insufficient antioxidant levels and increased oxidative stress and indicates a heightened inflammatory state in vivo. The inclusion of several confounding factors in the study of GGT and stroke, alongside the implementation of MR analysis and multivariable MR, are anticipated to yield more robust and reliable research findings. The investigation incorporated multiple factors such as alcohol intake [24], atrial fibrillation [25], and body mass index [26] as confounders. In this study, we investigated the causal effects of GGT level on stroke and stroke subtype in a two-sample MR analysis that used summary statistics from the UK Biobank (UKB) [27] as the exposures and summary statistics from the Stroke Consortium (GIGASTROKE Consortium) dataset as the outcomes [28]. Furthermore, to mitigate the impact of allele frequency analysis across racial groups, an analysis was conducted using data solely from a European population.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
The Institutional Review Board of the Veterans Health Service Medical Center approved this study protocol (IRB No. 2023-03-004) and waived the need for informed consent because of its retrospective design. This study was conducted in compliance with the tenets of the Helsinki Declaration.
2.2. Data Sources
Figure 1 is a schematic of the analytical study design. To investigate the causal effects of GGT level on the risk of stroke and stroke subtypes, we selected the following datasets. (1) As exposure data, we used the summary statistics from the UKB genome-wide association study (GWAS) (n = 437,194 for GGT) [27]. (2) As outcome data, we used the summary statistics from the stroke GWAS (2,036,031 (136,047 cases + 1,899,984 controls)) and stroke subtype GWAS [1,245,612 (10,804 cases + 1,234,808 controls) for cardioembolic stroke, 1,241,619 (6811 cases + 1,234,808 controls) for small vessel stroke, 1,241,207 (6399 cases + 1,234,808 controls) for large artery stroke] of European samples from the GIGASTROKE Consortium [28]. In addition, alcohol consumption, atrial fibrillation, and body mass index were considered as confounding factors. Table 1 describes the datasets whose summary statistics we used.
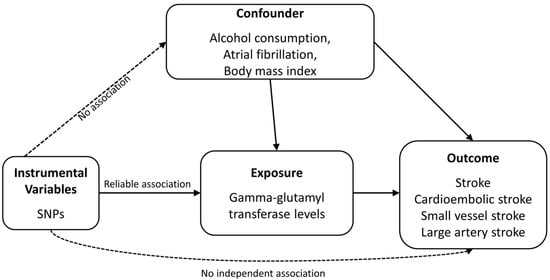
Figure 1.
Diagram of two-sample Mendelian randomization analysis. SNP, single-nucleotide polymorphism.

Table 1.
Data sources for the summary statistics.
2.3. Selection of the Genetic Instrumental Variables
Single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) associated with GGT at the GWAS threshold (p < 5.0 × ) were extracted. We pruned theses SNPs by linkage disequilibrium (LD; r2 = 0.001, clumping distance = 10,000 kb) to ensure that each IV was independent from the others. The linkage disequilibrium between the SNPs was calculated using the 1000 Genome Phase III European data as a reference. The MR analysis was conducted using the selected SNPs as IVs. We also checked the PhenoScanner GWAS database (http://phenoscanner.medschl.cam.ac.uk (accessed on 7 July 2023)) for each SNP and its proxy (LD: r2 > 0.8) to determine whether it was associated with alcohol consumption, atrial fibrillation, or body mass index (p < 1.0 × ) as confounding factors [24,25,26,32,33]. We conducted an additional MR analysis after eliminating confounding factor-related SNPs. We used the 1000 Genomes Phase III dataset (European population) as the reference panel to compute the LD. We assessed the F-statistics for each individual genetic instrument to ensure the reliability of the method. F-value > 10 indicated that the causal estimation was unlikely to be biased due to weak instruments [34].
2.4. Mendelian Randomization
The MR analysis was conducted based on the following assumptions for the IVs: (1) should demonstrate a substantial relationship with the exposure; (2) should have no connection to confounders of the exposure–outcome relationship; and (3) should influence the outcomes only through exposure, with no directional horizontal pleiotropy effect. As the primary analysis method, we used inverse variance-weighted (IVW) MR with multiplicative random effects [34,35,36]. Additionally, we used the weighted median [37], MR-Egger (with and without adjustment via the simulation extrapolation [SIMEX] method) regression [38,39], and MR polyhedral sum of residuals and outliers (MR-PRESSO) [40]. As a sensitivity analysis, we calculated MR estimates while excluding SNPs associated with confounding factors (alcohol consumption, atrial fibrillation, and body mass index). The IVW method is most effective when all genetic variations satisfy the three assumptions for IVs listed above [41]. If one or more of the variants is invalid, the IVW estimate can be biased [37]. The weighted median approach produces accurate estimates of causality even if 50% of the instruments are incorrect [37]. The MR-Egger technique allows estimation of appropriate causal effects even in the presence of pleiotropic effects, permitting a non-zero intercept that clearly demonstrates the average horizontal pleiotropic effects [38]. The MR-Egger with SIMEX can be used to rectify the bias when no measurement error assumption is broken [39]. The MR-PRESSO test, which identifies outliers, adjusts the results of the IVW analysis for horizontal pleiotropy by deleting the outliers [40]. Heterogeneity for IVW and MR-Egger was evaluated using Cochran’s Q and Rücker’s Q’ statistics, respectively [35,42]. We assessed directional horizontal pleiotropy using the MR-PRESSO global test. Therefore, we interpret the results according to the appropriate MR analysis method [43]. p-value < 0.05 for Cochran’s Q statistic, Rücker’s Q’ statistic, and the MR-PRESSO global test indicate possible pleiotropy in the genetic variations. We also performed multivariable IVW MR analysis to assess confounders. All analyses were performed using the TwoSampleMR and simex packages in R version 3.6.3 (R Core Team, Vienna, Austria).
3. Results
3.1. Heterogeneity and Horizontal Pleiotropy of the Instrumental Variables
Among the 16,901,631 genetic variants in the exposure GWAS data, 68,949 were significant for GGT (p < 5.0 × ), and the IVs finally selected after combining each outcome GWAS dataset and clumping numbered 321 for stroke, 319 for cardioembolic stroke, 315 for small vessel stroke, and 317 for large artery stroke. After removal of confounding factor-related SNPs, there were 272 IVs for stroke, 271 for cardioembolic stroke, 268 for small vessel stroke, and 268 for large artery stroke. The F values for all the SNPs selected as IVs are larger than 10, indicating a low probability of weak instrument bias, and the mean F values are greater than 130 (Table 2 and Supplementary Table S1). The premise of no measurement error was not broken in any of the outcomes (I2 > 90 in Table 2). Supplementary Table S1 contains detailed information about each IV, such as whether it is an MR-PRESSO outlier and whether it is known to be related to confounding factors. A pleiotropic effect was observed in stroke, small vessel stroke, and large artery stroke through the Cochran’s Q test (p < 0.05) from IVW, Rücker’s Q′ test (p < 0.05) from MR-Egger, and from the MR-PRESSO global test (p < 0.05) before removing SNPs related to confounding factors (Table 2). Therefore, the MR-PRESSO results were regarded as the key outcomes [43]. When confounding factor-related SNPs were eliminated, IV for large artery stroke satisfied assumptions (Q, p > 0.05; Q’, p > 0.05; MR-PRESSO global test, p > 0.05), at which point IVW was recommended (Table 2) [43]. For cardioembolic stroke, the IVs satisfied the assumptions (Q, p > 0.05; Q’, p > 0.05; MR-PRESSO global test, p > 0.05) regardless of whether confounding factor-related SNPs are removed, and IVW was recommended for MR analyses (Table 2) [43].

Table 2.
Heterogeneity and horizontal pleiotropy of the instrumental variables.
3.2. Mendelian Randomization for the Causal Association between Gamma-Glutamyl Transferase and Stroke
In the single-variable conventional MR analysis, GGT level had a significant causal association with stroke when the analysis used 321 SNPs (IVW MR OR = 1.23, 95% CI: 1.05–1.44, p = 0.012; MR-PRESSO OR = 1.19, 95% CI: 1.02–1.39, p = 0.031, three SNPs excluded) (Figure 2). The MR results after removing confounding factor-related SNPs were similar (MR-PRESSO OR = 1.19, 95% CI: 1.01–1.40, p = 0.034, with 269 SNPs) (Figure 2). The scatterplot (Figure 3) also indicates that the risk of stroke increases with the GGT level. In the multivariable MR analysis, the relationship between GGT and stroke was still significant after adjustment of alcohol consumption, atrial fibrillation, and body mass index (OR = 1.30, 95% CI: 1.07–1.60, p = 0.010) (Table 3).
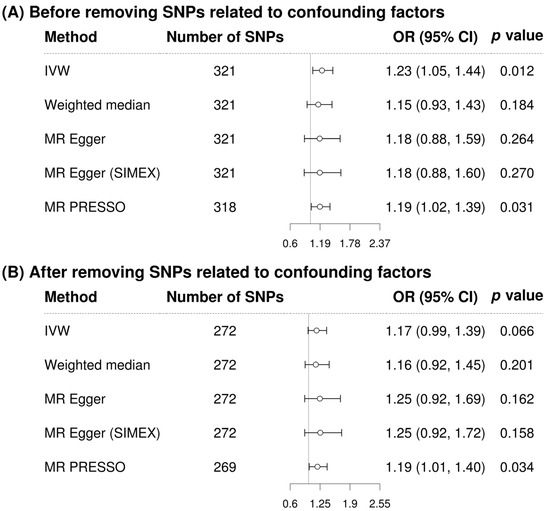
Figure 2.
Forest plot of causal associations between gamma-glutamyl transferase and stroke. (A) Before removing SNPs related to confounding factors; (B) After removing SNPs related to confounding factors. Alcohol consumption, atrial fibrillation, and body mass index were considered as confounding factors. MR, Mendelian randomization; SNP, single-nucleotide polymorphism; IVW, inverse-variance weighted; SIMEX, simulation extrapolation; MR–PRESSO, MR-pleiotropy residual sum and outlier test; OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval.
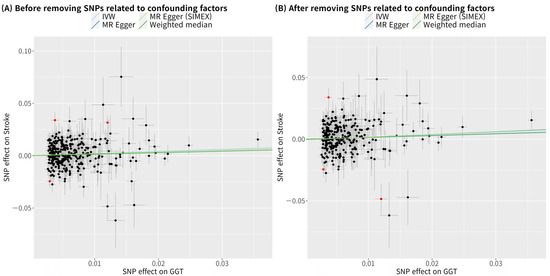
Figure 3.
Scatterplots of MR tests assessing the effects of gamma-glutamyl transferase on stroke. (A) Before removing SNPs related to confounding factors; (B) After removing SNPs related to confounding factors. Alcohol consumption, atrial fibrillation, and body mass index were considered as confounding factors. Light blue, dark blue, light green, and dark green regression lines represent the IVW, MR–Egger, MR–Egger (SIMEX), and weighted median estimates, respectively. Red dots indicate outliers found in the MR–PRESSO analysis. SNP, single-nucleotide polymorphism; GGT, gamma-glutamyl transferase; IVW, inverse-variance weighted; SIMEX, simulation extrapolation; MR, Mendelian randomization; MR–PRESSO, MR-pleiotropy residual sum and outlier test.

Table 3.
Multivariable IVW MR results of gamma-glutamyl transferase, alcohol consumption, atrial fibrillation, and body mass index on stroke and stroke subtypes.
3.3. Mendelian Randomization for the Causal Association between Gamma-Glutamyl Transferase and Stroke Subtype
GGT appears to significantly increase the risk of cardioembolic stroke according to IVW in the single-variable conventional MR analysis regardless of whether confounding factor-related SNPs are removed (IVW MR OR = 1.38, 95% CI: 1.03–1.84, p = 0.030; IVW MR OR = 1.45, 95% CI: 1.05–2.01, p = 0.026 with 48 confounding factor-related SNPs excluded) (Figure 4 and Figure 5). However, after adjusting for alcohol consumption, atrial fibrillation, and body mass index, the relationship between GGT and cardioembolic stroke (OR = 1.15, 95% CI: 0.75–1.77, p = 0.531) was not significant in the multivariable MR analysis (Table 3). GGT was not significantly associated with small vessel stroke and large artery stroke according to IVW method in the single-variable conventional MR analysis regardless of whether confounding factor-related SNPs are removed (Figure 4 and Figure 5). Although MR-PRESSO was recommended for small vessel stroke (with or without removal of SNPs related to confounding factors) and large artery stroke (before removing SNPs related to confounding factors) but found no outliers. In multivariable MR analysis, GGT was significantly associated with small vessel stroke (OR = 1.79, 95% CI: 1.01–3.16, p = 0.046) and large artery stroke (OR = 1.94, 95% CI: 1.06–3.56, p = 0.032) after adjusting for alcohol consumption, atrial fibrillation, and body mass index. Scatterplots show the genetic association of GGT level against the genetic association with stroke subtypes for each SNP (Figure 6).
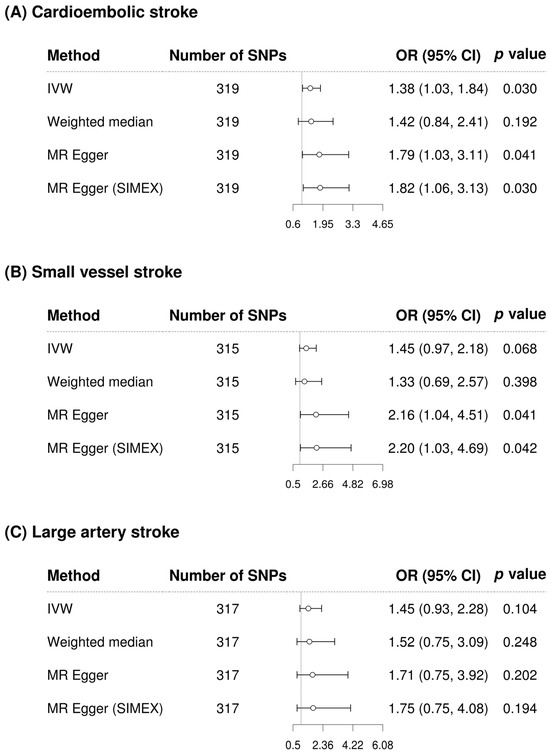
Figure 4.
Forest plot of causal associations between gamma-glutamyl transferase and stroke-subtypes before removing SNPs related to confounding factors. (A) Cardioembolic stroke; (B) Small vessel stroke; (C) Large artery stroke. Alcohol consumption, atrial fibrillation, and body mass index were considered as confounding factors. SNP, single-nucleotide polymorphism; IVW, inverse-variance weighted; MR, Mendelian randomization; SIMEX, simulation extrapolation; OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval.
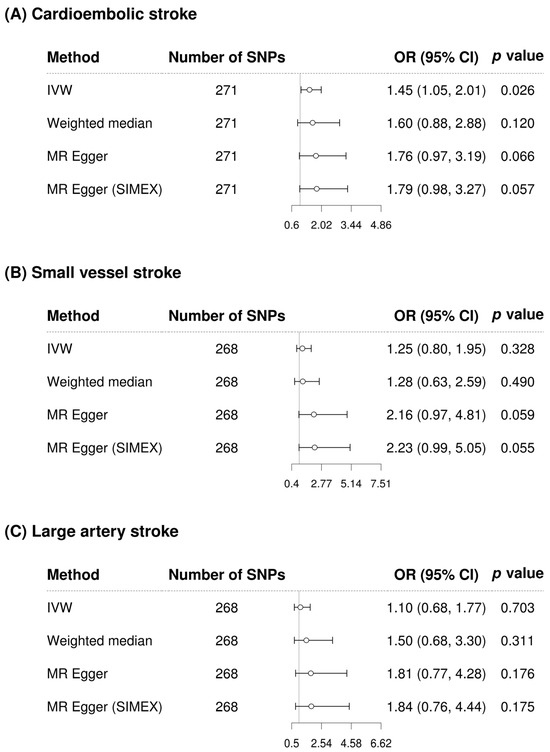
Figure 5.
Forest plot of causal associations between gamma-glutamyl transferase and stroke subtypes after removing SNPs related to confounding factors. (A) Cardioembolic stroke; (B) Small vessel stroke; (C) Large artery stroke. Alcohol consumption, atrial fibrillation, and body mass index were considered as confounding factors. SNP, single-nucleotide polymorphism; IVW, inverse-variance weighted; MR, Mendelian randomization; SIMEX, simulation extrapolation; OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval.
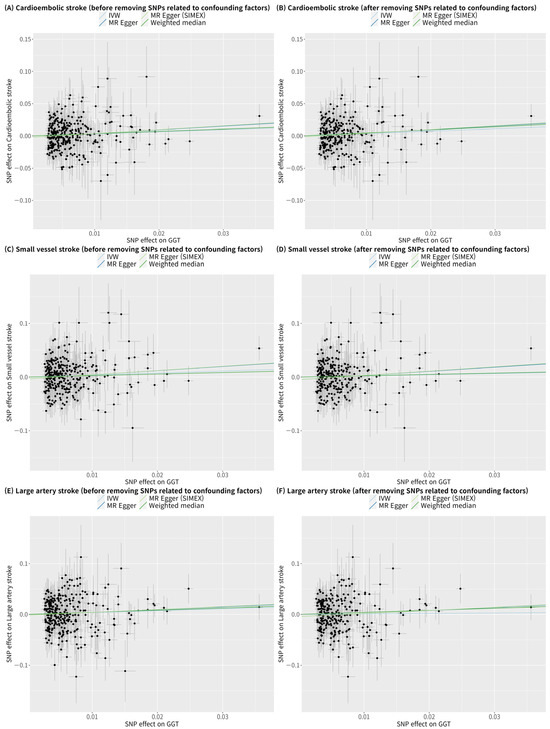
Figure 6.
Scatterplots of MR tests assessing the effects of gamma-glutamyl transferase on stroke-subtypes. (A) Cardioembolic stroke before removing SNPs related to confounding factors; (B) Cardioembolic stroke after removing SNPs related to confounding factors; (C) Small vessel stroke before removing SNPs related to confounding factors; (D) Small vessel stroke before removing SNPs related to confounding factors; (E) Large artery stroke before removing SNPs related to confounding factors; (F) Large artery stroke before removing SNPs related to confounding factors. Alcohol consumption, atrial fibrillation, and body mass index were considered as confounding factors. Light blue, dark blue, light green, and dark green regression lines represent the IVW, MR–Egger, MR–Egger (SIMEX), and weighted median estimates, respectively. SNP, single-nucleotide polymorphism; GGT, gamma-glutamyl transferase; IVW, inverse-variance weighted; SIMEX, simulation extrapolation; MR, Mendelian randomization.
4. Discussion
Our study demonstrated a possible causal association between high GGT level and stroke. Moreover, GGT level demonstrated a causal association with stroke subtypes of cardioembolic stroke, small vessel stroke, and large artery stroke. Alcohol consumption has an impact on liver function tests, particularly the level of GGT [24]. Atrial fibrillation is reported to be linked to both stroke and GGT level [25]. Additionally, body mass index is a popular index for obesity, which is a risk factor for stroke [26], we performed a further analysis with the confounding factor-related SNPs (alcohol consumption, atrial fibrillation, and body mass index) removed, and the GGT level still had a causal effect on stroke. To address the limitations of the SNP elimination strategy, a multivariate MR analysis was conducted and revealed a significant causal association between GGT level and stroke subtype.
Serum GGT has been widely used as an index of liver dysfunction and a marker of alcohol intake. Conditions that increase serum GGT, such as obstructive liver disease, excessive alcohol use, and the use of enzyme-inducing medications, result in increased free-radical generation and the risk of glutathione depletion. Important advances have been made in defining associations between serum GGT and risk of coronary heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and stroke [44]. Several studies on the relationship between GGT and stroke have revealed GGT’s potential as a novel biomarker for stroke prediction [16,25,45,46,47]. Nevertheless, it remains unclear why GGT is associated with stroke. Several studies have suggested that GGT is associated with atrial fibrillation [25,48,49], and half of the association between GGT and cardioembolic stroke was mediated by atrial fibrillation. A mediation study revealed that the potential causal effect was mediated by GGT as well as atrial fibrillation [25]. Our MR analysis confirmed a causal relationship between GGT and stroke, as well as stroke subtype, but our inability to demonstrate a mechanism is a limitation. Nonetheless, it is a crucial discovery that GGT is an independent risk factor for stroke, as previously demonstrated by a large-scale study of 456,100 representative Koreans [33]. A recently meta-analysis on the association between GGT level and stroke risk showed that high GGT level was positively associated with increased risk of stroke (relative risk = 1.28; 95% CI, 1.61–1.43) [11], and that also supports our study. Our study has significant insights beyond those previous results because we demonstrated that GGT is a causal risk factor for stroke using European genetic data with the MR method. The observed variations in learning disabilities among racial groups present challenges in generalizing the findings of our study to other ethnic populations.
Stroke is widely recognized as a prominent contributor to both mortality and disability on a global scale [12]. The identification of individuals at risk of stroke at an early stage can effectively decrease the rates of mortality and morbidity associated with this condition. This early identification enables physicians to swiftly implement primary prevention methods. The primary modifiable risk factors are hypertension, diabetes mellitus, tobacco smoking, and hyperlipidemia, with lifestyle variables including obesity, inadequate diet/nutrition, and physical inactivity [50]. The enzyme GGT expedites the progression of atherosclerosis by means of oxidative and inflammatory processes. The potential link between GGT and atrial fibrillation has been postulated to be attributed to oxidative stress, chronic low-grade inflammation, and metabolic syndrome [51]. When an excessive amount of oxidative stress is present, there is a greater need for antioxidants, such as glutathione, to resolve it. In the present scenario, the necessity for GGT may also have been increased due to its role in the recycling of glutathione. In this regard, the examination of risk factors can encompass the influence of nutrition and inflammation. A recent study showed that diet was a substantial mitigating factor in the impact of obesity on the ratio of pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory interleukins, as well as on the levels of TGFβ-1 and GGT [52]. When examined through the lens of inflammation and oxidative stress, it may be inferred that there is a commonality between high GGT level and risk factors for stroke. Nevertheless, the absence of empirical support for a direct association between GGT and the progression of atrial fibrillation implies the necessity for an alternate hypothesis.
Understanding the causes of stroke is essential to creating successful preventive measures. The MR method uses genetic variations associated with a particular exposure to examine how changing that exposure affects disease risk. The advantages of MR research are that, when a set of genomic data and clinical information are available, the design is cross-sectional, but it can be rigorously verified by randomization, as in a prospective study [53,54]. In addition, unlike animal experiments, the MR method reduces the burden of random verification on humans and can demonstrate causality without putting participants at risk [55]. Several MR studies on stroke were previously performed with various results [19,56,57,58,59]. Smoking behavior was a causal factor for ischemic stroke in an MR analysis [20], and another MR study showed that smoking, body mass index, and waist/hip ratio were causally associated with stroke [21]. In the literature we reviewed, we found no MR analysis results about a causal association between GGT level and stroke. We did find studies that used MR analyses to link stroke with another indication of liver function, such as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease or bilirubin level [6,23,60,61,62]; in those studies non-alcoholic fatty liver disease had a limited effect on stroke and showed controversial results. Although we used two-sample MR as a research method to reduce bias, we deemed alcohol to be a confounding factor because it has a substantial effect on GGT level. Thus, we eliminated all drinking-associated SNPs. Several reports indicate that GGT level can serve as a biomarker for alcohol intake [63,64], and we deemed it necessary to eliminate and revaluate variables that could influence GGT level. Furthermore, the presence of atrial fibrillation was considered as a potential confounding variable due to its known impact on stroke incidence. Additionally, obesity was included in the analysis. However, because the results of a previous meta-analysis indicated that GGT is a risk factor for stroke independent of alcohol consumption [11], we suggest the reliability of our results prior to exclusion of SNPs related to alcohol. To address this issue, a multivariable MR analysis was conducted, revealing a noteworthy causal relationship with stroke subtype.
The chief strength of our study is our use of a relatively large cohort dataset in finding a possible causal association between GGT level and stroke. However, this study also has a few limitations. First, we did not have access to individual-level data, so we could not explore any potential nonlinear relationships or stratification effects. Second, the test procedures used to validate MR hypotheses do not provide complete validation. Violations of the MR assumptions can lead to invalid conclusions, so our results should be interpreted cautiously. Third, the summary GWAS data used in this study were collected from individuals of European ancestry, which may restrict the generalizability of our findings to non-European populations. Fourth, although the two-sample MR method requires the use of GWAS results from independent data, we were unable to obtain exposure and outcome results from completely independent sources because we used consortium data. The exposure data were obtained from GWAS of UKB samples, and the stroke GWAS, conducted using GIGASTROKE, includes UKB samples, resulting in substantial overlap between the exposure and outcome data. However, in previous research using the large-cohort MR analysis methodology [65], the IVW and weighted median results remained unaffected, and they influenced the bias of the MR-Egger results.
5. Conclusions
Our study using the MR method demonstrated a causal association between GGT and stroke and stroke subtype (small vessel stroke, and large artery stroke) in multivariable results. In addition, after removal of confounding factor-related SNPs, GGT continued to show a causal relationship with stroke. Considering the significance of GGT and liver function, researchers should further clarify and investigate the association between GGT level and stroke.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/biom13111592/s1, Supplementary Table S1: List of single-nucleotide polymorphisms used as instrumental variables in the single-variable MR analysis.
Author Contributions
Y.L. and J.H.S. participated in the study concept and design. Y.L. and J.H.S. contributed to acquisition, analysis, and interpretation of data. Y.L. and J.H.S. carried out statistical analysis and provided administrative, technical, or material support. Y.L. and J.H.S. wrote and revised the manuscript. Y.L. and J.H.S. provided study supervision. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by a Veterans Health Service Medical Center Research Grant (grant no.: VHSMC23038) and by a National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean government (Ministry of Science and ICT) (No. 2022R1C1C1002929). The funders had no role in the study design; collection, analysis, or interpretation of data; writing of the manuscript; or the decision to publish the results.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was conducted in accordance with the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Institutional Review Board of the Veterans Health Service Medical Center (IRB No. 2023-03-004; 31 March 2023).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was not required because anonymized and de-identified data were used in the analyses. The requirement for patient consent was waived owing to the retrospective nature of this study.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and/or analyzed in the current study are available from the GWAS catalogue (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/gwas/summary-statistics, accessed on 7 July 2023). We used GWAS summary statistics from the following sources: GGT (study accession number GCST90013407), alcohol consumption (study accession number GCST90041731), atrial fibrillation (study accession number GCST006414), body mass index (study accession number GCST90029007), and stroke subtype GWAS generated by the GIGASTROKE consortium (study accession numbers GCST90104539, GCST90104541, GCST90104542, and GCST90104543).
Acknowledgments
We thank UK Biobank (UKB https://www.ukbiobank.ac.uk/ (accessed on 7 July 2023)), GIGASTROKE Consortium, and the GWAS catalogue (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/gwas/ (accessed on 7 July 2023)).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Campbell, B.C.V.; Khatri, P. Stroke. Lancet 2020, 396, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, E.J.; Muntner, P.; Alonso, A.; Bittencourt, M.S.; Callaway, C.W.; Carson, A.P.; Chamberlain, A.M.; Chang, A.R.; Cheng, S.; Das, S.R.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2019 Update: A Report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2019, 139, e56–e528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD 2016 Lifetime Risk of Stroke Collaborators; Feigin, V.L.; Nguyen, G.; Cercy, K.; Johnson, C.O.; Alam, T.; Parmar, P.G.; Abajobir, A.A.; Abate, K.H.; Abd-Allah, F.; et al. Global, Regional, and Country-Specific Lifetime Risks of Stroke, 1990 and 2016. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2429–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hankey, G.J. Stroke. Lancet 2017, 389, 641–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frerich, S.; Malik, R.; Georgakis, M.K.; Sinner, M.F.; Kittner, S.J.; Mitchell, B.D.; Dichgans, M. Cardiac Risk Factors for Stroke: A Comprehensive Mendelian Randomization Study. Stroke 2022, 53, e130–e135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Zha, M.; Lv, Q.; Xie, Y.; Yuan, K.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and stroke: A Mendelian randomization study. Eur. J. Neurol. 2022, 29, 1534–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajendran, P.; Rengarajan, T.; Thangavel, J.; Nishigaki, Y.; Sakthisekaran, D.; Sethi, G.; Nishigaki, I. The vascular endothelium and human diseases. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2013, 9, 1057–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foyer, C.H.; Noctor, G. Redox homeostasis and antioxidant signaling: A metabolic interface between stress perception and physiological responses. Plant Cell 2005, 17, 1866–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunutsor, S.K. Gamma-glutamyltransferase-friend or foe within? Liver Int. 2016, 36, 1723–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, W.; Choi, D.W.; Jung, K.J.; Jang, S.I. Dose-response relationship between gamma-glutamyltransferase and the risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases in Korean adults. Atherosclerosis 2020, 292, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.W.; Li, M.; Hou, W.S.; Li, K.; Zhou, J.R.; Tang, Z.Y. Association between Gamma-Glutamyltransferase Level and Risk of Stroke: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Prospective Studies. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2015, 24, 2816–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalirawna, T.R.; Rohilla, J.; Bairwa, S.S.; Gothwal, S.K.; Tak, P.; Jain, R. Increased concentration of serum gamma-glutamyl transferase in ischemic stroke patients. Brain Circ. 2021, 7, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, A.; Tian, X.; Zuo, Y.; Meng, X.; Zhang, Y. Elevated gamma-glutamyl transferase levels are associated with stroke recurrence after acute ischemic stroke or transient ischemic attack. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2022, 28, 1637–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, W.J.; Liu, Q.; Cao, J.L.; Zhao, S.J.; Zeng, X.W.; Deng, A.J. gamma-Glutamyl Transferase as a Risk Factor for All-Cause or Cardiovascular Disease Mortality among 5912 Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 2017, 48, 2888–2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emdin, M.; Passino, C.; Donato, L.; Paolicchi, A.; Pompella, A. Serum gamma-glutamyltransferase as a risk factor of ischemic stroke might be independent of alcohol consumption. Stroke 2002, 33, 1163–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weikert, C.; Drogan, D.; di Giuseppe, R.; Fritsche, A.; Buijsse, B.; Nothlings, U.; Willich, S.N.; Berger, K.; Boeing, H. Liver enzymes and stroke risk in middle-aged German adults. Atherosclerosis 2013, 228, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, S.; Thompson, S.G. Multivariable Mendelian randomization: The use of pleiotropic genetic variants to estimate causal effects. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 181, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, S.; Thompson, S.G. Interpreting findings from Mendelian randomization using the MR-Egger method. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 32, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yan, S.; Li, Y.; Kang, H.; Zhu, H.; Lv, C. Mendelian Randomization Study of Heart Failure and Stroke Subtypes. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 844733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, S.C.; Burgess, S.; Michaelsson, K. Smoking and stroke: A mendelian randomization study. Ann. Neurol. 2019, 86, 468–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harshfield, E.L.; Georgakis, M.K.; Malik, R.; Dichgans, M.; Markus, H.S. Modifiable Lifestyle Factors and Risk of Stroke: A Mendelian Randomization Analysis. Stroke 2021, 52, 931–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Peters, J.E.; Prins, B.; Persyn, E.; Traylor, M.; Surendran, P.; Karthikeyan, S.; Yonova-Doing, E.; Di Angelantonio, E.; Roberts, D.J.; et al. Systematic Mendelian randomization using the human plasma proteome to discover potential therapeutic targets for stroke. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.; Lee, S.J.; Spiller, W.; Jung, K.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kimm, H.; Back, J.H.; Lee, S.; Jee, S.H. Causal Associations Between Serum Bilirubin Levels and Decreased Stroke Risk: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2020, 40, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liangpunsakul, S.; Qi, R.; Crabb, D.W.; Witzmann, F. Relationship between alcohol drinking and aspartate aminotransferase:alanine aminotransferase (AST:ALT) ratio, mean corpuscular volume (MCV), gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT), and apolipoprotein A1 and B in the U.S. population. J. Stud. Alcohol. Drugs 2010, 71, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Kang, D.W.; Lee, S.H. Effects of Gamma-Glutamyl Transferase on Stroke Occurrence Mediated by Atrial Fibrillation. J. Clin. Neurol. 2020, 16, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Y.; Chen, J.; Liu, J.; Ma, H. Associations Between GGT/HDL and MAFLD: A Cross-Sectional Study. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2022, 15, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazoki, R.; Vujkovic, M.; Elliott, J.; Evangelou, E.; Gill, D.; Ghanbari, M.; van der Most, P.J.; Pinto, R.C.; Wielscher, M.; Farlik, M.; et al. Genetic analysis in European ancestry individuals identifies 517 loci associated with liver enzymes. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, A.; Malik, R.; Hachiya, T.; Jurgenson, T.; Namba, S.; Posner, D.C.; Kamanu, F.K.; Koido, M.; Le Grand, Q.; Shi, M.; et al. Stroke genetics informs drug discovery and risk prediction across ancestries. Nature 2022, 611, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Zheng, Z.; Fang, H.; Yang, J. A generalized linear mixed model association tool for biobank-scale data. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 1616–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, J.B.; Thorolfsdottir, R.B.; Fritsche, L.G.; Zhou, W.; Skov, M.W.; Graham, S.E.; Herron, T.J.; McCarthy, S.; Schmidt, E.M.; Sveinbjornsson, G.; et al. Biobank-driven genomic discovery yields new insight into atrial fibrillation biology. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 1234–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loh, P.R.; Kichaev, G.; Gazal, S.; Schoech, A.P.; Price, A.L. Mixed-model association for biobank-scale datasets. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 906–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuman, M.G.; Malnick, S.; Chertin, L. Gamma glutamyl transferase—An underestimated marker for cardiovascular disease and the metabolic syndrome. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 23, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Kim, C.K.; Kim, D.Y.; Jeong, H.G.; Lee, S.H. Gamma-glutamyl transferase predicts future stroke: A Korean nationwide study. Ann. Neurol. 2018, 83, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, S.; Butterworth, A.; Thompson, S.G. Mendelian randomization analysis with multiple genetic variants using summarized data. Genet. Epidemiol. 2013, 37, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowden, J.; Del Greco, M.F.; Minelli, C.; Davey Smith, G.; Sheehan, N.; Thompson, J. A framework for the investigation of pleiotropy in two-sample summary data Mendelian randomization. Stat. Med. 2017, 36, 1783–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Kim, Y.A.; Seo, J.H. Causal Association of Obesity and Dyslipidemia with Type 2 Diabetes: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study. Genes 2022, 13, 2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, J.; Davey Smith, G.; Haycock, P.C.; Burgess, S. Consistent Estimation in Mendelian Randomization with Some Invalid Instruments Using a Weighted Median Estimator. Genet. Epidemiol. 2016, 40, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, J.; Davey Smith, G.; Burgess, S. Mendelian randomization with invalid instruments: Effect estimation and bias detection through Egger regression. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 44, 512–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, J.; Del Greco, M.F.; Minelli, C.; Davey Smith, G.; Sheehan, N.A.; Thompson, J.R. Assessing the suitability of summary data for two-sample Mendelian randomization analyses using MR-Egger regression: The role of the I2 statistic. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2016, 45, 1961–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbanck, M.; Chen, C.Y.; Neale, B.; Do, R. Publisher Correction: Detection of widespread horizontal pleiotropy in causal relationships inferred from Mendelian randomization between complex traits and diseases. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgess, S.; Davey Smith, G.; Davies, N.M.; Dudbridge, F.; Gill, D.; Glymour, M.M.; Hartwig, F.P.; Holmes, M.V.; Minelli, C.; Relton, C.L.; et al. Guidelines for performing Mendelian randomization investigations. Wellcome Open Res. 2019, 4, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, M.F.; Minelli, C.; Sheehan, N.A.; Thompson, J.R. Detecting pleiotropy in Mendelian randomisation studies with summary data and a continuous outcome. Stat. Med. 2015, 34, 2926–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Lee, S.; Won, S. Causal Evaluation of Laboratory Markers in Type 2 Diabetes on Cancer and Vascular Diseases Using Various Mendelian Randomization Tools. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 597420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitfield, J.B. Gamma glutamyl transferase. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2001, 38, 263–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wannamethee, S.G.; Lennon, L.; Shaper, A.G. The value of gamma-glutamyltransferase in cardiovascular risk prediction in men without diagnosed cardiovascular disease or diabetes. Atherosclerosis 2008, 201, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strasak, A.M.; Kelleher, C.C.; Klenk, J.; Brant, L.J.; Ruttmann, E.; Rapp, K.; Concin, H.; Diem, G.; Pfeiffer, K.P.; Ulmer, H.; et al. Longitudinal change in serum gamma-glutamyltransferase and cardiovascular disease mortality: A prospective population-based study in 76,113 Austrian adults. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2008, 28, 1857–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, Y.; Imano, H.; Ohira, T.; Kitamura, A.; Kiyama, M.; Okada, T.; Sato, S.; Shimamoto, T.; Yamagishi, K.; Tanigawa, T.; et al. gamma-Glutamyltranspeptidase and incident stroke among Japanese men and women: The Circulatory Risk in Communities Study (CIRCS). Stroke 2010, 41, 385–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tekin, G.; Tekin, Y.K.; Senarslan, D.A.; Gocmen, A.Y.; Senarslan, O.; Erbay, A.R. Serum gamma-glutamyltransferase activity in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. Angiology 2013, 64, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunutsor, S.K.; Laukkanen, J.A.; Bluemke, D.A.; Butler, J.; Khan, H. Baseline and long-term gamma-glutamyltransferase, heart failure and cardiac arrhythmias in middle-aged Finnish men: Prospective study and pooled analysis of published evidence. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2016, 23, 1354–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzik, A.; Bushnell, C. Stroke Epidemiology and Risk Factor Management. Continuum 2017, 23, 15–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, A.; Misialek, J.R.; Amiin, M.A.; Hoogeveen, R.C.; Chen, L.Y.; Agarwal, S.K.; Loehr, L.R.; Soliman, E.Z.; Selvin, E. Circulating levels of liver enzymes and incidence of atrial fibrillation: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities cohort. Heart 2014, 100, 1511–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arouca, A.; Moreno, L.A.; Gonzalez-Gil, E.M.; Marcos, A.; Widhalm, K.; Molnar, D.; Manios, Y.; Gottrand, F.; Kafatos, A.; Kersting, M.; et al. Diet as moderator in the association of adiposity with inflammatory biomarkers among adolescents in the HELENA study. Eur. J. Nutr. 2019, 58, 1947–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, J.H.; Lee, Y. Causal Association between Iritis or Uveitis and Glaucoma: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomisation Study. Genes 2023, 14, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowden, J.; Holmes, M.V. Meta-analysis and Mendelian randomization: A review. Res. Synth Methods 2019, 10, 486–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birney, E. Mendelian Randomization. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2022, 12, a041302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.; Hu, X.; Wang, T.; Yang, Y.; Xu, R.; Zhang, X.; Luo, J.; Ma, Y.; Patel, A.B.; Dmytriw, A.A.; et al. Parkinson’s Disease and Ischemic Stroke: A Bidirectional Mendelian Randomization Study. Transl. Stroke Res. 2022, 13, 528–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Wu, M.; Gao, J.; Liu, C.; Xie, Y.; Lv, Q.; Zhang, X. Periodontitis and stroke: A Mendelian randomization study. Brain Behav. 2023, 13, e2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Zheng, S. Endometriosis Increases the Risk of Stroke: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Stroke 2023, 54, e30–e33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, M.C.; Haycock, P.C.; Zheng, J.; Hemani, G.; Holmes, M.V.; Davey Smith, G.; Hingorani, A.D.; Lawlor, D.A. Role of circulating polyunsaturated fatty acids on cardiovascular diseases risk: Analysis using Mendelian randomization and fatty acid genetic association data from over 114,000 UK Biobank participants. BMC Med. 2022, 20, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh, N.S. Mendelian randomization elucidates links between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and stroke. Eur. J. Neurol. 2022, 29, 1291–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Wang, S.; Wang, M.; Ye, Y.; Xue, E.; Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Fan, M.; Gao, W.; Qin, X.; et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and cardiovascular diseases: A Mendelian randomization study. Metabolism 2022, 133, 155220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Au Yeung, S.L.; Borges, M.C.; Wong, T.H.T.; Lawlor, D.A.; Schooling, C.M. Evaluating the role of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in cardiovascular diseases and type 2 diabetes: A Mendelian randomization study in Europeans and East Asians. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2023, 52, 921–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemela, O. Biomarkers in alcoholism. Clin. Chim. Acta 2007, 377, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, J.C.; Leggio, L.; Farokhnia, M. Blood Biomarkers of Alcohol Use: A Scoping Review. Curr. Addict. Rep. 2021, 8, 500–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minelli, C.; Del Greco, M.F.; van der Plaat, D.A.; Bowden, J.; Sheehan, N.A.; Thompson, J. The use of two-sample methods for Mendelian randomization analyses on single large datasets. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2021, 50, 1651–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).