Statistical Power Analysis for Designing Bulk, Single-Cell, and Spatial Transcriptomics Experiments: Review, Tutorial, and Perspectives
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Power Analysis for Bulk RNA-Seq Experiments
2.1. Bulk RNA-Seq Experiment
2.2. Bulk RNA-Seq Power Analysis Tools
2.3. Bulk RNA-Seq Power Analysis Tool Recommendation
3. Power Analysis for Single-Cell RNA-Seq (scRNA-Seq) Experiments
3.1. Power Analysis for Cell Subpopulation Detection
3.1.1. Ascertaining Cell Subpopulation Proportions in a Single Tissue
3.1.2. Ascertaining Differential Cell Subpopulation Proportions between Distinct Experimental Conditions
3.2. Power Analysis for DEG Detection
3.2.1. DEGs across Different Conditions for a Cell Type
3.2.2. DEGs across Different Cell Types
3.3. scRNA-Seq Power Analysis Tool Recommendations
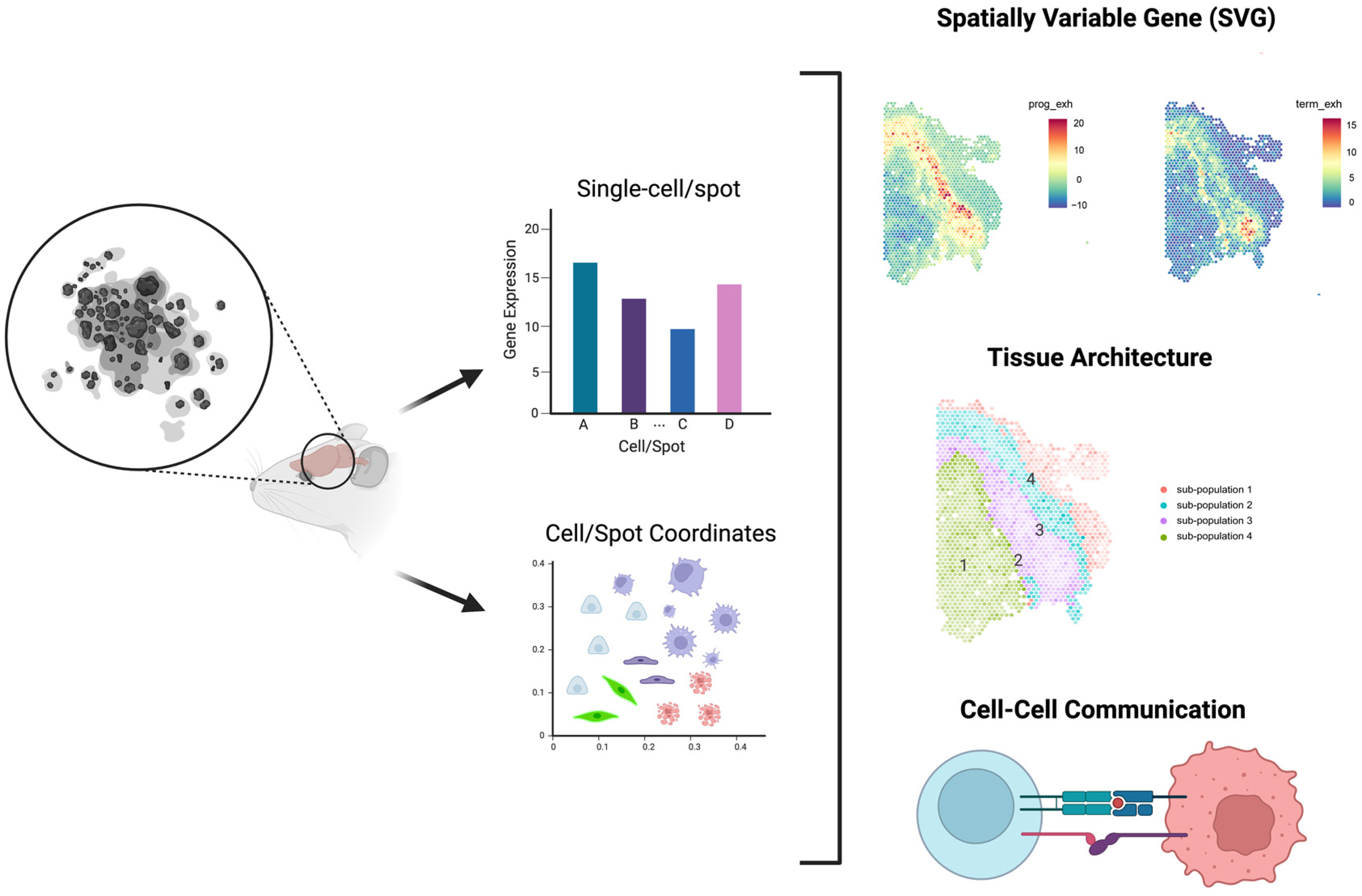
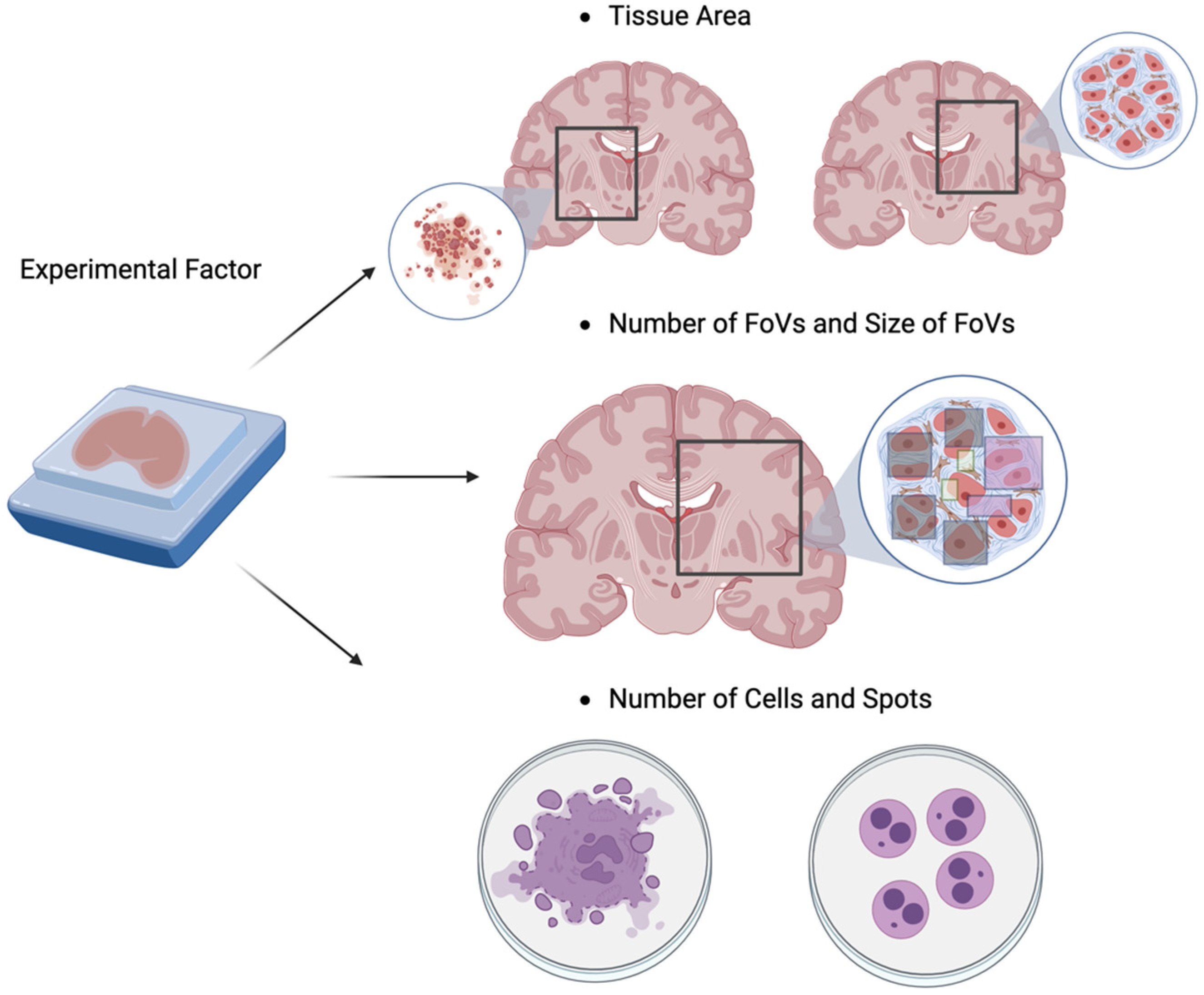
4. Power analysis for Spatial Transcriptomic Experiments
4.1. Introduction of High-Throughput Spatial Transcriptomics (HST) Technology
4.2. Literature Reviews of Power Analysis for HST Data
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Morozova, O.; Hirst, M.; Marra, M.A. Applications of new sequencing technologies for transcriptome analysis. Annu. Rev. Genom. Hum. Genet. 2009, 10, 135–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liang, K.-H. ScienceDirect. In Bioinformatics for Biomedical Science and Clinical Applications, 1st ed.; Woodhead Pub: Philadelphia, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Haque, A.; Engel, J.; Teichmann, S.A.; Lonnberg, T. A practical guide to single-cell RNA-sequencing for biomedical research and clinical applications. Genome Med. 2017, 9, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, M.; Tao, S.; Zhang, L.; Diao, L.T.; Huang, X.; Huang, S.; Xie, S.J.; Xiao, Z.D.; Zhang, H. RNA sequencing: New technologies and applications in cancer research. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, M.S.; Van Vleet, T.R.; Ciurlionis, R.; Buck, W.R.; Mittelstadt, S.W.; Blomme, E.A.G.; Liguori, M.J. Comparison of RNA-Seq and Microarray Gene Expression Platforms for the Toxicogenomic Evaluation of Liver from Short-Term Rat Toxicity Studies. Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burgess, D.J. Spatial transcriptomics coming of age. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2019, 20, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marioni, J.C.; Mason, C.E.; Mane, S.M.; Stephens, M.; Gilad, Y. RNA-seq: An assessment of technical reproducibility and comparison with gene expression arrays. Genome Res. 2008, 18, 1509–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bacher, R.; Kendziorski, C. Design and computational analysis of single-cell RNA-sequencing experiments. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schurch, N.J.; Schofield, P.; Gierliński, M.; Cole, C.; Sherstnev, A.; Singh, V.; Wrobel, N.; Gharbi, K.; Simpson, G.G.; Owen-Hughes, T.; et al. How many biological replicates are needed in an RNA-seq experiment and which differential expression tool should you use? RNA 2016, 22, 839–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, J.; White, K.P. RNA-seq differential expression studies: More sequence or more replication? Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 301–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pollen, A.A.; Nowakowski, T.J.; Shuga, J.; Wang, X.; Leyrat, A.A.; Lui, J.H.; Li, N.; Szpankowski, L.; Fowler, B.; Chen, P.; et al. Low-coverage single-cell mRNA sequencing reveals cellular heterogeneity and activated signaling pathways in developing cerebral cortex. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 1053–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cohen, J. The statistical power of abnormal-social psychological research: A review. J. Abnorm. Soc. Psychol. 1962, 65, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Statistical power analysis. Curr. Dir. Psychol. Sci. 1992, 1, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, L. Retrospective power analysis. Conserv. Biol. 1997, 11, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chuan, C.L.; Penyelidikan, J. Sample size estimation using Krejcie and Morgan and Cohen statistical power analysis: A comparison. J. Penyelid. IPBL 2006, 7, 78–86. [Google Scholar]
- Sanger, F.; Nicklen, S.; Coulson, A.R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1977, 74, 5463–5467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stark, R.; Grzelak, M.; Hadfield, J. RNA sequencing: The teenage years. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2019, 20, 631–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Berge, K.; Hembach, K.M.; Soneson, C.; Tiberi, S.; Clement, L.; Love, M.I.; Patro, R.; Robinson, M.D. RNA sequencing data: Hitchhiker’s guide to expression analysis. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Data Sci. 2019, 2, 139–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hart, S.N.; Therneau, T.M.; Zhang, Y.; Poland, G.A.; Kocher, J.P. Calculating sample size estimates for RNA sequencing data. J. Comput. Biol. 2013, 20, 970–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robinson, M.D.; McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. edgeR: A Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anders, S.; Huber, W. Differential expression analysis for sequence count data. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, R106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hardcastle, T.J.; Kelly, K.A. baySeq: Empirical Bayesian methods for identifying differential expression in sequence count data. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van den Berge, K.; Perraudeau, F.; Soneson, C.; Love, M.I.; Risso, D.; Vert, J.P.; Robinson, M.D.; Dudoit, S.; Clement, L. Observation weights unlock bulk RNA-seq tools for zero inflation and single-cell applications. Genome Biol. 2018, 19, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kvam, V.M.; Liu, P.; Si, Y. A comparison of statistical methods for detecting differentially expressed genes from RNA-seq data. Am. J. Bot. 2012, 99, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, D.; Zand, M.S.; Dye, T.D.; Goniewicz, M.L.; Rahman, I.; Xie, Z. An evaluation of RNA-seq differential analysis methods. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0264246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, S.P.; Nettleton, D.; McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. Detecting differential expression in RNA-sequence data using quasi-likelihood with shrunken dispersion estimates. Stat. Appl. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2012, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Law, C.W.; Chen, Y.; Shi, W.; Smyth, G.K. voom: Precision weights unlock linear model analysis tools for RNA-seq read counts. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, R29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poplawski, A.; Binder, H. Feasibility of sample size calculation for RNA-seq studies. Brief. Bioinform. 2018, 19, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.I.; Su, P.F.; Shyr, Y. Sample size calculation based on exact test for assessing differential expression analysis in RNA-seq data. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bi, R.; Liu, P. Sample size calculation while controlling false discovery rate for differential expression analysis with RNA-sequencing experiments. BMC Bioinform. 2016, 17, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, H.; Wang, C.; Wu, Z. PROPER: Comprehensive power evaluation for differential expression using RNA-seq. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Busby, M.A.; Stewart, C.; Miller, C.A.; Grzeda, K.R.; Marth, G.T. Scotty: A web tool for designing RNA-Seq experiments to measure differential gene expression. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 656–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, S.; Li, C.I.; Guo, Y.; Sheng, Q.; Shyr, Y. RnaSeqSampleSize: Real data based sample size estimation for RNA sequencing. BMC Bioinform. 2018, 19, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ching, T.; Huang, S.; Garmire, L.X. Power analysis and sample size estimation for RNA-Seq differential expression. RNA 2014, 20, 1684–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pierson, E.; Yau, C. ZIFA: Dimensionality reduction for zero-inflated single-cell gene expression analysis. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davis, A.; Gao, R.; Navin, N.E. SCOPIT: Sample size calculations for single-cell sequencing experiments. BMC Bioinform. 2019, 20, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, S.; Willis, J.; Dou, J.; Mohanty, V.; Huang, Y.; Vilar, E.; Chen, K. Sensei: How many samples to tell a change in cell type abundance? BMC Bioinform. 2022, 23, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millard, N.; Korsunsky, I.; Weinand, K.; Fonseka, C.Y.; Nathan, A.; Kang, J.B.; Raychaudhuri, S. Maximizing statistical power to detect differentially abundant cell states with scPOST. Cell Rep. Methods 2021, 1, 100120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, K.T.; Höllbacher, B.; Cruceanu, C.; Böttcher, A.; Lickert, H.; Binder, E.B.; Theis, F.J.; Heinig, M. scPower accelerates and optimizes the design of multi-sample single cell transcriptomic studies. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, K.D.; Langefeld, C.D. Hierarchicell: An R-package for estimating power for tests of differential expression with single-cell data. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieth, B.; Ziegenhain, C.; Parekh, S.; Enard, W.; Hellmann, I. powsimR: Power analysis for bulk and single cell RNA-seq experiments. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 3486–3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Su, K.; Wu, Z.; Wu, H. Simulation, power evaluation and sample size recommendation for single-cell RNA-seq. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 4860–4868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.V.; Li, J.J. A statistical simulator scDesign for rational scRNA-seq experimental design. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, i41–i50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qi, R.; Ma, A.; Ma, Q.; Zou, Q. Clustering and classification methods for single-cell RNA-sequencing data. Brief. Bioinform. 2020, 21, 1196–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maynard, K.R.; Collado-Torres, L.; Weber, L.M.; Uytingco, C.; Barry, B.K.; Williams, S.R.; Catallini, J.L., 2nd; Tran, M.N.; Besich, Z.; Tippani, M.; et al. Transcriptome-scale spatial gene expression in the human dorsolateral prefrontal cortex. Nat. Neurosci. 2021, 24, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.H.; Boettiger, A.N.; Moffitt, J.R.; Wang, S.; Zhuang, X. RNA imaging. Spatially resolved, highly multiplexed RNA profiling in single cells. Science 2015, 348, aaa6090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ståhl, P.L.; Salmén, F.; Vickovic, S.; Lundmark, A.; Navarro, J.F.; Magnusson, J.; Giacomello, S.; Asp, M.; Westholm, J.O.; Huss, M.; et al. Visualization and analysis of gene expression in tissue sections by spatial transcriptomics. Science 2016, 353, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Svensson, V.; Teichmann, S.A.; Stegle, O. SpatialDE: Identification of spatially variable genes. Nat. Methods 2018, 15, 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Zhu, J.; Zhou, X. Statistical analysis of spatial expression patterns for spatially resolved transcriptomic studies. Nat. Methods 2020, 17, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edsgärd, D.; Johnsson, P.; Sandberg, R. Identification of spatial expression trends in single-cell gene expression data. Nat. Methods 2018, 15, 339–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, M.; Xie, Y.; Xiao, G. Bayesian Modeling of Spatial Molecular Profiling Data via Gaussian Process. Bioinformatics 2021, 37, 4129–4136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Xiao, G.; Li, Q. A Bayesian modified Ising model for identifying spatially variable genes from spatial transcriptomics data. Stat. Med. 2022, 41, 4647–4665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dries, R.; Zhu, Q.; Dong, R.; Eng, C.L.; Li, H.; Liu, K.; Fu, Y.; Zhao, T.; Sarkar, A.; Bao, F.; et al. Giotto: A toolbox for integrative analysis and visualization of spatial expression data. Genome Biol. 2021, 22, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Luo, Z. Nonlinear dimensionality reduction of gene expression data for visualization and clustering analysis of cancer tissue samples. Comput. Biol. Med. 2010, 40, 723–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Dor, A.; Bruhn, L.; Friedman, N.; Nachman, I.; Schummer, M.; Yakhini, Z. Tissue classification with gene expression profiles. J. Comput. Biol. 2000, 7, 559–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, E.; Stone, M.R.; Ren, X.; Guenthoer, J.; Smythe, K.S.; Pulliam, T.; Williams, S.R.; Uytingco, C.R.; Taylor, S.E.B.; Nghiem, P.; et al. Spatial transcriptomics at subspot resolution with BayesSpace. Nat. Biotechnol. 2021, 39, 1375–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, C.; Chang, Y.; Neelon, B.; Chang, W.; Kim, H.J.; Li, Z.; Ma, Q.; Chung, D. A Bayesian multivariate mixture model for high throughput spatial transcriptomics. Biometrics 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browaeys, R.; Saelens, W.; Saeys, Y. NicheNet: Modeling intercellular communication by linking ligands to target genes. Nat. Methods 2020, 17, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yang, X.; Bi, G.; Liang, J.; Hu, Z.; Zhao, M.; Li, M.; Lu, T.; Zheng, Y.; Sui, Q.; et al. Ligand-receptor interaction atlas within and between tumor cells and T cells in lung adenocarcinoma. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 16, 2205–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Guerrero-Juarez, C.F.; Zhang, L.; Chang, I.; Ramos, R.; Kuan, C.H.; Myung, P.; Plikus, M.V.; Nie, Q. Inference and analysis of cell-cell communication using CellChat. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, C.G.; Lee, H.J.; Asatsuma, T.; Vento-Tormo, R.; Haque, A. An introduction to spatial transcriptomics for biomedical research. Genome Med. 2022, 14, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohoff, T.; Ghazanfar, S.; Missarova, A.; Koulena, N.; Pierson, N.; Griffiths, J.A.; Bardot, E.S.; Eng, C.L.; Tyser, R.C.V.; Argelaguet, R.; et al. Integration of spatial and single-cell transcriptomic data elucidates mouse organogenesis. Nat. Biotechnol. 2022, 40, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bost, P.; Schulz, D.; Engler, S.; Wasserfall, C.; Bodenmiller, B. Optimizing multiplexed imaging experimental design through tissue spatial segregation estimation. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, E.A.G.; Schapiro, D.; Dumitrascu, B.; Vickovic, S.; Regev, A. Power analysis for spatial omics. bioRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Zhou, X. BASS: Multi-scale and multi-sample analysis enables accurate cell type clustering and spatial domain detection in spatial transcriptomic studies. Genome Biol. 2022, 23, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, C.; Chang, Y.; Ma, Q.; Chung, D. MAPLE: A Hybrid Framework for Multi-Sample Spatial Transcriptomics Data. bioRxiv 2022, 2022, 482296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Li, X.; Coleman, K.; Schroeder, A.; Ma, N.; Irwin, D.J.; Lee, E.B.; Shinohara, R.T.; Li, M. SpaGCN: Integrating gene expression, spatial location and histology to identify spatial domains and spatially variable genes by graph convolutional network. Nat. Methods 2021, 18, 1342–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J.J.; Li, H.S.; Yan, H.; Zhang, X.F. EnDecon: Cell type deconvolution of spatially resolved transcriptomics data via ensemble learning. Bioinformatics 2023, 39, btac825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhou, X. Spatially informed cell-type deconvolution for spatial transcriptomics. Nat. Biotechnol. 2022, 40, 1349–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cable, D.M.; Murray, E.; Zou, L.S.; Goeva, A.; Macosko, E.Z.; Chen, F.; Irizarry, R.A. Robust decomposition of cell type mixtures in spatial transcriptomics. Nat. Biotechnol. 2022, 40, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Tool Name [Citation] (Implementation) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Pilot Data | Pilot Data with Stored Data | ||
| Type 1 Error | Poisson Log-normal | - | ‘Scotty’ [33] (Web Interface) |
| Negative Binomial | ‘RNASeqPower’ [19] (R package) | - | |
| FDR | ‘ssizeRNA’ [31] (R package) | ‘RnaSeqSampleSize’ [34] (R package) | |
| ‘RNASeqPowerCalculator’ [35] (R package) | ‘PROPER’ [32] (R package) | ||
| Detection Target | # of Samples | Tool Name | Experimental Factor | Software | Model | Power Assessment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell sub- population | Single sample | ‘SCOPIT’ [37] | (1) | R package & Web application | Multinomial | Analytical |
| ‘howmanycells’ | Web application | Negative Binomial | ||||
| Multi sample | ‘Sensei‘ [38] | (1), (2) | Beta Binomial | |||
| ‘scPOST’ [39] | R package | Linear mixed model | Simulation- based | |||
| DEG | ‘scPower’ [40] | (1), (2), (3) | R package & Web server | Negative Binomial | Pseudobulk | |
| ‘hierarchicell’ [41] | R package | Simulation- based | ||||
| Single sample | ‘powsimR’ [42] | (1) | ||||
| ‘POWSC’ [43] | (1), (3) | A mixture of zero-inflated Poisson and log-normal Poisson distributions | ||||
| ‘scDesign’ [44] | Gamma-Normal mixture model |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeon, H.; Xie, J.; Jeon, Y.; Jung, K.J.; Gupta, A.; Chang, W.; Chung, D. Statistical Power Analysis for Designing Bulk, Single-Cell, and Spatial Transcriptomics Experiments: Review, Tutorial, and Perspectives. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 221. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13020221
Jeon H, Xie J, Jeon Y, Jung KJ, Gupta A, Chang W, Chung D. Statistical Power Analysis for Designing Bulk, Single-Cell, and Spatial Transcriptomics Experiments: Review, Tutorial, and Perspectives. Biomolecules. 2023; 13(2):221. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13020221
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeon, Hyeongseon, Juan Xie, Yeseul Jeon, Kyeong Joo Jung, Arkobrato Gupta, Won Chang, and Dongjun Chung. 2023. "Statistical Power Analysis for Designing Bulk, Single-Cell, and Spatial Transcriptomics Experiments: Review, Tutorial, and Perspectives" Biomolecules 13, no. 2: 221. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13020221
APA StyleJeon, H., Xie, J., Jeon, Y., Jung, K. J., Gupta, A., Chang, W., & Chung, D. (2023). Statistical Power Analysis for Designing Bulk, Single-Cell, and Spatial Transcriptomics Experiments: Review, Tutorial, and Perspectives. Biomolecules, 13(2), 221. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13020221






